The Diencephalon
(Thalamus & Hypothalamus)
Gross Anatomy and Functional Localization
Done by
Dr.Rafid Remthan Al-Temimi
Clinical Radiology
CAMB,DMRD,M.B.Ch.B.,.
المرحلة
:
الثانية
المادة
:
التشريح
ج
امعة ذي قار
/
كلية الطب
1
الدكتور
رافد
رمثان التميمي
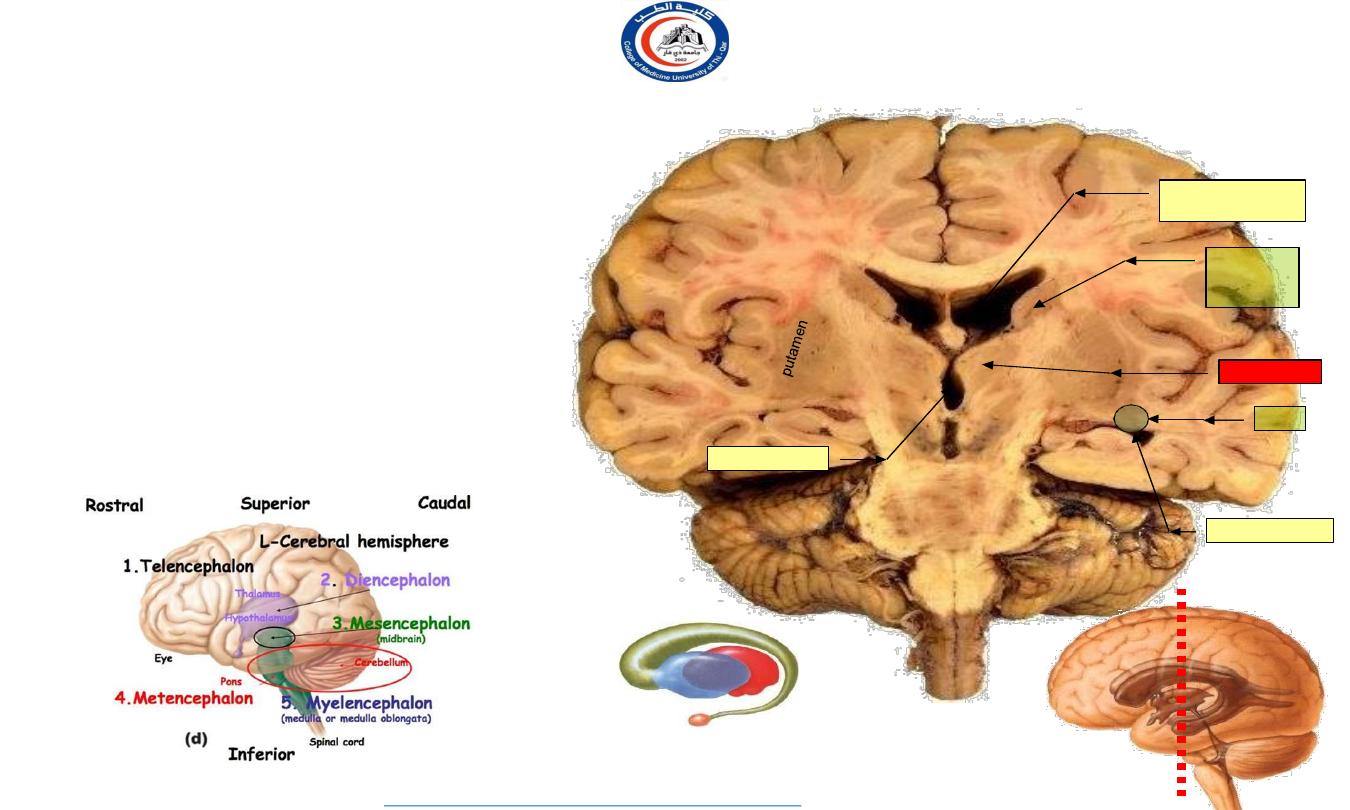
Features of a coronal section of the hemispheres
•
•
•
•
Corpus callosum
:
Lies in the depth of the median sagittal fissure.
Forms a roof for the body of the lateral ventricle.
The
body of the caudate nucleus
lies in the
inferolateral boundary of the body of the lateral
ventricle
The
tail of the caudate nucleus
is located at the
roof of the inferior horn of the lateral ventricle.
Each
thalamus
lies on either side of the midline
forming a floor for the body of the lateral ventricle
The
thalami
lie on either side of the 3
rd
ventricle.
insula
Corpus callosum
Body of lateral
ventricle
Inferior horn
Body
of
caudate
nucleus
tail
thalamus
3
rd
ventricle
Globus
pallidus
body
tail
The section passes through the body and inferior horn of the C-shaped lateral ventricle
•
2
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
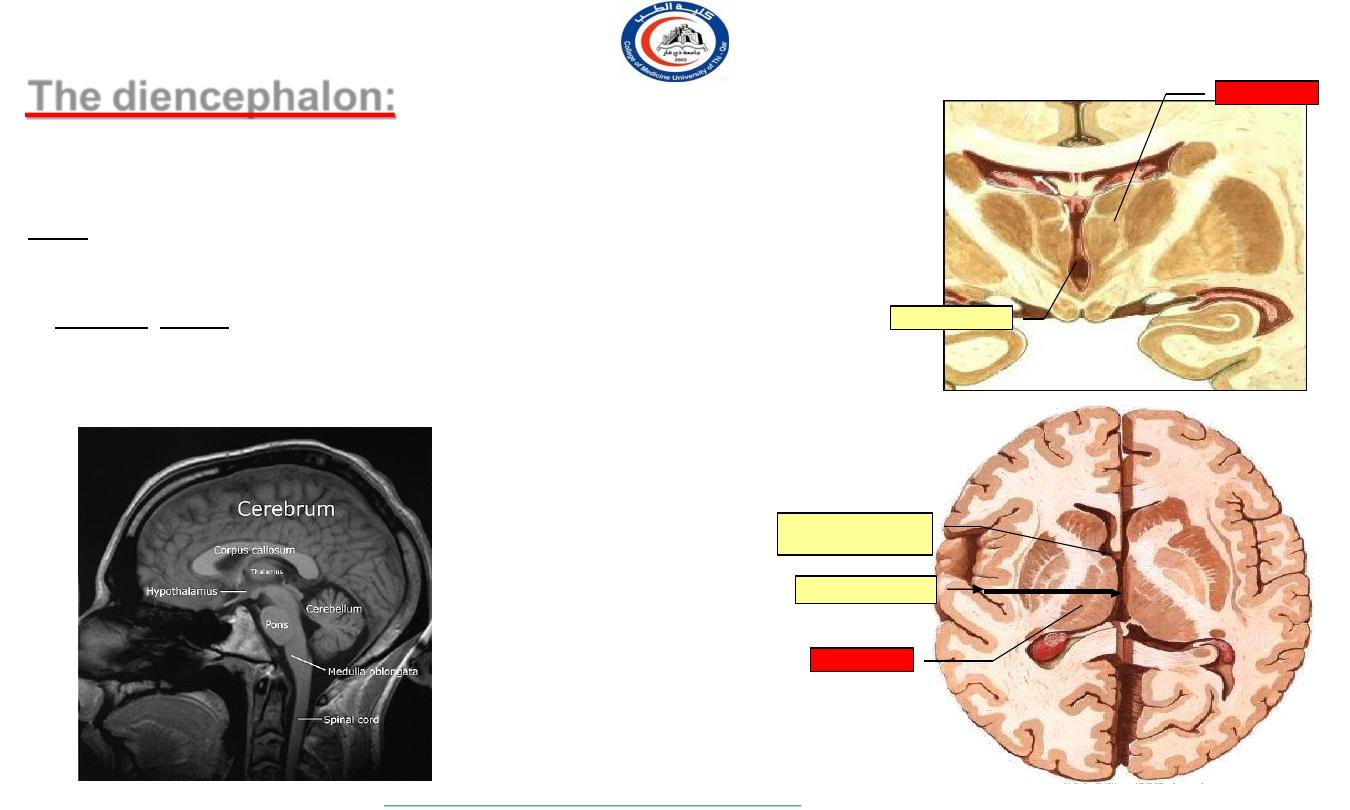
The diencephalon:
•
•
•
It consists of nuclear masses, mainly of the thalamus and hypothalamus
. Is egg-shaped.
The third ventricle lies between the 2 halves of the diencephalon.
Site:- It is the part of the forebrain which lies above the midbrain, Relay
between the brainstem & cerebral cortex, between the lower parts of the 2
cerebral hemispheres. Its cavity is the third ventricle.
• Function :Mainly: a relay station of sensory impulses: It receives sensory
afferents from the spinal cord and brain stem and projects efferents to the
primary sensory cortex.
Is also concerned with motor control.
•
thalamus
3
rd
ventricle
thalamus
Interventricular
foramen
3
rd
ventricle
3
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
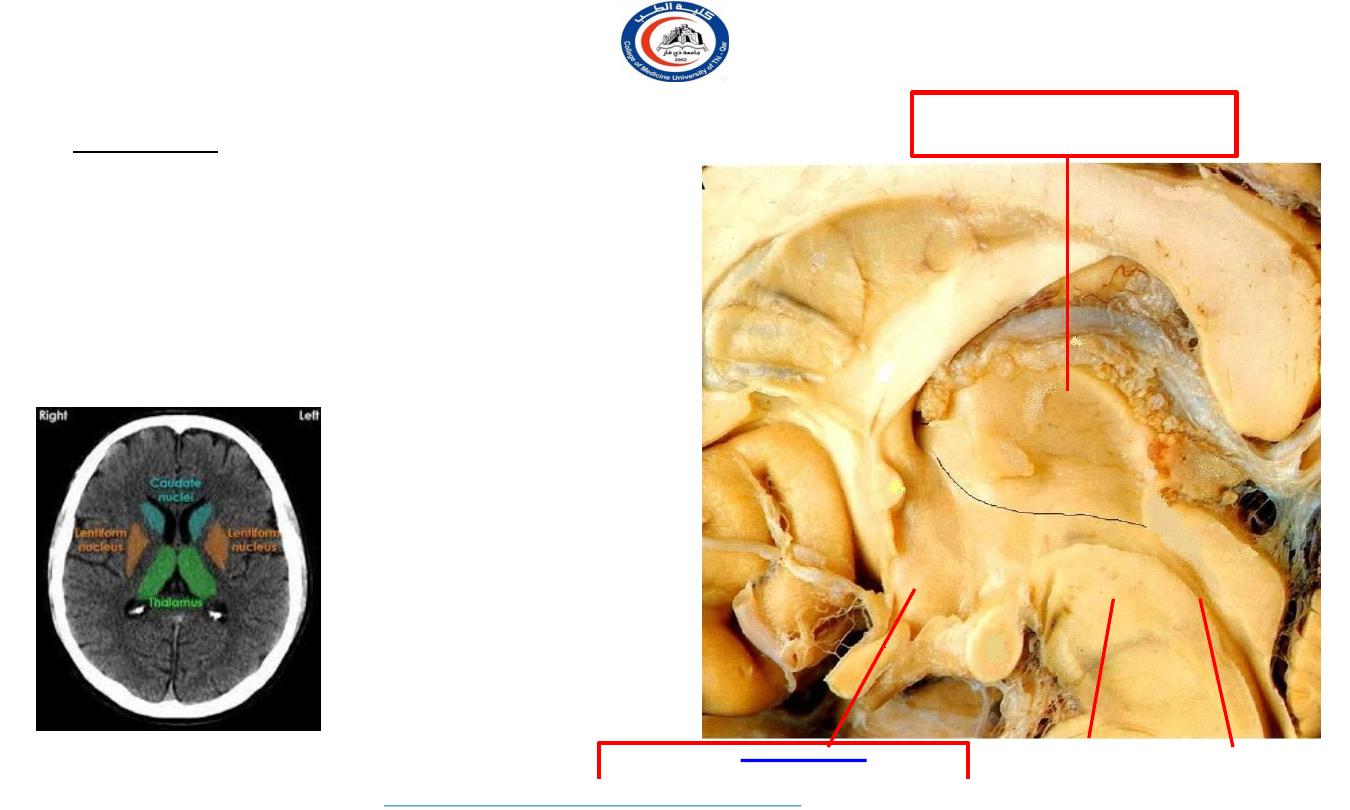
The diencephalon:
It consists of:
1. Thalamus
:-the large oval mass of grey matter
2. Subthalamus:-
it lies directly above midbrain
3. Hypothalamus
: lies infront of subthalamus
4. Metathalamus:
formed by lateral & medial geniculate body
5. Epithalamus:
Formed of pineal body, 2 habenular
complex (nuclei anterior and posterior commissure).
4
•
On the medial surface, the
diencephalon is subdivided,
by
hypothalamic sulcus
(indicated by black line)
into:
Dorsal
part:
Ventral
part:
Cerebral aqueduct
Dorsal
Ventral
Midbrain
Dorsal part
Thalamus & Epithalamus
Ventral part
Subthalamus & Hypothalamus
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
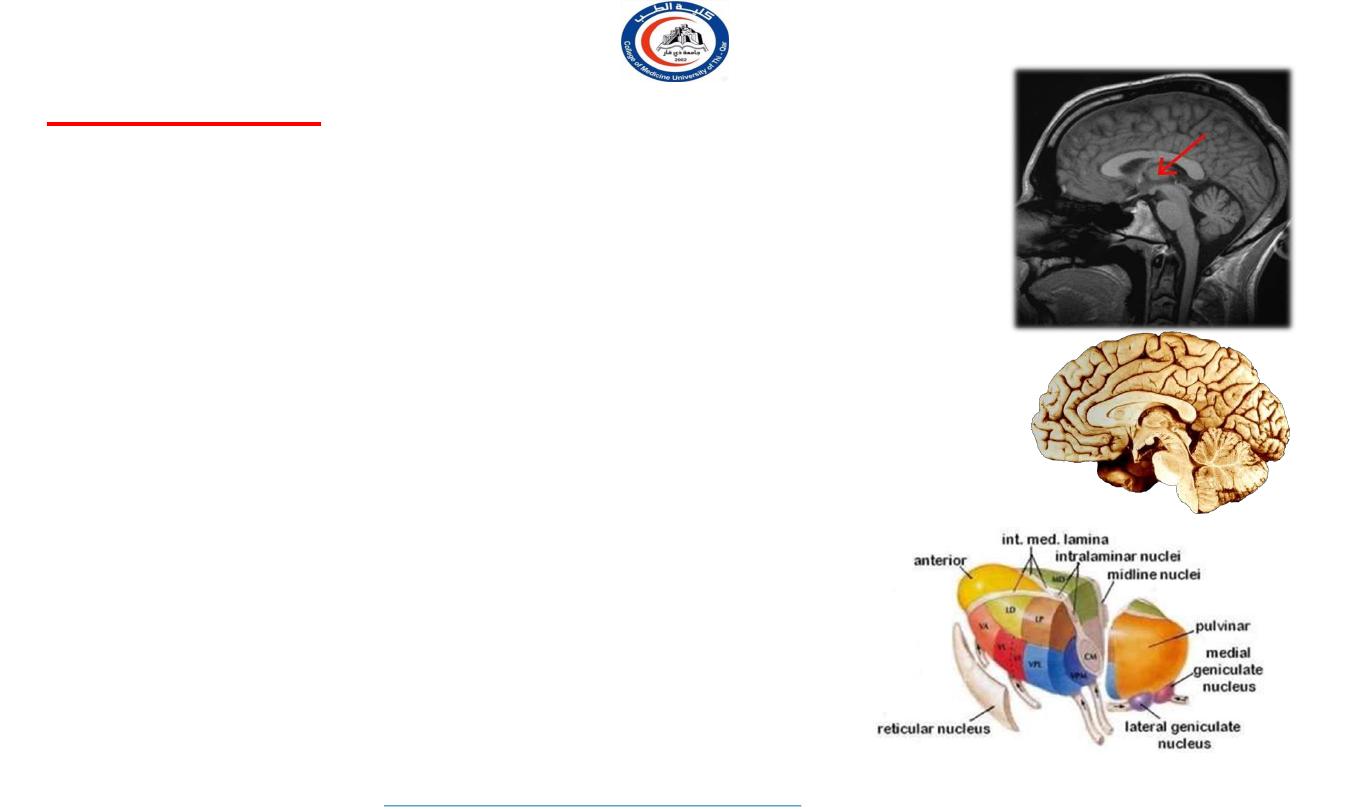
Thalamus is a very important relay station.
All general and special sensory impulses (except smell) & afferent
impulses from RAS are integrated here.
Thalamus however is the center of pain and protopathic sensations.
It has other non sensory functions as well, like motor control, sleep,
wakefulness.
It is the largest structure deriving from the embryonic diencephalon,
the posterior part of the forebrain situated between the midbrain and
the cerebrum.
The thalamus is part of a nuclear complex structured of 4 parts, the
hypothalamus, epithalamus, prethalamus (formerly called ventral
thalamus) and dorsal thalamus.
Name was first assigned by Wilhelm His,Sr. in 1893
Literally means ‘inner chamber’
It prepares a crude blue-print of the final product achieved by the
cortex.
5
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
The Thalamus

Physiological Anatomy
Each thalamus is a large, ovoid diencephalic mass of grey matter.
Two thalami lie close together in the cephalic 2/3
rd
& separated by 3
rd
ventricle.
Joined in the midline by mass intermedia.
Caudal 1/3
rd
are more divergent and the corpora quadrigemina lie
between them.
External medullary lamina consisting of thalamocortical and cortico
thalamic fibers covers the lateral surface.
Reticular nucleus separates internal capsule from External medullary
lamina.
Internal medullary lamina (‘Y’ shaped sheath of white matter) consisting
of internuclear thalamic connections dividing the thalamus into
lateral,medial and anterior nuclear masses.
It’s a afferent gateway of cerebral cortex.
6
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
Massa intermedia
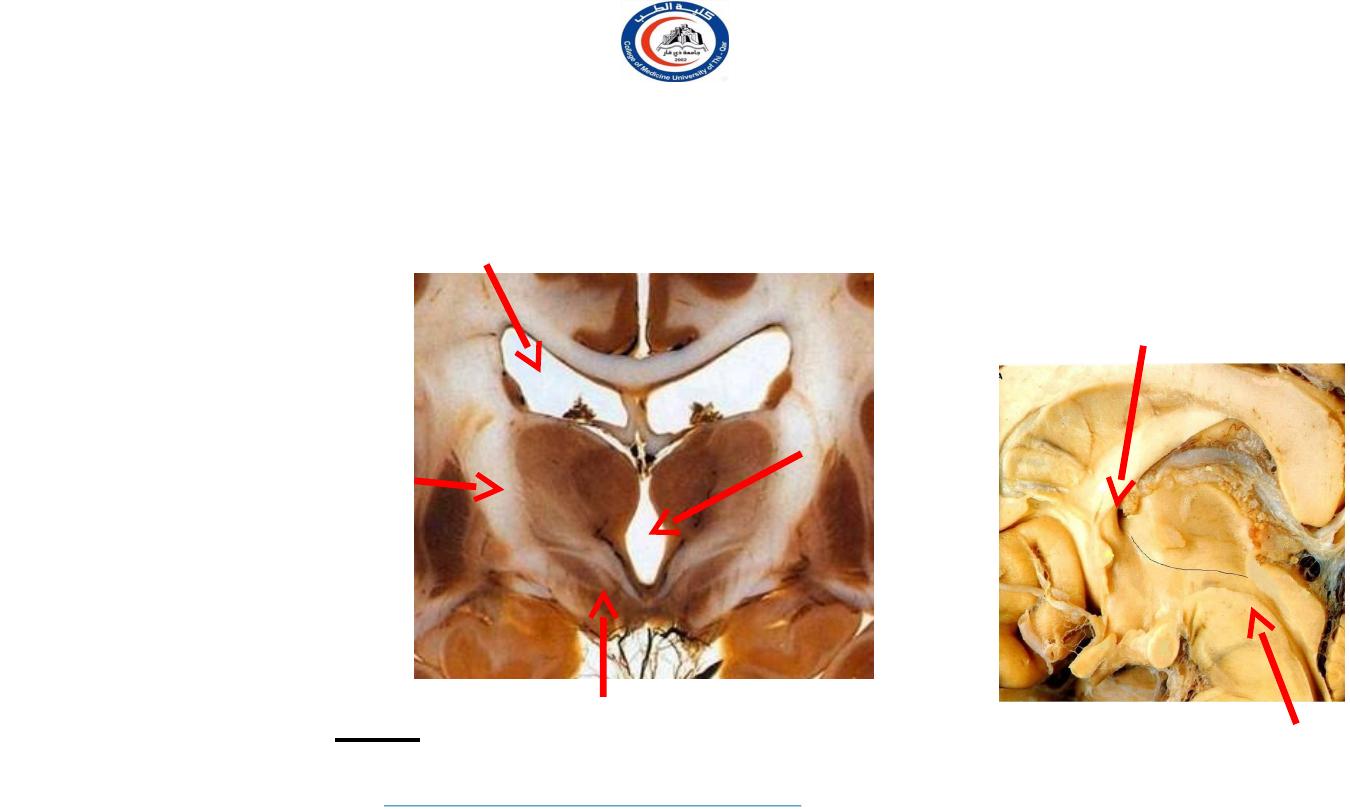
Largest component of the diencephalon
Monday, March 14, 2016
7
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
R e l at i o n s o f T h a l a m u s
Medial: 3
rd
ventricle
Dorsal: lateral ventricle
Ventral: Subthalamus & Hypothalamus
Lateral:
Internal
capsule
Caudal: midbrain
Rostrally
interventricular
foramen
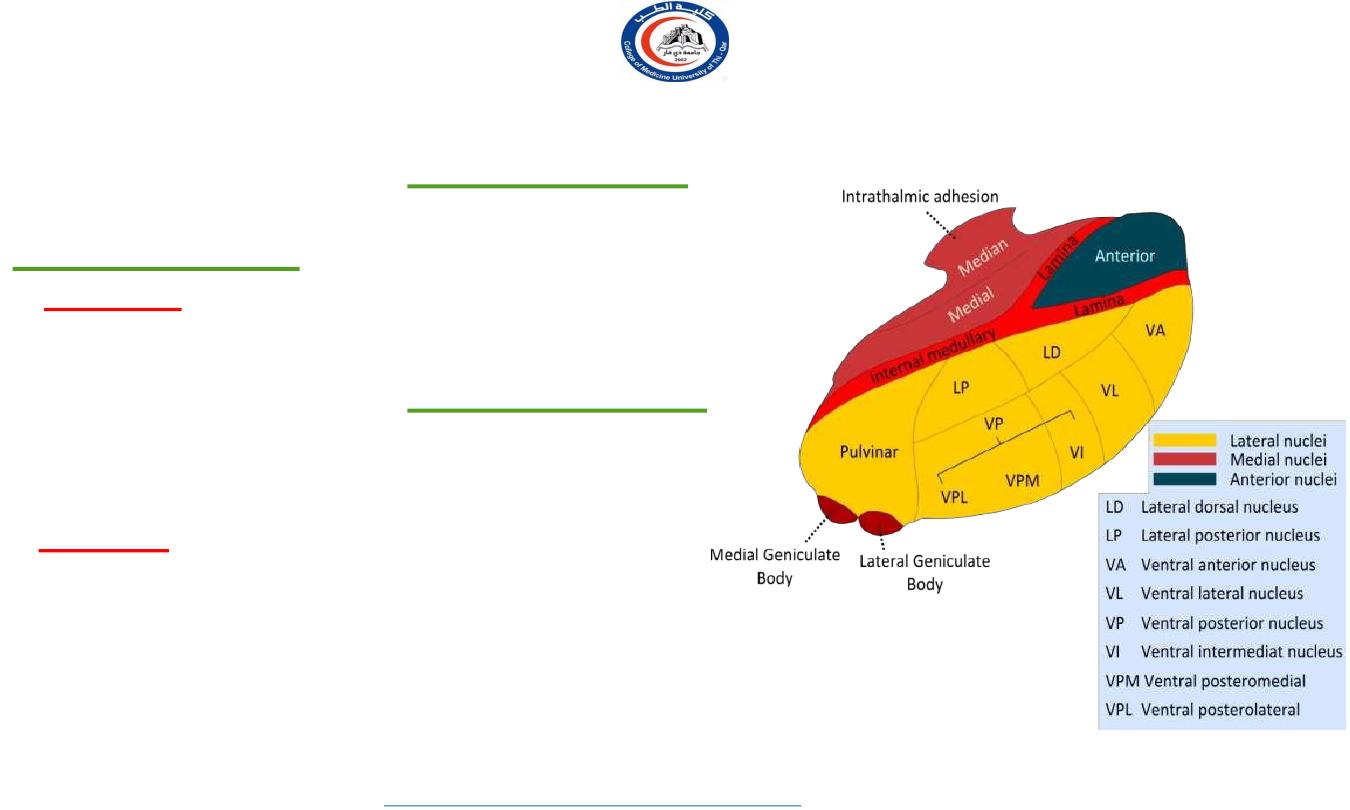
Classification of Thalamic nuclei.
Anatomical
classification-
A. Lateral group of Nuclei
1.
Ventral group-
Ventral anterior nu.
Ventral lateral nu.
Ventral posterior nu.
Medial geniculate body
Lateral geniculate body
2.
Dorsal group-
Pulvinar
nu.
Lateral posterior nu.
Lateral dorsal
nu.
B. Medial group of Nuclei
Centro-median nu.
Dorso-median nu.
Midline nucleus
C. Anterior group of Nuclei
Anterior ventral nu.
Ant dorsal nu.
Ant medial nu.
8
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
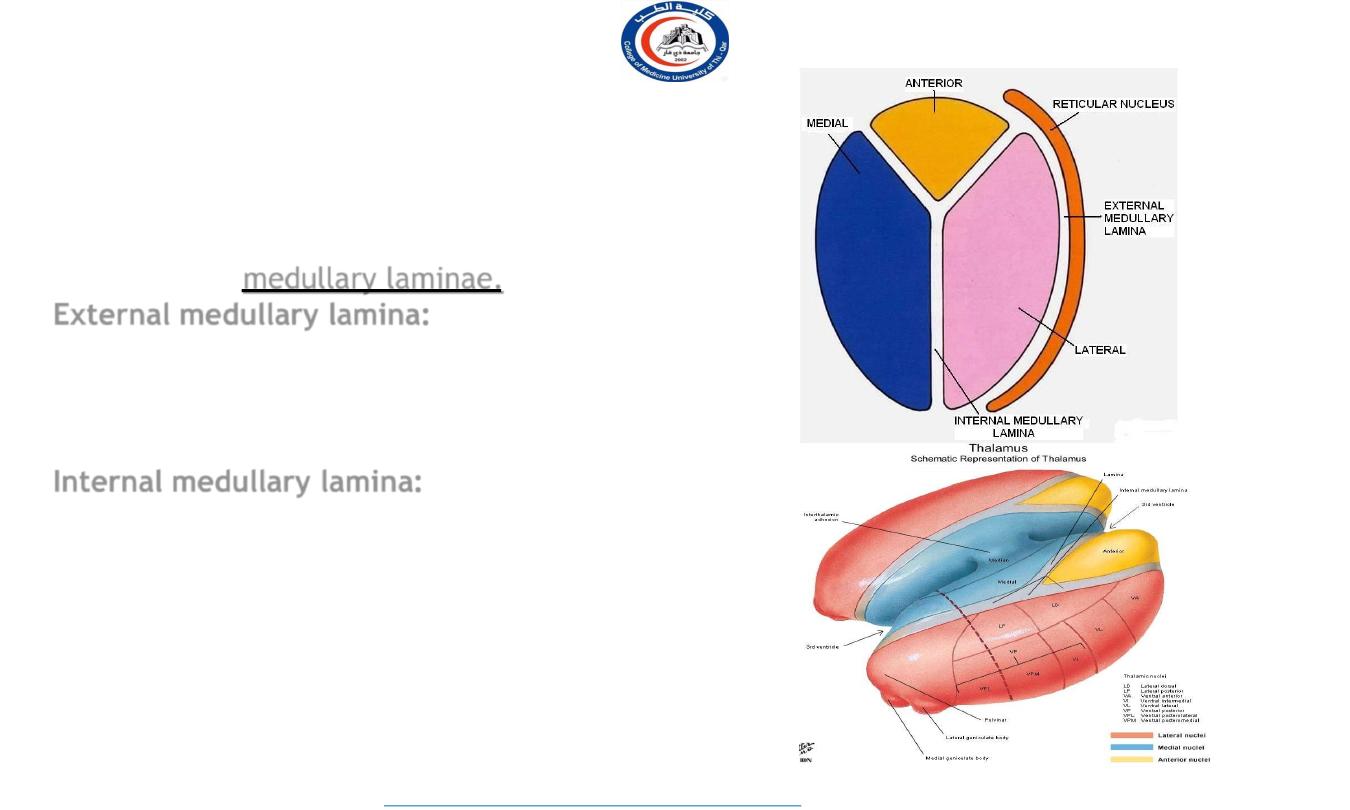
I n t e r n a l O r g a n i z a t i o n o f T h a l a m u s
9
•
•
•
Thalamus is composed of grey matter,
interrupted by 2 vertical sheaths of white
matter called
medullary laminae.
External medullary lamina:
Located laterally, separates reticular nucleus
from the rest of the thalamic mass . It
contains thalamocortical & corticothalamic
fibers
Internal medullary lamina:
Y shaped complex of nuclei and fibers,
separates the thalamus into anterior group
between the 2 limbs of Y shaped lamina and
two tiers of nuclei medial and lateral group on
each side of the stem of Y shaped lamina.
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
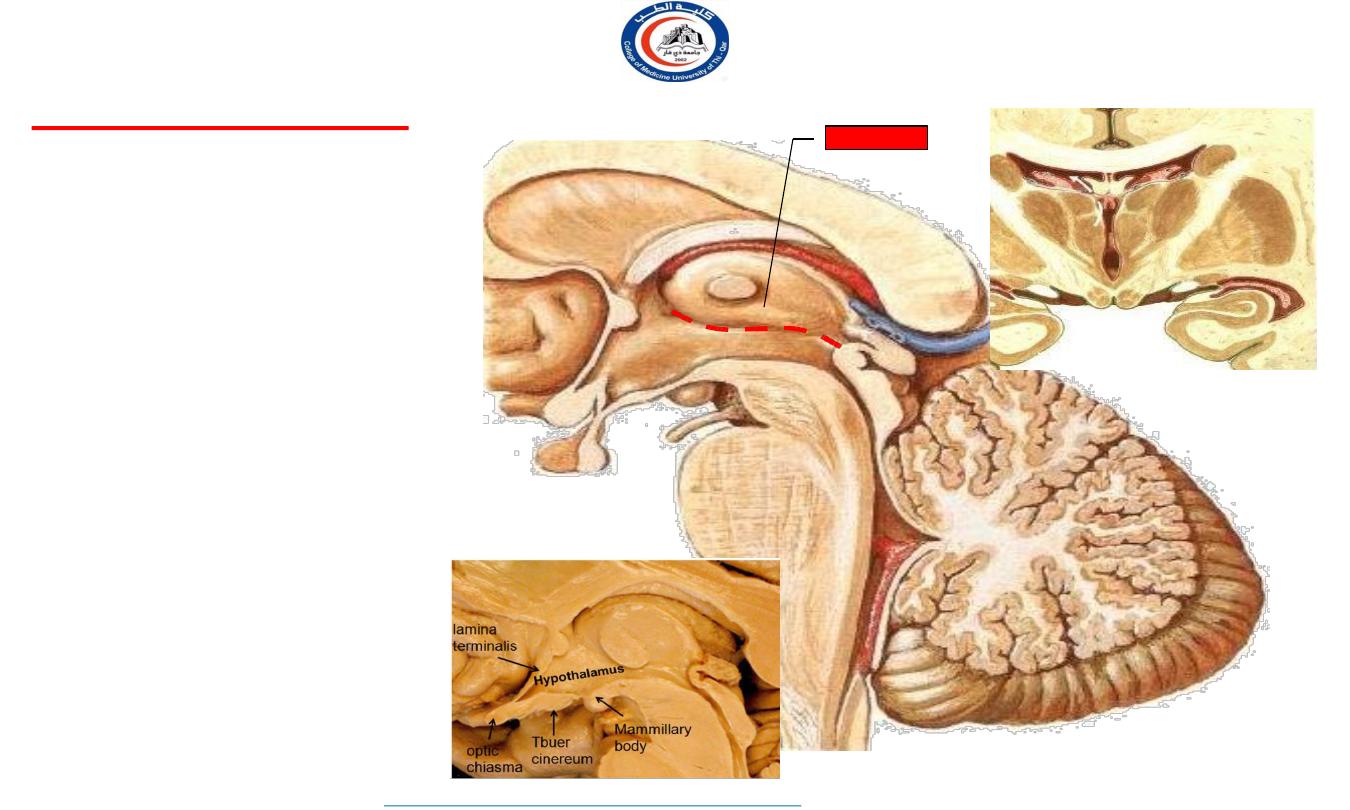
The Hypothalamus
hypothalamus
hypothalamus
thalamus
10
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
•
•
•
•
•
Below the thalamus.
The hypothalamus is the part of the
diencephalon forming the floor and
the lower part of the lateral wall of
the third ventricle. It extends from
the region of the optic chiasma to the
caudal border of the mammillary
bodies.
Relations
Above
: the thalamus.
Below
: the hypothalamus merges
into the tegmentum of the
midbrain.
Laterally
:
the internal capsule
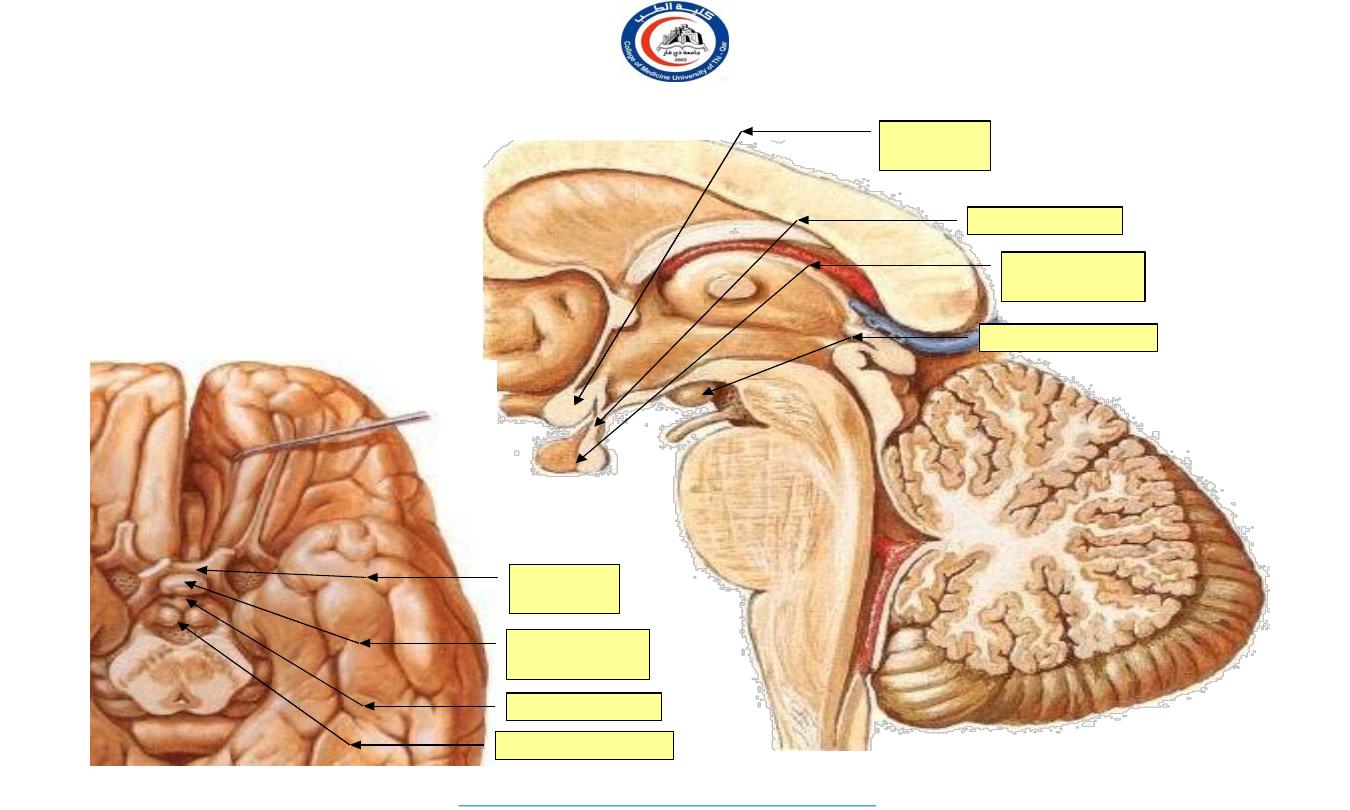
The hypothalamus
•
•
Behind the optic chiasma the
floor of the 3
rd
ventricle gives
rise to the stalk
(
infundibulum
) of the
hypophysis cerebri
.
The
mamillary bodies
lie behind.
infundibulum
Optic
chiasma
Hypophysis
cerebri
Mamillary body
Optic
chiasma
Hypophysis
cerebri
infundibulum
Mamillary body
11
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
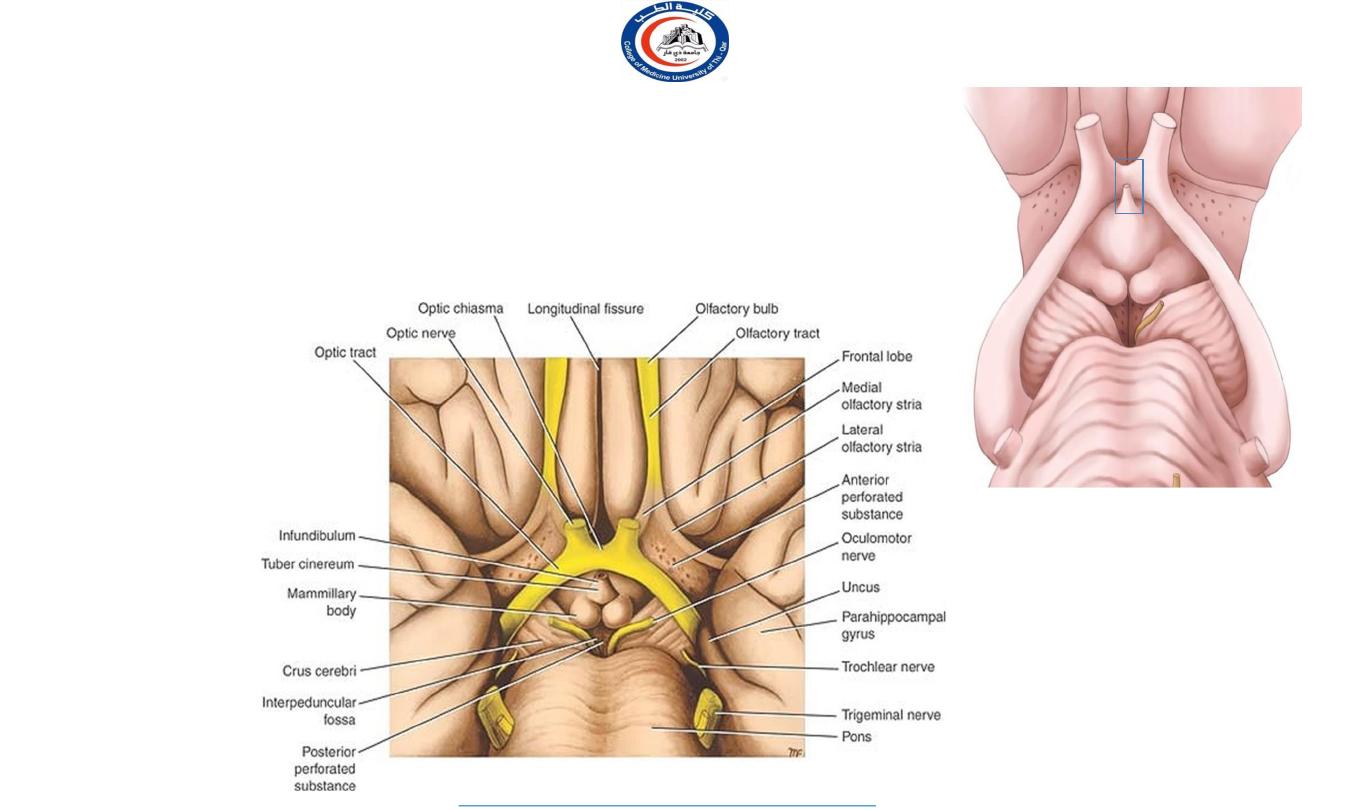
12
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
4
Structures forming the hypothalamus
1
2
3
4
4
• The structures forming the hypothalamus lie in the interpeduncular fossa, these
• structures are: optic chiasma, tuber cinerum and infundibulum, and mammillary
bodies.
• Anterior to the hypothalamus is an area that, for functional reasons, is often
included in the hypothalamus, it is referred to as the preoptic area.
1. optic chiasma
2. infundibulum
3. tuber cinereum
4. mamillary bodies
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
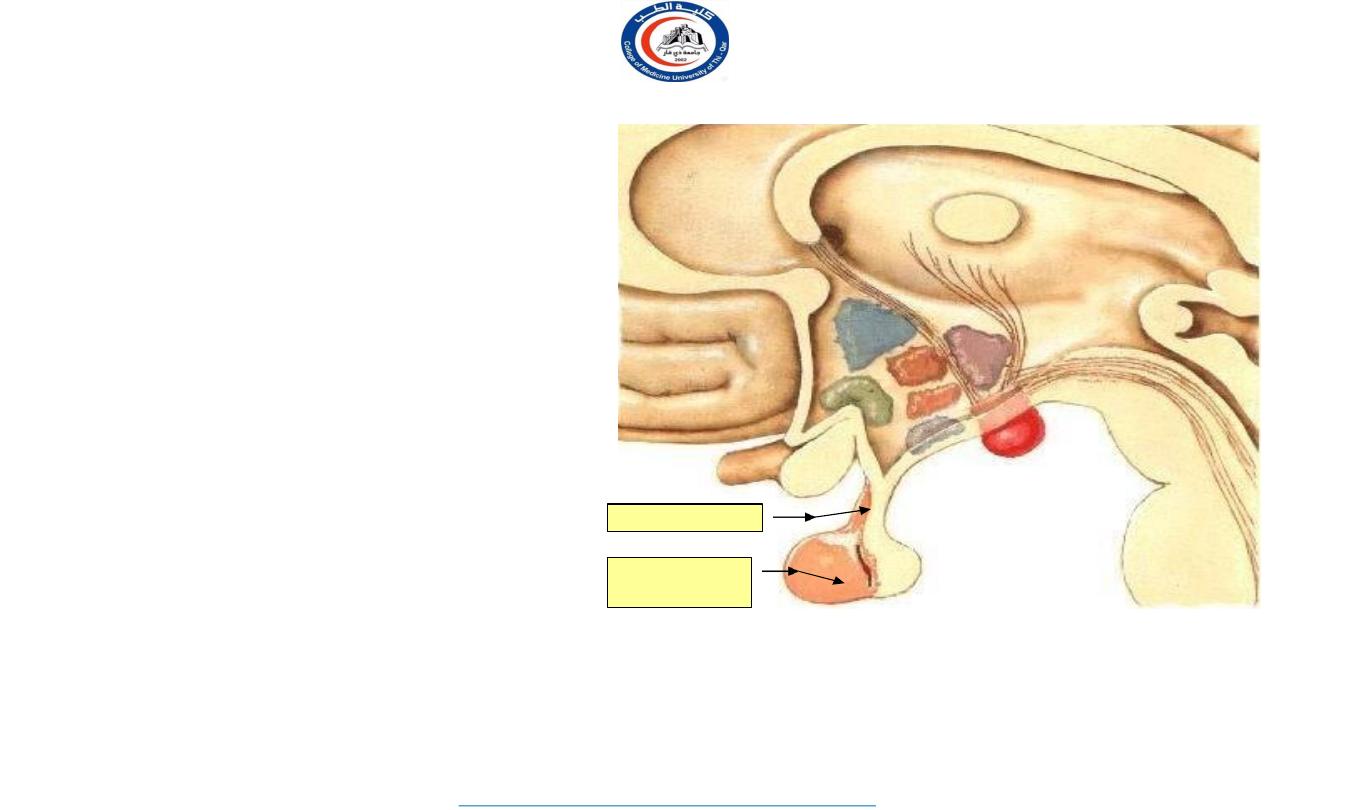
Functions of the hypothalamus
•
•
•
•
•
Regulation of the autonomic nervous system.
Regulation of endocrine glands through the
hypophysis cerebri.
Temperature regulation.
Regulation of food and water intake. Control of
sleep.
hypothalamus
thalamus
Hypophysis
cerebri
infundibulum
13
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
• It controls 3 system
1.
Autonomic nervous system
2.
Endocrine system
3.
Limbic system (emotional brain)
• Basically it has major role in maintaining
homeostasis.
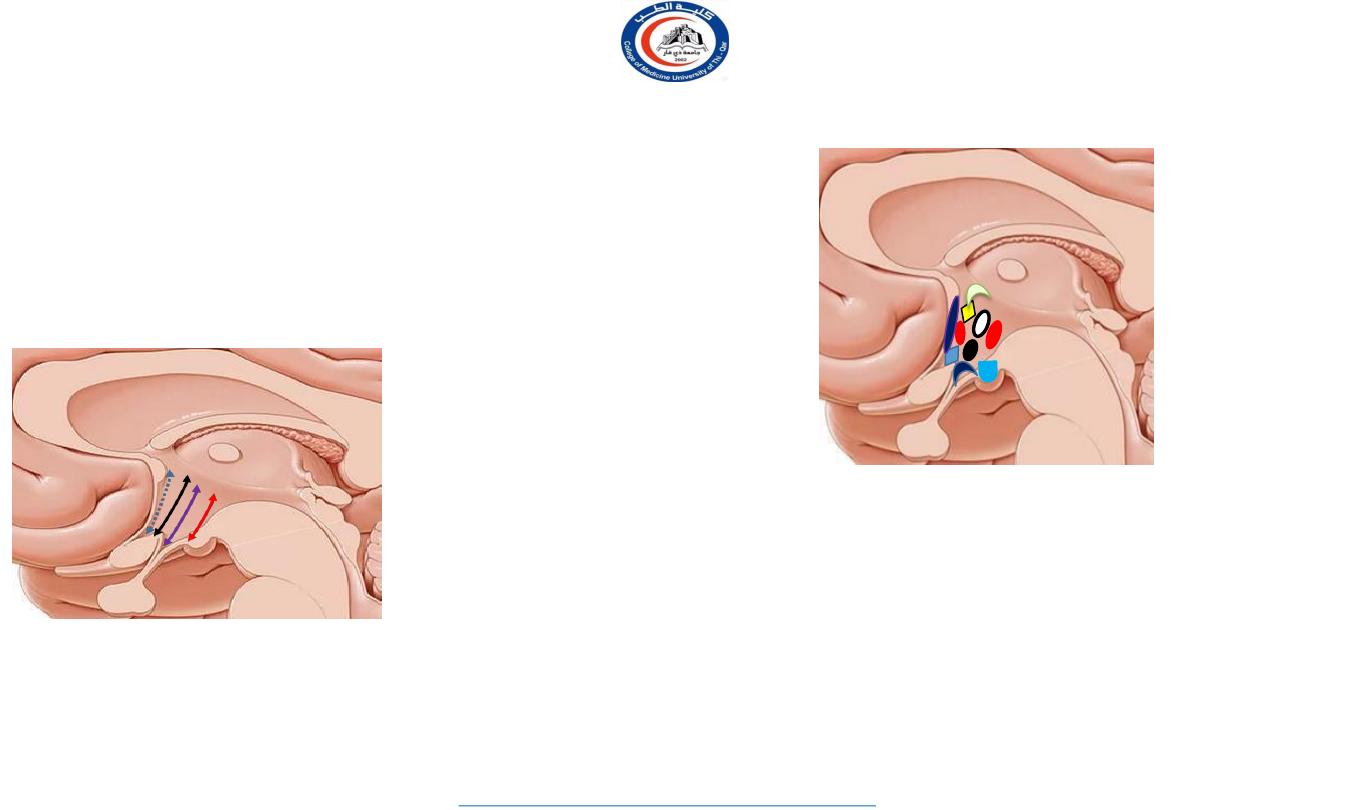
Ant-Post division
1. Preoptic region
2. Supraoptic region
3. Tuberal region
4. Mammillary region
Preoptic region
1.
Preoptic nucleus
Supra-optic region
1.
Anterior nucleus
2.
Supra optic nucleus
3.
Suprachiasmatic
nucleus
4.
Paraventricular
nucleus
Tuberal region
1.
Dorsomedial nucleus
2.
Ventromedial nucleus
3.
Arcuate nucleus
Mammillary region
1.
Posterior nucleus
2.
Mammillary nucleus
14
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
Divisions of the hypothalamus
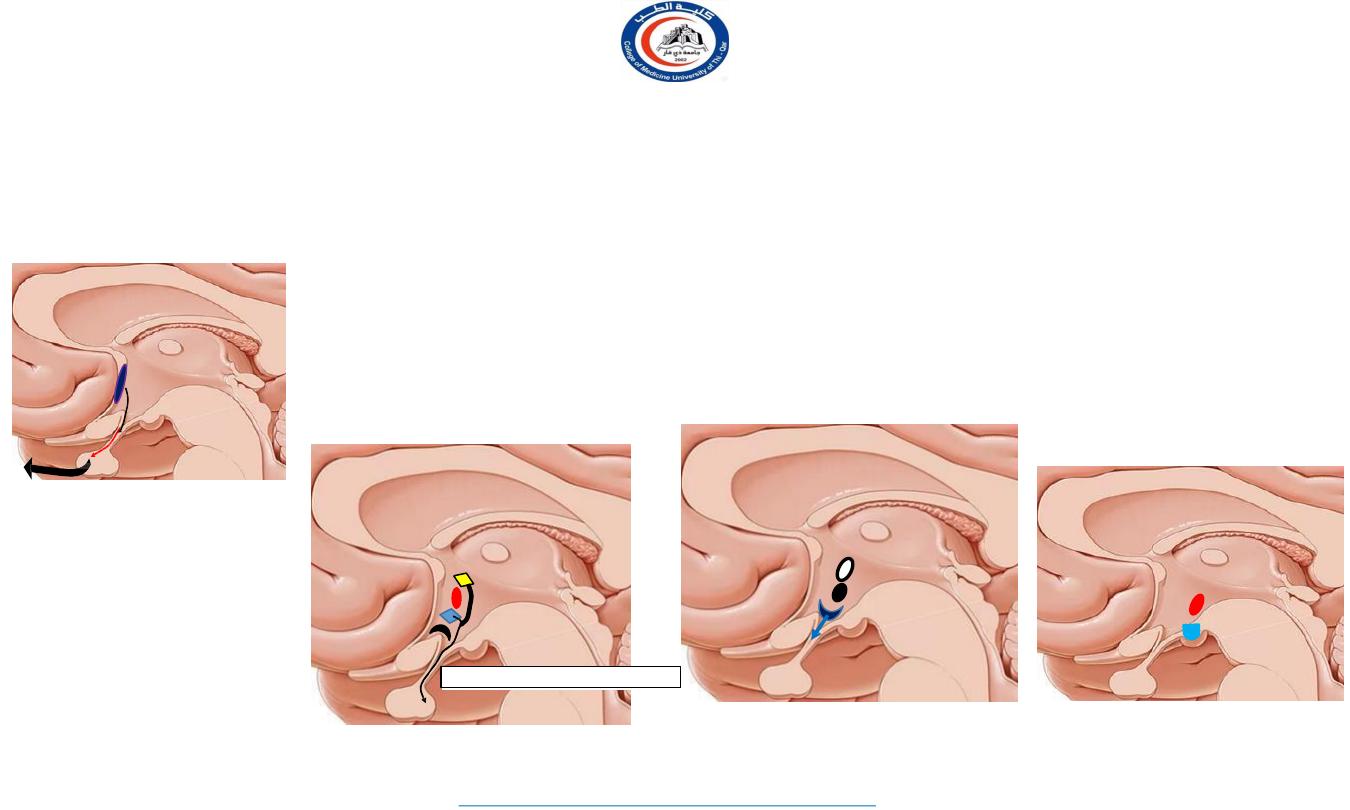
Preoptic region
1. Preoptic nucleus
FSH
LH
GnRH
Supra-optic region
1.
Supra-chiasmatic nucleus
2.
Anterior nucleus
3.
Supra-optic nucleus
4.
Paraventricular nucleus
Functions
1.
Circadian rhythm
2.
AC (cooling mechanism)
3.
ADH & oxytocin hormone
HHT- hypothalamo-hypophyseal tract
Tuberal region
1.
Arcuate nucleus
2.
Ventromedial nucleus
3.
Dorsomedial nucleus
Functions
1.
Releasing factors
2.
Satiety & reward center
3.
Savage behavior
Mammillary region
1.
Mammillary nucleus
2.
Posterior nucleus
Functions
1.
Behavior
2.
Part of papez circuit.
3.
Heating center
4.
Sympathetic center
15
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
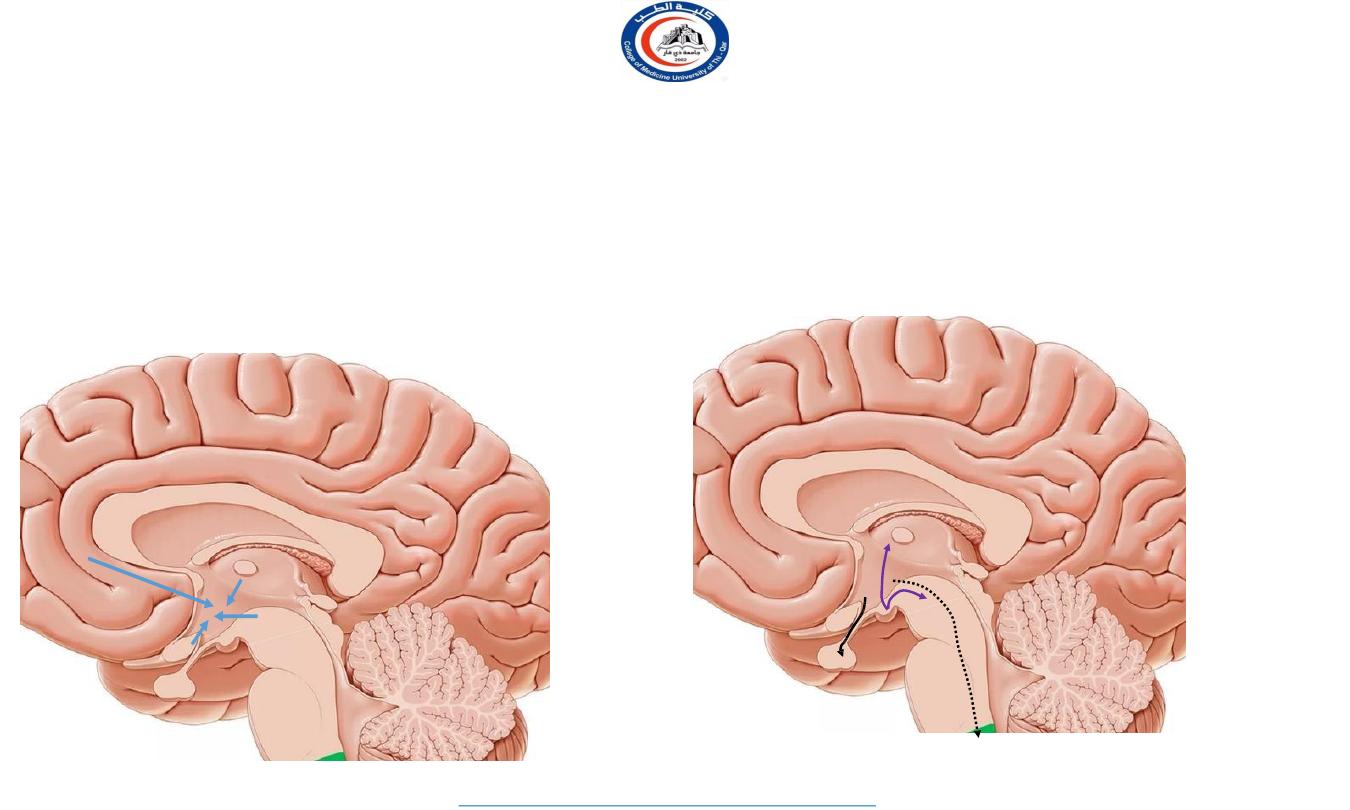
Afferent connection
•
Visual afferent
•
Corticohypothalmic
•
Fornix
•
Stria terminalis
•
Thalamohypothala
mic tract
•
Tegmental fibers
Efferent connection
•
Descending hypothalamic
tract
•
Mammillothalamic tract
•
Mammillotegmental tract
•
HHT
16
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
Subthalamus
• It lies between the thalamus and tegmentum of the midbrain
• It contains 3 nuclei
1. upper end of red nucleus,
2. upper end of substantia nigra
3. subthalamic nuclei
17
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
Epithalamus
•
•
•
Relatively small part, located in most
caudal and dorsal region
Lies immediately rostral to superior
colliculus
Consists of:
Pineal gland
Habenular nuclei
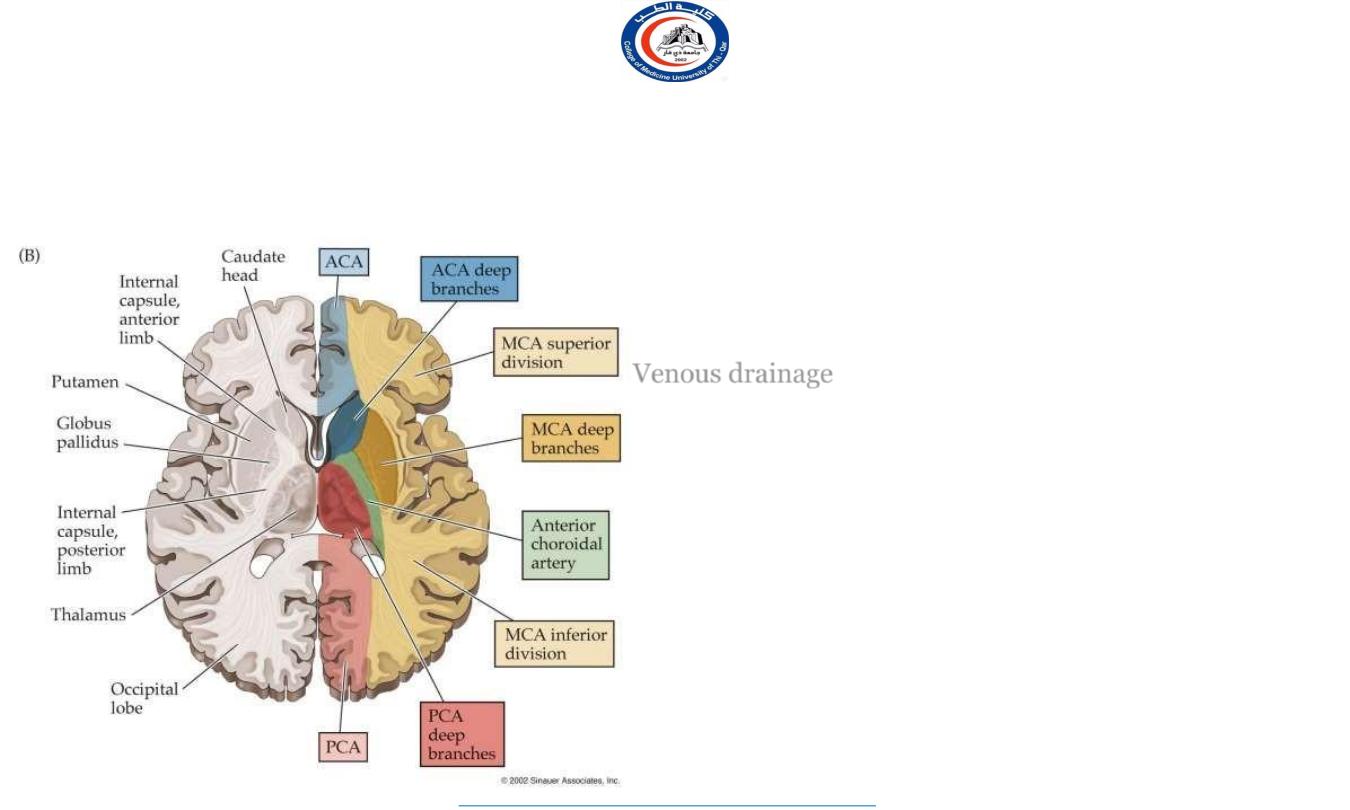
Thalamus-
Blood Supply
18
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
The thalamus is supplied by 2 sets of arteries derived
from the
posterior cerebral artery
1.
Thalamo-perforating arteries: supply the anterior and
medial parts of the thalasmus
2.
Thalamo-geniculate arteries: supply the lateral and
posterior parts of the thalamus
Venous drainage
of the thalamus by the thalamic veins
which join the thalamostriate vein
The thalamostriate vein with the choroidal vein form
the
internal cerebral vein
ADDITIONALLY…
The
ICA
, via its anterior choroidal branch, supplies
the lateral thalamic territory.
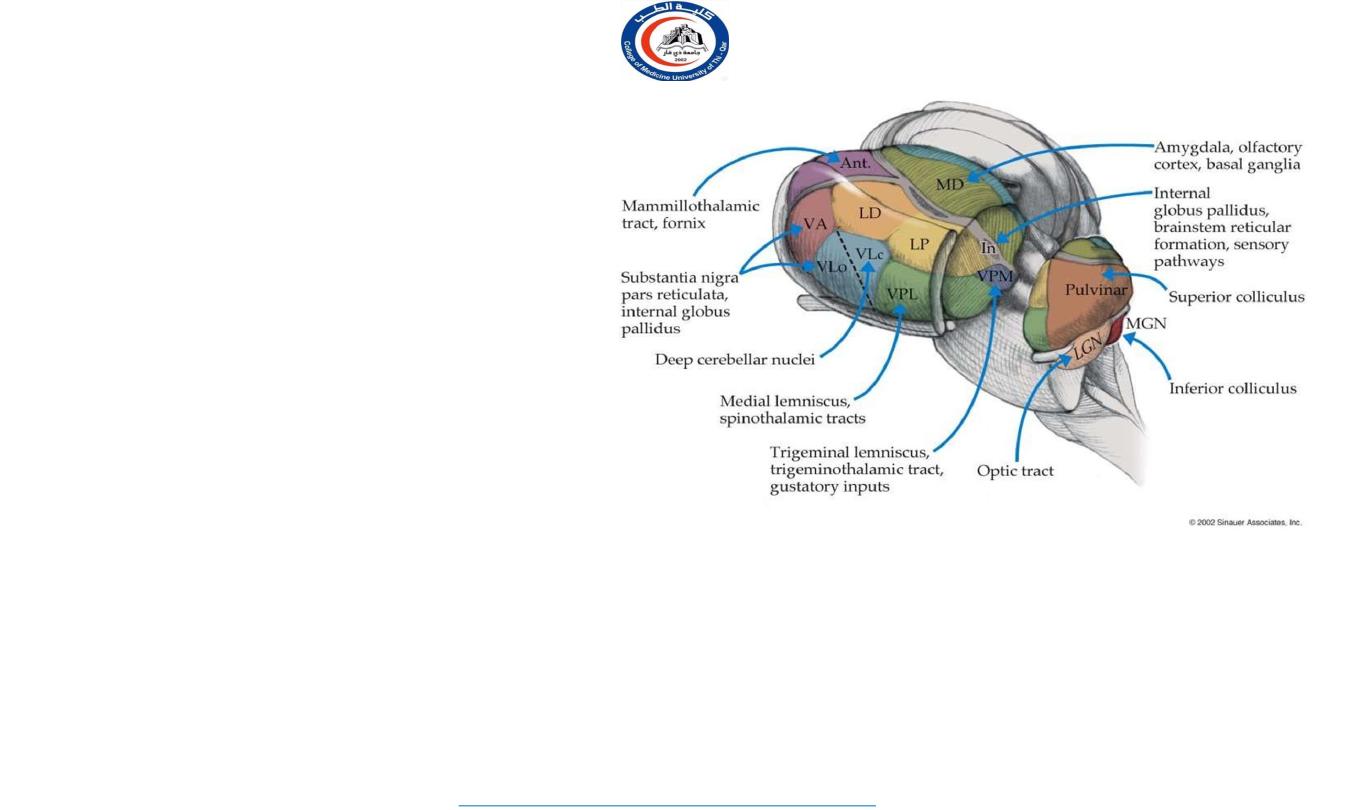
Connections of Thalamus
1.
Non specific Projection Nuclei
2.
Specific Projection Nuclei
3.
Reticular Nuclei
19
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
Every thalamic nucleus (except the reticular nucleus) sends axons to specific parts of the cerebral
cortex and every part of the cerebral cortex sends reciprocal fibers back to the thalamic nuclei.
Information received by the thalamus is always shared with the cerebral cortex and that the cortex
and thalamus can modify each other's activities.
20
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
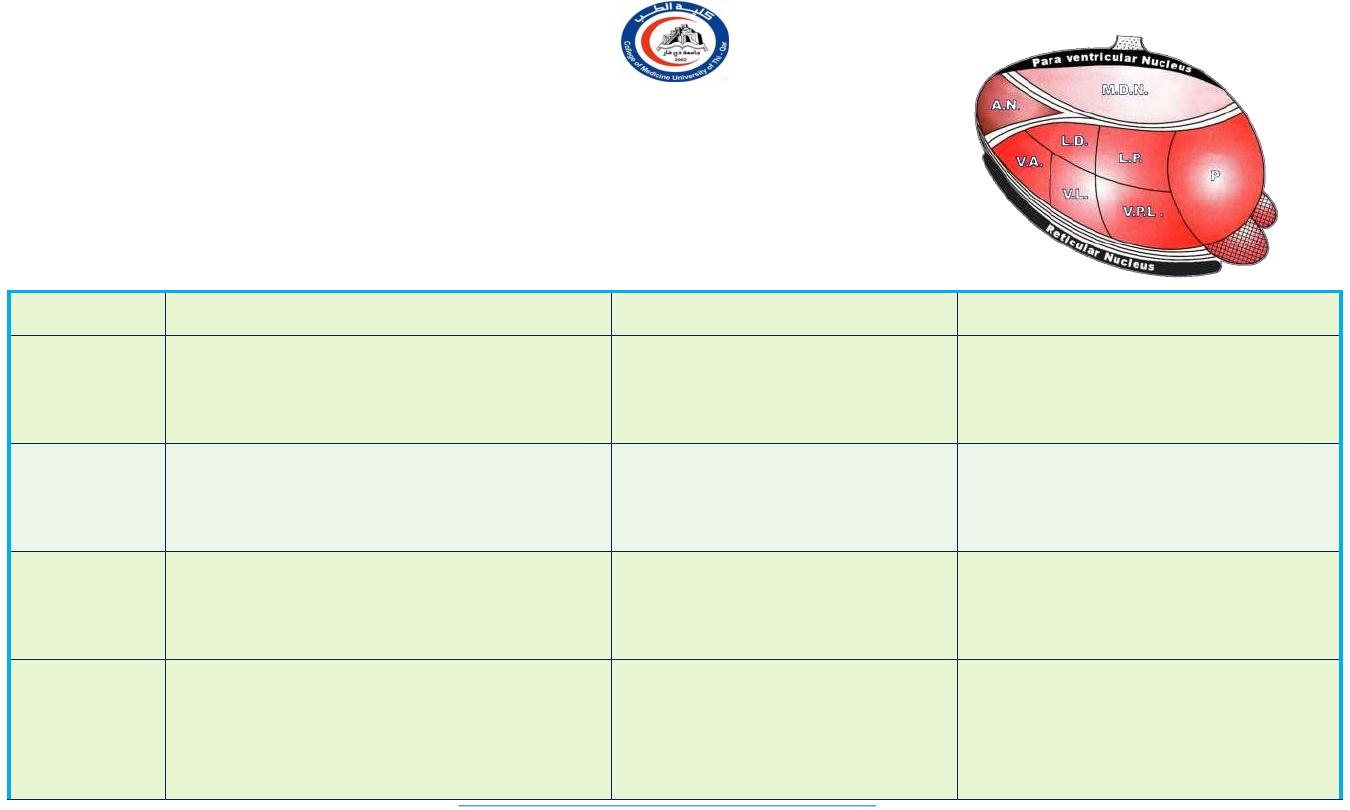
1.Non - Specific group
Do not receive afferents from ascending tracts, but have abundant
connections with other diencephalic nuclei. Project to cortical
association areas in frontal & parietal lobes.
Nucleus
Afferent
Efferent
Functions
Anterior
nucleus
Mamillothalmic tract (Mamillary body of
hypothalamus))
Cingulate gyrus (24)
1.Part of Papez circuit.
2.Attention,emotion & Recent
memory.
Dorso-
medial nu.
Prefrontal cortex &
Hypothalamus
Prefrontal
area(8,9,10,11)
Synthesis of crude somatic
sensation.
Midline
nu.
Spinothalamic,trigeminothalamic medial
leminiscus,reticular
formation,hypothalamus
Hypothalamus, neocortex,
basal ganglia
Crude visceral and somatic
sensation
Intra-
laminar
nu.
RAS, basal ganglia, other
thalamic nu.
Prefrontal cortex
Integrate somatic and visceral
sense.
Responsible for alerting affects of
RAS
21
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
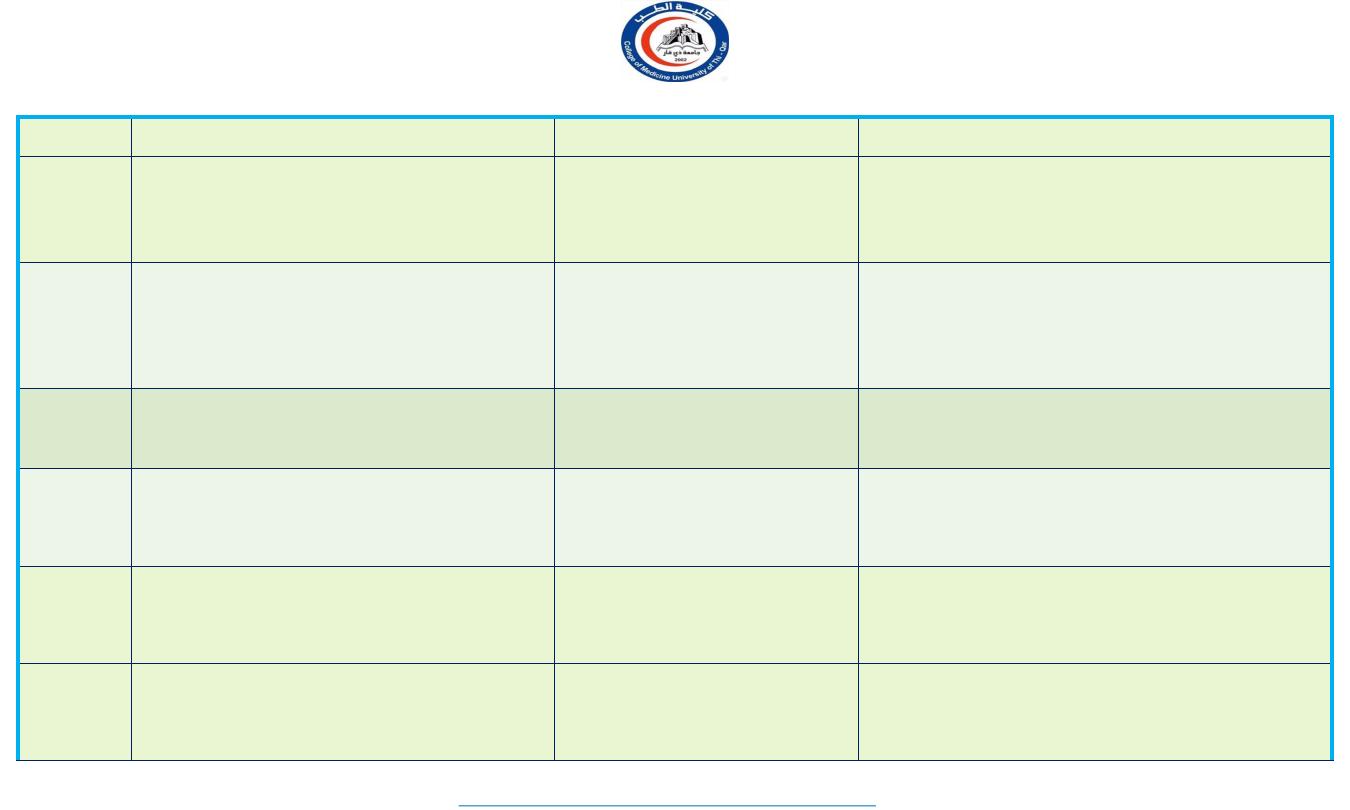
2.Specific Projection nuclei -
Nucleus
Afferent
Efferent
Functions
Postero-
ventral
nu.
Spinothalamic tract,medial
leminiscus.
Trigeminal,face,taste fibre
Sensory cortex(3,1,2)
1.Relay somatosensory impulse
(touch,pressure,pain,temp,proprioc-
eption,Kinesthetic) from trunk and limb.
2.Relay sensory impulse from Face.
Lateral
Ventral
nu.
Dentate nu.of Cerebellum & Globus
pallidus
(dentato-rubro-thalamic fibres)
(Dentato-thalamic fibres)
Motor & premotor areas
Area 4 & 6
Relay proprioceptive information and
voluntary motor functions.
Dorso-
lateral
nu.
Other thalamic nu.& parietal lobe of
cerebral cortex
Parietal lobe of cerebral
cortex
Speech & other complex integrated
function
Pulvinar
nu.
Other thalamic nu., cerebral
cortex(parietal, temporal,
occipital)
Cerebral cortex
Integrate auditory, visual,somatic
informations.
MGB
Topically organized project of Auditory
fibres from cochlear nu & Inferior
Colliculus
Primary auditory area 41 &
42, via internal capsule
Auditory impulses/Hearing
LGB
Optic tract
Ipsilateral calcarine
cortex (Geniculate
Calcarine tract)
Visual impulses
22
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
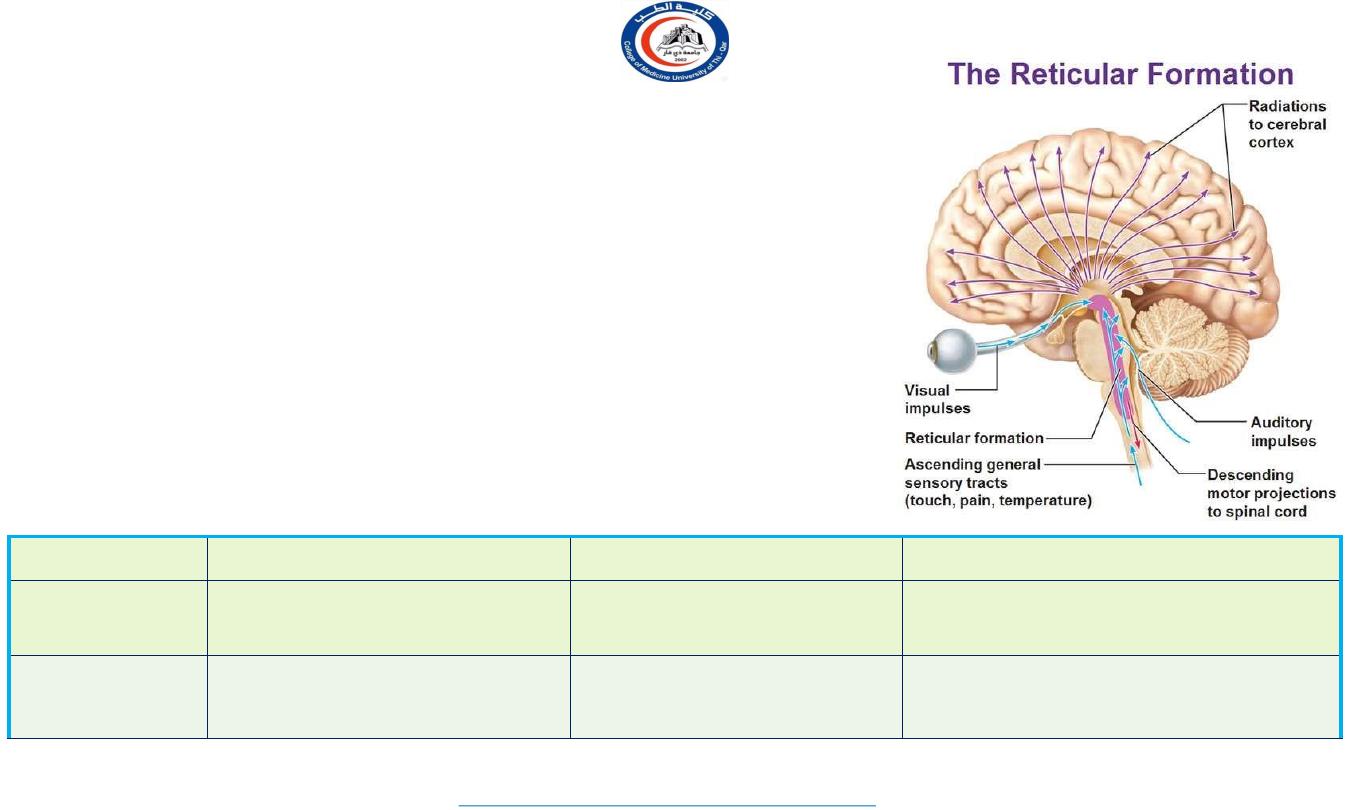
3. Reticular nuclei
Reticular nucleus, Intralaminar nuclei & Median nuclei
(Paraventricular nucleus)
Connected with Reticular formation
Nucleus
Afferent
Efferent
Functions
Reticular
Brain stem reticular
formation
Whole of cerebral
cortex
Forms part of reticular activating
system (RAS)
Intralaminar &
Centro median
Brain stem reticular
formation
Other thalamic nuclei &
Corpus striatum
Involved in awareness of painful
stimuli at thalamic level
23
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
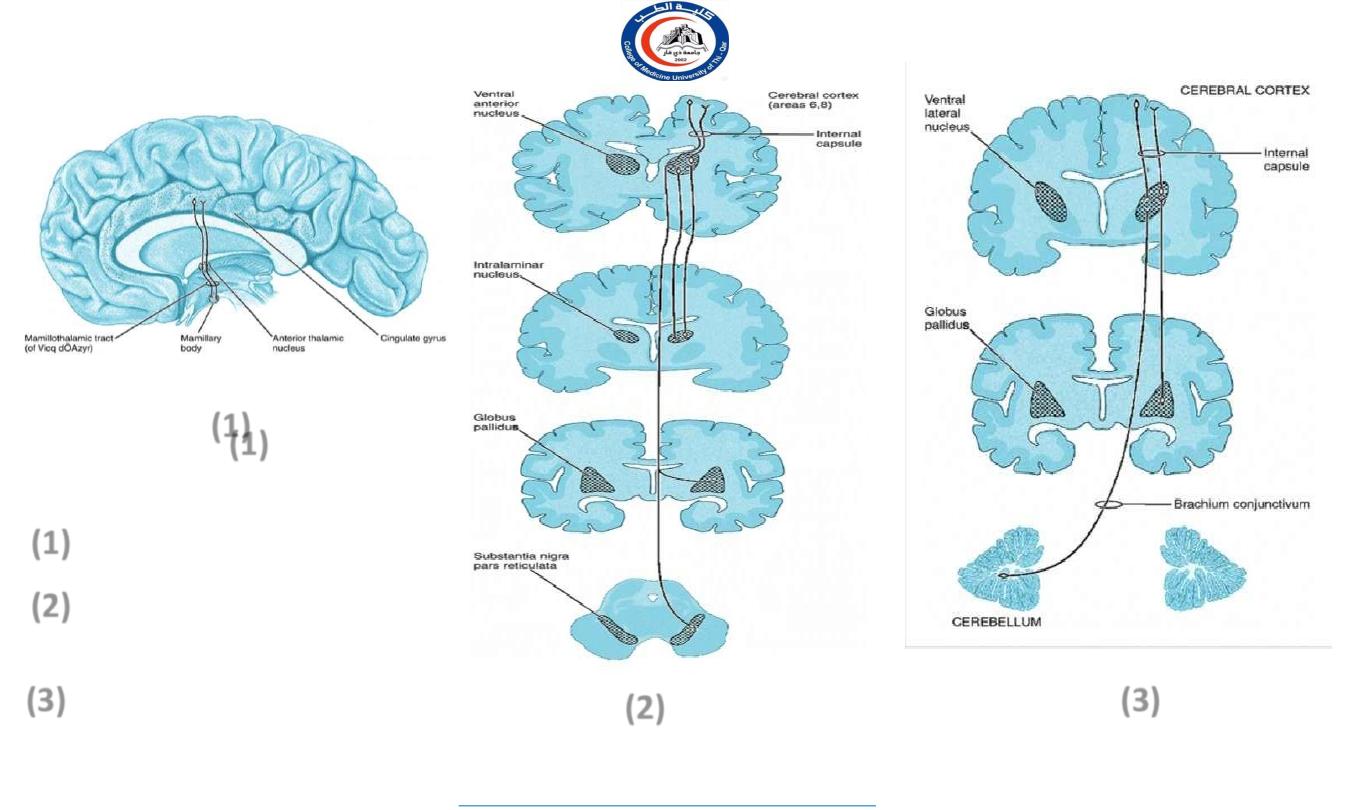
Schematic diagram showing the
major connections of the :
anterior nuclear
ventral anterior nucleus of
the thalamus.
nucleus ventralis lateralis of
the thalamus
(1)
(2)
(3)
(1)
(1)
(2)
(3)
24
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
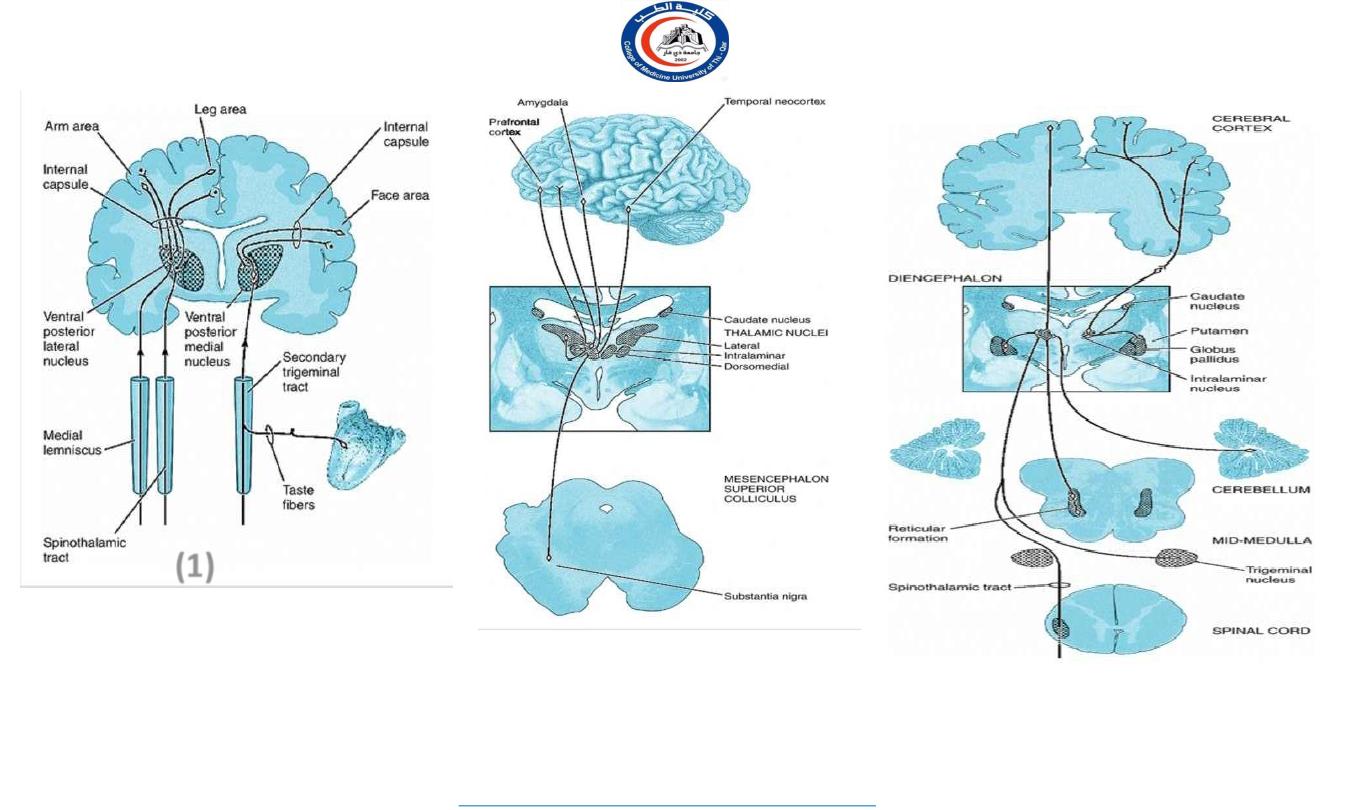
(1)
Schematic diagram showing the
major afferent and efferent
connections of the ventral
posterior lateral and ventral
posterior medial nuclei of the
thalamus
Schematic diagram showing the major
afferent and efferent connections of the
dorsomedial nucleus of the thalamus
Schematic diagram showing the major
afferent and efferent connections of the
intralaminar nuclei of the thalamus

25
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
Conclusion
• Thalamus acts as relay and integrative station for all the sensory
information except smell.
• Hypothalamus lies anterior to and inferior to the thalamus. It is center
of integration of autonomic and endocrine function.
• Both thalamus and hypothalamus makes the boundaries of 3
rd
ventricle.
• Both thalamus and hypothalamus also play a role in memory and
emotion.
There are many nuclei and it is very hard to remember…
But not impossible !!!!!!!!!

Done by
Dr. Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi Clinical Radiology CABM ,DMRD,MBCHB,
26
Thank you with best wishes
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
