Early pregnancy
bleeding:-
1- Abortion
2- Ectopic pregnancy
3- Gestational trophoblastic
disease.
4- other local and systemic

GTD
(gestational trophoblastic
disease)
It is a spectrum of diseases
arises from abnormal
fertilization event leading to
an abnormal pregnancy

CLASSIFICATION:
1- Benign hydatidiform mole which
further subdivided into partial and
complete mole.
2- Invasive mole (chorioadenoma
destruens) which can metastasize.
3- Choriocarcinoma (frankly malignant).
4- Placental site trophoblastic tumour
(PSTT).

GTD
The majority of the patients
follow a benign course and
their disease remitting
spontaneously.

The disease is characterized
by the sensitive tumour
marker (β-hCG) which is
secreted by the tumour cells
and allows accurate
diagnosis and follow up of
the disease.

Risk factors for gestational
trophoblastic disease (GTD)

Etiology and epidemiology
blood group A woman if married to a
man with blood group O (there is 10
folds higher risk of choriocarcinoma),
and if the woman of bl.gp AB it carries
a relatively worse prognosis.
Diet may play a role:
low dietary intake
of carotene
low protein,
animal fat
and
folic acid intake predispose to GTN
Low estrogen status?
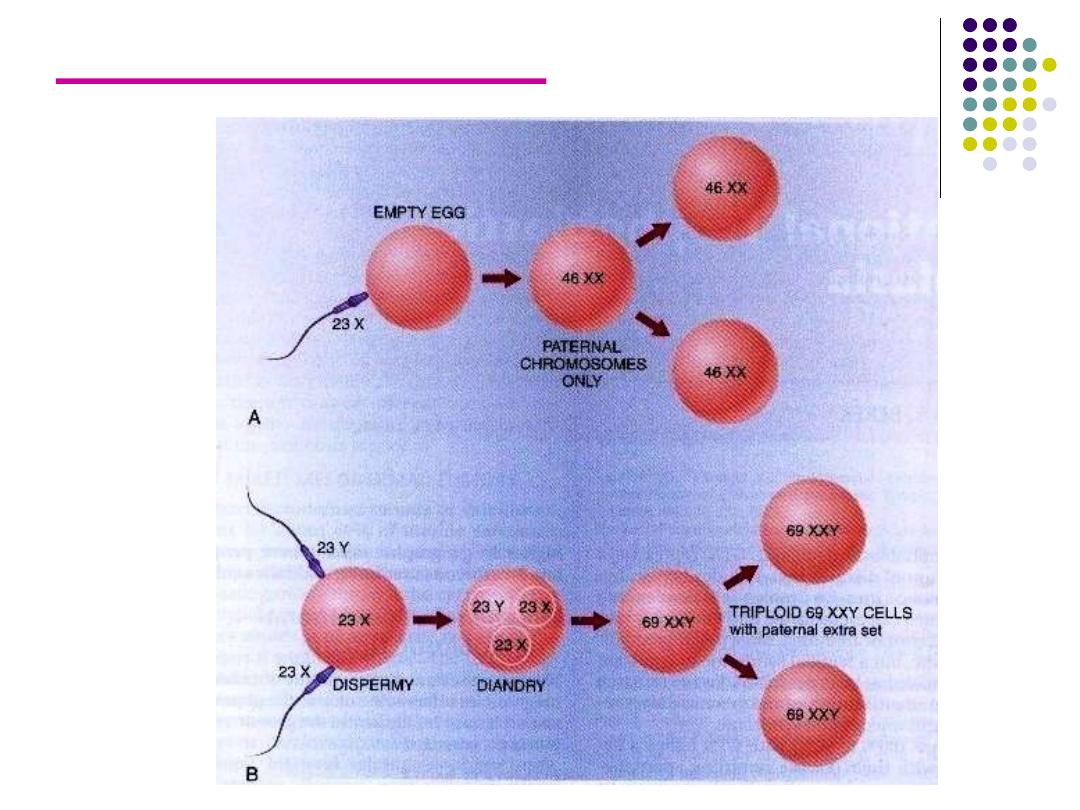
Genetics of H. mole
complete
partial
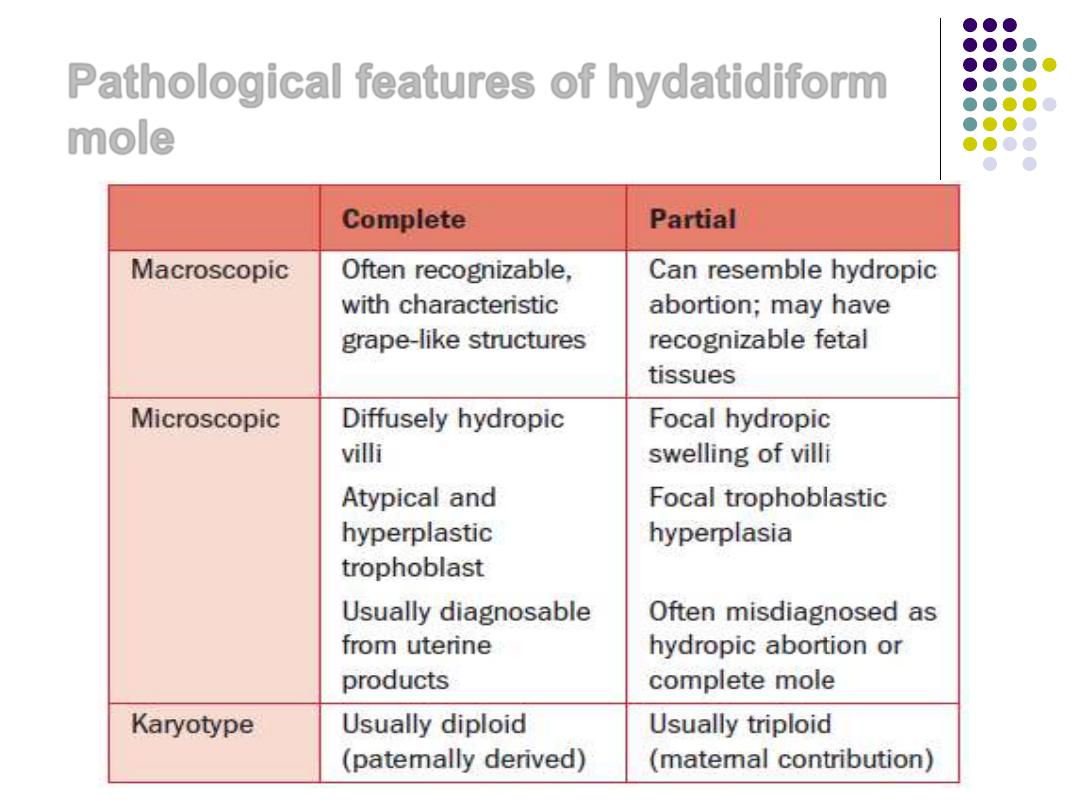
Pathological features of hydatidiform
mole
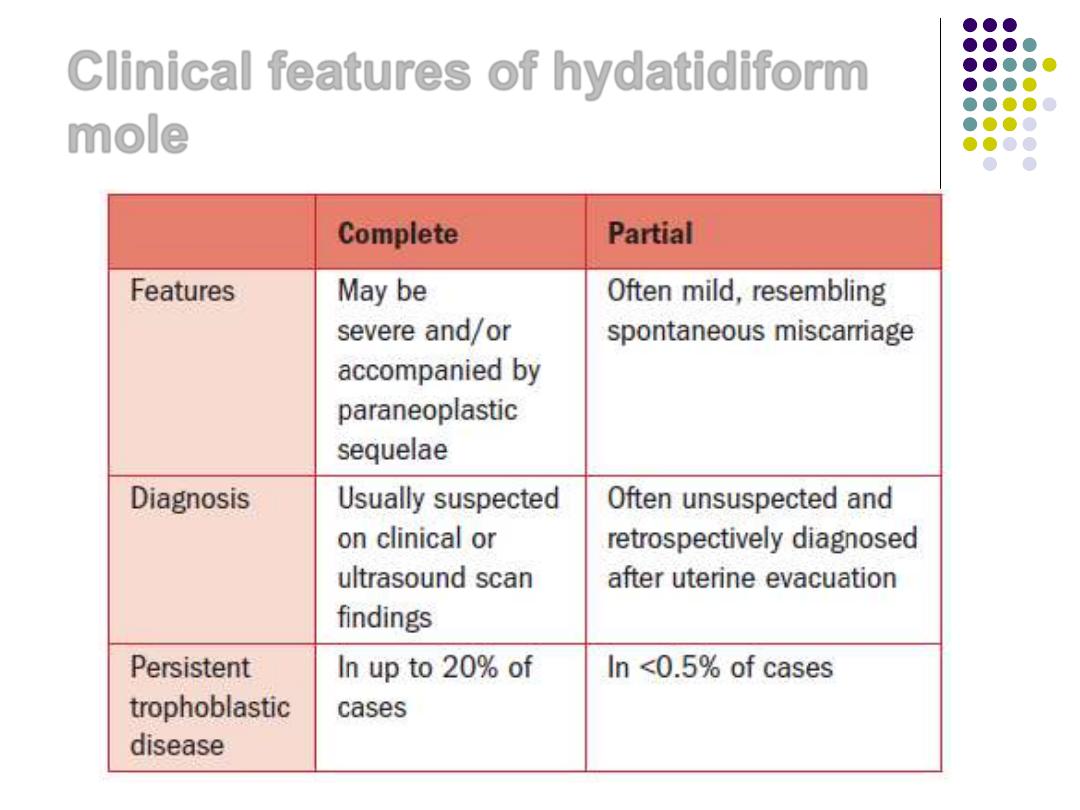
Clinical features of hydatidiform
mole

Diagnosis of H.Mole:
1) Symptoms and signs:
Abnormal vaginal bleeding
in the 1st
and the beginning of the 2
nd
trimesters in > 90% of the patients.
Anemia
:
dilutional
or may be due to
hemorrhage.
large for date
uterus with soft
(doughy) in consistency
No fetal parts
with negative fetal heart
tones

Symptoms and signs:
Pre eclampsia
early before 20
th
week
of gestation.
Hyperemesis
in 1/3 of the patients.
ovarian cysts
: multiple theca leutin
cyst due to high hCG.
Hyperthyroidism:
it is mild or
subclinical
Expulsion of vesicles vaginally

Investigations
)
2
1.
(β-hCG):
It is higher than normal pregnancy
values and can be detected in the
serum or urine of all patients (its level
correlate closely with the number of
viable tumour cells).(>200 000 U/L)
2.
U/S it is the diagnostic method of
choice (snow storm appearance)
3.
CXR to show metastatic disease

Treatment:
Evacuation of the uterus
preceded by
B hCG level
,
complete blood count, renal
function test, liver function test,
coagulation profile, ECG and
chest X- ray.
Blood loss is moderate
SO
(prepare blood)

The
GOLD standard
for termination of
pregnancy is by
suction curettage
which is safe
rapid and effective method.
when the conceptus nearly totally
evacuated we start the oxytocin to induce
uterine contractions and avoid
perforation.
Treatment: (continued)
* Hysterectomy
is done in certain
situations:
1- the woman >35 years completed family
2- high risk of persistent GTN may be lowered
by hysterectomy from 20% to 3.5% only.
Medical inducion
is
not
recommended
because fear of showering emboli through
the blood stream.
Hysterotomy is not recommended.
All Rh negative women should receive anti-D
immunoglobulin

Complications
1.
perforation
2.
hemorrhage
3.
Deportation of trophoblastic tissues to the
lungs is frequent which may regress
spontaneously but sometime
postevacuation acute pulmonary
insufficiency may result leading to
dyspnoea, and cyanosis 4-6 hours after
evacuation .
4.
Pulmonary edema from high output heart
failure , pre eclampsia, anemia, and
hyperthyroidism .
5.
Sepsis.

Surveillance following molar pregnancy
Following evacuation (β-hCG) titers
should be estimated serially because
of the 20-30% risk of persistent
disease.
The determination should be started 48
hours after the evacuation and weekly
until it becomes undetectable (< 5mIU).
Effective contraceptive measures is
essential

The titer remission should
occur spontaneously by
12 - 14 weeks
then the
patient should be followed
up monthly for 6-12 months
before the patient is
released from close medical
supervision

Gynecological examination 1week after
evacuation for uterine size, adnexial
mass, vulval and vaginal deposits
(metastasis).
1 year after negative titers pregnancy
is allowed

GTD
2
nd
PART

Prophylactic chemotherapy in molar
pregnancy for those with high risk of
persistent disease and risk of GTN
High initial hCG > 100,000 mIU/ml
Age > 40
Large for date uterus
Big ovarian cysts
Presence of embolizations
Poor compliance to follow up
Unavailability of health services and hormonal
follow up

Invasive mole:
1.
It occur in 20% of patients with H.mole,
2.
pathologically it is the same as
hydatidiform mole but penetrates deeply
into the myometrium or the adjacent
structures
3.
C/F: profuse hge, lower abd pain,
hematuria, rectal bleeding, intra peritoneal
bleeding, emboli to the lung
4.
It may regress spontaneously

Malignant GTN
The malignant GTN can be classified into:
the non-metastatic: invasive mole
and the metastatic: choriocarcinoma
and the PSTT

Malignant disease can be
suspected when
1- Plateauing or rising B-hCG value over a
period of 3 consecutive weeks.
2- A rise of B-hCG over a period of 2 weeks.
3- Persistence of a detectable B-hCG after 6
months of evacuation
4- appearance of metastasis during follow
up

The frankly malignant disease
is further subdivided into
1.
Good prognosis group (low
risk group)
2.
And the poor prognosis
group (high risk group).

Choriocarcinoma
The
antecedent pregnancy
is
1- H. mole in 50%,
2- normal pregnancy in 25%
3- abortion or ectopic pregnancy in
25%.

Clinical Presentation
1- Vaginal bleeding is the most common
symptom.
2- Lower abdominal pain because of invasion
of the surrounding structures.
3- Abdominal AND/OR vaginal mass.
4- Amenorrhea may precede bleeding caused
by the high B-hCG produced by the tumor
mass.

5- Pulmonary metastasis may cause dyspnoea
and haemoptysis it may be misdiagnosed as
pulmonary T.B and it can be diagnosed by
CXR.
6- Neurological abnormality may indicate brain
invasion.
7-
High index of suspicion is required to
diagnose it especially if it follows normal
pregnancy or abortion.
8- it invade the myometrium and metastasizes to
the lungs, brain, liver, and other organs.
Clinical Presentation

On examination:
Most of the patients have enlarged
uterus as well as ovarian enlargement
by theca lutein cysts.
Sites of metastasis should be looked
for especially in the vagina cervix and
the adnexia
Investigations:
1- B-hCG level in the serum or the urine.
it is very high > 100 000 IU / L
2-
U/S for the pelvis, liver, kidneys…
3- CXR.
4- CT for the brain, liver, and pelvic organs metastasis.
5- MRI for the brain metastasis.
6- Lumber puncture: CSF to measure the B-hCG level in
the CSF it should be greater than 1:40 (the ratio of the
level in the CSF to that in the serum)
7- CBP, LFT, RFT, and the coagulation study.

Confirmation of the diagnosis is
made by Histopathology of
curettage products but curettage
carry high risk of uterine
perforation and dissemination of
the disease, so it can be
diagnosed basically depending on
the clinical suspicion and high B-
hCG levels

Classification of the disease
according to the prognostic
:
factors
1- Good prognosis metastatic disease:
2- Poor prognosis metastatic disease:

1- Good prognosis metastatic
disease (criteria)
a- short duration (<4 months) between
the antecedent pregnancy and
chemotherapy.
b- Serum B- hCG <40 000 mIU /ml
c- No metastasis to the brain and the
liver.
d- No prior chemotherapy.

2- Poor prognosis metastatic
disease (criteria)
a- long duration from the antecedent
pregnancy (>4 months) to chemotherapy.
b- Serum B- hCG >40 000 mIU /ml.
c- Metastasis to the brain.
d- Unsuccessful prior chemotherapy.
e- If the disease is following term pregnancy.

Treatment of GTD
A) For the non metastatic GTD (CM & invasive
mole) and for the low risk metastatic disease:
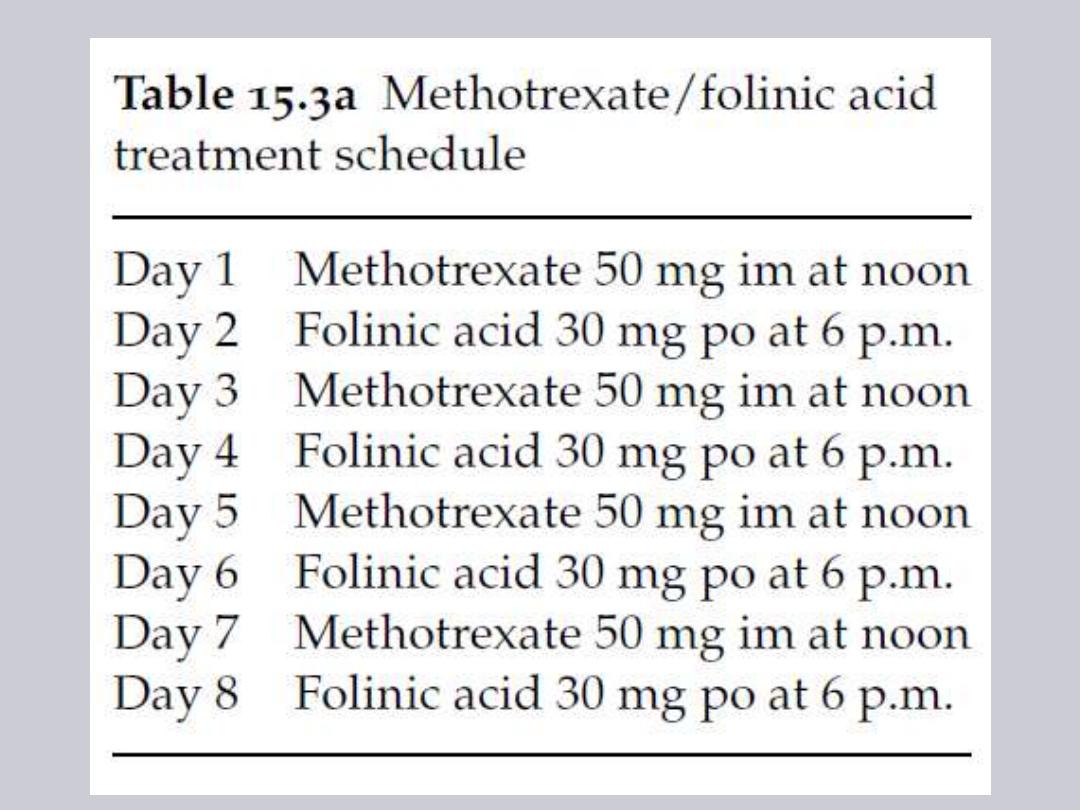
1- Single agent chemotherapy: either
methotrexate
(MTX) or actinomycin
–D
(dactinomycin).
2- Combine chemotherapy with hysterectomy in
female who not wish to preserve reproductive
function and her disease is confined to the
uterus.

Important notes:
When the patient is not responding to this
chemotherapeutic agent, this will indicate
switching to new agent or combination
chemotherapy
Effective contraception should continue for
1 yr after remission

follow up program:
B-hCG weekly until 3 consecutive
negative titer, then monthly for a year,
then 2 monthly for another year, then 6
monthly for life,
the follow up need Pelvic examination
and CXR together with the hCG titer

Poor prognosis (high risk)
metastatic disease group:
Should be treated by combined
chemotherapy (multiple agents)
Usually respond poorly (<40% response
rate) to single agent chemotherapy.
Prior unsuccessful chemotherapy is
one of the worst prognostic factors
because of considerable toxicity and
depleting bone marrow reserves.

IF RESISTANCE OCCURS TO
COMBINED CHEMO then
Adjuvant surgery: hysterectomy,
thoracotomy or craniotomy for
chemotherapy resistant malignant
masses.

Prognosis of GTD:
1.
For H. Mole the prognosis is
excellent,
2.
For the good prognostic group the
cure rate is 75-85%,
3.
the poor prognosis group if there is
liver metastases the survival from (0-
60%).
4.
The survival is <20% if previous
failed chemotherapy

Subsequent pregnancy
There are no extra complication during
pregnancy but require good follow up by
U/S and B-hCG levels because of the 2%
risk of recurrence after 1 mole and 20%
after 2 moles and 50% after 3 moles.
After delivery placenta should be sent for
histopathological study, and B-hCG level
must be measured 6 weeks postpartum.
