
REMOTE SENSING
PLATFORMS
BALLONS
HELICOPTERS
AIRPLANES
SATELLITES
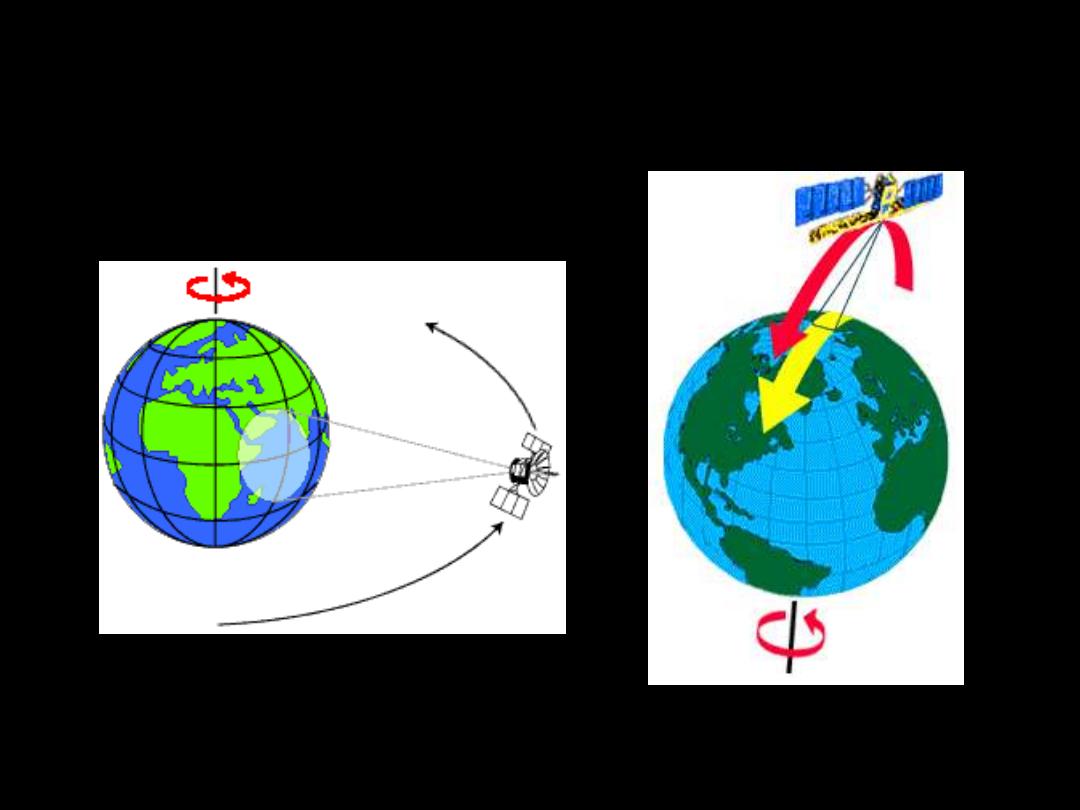
ORBITS
Geostationary orbit Near Polar orbit
(appr.36.000 km) (appr. 500-1000 km)

MAJOR EARTH OBSERVING
SATELLITES
• Landsat
• SPOT
• Ikonos
• AVHRR
• Seawifs
• GOES
• Meteosat
• Terra EOS Satellite (ASTER, MODIS,
CERES, MOPITT, MISR)

MAJOR EARTH OBSERVING
SATELLITES (contd.)
• Radarsat
• ESA Satellites (ERS, ATSR)
• India Satellites (IRS, LISS, OCM)
• Japanese Satellites (JERS, ADEOS, AVNIR,
OCTS, MOS, ALOS)
• Russian Satellites (Priroda, etc)

LANDSAT

LANDSAT
•
Swath Width: 185 km
• Repeat Cycle 16 days
• Orbit Altitude: 705 km
• Equatorial Crossing: at around 10 a.m. local solar time
Spectral Bands of Landsat-7
Band
Spectral Range (mm)
Ground Resolution
1 (Blue)
.450- .515
30
2 (Green)
.525- .605
30
3 (Red)
.630- .690
30
4 (Near IR)
.750- .900
30
5 (Mid IR)
1.55- 1.75
30
6 (Thermal IR)
10.4- 12.5
60
7 (Mid IR)
2.09- 2.35
30
Panchromatic
.520-.900
15
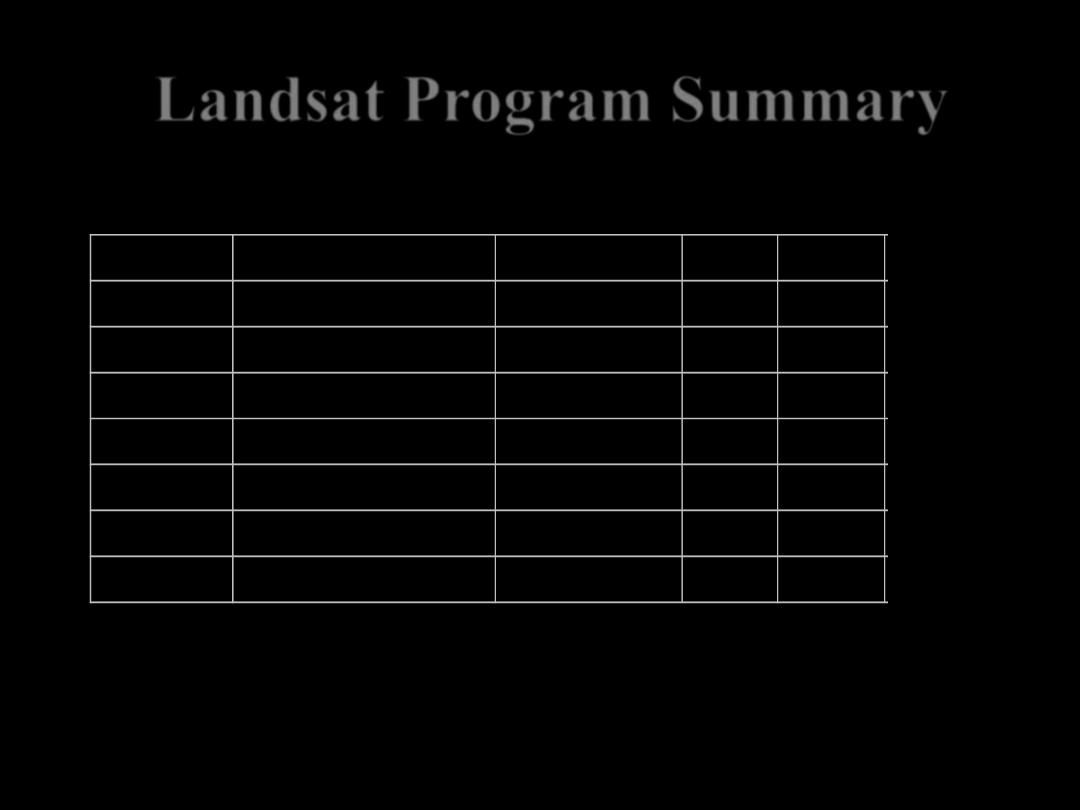
Landsat Program Summary
System
Lounch (End Of Service)
Res (m)
Alt (km) R (days) D (Mbps)
Landsat 1 7/23/1972 (1/6/1978)
80 (RBV), 80 (MSS)
917
18
15
Landsat 2 1/22/1975 (2/25/1982)
80 (RBV), 80 (MSS)
917
18
15
Landsat 3 3/5/1978 (3/31/1983)
30 (RBV), 80 (MSS)
917
18
15
Landsat 4
7/16/82
80 (MSS), 30 (TM)
705
16
85
Landsat 5
3/1/84
80 (MSS), 30 (TM)
705
16
85
Landsat 6 10/5/1993 (10/5/1993)
15 (PAN), 30 (MS)
705
16
85
Landsat 7
Dec-98
15 (PAN), 30 (MS)
705
16
150

SPOT 4 Characteristics
Band (m) Spectral range (µm) Spatial resolution (m)
B1 (Green) .500 - .590 20
B2 (Red) .610 - .680 10 and 20
B3 (Near IR) .790 - .890 20
SWIR (MIR) 1.58 - 1.75 20

IKONOS
September 1999
Space Imaging Inc.

Launch Date September 24, 1999
Launch Vehicle Athena II
Launch Vehicle Manufacturer Lockheed Martin
Ground resolution
1-meter panchromatic (nominal at <26deg off nadir)
4-meter multi-spectral (nominal at <26deg off nadir)
The ground processing software has the capability to rapidly process and mosaic imagery so as to
create seamless image products with a consistent pixel ground sample distance (GSD).
Imagery Spectral Response
Panchromatic: 0.45 - 0.90 microns
Multispectral: #1: Blue 0.45 - 0.52 #2: Green 0.52 – 0.60
#3: Red 0.63 - 0.69 #4: Near IR 0.76 - 0.90
(same as Landsat 4&5 TM Bands #1-4)
Nominal Swath Width 11 km at nadir
Areas of Interest
a nominal single image at 13 km x13 km
strips of 11km x 100 km up to 11 km x 1000 km
image mosaics of up to 12,000 sq. km.
up to two 10,000 square kilometer contiguous areas in a single pass within a region
Metric Accuracy 12-meter horizontal and 10-meter vertical accuracy with no ground control
2-meter horizontal and 3-meter vertical accuracy with ground control
These are specified as 90% CE (circular error) for the horizontal and 90% LE (linear error) for the
vertical
Orbital Information
Altitude 423 miles / 681 Inclination 98.1 degrees
Speed 4 miles per second / 7 kilometers per second
Revisit Frequency
2.9 days at 1-meter resolution;
1.5 days at 1.5-meter resolution
Orbit time 98 minutes Orbit type sun-synchronous
IKONOS Specifications
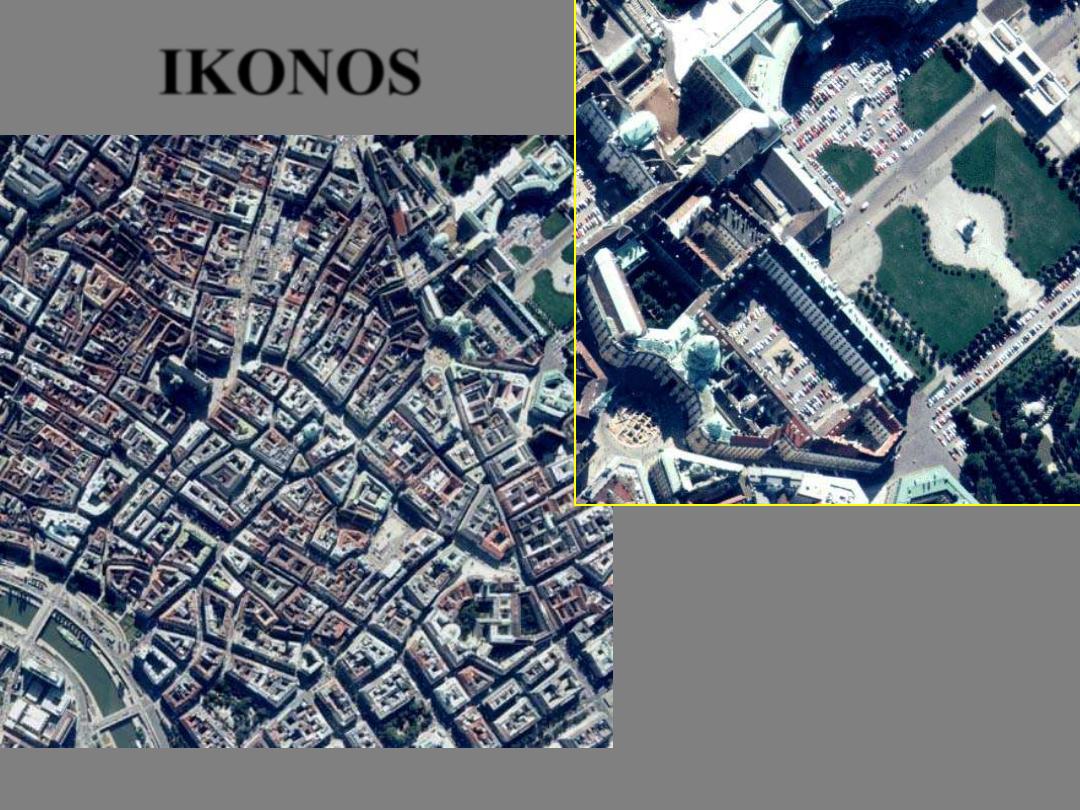

Vienna, Austria
(full) April 2000
Vienna, Austria
(enlargement)
One-meter pan-sharpened image
of Vienna, Austria. Shown here
are the Imperial Palace and gardens.
This imagery is useful for trans
-portation network monitoring,
tourism, real estate and other applications
IKONOS
GOES
(Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellites)
• The GOES series of satellites is the
primary
weather
observation platform for the United States.
• The latest generation, GOES I-M, represent an advance in
data products for weather forecasting and storm warnings
over the previous series of geostationary satellites.
• GOES I-M is a 3-axis stabilized system vs. the older spin-
scan system, providing more accurate geo-location of earth
images.

METEOSAT
• Europe's geostationary weather observation satellite
• Meteosat was launched in November 1993.
• The 4 channel, 3-spectral-band high resolution radiometer constitutes
the main payload on board Meteosat.
• The radiometer scans in
3 spectral bands: Visible, Infrared, and Water
Vapor.
• The instrument allows continuous imaging of the Earth with images
sent
every half-hour.

RADARSAT
Canadian Space Agency

SAR Characteristics
Frequency / Wavelength
5.3GHz/C-band 5.6 cm
RF Bandwidth
11.6, 17.3 or 30.0 Mhz
Transmitter Power (peak)
5 kW
Transmitter Power (average)
300 W
Maximum Data Rate
85 Mb/s (recorded) - 105 Mb/s (R/T)
Antenna Size
15m x 1.5m
Antenna Polarization
HH
Orbit Characteristics
Altitude
793-821 kilometres
Inclination
98.6 degrees
Period
101 minutes
Ascending node
18:00 hours
Sun-synchronous
14 orbits per day
Coverage Access Using Maximum Swath Width
North of 70 degrees N
Daily
North of 48 degrees N
Every 4 days
The Whole Earth
Every 6 days
RADARSAT Specifications

Imaging Modes
MODE NOMINAL NO. OF SWATH INCIDENCE
RESOLUTION (m) POSITIONS/BEAMS WIDTH (km) ANGLES (degrees)
Fine 8 15 45 37-47
Standard 30 7 100 20-49
Wide 30 3 150 20-45
ScanSAR Narrow 50 2 300 20-49
ScanSAR Wide 100 2 500 20-49
Extended(H) 18-27 3 75 52-58
Extended(L) 30 1 170 10-22
RADARSAT Specifications (cont.)

ESA Satellites
and
Earth Observation System

ATSR (Along Track Scanning Radiometer)
•
Objective: sea surface temperature, cloud
observations, land and ice surface emissivity
• Spectral channels: 4 co-registered channels at 1.6,
3.7, 10.8 and 12 micro-meter
• IFOV: 1 km x 1 km (nadir), 1.5 km x 2 km
(forward view)
• Swath width: 500 km

India Satellites
and
Earth Observation System
The earliest Indian satellite IRS-1C was launched in December 1995 and carried
instruments with both high and medium spatial resolutions.
IRS-1C
IRS-1C data is available from January 1998 to till date
IRS-1C WIFS data is available from October 4th 1999 to till date
SENSOR
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
SCALE
AREA
LISS – III
Standard Full scene based path row products
1:250,000
141 kmx 141
km
LISS -III
Standard Quadrant scene based path row
products
1:125,000
72 km x 72
km
PAN
Standard Full Scene based path row products
Not Applicable
70 km x (70-
91) km
PAN
Standard Quadrant scene based path row
products
Not Applicable
35 km x 35
km
PAN
Standard Sub-scene based path row products
1:50,000
23 km x (23-
30) km
PAN
Geocoded data products as per SOI toposheet
for Indian region
1:25,000
14 km x 14
km
PAN
Point geocoded products
1:12,500
9 km x 9 km
WiFS
Standard Scene based path row products
1:2M
810 km x 810
km
IRS-1C data is available from January 1998 to till date
IRS-1C WIFS data is available from October 4th 1999 to till date
SENSOR
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
SCALE
AREA
LISS – III
Standard Full scene based path row products
1:250,000
141 kmx 141
km
LISS -III
Standard Quadrant scene based path row
products
1:125,000
72 km x 72
km
PAN
Standard Full Scene based path row products
Not Applicable
70 km x (70-
91) km
PAN
Standard Quadrant scene based path row
products
Not Applicable
35 km x 35
km
PAN
Standard Sub-scene based path row products
1:50,000
23 km x (23-
30) km
PAN
Geocoded data products as per SOI toposheet
for Indian region
1:25,000
14 km x 14
km
PAN
Point geocoded products
1:12,500
9 km x 9 km
WiFS
Standard Scene based path row products
1:2M
810 km x 810
km
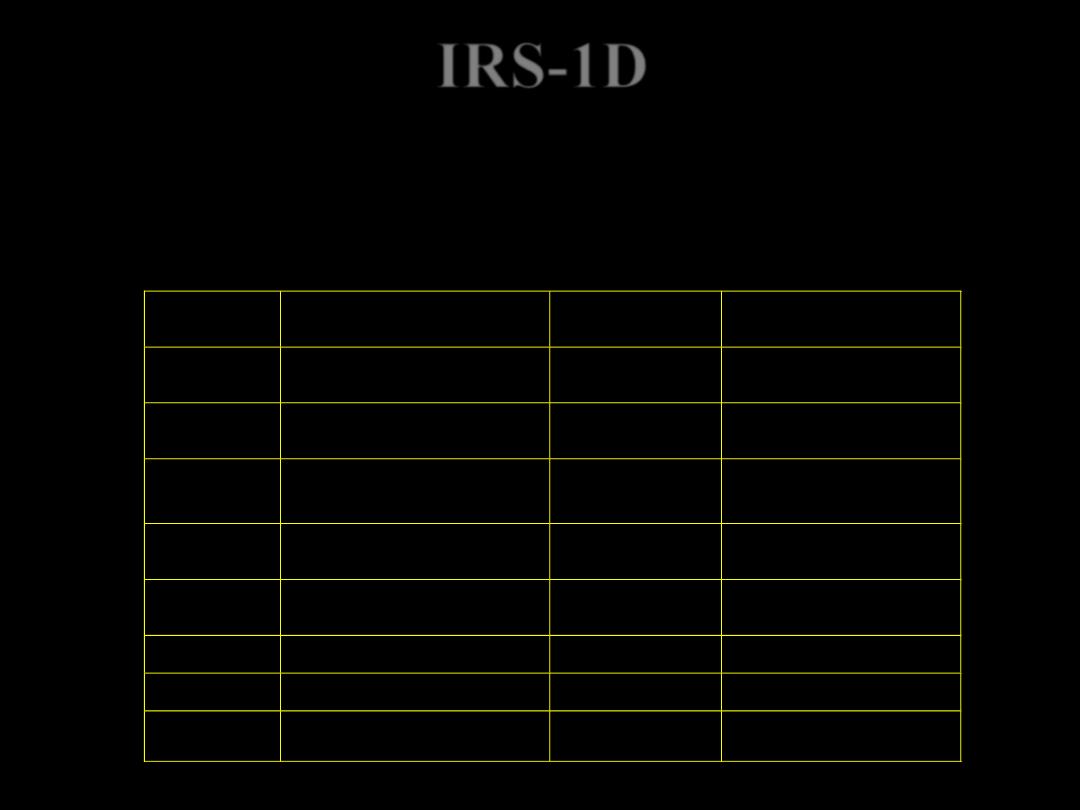
IRS-1D was successfully launched on September 29, 1997. The satellite is
an identical twin to IRS-1C. Thus this satellite couple together gives a
revisiting cycle of 12 days as opposed to the single-satellite 24-day revisit
cycle.
IRS-1D data is available from April 15th 1998 to till date
SENSOR
PRODUCT
DESCRIPTION
SCALE
AREA
LISS – III
Standard Full scene based path row
products
1:250,000
127 km x 145.5 km
LISS -III
Standard Quadrant scene based path
row products
1:125,000
63.5 km x 71 km
PAN
Standard Full Scene based path row
products
NotApplicable
63 km x 71.8 km
PAN
Standard Quadrant scene based path
row products
NotApplicable
31.5 km x 34.5 km (Nadir)
PAN
Standard Sub-scene based path row
products
1:50,000
21 km x 23 km (Nadir)
PAN
Geocoded data products as per SOI
toposheet for Indian region
1:25,000
14 km x 14 km
PAN
Point geocoded products
1:12,500
9 km x 9 km
WiFS
Standard Scene based path row
products
1:2M
720 km x 778 km
IRS-1D

IRS-P3 is a purely research satellite, successfully launched 21 March, 1996
with WiFS sensor such as IRS-1 C/D with SWIR band at resolution 188 x 246
meter.
IRS-P4 (OCEANSAT-1) was successfully launched 26 May, 1999. The
satellite is equipped with two instruments:
OCM ( Ocean Color Monitor )
•
Sun synchronous at an altitude of 720 km.
• Operating in eight narrow spectral bands, 0.400 - 0.885 micrometer,
• A resolution of 350 m and a swath of 1420 km
• Used to collect data on chlorophyll concentration, detect and monitor
phytoplankton blooms and obtain data on atmospheric aerosols and suspended
sediments in the water.
MSMR ( Multifrequency Scanning Microwave Radiometer ).
•
A swath of 1360 km
• Operating in four microwave frequencies both in vertical and horizontal
polarization
• Used to collect data on sea surface temperature, wind speed, cloud water content
and water vapor content in the atmosphere above the ocean.
IRS-P3 and IRS-P4

Japanese Satellite
and
Earth Observation System

JERS-1
(Japanese Earth Resources Satellite)
1. Objective:
Gather data on global land masses while conducting observation for land
surveys, agricultural-forestry-fisheries, environmental protection, disaster
prevention and coastal surveillance, with emphasis on locating natural resources.
2. Operation Time :
1992 - 1998
3. Sensors:
• SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) which is an active microwave sensor
• OPS (Optical Sensor) that measures light reflected from the earth's surface
ranging from visible light to short-wave infrared light.

ADEOS
(Advanced Earth Observing Satellite)
1. Goal:
Monitoring global environmental changes such as maritime meteorological
conditions, atmospheric ozone, and gases that promote global warming
2. Operation Time :
August 1996 - June 1997
3. Sensors:
•
AVNIR (Advanced Visible Near Infrared Radiometer)
•
OCTS (Ocean Color and Temperature Scanner)
•
NSCAT (NASA Scatterometer)
•
TOMS (Total Ozone Mapping Spectrometer)
•
POLDER (Polarization and Directionality of the Earth's Reflectance)
•
IMG (Interferometric Monitor for Greenhouse Gases)
•
ILAS (Improved Limb Atmospheric Spectrometer)
•
RIS (Retroreflector In-Space)

AVNIR
(Advanced Visible Near Infrared Radiometer
)
Measurement Objectives: Land and Coastal Zone
Scanning Method : Electronic(CCD)
Wavelength: Visible( 3 Bands),Near-infrared(1)
Panchromatic-Band (visible): 1Bands
Spatial Resolution:
16m
, Panchromatic-Band:8m
Swath Width: 80km

OCTS
(Ocean Color and Temperature Scanner)
Measurement Objectives: Ocean Color and Sea Surface Temperature
Scanning Method: Mechanical
Wavelength: Visible: 6 Bands, Thermal-infrared:3 Bands,
Middle-infrared: 1 Bands
Spatial Resolution:
700m
Swath Width: 1400km

MOS
(Marine Observation Satellite MOS-1 / MOS-1b)
1. Objective:
Japan's first marine observation satellite, was launched as a link in a global satellite
observation system for more effective natural resource utilization and for
environmental protection.
2. Operation Time:
1987 - April 1996
3. Sensors:
• MESSR ( Multi-spectral Electronic Self-scanning Radiometer )
An electronic scanning radiometer that observes solar light reflected from the earth
surface. It is equipped with two camera systems that are set parallel to the satellite's flight
direction.
• VTIR (Visible and Thermal Infrared Radiometer )
Using a rotating scanning mirror, the VTIR mechanically scans from right to left at right
angle to the satellite's flight direction.
• MSR ( Microwave Scanning Radiometer )
A radio sensor scanning the earth surface along the flight path with its rotating dish
antenna.
