- 1 -
College of Medicine
Time : 2 hrs
Dept. of Physio& Medical Physics Jun:10 ,2020
Light in Medicine Course : MPH2
****************************************************************************
Light in Medicine
/PART2
Applications of ultraviolet and infrared light in medicine
The wavelengths adjacent to the visible spectrum also have
important uses in medicine. Ultraviolet photons have energies greater than
visible photons, while IR photons have lower energies, because of their
higher energies, UV photons are more useful than IR photons.
Ultraviolet light with wavelengths below about 290 nm is germicidal-
that is, it can kill germs-and it is sometimes used to sterilize medical
instruments. Ultraviolet light also produces more reactions in the skin than
visible light. Some of these reactions are beneficial, and some are harmful.
One of the major beneficial effects of UV light from the sun is the conversion
of molecular products in the skin into vitamin D and improves certain
skin condition.
Ultraviolet light from the sun affects the melanin in the skin to cause
tanning. However, UV can produce sunburn as well as tan the skin. The
wavelengths that produce sunburn are around 300 nm, just at the edge of the
solar spectrum. The amount of 300 nm light in the sun's spectrum
depends
on the amount of atmosphere that the sunlight must pass through. In winter
in northern climates the angle of the sun is such that the atmosphere absorbs
nearly all of the wavelengths that produce sunburn. In the early morning and
late afternoon of summer days the angle of the sun is again such that the
UV wavelengths that produce sunburn are filtered out by the atmosphere.
- 2 -
Ordinary window glass permits some near UV to be transmitted but
absorbs the sunburn component.
Solar UV light is also the major cause of
skin cancer in humans.
The high incidence of skin cancer among people, who have been exposed to
the sun a great deal, such as fishermen and agricultural workers, may be
related to the fact that the UV wavelengths that produce sunburn are also
very well absorbed by the DNA in the cells. Skin cancer usually appears on
those portions of the body that have received the most sunlight, such as the
tip of the nose, the tops of the ears, and the back of the neck. Fortunately,
skin cancer is easily cured if it is detected in its early stage.
You probably know that the sky is blue because light of short (blue)
wavelengths is scattered more easily than light of long wavelengths.
Ultraviolet light has even shorter wavelengths than blue light and is
scattered even more easily. About half of the UV light hitting the skin on
a summer day comes directly from the sun and the other half is scattered
from the air in other parts of the sky. Thus you can get a sunburn even
when you are sitting in the shade under a small tree. Even when the sky is
completely covered with clouds about one half of the UV light gets
through.
Ultraviolet light cannot be seen by the eye because it is absorbed before it
reaches the retina . The large percentage of near-UV light absorbed by the
lens may be the cause of some cataracts (
opacities of the lens).
Individuals who have had the lens of an eye removed because of a cataract are
able to see in to the near–UV region because the major absorber is no longer
present.
About half of the energy from the sun is in the IR region. The warmth we
feel from the sun is mainly due to the IR component. The IR rays are not
usually hazardous even though they are focused by the cornea and lens of
- 3 -
the eye onto the retina. However, looking at the sun through a filter (
e.g.,
plastic sunglasses) that removes most of the visible light and allows most
of the IR wavelengths through can cause a burn on the retina . Some people
have damaged their eyes in this way by looking at the sun during a solar
eclipse. Dark glasses absorb varying amounts of the IR and UV rays from
the sun.
Heat lamps that produce a large percentage of IR light with
wavelengths of 1000 to 2000 nm are often used for physical therapy
purposes. Infrared light penetrates further into the tissues than visible light
and thus is better able to heat deep tissues.
Two types of IR photography are used in medicine:
reflective IR
photography and
emissive IR photography. The latter, which uses the long IR
heat waves emitted by the body that give an indication of the body
temperature, is usually called
thermography. Reflective IR photography,
which uses wavelengths of 700 to 900 nm to show the patterns of veins just
below the skin. Some of these veins are visible to the eye, but many more
can be seen on a near-IR photograph of the skin. Since the temperature at
the skin
depends on the local blood flow, a thermogram with good
resolution shows the venous pattern much like a near-IR photograph.
There is considerable variation in the venous patterns of normal
individuals. Even in the same individual the venous patterns in the two
breasts may be quite different. Cancer and other diseases can cause
changes in the venous pattern, but these changes can be masked by the
normal variations. Also, a layer of fat beneath the skin can reduce the
appearance of the venous pattern. Nevertheless, IR photograph can be used
to follow changes in the venous pattern.
Near IR penetrates about 3mm below the skin regardless of the color of the
skin. Also, differently colored skins reflect about the same amount of IR, so that
- 4 -
IR photographs of blacks and whites appear about the same. The IR photograph
shows the venous pattern, but the variations in the melanin content of the skin
due to the suntan are not apparent.
Infrared can also be used to photograph the pupil of the eye without
stimulating the reflex that changes its size.
Infrared photographs of biological specimens illuminated with blue-green
light sometimes show IR luminescence (fluorescence or phosphorescence).
Lasers in medicine
A laser is a unique light source, that emits a narrow beam of light of a
single wavelength (monochromatic light) in which each wave is in phase
with the others near it (coherent light). Laser is an acronym for Light
Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation.
While the basic theory for lasers was proposed by Albert Einstein in
1917, the first successful laser was not made until 1960, when T. H.
Maiman produced a laser beam from a ruby crystal. Since 1960 scientists
have made many types of lasers using gases and liquids as well as solids
as the laser materials.
In a laser, energy that has been stored in the laser material (e.g., ruby) is
released as a narrow beam of light-either as a steady beam continuous
wave (CW) or an intense pulse. The beam remains narrow over long
distances and can be thought of as an ideal "spot" light. A laser beam can
be focused to be a spot only a few microns in diameter. When all of the
energy of the laser is concentrated in such a small area, the power density
becomes very large. The total energy of a typical laser pulse used in
medicine, which is measured in millijoules (mJ), can be delivered in less,
than a microsecond .
- 5 -
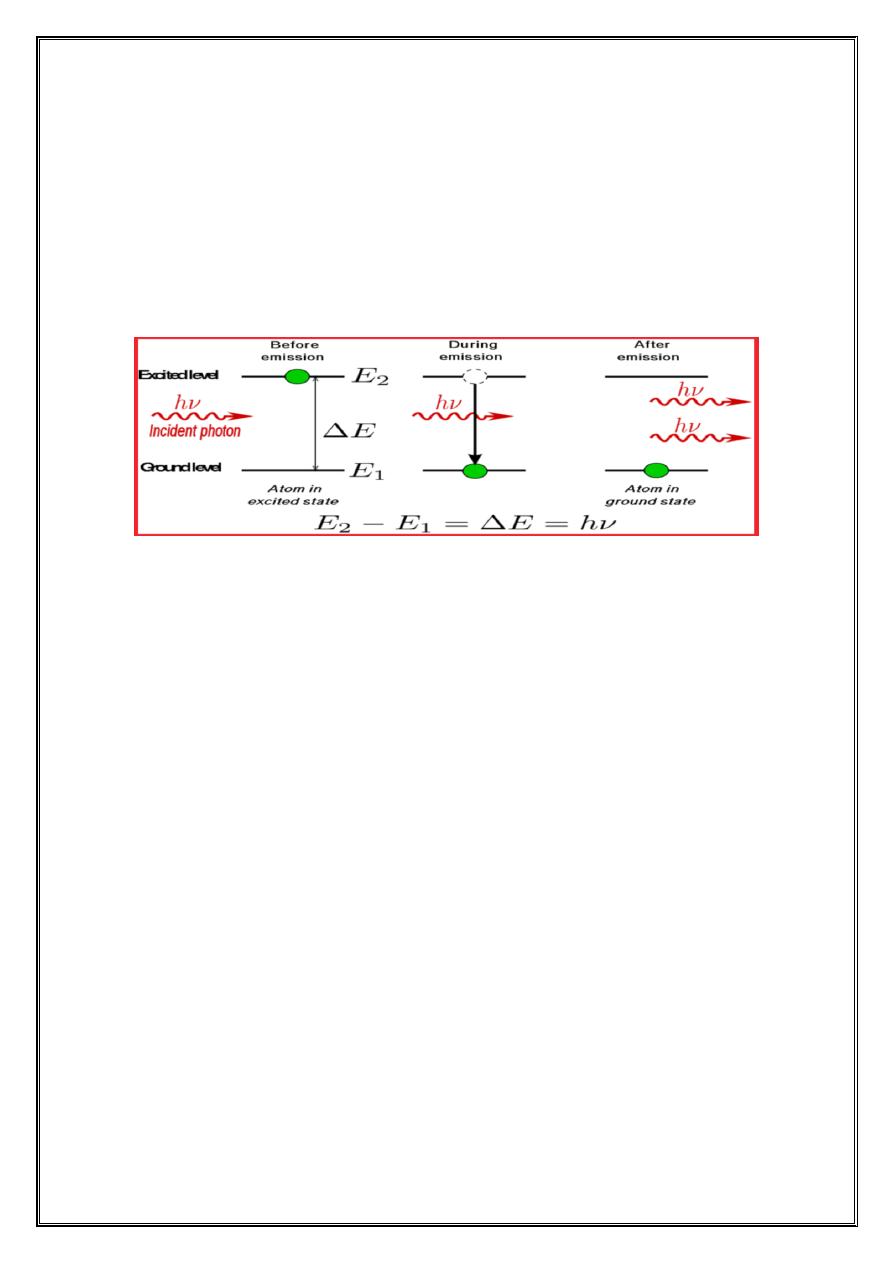
When an electron makes a transition from higher energy to lower
energy state, a photon is emitted . The emission process can be one of two
types, spontaneous emission or stimulated emission.
• In spontaneous emission the photon is emitted spontaneously, in a
random direction, without external provocation .
• In stimulated emission an incoming photon stimulates the electron to
change energy levels. To produce stimulated emission, however, the
incoming photon must have energy that exactly matches the difference
between the energies of two levels .
The operation of lasers depends on stimulated emission.
Stimulated emission has three important features.
1
-One photon goes in and two photons come out .The process amplifies
the number of photons. This is the origin the word laser which is an a
crony for light amplification by the stimulated emission radiation
2
-The emitted photon travels in the same direction as incoming photon.
3
-The emitted photon is exactly in step with or has same phase as the
incoming photon. In other word, the two electromagnetic waves that these
two photons represent are coherent.
In medicine laser are used primarily to deliver energy to tissue.
i.The laser wave length used should be strongly absorbed by tissue .The
short wave (400-600nm) are always absorbed better than the long wave
(700nm) .
ii. Laser energy directed to human tissue cause a rapid rise in temperature
and can destroy the tissue .The amount of damage to living tissue depends
on time the tissue is exposed to increased temperature.
- 6 -
Useful
1. It is used by surgeons for the painless removed of eye tumors
2. It is used as a (bloodless knife) in surgery.
3. Repairing retinal tears or holes that develop prior to retinal detachment.
(Photocoagulation).
4. Treatment of the diabetic ethnography i.e. the complications of
diabetes that affect the retina, (photocoagulation).
5. In medical research it is used for special three-dimensional imaging
called(holography).
6.The amount of laser energy needed for photocoagulation depends on
the spot size used. In general, the proper dose is determined visually by
the ophthalmologist at the time of the treatment.
The minimum amount of laser energy that will do observable damage to
the retina is called the minimal reactive dose (MRD).
