بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم
أفلا تبصرون وفي الارض آيات للموقنين
من سورة الذاريات اية 20 و21
MOSUL - UNIVERSITY PETROLEUM AND MINING ENGINEERING COLLEGEPETROLEUM RESERVOIR DEPARTMENT Dr. MOHMMED SALEEM Y.AL-BAKKAL
Crystal Axes, Systems, Mineral Face Notation (Miller Indices)
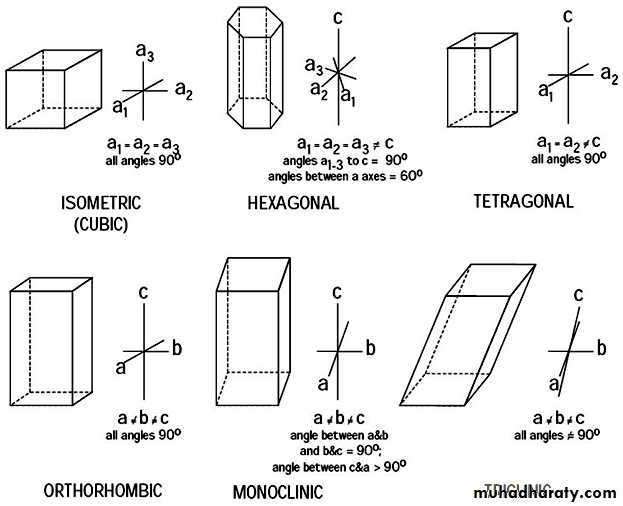
A CRYSTAL is the outward form of the internal structure of the mineral.The 6 basic crystal systems are:
ISOMETRIC
HEXAGONAL
TETRAGONAL
ORTHORHOMBIC
MONOCLINIC
TRICLINIC
Drusy Quartz on Barite
Acknowledgement: the following images from Susan and Stan Celestian, Glendale Community College
USC Mineralogy Geol 315 (Anderson)
Crystallography
Crystallography: the study of these solid bodies and laws that govern their , external shape, and internal atomic structures using x-ray and x-ray diffraction.Crystals: A homogeneous solid body possessing
long-range three dimensional internal order bounded by natural plane faces that are external expression of a regular internal arrangement of constituent atoms , molecules or ions .
• Crystals and degree of crystallinity
Euhedral : A crystalline solid with well-formed facesSubhedral : If it has imperfectly developed faces. Anhedral : If it is with-out faces
Avery fine crystals can be determined only with aid of microscope designated as Microcrystalline.
Crystalline aggregated so finely divided that the crystals cannot be resolved with the microscope yet pattern give a diffraction pattern with x-ray are cryptocrystalline.
A few solids lack any ordered internal structure
These said to be Amorphous.
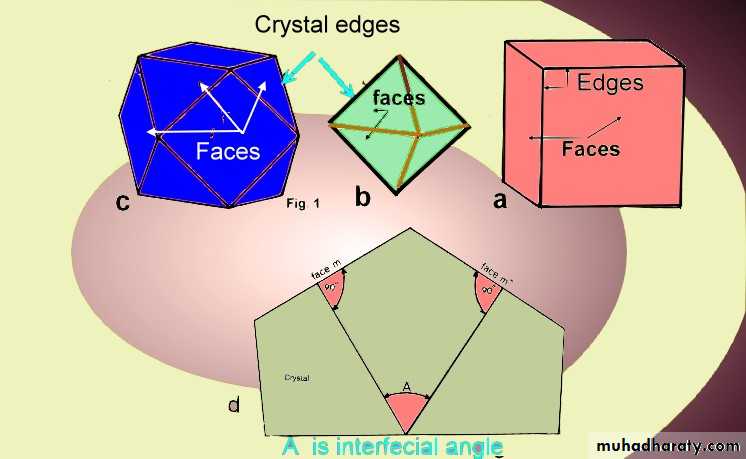
• crystal parts are divided in to two groups:first Real Parts. 1- Crystal Faces : The Plane surface that are the more obvious feature of crystals are parallel to net planes in crystal-structure, faces are two kinds, like and unlike. Crystals with like faces termed a simple form.A Crystals which are consist of two or more simple forms is called a combination.2- Edge: Line is formed by intersection of any two adjacent faces.3- Solid Angle :Angle is formed by intersection of Three or more faces.4- Interfacial Angle : The angle between two faces of crystal as in fig.
Crystal Real Parts
Second Imaginary Parts
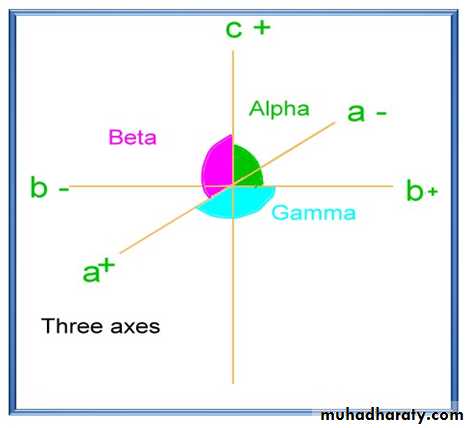
1- Crystallographic axes: Imaginary lines passing through the crystal parallel to intersection of major crystal faces. All the crystals, are referred to three crystallographic axes designated as a , b and c, except of those belonging to hexagonal system is referred to four crystallographic axes.Crystals with three crystallographic axes:
The (a) axis is horizontal and in a front-back position.
The (b) axis is horizontal and right left position.
The (c) axis is vertical.
The ends of each axis are +or -
The front end of(a) the
right-hand end of (b) ; the
upper end of (c) are positive;
the opposite ends are negative
2-Interaxial angles: they are three angles( α , β & γ) at the center of crystals in between crystallographic axes.
(α) Is between the axes (b & c)
(β )between the axes (a &c )
(γ) Is between the axes (a & b)
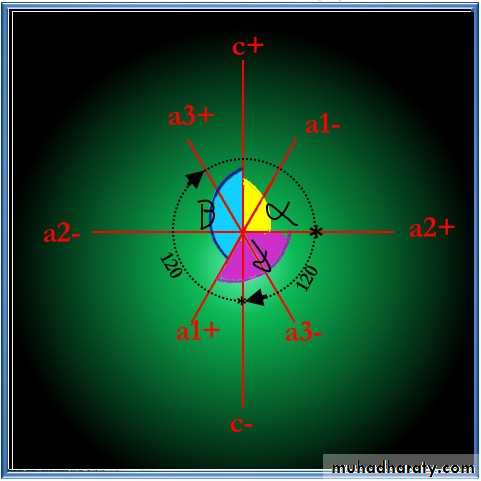
• Hexagonal System referred to four crystallographic axes , three equal horizontal axis (a1 ,a2 ,a3) intersect at angles of 120°, the fourth is (c) of different length and perpendicular to plane of the other three .
• a² axis is horizontal and right left position (position of b) .
• a1+ axis is 120°in horizontal clock wise direction from a² +
• a³+ axis position 120 in horizontal
• clock wise direction from a1+.
• α the angle is between c & a2+
• β the angle is between a1+ & c+
• γ the angle is between a²+ & a1+
Crystal Systems
Crystal Systems
CRYSTAL SYSTEMS are divided into 6 main groups• The first group is the ISOMETRIC
• This literally means “equal
• measure” and refers to the equal
size of the crystal axes.
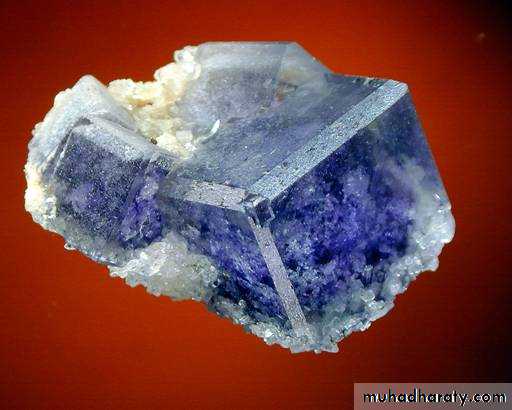
ISOMETRIC - Fluorite Crystals
• Crystal Systems ISOMETRIC CRYSTALS• ISOMETRIC
• In this crystal system there are 3 axes. Each has the same length (as indicated by the same letter “a”).
• They all meet at mutual 90o angles in the center of the crystal.
• Crystals in this system are typically blocky or ball-like.
• ALL ISOMETRIC CRYSTALS HAVE 4 3-FOLD AXES
• ISOMETRIC Basic Cube
• a3• a2
• a1
Crystal Systems
• ISOMETRIC BASIC CRYSTAL SHAPES
• Cube
• Fluorite• Pyrite
• Cube with Pyritohedron Striations• Trapezohedron
• Garnet
Crystal Systems
ISOMETRIC CRYSTALS• ISOMETRIC - Basic Cube
• a1
• a3
• a2
• a3
• a2
• a1
• Fluorite cube with crystal axes.
• Crystal Systems HEXAGONAL CRYSTALS
• HEXAGONAL - Three horizontal axes meeting at angles of 120o and one perpendicular axis.• ALL HEXAGONAL CRYSTALS HAVE A SINGLE 3- OR 6-FOLD AXIS = C
• HEXAGONAL Crystal Axes
• a2
• c
• a3
• a1
• Crystal Systems HEXAGONAL CRYSTALS
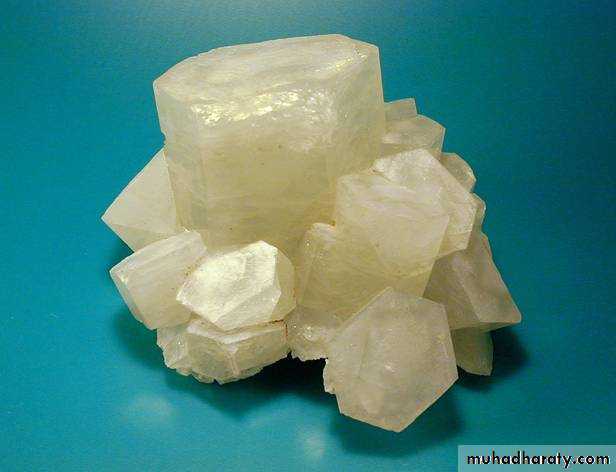
• These hexagonal CALCITE crystals nicely show the six sided prisms as well as the basal pinacoid.Two subsystems':
1. Hexagonal
2. Trigonal
• Crystal Systems TETRAGONAL CRYSTALS
• The C-axis is always 4, 4bar, or 4/m• TETRAGONAL Crystal Axes
• a1
• a2
• c
• c
• a2
• a1
• This is an Alternative Crystal Axes
• TETRAGONAL
• Two equal, horizontal, mutually
• perpendicular axes (a1, a2)
• Vertical axis (c) is perpendicular to the
• horizontal axes and is of a different length
Crystal Systems
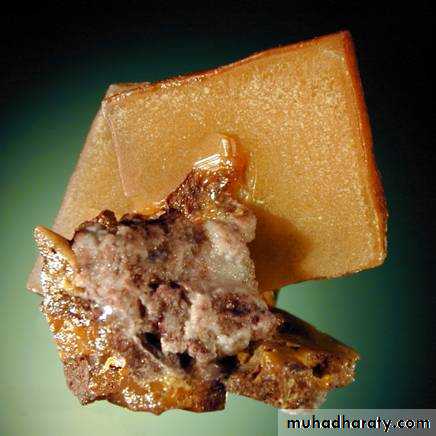
TETRAGONAL CRYSTALSWULFENITE
Same crystal seen edge on.
ALL TETRAGONAL CRYSTALS HAVE A SINGLE 4-FOLD AXIS = CSame crystal seen edge on.
Same crystal seen edge on.
Crystal SystemsORTHORHOMBIC CRYSTALS
ORTHORHOMBIC
Three mutually perpendicular axes of different lengths.
ORTHORHMOBIC Crystal Axes
ab
c
a
c
b
An Alternative Crystal Axes Orientation
Each axis has symmetry, either 2-fold or m-normal
Crystal Systems
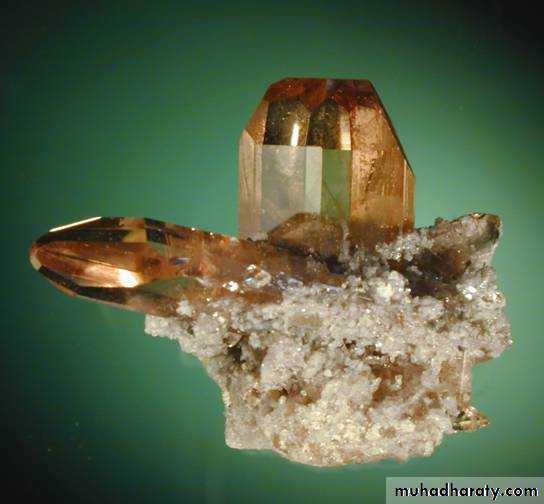
ORTHORHOMBIC CRYSTALSTopaz from Topaz Mountain, Utah.
Crystal Systems
ORTHORHOMBIC CRYSTALSBARITE is also orthorhombic. The view above is looking down the “c” axis of the crystal.
Crystal Systems
ORTHORHOMBIC CRYSTALSSTAUROLITE
Prism View
Pinacoid ViewCrystal Systems
MONOCLINIC CRYSTALSMONOCLINIC
In this crystal form the axes are of unequal length.
Axes a and b are perpendicular.
Axes b and c are perpendicular.
But a and c make some oblique angle and with each other.
MONO = ONE AXIS OF SYMMETRY (2-FOLD OR MIRROR) = TO “b”
MONOCLINIC Crystal Axesa
b
c
Crystal Systems
MONOCLINIC CRYSTALS
Gypsum
Mica
Orthoclase
Crystal SystemsTRICLINIC CRYSTALS
TRICLINIC
In this system, all of the axes are of different lengths and none are perpendicular to any of the others.
SYMMETRY: ONLY 1 OR 1-BAR
TRICLINIC Crystal Axesa
b
c
Crystal Systems
TRICLINIC CRYSTALSMicrocline, variety Amazonite
c
b
a
O
Y
X
Z
A
B
C
3-D Miller Indices (an unusually complex example)
a b c
unknown face (XYZ)
reference face (ABC)
2
1
2
4
Miller index of face XYZ using ABC as the reference face
2
3
invert
1
2
4
2
3
2
clear of fractions
(1
3)
4
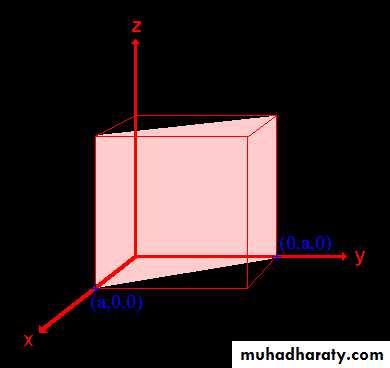
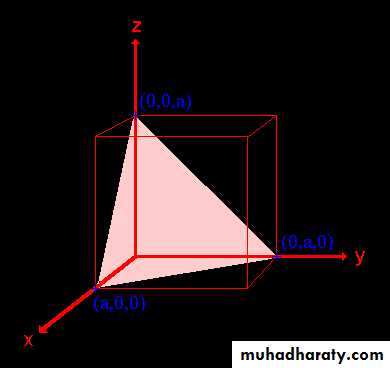
Example: the (110) surface
Example: the (111) surface
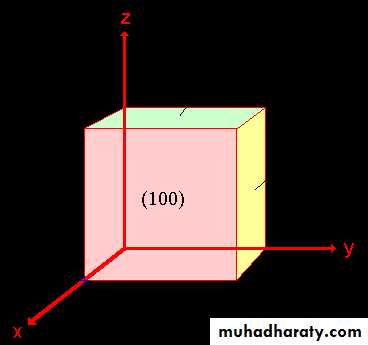
Example: (100), (010), and (001)
(001)(010)
For the isometric system, these faces are equivalent (=zone)
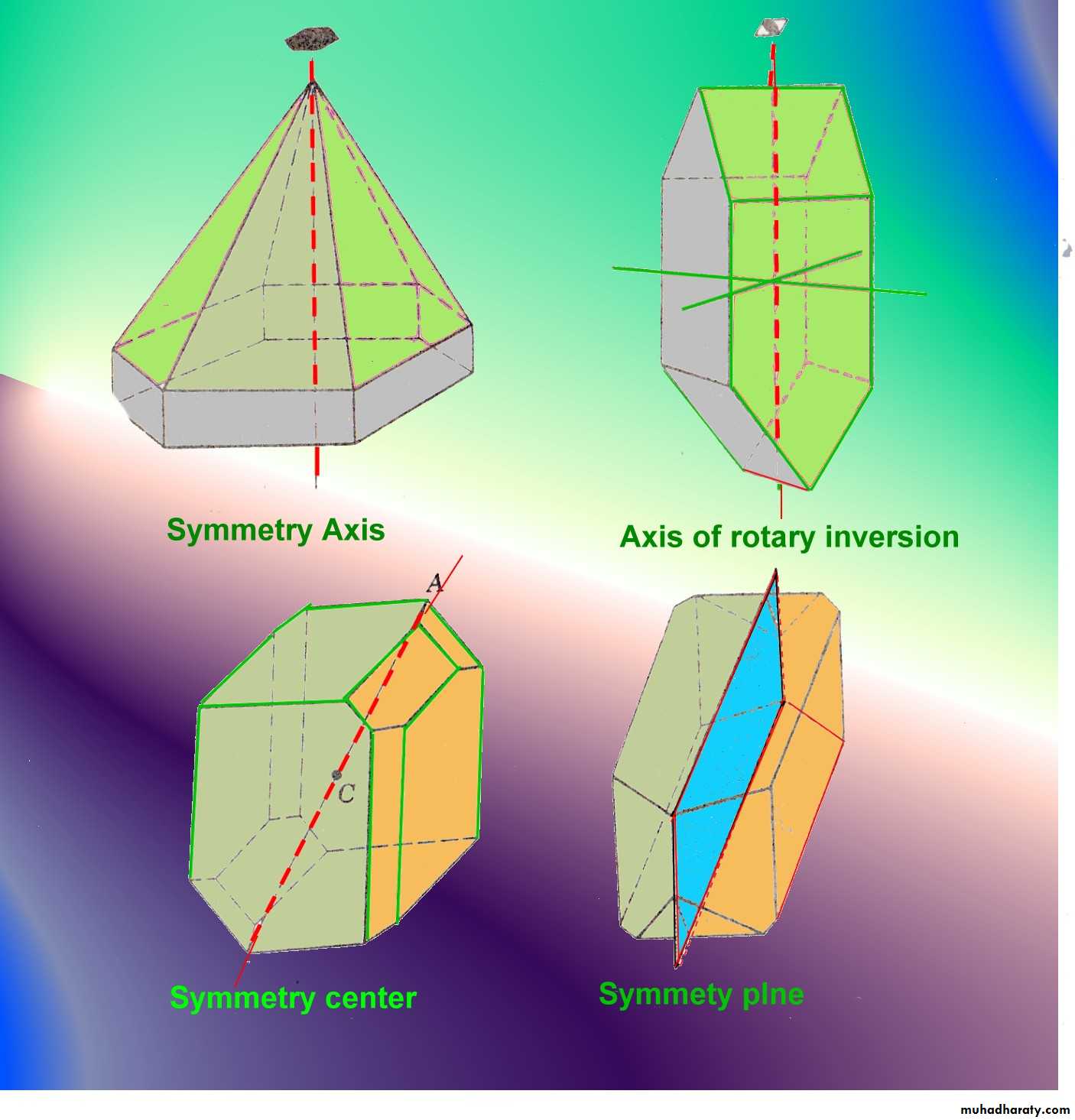
Crystal Symmetry Crystal Symmetry : Is regularity of arrangement of similar faces and angles, and by preforming certain operations on them the like faces and angles can be brought into coincidence
There four types of Symmetry :-
1-Symmetry Plane :Is an imaginary plane that divides a crystal in two halves . each of which, in a perfectly developed crystal , is the mirror image of the other.
2-Symmetry Axis of Rotation : Is an imaginary line through the crystal about which the crystal may rotated and repeat itself in appearance two or more times during a complete rotation.3-symmetry center : If a crystal have center of symmetry , imaginary line can be pass from any point on its surface through its center and similar point at an equal distance is found beyond the center .
4-Symmetry Axis of Inversion : This composite symmetry element combines a rotation about the axis with inversion through center .