Foundation of Medicine
L5-medical terminology / onlineJune 11th , 2020
Family & Community medicine dept.
Dr. Muslim N. Saeed
Objectives
1. Identify and describe the major structures and functions of the respiratory system.2. Recognize, define, spell, and pronounce terms related to the pathology and the diagnostic and treatment procedures of the respiratory system.
The respiratory system
The respiratory system brings oxygen into the body cells, and removes carbon dioxide.Consist of :
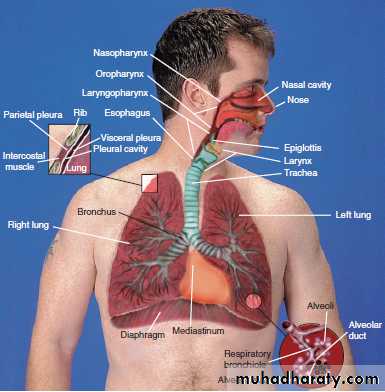
1-The upper respiratory tract ; the nose, mouth, pharynx, epiglottis, larynx, and trachea.
2-The lower respiratory tract; the bronchial tree and lungs. These structures are protected by, the thoracic cavity which is also known as the rib cage.
The Nose
Air enters the body through the nose and passes through the nasal cavity.The Tonsils
The tonsils form a protective circle of lymphatic tissue around the entrance to the respiratory system.
The Pharynx
(FAR-inks),the throat, receives the air after it passes through the nose.
The Larynx
(LAR-inks), also known as the voice box, is a triangular chamber.The thyroid cartilage is the largest, it is commonly known as Adam’s apple, protect the larynx.
-The larynx contains the vocal cords . During speech, sound is produced, causing the cords to vibrate against each other.
-The epiglottis (ep-ih-GLOT-is) located at the base of the tongue, swings and closes off so that food does not enter the trachea and the lungs.
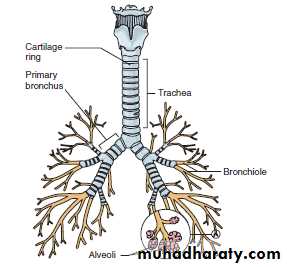
The Trachea
(TRAY-kee-ah), commonly known as the windpipe, is a tube extends from the neck to the chest.The Bronchi :(BRONG-kye) trachea divides into two branches known as the primary bronchi.
-Within the lung, each primary bronchus divides and
subdivides into smaller bronchioles(BRONG-kee-ohlz), which are the smallest branches of the bronchi.
The Alveoli (al-VEE-oh-lye), also known as air sacs, are the
very small grape-like clusters found at the end of each bronchiole (singular, alveolus).
bronchial tree
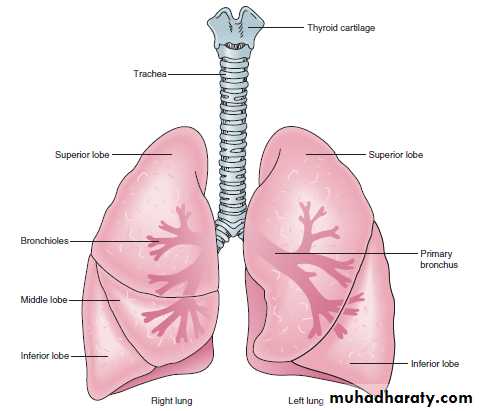
The Lungs
are the organs of respiration, are divided into lobes.-The right lung has three lobes: the superior, middle, and inferior.
-The left lung has only two lobes: the superior and inferior. It is slightly smaller than the right lung because of the space taken up by the heart.
The Mediastinum
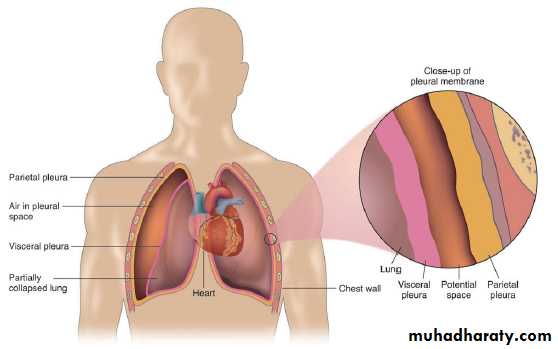
(mee-dee-as-TYE-num) is the cavity located between the lungs.The Pleura (PLOOR-ah) is a thin, moist membrane that covers the outer surface of the lungs and lines the inner surface of the rib cage.
I-The parietal pleura (pah-RYE-eh-tal) is the outer layer of the pleura, Parietal means relating to the walls of a cavity.
II-The visceral pleura (VIS-er-al) is the inner layer of pleura that surrounds each lung.
Visceral means relating to the internal organs.
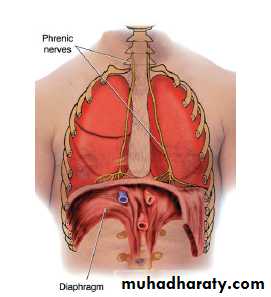
The Diaphragm
(DYE-ah-fram) is the muscle that separates the thoracic cavity from the abdomen . the contraction and relaxation of this muscle that makes breathing possible.MEDICAL SPECIALTIES RELATED TO THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
Otolaryngologist:(oh-toh-lar-in-GOL-oh-jist), also known as an ENT (Ear, Nose, Throat), is a physician specialized in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the ears, nose, throat, (ot/o means ear, laryng/o means larynx, and -ologist means specialist).-A pulmonologist (pull-mah-NOL-oh-jist) is a physician who specializes in diagnosing and treating diseases of the lungs (pulmon means lung, and -ologist means specialist).
Diseases of respiratory system
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, also known as COPD, is a lung disease in which it is hard to breathe.Chronic Bronchitis (brong-KYE-tis), the airways have become inflamed and thickened, (bronch means bronchus, and -itis means inflammation).
Emphysema (em-fih-SEE-mah) is the progressive loss of lung function.
Asthma (AZ-mah) is a chronic allergic disorder with episodes of severe breathing difficulty, coughing, and wheezing.
Wheezing is a breathing sound caused by a partially obstructed airway.
A bronchospasm (brong-koh-spazm) is a contraction of the smooth muscle in the walls of the bronchi and bronchioles(bronch/o means bronchi, and -spasm means involuntary contraction).
Common cold is an upper respiratory infection can be caused by different viruses.
Allergic rhinitis (rye-NIGH-tis),is an allergic reaction to airborne allergens (rhin means nose, and -itis means inflammation).
Epistaxis (ep-ih-STACK-sis), is bleeding from the nose.
-Influenza (in-flew-EN-zah), also known as the flu, is an acute viral respiratory infection.
Rhinorrhea (rye-noh-REE-ah), also known as a runny nose, is the watery flow of mucus from the nose (rhin/o means nose, and -rrhea means abnormal discharge).
Sinusitis (sigh-nuh-SIGH-tis) is an inflammation of the sinuses.
Pharynx and Larynx
Pharyngitis (fah-rin-JIGH-tis), also known as a sore throat, is an inflammation of the pharynx (pharyng means pharynx, and -itis means inflammation).Laryngitis (lar-in-JIGH-tis) is an inflammation of the larynx (laryng means larynx, and -itis means inflammation).
Voice Disorders
Aphonia (ah-FOH-nee-ah) is the loss of the ability of normal speech sounds (a- means without, phon means voice or sound, and -ia means abnormal condition).Dysphonia (dis-FOH-nee-ah) is any change in voice quality,(dys- means bad, phon means voice or sound, and -ia means abnormal condition).
Pleural Cavity
Pleurisy (PLOOR-ih-see),or pleuritis, is an inflammation of the pleura (pleur means pleura, and –itis means inflammation).Pneumothorax (new-moh-THOR-racks) is the accumulation of air in the pleural space (pneum/o means lung or air, and -thorax means chest).
Hemothorax ….. ?
Pleural effusion (eh-FEW-zhun) is accumulation of fluid in the pleural space.
Hemoptysis (hee-MOP-tih-sis) is coughing of blood or bloodstained sputum (hem/o means blood, and -ptysis means spitting).Pyothorax (pye-oh-THOH-racks) is the presence of pus in the pleural cavity(py/o means pus, and -thorax means chest). This condition is also known as empyema (em-pye-EE-mah).
Pulmonary edema (eh-DEE-mah) is an accumulation of fluid in lung tissues. Edema means swelling.
Tuberculosis (too-ber-kew-LOH-sis) (TB), which is an infectious disease caused by Bacteria.
Pneumonia (new-MOH-nee-ah) is an infection or inflammation of the lungs (pneumon means lung, and -ia means abnormal condition).
Apnea (AP-nee-ah) is the absence of spontaneous respiration (a- means without and -pnea means breathing).
Tachypnea (tack-ihp-NEE-ah) is rapid rate of respiration(tachy-means rapid, and –pnea means breathing).
Tachypnea is the opposite of bradypnea (slow rate of respiration).
Dyspnea (DISP-nee-ah), also known as shortness of breath (SOB), is difficult breathing (dys means difficult, and -pnea means breathing).
Cyanosis (sigh-ah-NOH-sis) is a bluish discoloration of the skin (cyan means blue, and -osis means abnormal condition).
Hypoxia (high-POCK-see-ah) is below-normal oxygen levels in the body tissues and cells, (hyp- means deficient, ox means oxygen, and -ia means abnormal condition).