
Biochemistry lectures
By
Assistant professor Dr.Suhayr Aessa Hussein
Clinical Biochemistry
College of Medicine University of Babylon

Classification of Lipids and Fatty
Acids
Biochemistry for medics

Objectives
• Know the types of lipids
• Know the structure, function,
classification and clinical
importance of lipids

REFERENCES
1.Lehninger Principle of Biochemistry, 4
th
ed.
2005.
2.
Lippincott’s Reviews of Biochemistry, 3
rd
ed. ,
2018.
3.General , Organic , and Biological Chemistry,
5
th
edition , H. Stephen Stoker, 2010.

lipids
lipids are a heterogeneous group of
compounds, including fats, oils, steroids, waxes,
and related compounds, that are related more by
their physical than by their chemical properties.
They have common properties :
(1) relatively insoluble in water and
(2) soluble in nonpolar solvents such as ether and
chloroform.

Functions of lipids
Storage form of energy
Important dietary components because of their high
energy value and also because of the fat-soluble
vitamins and the essential fatty acids contained in
the fat of natural foods.
Structural components of biomembranes
Serve as thermal insulators in the subcutaneous
tissues and around certain organs
Nonpolar lipids act as electrical insulators,
allowing rapid propagation of depolarization
waves along myelinated nerves

Functions of lipids (Contd)
Provide shape and contour to the body
Act as metabolic regulators
Combinations of lipid and protein (lipoproteins) are
important cellular constituents, occurring both in the
cell membrane and in the mitochondria, and serving
also as the means of transporting lipids in the blood.

Classification of lipids
1-Simple lipids: Esters of fatty acids with various
alcohols.
a. Fats: Esters of fatty acids with glycerol. Oils are
fats in the liquid state.
b. Waxes: Esters of fatty acids with higher
molecular weight monohydric alcohols.

Classification of lipids(Contd)
2. Complex lipids: Esters of fatty acids containing groups in
addition to an alcohol and a fatty acid.
a. Phospholipids: Lipids containing, in addition to fatty acids
and an alcohol, a phosphoric acid residue. They frequently
have nitrogen-containing bases and other substituents, eg, in
glycerophospholipids the alcohol is glycerol and in
sphingophospholipids the alcohol is
sphingosine.
b. Glycolipids (glycosphingolipids): Lipids containing a fatty
acid, sphingosine, and carbohydrate.
c. Other complex lipids: Lipids such as sulfolipids and
aminolipids. Lipoproteins may also be placed in this
category.

Classification of lipids(Contd)
3) Precursor and derived lipids: These include-
fatty acids
glycerol
steroids
other alcohols
fatty aldehyde
ketone bodies
hydrocarbons, lipid-soluble vitamins, and
hormones.

FATTY ACIDS
Fatty acids are aliphatic carboxylic acids
Have the general formula R-(CH2)n-COOH
They occur mainly as esters in natural fats and oils
but do occur in the unesterified form as free fatty
acids, a transport form found in the plasma.
Fatty acids that occur in natural fats are usually
straight-chain derivatives containing an even
number of carbon atoms.
The chain may be saturated (containing no double
bonds) or unsaturated (containing one or more
double bonds).

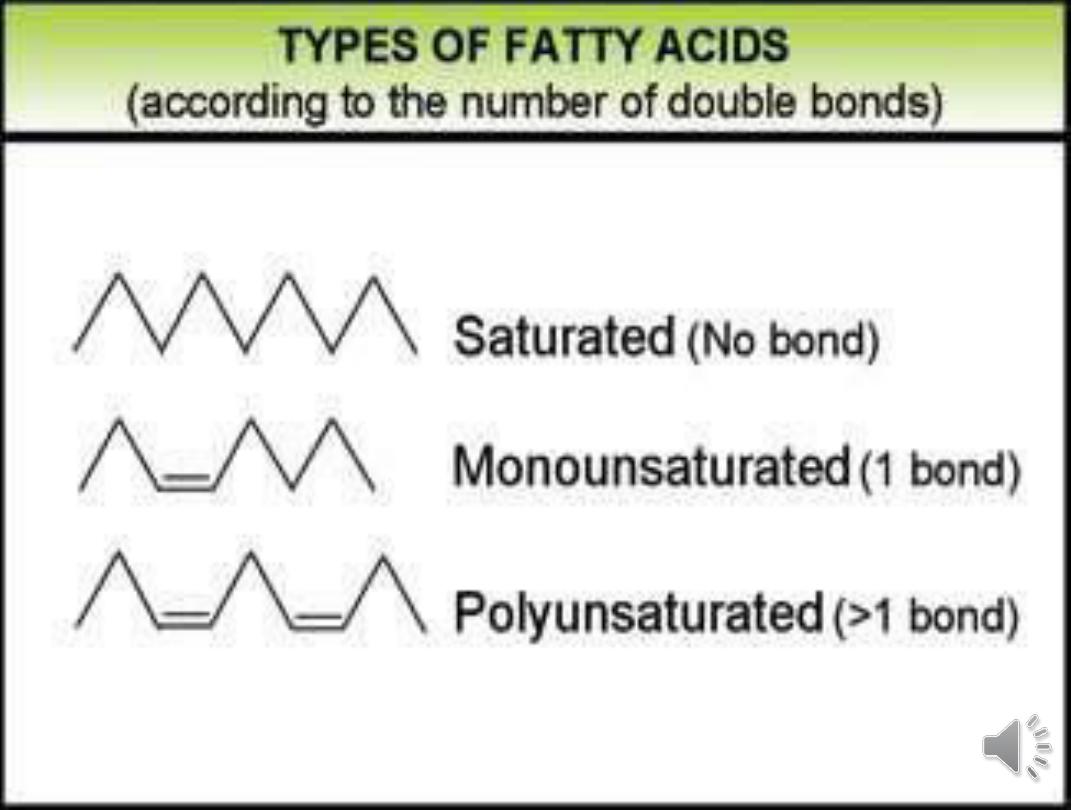
Classification of Fatty Acids
Fatty acids can be classified in many ways-
1) According to nature of the hydrophobic
Chain
a)
Saturated
b)
Unsaturated
c)
Branched chain fatty acids
d)
Substituted Fatty acids
Saturated fatty acids do not contain double
bonds, while unsaturated fatty acids contain
double bonds
Biochemistry

Biological Importance (functions) of
Fatty Acids
1-Fatty acids are the building blocks of dietary fats. The
human body stores such fats in the form of triglycerides.
2)- Fatty acids are also required for the formation of
membrane lipids such as phospholipids and glycolipids.
3) -They are required for the esterification of cholesterol to
form cholesteryl esters.
4) They act as fuel molecules and are oxidized to produce
energy.

Biological roles of Fatty Acids
Acts as fuel in the body.
(caloric value: 9
Kcals/gm)
Deposits of fats underneath the skin = exert
insulating effects.
The mesenteric fat around organs (kidney) =
padding and protecting internal organs.
Building materials
. (cholesterol
– hormone
synthesis)

Lipids supply the essential fatty acids
which cannot
be synthesized in the body..
The
Nervous system
is particularly rich in lipids.
Vitamins A, D, E and K are fat soluble.
( lipid/fat is needed for absorbing these vitamins)
Lipoproteins and phospholipids
are important
constituents of cell wall & mitochondria.
Biological roles of Fatty Acids
Adult:
ingests 60-150g of lipids per day of
which 90% is triacylglycerol (TAG).
Balance:
cholesterol, cholesteryl, esters,
phospholipids and free fatty acids (FFA)
Biological roles of Fatty Acids

Clinical significance of lipids
• Following diseases are associated with
• abnormal chemistry or metabolism of
lipids-
•
Obesity
•
Atherosclerosis
•
Diabetes Mellitus
•
Hyperlipoproteinemia
•
Fatty liver
•
Lipid storage diseases
•
Biochemistry

W e
hope
to
reach
w ith
you
for
useful
and
appropriate
inform ation
Best regards
