Done by
Dr.Rafid Remthan Al-Temimi
Clinical Radiology
CAMB,DMRD,M.B.Ch.B.,.
المرحلة
:
الثانية
المادة
:
التشريح
ج
امعة ذي قار
/
كلية الطب
الدكتور
رافد
رمثان التميمي
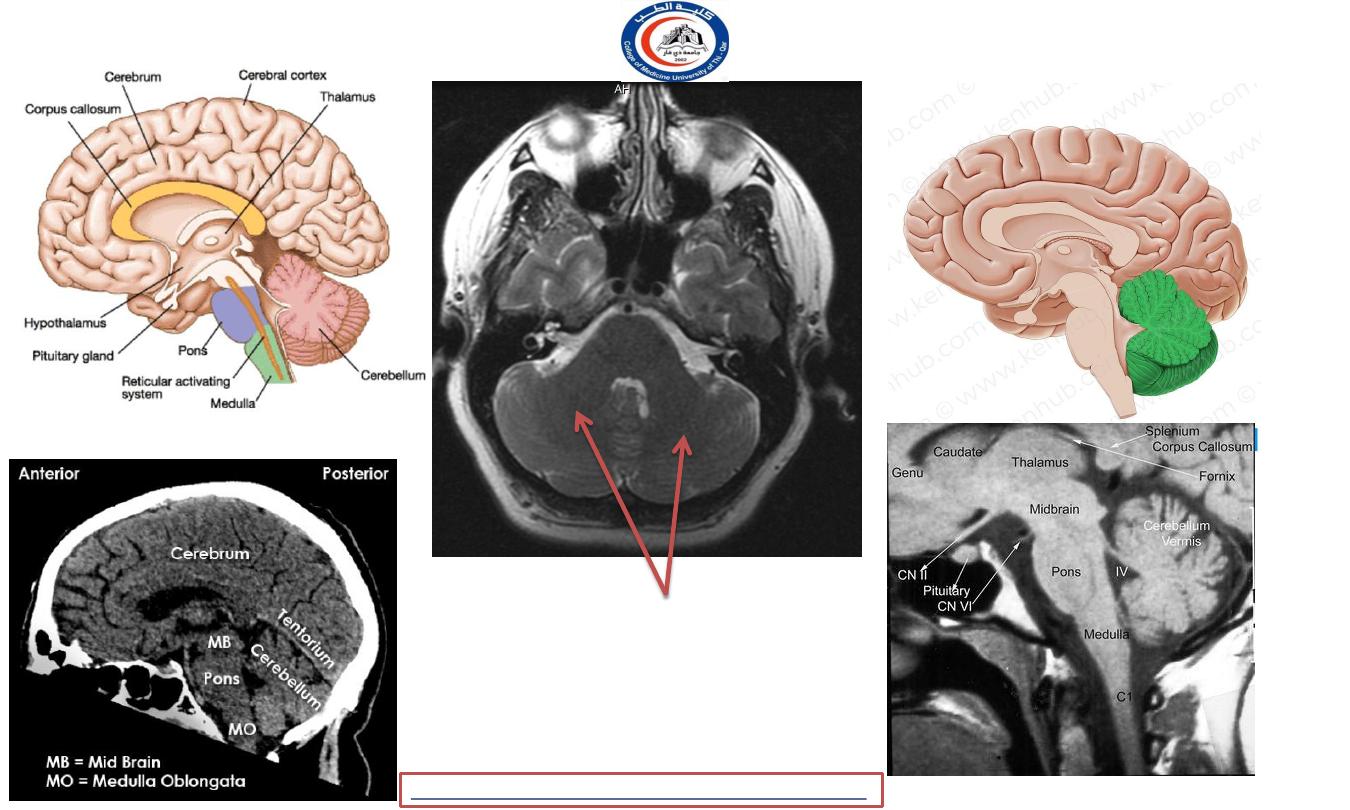
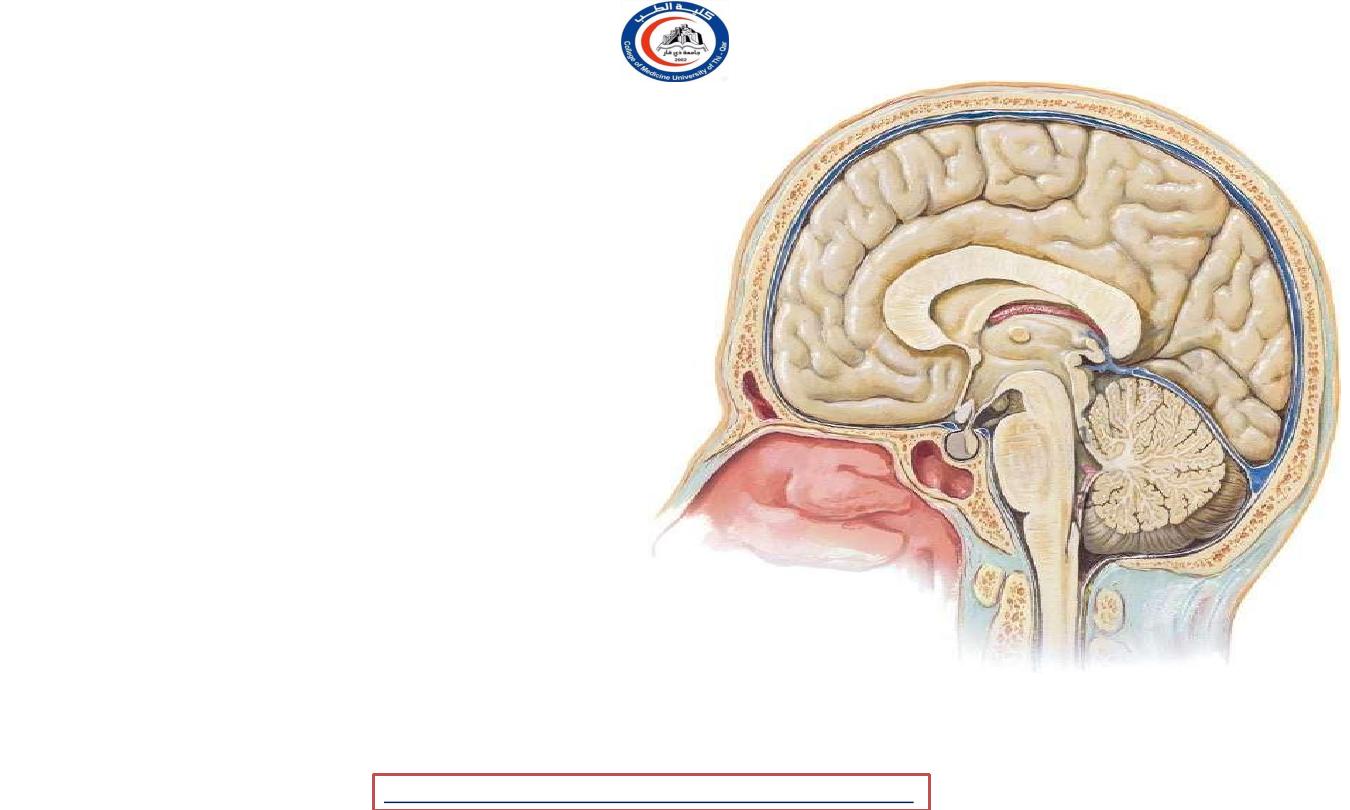
CEREBELLUM
In posterior fossa
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
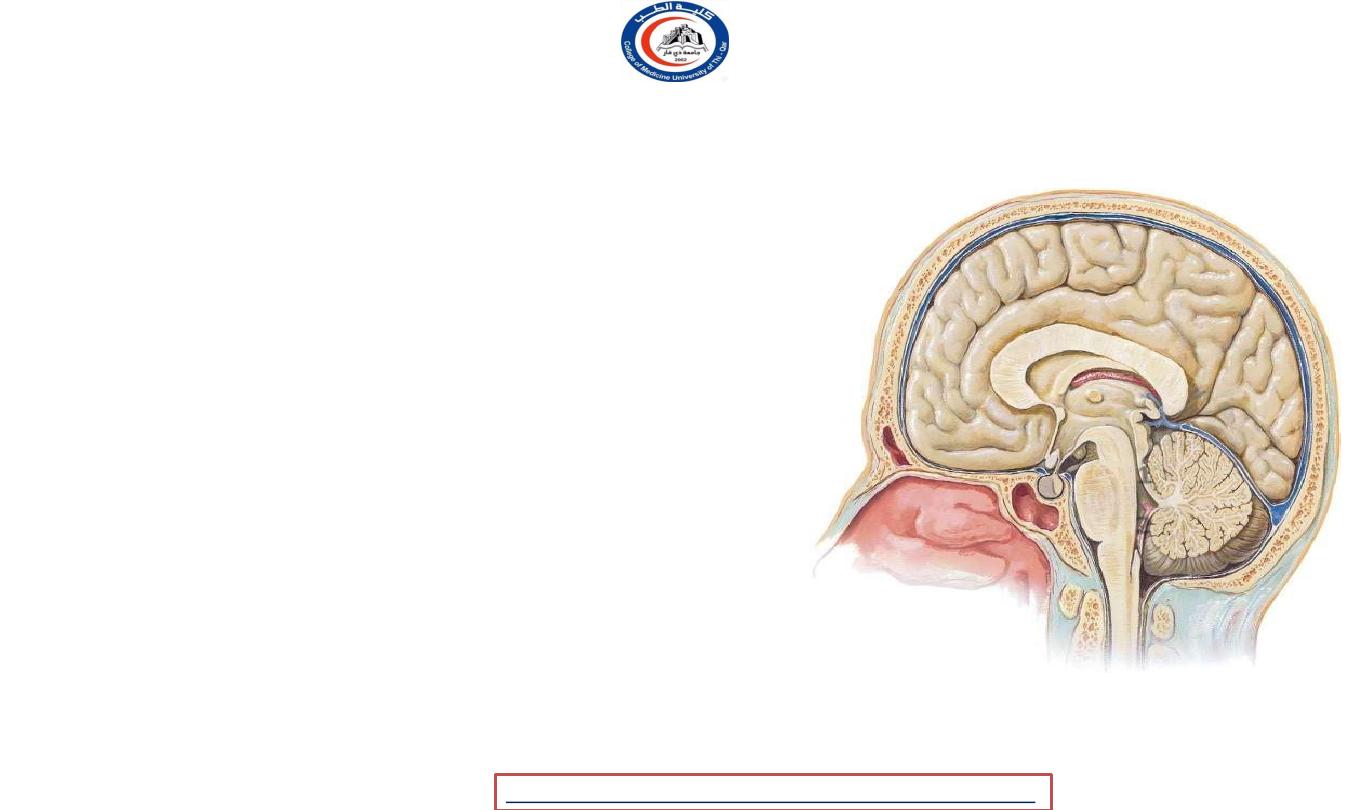
Cerebellum
fossa, and consists of
• It occupies the posterior cranial
two
hemispheres united in the midline
by the
vermis
.
• Three
peduncles
connect each
hemisphere to the three parts of the brainstem.
• The superior peduncle enters the
midbrain,
• the middle peduncle consists of the transverse
fibres of the pons
• the inferior peduncle connects it
to the medulla.
• The
ventral surface of the vermis
lies upon the roof of the
4
th
ventricle …
• 1- the superior medullary velum
• 2- the inferior medullary velum
1
2
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
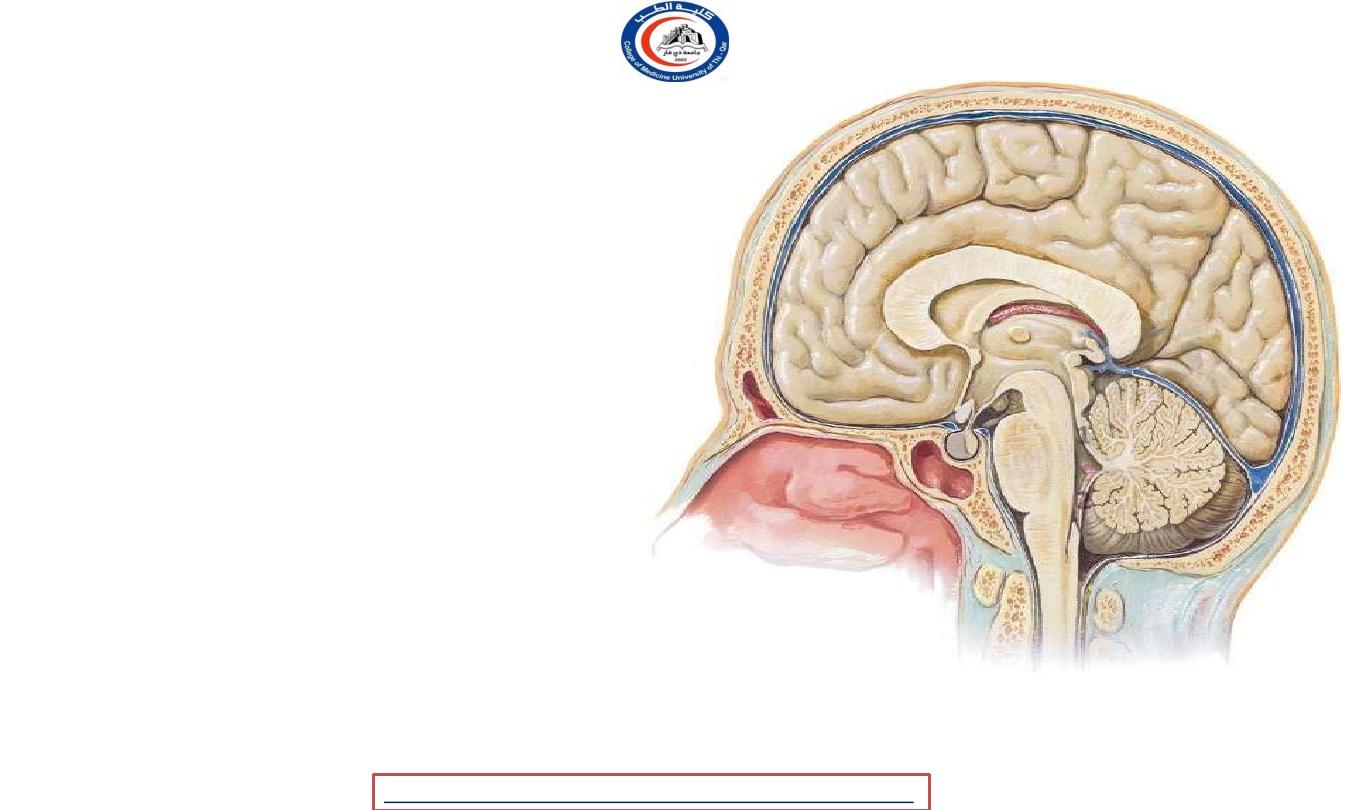
Cerebellum
• Separate from the cerebrum by the
tentorium ..
• shallow
sulci
and
foliae
( equivalent to gyri in cerebrum ) !!
• Question You Should Answer After
Complete Reading The Lecture !!
• WHY cerebrum cerebellum ratio in neonates
is 1:20 while in adults is 1:8 ?!
1
2
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Cerebellum
• Arbor viti cerebelli :
the white mater of
cerebellum run from and to the cortex ..
• SO,
• Cortex = grey mater
• Arbor veli cerebelli = white mater
• Is there is other grey mater in
cerebellum ?!
• YES
• 4 nuclei
embedded in the white
mater ( to some extent it resemble
the Basal ganglia as the letter embedded
within white mater but it is a grey mater
rather than the cortex )
1
2
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
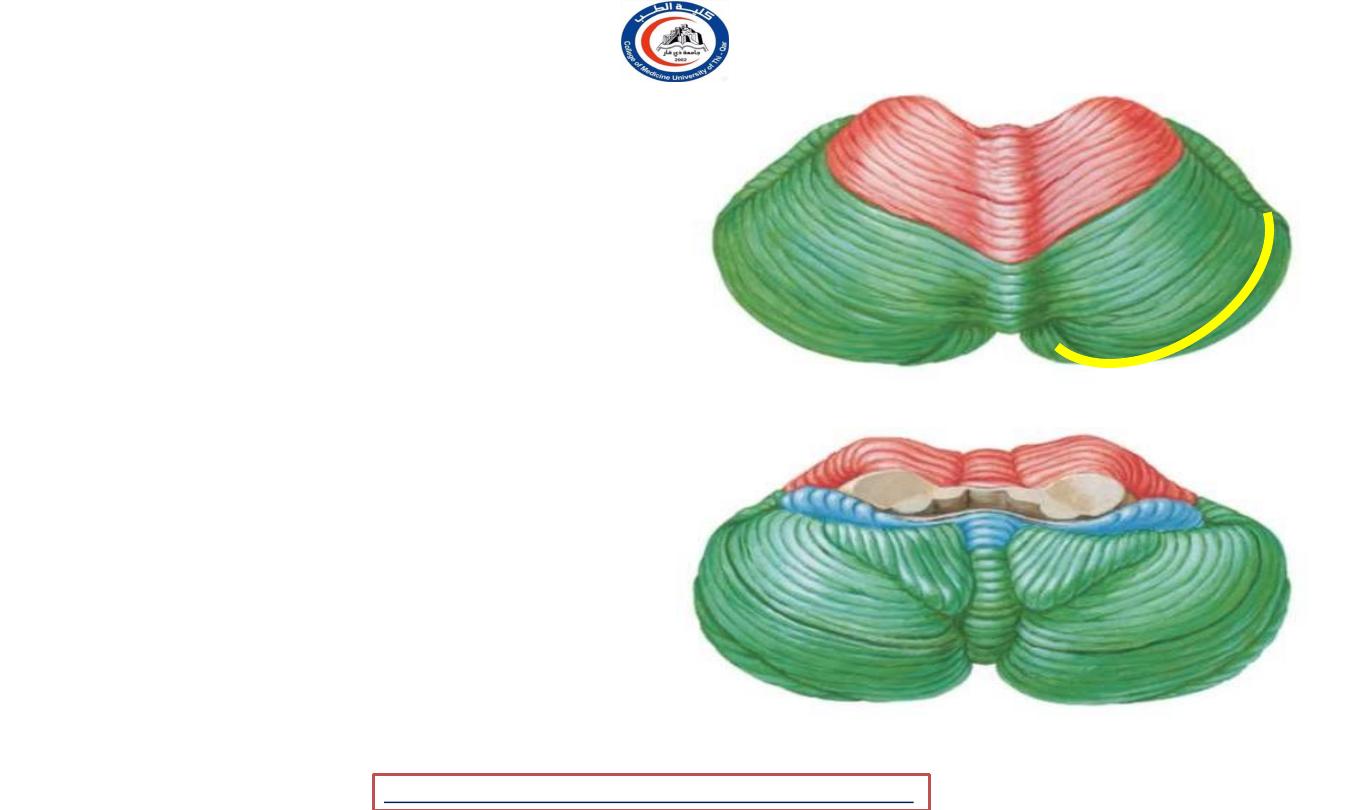
Fissures
1. Primary fissure
- V shaped.
- Separate the anterior lobe from
the posterior ( middle ) lobe.
2. Horizontal fissure
- Deepest one.
- Separate the cerebellum to uppe and lower
portios.
r
e
3. Uvulonodular fissure
• Separate the middle lobe from th
flocculonodular lobe.
1
2
2
3
2
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
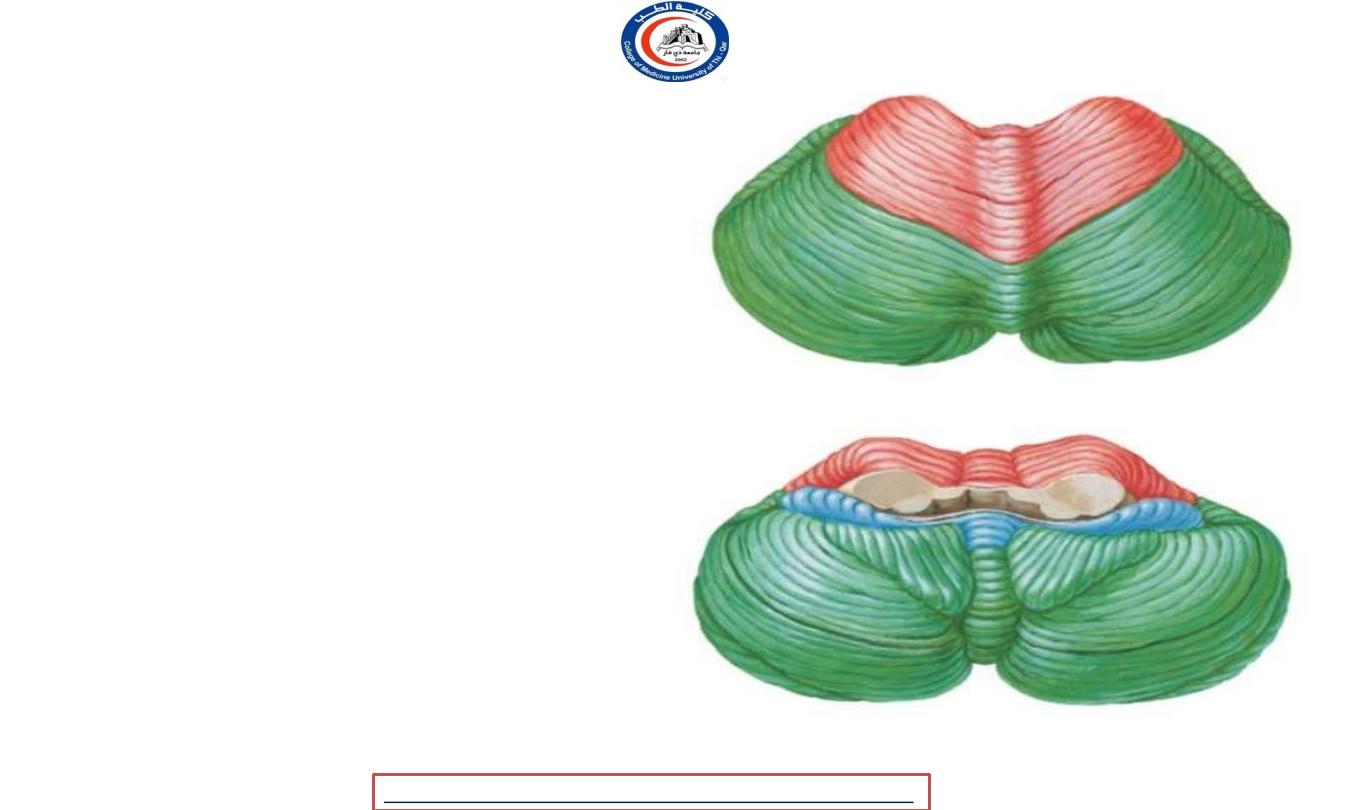
Lobes
1. Anterior lobe
2. Posterior ( middle lobe )
3. Flocculonodular lobe
1
2
3
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
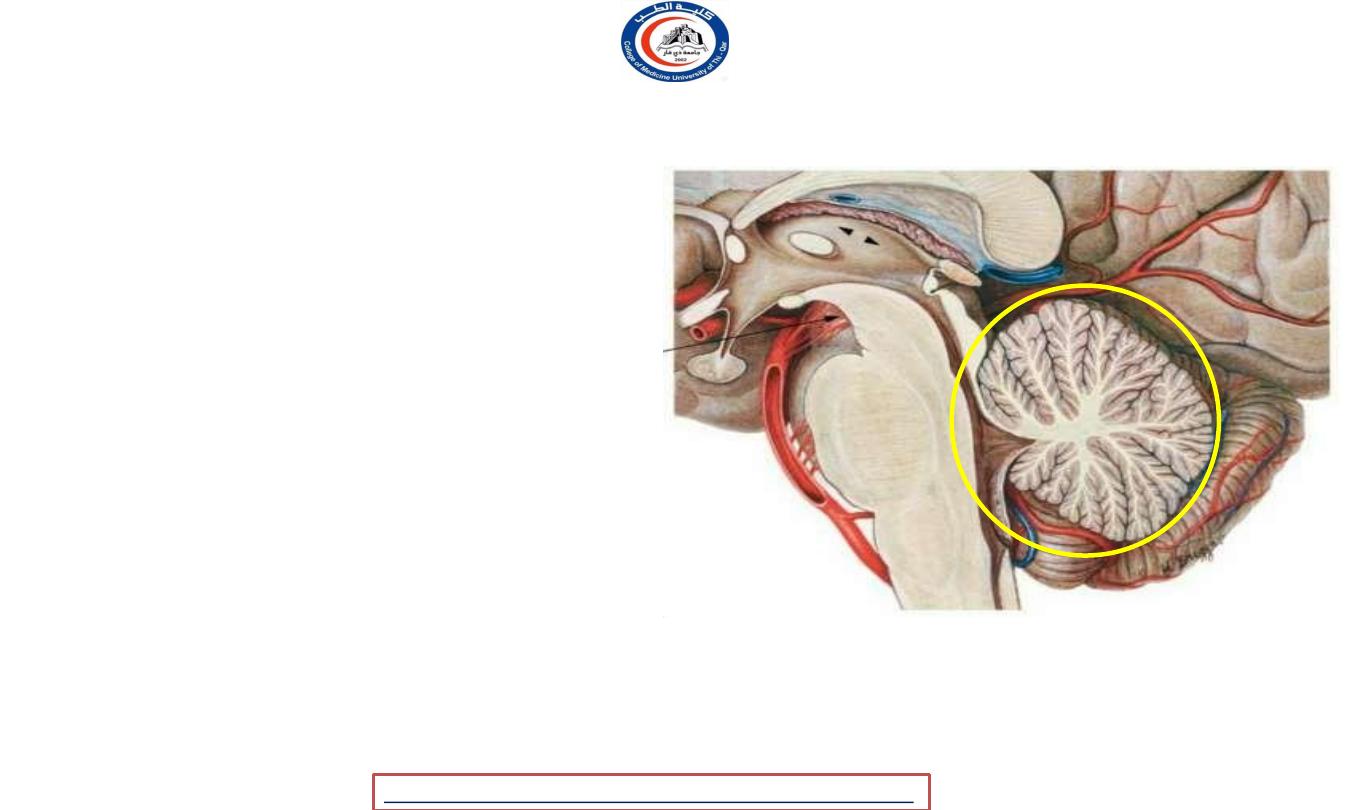
Vermis
• Disk like structure
divided
into
regions as seen in sagggital
sections.
connected to
• This regions are other
regions in the
cerebellum
forming the usual structure of this
organ.
• Primary fissure dived it into
superior
and inferior portions
!!
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
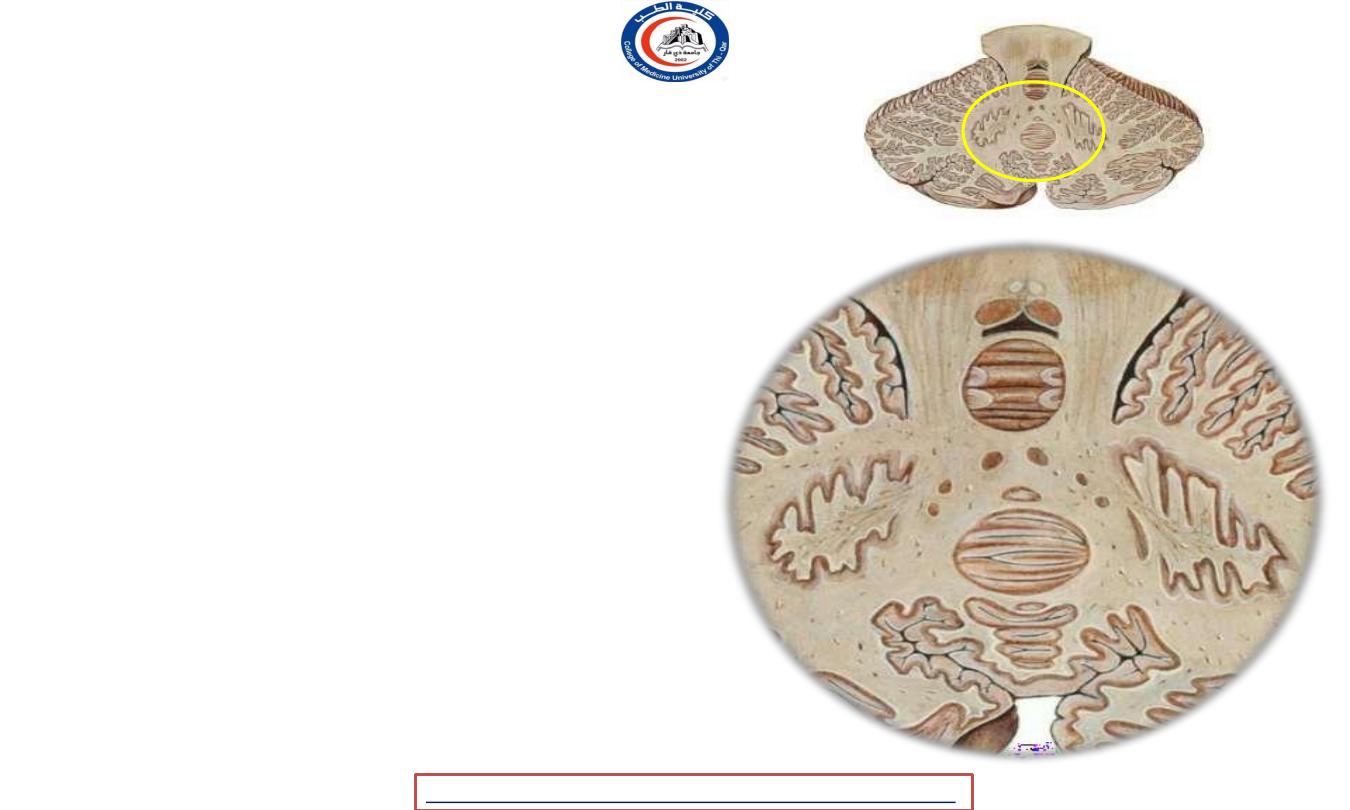
Cerebellar nuclei
through
• 1- dentate nucleus
-
Medial to the center
-
Most efferent fibers go
superior cerebellar peduncle
• 2- nucleus emboliformis
- At the medial side of dentate nucleus
• 3- nucleus globosus
- To the medial of nucleus emboliformis
• 4- fastigial nucleus
-
Larger than other two .. ( 2+3)
-
Situated near the midline at the anterior
end of superior vermis
- 2+3 = interposed nucleus !!
1
3
2
4
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
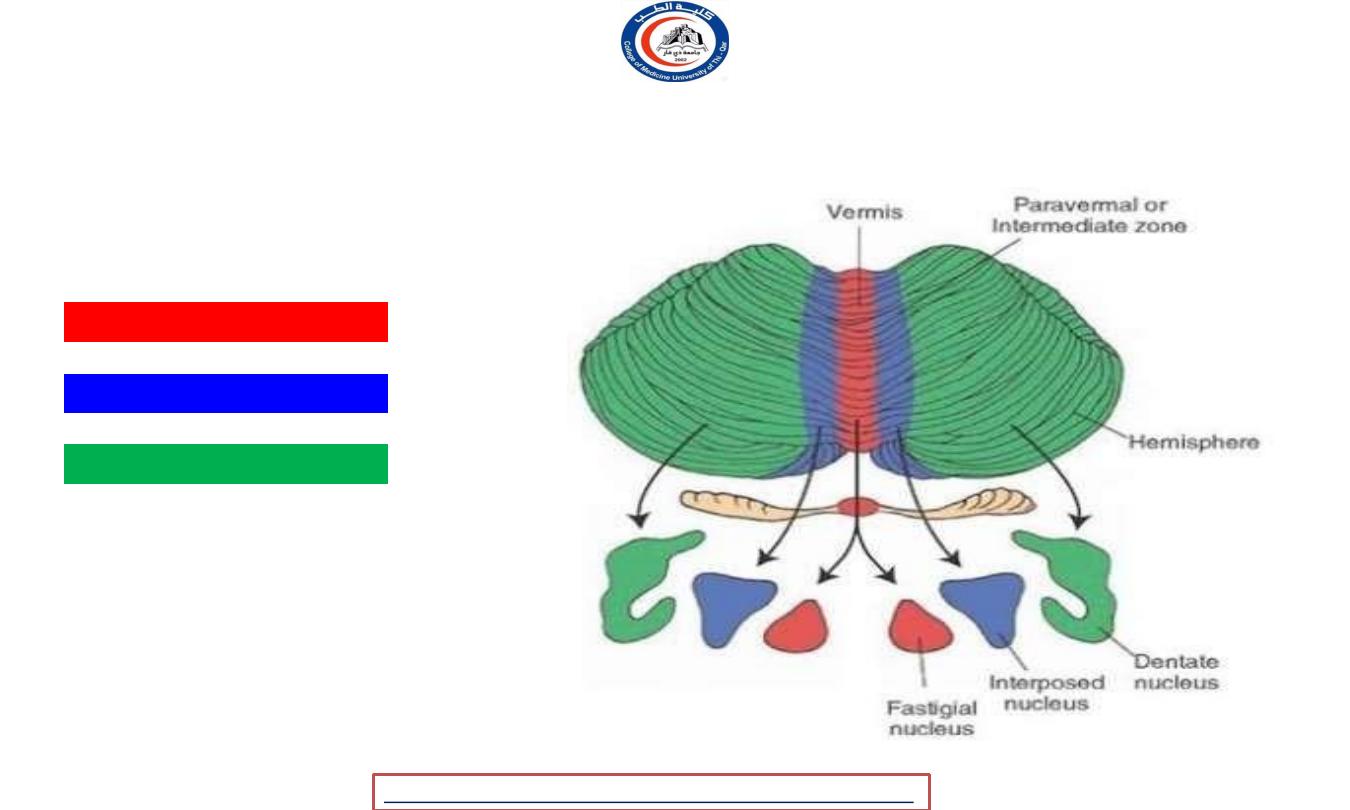
Functional parts of the cerebellum
Vetibulocerebellar
spinocerebellar
Cerebrocerebellar
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
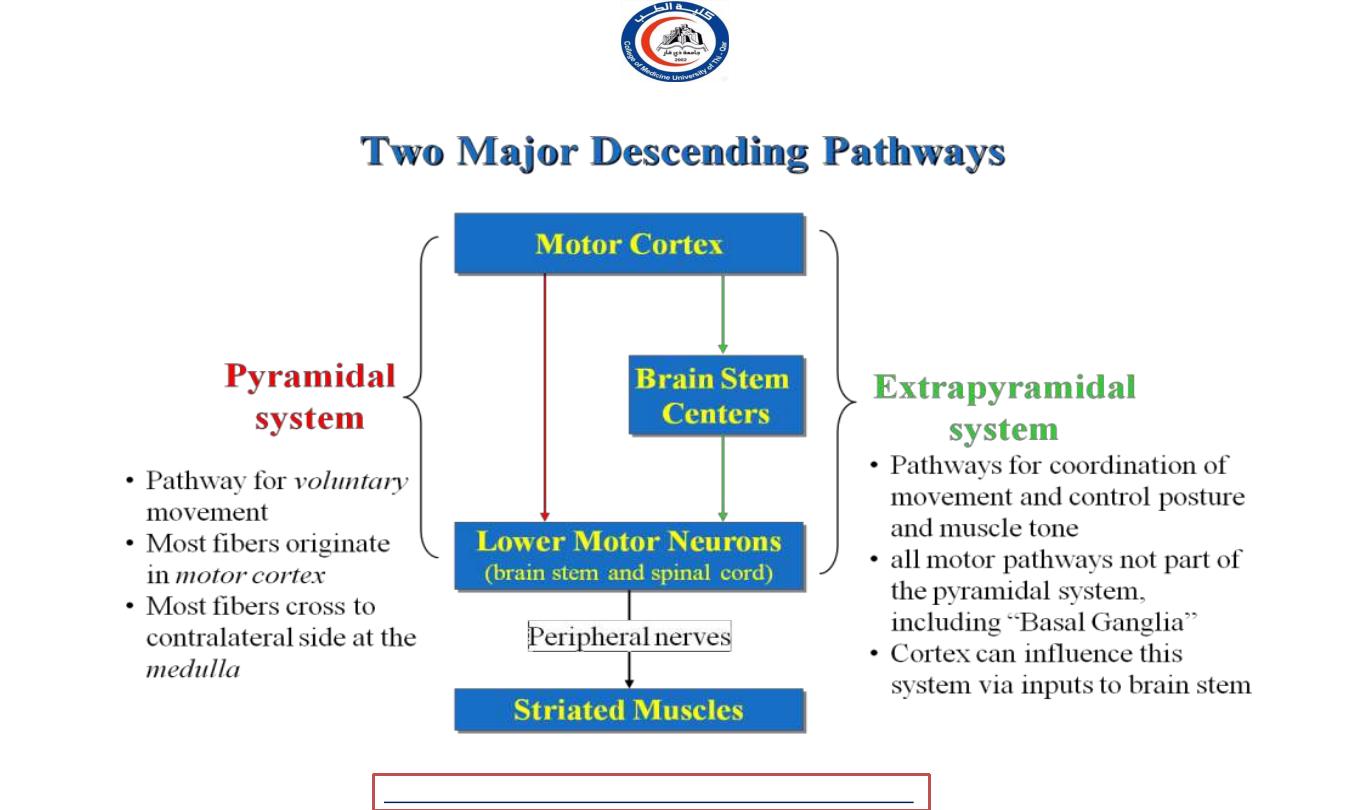
Extrapyramidal system ?
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
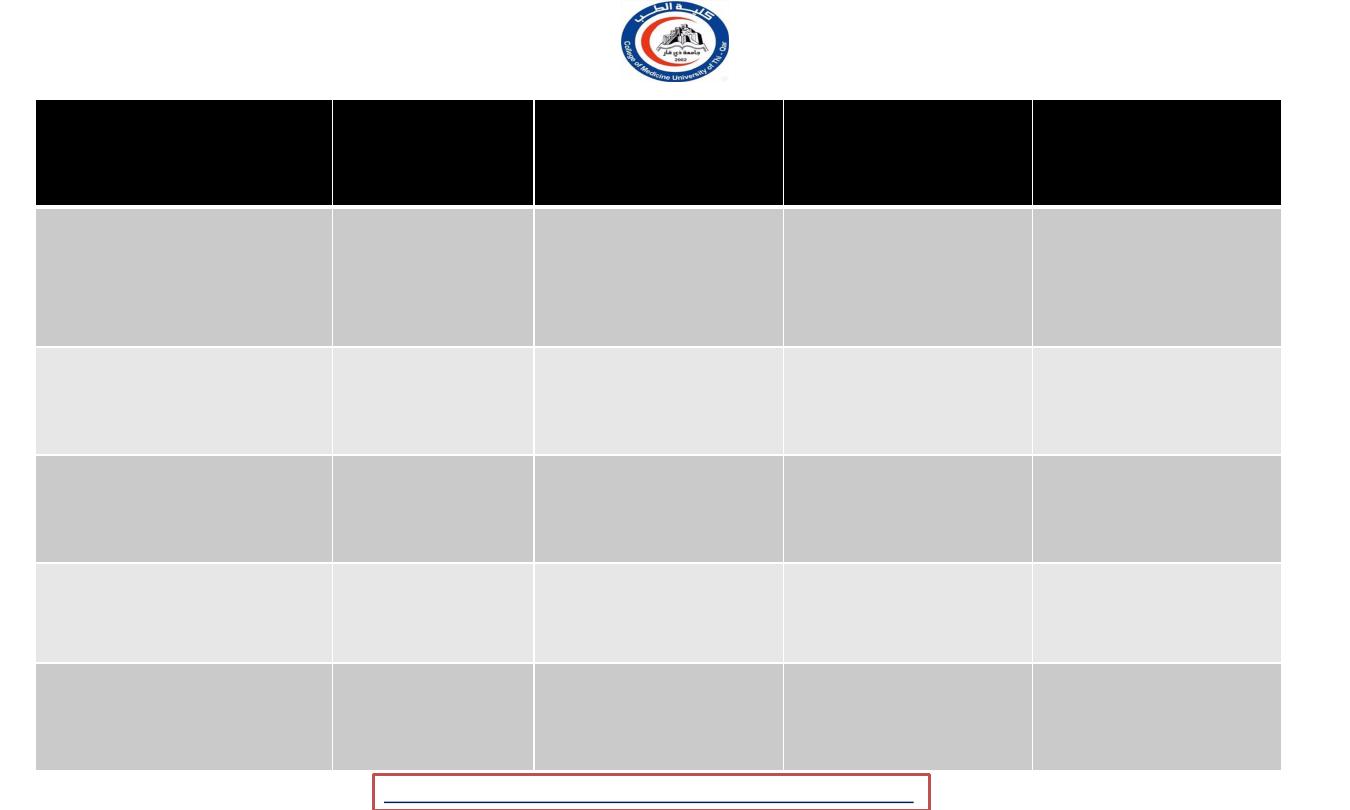
Extrapyramidal system tracts
Input
Nuclei
Tract
Termination
( anterior horn
cells )
Function
- Cerebellum
( opposite side )
- Motor cortex (
same side )
Red nucleus
Rubrospinal
Cervical spinal
cord
Control the
muscle tone
- Cerebellum
- Cortex
Reticular
formation
nuclei
Reticulospinal
Anterior horn
cells
Locomotion
and
posture
control
- Cerebellum
- Brainstem
- Spinal cord
Inferior
olivary
nucleus
Olivospinal
Anterior horn
cells
Control reflexes
- Retina
- Cortex
Superior
colliculi
Tectospinal
Cervical spinal
cord
Body response to
visual stimuli
- Vestibular
nerve
Vestibular
nuclei
Vestibulospinal
Anterior horn
cells
Maintaining
balance of the
body
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
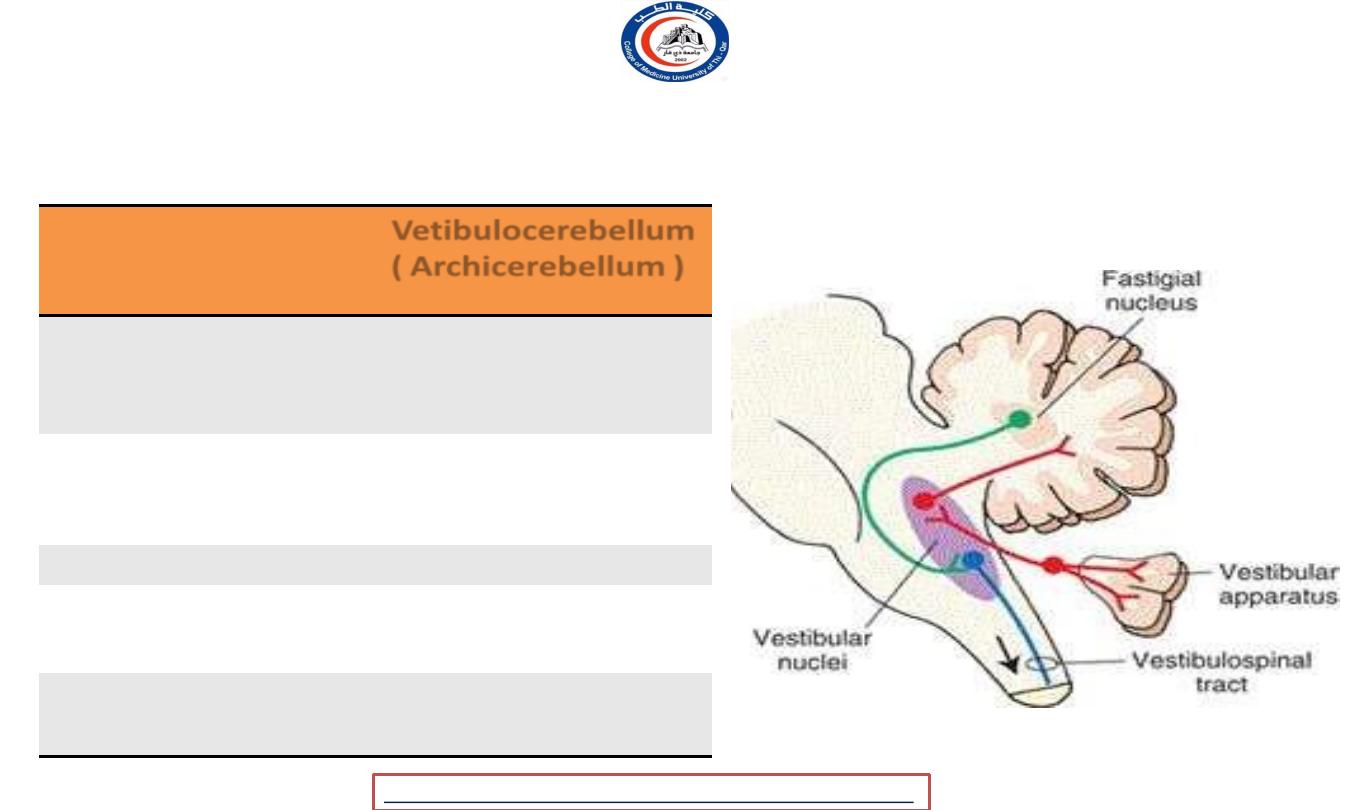
Vestibulocerebllum ( Archycerebellum )
Part
Vetibulocerebellum (
Archicerebellum )
Positon
Flocculonodular lobe
+ part of the vermis
Cerebellar
Nucleus
Fastigial n.
Connection
Vestibular n.
Tract
Vetibulospinal
Function
Balance in spatial
orientation
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
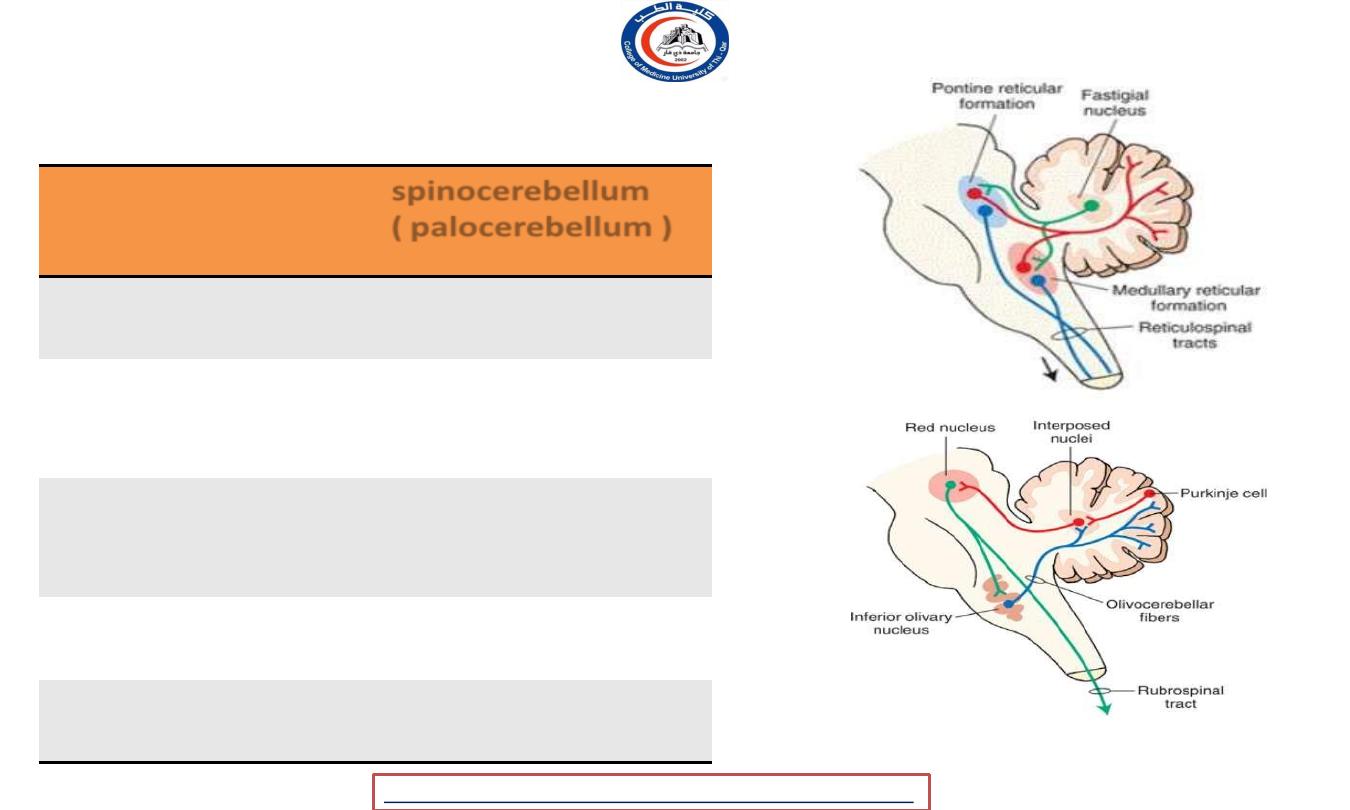
spinocerebllum ( palocerebellum )
Part
spinocerebellum
(palocerebellum
)
Positon
Vermis + paravermis
zone
Cerebellar
Nucleus
Interposed n. (
globosus +
emboliformis
)
Connection
• DC
• Spinocerebellar
system
Tract
Rubrospinal
Reticulospinal
Function
Tone and fine
tuning
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
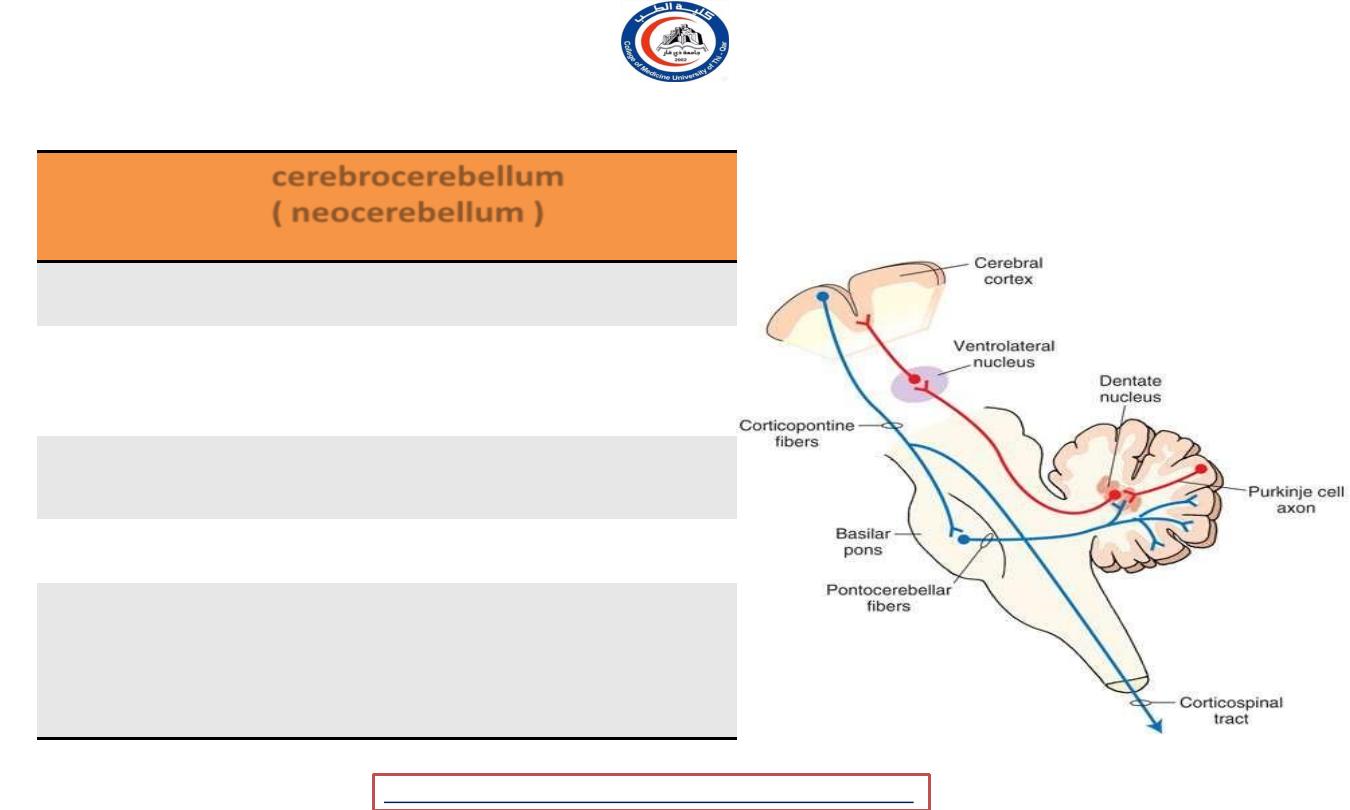
cerebrocerebllum ( neocerebellum )
Part
cerebrocerebellum (
neocerebellum
)
Positon
Lateral part of hemisphere
Cerebellar
Nucleus
Dentate n.
Connection
• Cerebral cortex
• thalamus
Tract
Corticospinal
Function
-
Planning movemen
-
Evaluation the sensory
information for action
-
Cognitive and speech
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
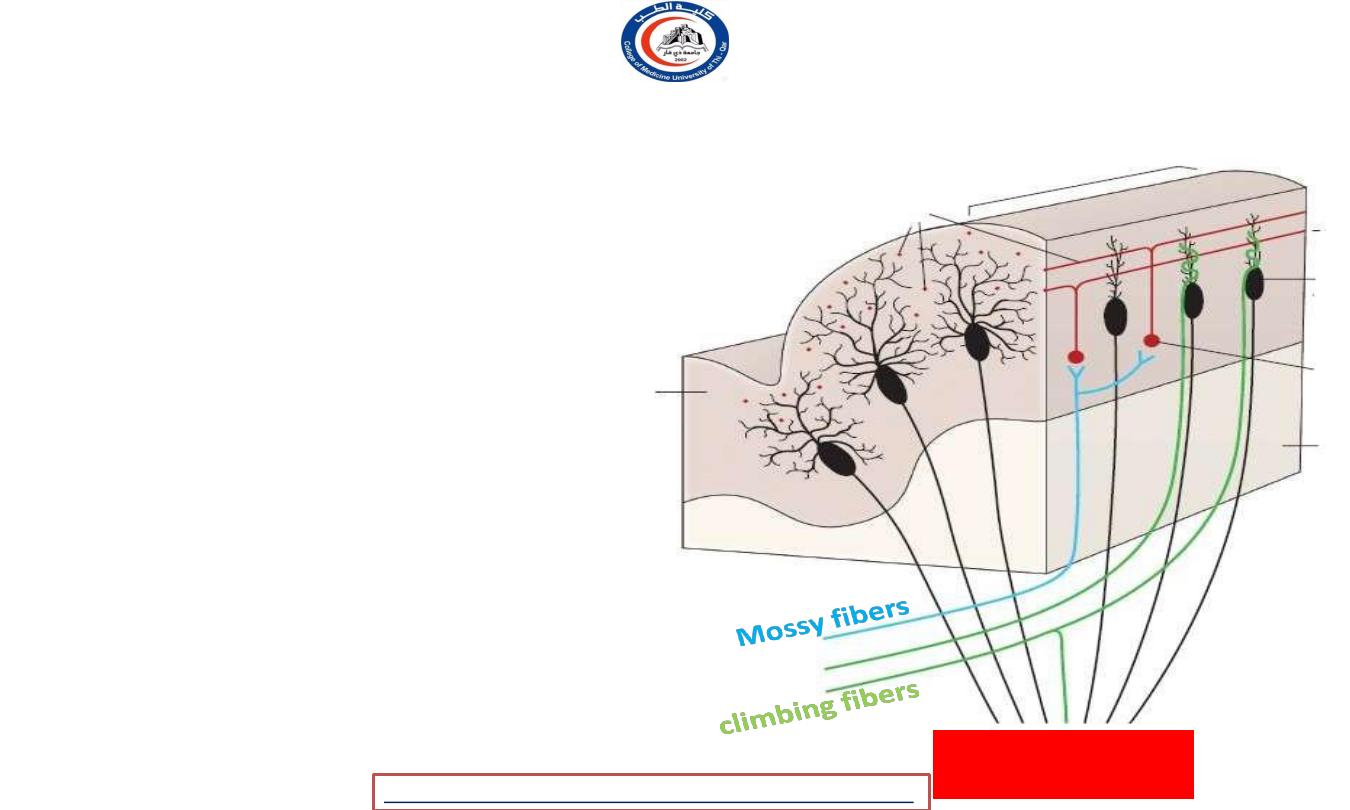
Connections inside the cerebellum
• Two main input fibers excitatory to
purkinje cell …
• 1- climbing fibers
- From olivary n.
- Ascend to molecular layer to synapse with
dendrites of purkinje cell.
- A single Purkinje neuron makes synaptic
contact with only one climbing fiber
- 2- mossy fibers
- the terminal fibers of all other
cerebellar afferent tracts.
- exert a much more diffuse excitatory
effect.
- A single mossy fiber may stimulate
thousands of Purkinje cells through the
granule cells
Efferent to
cerebellar nuclei
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
Cerebellum inputs
Area
Fibers
Function
1
Cortex
Cortico-ponto-cerebellar Cortico-
olivo cerebellar
Cortical control
2
Posterior horn cells of
spinal cord
Anterior and posterior
spinocerebellar tract
Information from
muscle and joints
3
Cuneate nucleus
Cuneocerebellar
Information from
muscle and joints
4
Vestibular nuclei
Vestibulocerebellar
Information about head
position and eye movement
Cerebellum
Spinal cord
Brainstem
Cortex
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
Cerebellum outputs
Area
Fibers
Function
1
Contralateral red
nucleus
Cerebellorubral
Ipsilateral motor
activity
2
Thalamus
Dentato-thalamic
Ipsilateral motor
activity
3
Vestibular nuclei
Cerebellovestibular
Ipsilateral extensor
muscle tone
4
Reticular formation
Cerebelloreticular
Ipsilateral muscle tone
Thalamus
brainstem
Cerebellum
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
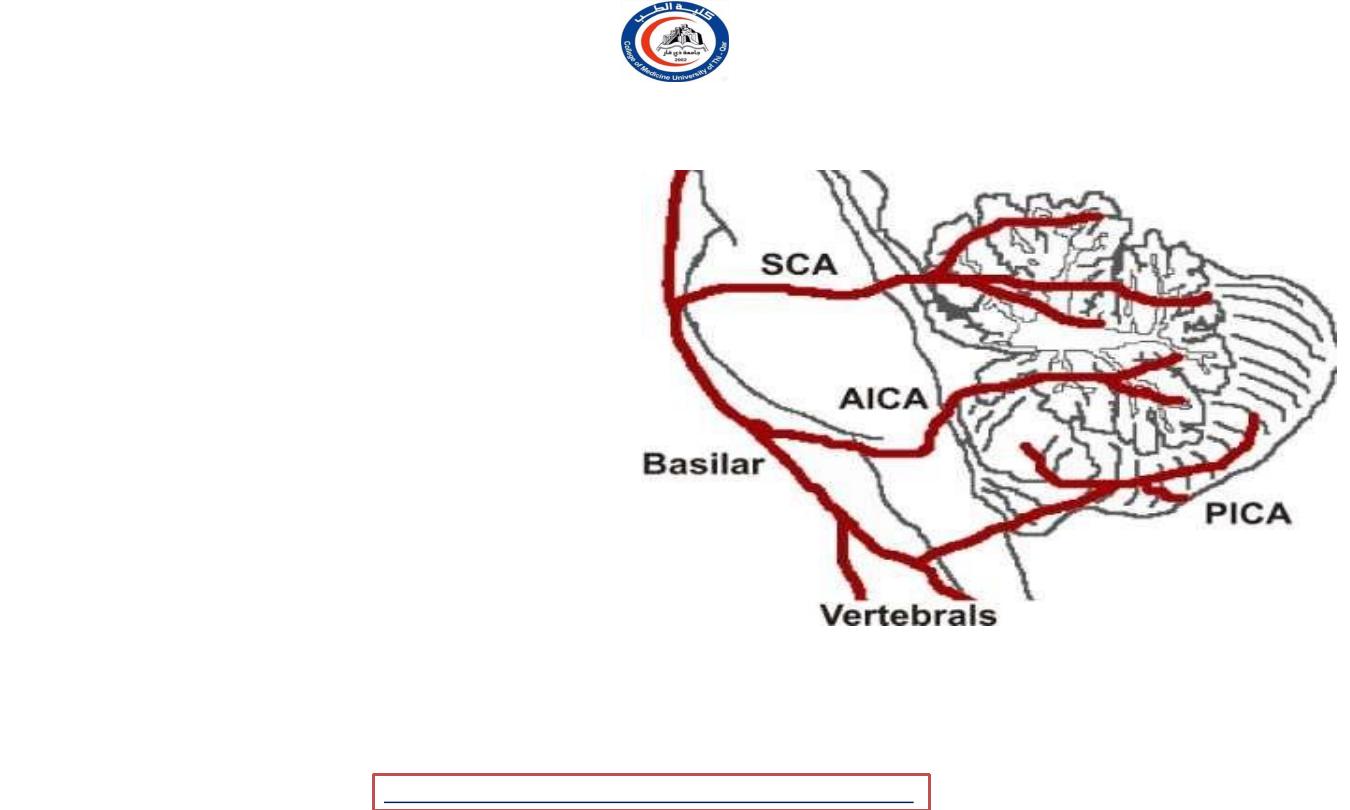
Blood supply to cerebellum
1. Posterior inferior cerebellar artery
(
vertebral a. )
2. Anterior inferior cerebellar
artery
( basilar a. )
3. Superior cerebellar artery
(
basilar a. )
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
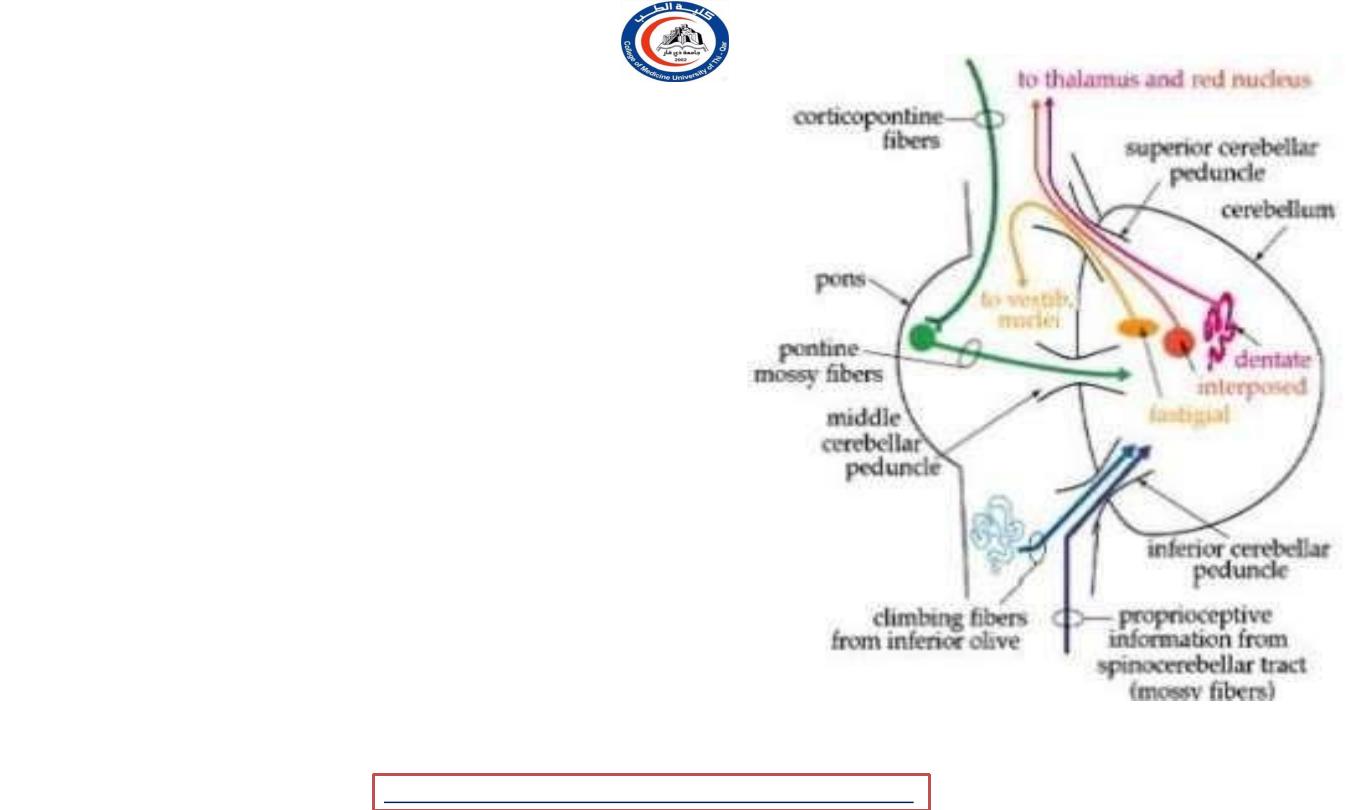
Superior cerebellar peduncle
• Connect
cerebellum
to midbrain
• Main output from cerebellum
(efferent
)
• Small afferent
!!
• Efferent :
-
1. Cerebello-rubral fibers
2. Dentato-thalamic fibers
3. Cerebello-vestibular fibers
• Afferent fibers
• Anterior spinocerebellar tract
• trigeminothalamic
fibers (
proprioceptive information
• tectocerebellar fibers ( auditory
and visual information
)
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
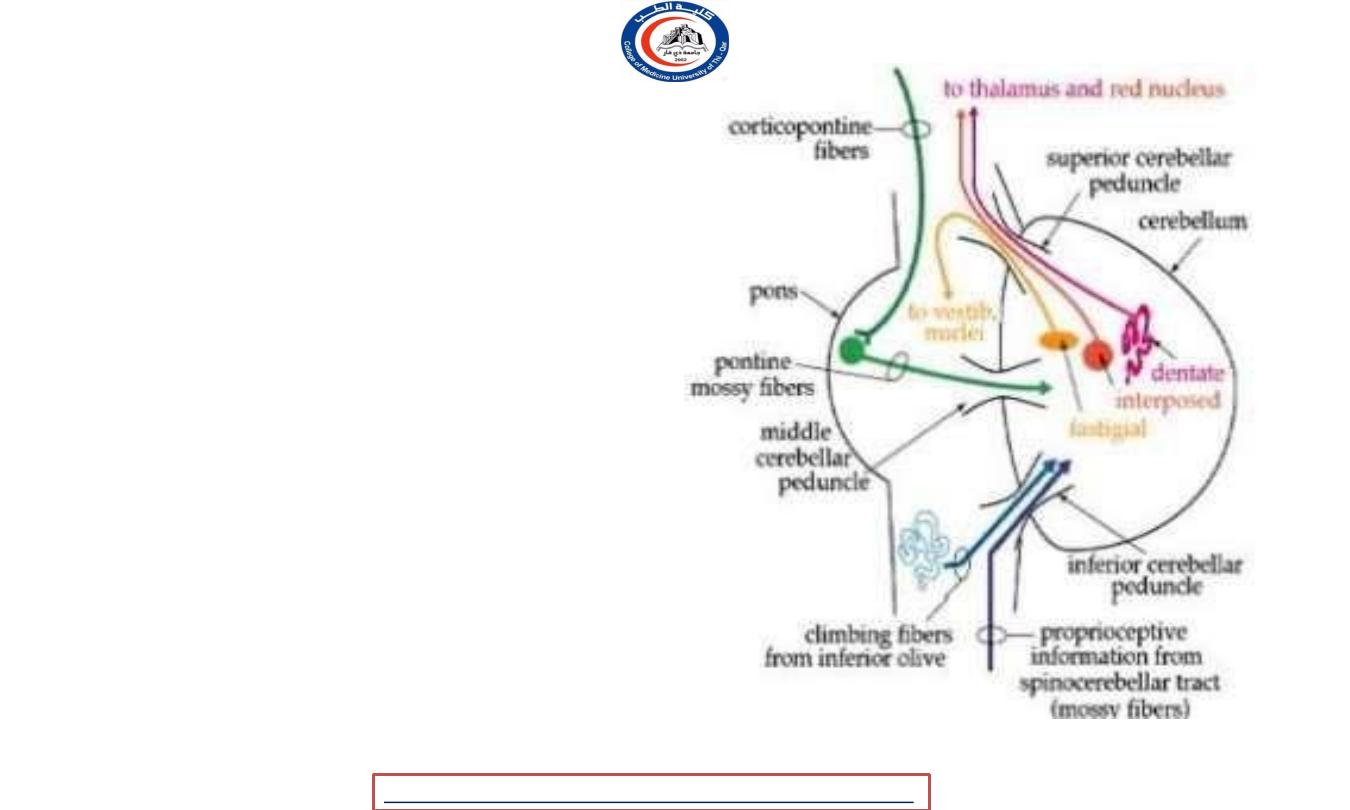
middle cerebellar peduncle
• Connect cerebellum to pons
• Main input to cerebellum !!
• Composed exclusively from
cortico-
ponto-cerebellar fibers
.
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
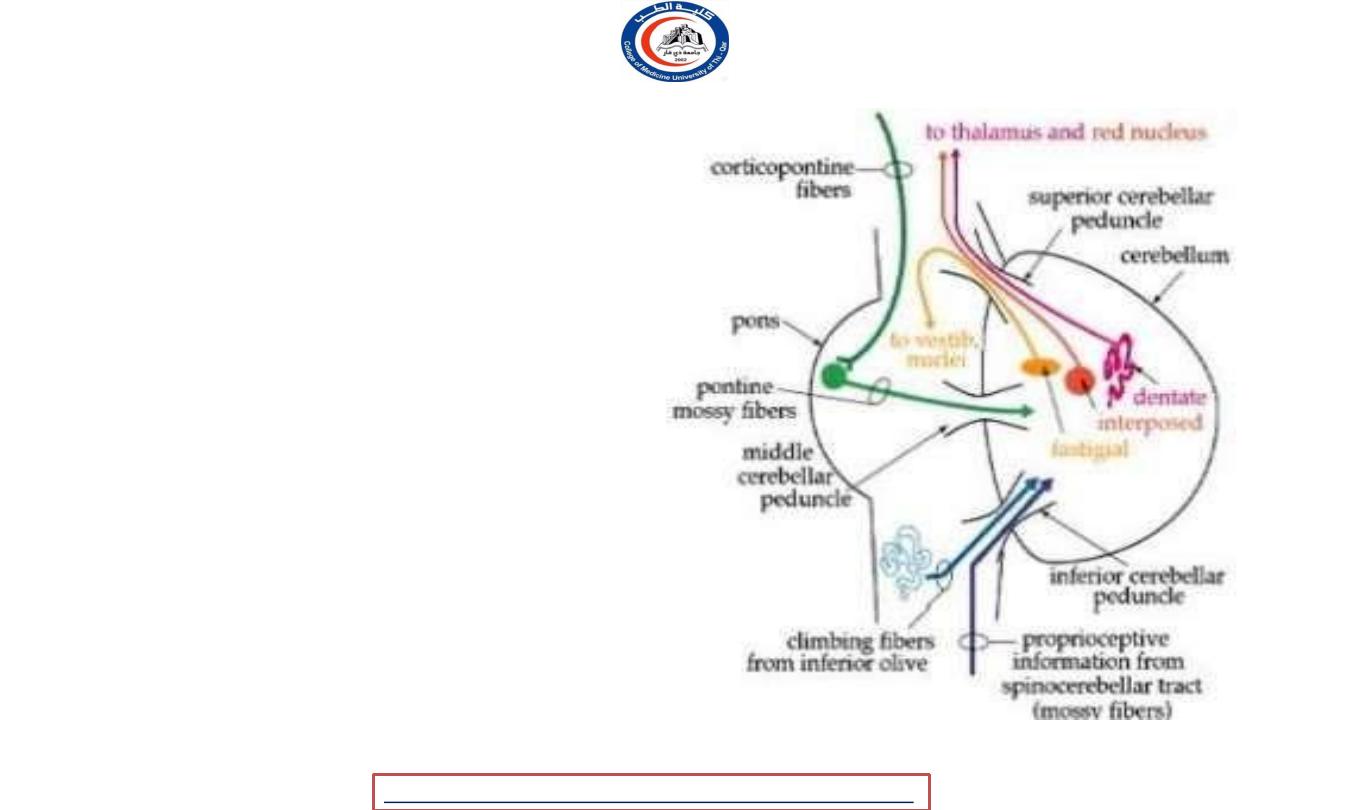
Inferior cerebellar peduncle
• Connect the cerebellum to
medulla oblongata ..
• Efferent :-
• Cerebello-olivary fibers
• Cerebello reticular fibers
• Afferent :-
• Posterior spinocerebellar fibers
• Cuneocerebellar fibers
• Reticulocerebellar
• Vestibulocerebellar
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020

Functions of the cerebellum
• Afferent information about
• Voluntary movement
• Balance
• Site
will enter to cerebellum !!
• The output of the vermis projects to the
fastigial nucleus,the intermediate regions
of the cortex project to the globose and
emboliform nuclei, and the output of the
lateral part of the cerebellar hemisphere
projects
to the dentate
nucleus ..
AS
PREVIOUS
IN
MENTIONED
LECTURE !!
• A few Purkinje cell axons pass directly
out of the cerebellum.
• Purkinje axons are inhibitory !!
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020

• Cerebellum exerts its influence indirectly through the cerebral cortex and brainstem
( not
connect to anterior horn cells ) !!
• the cerebellum functions as a
coordinator of precise movements
by continually comparing the
output of the motor area of the cerebral cortex with the proprioceptive information received
from the site of muscle action; it is then able to bring about the necessary adjustments by
influencing the activity of the lower motor neurons
• This is accomplished by
controlling the timing and sequence of firing
of the motor neurons.
Functions of the cerebellum
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
• It is
also
believed that the
cerebellum
information
can
to
send back
the
motor
cerebral cortex
agonist muscles the
antagonist
to inhibit the and
stimulat muscles,
thus
limiting the extent of voluntary
movement.
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi

Thank you
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
