الدكتور
رافد رمثان حسين
التميمي
دكتوراه أشعة تشخيصية
Spinal Cord Anatomy
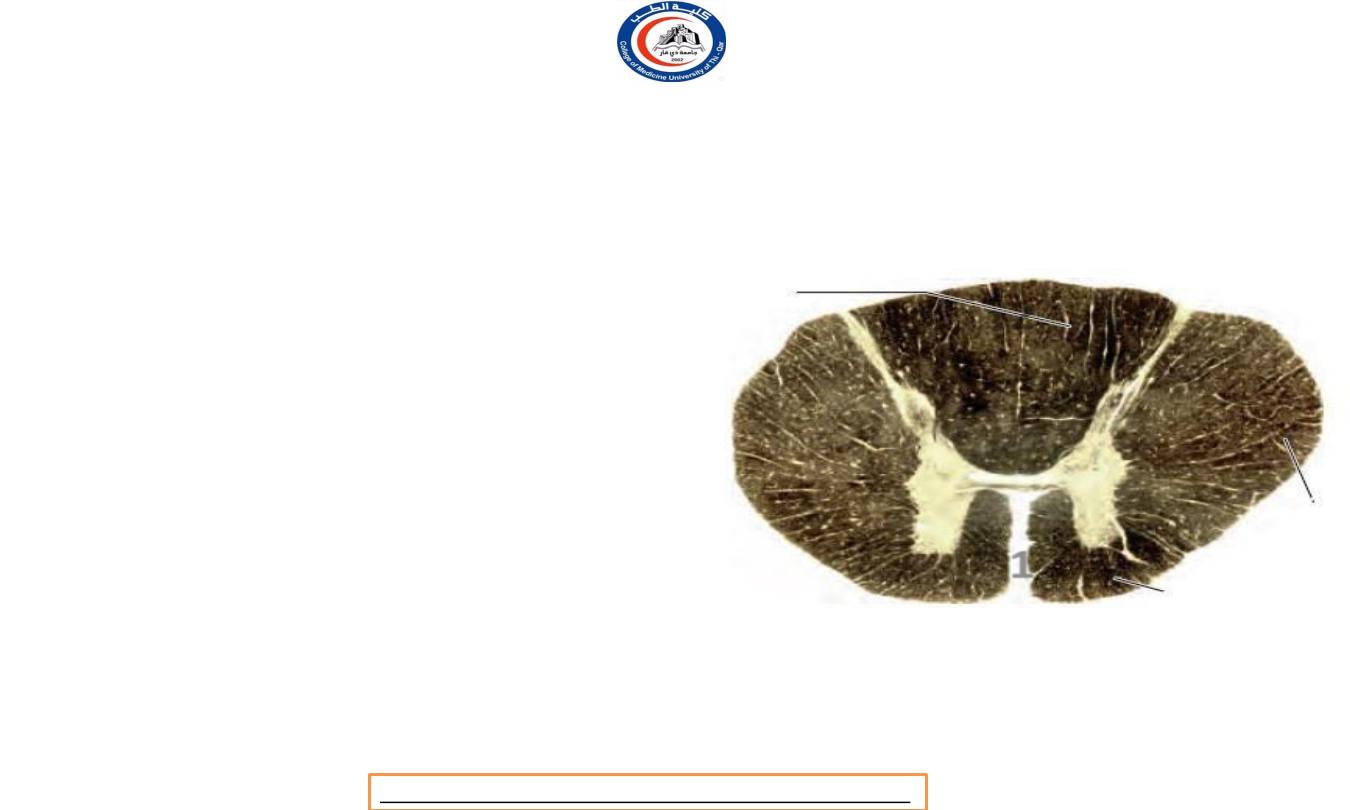
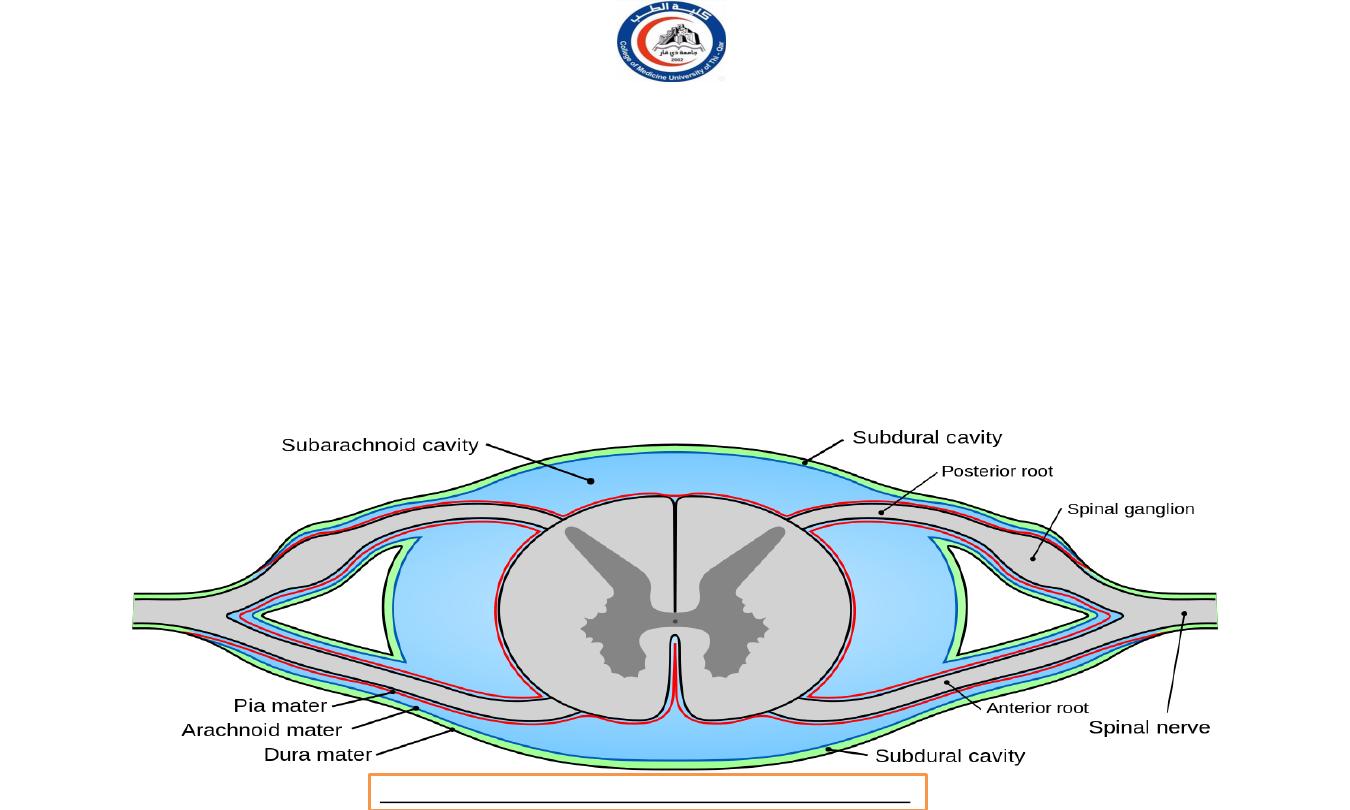
Spinal cord
• Ventrally it possesses a deep midline
groove,
the anterior
median fissure (1)
, and dorsally it
shows a shallow
posterior median
sulcus (2)
, from which a posterior
median septum of neuroglia extends
into its substance.
• The posterior median septum
within
attached
the spinal cord is
to the incomplete
posterior median septum of arachnoid
in the subarachnoid space.
1
2
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Lower limit of spinal cord
• In the fetus the spinal cord extends to the
lower limit of the spinal dura mater at the
level of
S2
vertebra.
•
The spinal dura remains attached at this
level throughout life, but the spinal cord
becomes relatively shorter, which is to say
that
the bony spinal column and the dura
mater grow more rapidly than the spinal
cord.
• Thus at birth the conus medullaris lies
opposite L3 vertebra and does not reach its
permanent level opposite L1 or L2 until
about the age of 20 years.
• The spinal nerve roots, especially those of
the lumbar and sacral segments, thus come
to slope more and more steeply
downwards
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Lower limit of spinal cord
• In fetus
⁻ conus medularis ( lower limit of
spinal cord ) = S2
⁻ Spinal dura mater = S2
• At birth
⁻ Conus medularis = L3
⁻ Spinal dura mater = S2
• In Adults
⁻ Conus medularis = L1 or L2
⁻ Spinal dura mater = S2
⁻ Subarachnoid space = S2
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
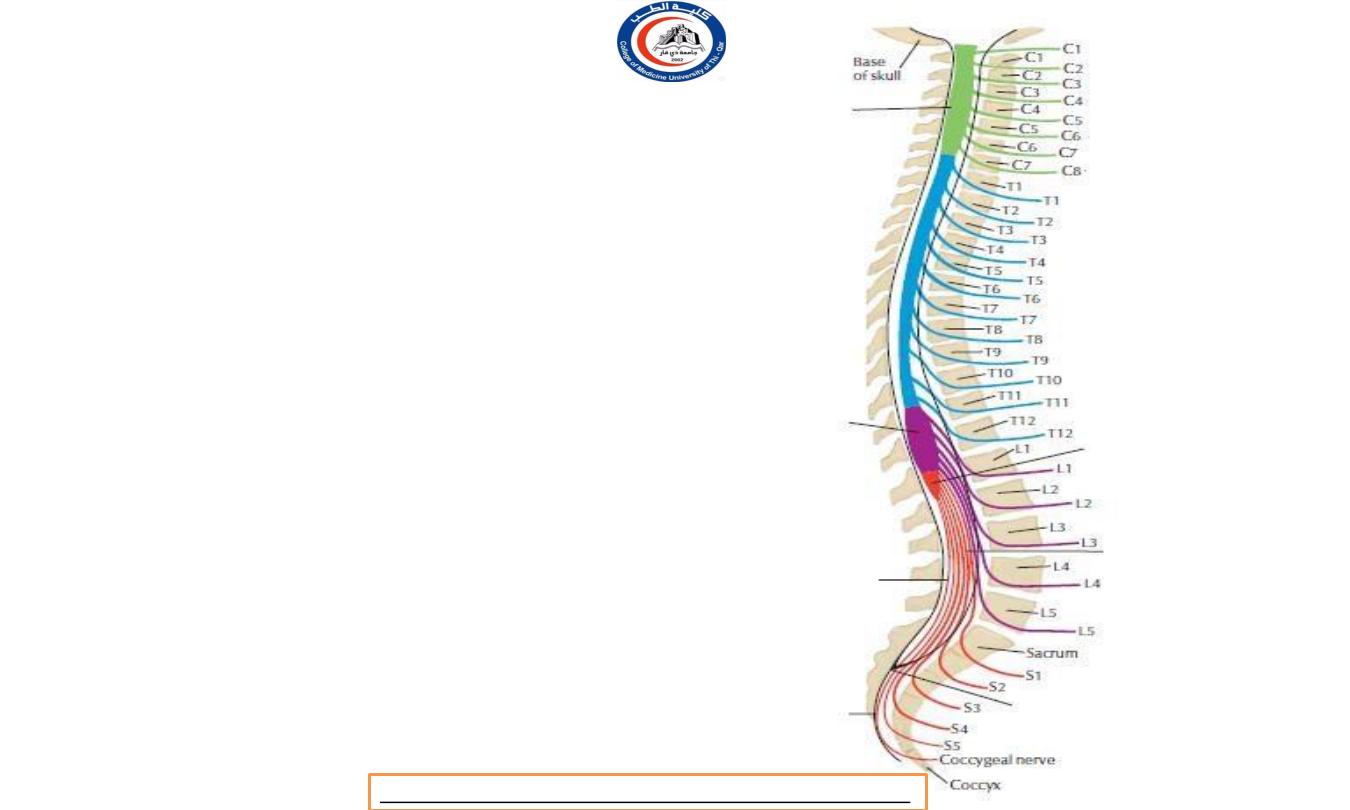
Spinal cord enlargement
• They occupy, in the cord, the segmental levels of
the plexuses concerned
C5 to Tl
for the cervical
enlargement and
L2 to S3
for the lumbosacral
enlargement),
but their levels measured by
vertebrae are, of course, quite different.
•
roughly
corresponding
vertebrae
C3
to
Tl
,
Thus the cervical enlargement lies
to
the
but
the
lumbosacral extends only from
T9 to L1
.
•
Both enlargements are due to the greatly
increased mass of motor cells in the anterior
horns of grey matter
in these situations.
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
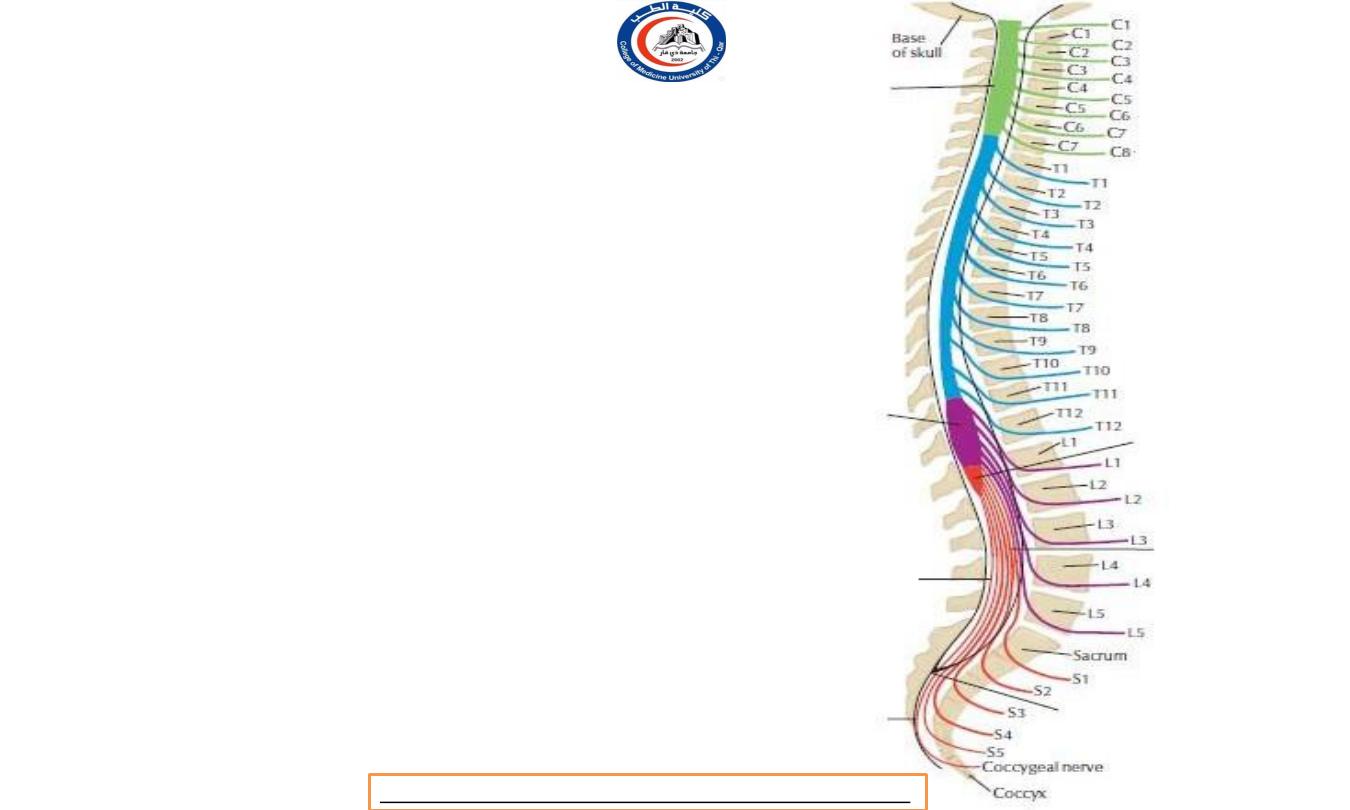
Spinal cord segments
• Spinal cord segments with related to
the vertebral levels
• Cervical = C1-C7
• Thoracic = C7-T11
• Lumbar = T11-L1
• Thoracic = L1-L2
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Spinal dura matter
•
a prolongation of the inner layer of the
dura mater of the posterior cranial fossa.
•
It extends downwards through the foramen magnum
to the level of
S2
vertebra.
•
It is attached rather firmly to the
tectorial membrane (
in cochlea )
and to the
posterior longitudinal ligament
on the
body of the axis vertebra
, but
elsewhere in the spinal
canal it lies free of bony or ligamentous attachments.
•
It is separated from the spinal canal by a layer of fat
in which lies the external vertebral venous plexus.
•
pierced segmentally by the anterior and posterior
roots of the spinal nerves and is prolonged over these
roots to form a series of lateral projections, one
entering each inter vertebral foramen.
•
Thus the loose-fitting theca is stabilized
within the spinal canal.
S2
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Spinal arachnoid matter
•
The spinal arachnoid mater is supported by the inner surface of the spinal dura; nothing but
a thin film of lymph
separates these two membranes.
•
The arrangement is similar to that in the skull. Below the level of the spinal cord (i.e. over the cauda equina) the
arachnoid is nothing but a delicate membrane that is supported by the dura mater, but over the spinal cord itself
the spinal arachnoid sends many delicate web-like processes across the subarachnoid space to the pia mater on
the cord.
•
They are rather well developed in the posterior midline, where they form an
incomplete
posterior median septum.
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
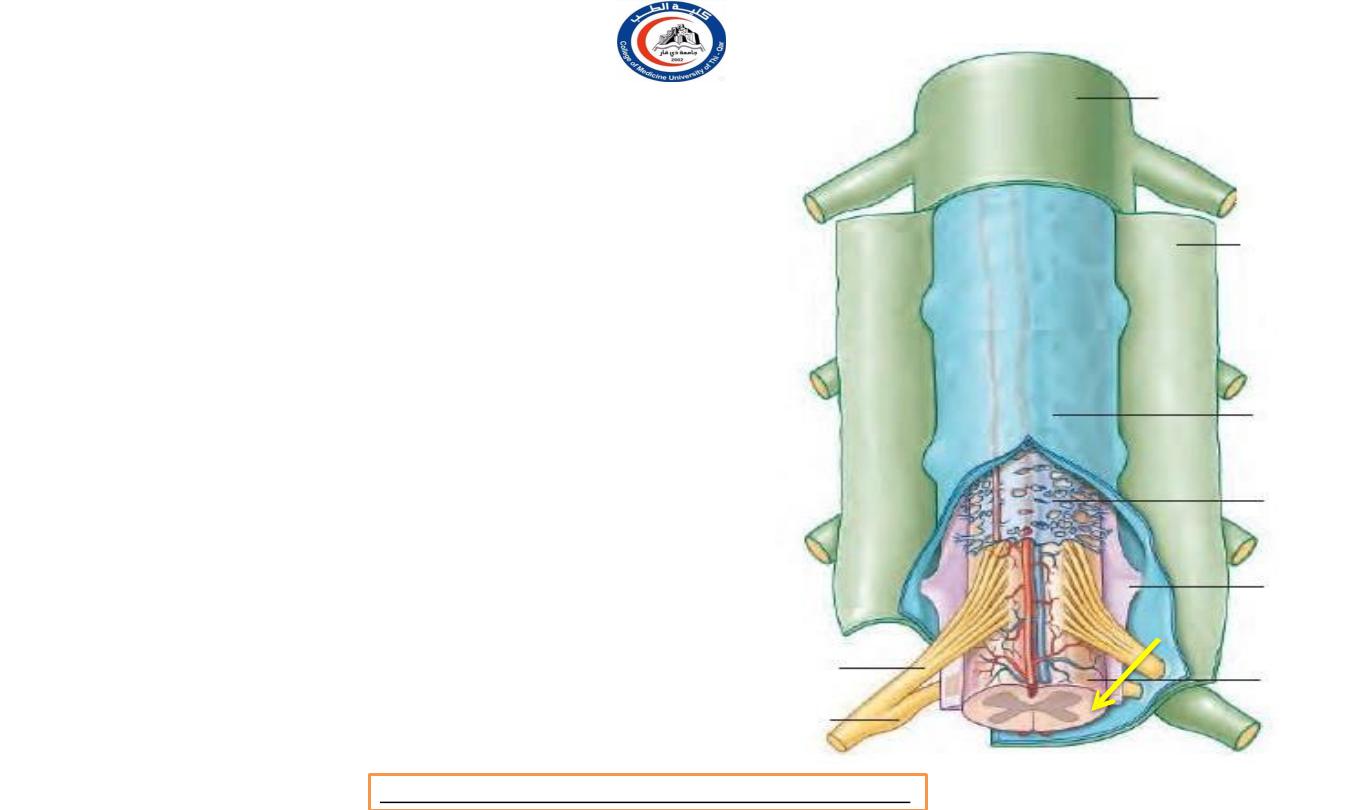
Spinal pia mater
• It clothes the spinal cord and enters to
line the anterior median sulcus. It is
prolonged over the spinal nerve roots
and blends with their epineurium.
• It is projected below the apex of the
conus medullaris, whence it extends
as
the filum terminale to perforate the
spinal dura at the level of S2 vertebra.
It then descends to the back of the
coccyx .
• The filum terminale lies centrally in
the cauda equina, but is not classified
as part of the cauda which consists of
nerve roots only.
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
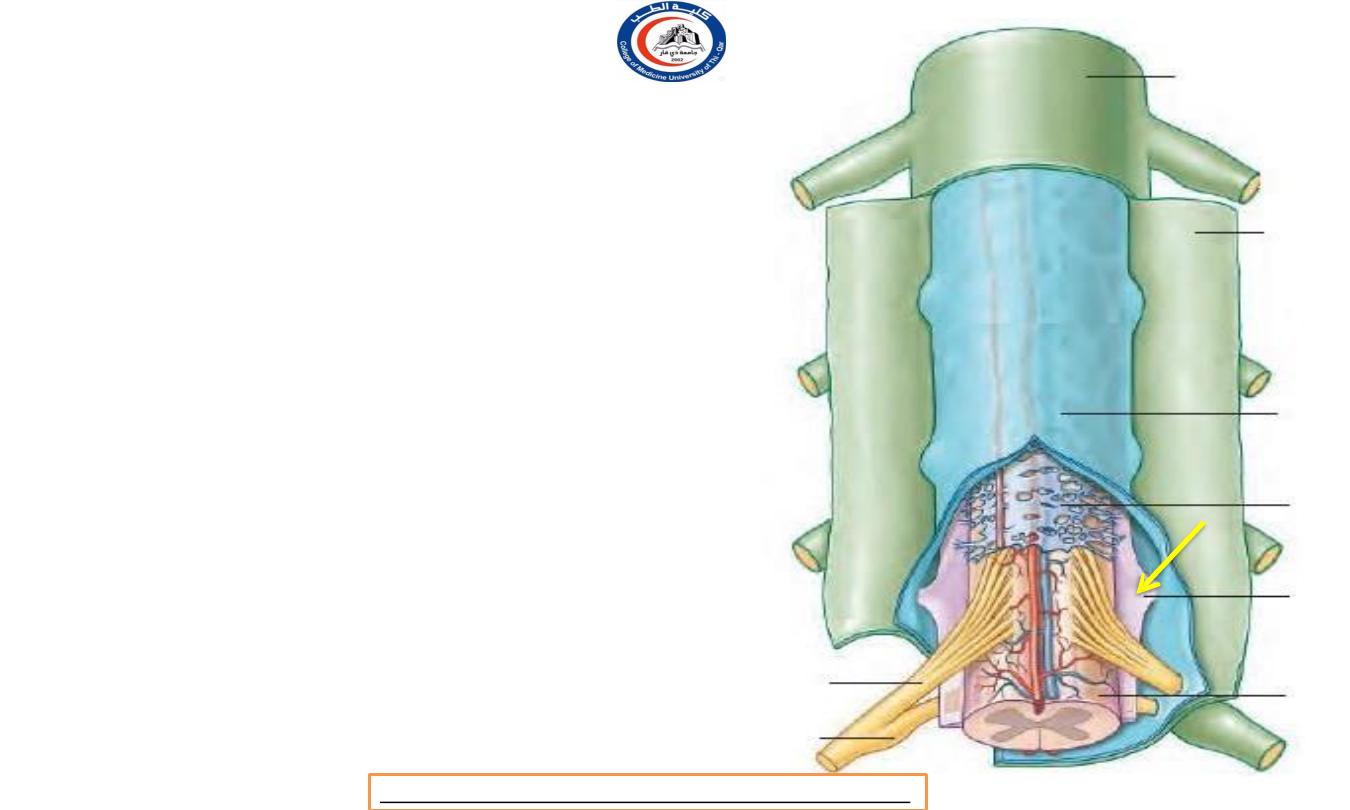
Spinal pia mater
• A lateral projection of pia mater on each side
forms the
denticulate ligament
. This forms a
flange which crosses the subarachnoid space
and, piercing the arachnoid,
connects the side
of the spinal cord to the dura mater.
• Pia mater is attached in an unbroken line along
the spinal cord from the foramen magnum to
the conus medullaris, but its lateral edge is
connected to the spinal dura by a series of
'teeth', which are attached to the spaces
between the issuing nerve roots.
• The root of L1 lies at the lowest
denticulation.
• The denticulate ligament,
filum
terminale and the attached nerve
roots serve to stabilize the loose- fitting spinal
cord within the spinal dura mater
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
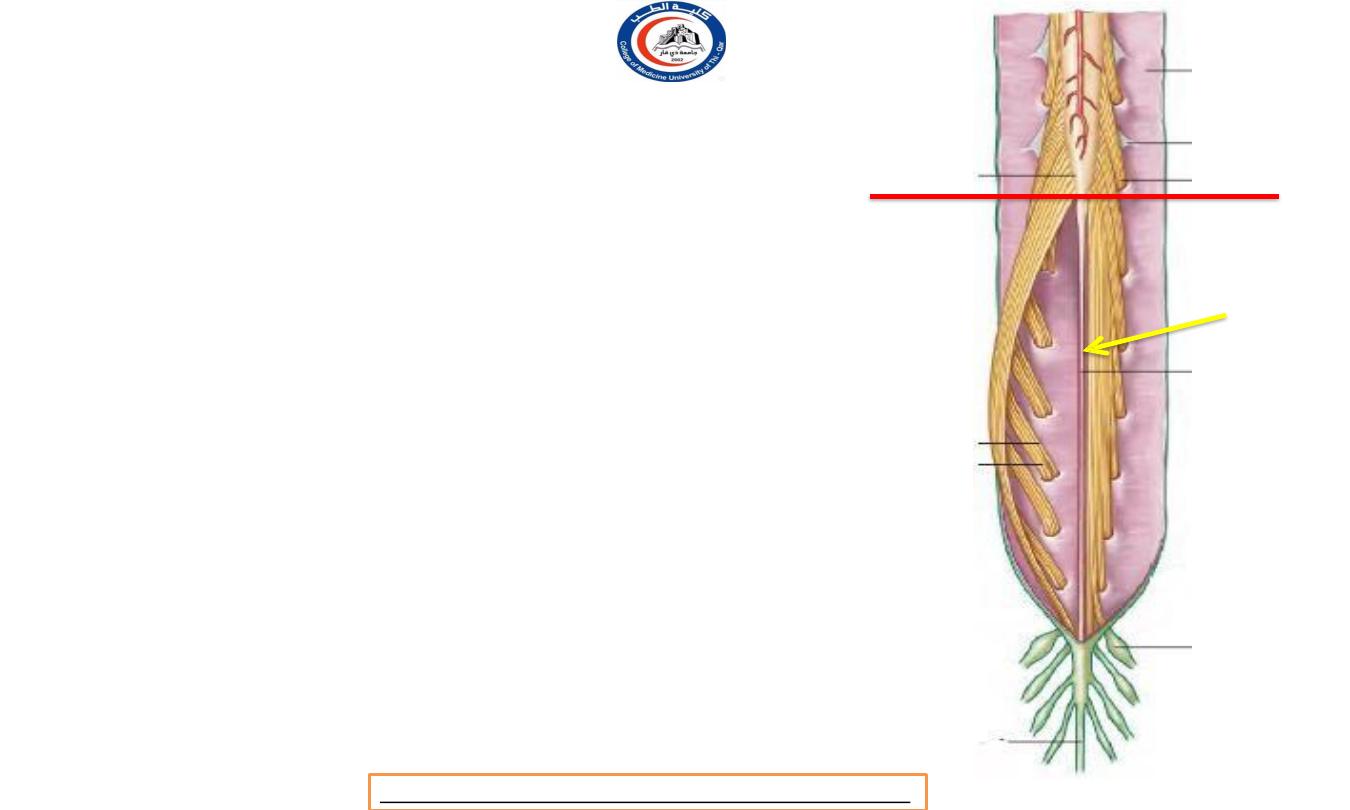
L1 / L2 level
Arrow is on filum
terminale !
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Spinal dura matter
• In summary , the stabilizing factors of
theca ( dura mater ) in bony column ..
1. Attaching to Tectorial membrane
2. Attaching to PLL in level of axis
3. Segmentally piercing of anterior and posterior
spinal roots in their way to pass through the
intervertebral foramina.
4. denticulum ligament
5. Filum terminale
S2
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
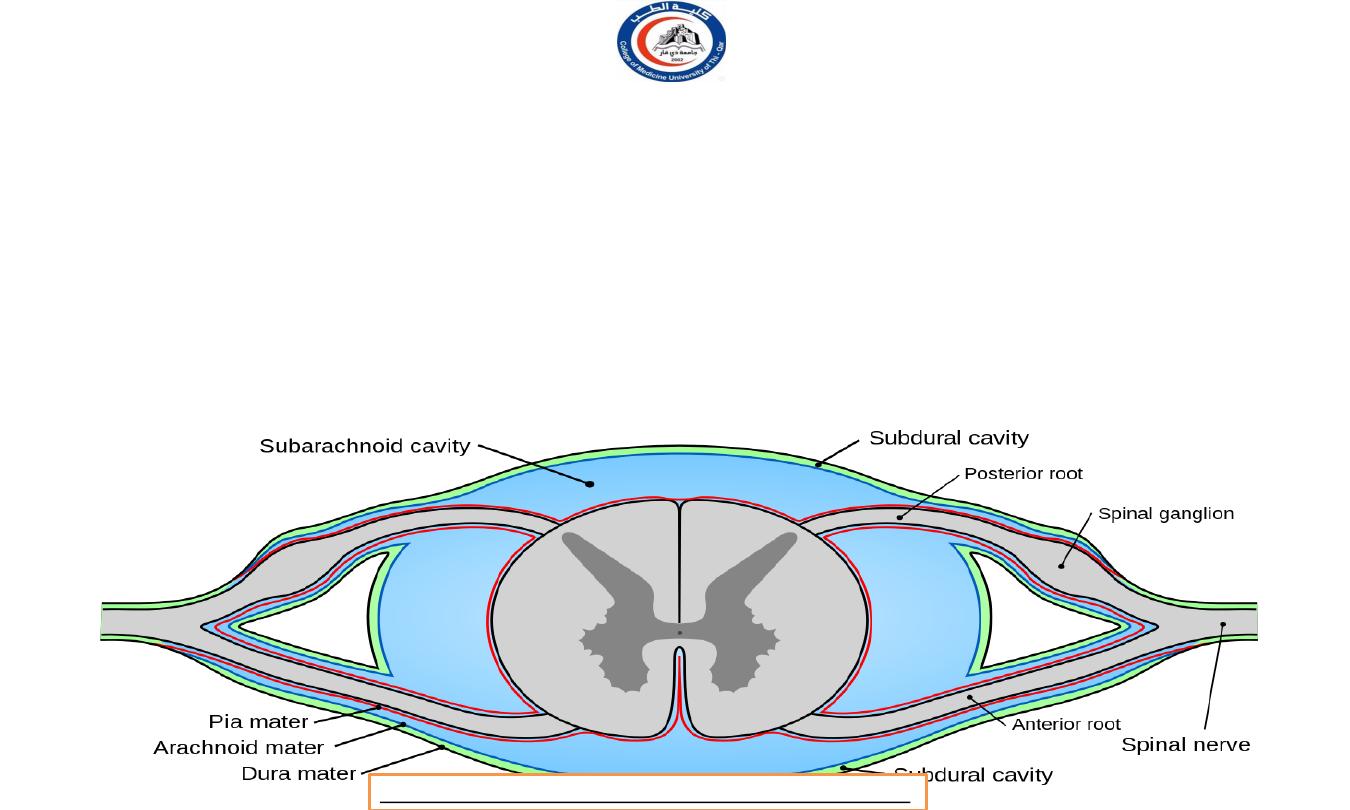
Subarachnid space
• The spinal subarachnoid space is relatively large,
accommodating about half of the total volume of
cerebrospinal fluid (75 ml out of 150 ml).
•
It communicates through the foramen magnum with the subarachnoid space of
the posterior cranial fossa.
•
Some cerebrospinal fluid percolates away along the meningeal sheaths of the spinal nerves.
• Below the level of the conus medullaris it contains only the cauda equina and filum terminale, and it
ends at the level of S2 vertebra.
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
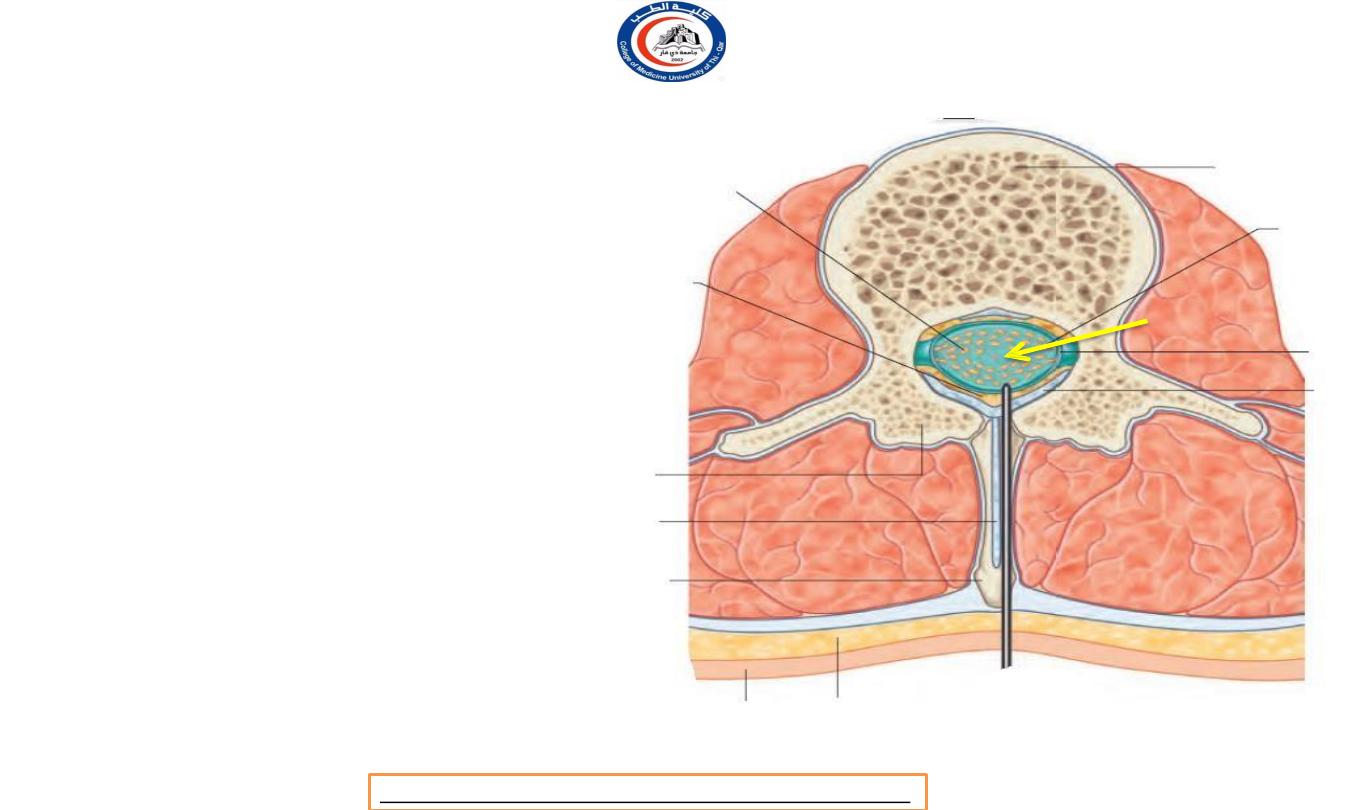
Lumbar puncture
• When no spinal cord is exist !
• When the larger volume is
the subarachnoid space !
• When vertebrae are flexed
!
*Arrow is on filum terminale
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi

Lumbar puncture
• In lumbar puncture the needle is inserted
between the spines of
L3 and L4
or
L4 and
L5
vertebrae when the patient's back is
flexed, usually when curled up lying on one
side.
• The needle passes through the
supraspinous
and interspinous ligaments and through or
between ligamenta flava
before reaching
the dura which is penetrated with a
characteristic 'give'.
• Since the spinal cord ends at the level of LI
vertebra, it is in no danger.
• Lumbar puncture do not penetrate the
posterior longitudinal ligament.
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi

Spinal anesthesia
• In spinal anaesthesia,
the anaesthetic
solution
is
injected
into
the
subarachnoid space
(with the needle in
a similar position to that used for
lumbar puncture), so mixing with the
cerebrospinal fluid surrounding the
nerve roots and percolating into them
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi

Epidural anesthesia
• In epidural anaesthesia (commonly used in child
birth),
the solution is injected into the epidural
(extradural) space without penetrating as far as
the dura,
so that the solution can
infiltrate
sheaths
through the meningeal
containing the lumbar and
sacral nerve roots.
• The approach is similar to that for
lumbar
puncture,
but
formerly
(though less
alternative approach was
common now) an
into the
sacral canal through the sacral hiatus.
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
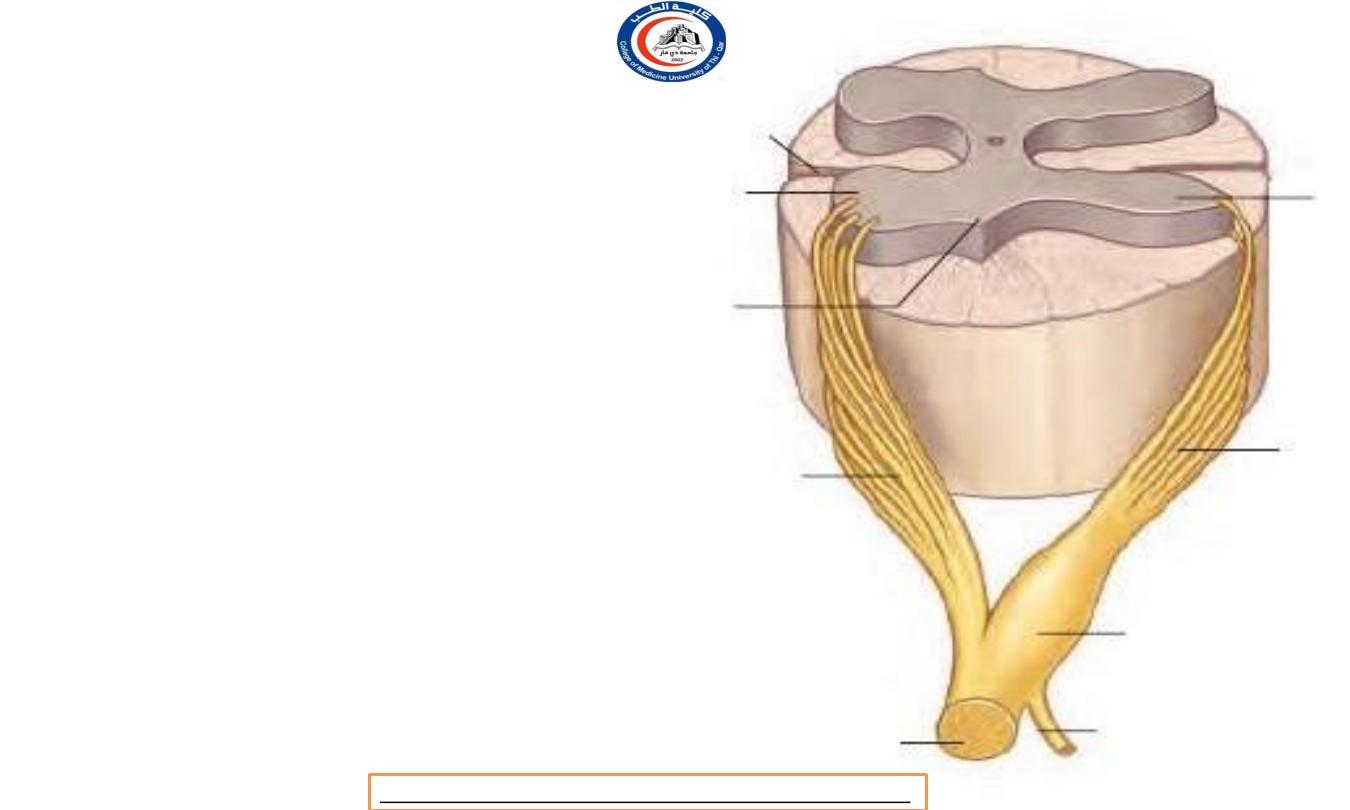
Spinal nerves roots
• No spinal nerves lie inside the
spinal theca ( dura ) ; indeed, no nerve lies,
strictly speaking, within the vertebral canal.
• The anterior and posterior roots of the
spinal nerves
unite within the intervertebral
foramina
.
• Within the subarachnoid space
the nerve
roots are attached to the spinal cord each by
a series of
rootlets
.
•
Each
anterior root
is formed by three or
four rootlets which
emerge irregularly along the anterolateral
surface of the spinal cord.
( see 1 )
• Each
posterior root
is formed by several
rootlets, attached vertically to the
posterolateral surface of the cord.
( see 2 )
1
2
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
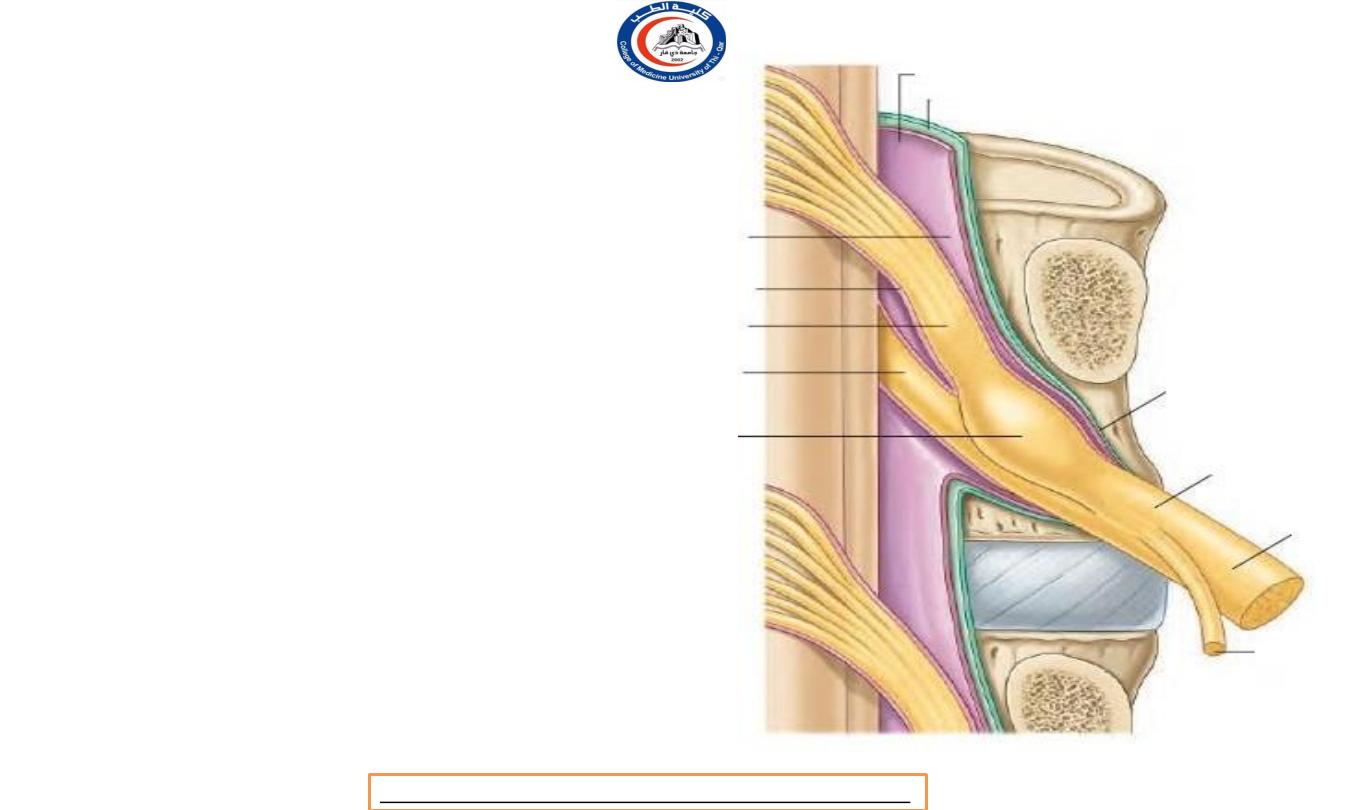
Spinal nerves roots
• The anterior
and posterior
roots pass from
the cord to
their appropriate intervertebral
where
each
mater
foramina,
evaginates
separately
the dura
before uniting to
form the mixed spinal nerve.
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
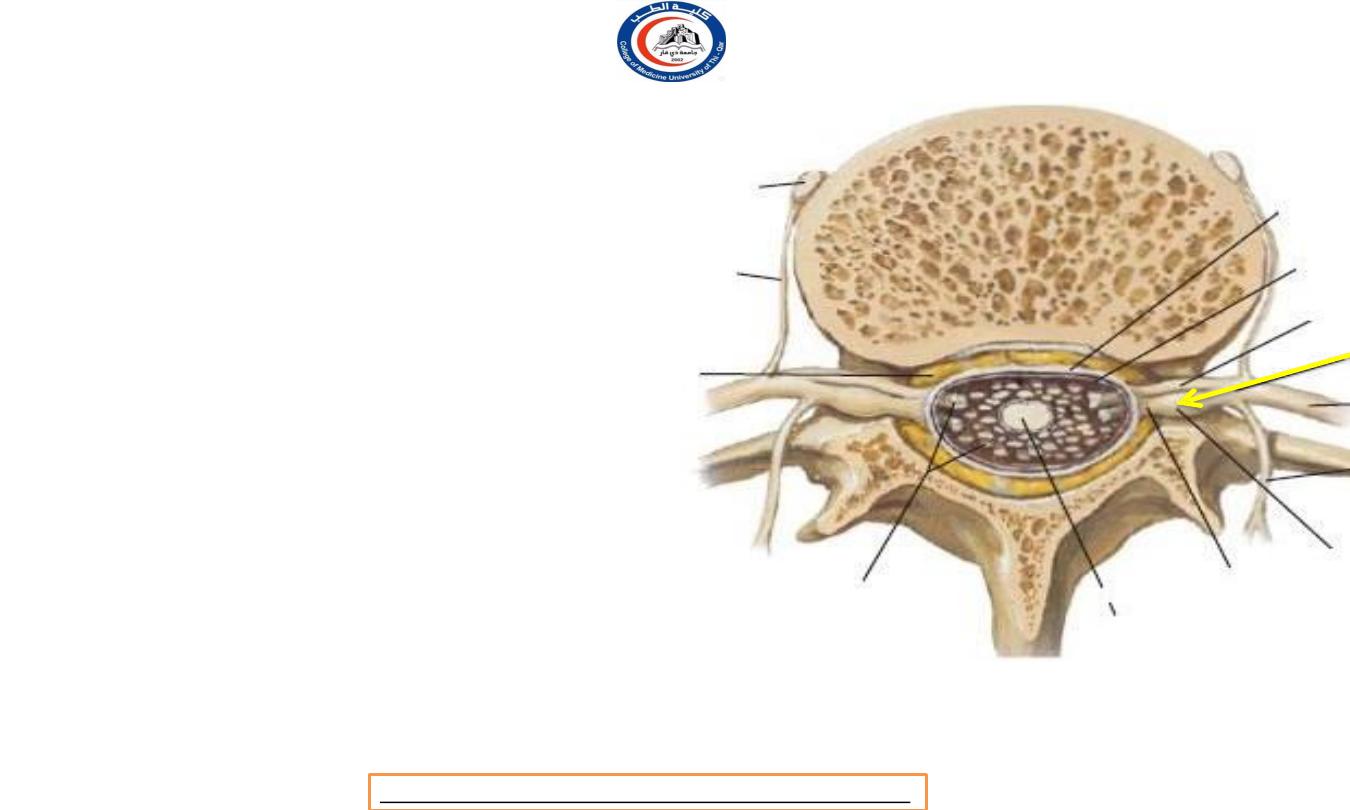
Posterior root ganglion
• The ganglion on the posterior
nerve root
lies in the
intervertebral foramen
, within
the tubular evagination of dura
and arachnoid immediately
proximal to the point of union
of anterior and posterior nerve
roots.
• the posterior root ganglia of
cervical nerves lie just
lateral
to
intervertebral
the
foramina,
in contact with
the
vertebral artery !!
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi

Spinal nerves roots
• all levels from C1 to L1 vertebrae the
anterior and posterior nerve roots
pass in
front of and behind
the
denticulate
ligament
dura
mater
between
respectively, and evaginate the
the
denticulations
• In conformity with the shortness
of the spinal cord,
the lower a
nerve root the more steeply it slopes down
to the intervertebral foramen.
• The upper cervical roots are
horizontal, the upper
thoracic
to their
roots
point
first slope down
of evagination of the
meninges only to become kinked upwards
at an angle to reach their foramen
C1
T1
L1
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
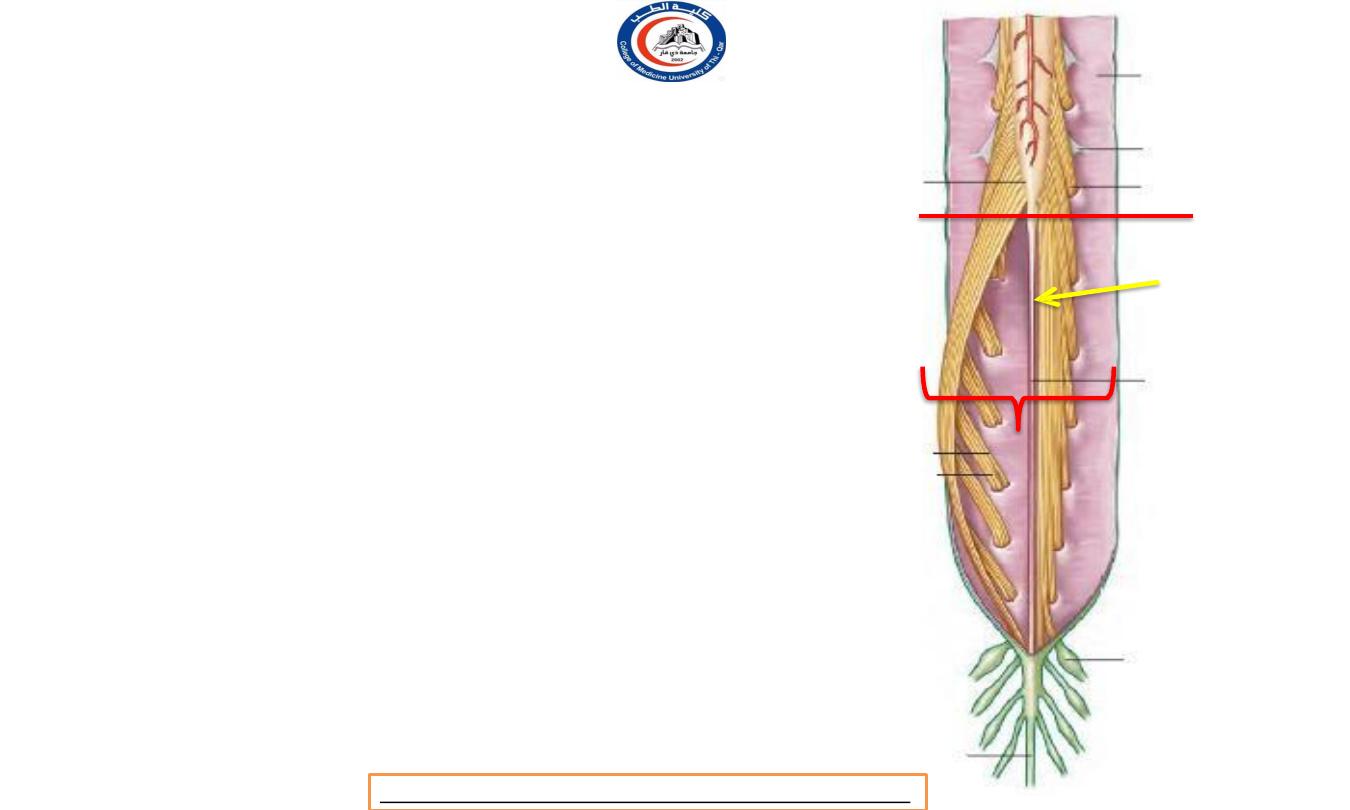
Spinal nerves roots
• Below L1 vertebra the roots pass almost
vertically
downwards
through the subarachnoid space, forming
the
cauda equina (1)
• note that this consists NOT of
spinal nerves but of nerve roots.
•
The
filum
terminale
(pia
matter's
derivatives ) ( arrow )
extends down from
the tip of the conus medullaris among the
nerve roots of the cauda (but is not
classified as part of the cauda).
• The roots of the spinal part of the accessory
nerve emerge from the lateral surface of the
upper five or six segments of the cord,
behind the denticulate ligament
. They unite
into a single trunk which
foramen
magnum
into
passes upwards through the
the
cranium to join the cranial root
1
L1 / L2 level
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
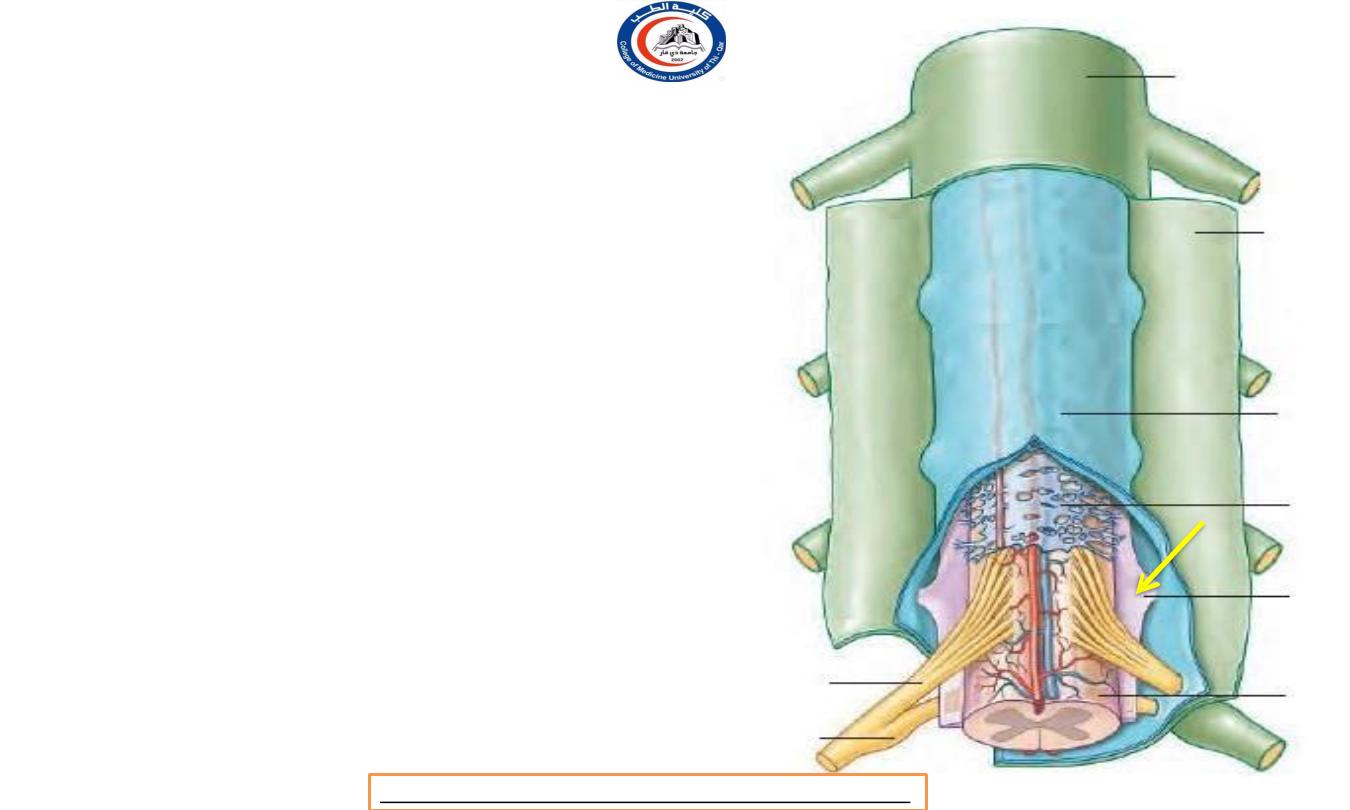
Remember !
• all levels from C1 to L1 vertebrae the
anterior and posterior nerve roots
pass
in front of and behind the denticulate
ligament
respectively, and
evaginate the dura
mater between the denticulations.
• The roots of the spinal part
of the accessory nerve emerge
from the lateral
surface of the upper five or six
segments of the cord,
behind the
denticulate ligament.
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
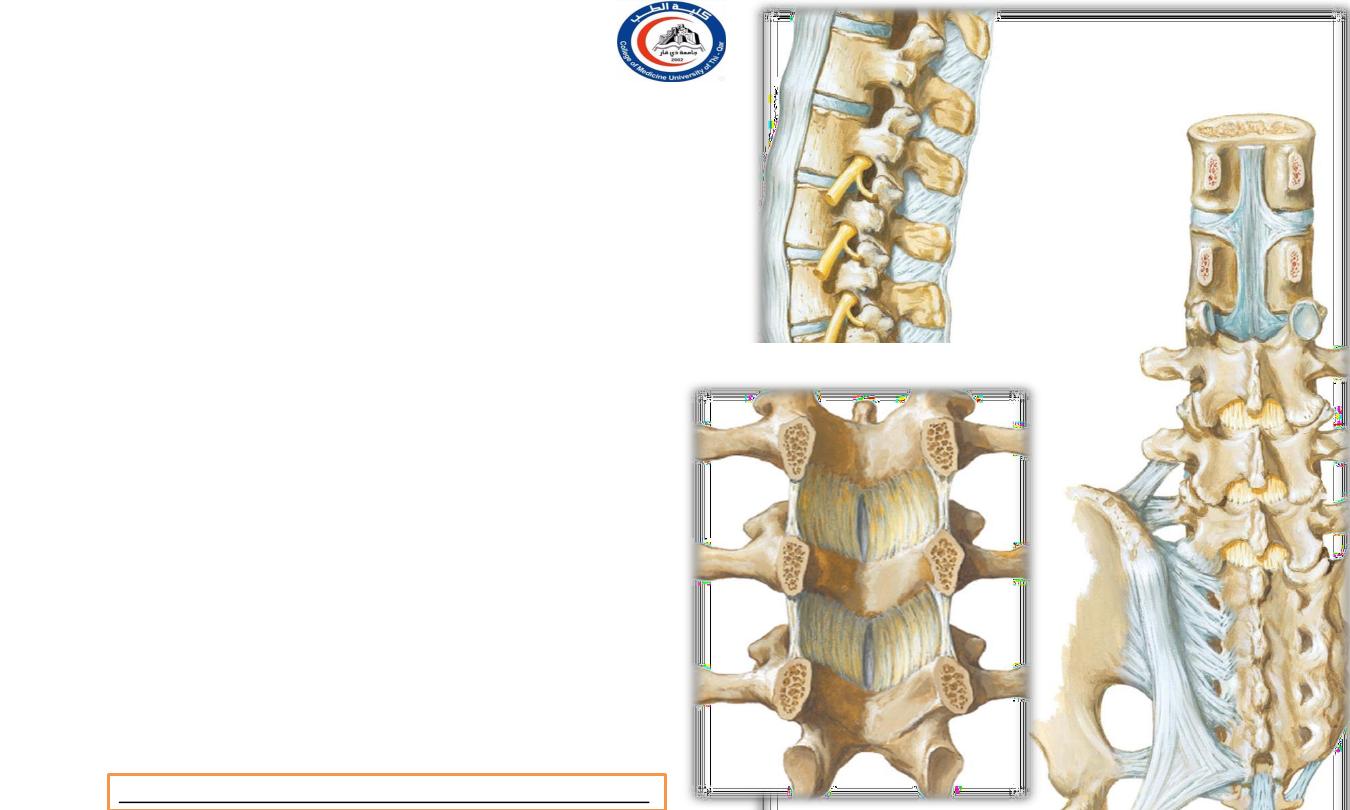
Important ligaments in the spine
1.
Anterior longitudinal ligament (ALL)
2.
Posterior longitudinal ligament (PLL)
3.
Supraspinous ligament
4.
Intraspinous ligament
5.
Ligamentum flav ( between pedicles - between
spinous and transverse processes )
1
2
3
4
5
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
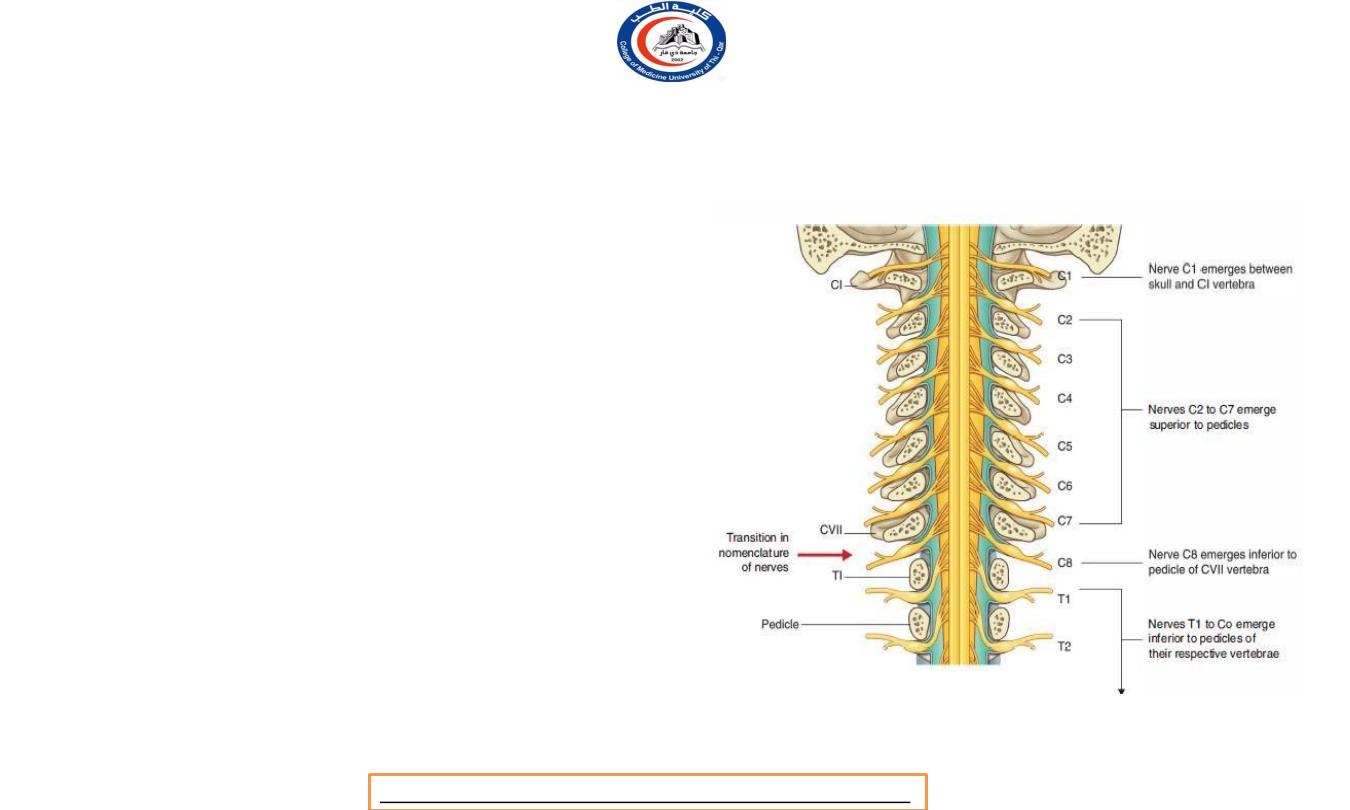
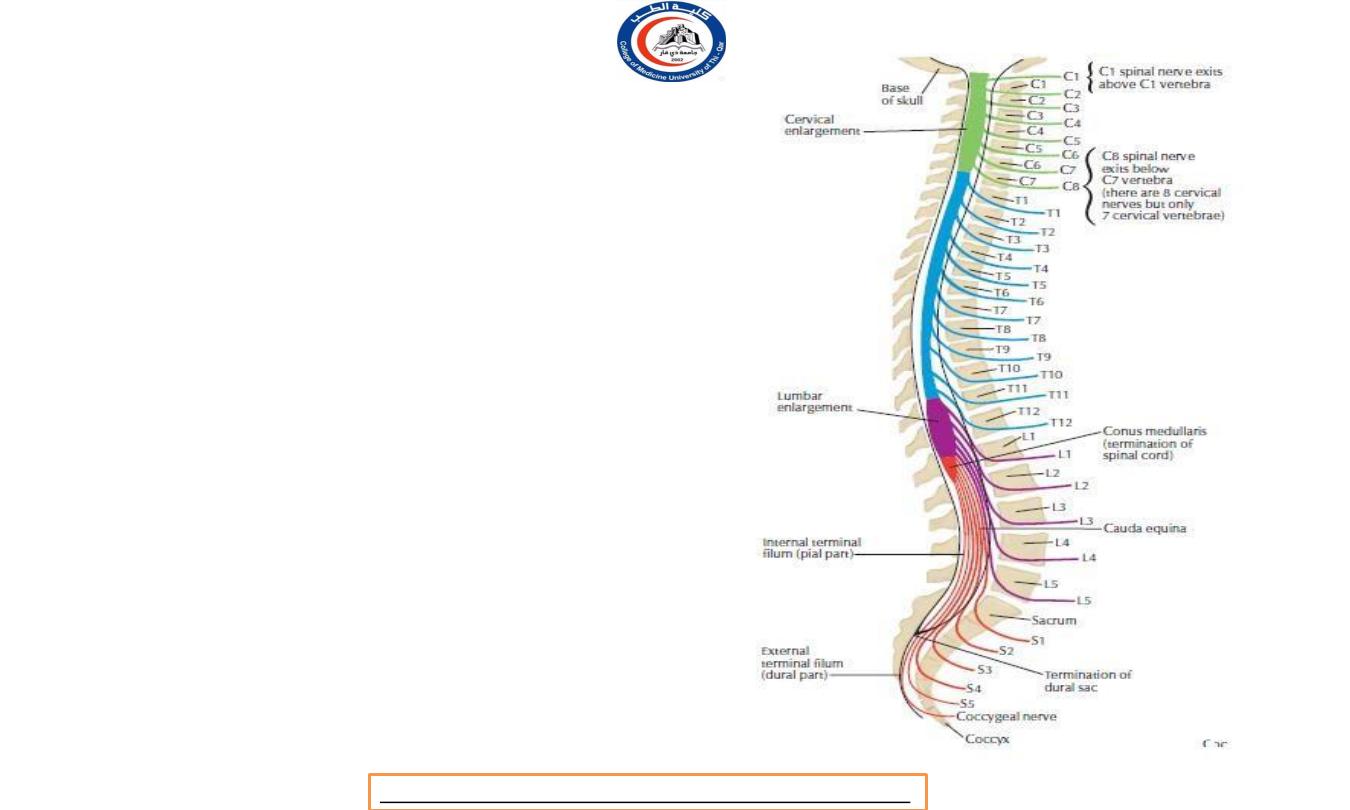
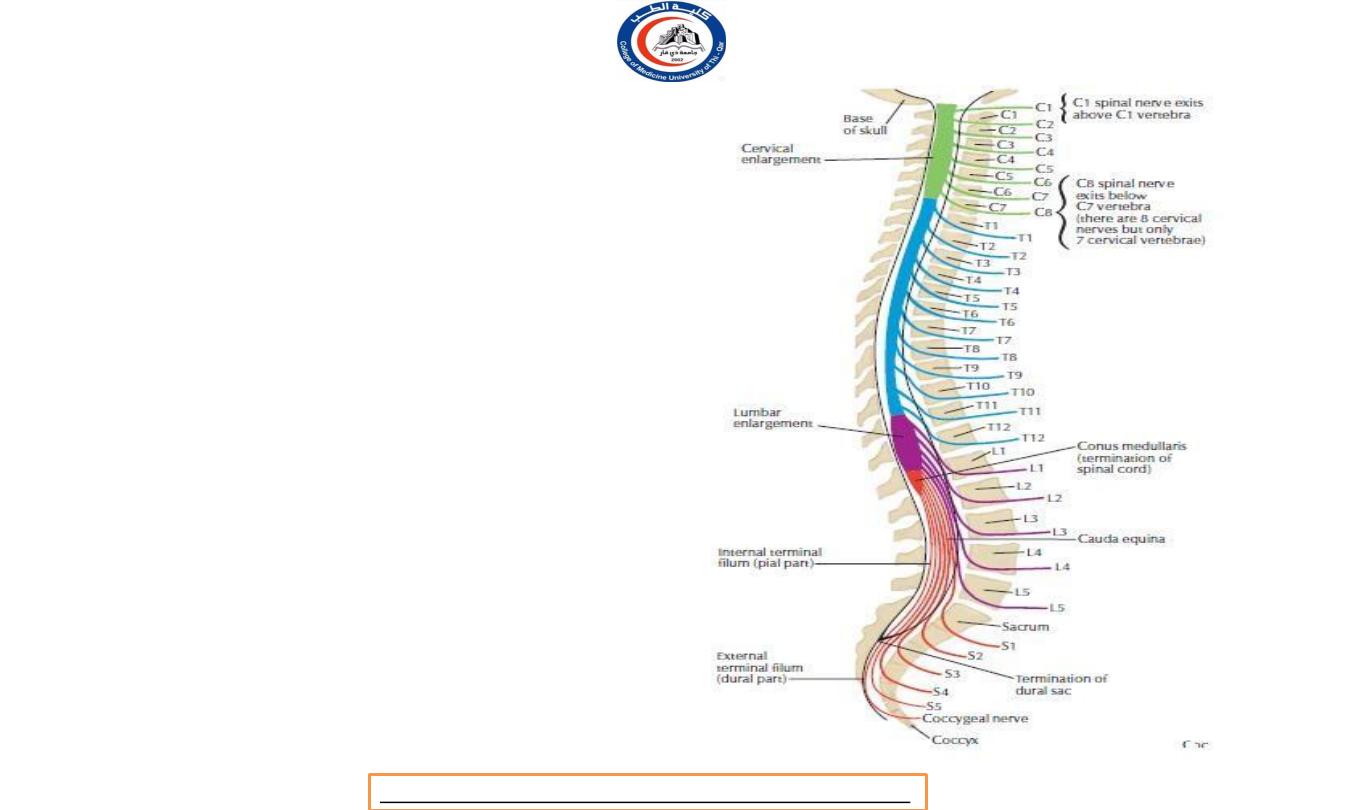
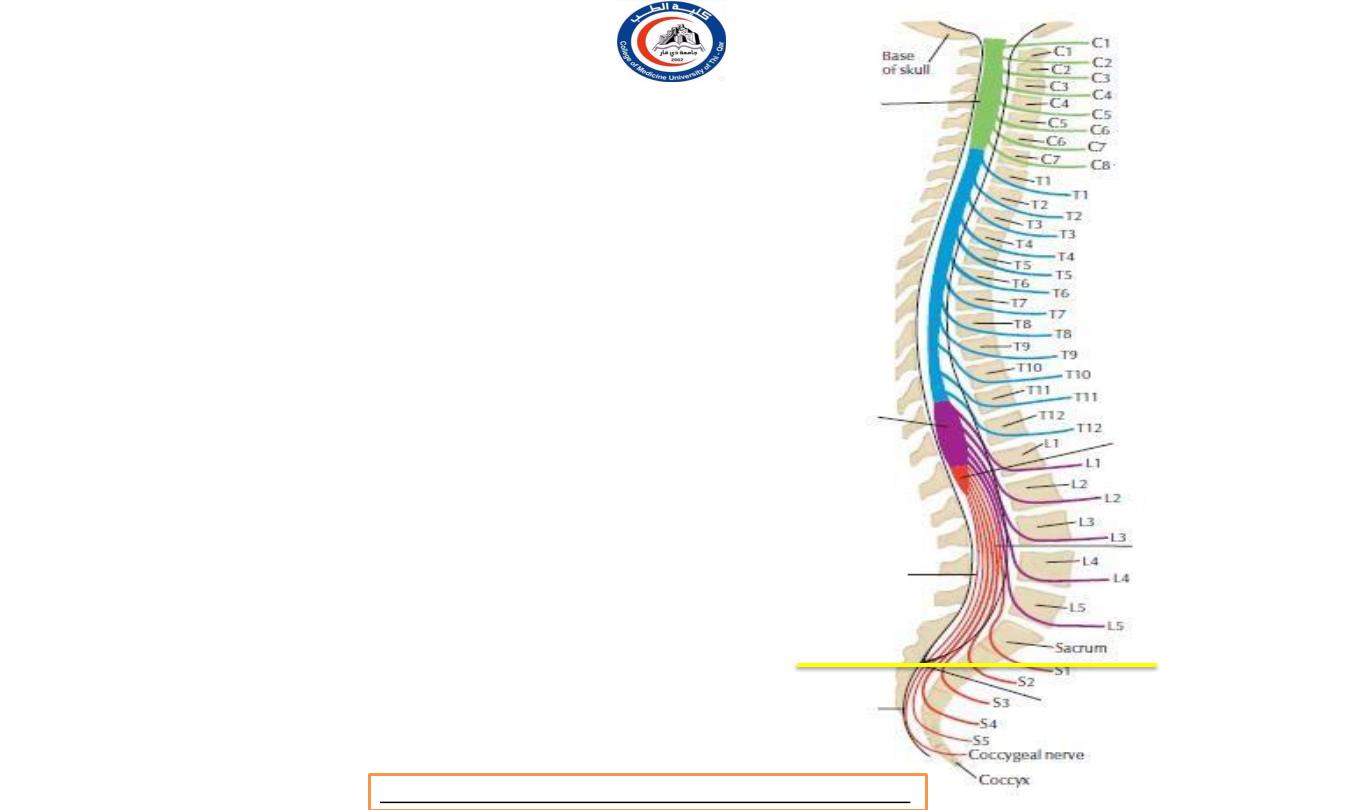
Nomenclature of spinal nerves
• Notice this C1 nerve root exit above C1
vertebra
• C8 nerve root exit below C7 vertebra
• Also, T1 nerve root exit below T1 vertebra
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
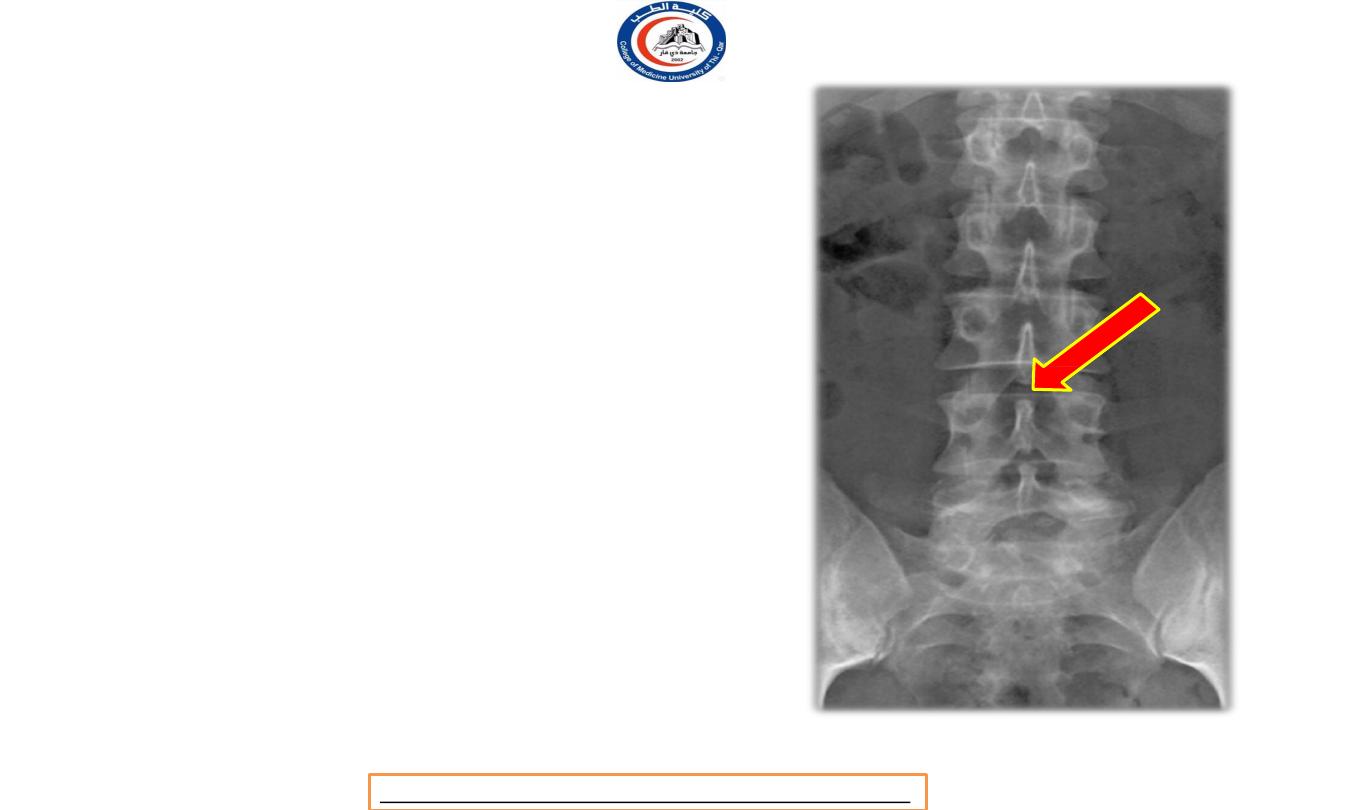
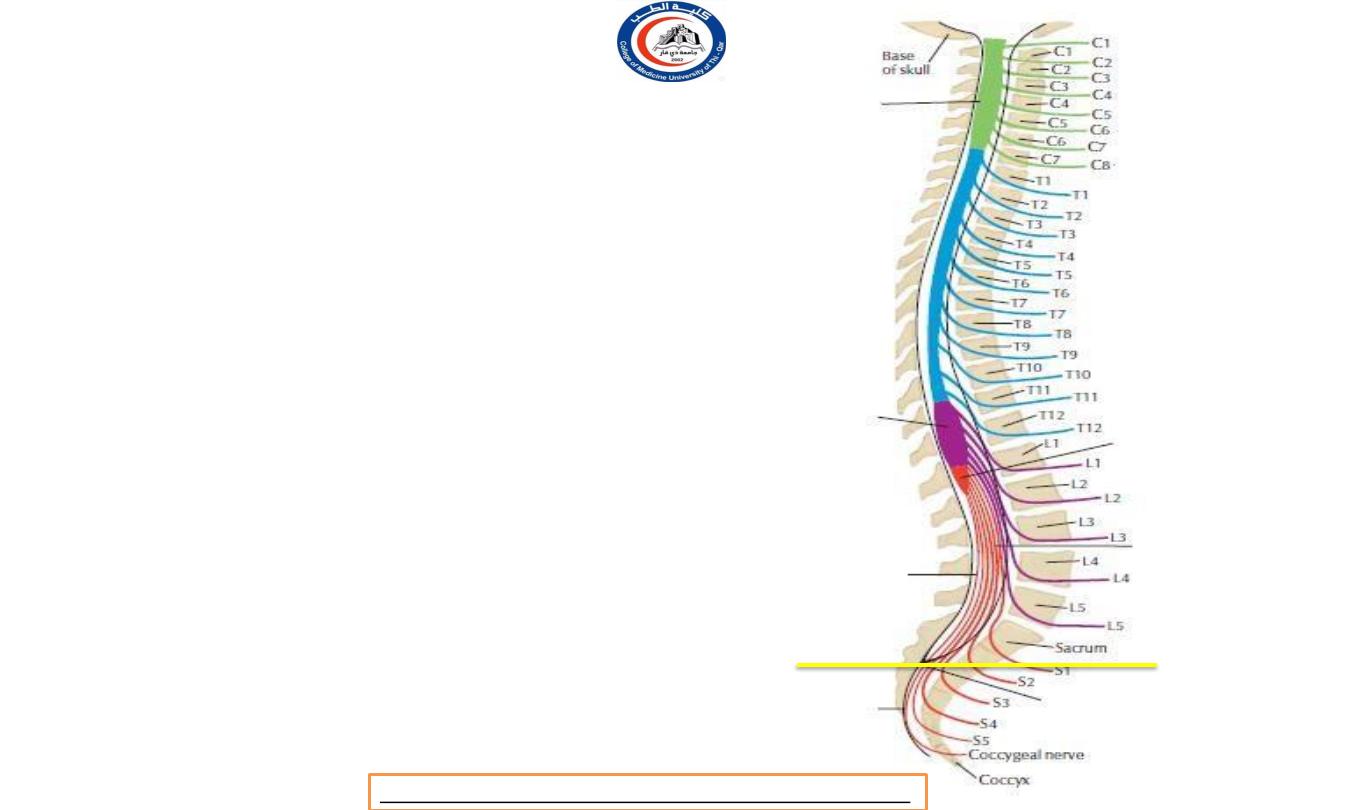
Quiz
• If there is herniation for
nucleus pulposus in the level
showed by the arrow , which
nerve root will be affected ?!
• Answer is
L3
Dr.Rafid Remthan AL-Temimi,Clinical Radiology,CAMB, 2020
University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi

University Of Thi-Qar
College Of medicine
Anatomy lecture . 2
nd
stage
Dr.Rafid Al-Temimi
Thank you
