Stage
th
4
Dr. Ali
Community
1
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Definition of COPD
. The
not fully reversible
a disease state characterized by airflow limitation that is
“
abnormal
and associated with an
progressive
airflow limitation is usually both
of the lungs to noxious particles or gases”.
inflammatory response
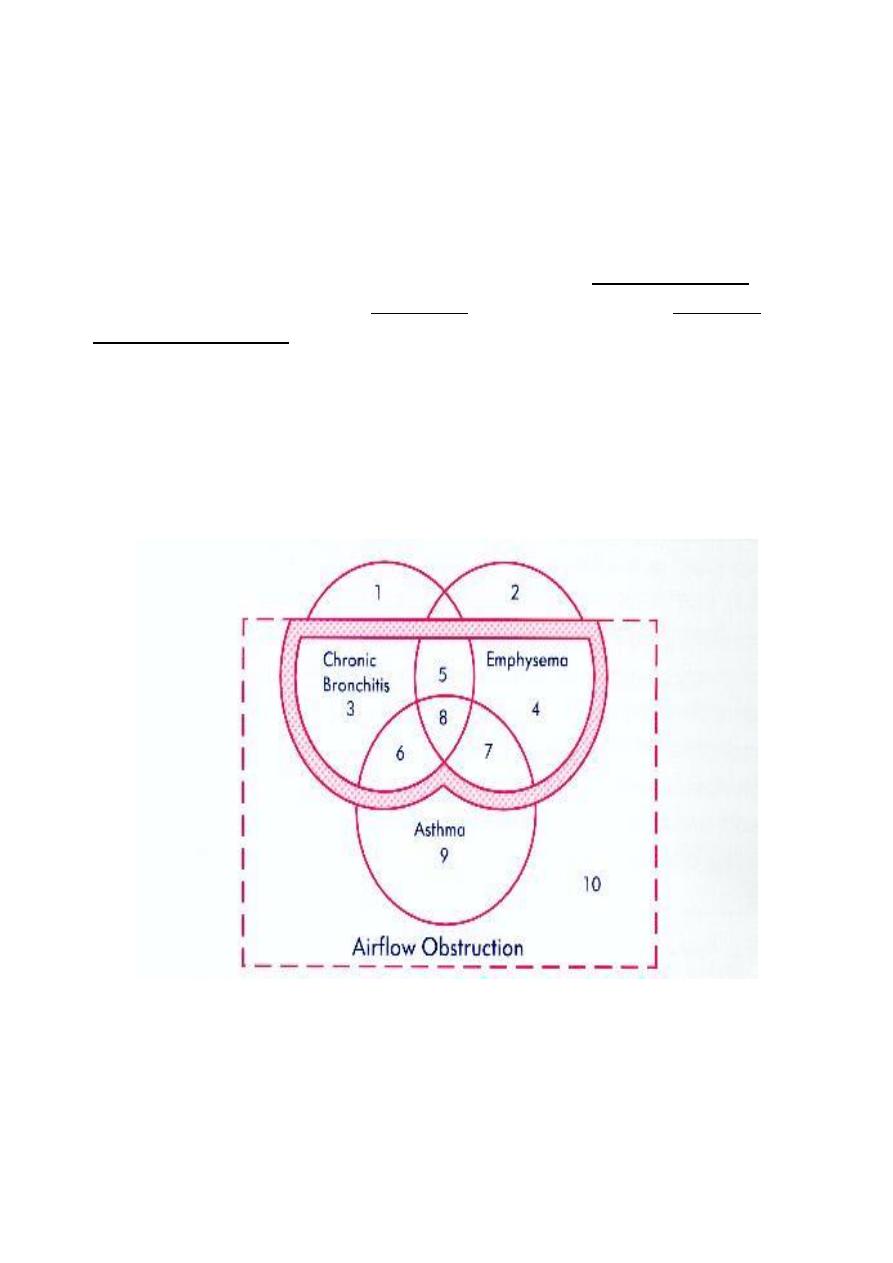
COPD is an umbrella term encompassing: ( Look: Venn diagram)
- Chronic bronchitis
- Emphysema
- Chronic severe asthma
Lecture [21]
Stage
th
4
Dr. Ali
Community
2
Global burden of COPD
COPD is one of the few major causes of death that increases in prevalence. It is
estimated that by 2020, COPD will be the fifth leading cause of death
internationally.
Further, epidemiological data show that COPD is rapidly increasing in prevalence
in women, and mortality data reflect this trend.
Stage
th
4
Dr. Ali
Community
3
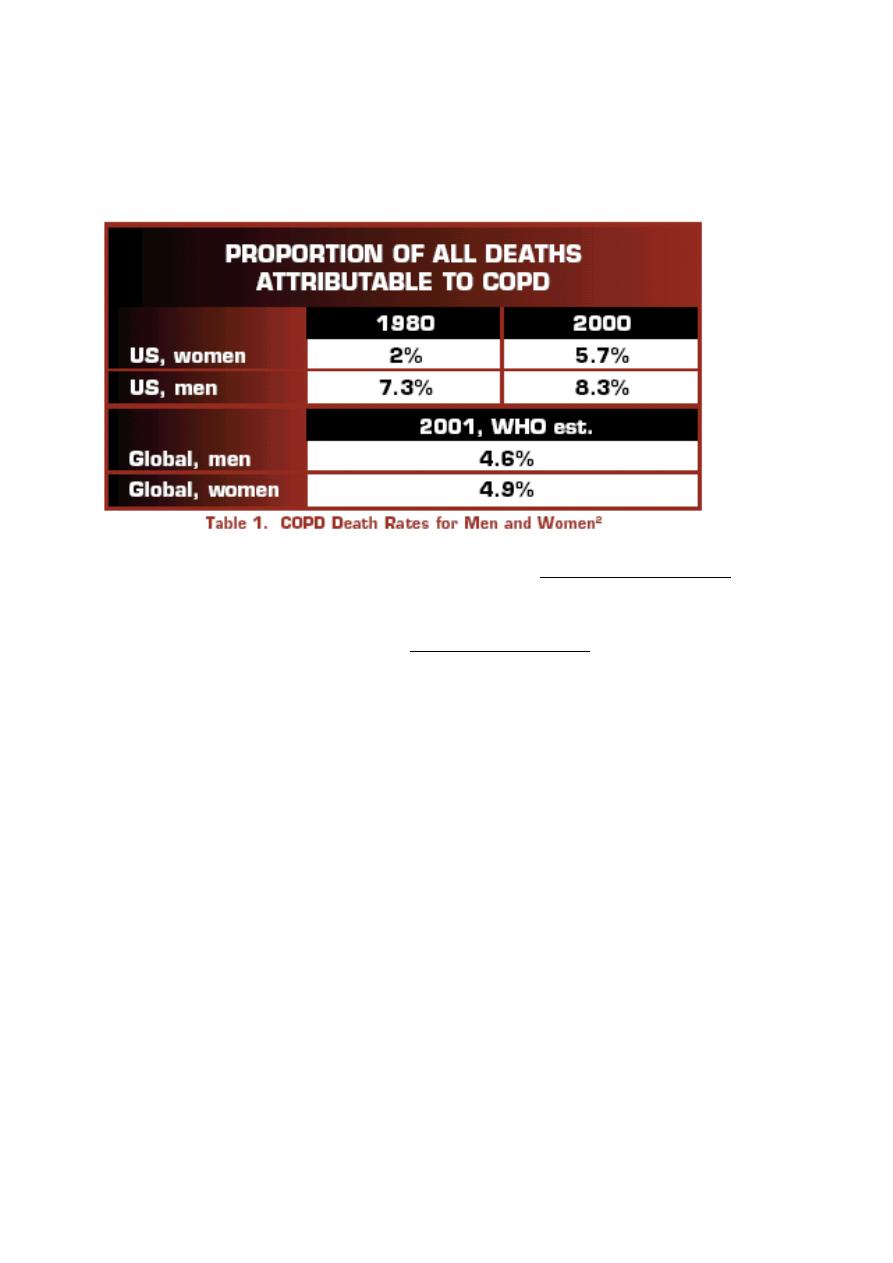
Internationally, the World Heath Organization (WHO) estimates that in 2001, 4.6%
of all deaths among men (1,355,000 total), and 4.9% of all deaths among women
(1,317,000 total) were directly attributable to COPD.
and
recognized
not usually
The burden of COPD is underestimated because it is
diagnosed until it is clinically apparent and moderately advanced.
but in all countries
vary across countries
Prevalence, morbidity, and mortality
where data are available, COPD is a significant health problem in both men and
women.
30% of smokers develop COPD
20% of adult males have COPD
15% of COPD patients are severely symptomatic
Mortality rate still rising
How common is COPD?
About 13.9% of the U.S. adult population (25+ years) have been diagnosed with
COPD*
An estimated 15-19% of COPD cases are work-related**

Stage
th
4
Dr. Ali
Community
4
24 million other adults have evidence of troubled breathing, indicating COPD is
under diagnosed by up to 60%***
Economic Impact of COPD
economic costs of COPD are significant because hospital admissions and
direct
The
economic costs of COPD are
indirect
expensive treatments are often needed. The
also significant and include lost years of life, disability, loss of working capacity,
and reduction in quality of life.
The economic costs of COPD are high and will continue to rise in direct relation to
the ever-aging population, the increasing prevalence of the disease, and the cost
of new and existing medical and public health interventions.

Stage
th
4
Dr. Ali
Community
5
Pathogenesis and Pathophysiology
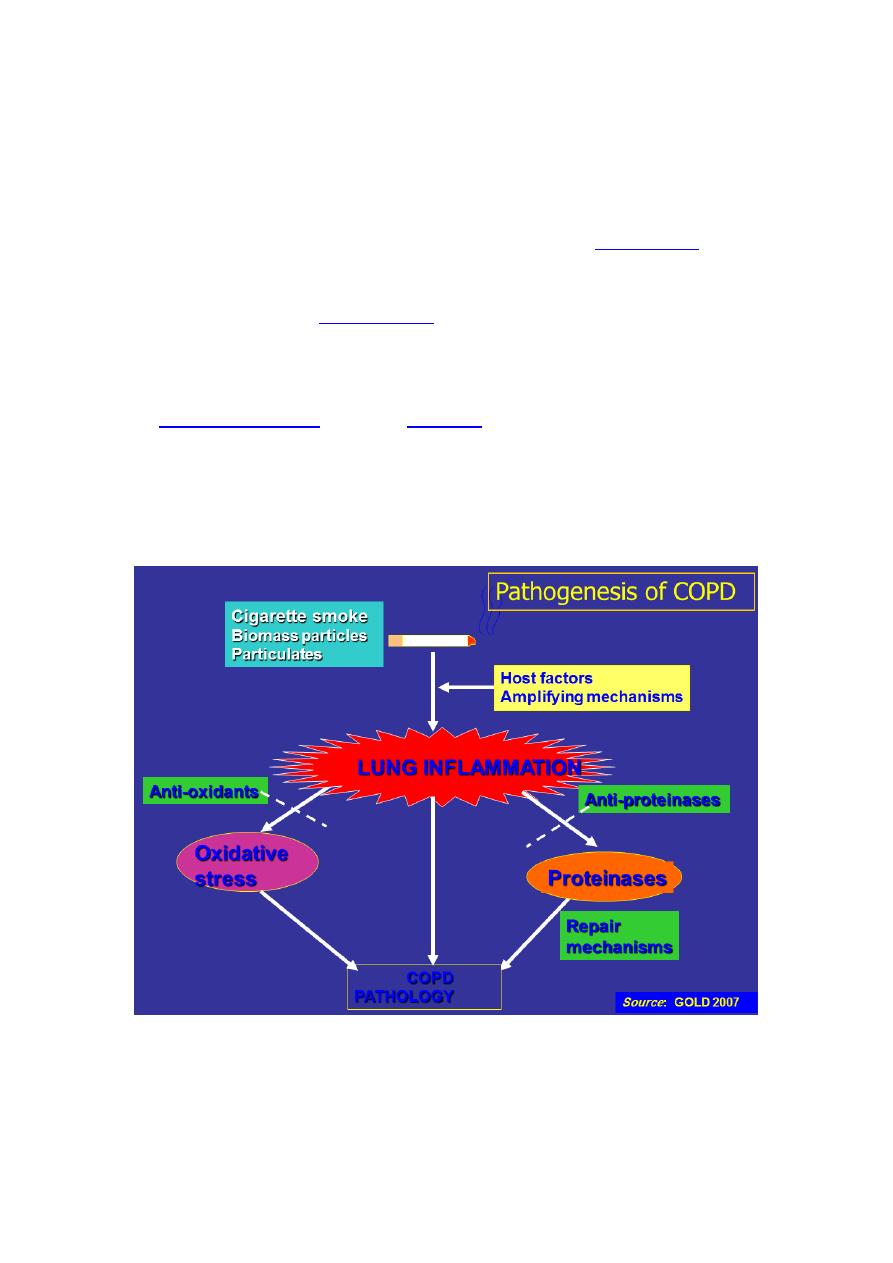
Pathogenesis
Tobacco smoking is the main risk factor for COPD, although other inhaled noxious
particles and gases may contribute.
In addition to inflammation, an imbalance of proteinases and antiproteinases in
the lungs, and oxidative stress are also important in the pathogenesis of COPD.
Pathophysiology
The different pathogenic mechanisms produce the pathological changes which, in
turn, give rise to the physiological abnormalities in COPD:
mucous hypersecretion and ciliary dysfunction,
airflow limitation and hyperinflation,
gas exchange abnormalities,
pulmonary hypertension,
systemic effects.
Stage
th
4
Dr. Ali
Community
6
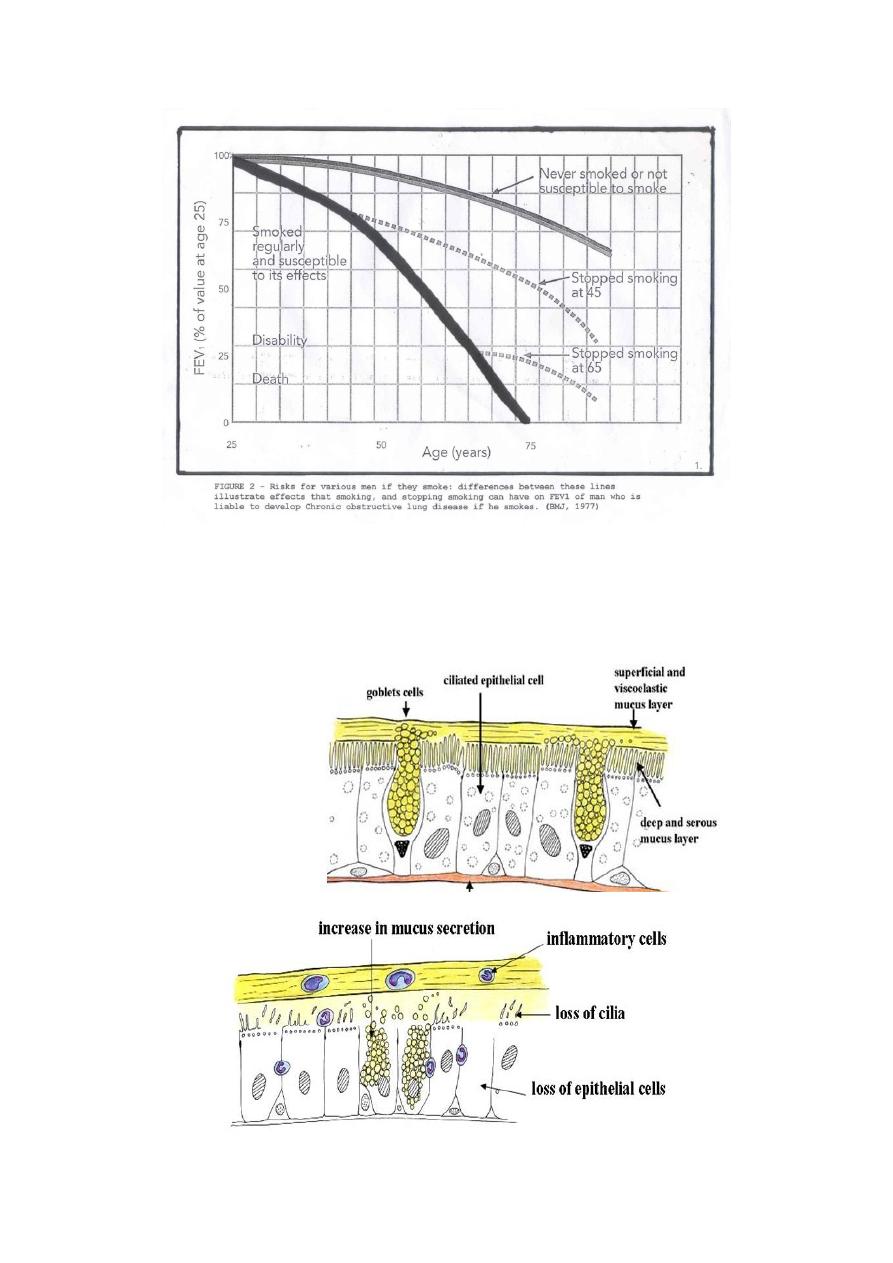
Smoking & COPD
It is not fully understood how tobacco smoke and other inhaled particles damage
the lungs to cause COPD. The most important processes causing lung damage are:
in tobacco
produced by the high concentrations of
1. Oxidative stress
smoke
as the body responds to irritant particles
release due to
2. Cytokine
such as tobacco smoke in the airway
3-Tobacco smoke and free radicals impair the activity of antiprotease enzymes
enzymes to damage the lung
, allowing
such as
4- levels of myeloperoxidase and eosinophilic cationic protein broncho-
constriction
Stage
th
4
Dr. Ali
Community
7
Schematic view of ciliotoxic damage and mucus hypersecretion in early-stage
COPD
Normal airway mucosa
Early COPD
Stage
th
4
Dr. Ali
Community
8
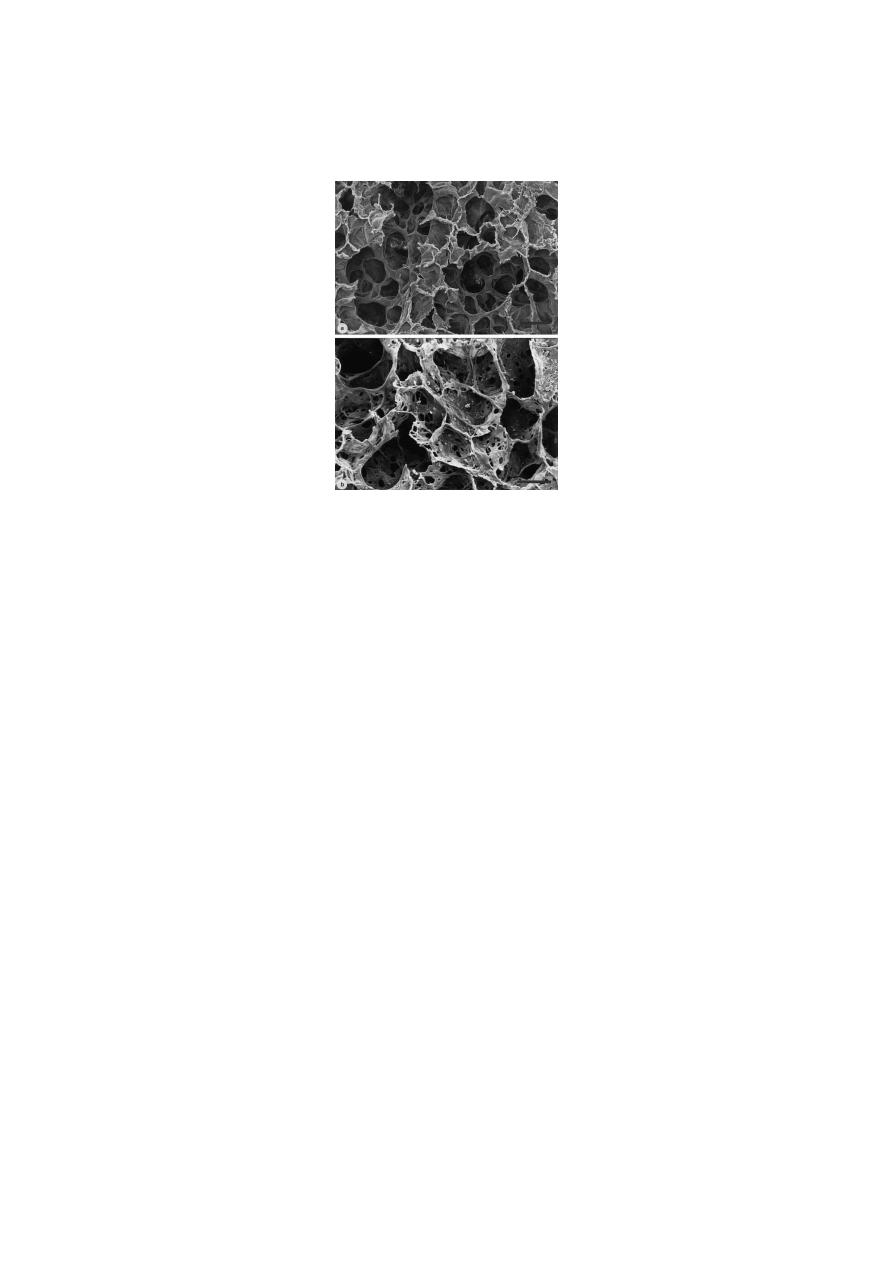
“Moth-eaten” appearance of autopsied lung from smoker with advanced COPD
emphysema
Risk Factors for COPD
Host factors:
- Genetic factors (e.g. alpha1-antitrypsin deficiency)
- Sex
- Airway hyperreactivity
- IgE and asthma
Exposures:
- Smoking: primary cause in 80-90% of cases
- Socioeconomic status
- Occupation
- Environmental pollution
- Perinatal events and childhood illness
- Recurrent bronchopulmonary infection
- Diet
Stage
th
4
Dr. Ali
Community
9
Diagnosis of COPD
Diagnosis of COPD should be considered in any patient who has the following:
symptoms of cough
sputum production
dyspnoea
history of exposure to risk factors for the disease
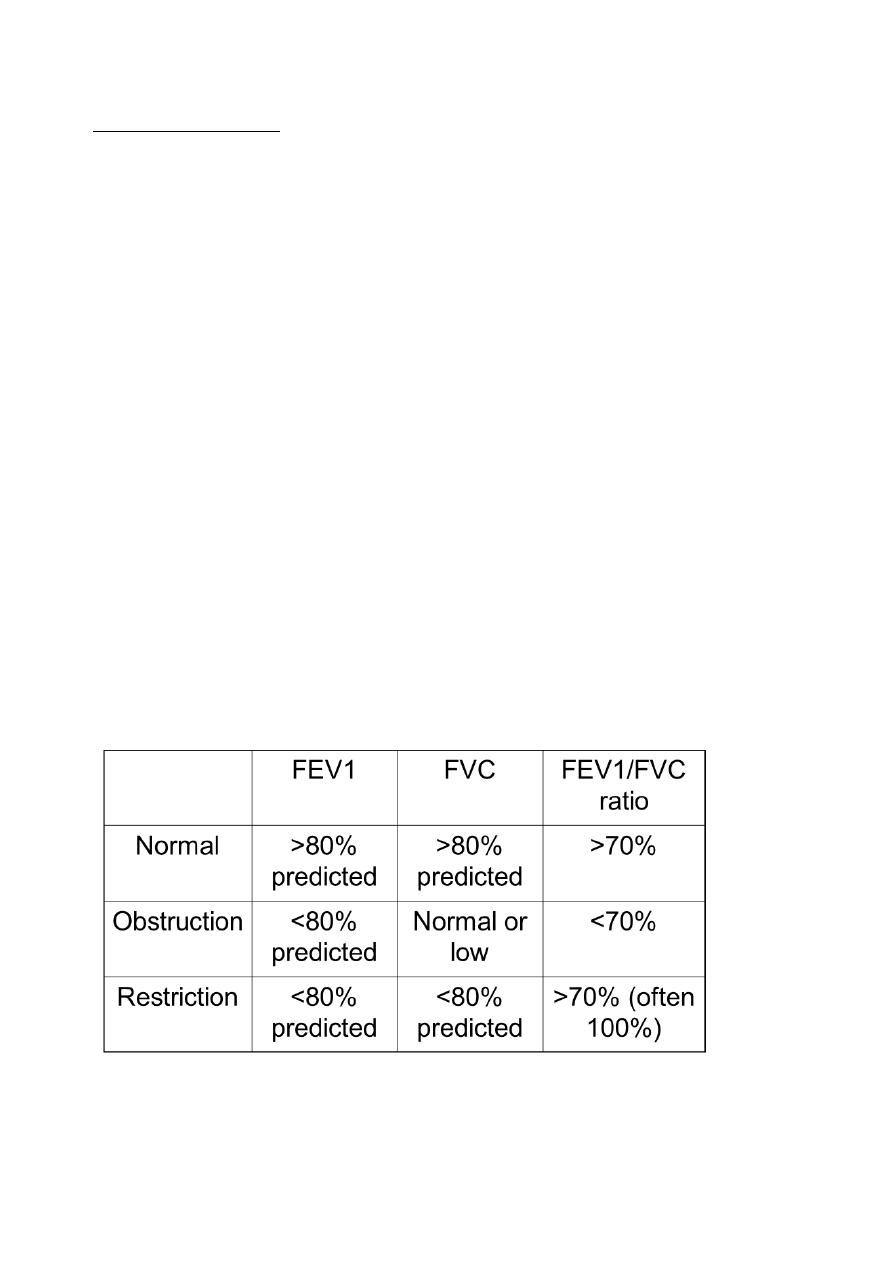
Spirometry : Decreased FEV1/FVC
Stage
th
4
Dr. Ali
Community
10
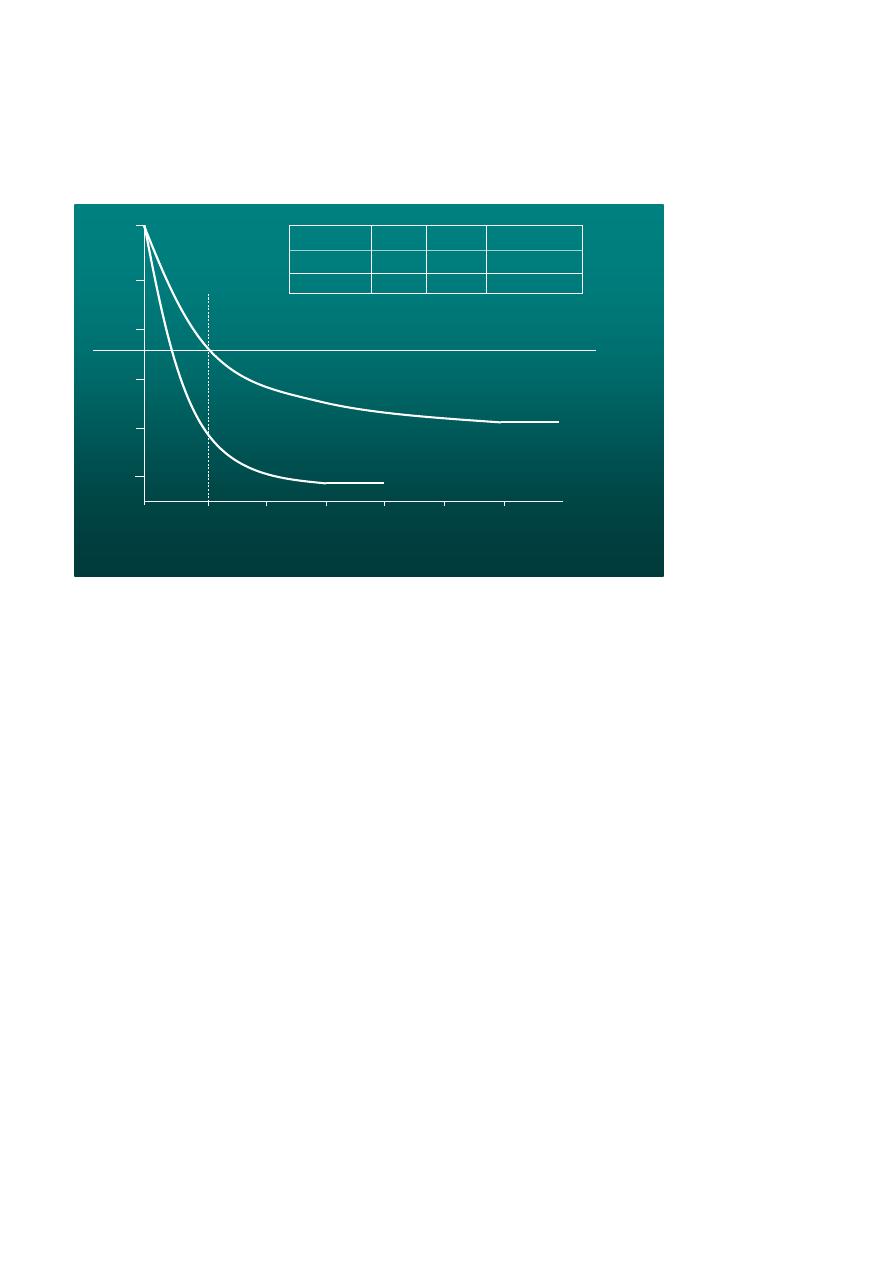
Spirometry: Normal and COPD
Radiology
Chest X-ray
Bullae, often bilateral upper lobes in smokers
Flat diaphragms (best seen on lateral) and retrosternal airspace can indicate air
trapping
High Resolution CT of Chest
Most sensitive to detect above changes
No role in routine care of COPD patients
Can be useful for giant bullous disease surgeries or lung volume reduction surgery
planning
0
5
1
4
2
3
L
it
e
r
1
6
5
4
3
2
FVC
FVC
FEV
1
FEV
1
Normal
COPD
3.900
5.200
2.350
4.150
80 %
60 %
Normal
COPD
FVC
FEV
1
FVC
FEV
1
/
Seconds
Stage
th
4
Dr. Ali
Community
11
GOLD Staging Criteria
Stage 0: Normal spirometry; chronic symptoms
Stage 1 (Mild):
FEV1/FVC < 70%; FEV1 > 80% predicted
Stage 2 (Moderate):
FEV1/FVC < 70%; FEV1 30-80% predicted
2A: FEV1 50-80% predicted
2B: FEV1 30-50% predicted
Stage 3 (severe):
FEV1/FVC < 70% AND:
FEV1 < 30% predicted OR:
FEV1 < 50% predicted and clinical evidence of Right heart failure
Patterns of spirometry

Stage
th
4
Dr. Ali
Community
12
Other Diagnostic tests
Full pulmonary function tests : Lung volumes: Increased TLC, RV, RV/TLC
Alpha-1 antitrypsin level & phenotype
Arterial blood gas (ABG): Measurement of arterial blood gas tension should be
< 40% predicted or clinical signs suggestive of
1
considered in all patients with FEV
respiratory failure or right heart failure.
Sputum gram stain/culture
Prevention & control
Avoidance of noxious agents
- Smoking cessation
- Reduction of indoor pollution
- Reduction of occupational exposure
Influenza vaccination
Management of COPD
Pharmacological therapy
Long-term oxygen therapy
Pulmonary rehabilitation
Nutrition: Nutritional therapy may only be effective if combined with exercise or
other anabolic stimuli. Weight loss and a depletion of fat-free mass (FFM) may be
observed in stable COPD patients.
Surgery in and for COPD: Bullectomy and lung volume reduction surgery &Lung
transplantation
Stage
th
4
Dr. Ali
Community
13
Exercise and Nutrition
COPD makes the lungs and heart work harder to carry oxygen to all parts of the
body. Because of this, weight control is a must to reduce heart and lung strain.
Special exercises to strengthen chest muscles can improve breathing
Eat several small meals
Avoid gas-producing foods, this can cause the stomach to swell and press against
the diaphragm.
Sleep: Management of sleep problems in COPD should particularly focus on
minimising sleep disturbance by measures to limit cough and dyspnoea, and
nocturnal oxygen therapy is rarely indicated for isolated nocturnal hypoxaemia.
Hypnotics should be avoided, if possible, in patients with severe COPD.
Air travel: Patients with COPD can exhibit falls in arterial O2 tension (Pa,O2).
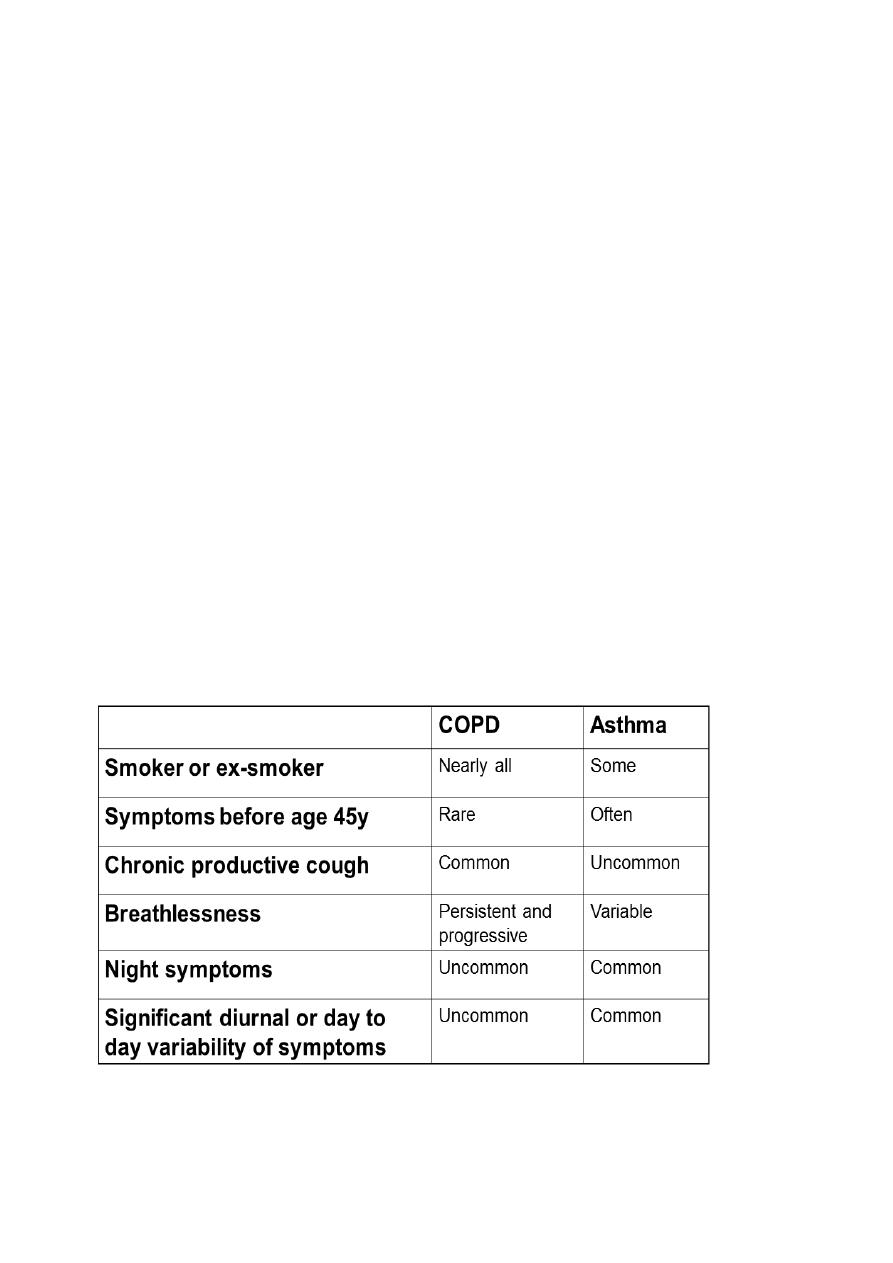
Distinguishing asthma and COPD clinically
Stage
th
4
Dr. Ali
Community
14
Distinguishing asthma and COPD
Spirometry needs to be interpreted in the light of clinical history
Spirometry in asthma may be normal
Spirometry in COPD is never normal
There is overlap – some patients have both
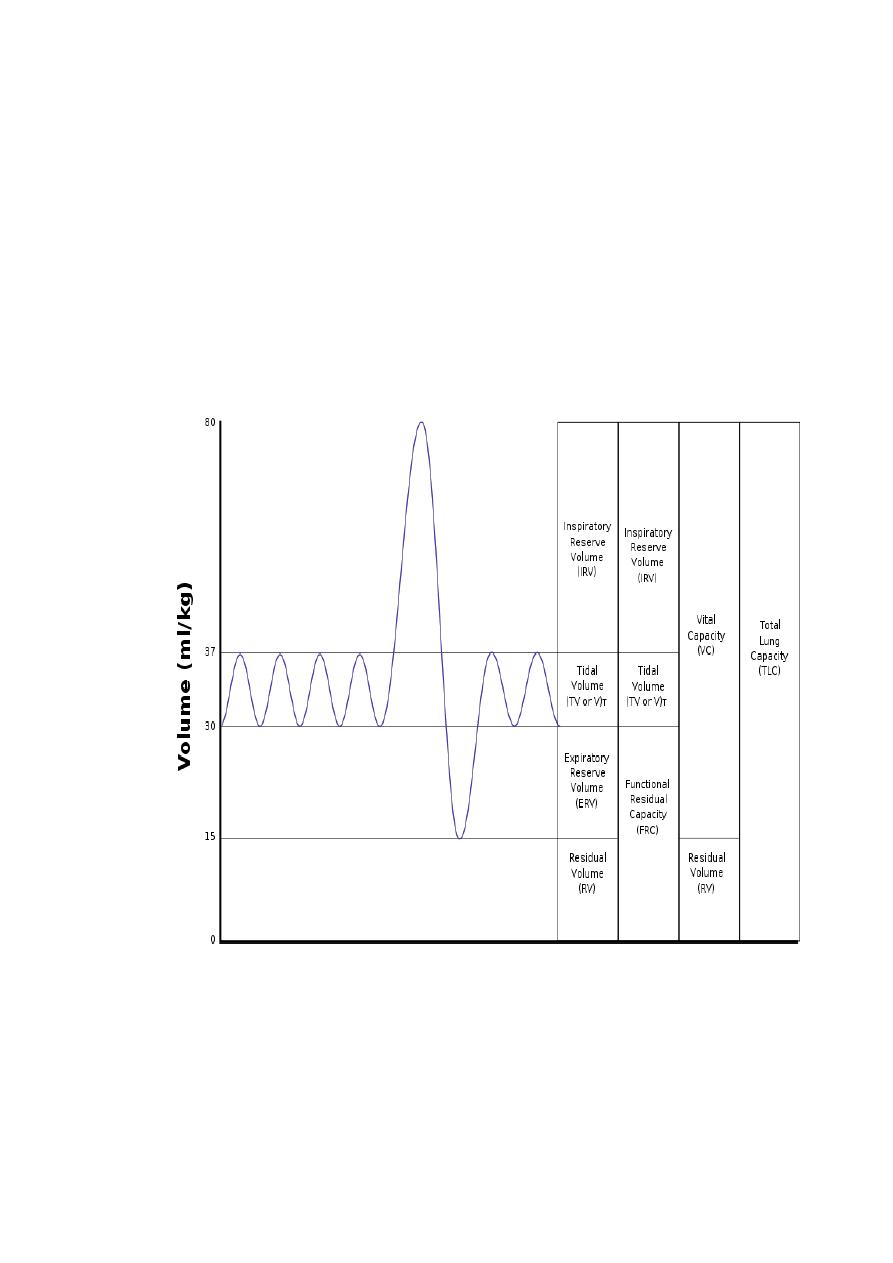
Lung volumes
