
Are attached to the latera
pelvic walls by the
suspensory ligament
containing the ovarian
vessels and to the cornua of
the uterus by a ligamentous
condensation of the broad
ligament.

•E ach ovary is (3x2x1 cm) in size
in the resting state, but will
increase in the resting state but
will increase in size during
physiological stimulus, they will
shrink after the m enopause,

•The surface is covered by a
flattened m ono-layer of
epithelial cell, and beneath
this are the ovarian follicles,
with oocyte, granulose layer
and surrounding theca,

•th en stroma m edulla and a
hilum where the vessels enter
through the mesovariuim the
size and position o f the ovaries
varies between puberty and
m enopause,

• Ovarian Enlargement:
Due to FSH and LH hormones.
Follicular luteal cysts can occur
and theca -lutein cyst up to(15
cm) in size in response to very
high level of chorionic
gonadotrophin as with
trophoblastic disease.

•H yper stim ulation syndrome
can occur with massive
enlargement o f ovaries and
development o f ascites in
response to doses o f
gonadotropins injection during
fertility treatment.

•Polycystic disease.
•Ovarian pregnancy^
uncom m on
associated with IUCD use or tubal
pathology and infertility, patients
usually present with feature of extra
uterine pregnancy or bleeding from
corpus luteum.

1. The tube including the fimbria is
intact and separate from the ovary
2. Gestational sac occupies the
normal position of the ovary.

3. The sac be connected with the
uterus by the ovarian ligament.
4. Ovarian tissue dem onstrated
in the wall o f the sac.

•Ovarian Endometriosis:
•Associated with endometriosis,
if endometriosis more than
10cm may need lapratomy with
possibility of oophorectomy or
laparoscopic cyst aspiration ,

•FJ by LHIP.H analogue, the
laparoscopic dissection of the
cyst lining or destruction with
KTP (potassium -titan YL
phosphate laser).

•Functional cysts:
Rarely exceed s diameter of 5cm, if
its occur in follicular phase when
the Graafian follicle fail to rupture
at the expected time. Follicular
cysts may arise as

a consequence o f excessive
ovarian stim ulation with drug
like clomiphene or H C G and
less in women on CCP,

• if its occur in early normal
- pregnancy they will usually
disappear in the second or third
month of the pregnancy
•Ovarian Tumours:
•50% are benign epithelial tumors
O f malignant tumors,

• 90% are epithelial in origin, 10% of
sex cord or germ cell origin or
metastases from primary tumors
elsewhere in the body.
•Tumours of Border Line Malignancy
Group of tumours which are
intermediate in both behavior and
histological features between benign
and
♦
#

•those obviously malignant
about 10%, clearly defined
histopathological group of
serous and mucinous
tum ors. Show all feature of
malignancy but no stroma
invasion.

•Prognosis depend on tumour type
and extent of spread if occur in
young ovarian cystectomy or
unilateral oophorectomy if > 40
years or complete her family do
TAH+ Bilat salpingo
oophorectomy.

•Malignant Disease of the Ovary
•Risk factors:
1 Reduced family size.
2 Late age at first conception.
3 Null parity
4 Early menarche.

5. Late menopause,
e Family HX.
7. Fertility drugs.
8. Irradiation to ovaries.
9. White patient.
10. High socio economic state.
11. Blood group A.

•Reduced Risk:
.Multi porous patients.
2. Breast feeding,
3. Low social class,
4. Japans, Chins and black
women,
5. Blood group O.
'/Peak age 55-6o yr.

Etiology:
l.Fertility drugs.
2 Null parity
3 Relation with endometriosis, viral
infection like mump and ovarian
ca unclear.
4 High animal fat intake in western.

5. Strong genetic
predisposition, breast-
ovarian, colon-ovarian ca
and incessant ovulation
theory.
Classification:
Benign Ovarian Diseases:
• Benign Ovarian Diseases: Its
4th common cause of
admission to

gynecological parts it's about
(90% ) of all ovarian tumors.
Physiological Cyst:
1. Follicular cyst.
2. Luteal cyst: less common
then follicular cyst usually in
right ovary. Its size ffro m
day (20-26) of menstrual
cycle,

its diameter usually< 3cm but
maybe £ 3cm.
Indication of Surgical Intervention
if:
1 .Complicated cyst (like rupture
or torsion cyst).
2.Large cyst more than 10cm.
3.If cause pressure symptoms.
4.If U/S revealed malignant
changes.

Pathological Cysts:
flQerm Cell Tumour:
it’s the
commonest pathological tumour,
Usually in patients<30 years of
age,
the overall germ cell
tumours can change to
malignancy 2-3% and once they
present 20 years about 1/3 Will

1. Dermoid cyst: commonest
germ cell tumour if ? <30
years. It occurs bilateral in
11%, Its unilocular< 15cm has
smooth surface with
greenish-yellowish color and
doughy in consistency;
contain 3germ cell layer
endoderm, mesoderm and
ectoderm which is the
predominant layer,

so it’s often lined with epithelial like
epidermis and contain skin
appendage, teeth; sebaceous
material; hair and nervous tissue,
endo dermal derivatives include
thyroid; bronchus; intestine and
mesoderm include bone,
•cartilage and smooth muscle
Monodrarna Teratoma, the
classical example is Struma
ovary which contain hormonally
active thyroid tissue the 60% of
cases are asymptomatic 1-4%
may rupture 3.5-10% may
undergo torsion, and 2%
contain malignant component.

2. Mature Solid Teratoma: Rare
tumour contains mature
tissues and wide variety of
tissue from (2-3) germ layers.
Metastases usually to brain or
lung grading of tumour
according to amount of
immature neural tissue

3. Dysgerminomas: In second
and third decades of life,
bilateral in (10-20%) of cases
Presentation:
■abdominal swelling.
■abdominal pain.
■Acute abdomen due to
accident to tumour like torsion.

• Secret AFP and BHCG, good
prognosis
•Endoderm Sinus Tumours (Yolk
Sac Tumours).
• Embryonal CA.

B. Epithelial Tumour: common in
old age.
. Serous Cyst adenoma: 50%
bilateral, unilocular, smooth outer
surface, lining contain
papilliferous processes, thin
serous fluid, lining resembling
tubal epithet. Psommoma Bodies
(concentric calcified bodies in the
cells).

Mucinous TM : Called endo
cervical tumor (15-25%)
unilateral large reach 91kg, multi
locular, smooth surface, lined by
columnar mucus secreting cells,
thick glutinous fluid, 5-10%
change to malignancy,

•Pseudomyxoma Peritonea: Is a
rare complication ,of border
line tumour .occur if
spontaneous perforation of
cyst lead to implantation of
cells on the peritoneum and
continue to secret mucin
causing matting and
obstruction of bowel loops.
3* Endometrioid TM : less common,
contain tubular glands like
proliferative endometrium
4. Brenner T M 1-2% ; 10-15%
bilateral, lined transitional
epithet. Resembling urinary
bladder

5.Clear Cell TM : associated with
pelvic and ovarian endometriosis
histological cells of hobnail cells
arranged in mixed patterns like cells
in cervix, vagina and broad
ligament.

C. Sex Cord Struma Tumours:
4% OF benign T.M. , produce
hormones:
Granulose Cell T.M: occur at
any age, secret estrogen in
prepubertal age produce
precocious puberty,
abnormal uterine bleeding in
reproductive age,

and post menopausal bleeding in
—m-en-opause. CalbExner Bodies—
granulose cells taken micro
follicular pattern.
2Theca Cell XM : Usually benign
solid unilateral and 10% bilateral.
Hard, mobile,

often with as cites and
hydrothorax in F T side like
in fibroma, Meigs Syndrome:
ascites and pleural effusion
in 1%. Theca cells contain
lipid rich contents.

3. Sertoli -Ledig T.M (And
roblastoma): Low grade
malignancy, unilateral, may
produce androgen lead to
sign of virilazation, 1-3%
bilateral.
9
Ovarian Metastases: 8-10%
presented with adenxal mass,

is metastatic from primary site in
GIT or breast, tubes, vulva, vagina,
and cervix.
Kruken berg TM : metastatic tumors
from primary site in stomach,
colon or breast, contain signet-ring
cells with
peripheral nucleus and mucous
spongy or vacuolated cytoplasm
which stain for mucin.
Spread:
1 .Direct: peritoneal fluid flowing to
the lymphatic channel on the
under surface of diaphragm carries
malignant cells to omentum,

peritoneal surface of smalal and
large bowel, liver, parietal
peritoneum and surface of
diaphragm,
2
Lymphatic: pelvic and par aortic
lymph node and to nodes in neck
or inguinal region.

3. Haematogenous spread:
occur late
main area involve are liver, lung,
bone and brain.
Presentation:
• Asymptomatic
• Pain due to:
I. Torsion.
II.
Rupture.
IILlnfection.

•Abdominal swelling.
•Pressure effects.
•Hormonal effects: Estrogen.
) Androgen__ hirustism, acne,
virilism with deepening of voice.
) Thyroid hormone —thyrotoxicosis

D.DX: According to pain
1 Ectopic pregnancy.
2.Spontaneous abortion.
3
PID .
4 Meckles diverticulum.
5. Diverticulitis.
6 Appendicitis.

Abdominal swelling
Pregnant uterus.
2) Fibroid uterus,
3) Full bladder,
4) Distended bowel,
5) Colo'rectal ca .

Pressure Effects*
A-UTI.
B.Constipation.
Hormonal Effects: from all causes of
irregular bleeding.
Genetic Predisposing: BRCA1 GENE
on
chromosome
17. BRCA2
on
chromosome
13 Q;
associated with
breast/ ovarian syndrome.

Women with family HX of ovarian
ca:
1 Annular ovarian U /S+ color flow
Doppler.
2. CA 125 every 6-12 moths.
3. Prophylactic oophorectomy +TAH
for high risk group at
45 yn +
complete her family.

Staging of SPumours: ( FIGO Stage)
L Growth limited to ovaries*
a. Tumor in ovary no ascites, capsule
intact; no tumour on surface.
b. As in a but tumour on both ovaries
c.
Either la or lb, but as cites with
cancer cells or capsule rupture or
tumour on surface or positive
peritoneal washing.
ll. Growth on one or both ovaries with
peritoneal implants within pelvis:
a.
Extension to uterus or fallopian
tubes,
b. Extension to other pelvic organs,
c.
As in II a or II b but with findings in
Ic,
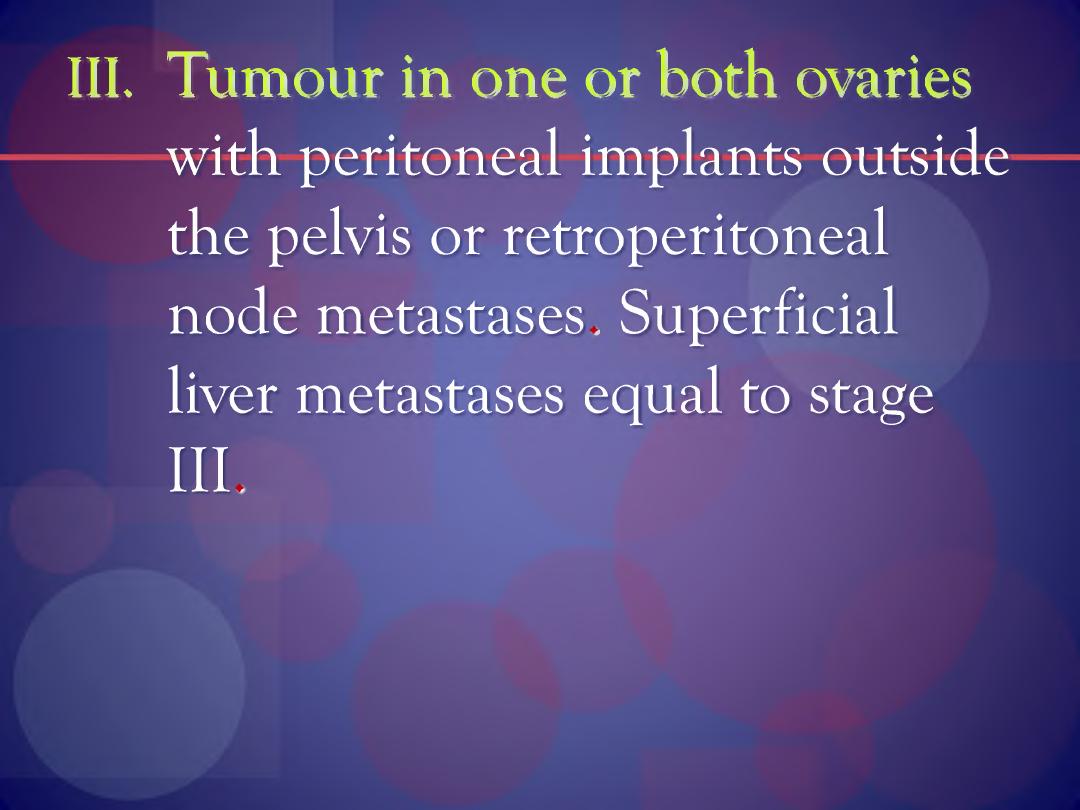
III. Tumour in one or both ovaries
with peritoneal implants outside
the pelvis or retroperitoneal
node metastases. Superficial
liver metastases equal to stage
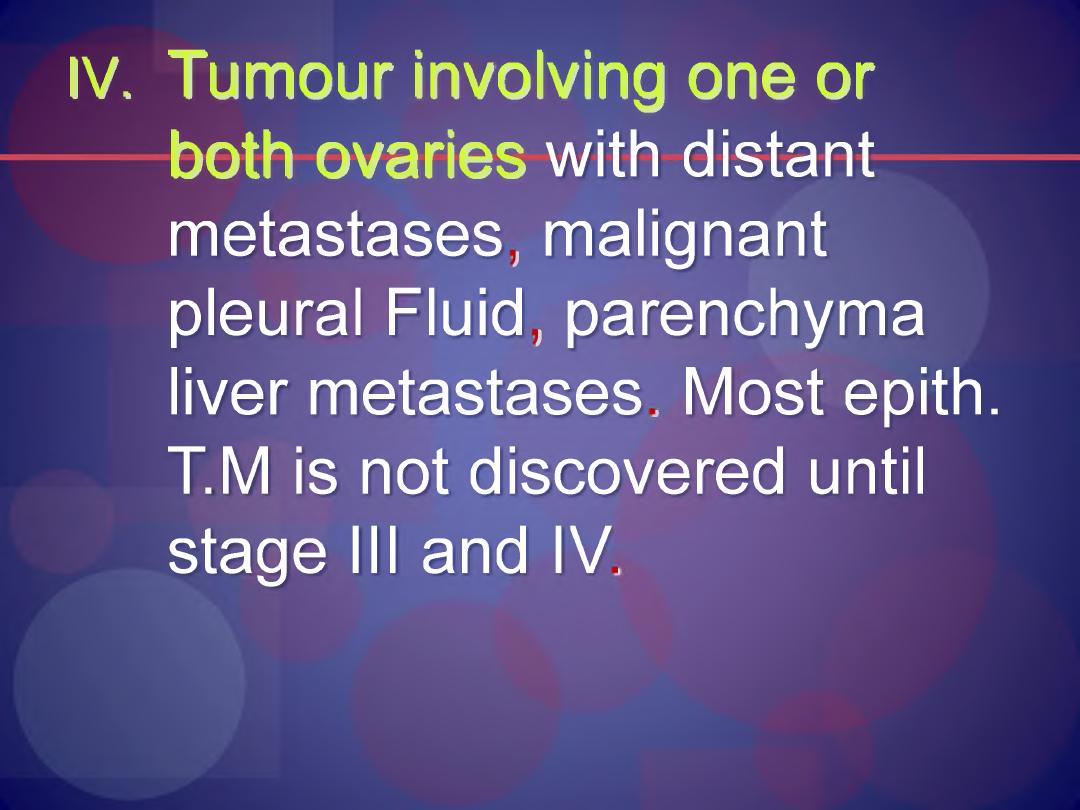
IV. Tumour involving one or
both ovaries with distant
metastases, malignant
pleural Fluid, parenchyma
liver metastases. Most epith.
T.M is not discovered until
stage III and IV

MX:
History gynecological HX, family
HX and general HX.
2.Examination general and specific.
Investigations:
■ Trans vaginal and Tran’s abdominal
U /S,
■ Color flow Doppler U /S.
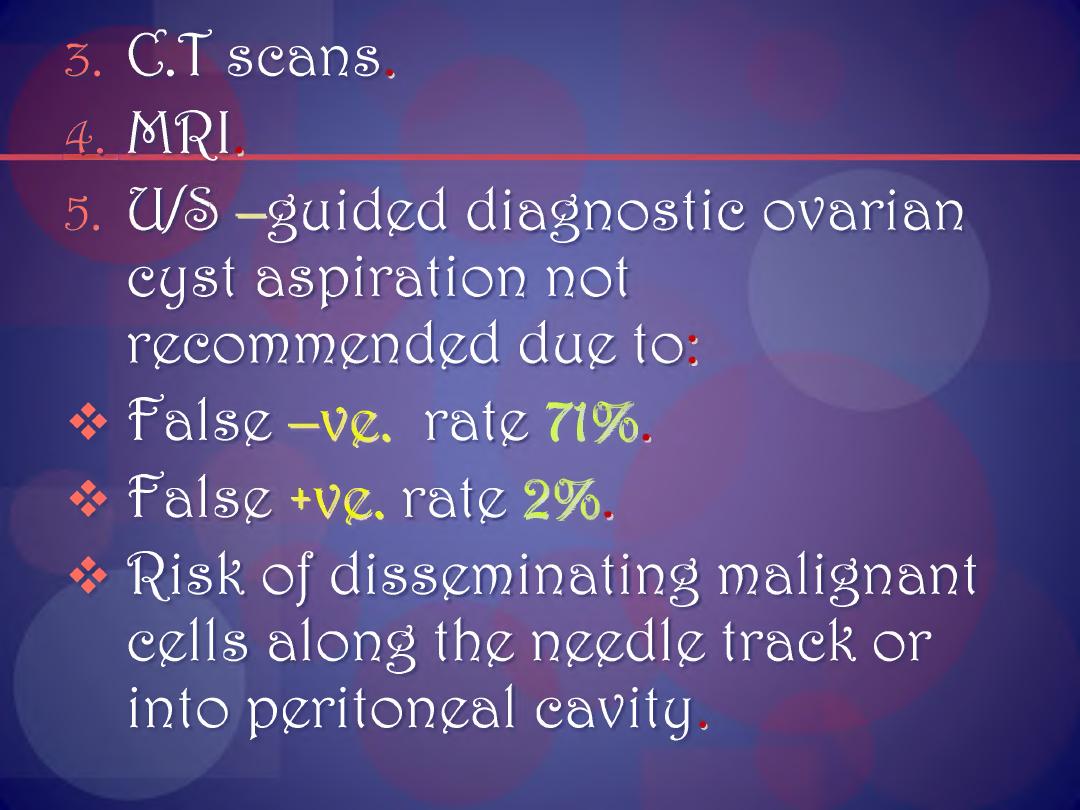
3
.
C.T scans.
fL.MRI.
5. U/e> -guided diagnostic ovarian
cyst aspiration not
recommended due to:
❖ false -V£. rate 71%.
❖ false +ve. rate 2%.
❖ "Risk of disseminating malignant
cells along the needle track or
into peritoneal cavity.

Radiological lx:
1.Chest X-ray pCaral effusion.
2Abdominal X^ray calcification.
3. LV.U,
4. Barium enema if Bowel symptoms.
5. C.T scan.

Blood Tests:
>Hb=anemia.
> W BC=|=Infection,
> Platelet count, clotting screen.
> Renal function test.
> Liver function test.

Serum Markers:
a. CA 125,
b. BHCG.
Oestradiol Level | in:
1.Physiological follicular cyst.
2.Sex cord stroma tumours.
• Androgen f in Sertoli -ledge T.M
• Alpha -feto protein -4- in yolk sac

*R. ©gpgnd on:
l.§everity of the symptoms,
llflge of patient,
III. 'Risk of malignancy.
IV. fler desire for further children.

•R-of asymptomatic patients
Conservative Treatment:
1 .If unilateral T.M,
2. Unilocular cyst without solid
elements.
3. Premenopausal women size of
tumors no more than 10cm.

4. Post menopause women: 2-6cm,
5. Normal CA 125,
6. No free fluid or masses
suggesting omental lack or
matted bowel loops . In all may
be need follow up by monthly
U /S +CA125 for at least 6
months.
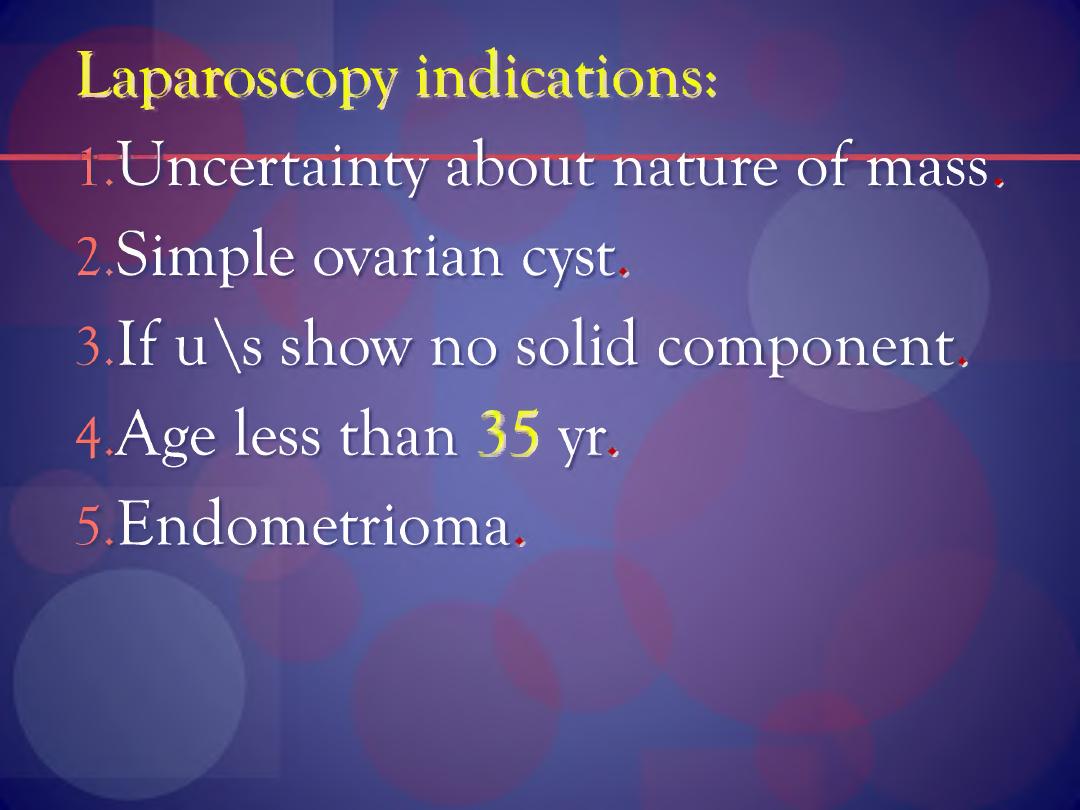
Laparoscopy indications:
l.Uncertainty about nature of mass.
2.Simple ovarian cyst.
3.If u \s show no solid component.
4 Age less than 35 yr.
5 Endometrioma.

•Thgrapgutie U/l> guided cyst
aspiration: it can perform in
young women with unilateral,
unilocular, thin wall cyst, if
surgery is contraindicated, if
co-existing medical problems or
dens pelvic adhesions envelop
the ovaries.

Advantage:
1 Avoidance of surgery.
2. Reduction in cyst accidents.
3. Cytological assessment of aspirated
fluid is performed.

Advantage of laparoscopy:
l.Less post operative pain.
2.Shorter hospital stay.
3. Quicker return to normal
activities.
4. Less adhesion formation.

Disadvantage of laparoscopy:
1 .Spillage of cyst contents,
2.Incomplete excision of the cyst
wall.
3.Unexpected histological DX of
malignancy.

Treatment:
l
Primary Surgery.
a.Total abdominal hysterectomy,
trila te ra l sapling- oophorectomy,
e.Injracolic omentectomy,
d. Appendectomy,
e.
Pelvie +Para-aortie lymph
adenectomy,
f.
Bowel surgery when indicated.

II. f onser/ative primary surgery:
a.
Young nulliparous women
with stage la.
b. No evidence of synchronous
endometrial cancer.
c.
Unilateral sapling -
oophorectomy.

III. Inter al debunking surgery:
a) Women with bulky disease
after primary surgery.
b) Must responds after 2-4
courses of chemotherapy.

Chemotherapy resumed after
surgery.
Second —lock surgery: at the end
of chemotherapy, now not used.
Principle of ovarian surgery:
ajAll visible cancer should be
removed,

b) The primary routes of spread
should be assessed.
c) Staging of cancer should be
performed accurately.
d) Bowel and other organ
resection should be
performed to achieve the
removal of all visible cancer.

If border line tumours, ovarian
cystectomy or oophorectomy
adequate in young women.
Hysterectomy +bilateral sapling -
oophorectomy in old women.
Chemotherapy it’s given to:
l.Prolong clinical remission and
survival.

2. Palliation in advanced and
recurrent disease (stage Ic, II-
IV)
A. isplatin -^very toxic:
1. Nausea and vomiting.
2. Permanent renal damage can
be prevented with adequate
hydration and IV. Fluids.

3. Nausea and vomiting,
4 Electrolyte disturbance like
hypo Mg,
B. Carboplatin: effective less
S/E rare toxicity.
j.Taxol Pa I its el):
Standard
treatment Cause sensory
neuropathy and neutropenia
are common with higher
doses.
