
THE MENOPAUSE
AND HRT

Learning Objectives
• Physiology of the Menopause and Climacteric
• Role of Hormones in the Menstrual Cycle
• Symptoms of the Climacteric
• Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT)
• Alternatives to HRT

Definition of the Menopause
The menopause is the last menstrual
period (LMP).
The
perimenopause or climacteric
is the
phase encompassing the menopause.
The
climacteric
lasts for about two years, but
may last for 10 years or longer.
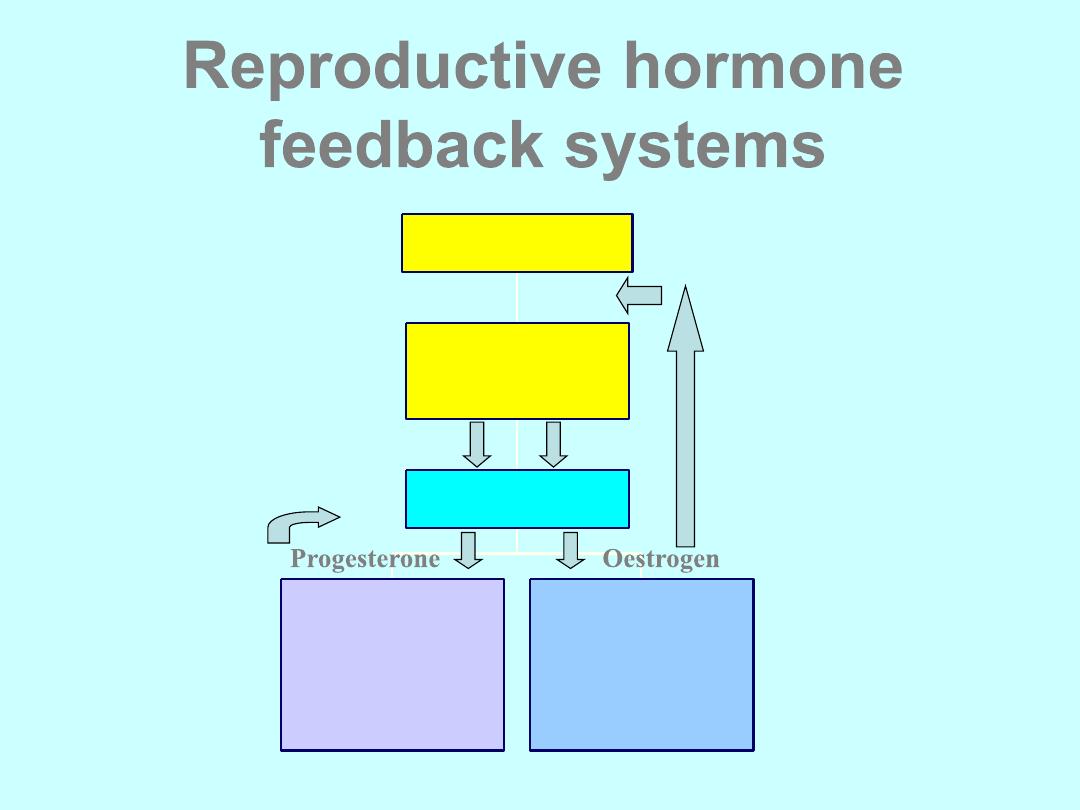
Reproductive hormone
feedback systems
Endometrium
Vagina,uterus
Lipoproteins
Breasts
Osteoblasts
Ovaries
Anterior
pituitary
Hypothalamus
GnRH
LH FSH
Progesterone Oestrogen

The Role of Hormones in
The Menstrual Cycle
Gonadotrophin hormones stimulate the ovaries:
follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
luteinising hormone (LH)
At the menopause ovaries run out of oocytes and they
become resistant to the gonadotrophin hormones
Levels of FSH and LH increase throughout the latter
stages of the Climacteric and reach a peak 2 to 3
years after the menopause
A level of FSH of more than 30IU/L on 2 separate
occasions indicates Ovarian Failure

The Role of Hormones in The
Menstrual Cycle
There are 3 important oestrogens in
women:
oestradiol,oestriol & oestrone
Oestradiol is predominant in
premenopausal women:
produced by
the ovaries.
Oestrone is predominant in
postmenopausal women :
produced by
peripheral conversion of androgens in
the adipose tissue.
E1 is less biologically active than E2.

• The menopause may be
– Natural or induced
• Natural menopause is the permanent
cessation of the menstrual cycle due to
loss of ovarian follicular activity
• Only known retrospectively one year after
the last period
• Average is 51 years

Induced menopause
• Specific treatment e.g. chemotherapy or
radiotherapy
• Oophorectomy
• Treatment with gonadotrophin-releasing
hormone (GnRH) analogues

Investigations
• FSH is only used if diagnosis is in doubt
• FSH >30 iu/L
• Don’t do LH, oestradiol and progesterone
as not helpful
• TFTs if confusion about symptoms
• BMD if significant risk of osteoporosis

The Menopause - Acute Symptoms
• Hot flushes
• Night sweats
• Headaches
• Panic attacks
• Mood swings
• Indecisiveness
• Insomnia leading
to:
• irritability
• poor short term
memory
• difficulty with
concentration

MEDIUM TERM SYMPTOMS
• Vaginal dryness
• Dyspareunia
• Reduced libido
• Thinning skin/ hair
• Skin formication
• Urethral syndrome (frequency,
nocturia and urge incontinence)

LONG TERM SYMPTOMS
• CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE
• OSTEOPOROSIS
• CEREBROVASCULAR DISEASE
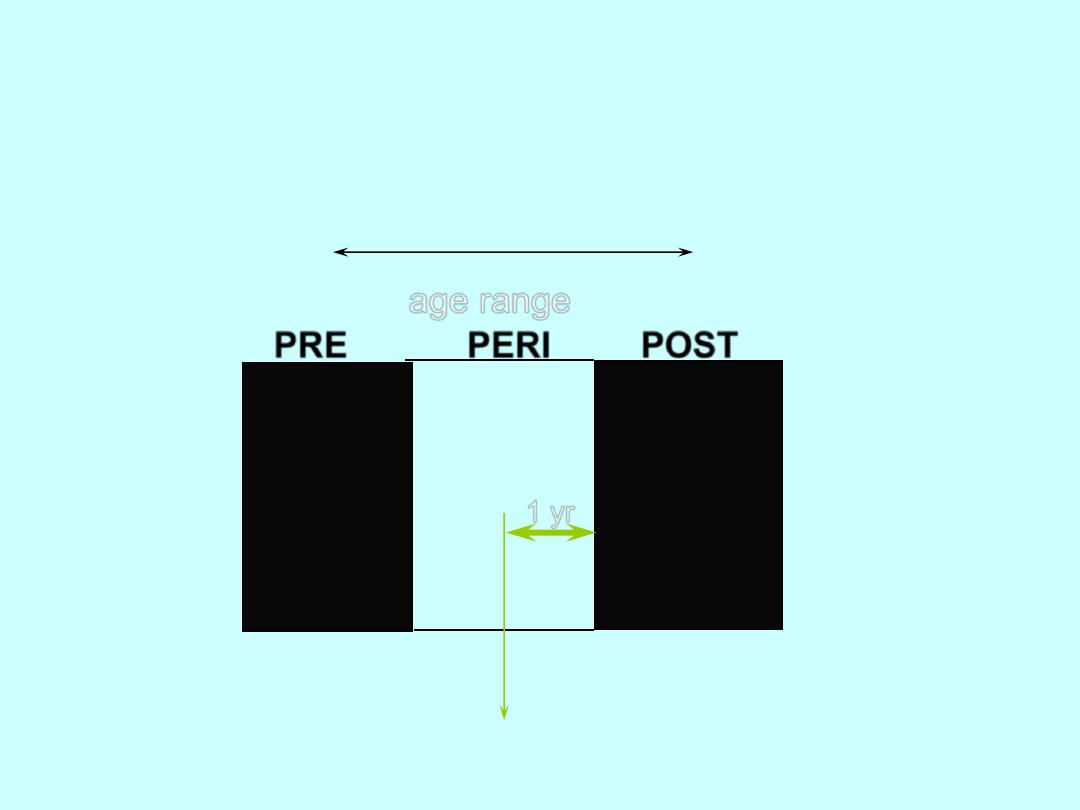
Symptoms of the Climacteric
age range
PRE PERI POST
35-45 46-55 56-65
Last menstrual
period
1 yr

Symptoms of the Menopause
At least 60% of
women have hot
flushes and
night sweats as
their main
symptom

Hormone Replacement
Therapy (HRT)

OESTROGENS
• oestradiol
• oestradiol valerate
• conjugated equine oestrogens
• oestriol
These should not be confused with the oestrogens used in the
COC. They are used at a dose which is effectively 1/6
th
of the
dose used in the COC.

PROGESTOGENS
19 NORTESTOSTERONE
DERIVATIVES
• norethisterone
• levonorgestrel
• norgestrel
17 HYDROXY-PROGESTERONE
DERIVATIVES
• dydrogesterone
• medroxy progesterone
acetate
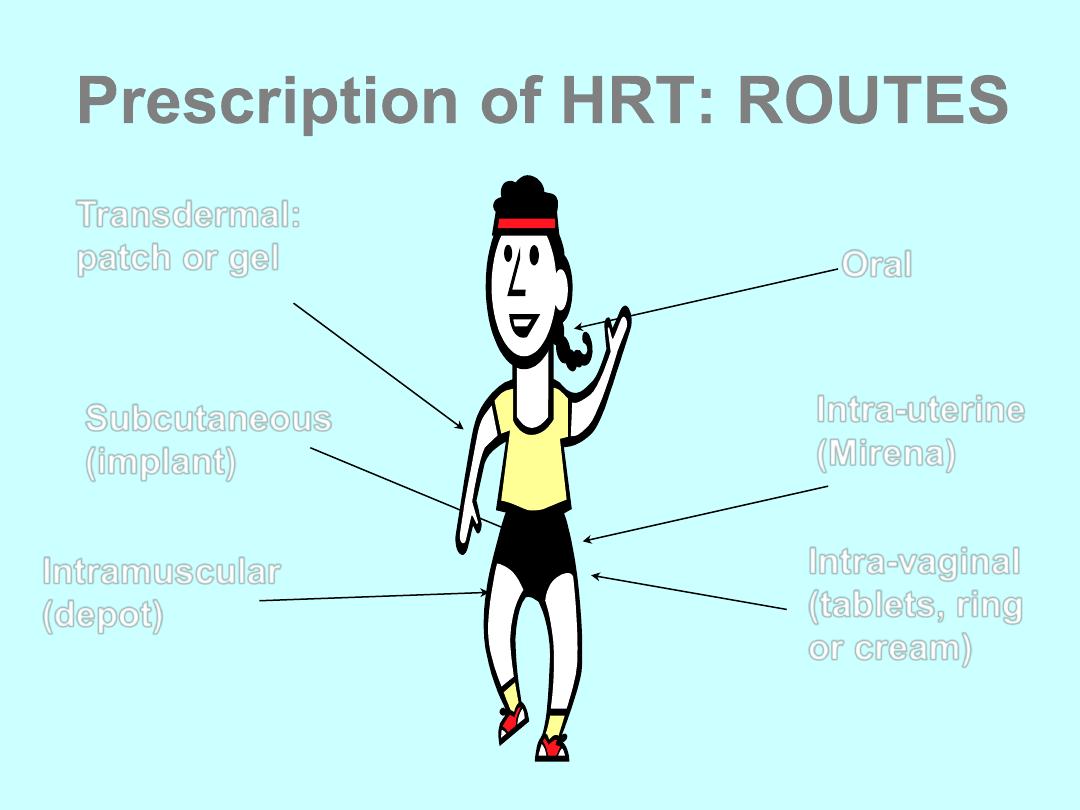
Prescription of HRT: ROUTES
Oral
Transdermal:
patch or gel
Subcutaneous
(implant)
Intramuscular
(depot)
Intra-uterine
(Mirena)
Intra-vaginal
(tablets, ring
or cream)

Preparations of HRT
• Oestrogen Only HRT (tablet, patch, gel,
implant)
• Sequential Combined HRT - oestrogen
and progestogens (tablets or patch)
• Continuous Combined HRT - oestrogen
and progestogens (tablets or patch)

Oestrogen Only HRT
• Only to be used in women who have had a total
hysterectomy
• If the hysterectomy was subtotal, then may need
to use progestogens as well (some endometrium
may be left behind)
• If the hysterectomy was for endometriosis, then
progestogens continuously along with oestrogen
should be used at least initially
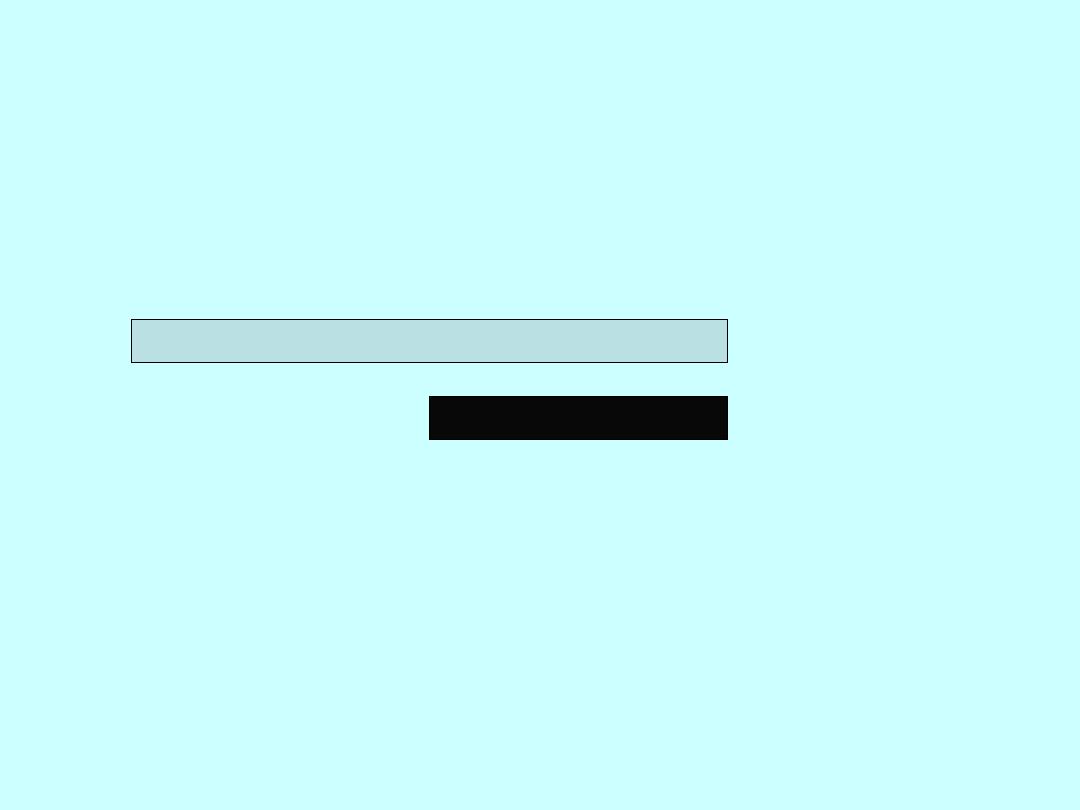
Sequential Combined HRT
• Sequential oestrogen and progestogen
• The addition of the progestogen protects the
endometrium and leads to a regular bleed
• Single named product available as patch or
tablet but individualisation possible eg gel and
IUS
Oestrogen for
28 days
Progestogen for
14 days
Continuous Combined HRT
• Continuous Combined HRT (CCT)
• This should not be started until 1 year after the
LMP or aged 54. Should also be used after 2
years of cyclical therapy if under the age of 54.
• No monthly bleed
Oestrogen
combined with
progestogen for 28
days

Continuous Combined HRT
• This preparation leads to no bleeding after the
first 6 months of use
• Single named product available as tablets or
patches
• Any oestrogen continuously + any progestogen
continuously
The Mirena is now licensed for use with
Oestrogen only HRT for 4 years. The
advantage is that it can be used in younger
women to induce a no-bleed regime.

Non-hormonal treatments for
vasomotor symptoms
• Alpha-adrenergic agonists Clonidine
• Beta-blockers Propanolol
• Modulators of central
neurotransmission Venlafaxine
Fluoxetine
Paroxetine
Citalopram
Gabapentin

Tibolone or Livial
• This is an alternative CC HRT
• It is a gonadomimetic containing oestrogen,
progestogens and androgens
• Licensed for vasomotor symptoms and osteoporosis
• The risk:benefit ratio similar to HRT in women under 60,
but over 60 increased risk of stroke
• Slightly increased risk for endometrial cancer
• Less risk of breast cancer compared with CCT but
increased over E2 only HRT
• May help libido due to androgen content

Local oestrogen preparations
• For women with vaginal and bladder
symptoms who do not need systemic HRT
local oestrogens can be used
• Vaginal creams and tablets are available
• There has been some concern that long
term use without progestogens may cause
endometrial hyperplasia or cancer

Long term treatment of atrophic vaginitis
with low-dose oestradiol vaginal tablets*
• Women treated with
twice weekly Vagifem
tablets had an
atrophic endometrium
after 2 years
• Licensed for long
term use as required

MANAGEMENT OF HRT
• Initial visit
• 3 months
• 6 months
• Yearly: BP, breast examination and
vaginal examination (3 yearly
smears to age 60 and 3 yearly
mammography aged 50-64)
• Invite earlier visit for specific
problems

Contraindications to HRT
• Hormone dependent cancer – endometrial
cancer, current or past breast cancer*
• Active or recent arterial thrombotic disease
(CVD, CVA)*
• VTE*
• Otosclerosis*

• Severe active liver disease (oral
oestrogen)
• Undiagnosed breast mass
• Undiagnosed abnormal vaginal bleeding
• Dubin-Johnson and Rotor syndromes

Relative contraindications
• May require extra supervision
– Uterine fibroids
– Endometriosis
– Hypertension
– Migraine

Side Effects of HRT
• Nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramps,
bloating
• Weight changes
• Breast tenderness
• PMS-like syndrome
• Sodium and fluid retention
• Glucose intolerance

• Altered blood lipids
• Mood changes
• Headache, migraine, dizziness
• Leg cramps

Benefits of
HRT

Benefits and HRT:
Menopausal Symptoms
• HRT effectively relieves vasomotor
symptoms
• In most cases, 2-3 years therapy is
sufficient, but some women may need
longer
• Symptoms may recur for a short time after
stopping it.

Benefits and HRT:
Coronary Heart Disease
• cardio-protective effect if HRT taken in the early
menopausal years
• No increased risk of CHD has been identified to
date with oestrogen-only HRT
• An increased risk of CHD in women who started
combined HRT more than 10 years after the
menopause.

Benefits and HRT:
Colorectal Cancer
• HRT reduces the
risk of colorectal
cancer
• This is likely to be
the anti-oxidant
effect of oestrogen

Benefits and HRT: Osteoporosis
• “osteoporosis is a skeletal disorder
characterised by compromised bone
strength predisposing to an increased
risk of fracture
”

RISK FACTORS FOR
OSTEOPOROSIS
MINOR
• Cigarette smoking
• Sedentary lifestyle
• Low Calcium intake
MODERATE
• FH of osteoporosis
• Underweight
• High C
2
H
5
OH
consumption
MAJOR
• Early menopause
• Prolonged steroid
therapy
• Prolonged
amenorrhoea

Benefits and HRT: Osteoporosis
• HRT is effective for the prevention of
osteoporosis but its beneficial effect on bone
diminishes soon after stopping treatment
• Because of the risks associated with long term
use of HRT, it should only be used for
prevention in women who are unable to use
other medicines that are authorised for this
purpose
• However HRT remains the treatment of choice in
women with premature ovarian failure

Risks and HRT: Stroke
• HRT increased the risk of stroke (mostly
ischaemic) compared with placebo
• Older women have a greater absolute risk
of stroke
• Risk may depend on oestrogen dose

Risks and HRT:
Venous Thromboembolism
• Oral HRT has been associated with an
increased risk of DVT and PE.
• Evidence suggests that it is higher with
combined HRT than oestrogen-only HRT and
that these events are more likely in the first year
of use
• One study suggests that risk may be lower with
a non-oral route
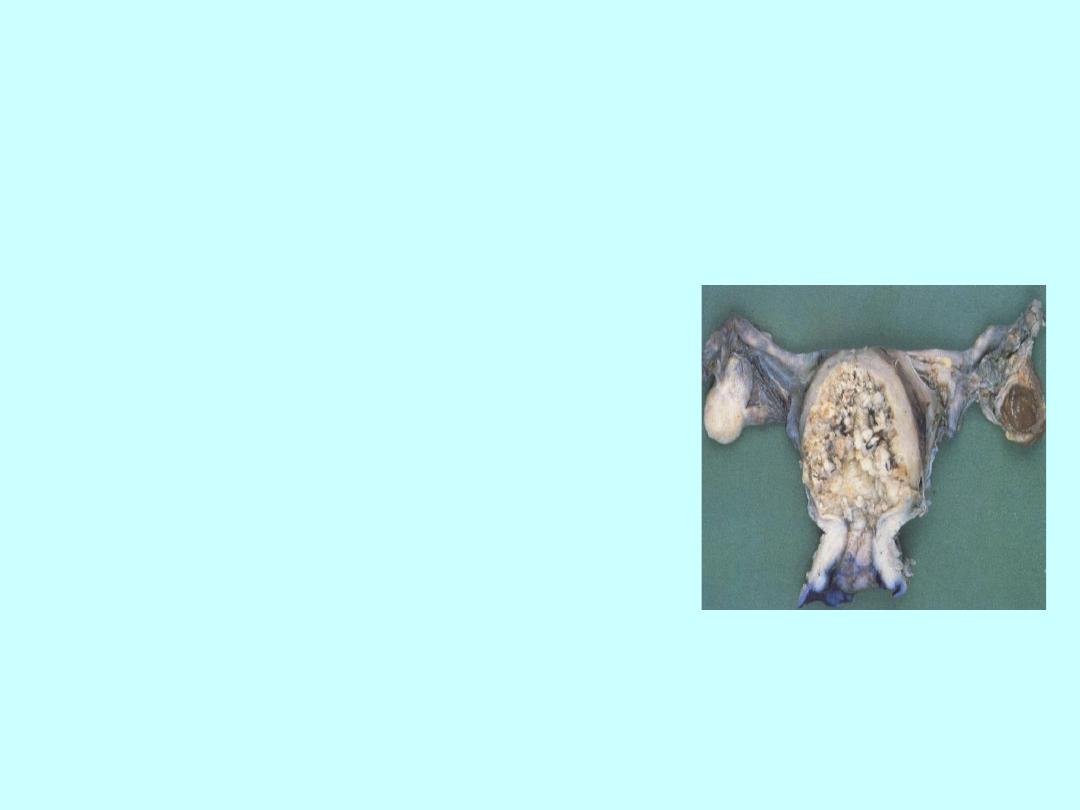

Risks and HRT:
Endometrial Cancer
• In women with a uterus, use of
oestrogen-only HRT
substantially increases the risk
of endometrial hyperplasia and
cancer in a way that depends
on dose and duration
• Addition of progestogen
cyclically for at least 10 days
per 28 day cycle reduces the
risk and progestogen
continuously eliminates risk

Risks and HRT: Ovarian Cancer
• Observational studies suggest that
long-term use of all HRT
’s may be
associated with a small increased risk
of ovarian cancer which returns to
baseline a few years after stopping it.
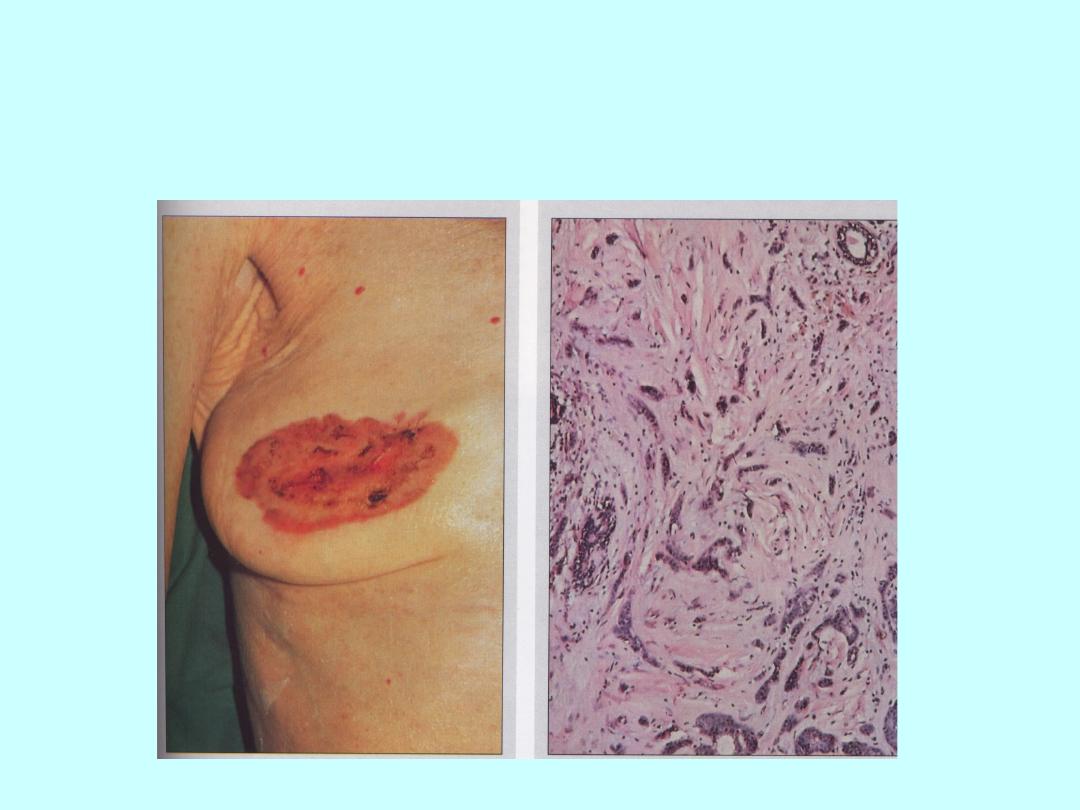
Risks and HRT: Breast Cancer

Risks and HRT: Breast Cancer
• The risk is increased in women who take HRT
for several years
• Combined HRT has the highest risk
• For oestrogen-only HRT the risk is lower
• Risk increases with duration of use and returns
to baseline within a few years of stopping
treatment
Are there any alternatives to
HRT?
SERMS
Specific
Estrogen
Receptors
Modulators

THE IDEAL
‘SERM’
WOULD:
• Give oestrogen agonism where it is needed
ie. skeleton, CVS and CNS
• Give oestrogen antagonism where it is
needed ie. breast and uterus

TAMOXIFEN
• BONE probably favourable but no
large trials
• CVS favorable effect on lipids but no
effect on mortality
• UTERUS increase risk of endometrial
proliferation, endometrial polyps and
Ca body

RALOXIFENE
• Approved for the prevention of
non-traumatic vertebral
fractures in post menopausal
women at increased risk of
osteoporosis
Summary of Raloxifene
• Prevents bone loss
• Favourable effect on lipid mechanism
• Minor side effects
• VTE risk similar to HRT
• No endometrial stimulation
• No increase in breast or endometrial
cancer risk
BUT
• Does not help menopausal symptoms

Alternatives to HRT:
PHYTOESTROGENS
ISOFLAVONES
• red clover
• soy beans
• soy products
• legumes
LIGNANS
• whole cereals
• oilseeds
• cereals
• berries
Phytoestrogens are plant substances that have effects
similar to oestrogen

Other alternatives
• Herbalism: eg. Black cohosh, ginseng
• Homeopathy
• DHEA
• Acupuncture, magnets
None of these have definitively proven to be of
benefit and drug interactions can occur

Premature Ovarian Failure
(Dysfunction)
• Cessation of menses before the age of 45
• Definition varies with the reference
population (2SD below mean)
• Affects 1% women under 40
• Primary and secondary causes

Premature Ovarian Dysfunction
• Primary due to chromosome
abnormalities eg Turner
’s (XO);
autoimmune disorders; enzyme defects
• Secondary due to chemotherapy,
radiotherapy, surgery
• Spontaneous ovulation may occur with
pregnancy rates up to 5-10%

Premature Ovarian Dysfunction
• Hormone replacement required to keep tissues
healthy including bones and heart
• HRT (higher doses) or COCP to age 52
• Testosterone as patch or implant
• Risks are none use of HRT rather than use at
this age. On HRT same risk as age equivalent
population for breast Ca, VTE etc

Thank you
