
MSK Series
Tikrit University
College of Medicine
Department of Radiology
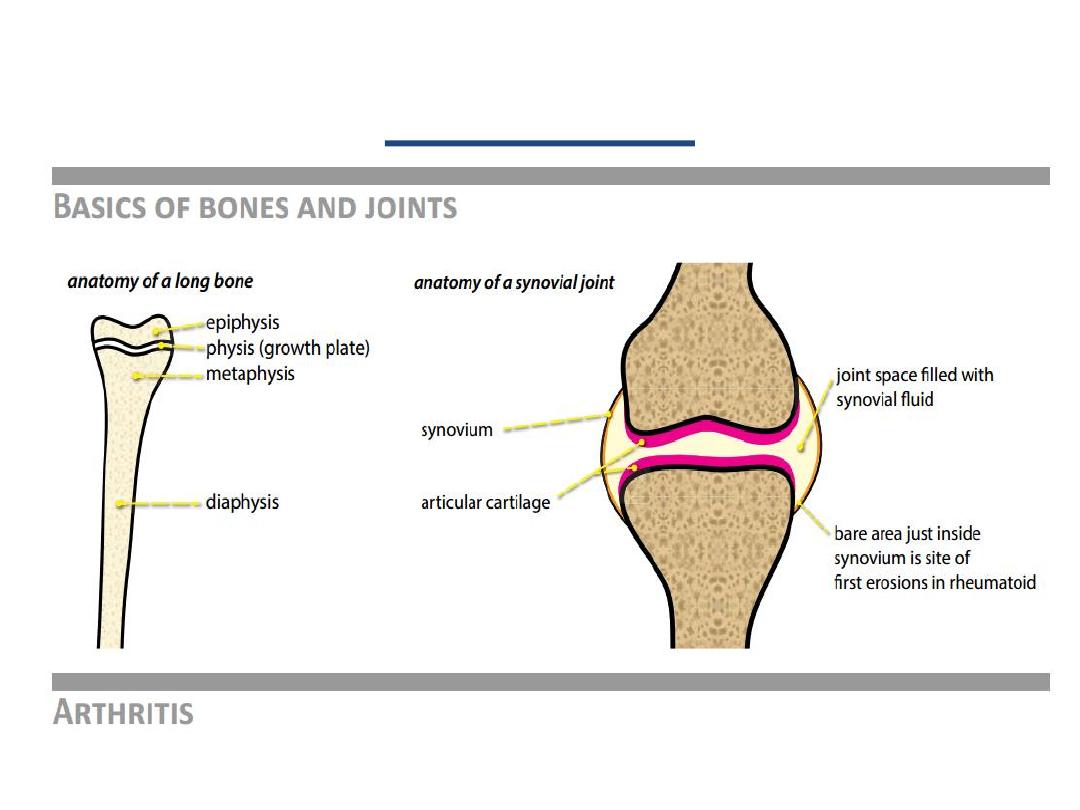
Arthritis
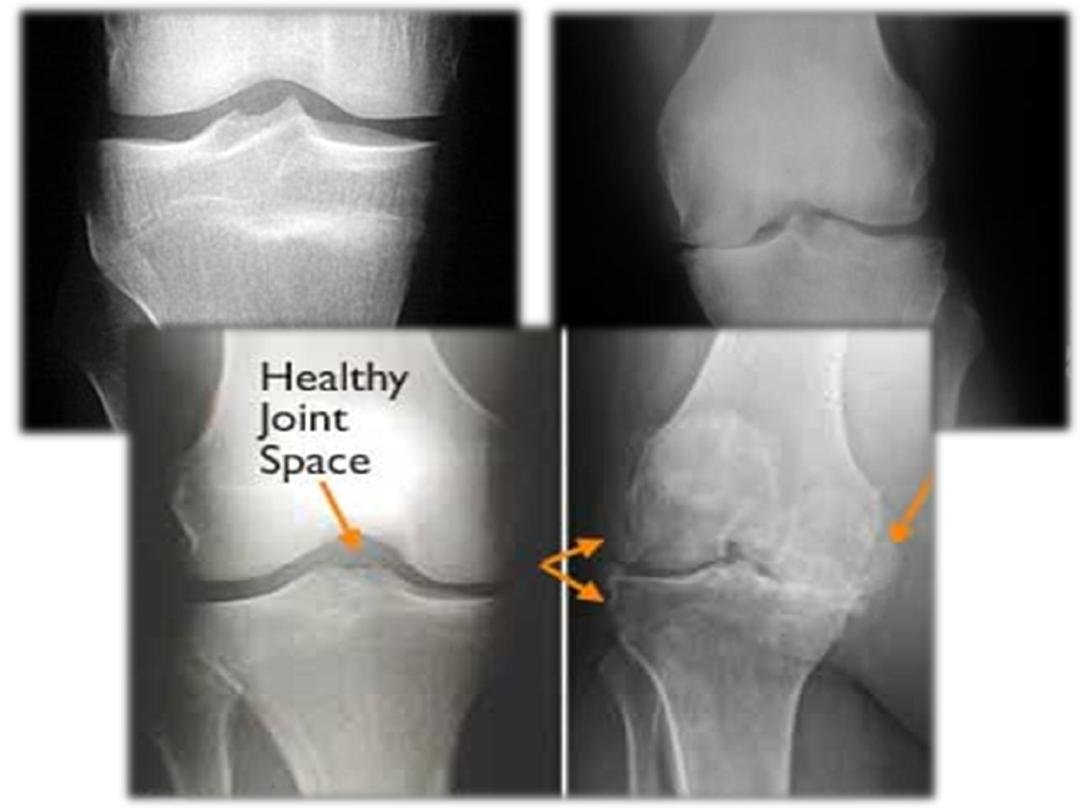
Affect bones on both sides of the joint space
due to cartilage destructing evident on
radiographs by joint space narrowing.

Approach to an Image
Soft tissues
: effusions, calcification, masses
Mineralization
: diffuse demineralization, periarticular
demineralization
Joint space
narrowing and subchondral bone sclerosis,
intraarticular bodies, ankylosis
Erosions
: central (articular surface), marginal (bare area),
periarticular.
Proliferation
: osteophytes, periostitis
Deformity
: varus/valgus, flexion/extension, subluxation,
dislocation, collapse
Distribution
: monoarticular, pauciarticular, polyarticular,
symmetric/asymmetric
Arthritis can be divided into:
• Degenerative (osteoarthritis)
– Primary : idiopathic, seen in aging
– Secondary: arthritis in adult 2
nd
to - e.g. trauma
– Neuropathic -
Charcot join
• Inflammatory:
• Crystal deposition:
– Gout
– Calcium pyrophosphate deposition (CPPD)
• Hematologic
(hemophilia)
• Septic
(due to joint infection)
• RF blood test is positive, include:
• RA
• Lupus
• Scleroderma
• Others
Sero +ve
• RF blood test is Negative. Usually +ve HLA-B27
• Ankylosing spondylitis
• Psoriatic arthritis
• Reiter's syndrome
• Enteropathic arthritis (with IBD)
Sero -ve

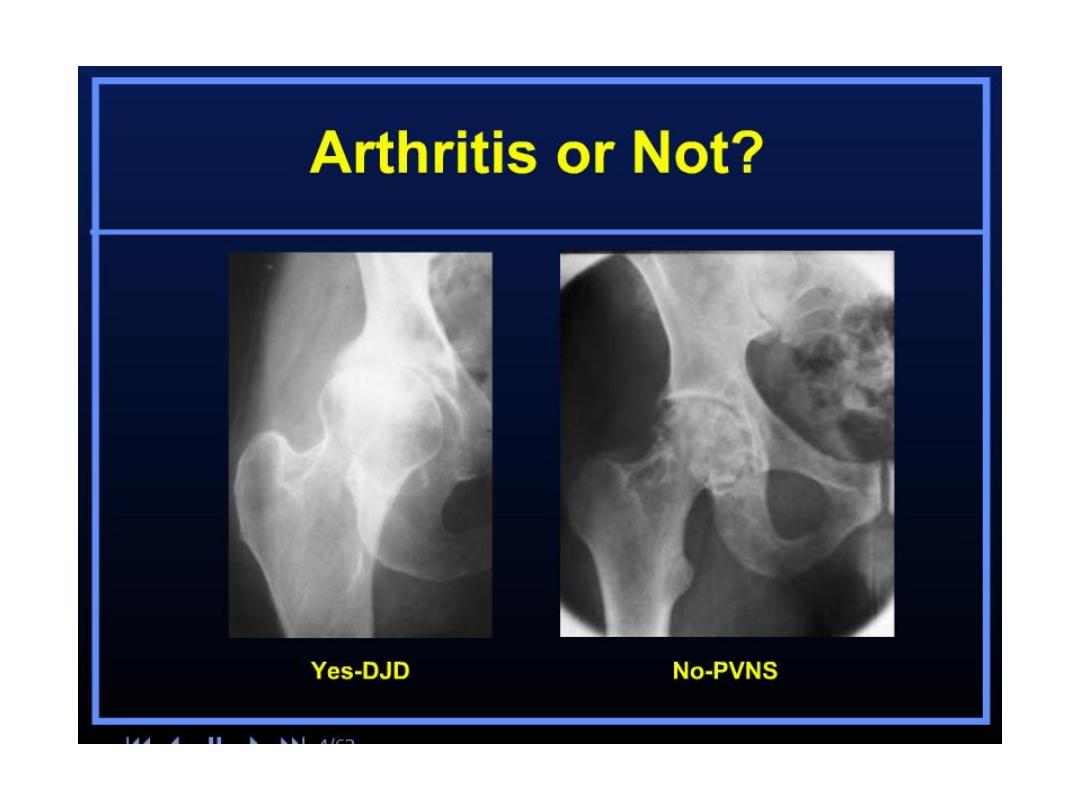
Osteoarthritis (OA)
• Also called osteoarthrosis or degenerative
joint disease (DJD).
• OA is the result of articular cartilage breakdown from
local mechanical factors.
• OA typically occurs in
weight-bearing joints
and the
hands .
• Commonly seen in
Knee
&
Hip
joints
.
• When radiographic findings of OA are seen in
younger patients
or in
unusual locations
,
such as the
(shoulder, elbow, or ankle) usually its
secondary OA
due to
trauma
or other condition
.

The radiographic features of OA
• A
symmetrical joint space narrowing -
dependent
part of the joint
(
medial in Knee & supero lateral in Hip
)
• Subchondral Sclerosis, loss of hyaline cartilage
and reactive remodeling.
• Subchondral cystic change – Geode
- due to
herniation of joint fluid into bone through a cartilage defect.
• Osteophytosis.
• Lack of periarticular osteopenia (
vs RA
).

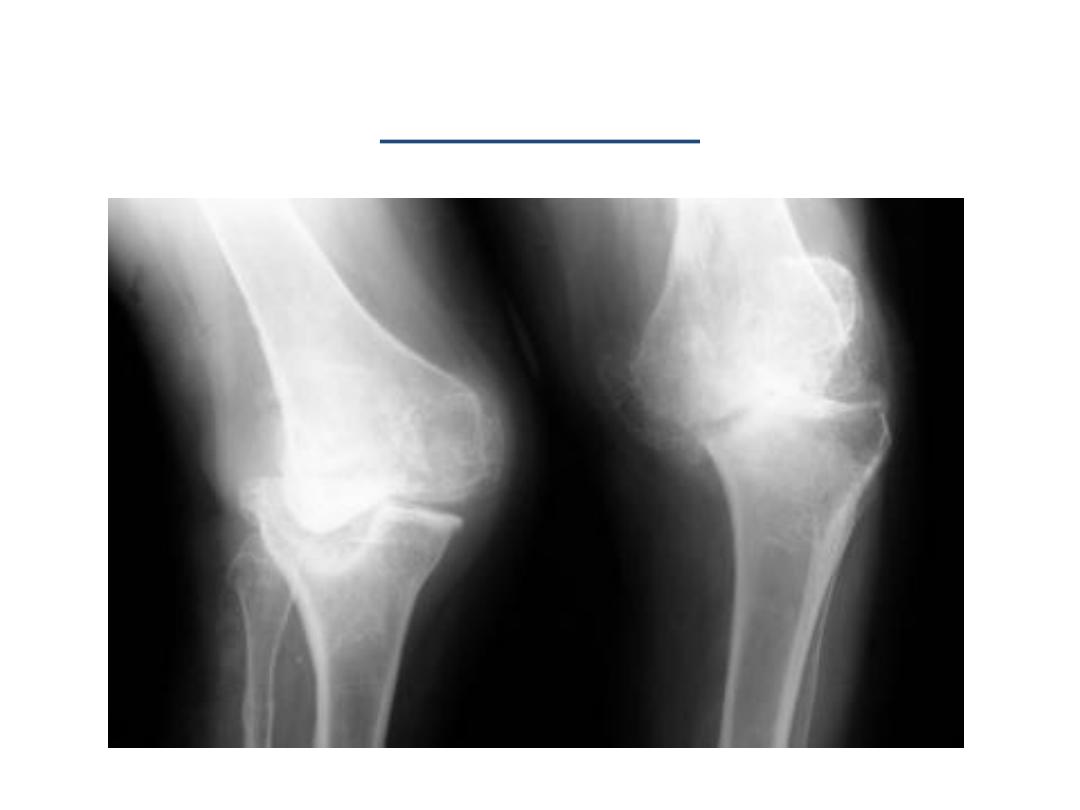
OA of the knee joint
• There are three joint compartments in the knee:
– The medial and lateral tibiofemoral compartments
– The patellofemoral compartment.
• The typical pattern for OA of the knee is
asymmetrical
involvement of the medial
tibiofemoral
compartment.
• Severe
osteoarthritis can involve all three compartments.
• The degree of joint space narrowing reflects the severity
of OA.
Best assessed on standing weight-bearing views
.
• Bilateral
involvement of the knees is
typical
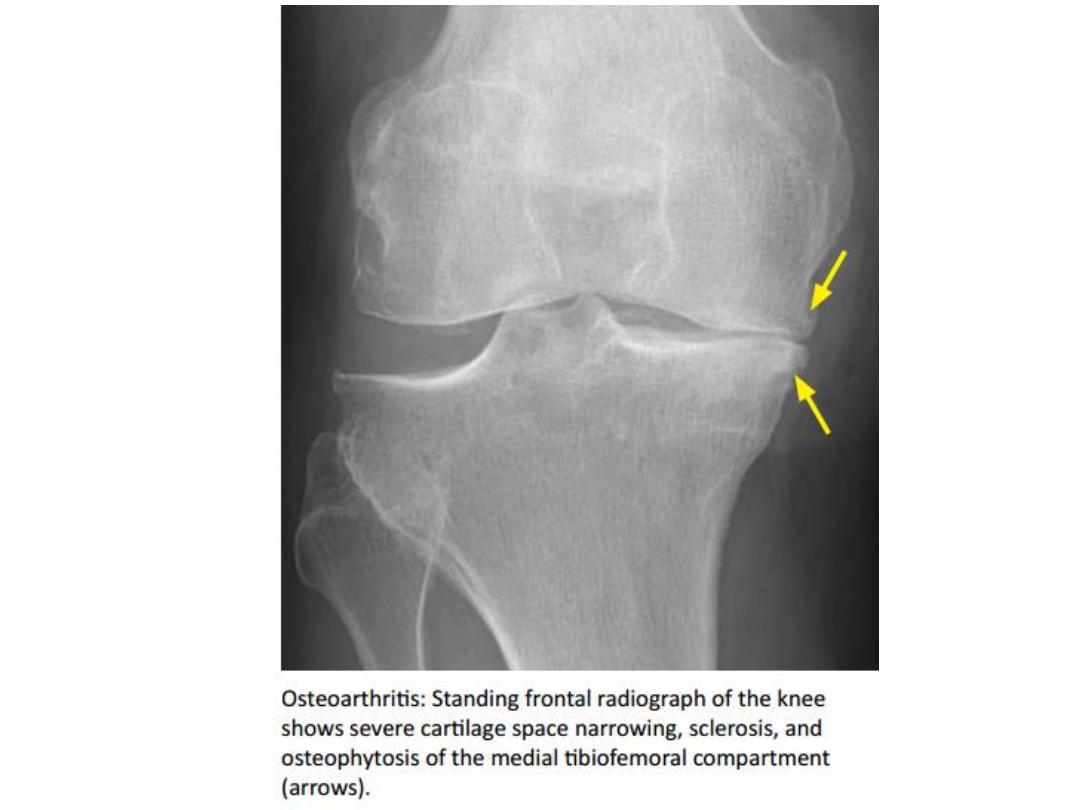

• Tends to be bilateral - Similar to the knee.
• Typical features of OA in general including:
– joint space narrowing
– Osteophytosis
– subchondral cystic change
– Sclerosis
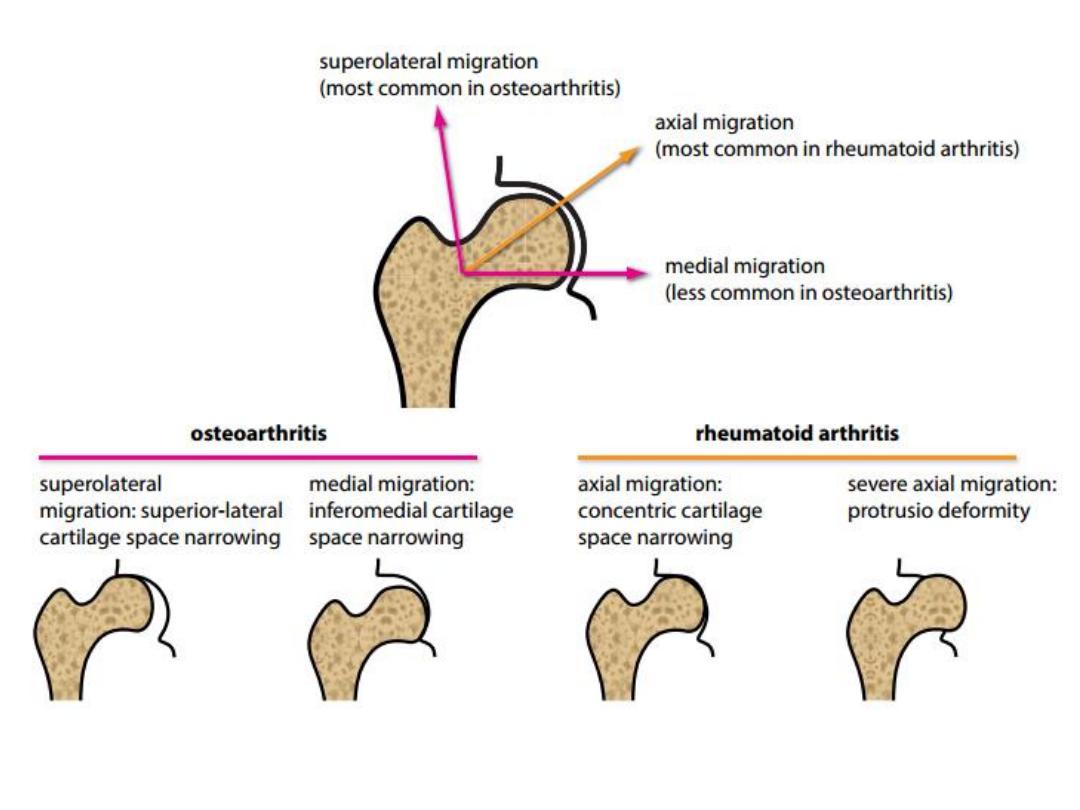
• Plus hip OA features including:
– migration of the femoral head in a
supero-lateral
direction. Less commonly, medial migrating
– axial
migration is seen more commonly in
inflammatory arthritis
OA of the Hip joint

• RA is an autoimmune disorder targeting the
synovium.
• Rheumatoid factor
(RF) is typically +ve
, not
specific (RF is an antibody).
• RA clinically presents with
symmetrical
joint
pain
,
swelling
, and
morning stiffness
.
• RA first affects the small joints in the hands and
wrists. .
• In more
advanced
cases, RA affects the cervical
spine, knees, shoulders, and hips
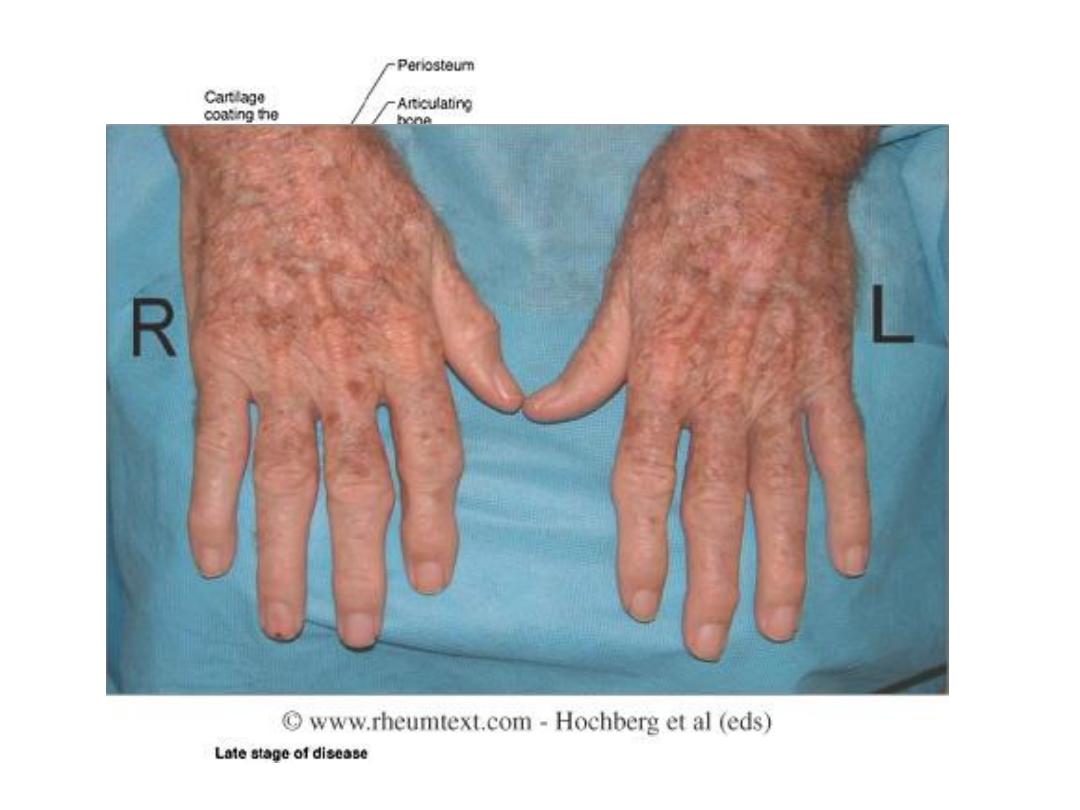
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)

• Marginal erosions
,
which first occur at the intra-capsular
articular margins in the:
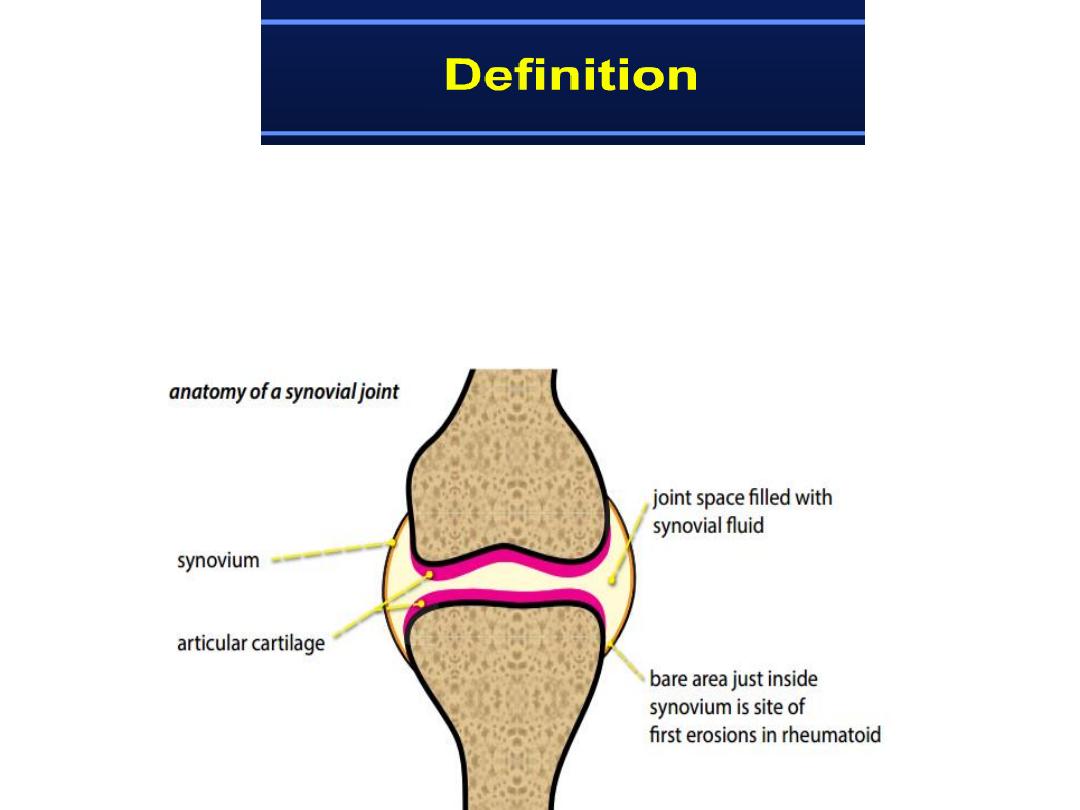
“bare area”
The bare area is a region of exposed bone just within the joint
capsule that is not covered by thick cartilage.
• Soft tissue swelling.
• Diffuse, symmetrical joint space narrowing.
• Peri-articular osteopenia.
• Joint subluxation.
Radiographic features of RA
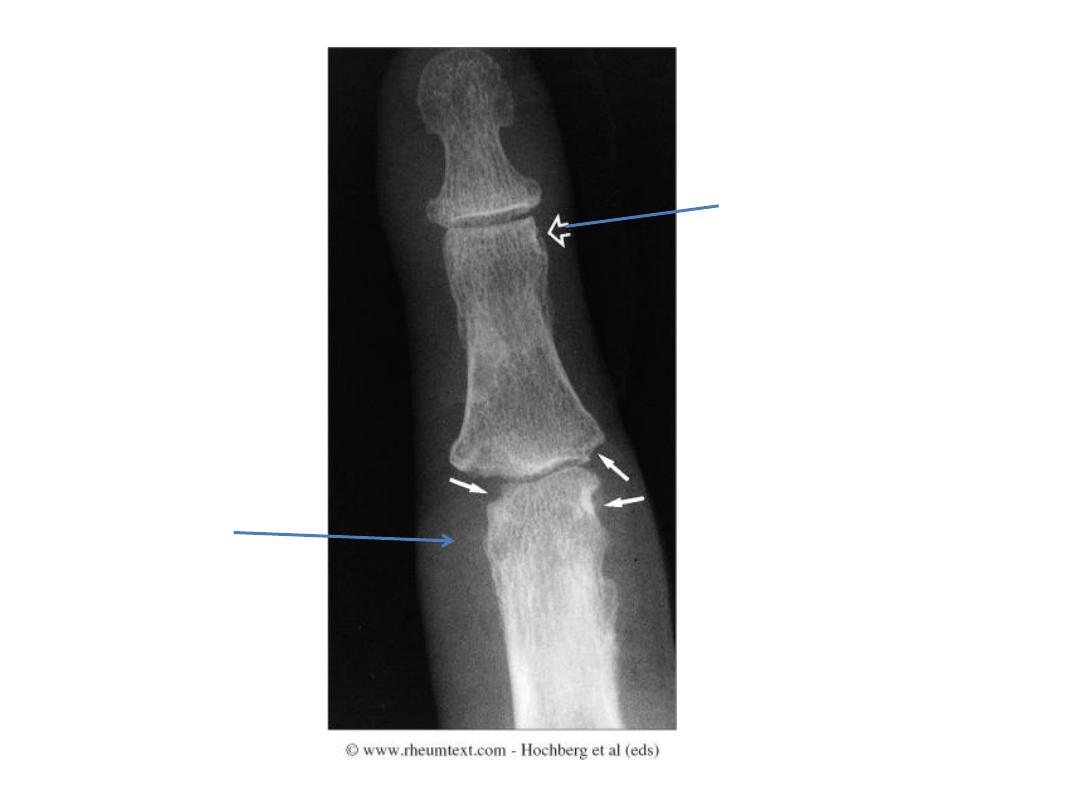
Marginal erosion
Erosions
Soft tissue
swelling
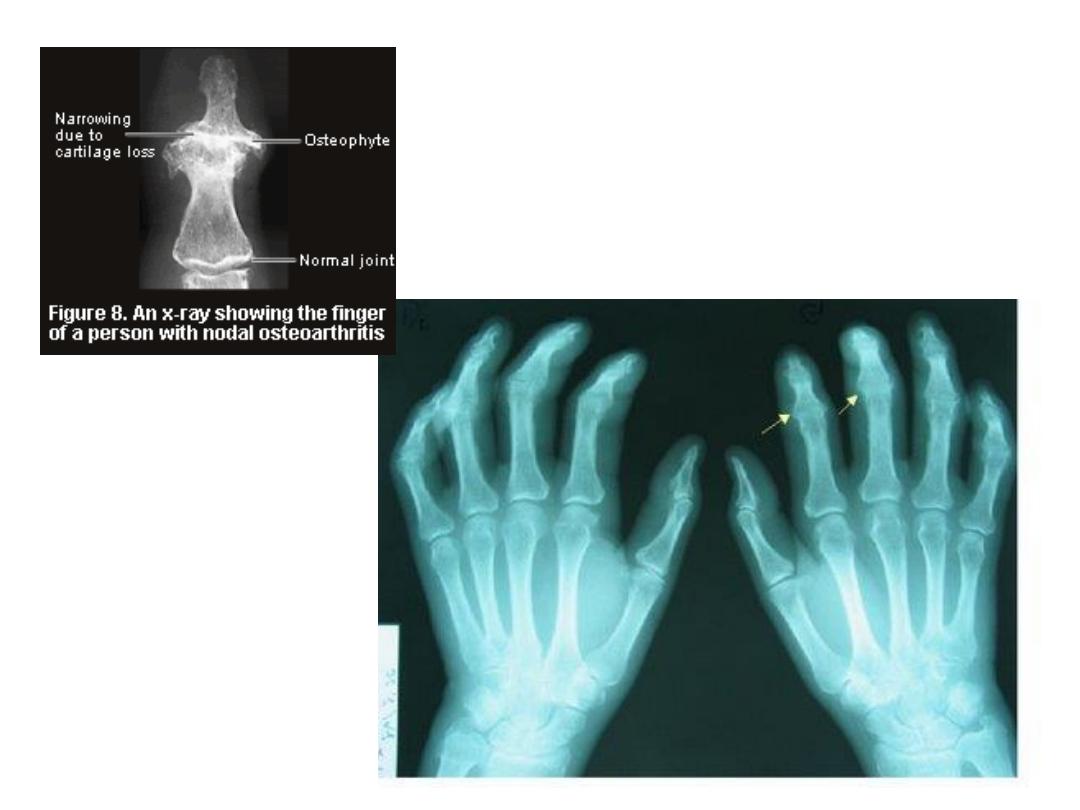
• The
hands
are commonly affected
in patients with RA.
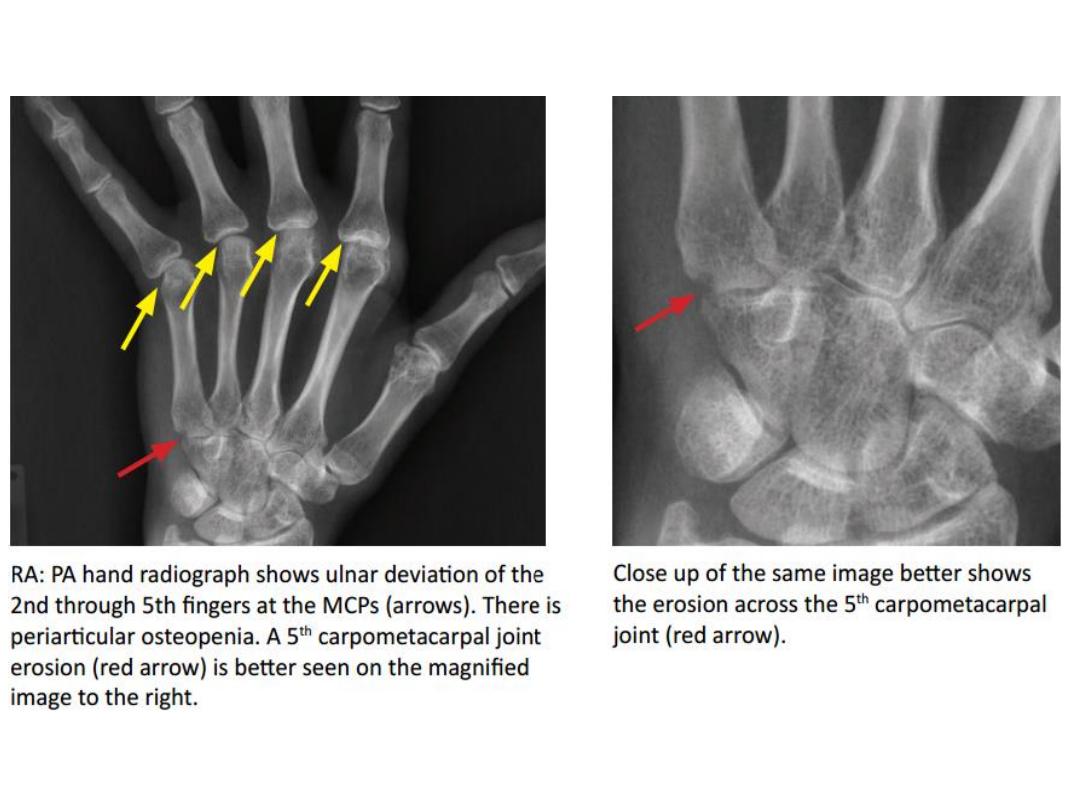
• The earliest radiographic changes
of RA are
soft tissue swelling
and
peri articular osteopenia
due to
synovitis and hyperemia.
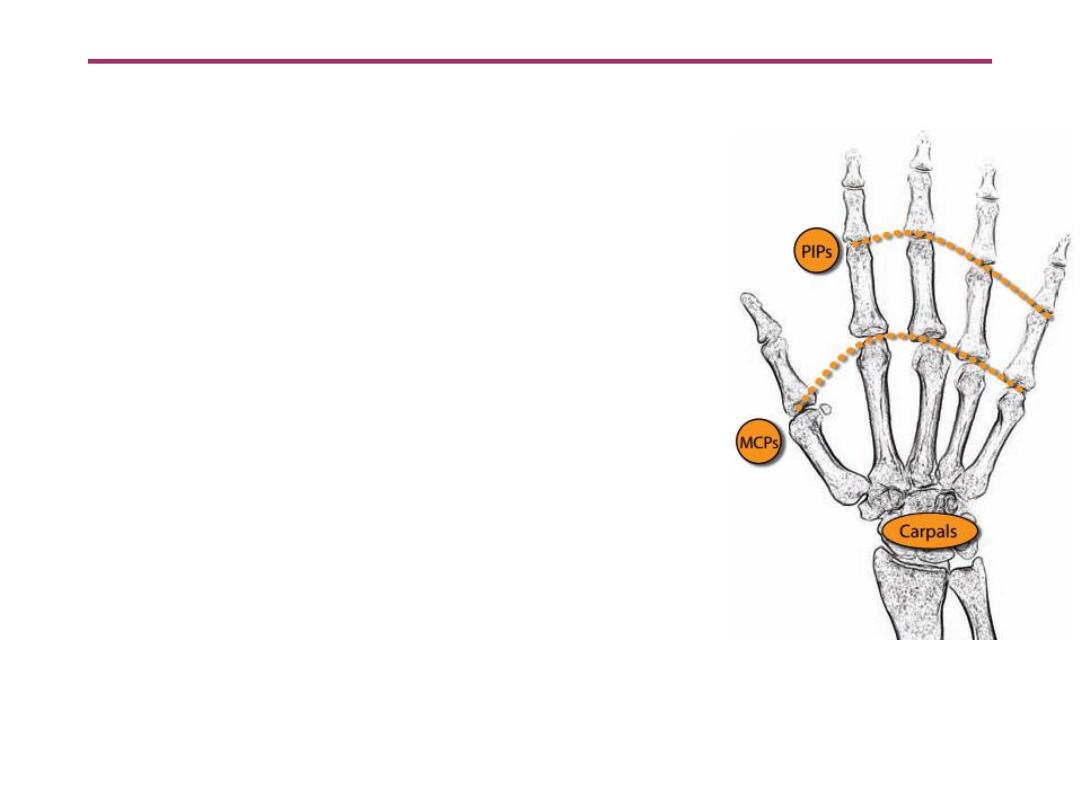
• Typical joints involved are the
MCPs
,
PIPs
, and the carpal
articulations.
The DIPs are usually
spared.
Rheumatoid arthritis in the hand and wrist

• Joint subluxatins
are present in more advanced
disease, which typically are not reducible and lead to
several common deformities, including:
– Boutonnière deformity
(PIP flexion and DIP
hyperextension).
– Swan neck deformity
(PIP hyperextension and DIP
flexion).
– Ulnar deviation
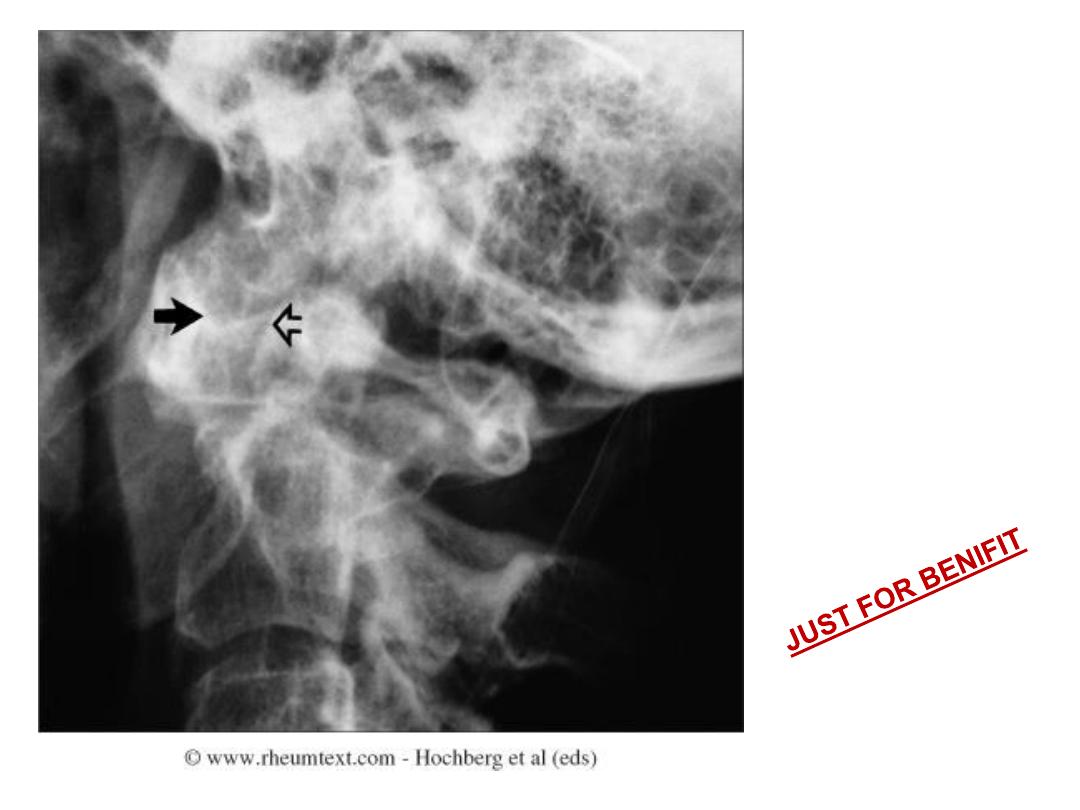
Atlantoaxial
subluxation in RA
Always a concern in
patient with
longstanding RA
and neck pain or
cervical neurological
symptoms
Order a view of the atlantoaxial articulation through an open mouth
to fully assess. This shows lateral atlantoaxial subluxation of the
odontoid process with respect to the lateral masses of the atlas.


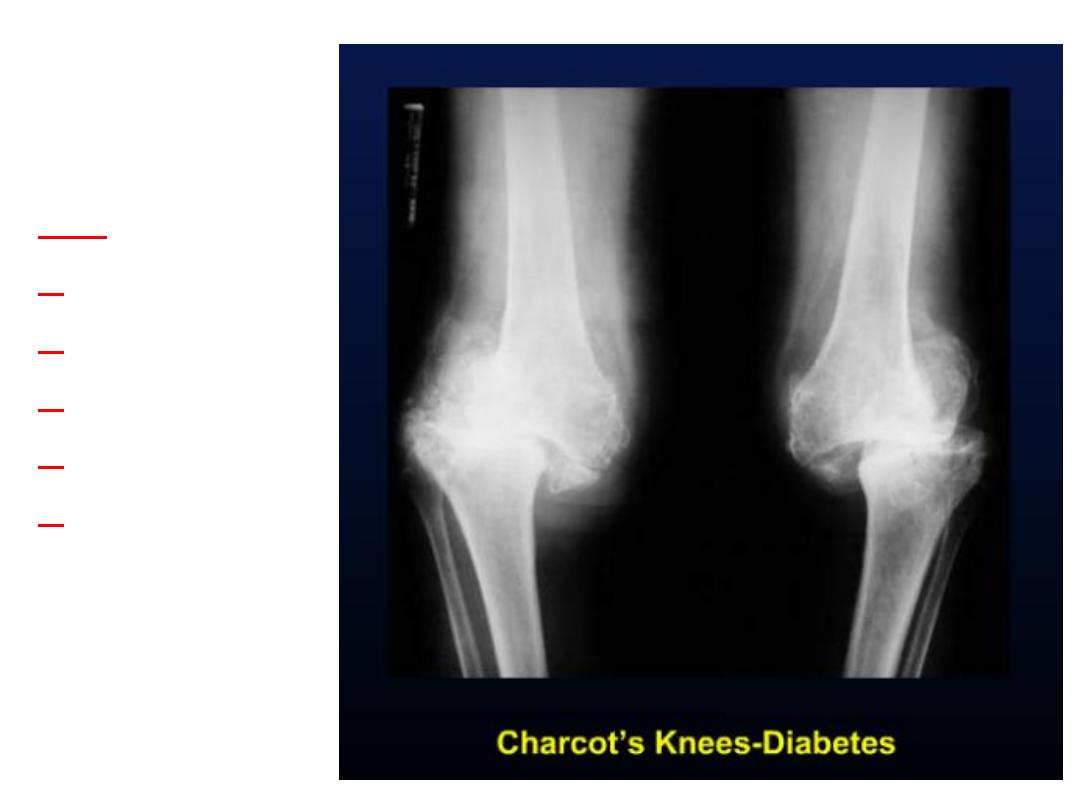
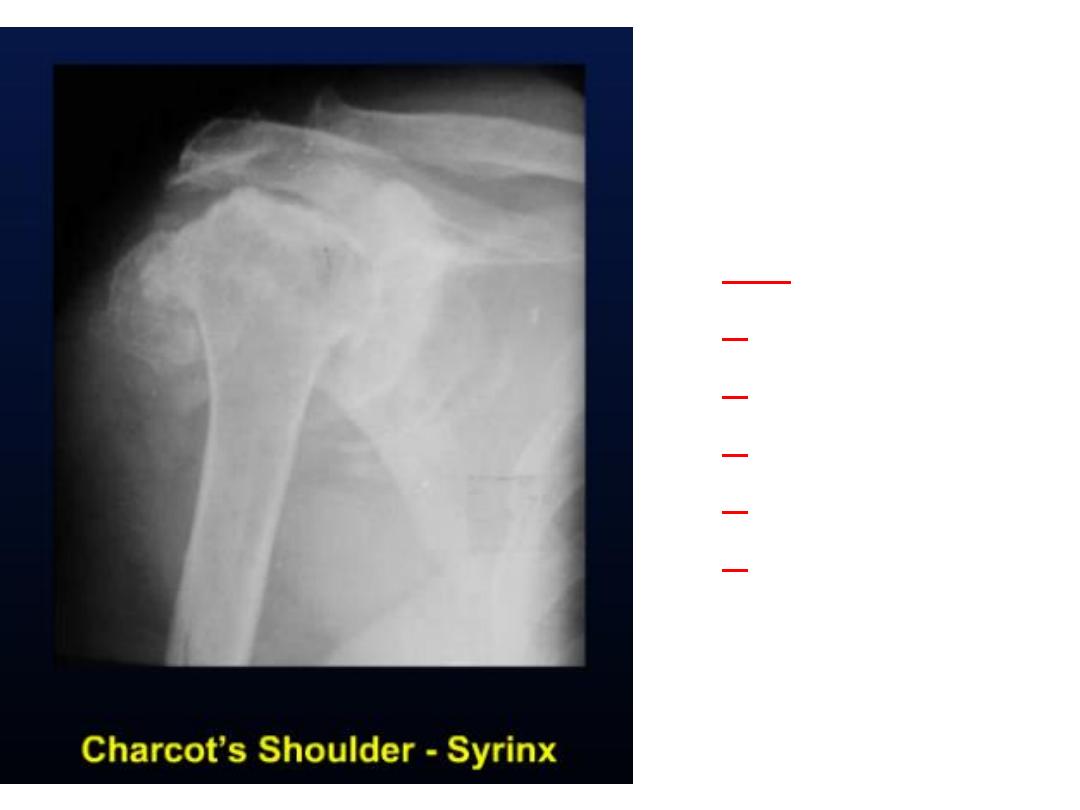
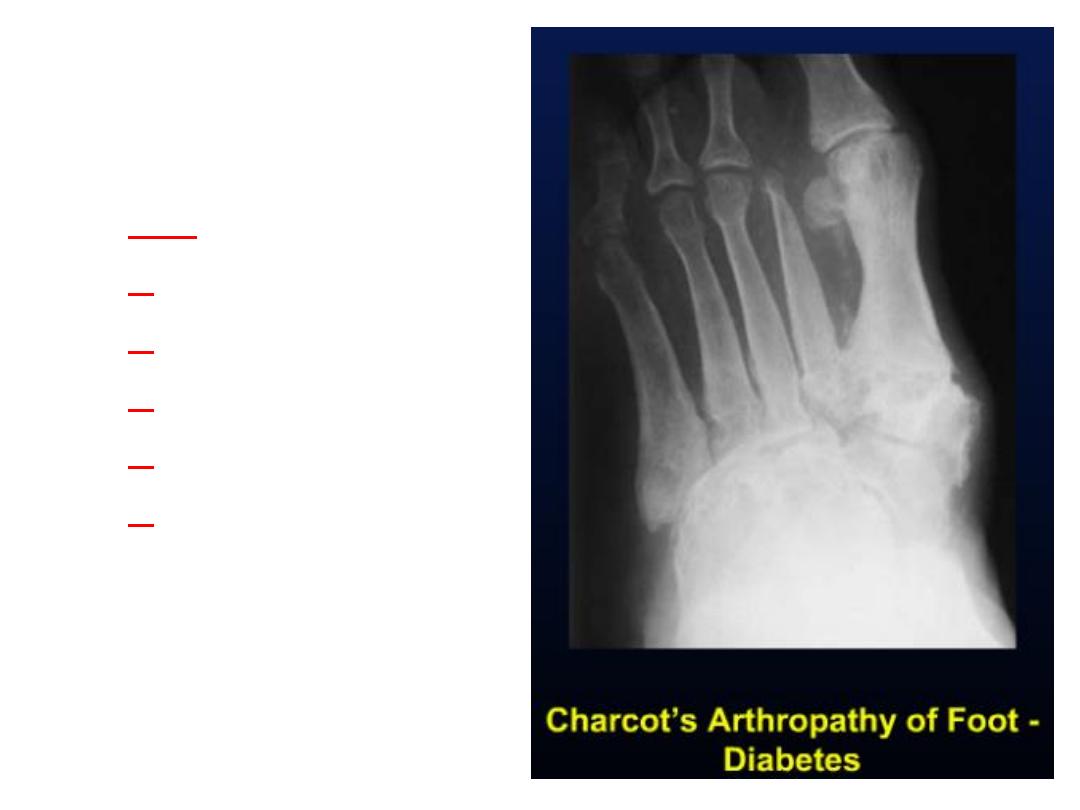
Charcot joint
• also known as a
neuropathic joint
refers to a
progressive degenerative / destructive joint
disorder in patients with
abnormal pain
sensation
.
Charcot joint

Causes of a Charcot joint
• can be remembered as they (all) start with the
letter
S
.
Mnemonic
– sugar (
diabetes
)
– syphilis
– steroid use
– syringomyelia
– spinal cord injury
– spina bifida
– scleroderma
– (leprosy)
Radiographic findings
• 6
Ds of Charcot joint
Mnemonic
– increased
d
ensity (subchondral sclerosis)
– d
estruction
– d
ebris (intra-articular loose bodies)
– d
islocation
– d
istention
– d
isorganization
↑d
ensity
d
estruction
d
ebris
d
islocation
d
istention
d
isorganization
↑d
ensity
d
estruction
d
ebris
d
islocation
d
istention
d
isorganization
↑d
ensity
d
estruction
d
ebris
d
islocation
d
istention
d
isorganization


Psoriatic Arthritis
Characterized by
erosions
and
bony
proliferations
RA does not typically have new bone formation
Asymmetric
distribution
Soft tissue findings:
fusiform
soft tissue
swelling around the joints; can progress so the
whole digit is swollen (
sausage digit
)
Marginal
erosions also often show fluffy
periostitis from new bone formation

Psoriatic Arthritis
• Deformities
– Pencil and cup – end
– Complete destruction of bone (
arthritis mutilans
)
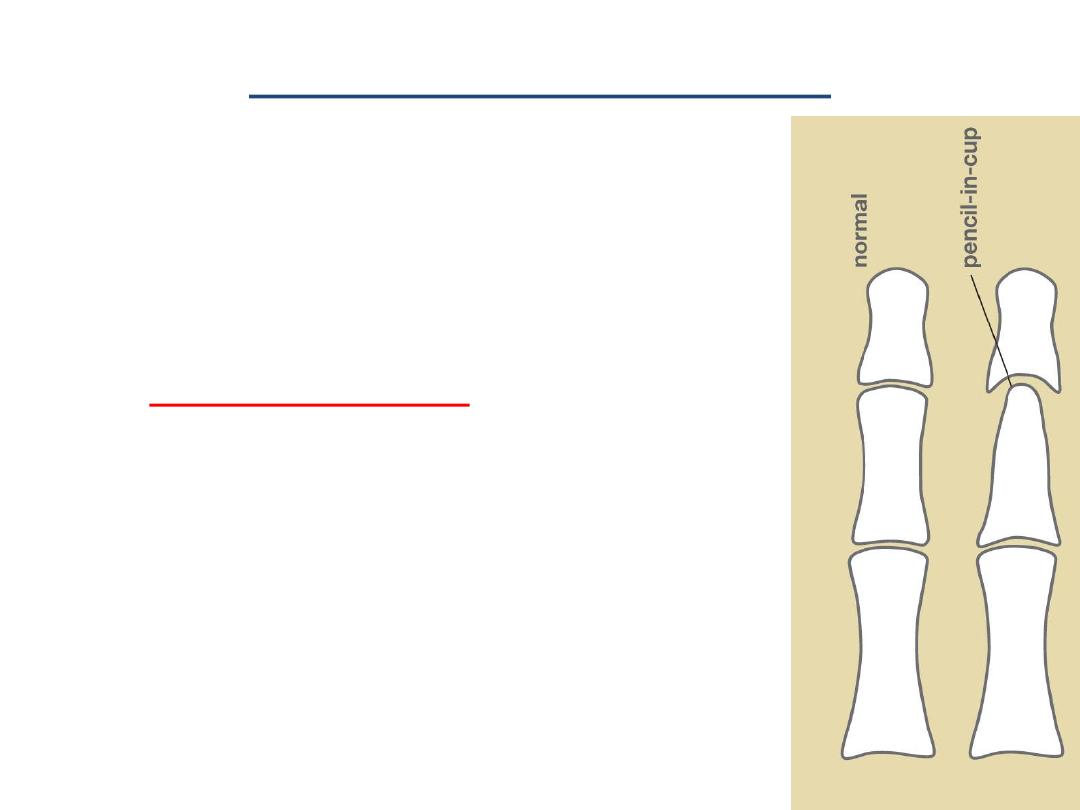
Pencil-in-cup deformity
• Pencil-in-cup deformity is the
description given to one of the
appearances on plain radiograph
in
psoriatic arthritis
.
• The appearance results from
periarticular erosions and bone
resorption
giving the appearance of
a pencil in a cup.
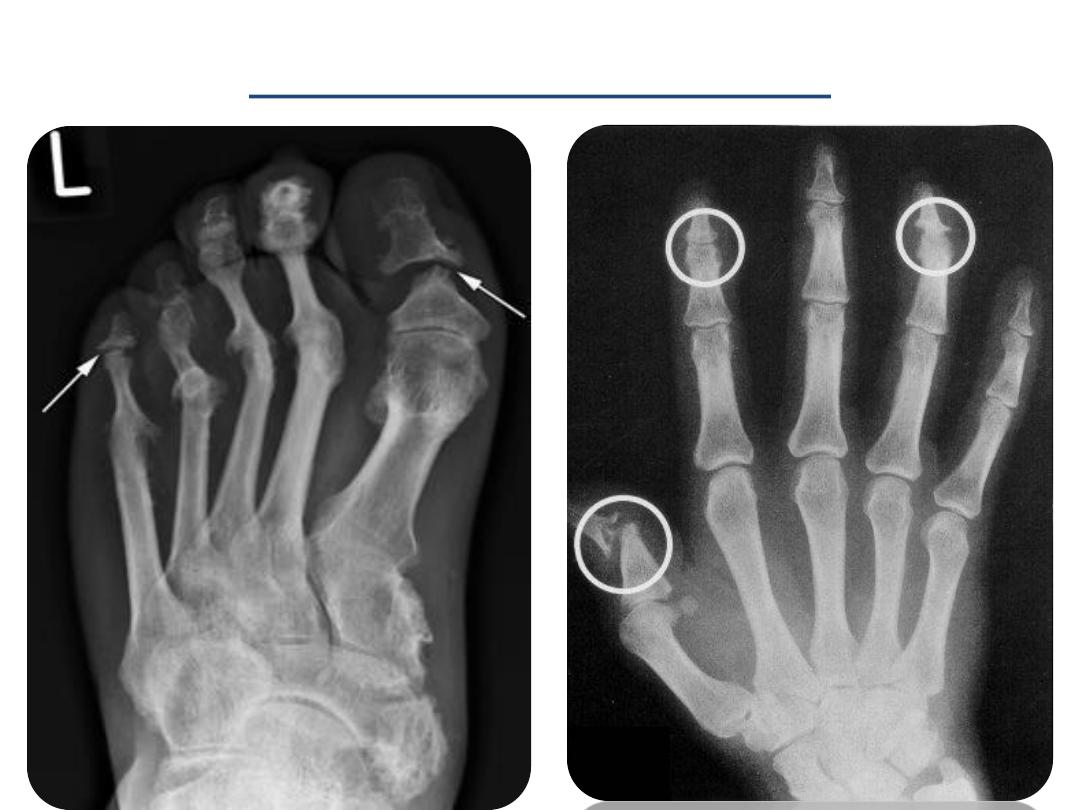
Pencil-in-cup deformity
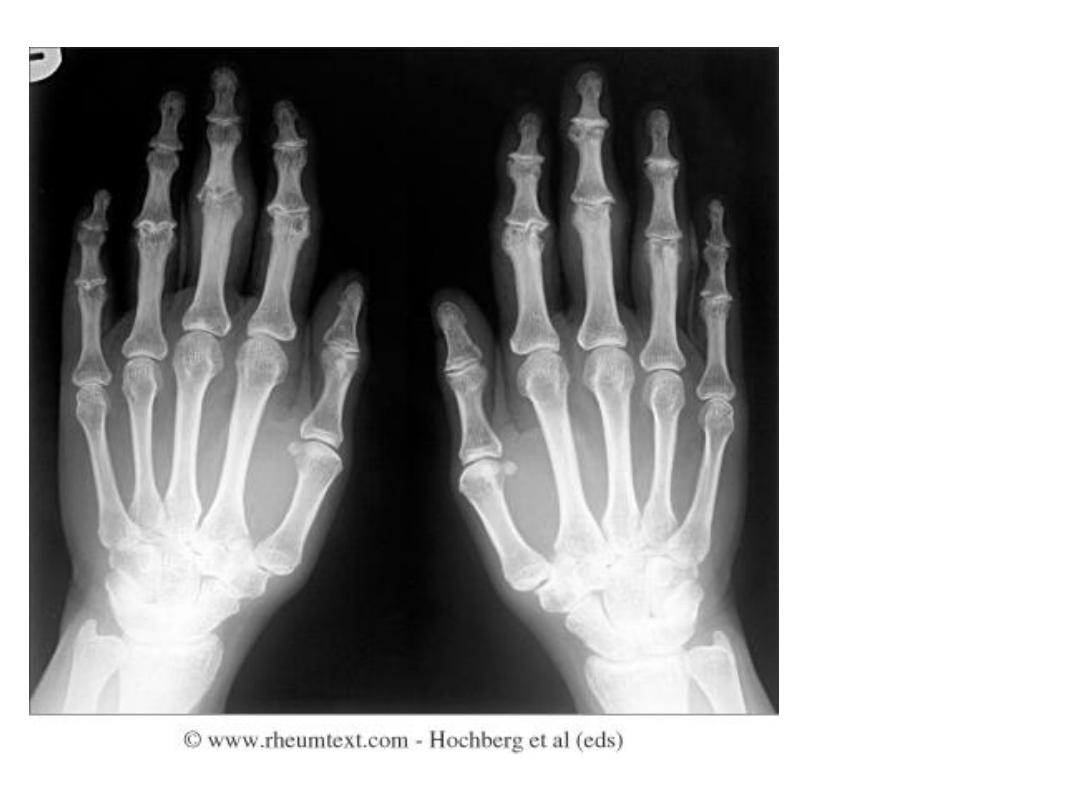
Psoriatic hands
Erosive changes
at the DIPs and
PIPs
Sparing of MCPs
and wrists
Arthritis mutilans
Pencil and cup deformity
Pencilling

Psoriatic Arthritis
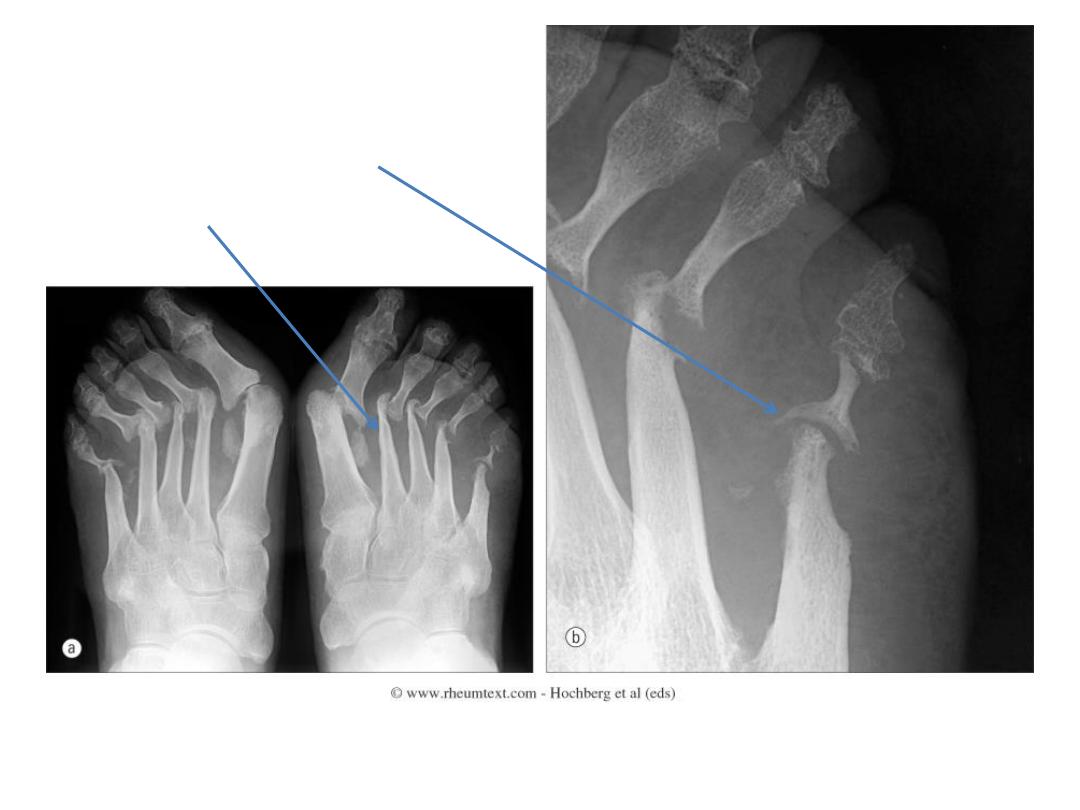
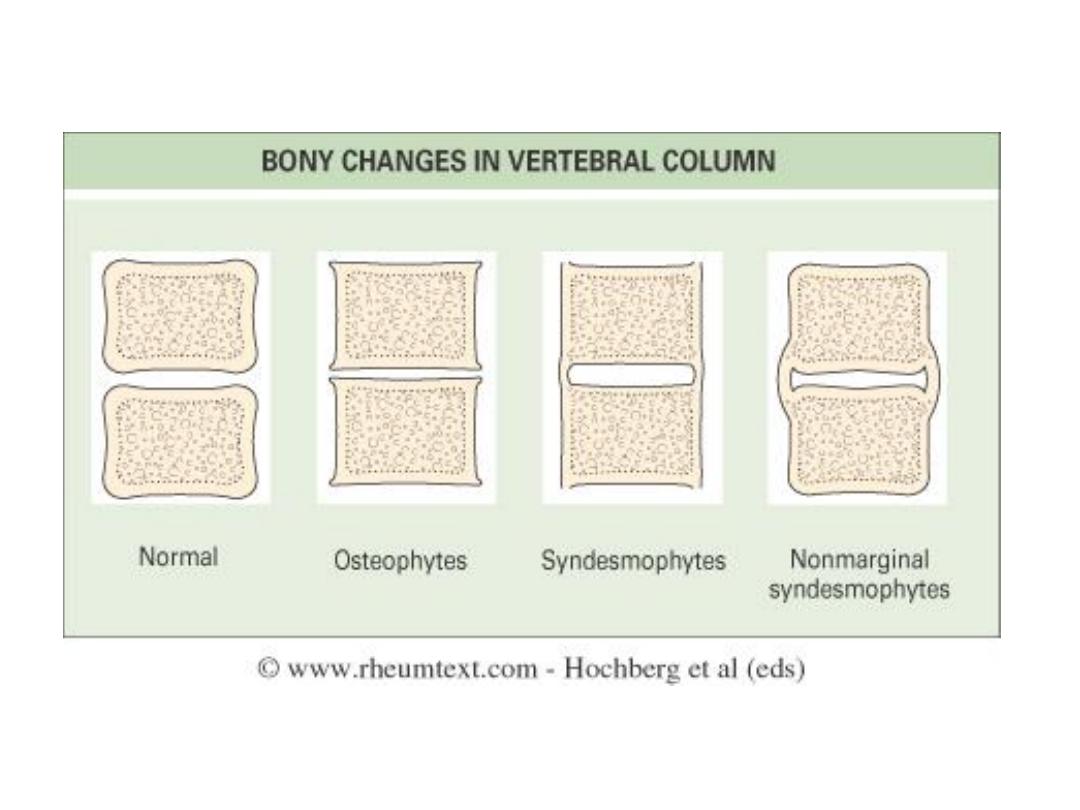
• Spine
– Asymmetric sacroiliitis
– Asymmetrical syndesmophytes (bony bridges
between vertebrae)
Asymmetric
sacroiliitis
with left sided
erosions and
sclerosis
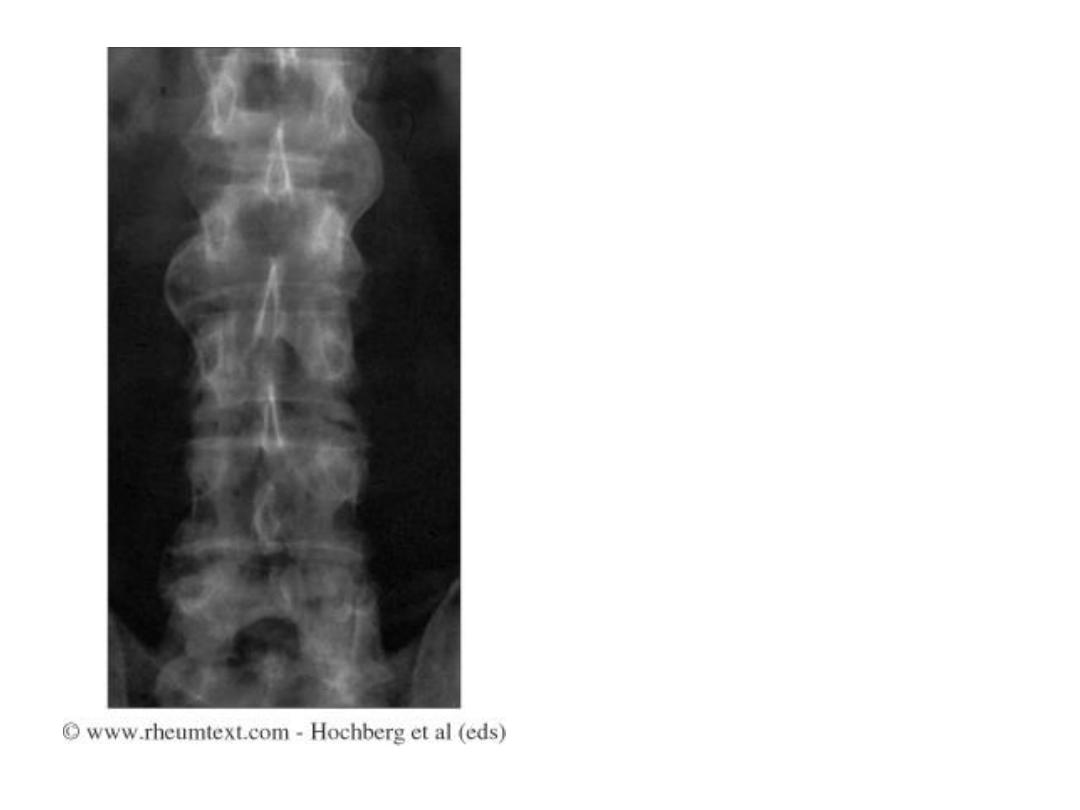
Non-marginal syndesmophytes
typical of psoriatic arthritis

Ankylosing Spondylitis
• Changes begin at SI joints and lumbosacral
junction, then typically move up the spine
• SI joints:
– Initially subchondral
sclerosis
– Erosions occur first at
iliac side
, which has thinner
cartilage
– Remember that the synovial part of the SI joint is
the anterior,
inferior
portion
– Reactive sclerosis with eventual
fusion

Ankylosing Spondylitis
• Spine
– Early changes include squaring of the anterior
vertebral body
– Enthesitis
and sclerosis
– Progressive mineralization form osseous
bridging
syndesmophytes
– Ossification of the interspinous ligaments
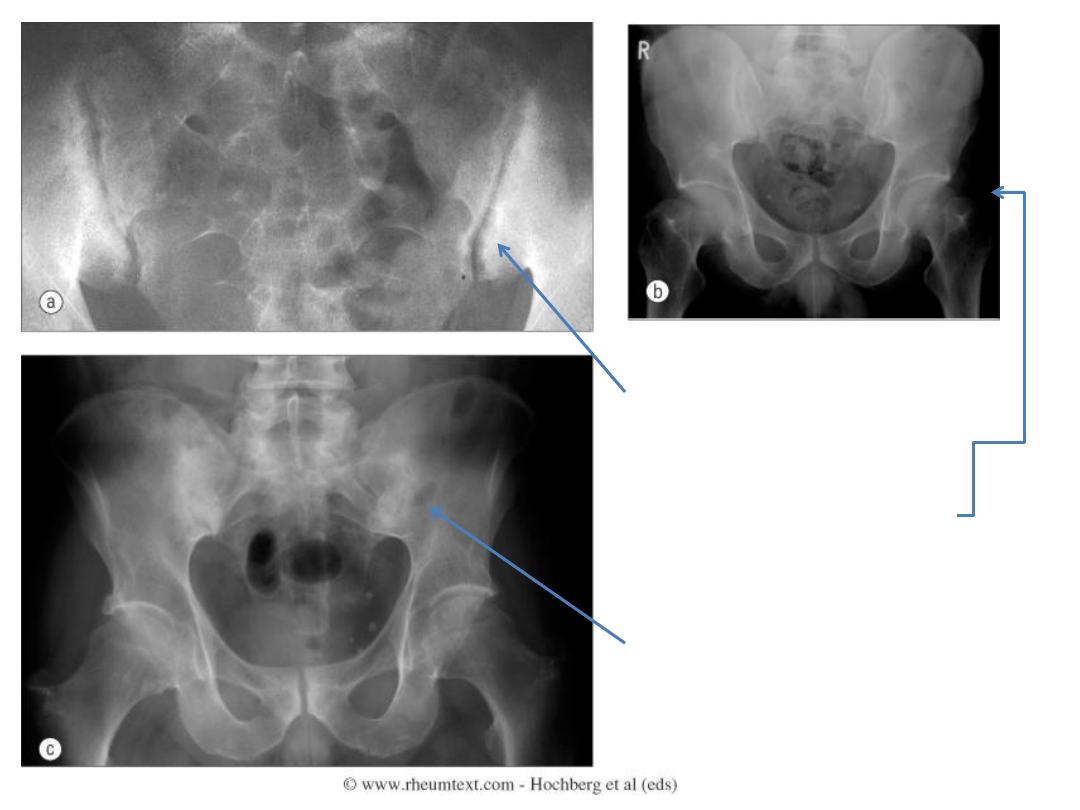
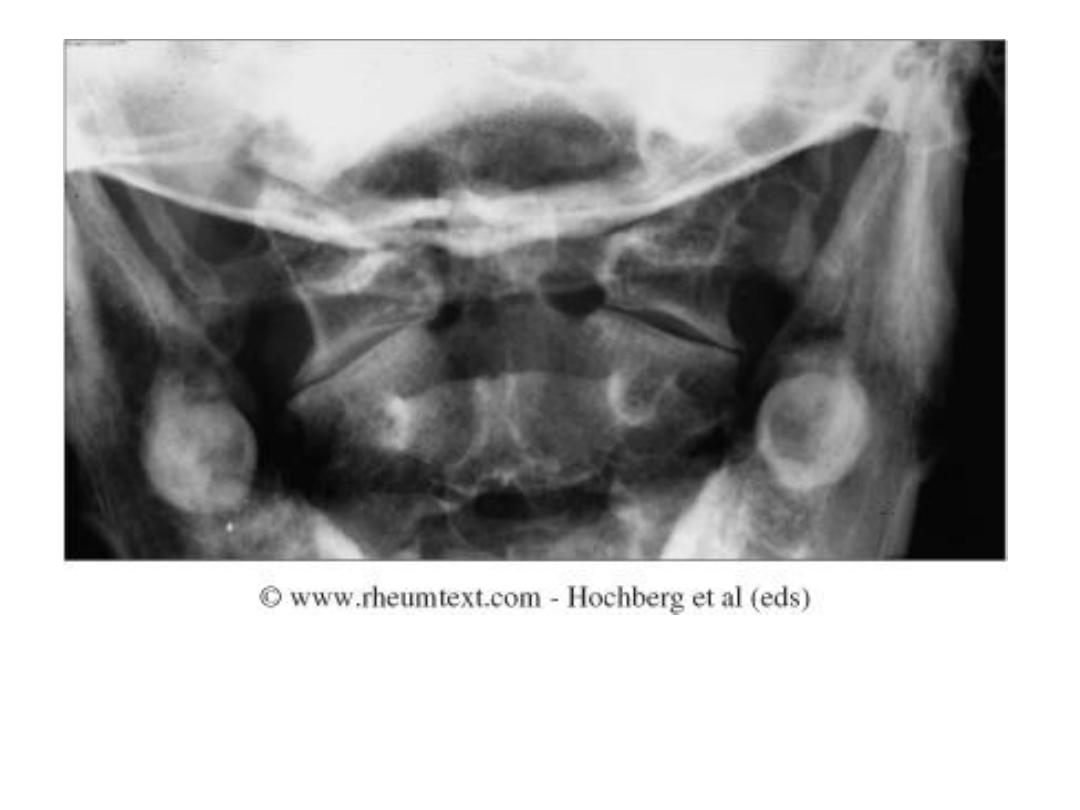
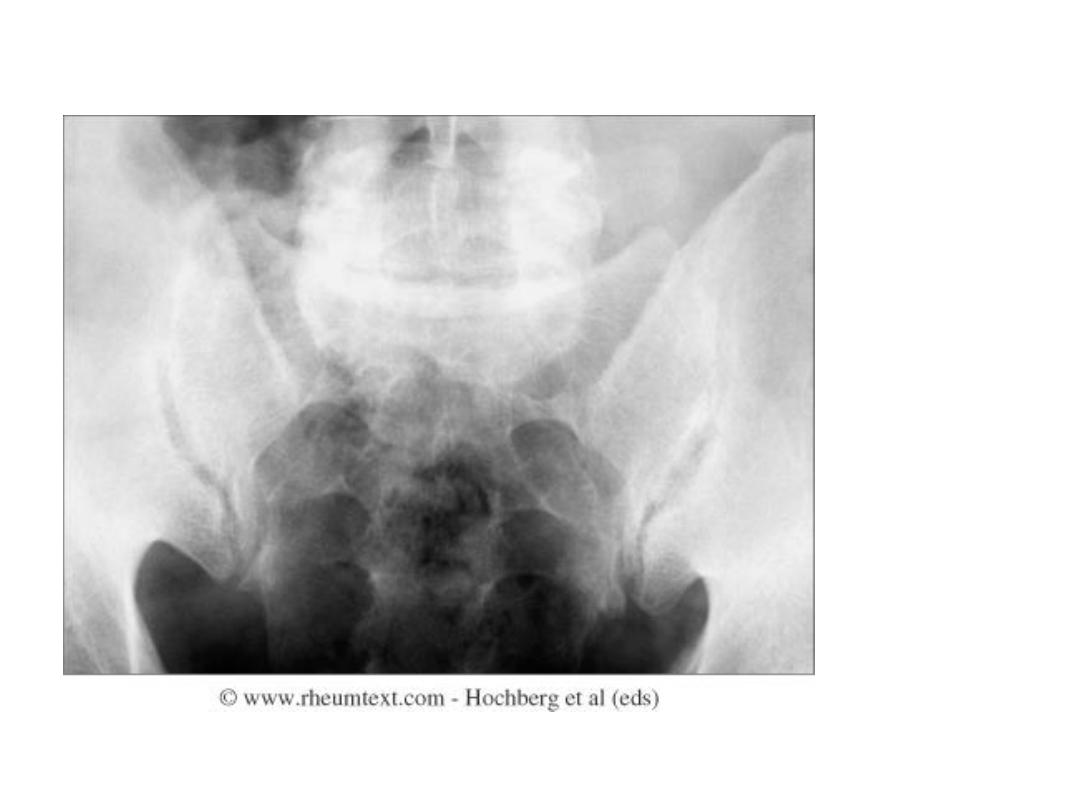
Erosions and sclerosis on iliac side
Bilateral sacroiliitis with
erosions, bony sclerosis and
joint width abnormalities
Bilateral sacroiliitis, definite
erosions, severe juxta-
articular bony sclerosis and
blurring of the joint
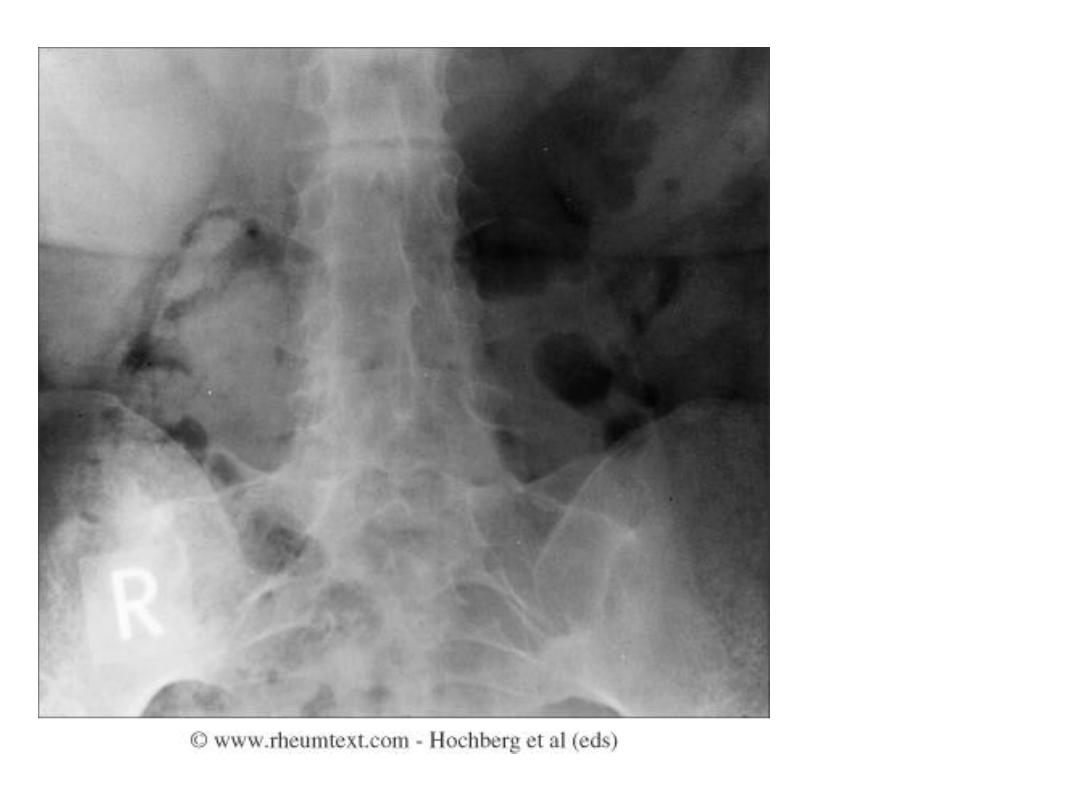
Advanced AS
Fused sacroiliac
joints
Ankylosis of the
lower lumbar
spine (bamboo
spine)


Gout
• Erosions and masses, especially in the peripheral
joints
• Masses may be dense, due to crystals or
associated calcification
• Erosions are juxtaarticular from adjacent soft
tissue tophi or intraosseous crystal deposition
– Appear rounded with a well circumscribed sclerotic
margin
• Deformity occurs early
• Olecranon and prepatellar bursitis may calcify
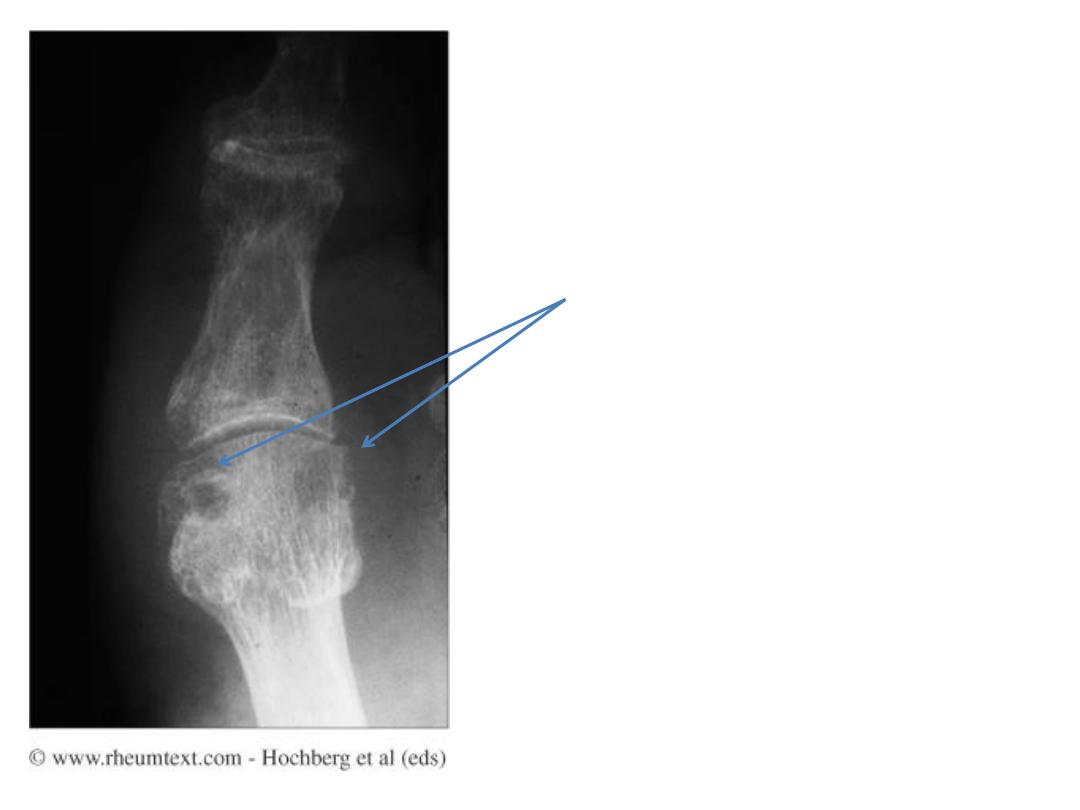
Gouty changes in the big
toe
Erosions due to tophi
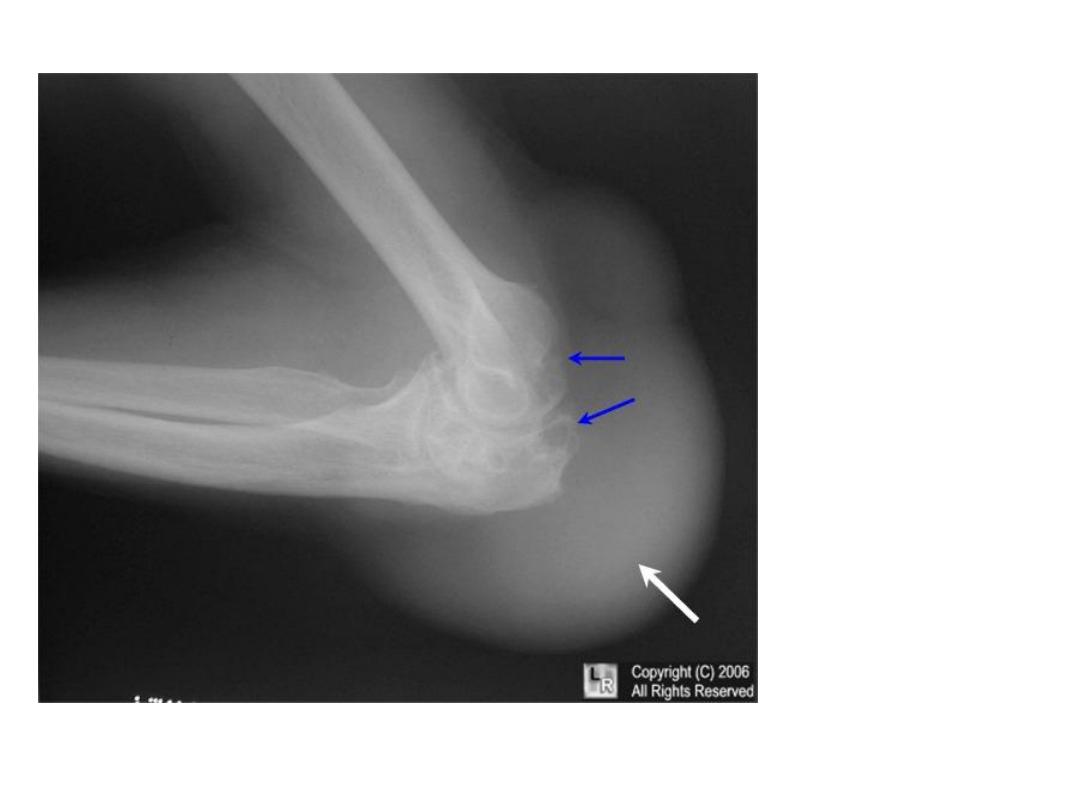
Olecranon
bursitis with
erosions due to
gout
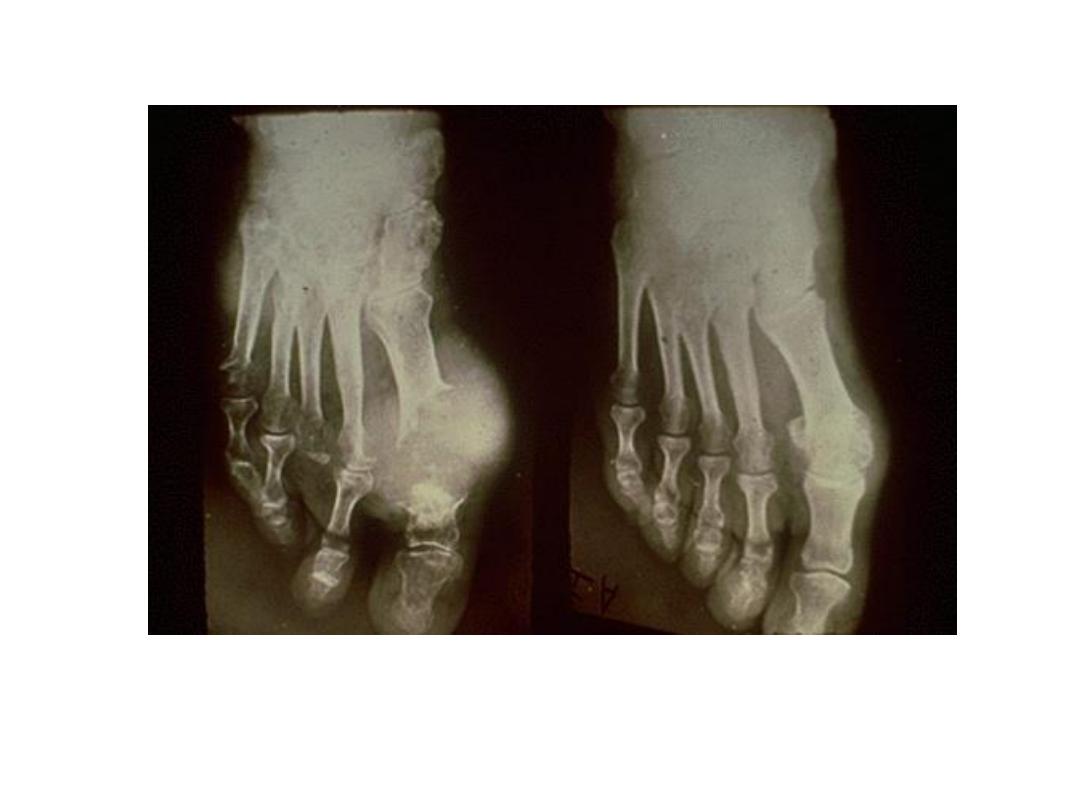
Large, destructive tophus of first MTP

Pseudogout (CPPD)
• Usually manifests as OA in an
unusual
distribution
• Prominent osteophytes
• Soft-tissue calcification in the joint capsule,
synovium, bursa, tendons, ligaments,
periarticular soft tissues
• Chondrocalcinosis
(cartilage calcification)
• No erosions
• Subchondral cysts are prominent
• No periosteal reaction or new bone formation
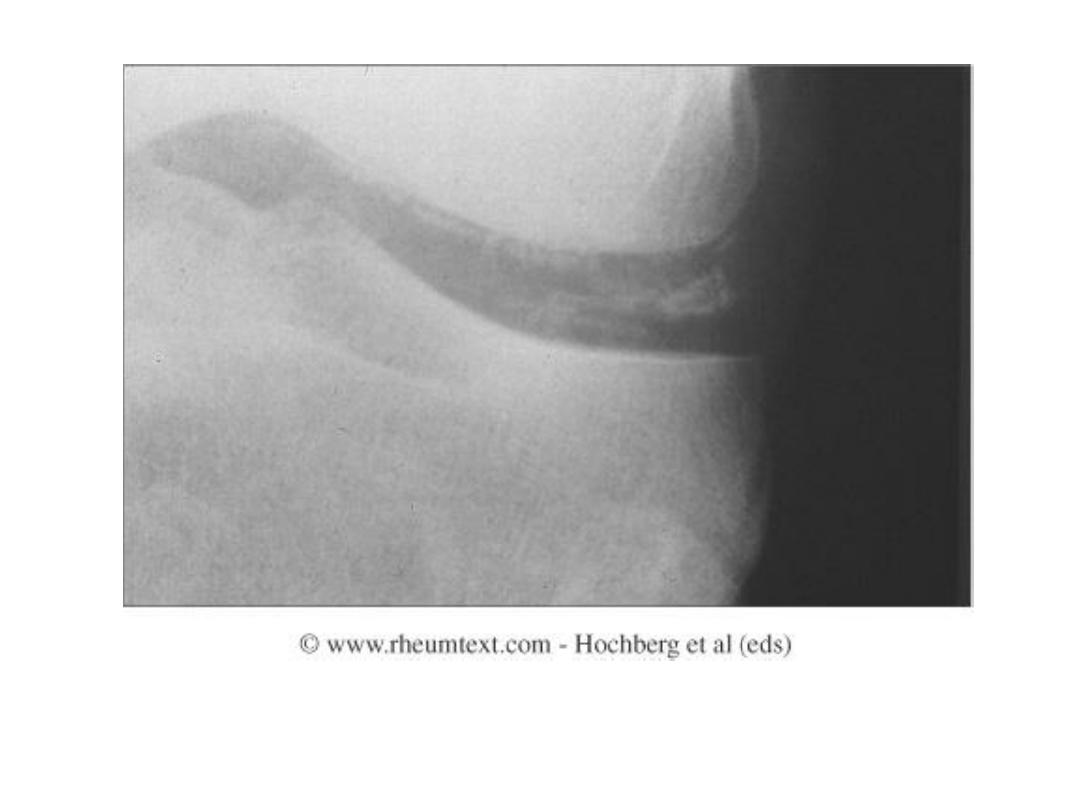
Chondrocalcinosis
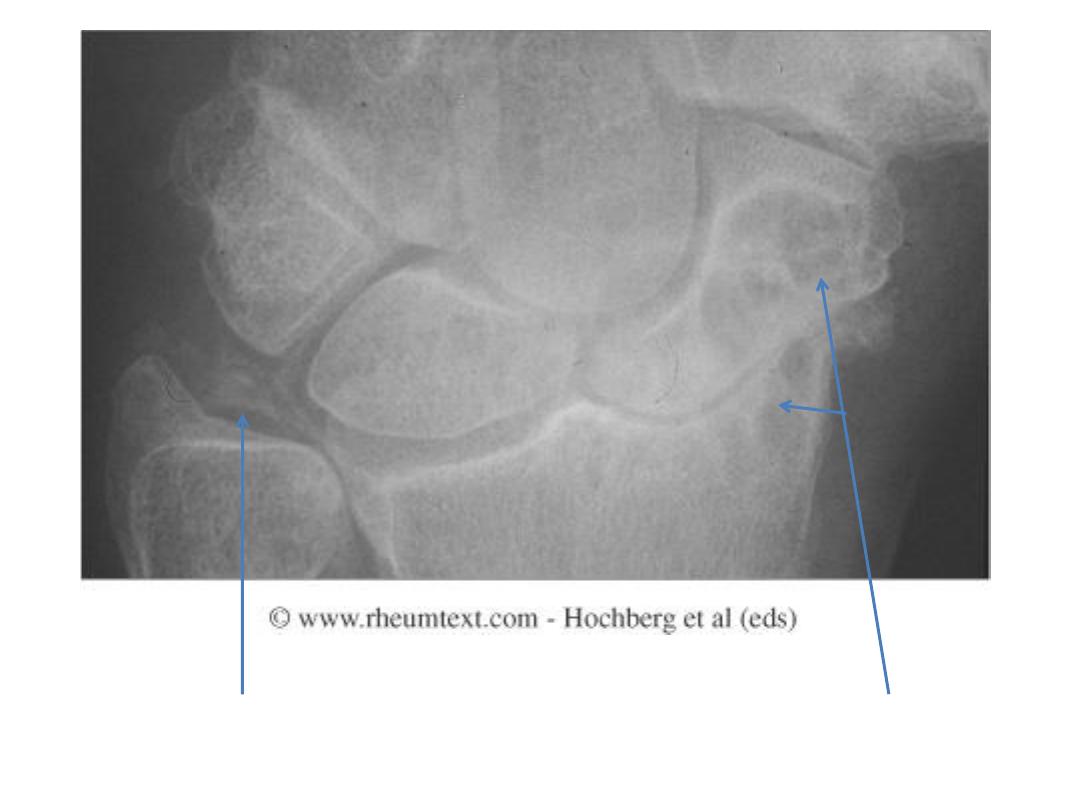
Multiple cysts
Chondrocalcinosis of the
triangular ligament

thank you
