MSK series

osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is defined as a condition
characterized by diminished but otherwise
normal bone.
(T-score of –2.5 or less) as measured with dual-
energy x-ray absorptiometry(DEXA).

An osteoporotic state may arise either when
bone
formation is inadequate
or when bone
resorption exceeds bone formation
.
Osteoporosis may be a
local
phenomenon (as in
disuse osteoporosis) or a
generalized
condition.

CAUSES
Primary/senile osteoporosis
– Most common, increased
risk with low body weight, Postmenopausal
Secondary osteoporosis (5%)
– From
-
drugs
(cortisol/steroids, heparin)
-
congenital
(OI, homocystinuria,)
-
endocrine disorders
(hyper/hypo-thyroidism,
hyperparathyroidism, Cushing’s disease)
-
GI
(malnutrition, malabsorption,vitamin C/D deficiency)
-
immobilization
.
يهببعسث

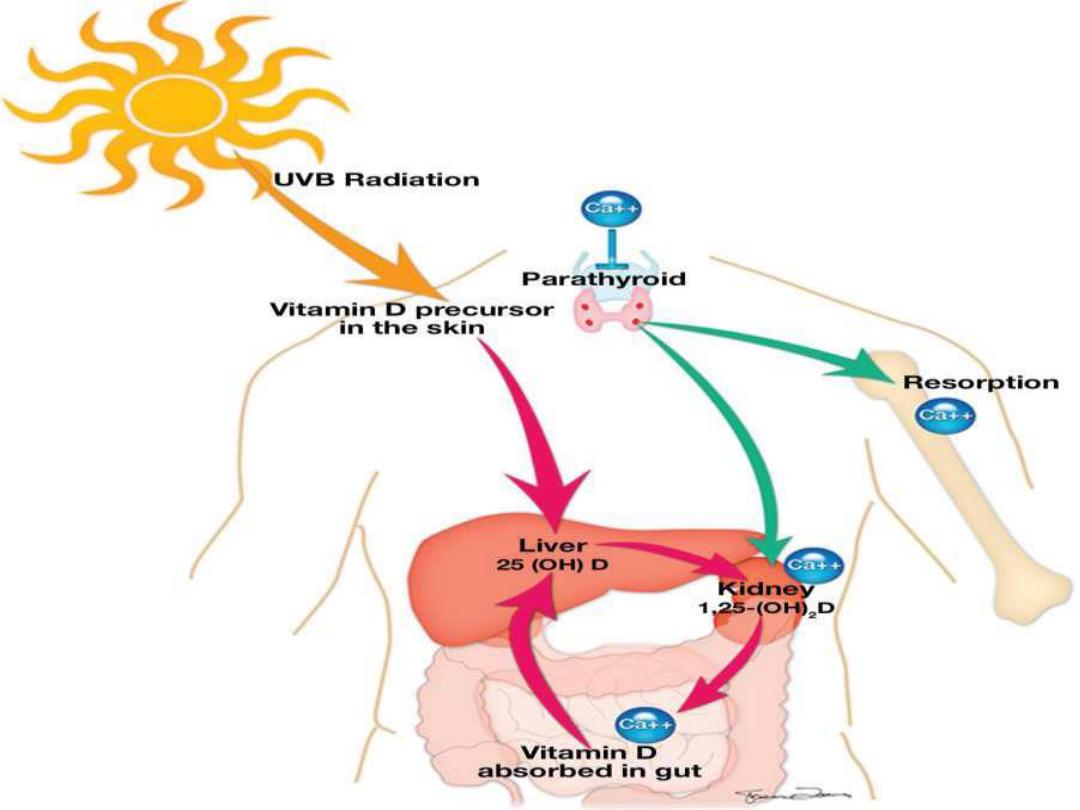
Rickets and osteomalacia
Rickets is the interruption of orderly
development and mineralization of growth
plates.
Osteomalacia is inadequate or abnormal
mineralization of osteoid in cortical and
trabecular bone.

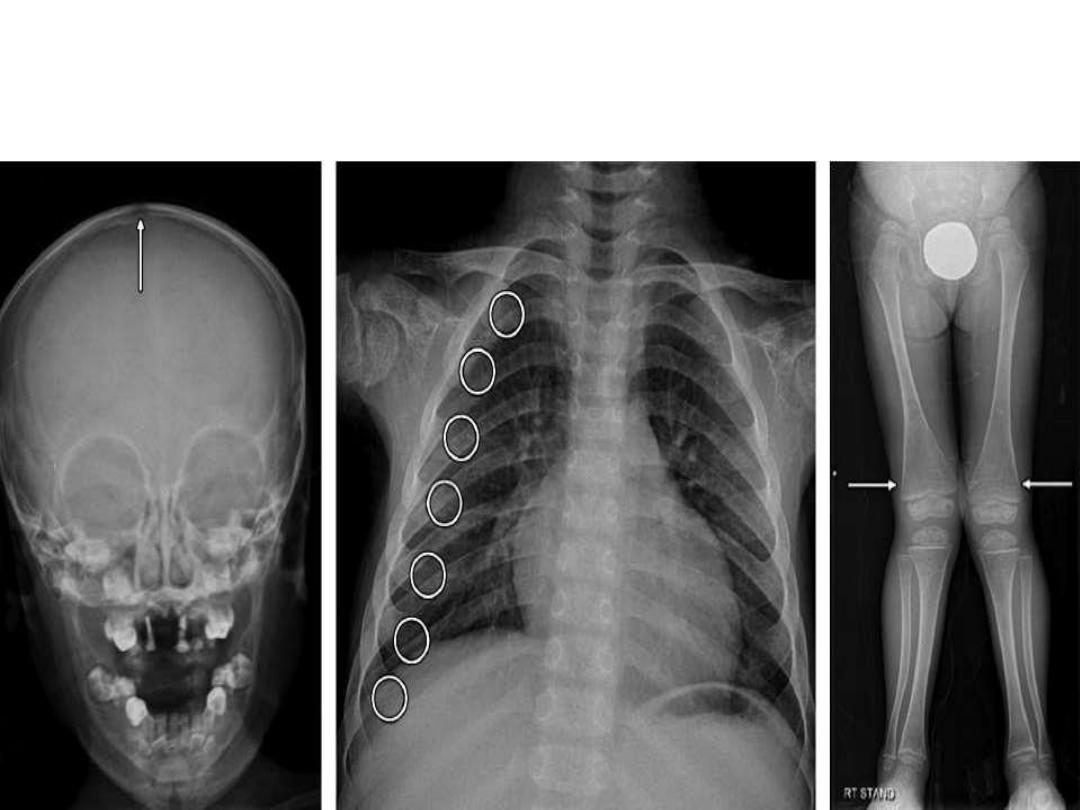
Radiographic findings of Rickets
Extremity
: Widened growth plate;
irregularity and osteopenia along
metaphyseal side of growth
plate; fraying , bowing.
Chest
: Rachitic rosary
Skull
: Flat occiput, widened
sutures, basilar invagination
RICKETS
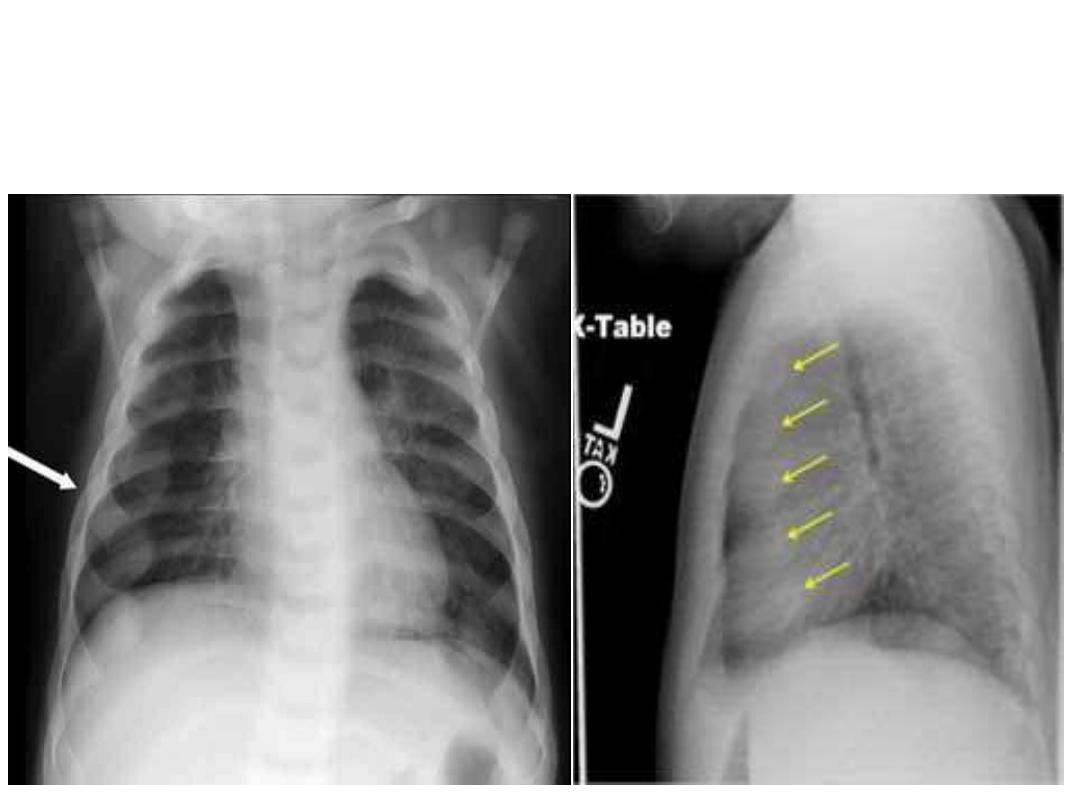
Rachitic Rosary-enlarged costochondral junctions of
the ribs in rickets resembling a string of rosary beads.
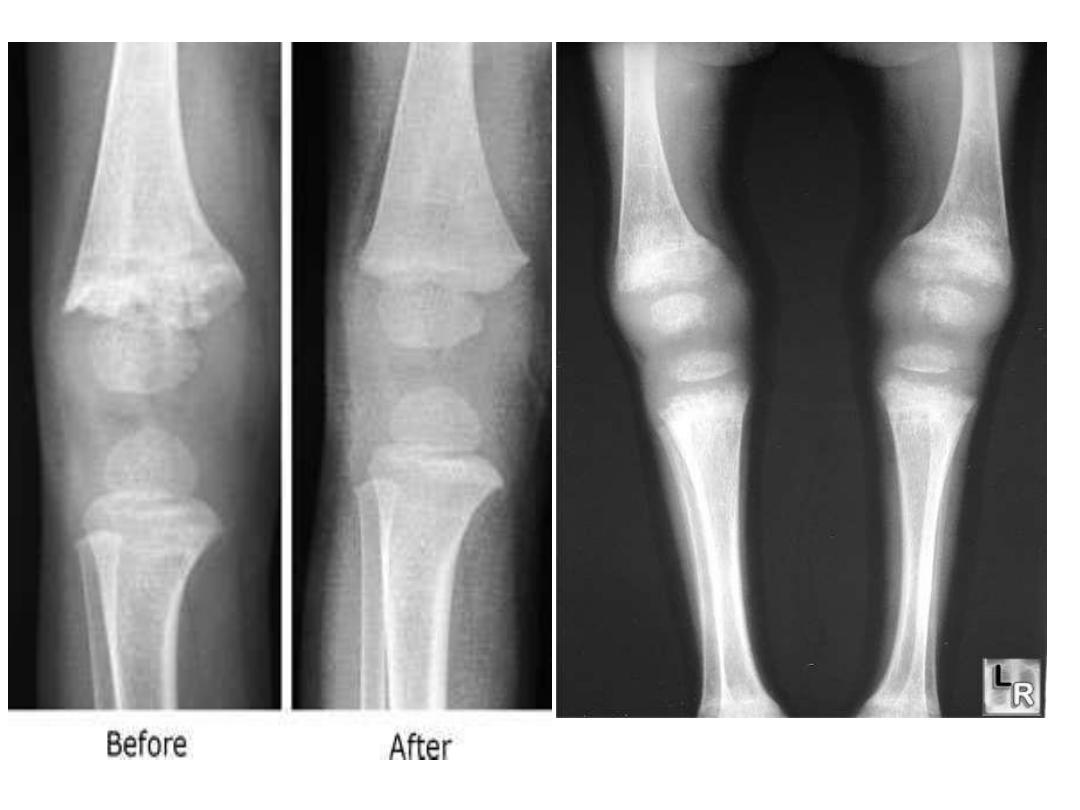
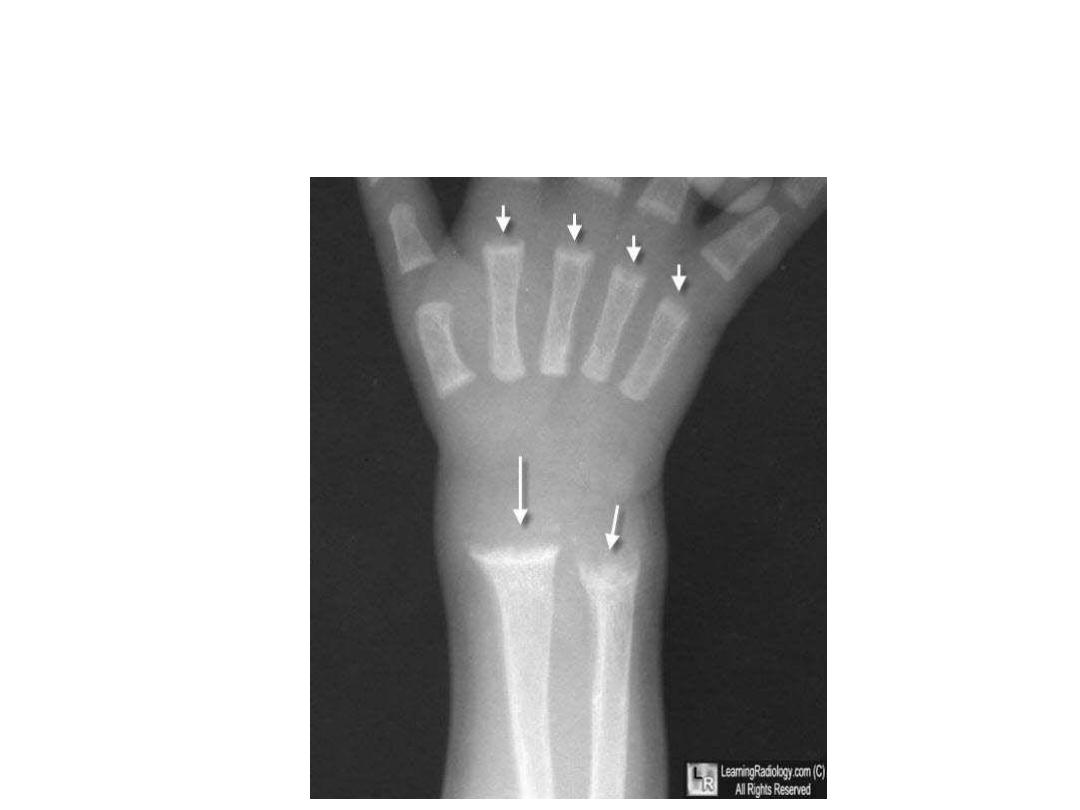
Rickets. There is cupping and fraying of all of the metaphyses
(white arrows) in this skeletally-immature child.

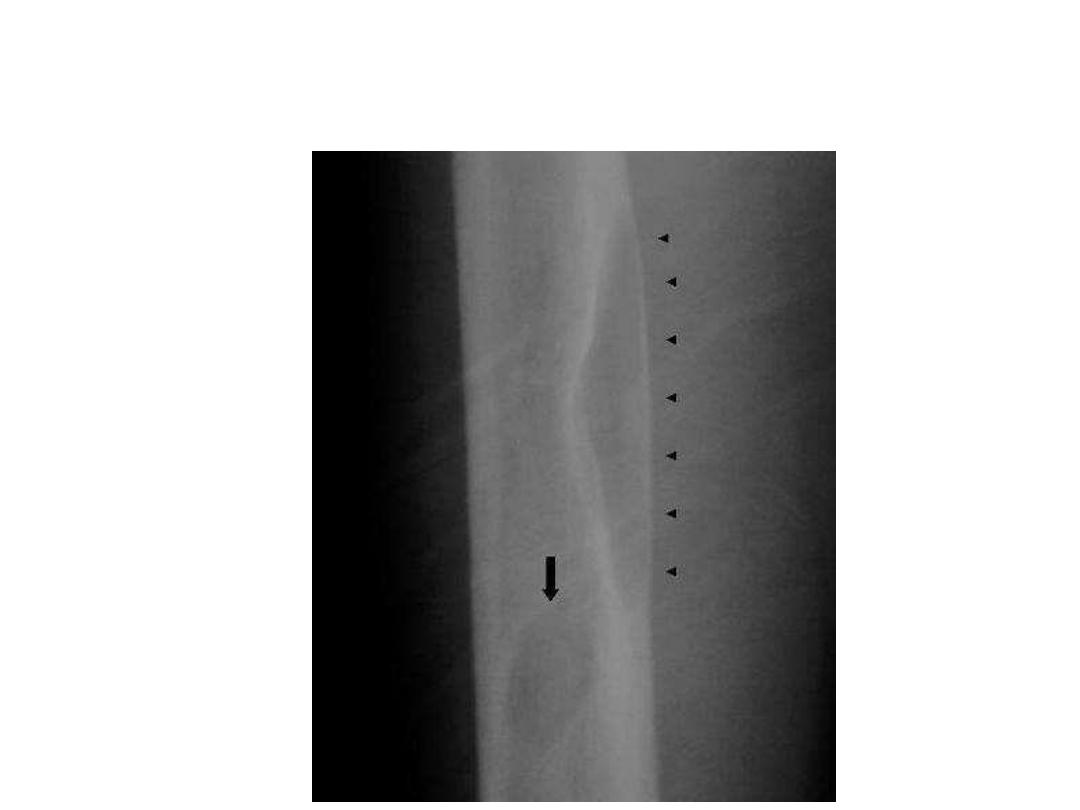
- Looser zones are distinctive feature of osteomalacia.
- Looser zones are the result of deposition of
unmineralized osteoid at sites of stress .
-
- zones can occur with
no or minimal trauma,
are
often bilateral and symmetric, and appear as
transverse lucent bands oriented at
right angles to
the cortex
that only span a
portion
of the bone
diameter.
- Although known as
pseudofractures
, Looser zones are
a type of insufficiency fracture
.

Some of the common locations of Looser zones
are similar to those of stress fractures, such
as:
- inner margin of the femoral neck
- pubic rami
- lateral scapula
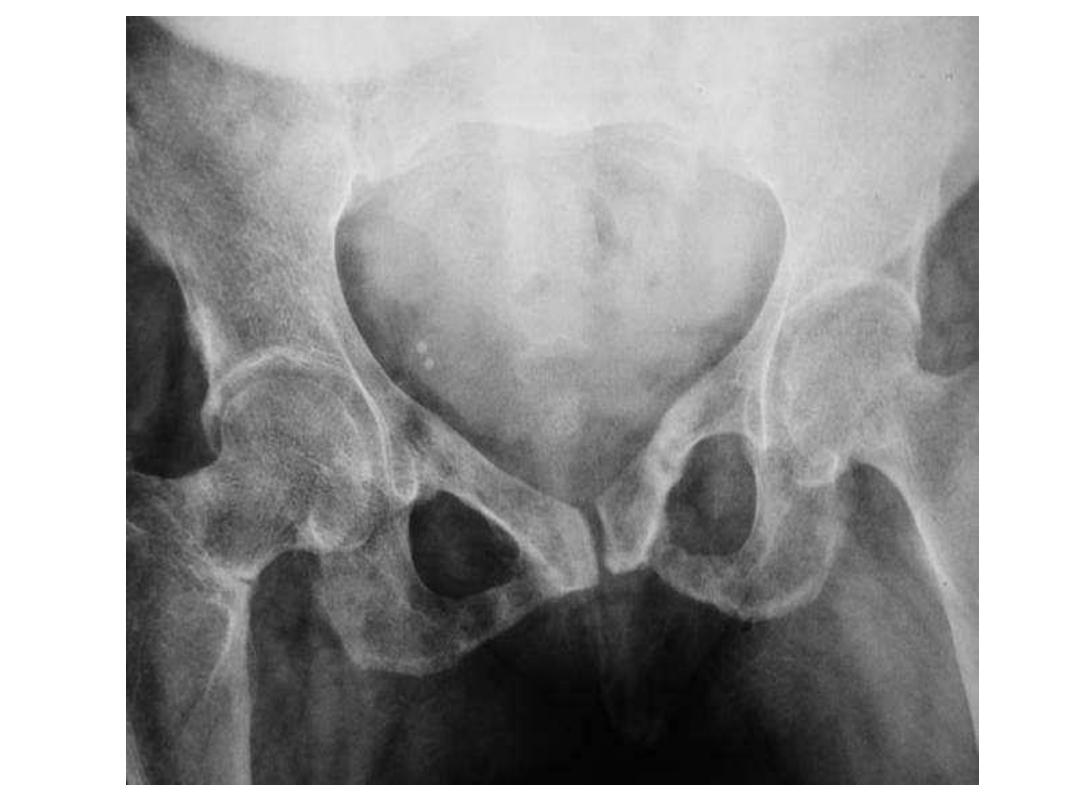
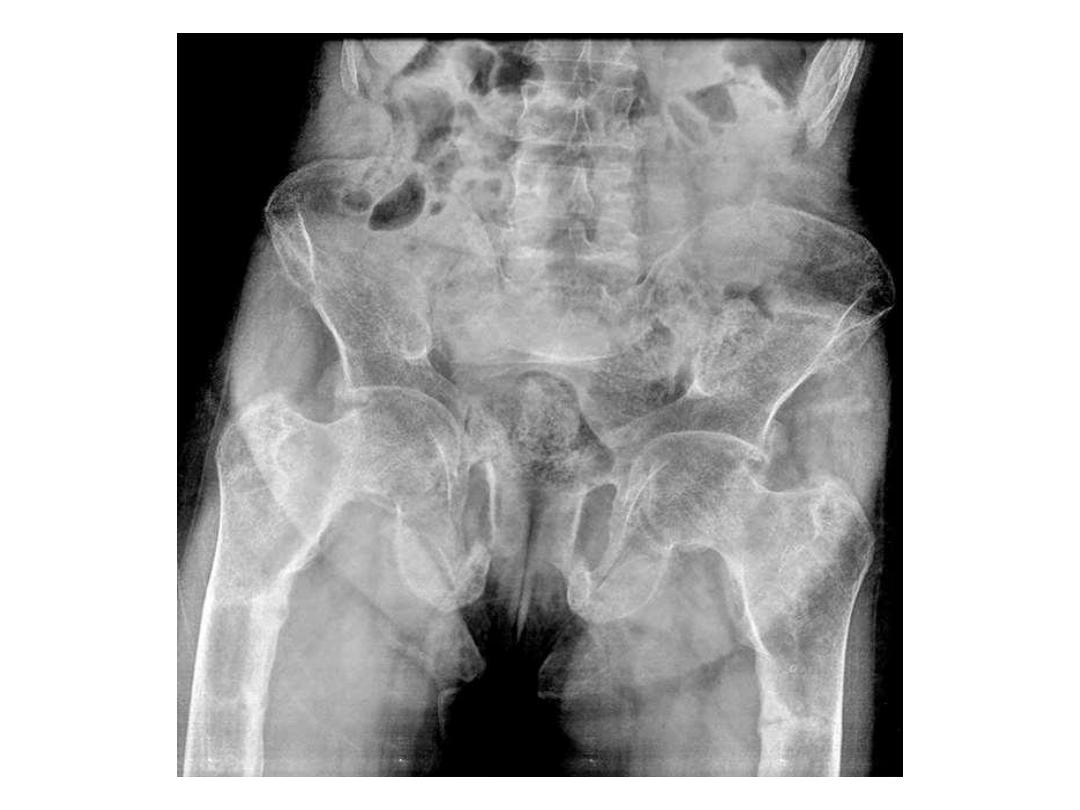
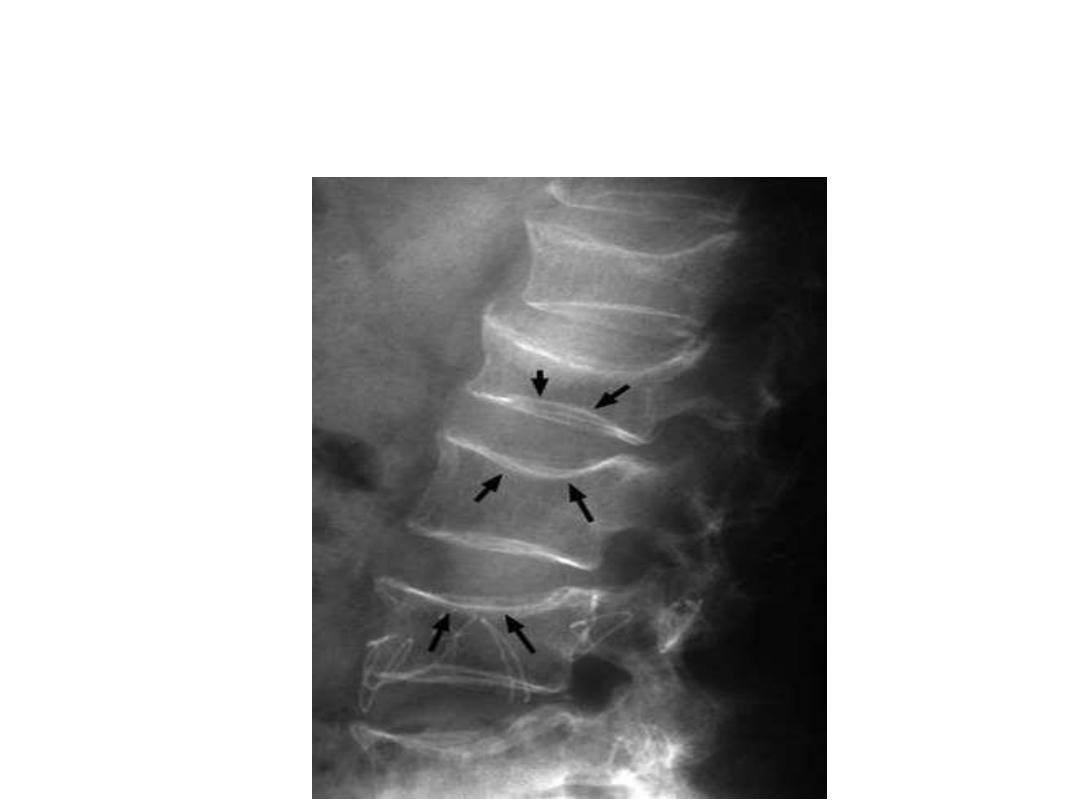
Osteomalacia with biconcave (fish vertebra) with endplate
depression.

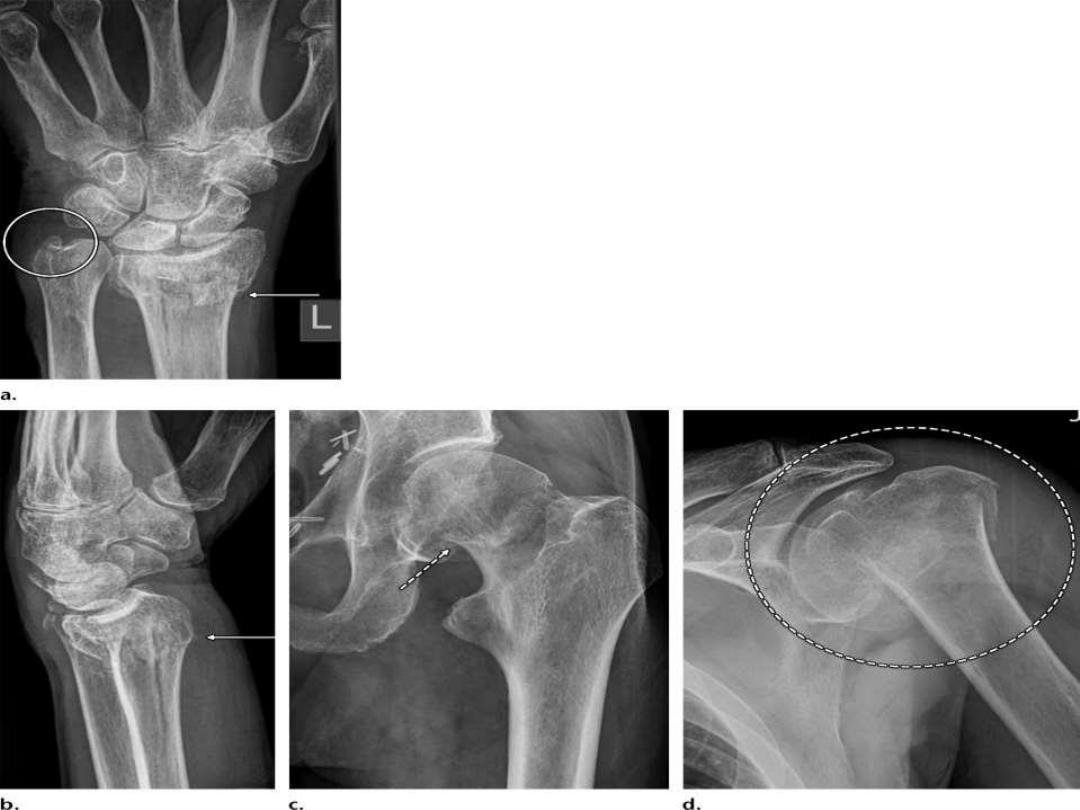
Hyperparathyroidism
- Hyperparathyroidism is a pathologic state of elevated
parathyroid hormone concentrations, which causes
increased bone resorption.
- Primary hyperparathyroidism is a state of
autonomous
parathyroid hormone secretion by the parathyroid
glands and lack of feedback inhibition by serum
calcium.
- Primary hyperparathyroidism is usually caused by a
parathyroid adenoma
, but in approximately 10% of
cases, it is a result of
four-gland hyperplasia
, and in
extremely rare cases, primary hyperparathyroidism is
due to
parathyroid carcinoma

Secondary hyperparathyroidism
Secondary hyperparathyroidism is more
common than primary hyperparathyroidism
and is a
response to low serum calcium
levels.
The most common cause is
chronic renal
failure .
Secondary hyperparathyroidism can also be
observed in vitamin D deficiency and dietary
calcium deficiency .

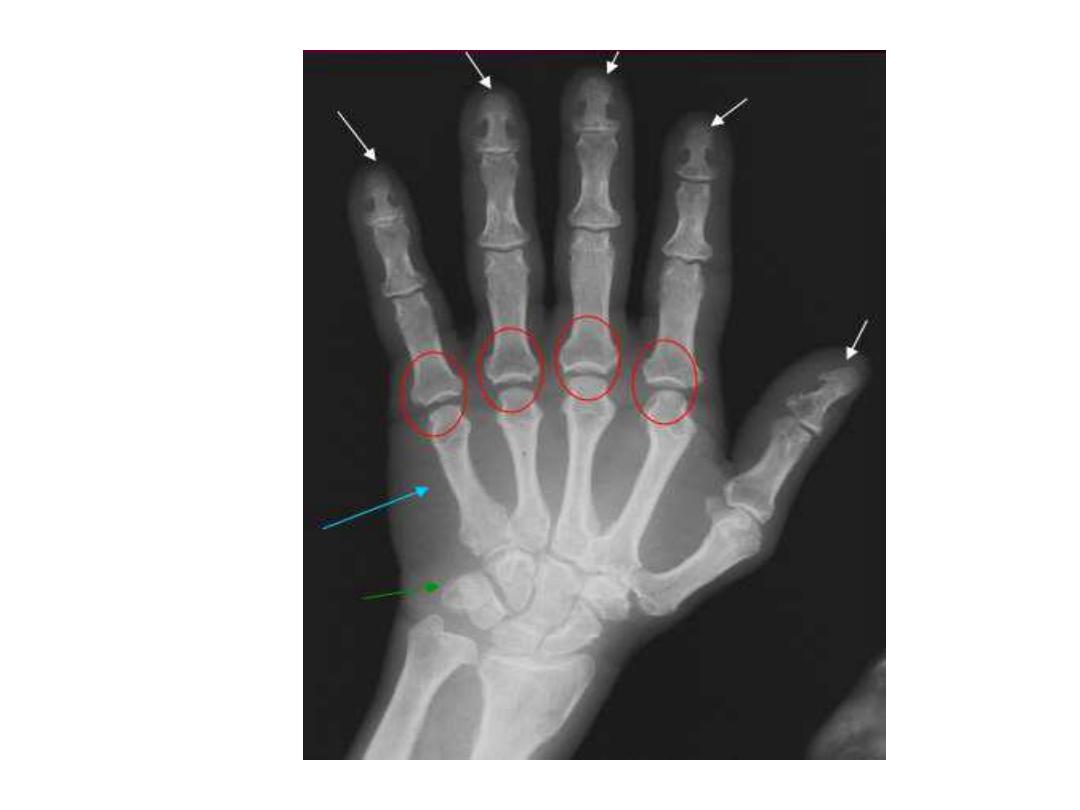
Skeletal manifestations
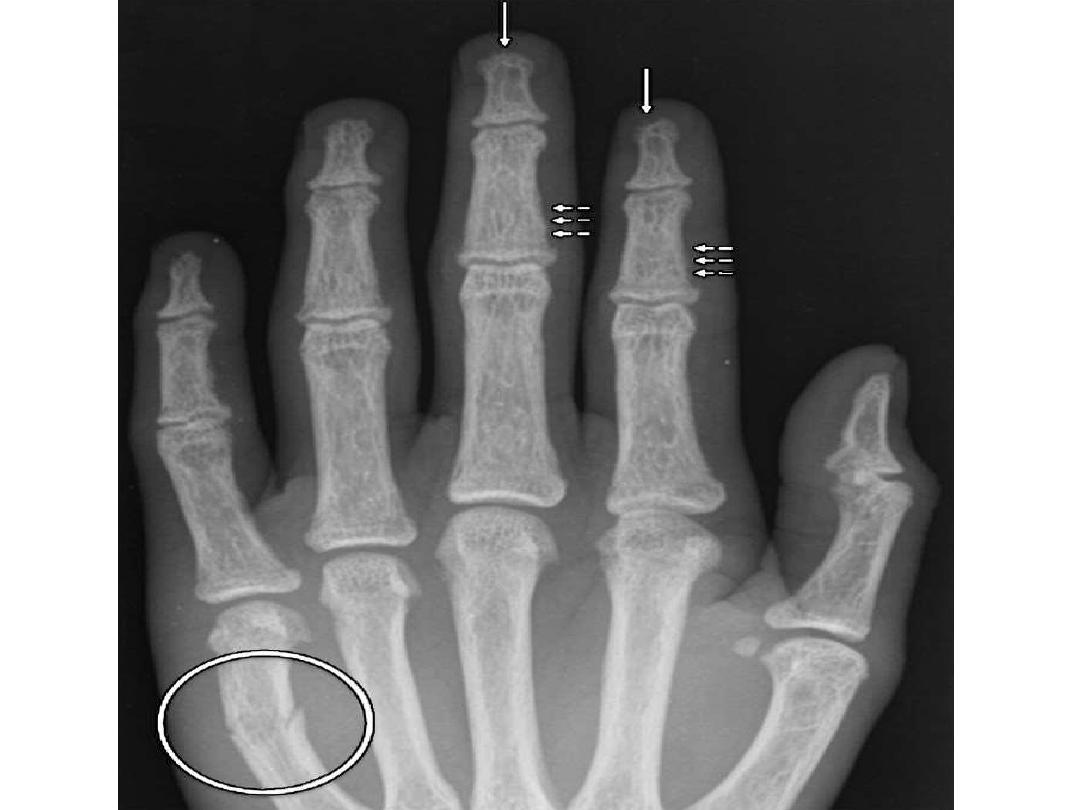
- In 95% of patients with hyperparathyroidism, skeletal
findings are most readily recognized in the hand.
- The pathognomonic
subperiosteal bone resorption
in
hyperparathyroidism begins at the radial aspects of the
middle phalanges of the middle and index fingers as
and at the distal phalangeal tufts as
acro-osteolysis
.
- Subperiosteal resorption can also be observed in the
ribs,
loss lamina dura
(bone that surrounds the tooth
sockets), .
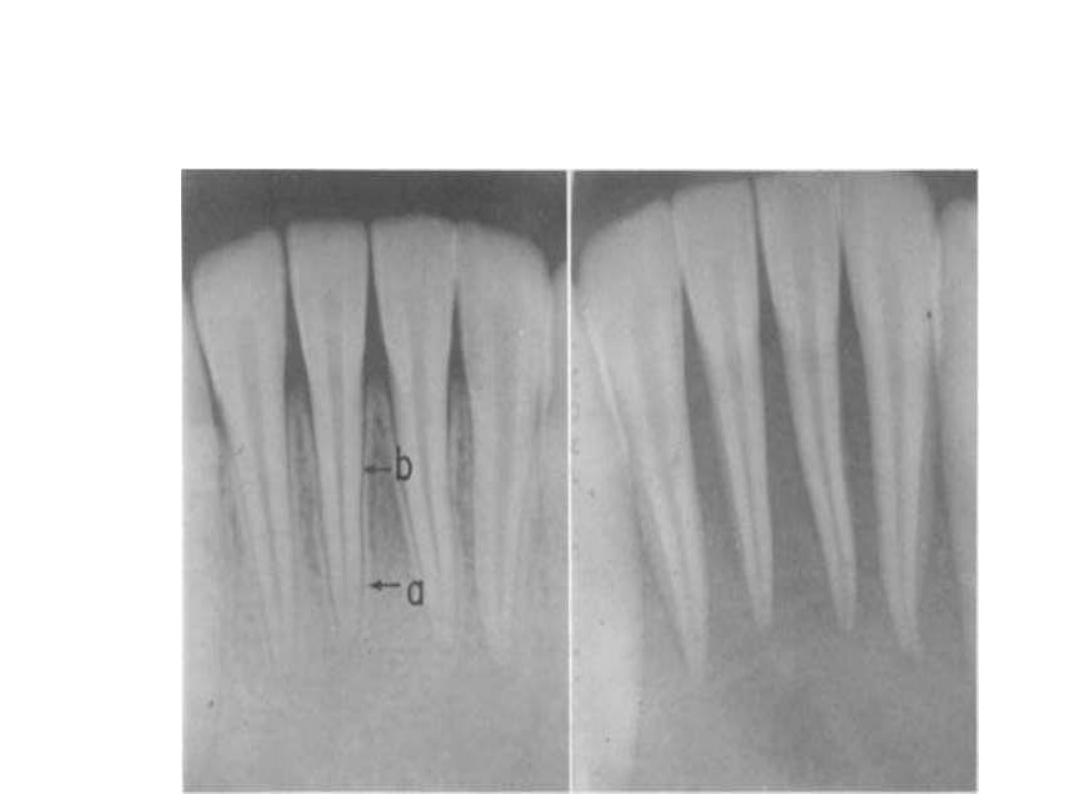
Loss of Lamina dura in Hyperparathyroidism.

- In the skull, bone resorption is described as a salt-and-
pepper appearance
- Brown tumors, also known as osteoclastomas, are lytic
lesions that result from the parathyroid hormone
activate osteoclasts.
- Brown tumors are generally solitary but can be
multifocal and are at risk for pathologic fracture.
- Brown tumors commonly involve the facial bones, ribs,
pelvis, and femoral bone
- Treatment of hyperparathyroidism may also lead to
resolution of brown tumors.
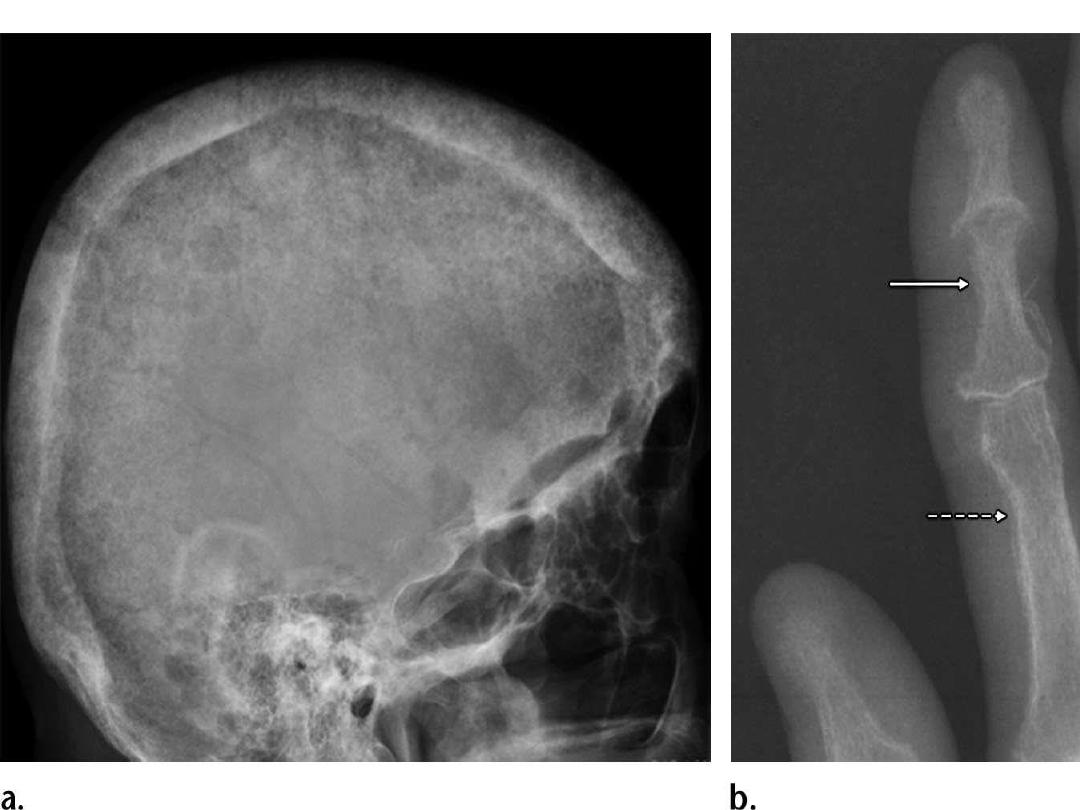
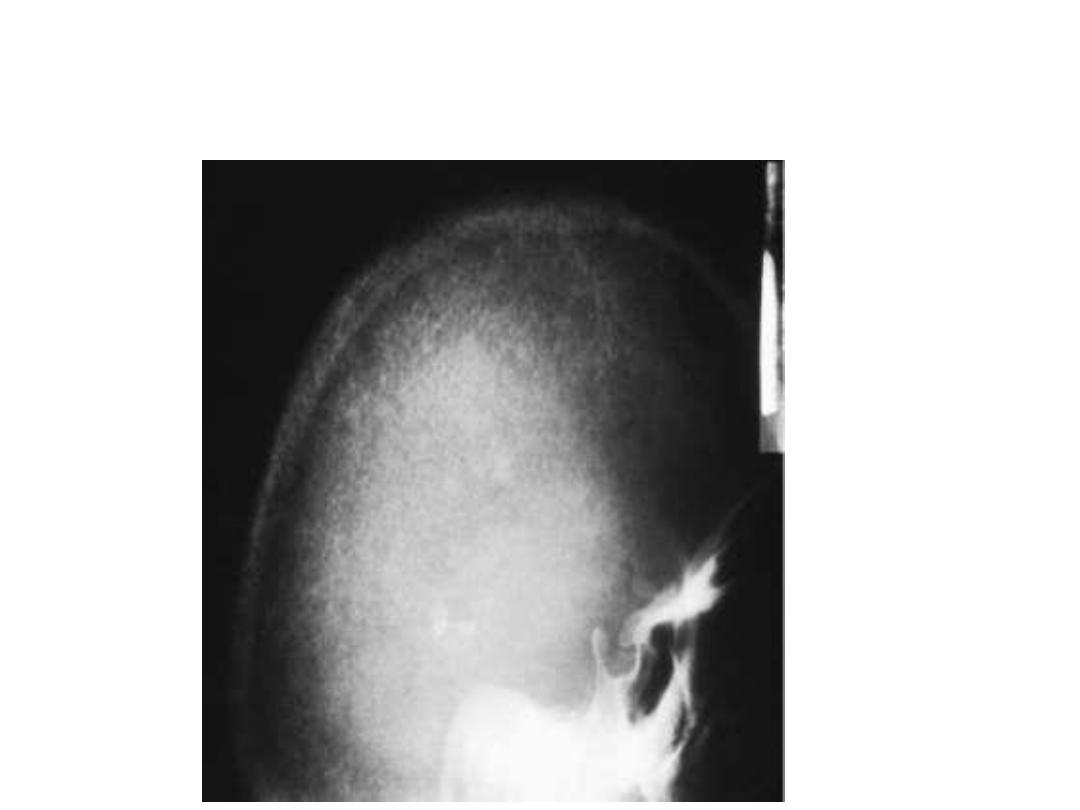
hyperparathyroidism the skull takes on a mottled or "pepper
pot" appearance.
Brown tumor

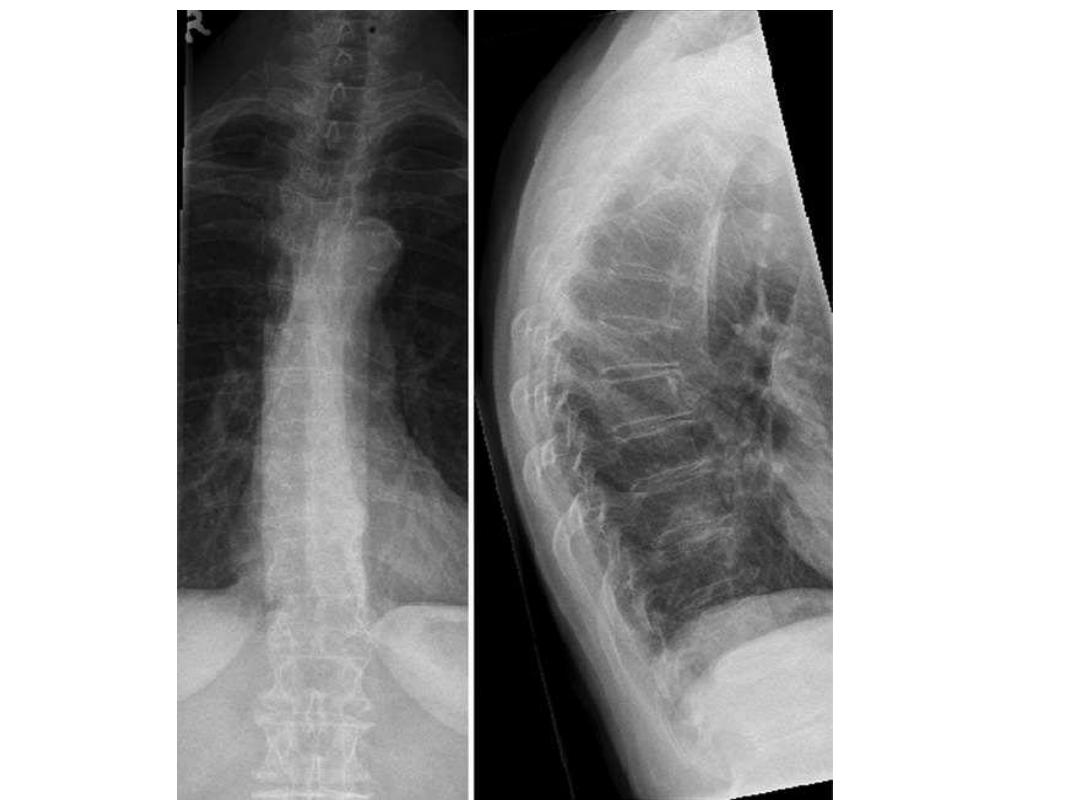
Renal osteodystrophy
- Renal osteodystrophy refers to the complex of findings
observed in the setting of chronic renal insufficiency
- These include the findings of:
osteomalacia
(and rickets
in children) and
secondary hyperparathyroidism
- In patients with chronic renal insufficiency, radiographs
may show a
diffuse increase in bone radiodensity
a finding
that is seen more often in the axial skeleton, which has
more trabecular bone than cortical bone .Despite the
increased radiodensity, the bone is structurally
weak
and
prone to stress fractures
.

- The spine often demonstrates a characteristic
striped
appearance (alternating bands of
increased density along the endplates and
decreased density in the central portion of the
vertebral body), which is also known as the
rugger-jersey spine
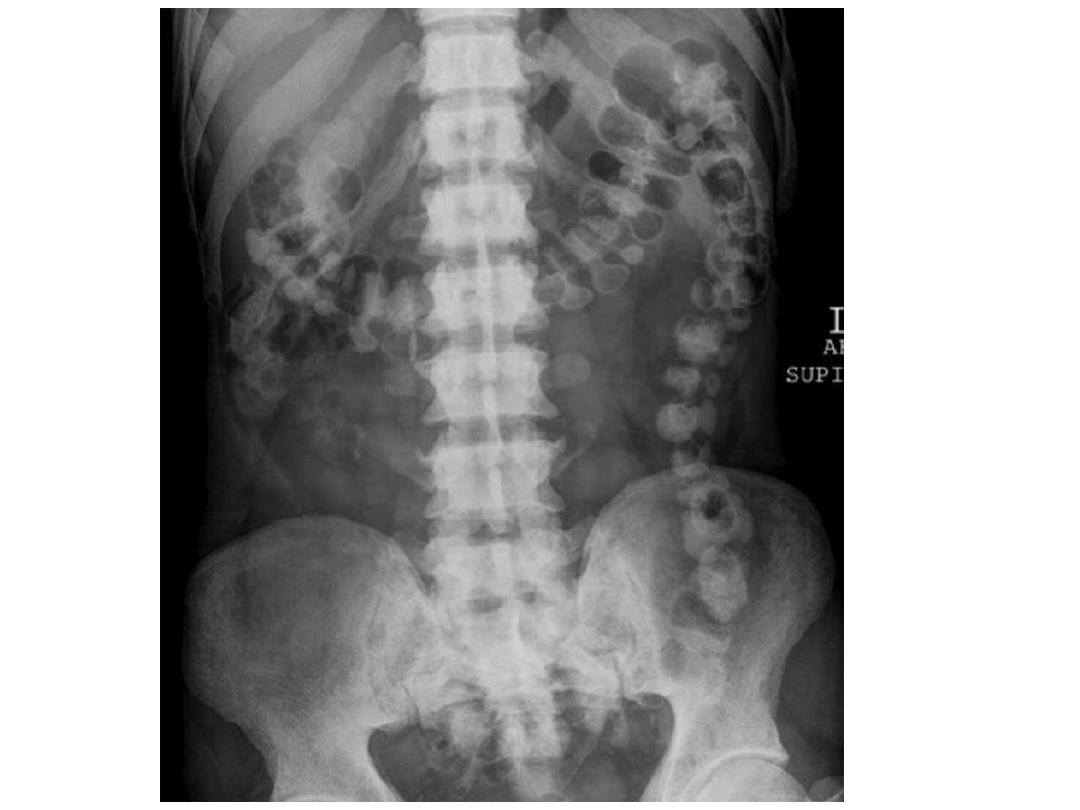
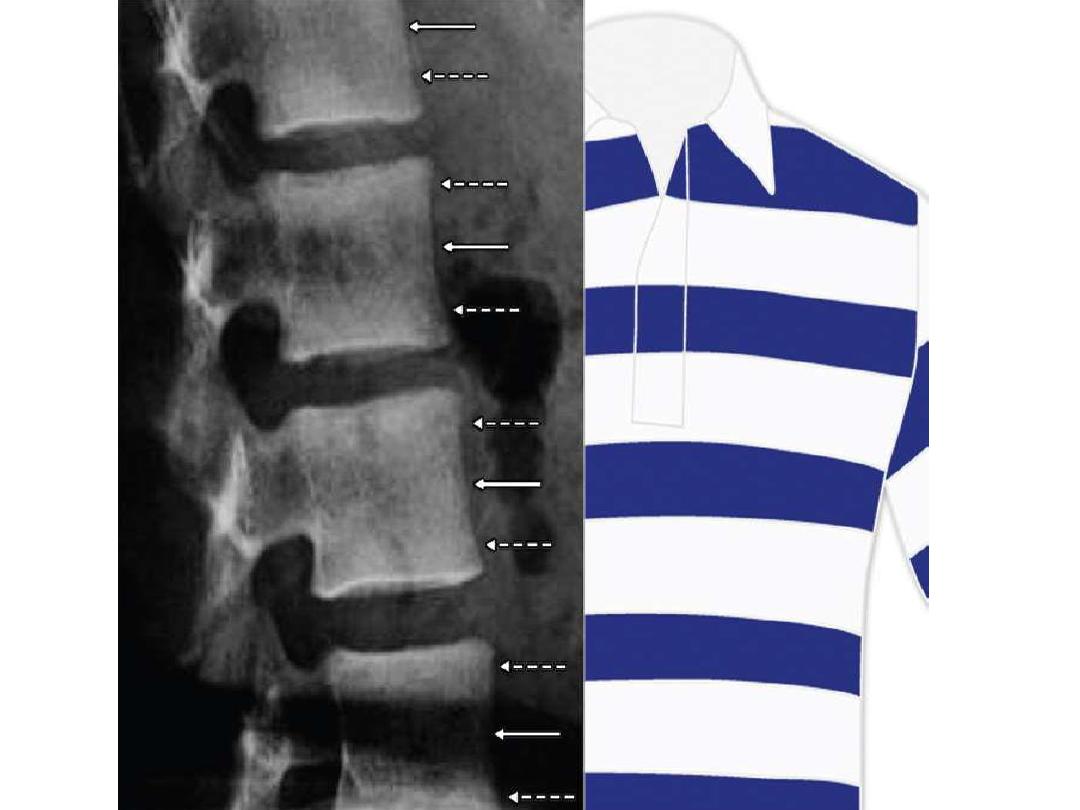

hypoparathyroidism
- Hypoparathyroidism is caused by iatrogenic injury to the
parathyroid glands during thyroid surgery or excision of
the parathyroid glands
- End-organ insensitivity to parathyroid hormone is called
pseudohypoparathyroidism
and has different radiographic
Findings
- Radiographic findings of Hypoparathyroidism reflect an
overall increase in bone mass, including
generalized or
localized osteosclerosis
and
thickening of the calvaria

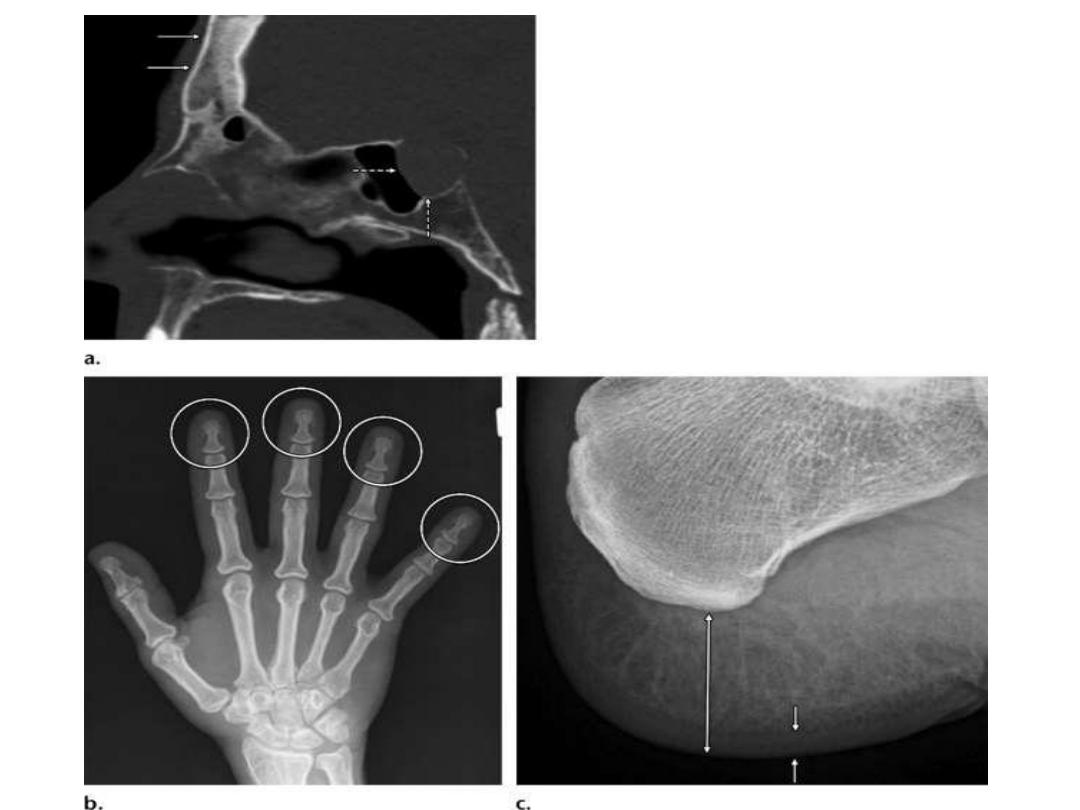
Acromegaly
- Acromegaly is due to excess growth hormone secretion
from the anterior lobe of the pituitary.
Radiographic Findings:
-
Hand
: Spade-shaped tufts, tubulation of phalangeal
shafts, exostoses, widened joint spaces, sesamoid
enlargement.
-
Feet
: Heel pad thickness > 25 mm in men and > 23 mm in
women, skin thickening, tendon insertion ossification
- Skull
:Thick skull bones; enlarged sella; frontal bossing;
prominence of frontal and maxillary sinuses,
, prognathism (protrusion of jaw); enlargement of the
mandible.