
.
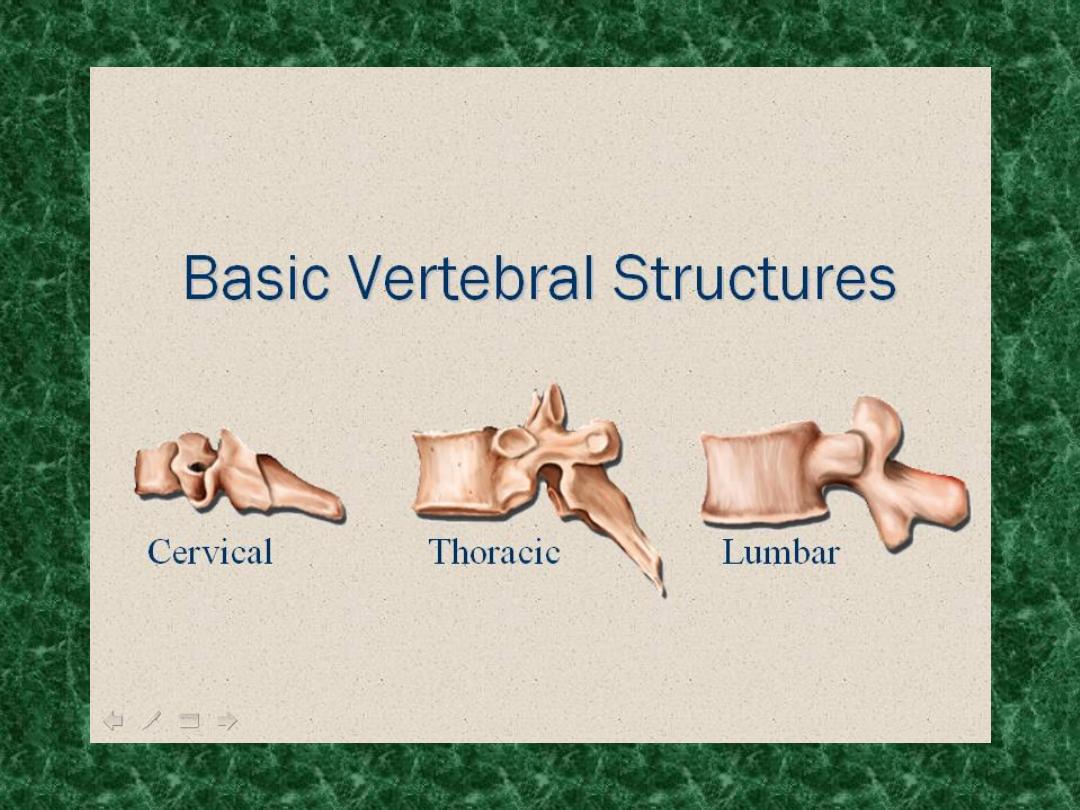
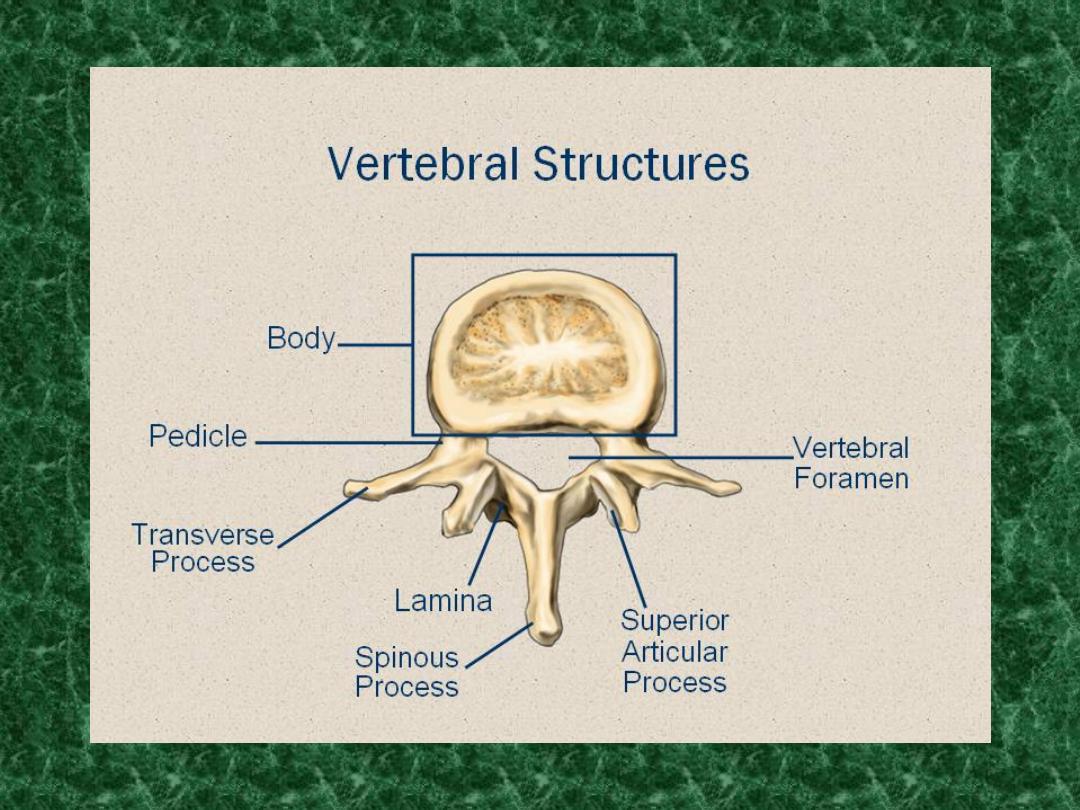
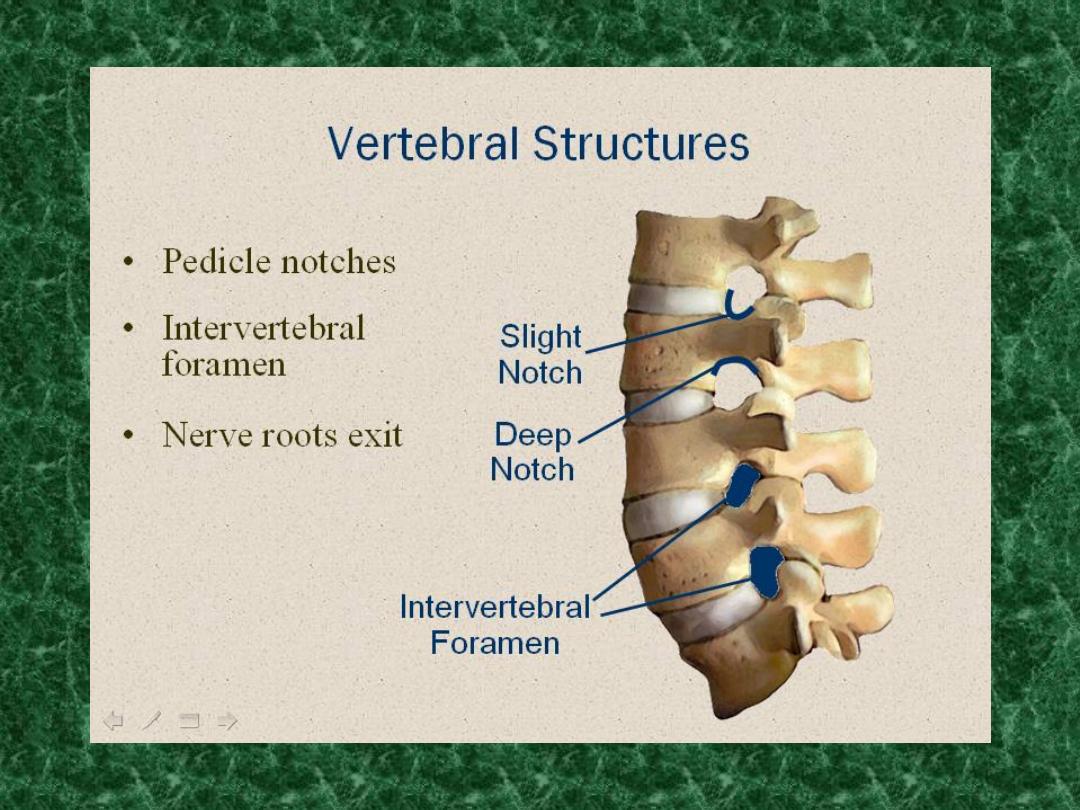
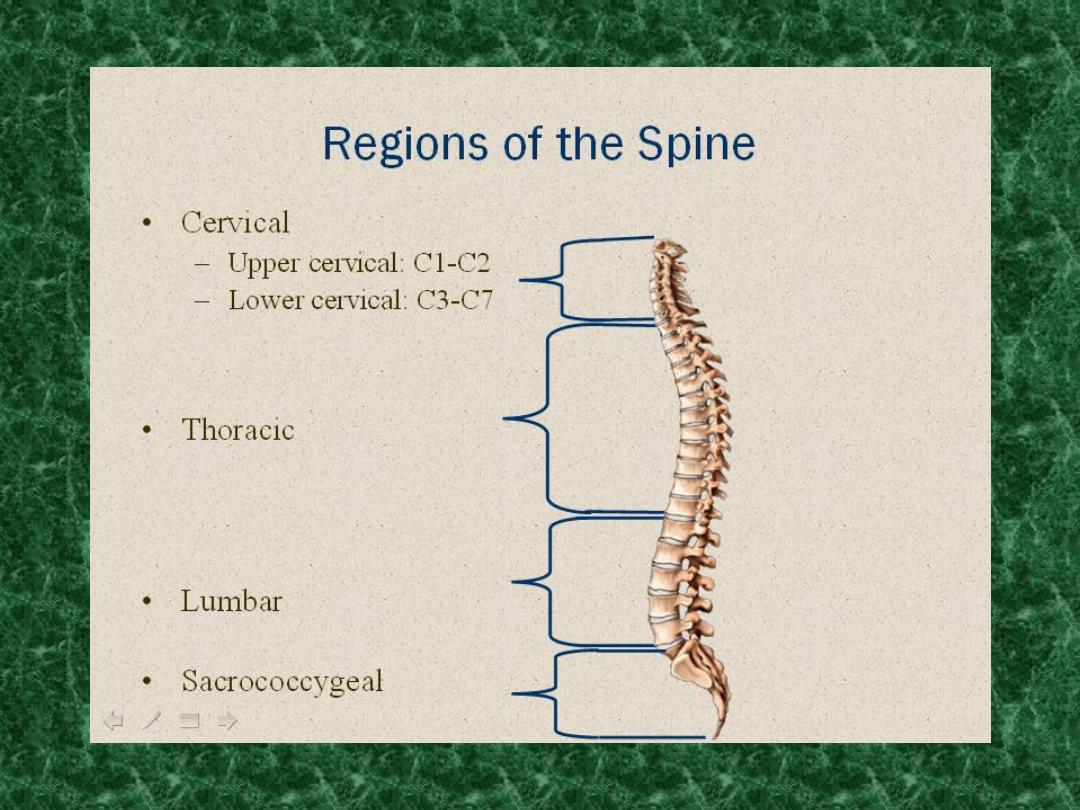
Anatomy of spine




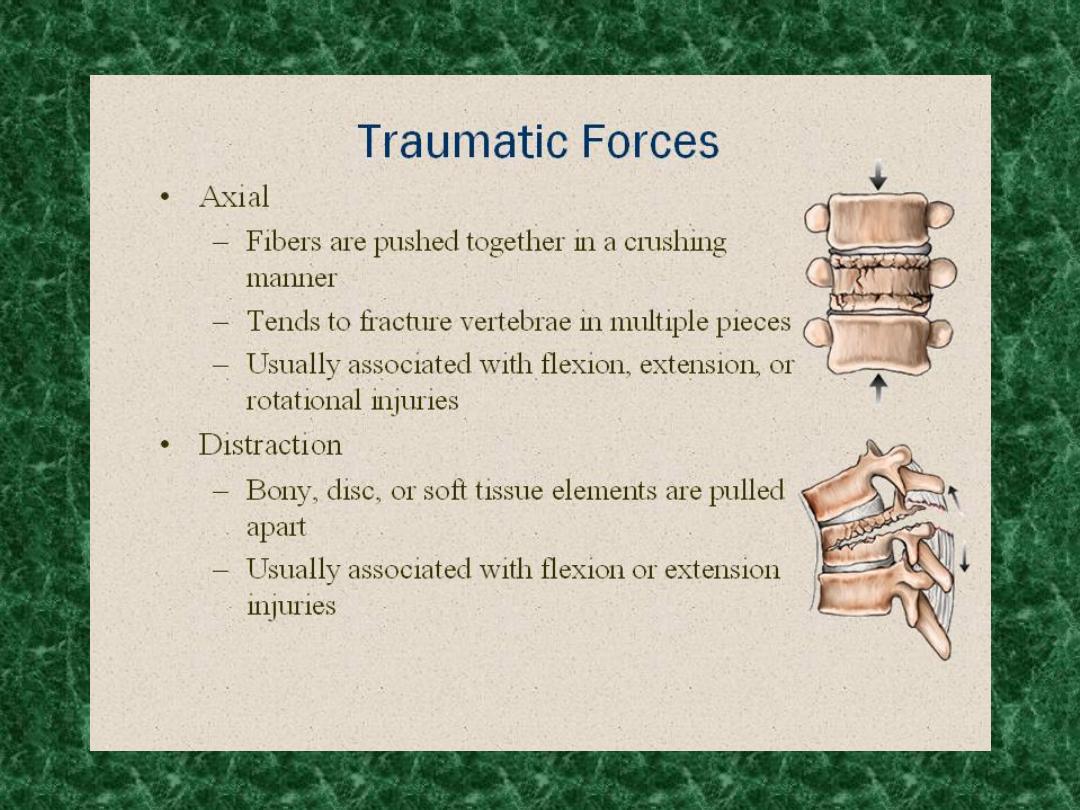
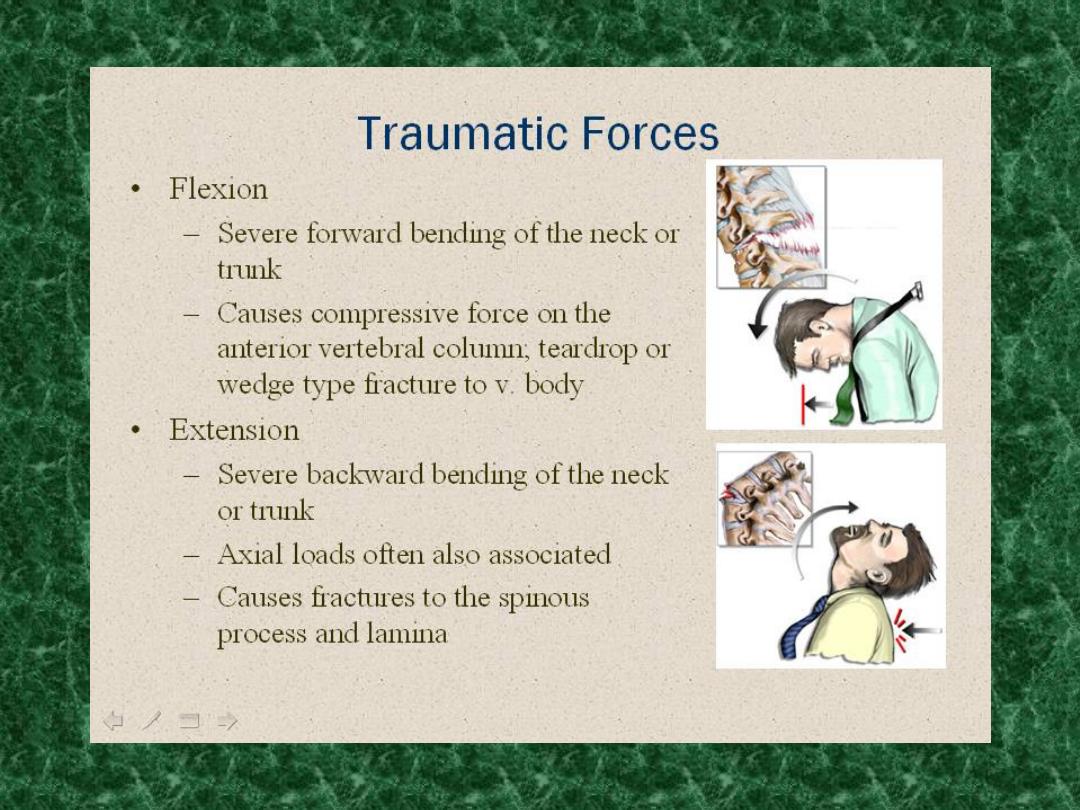
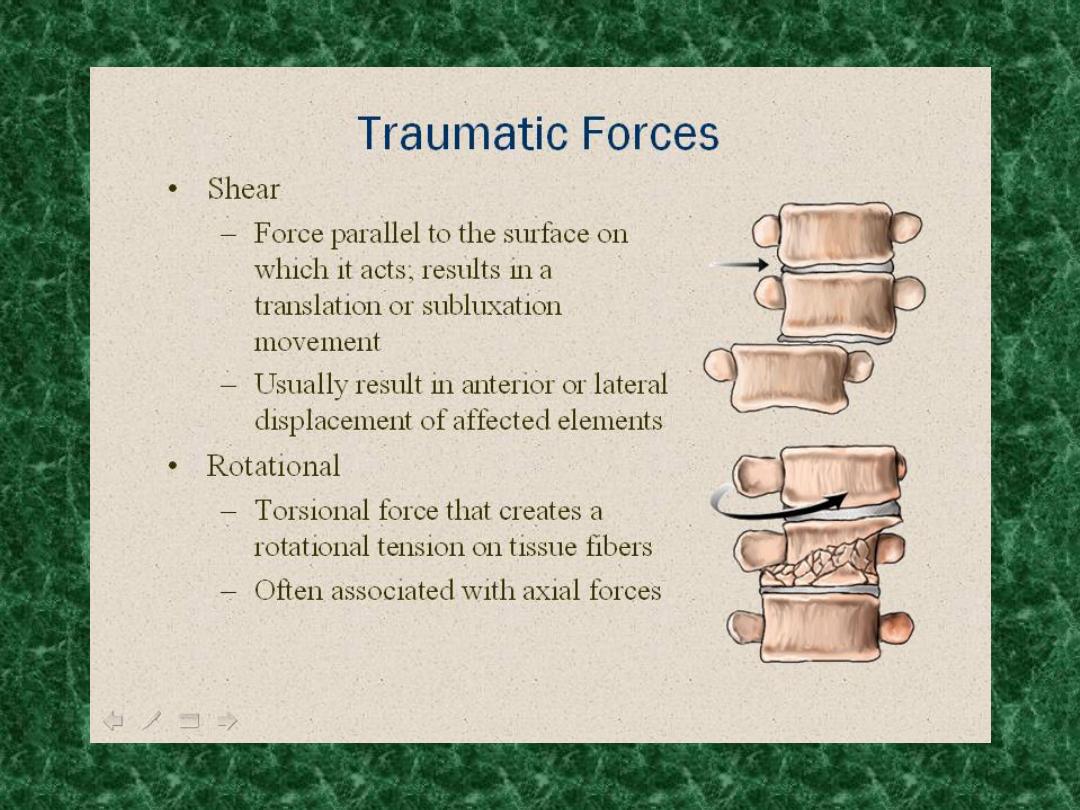
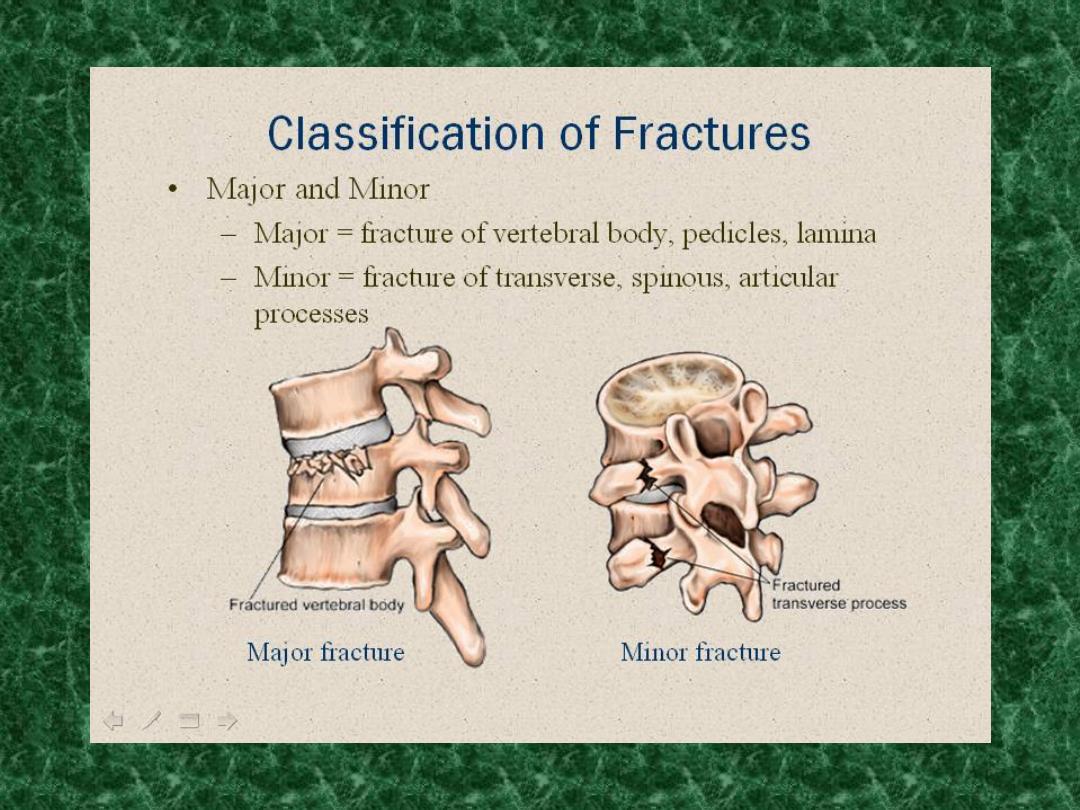
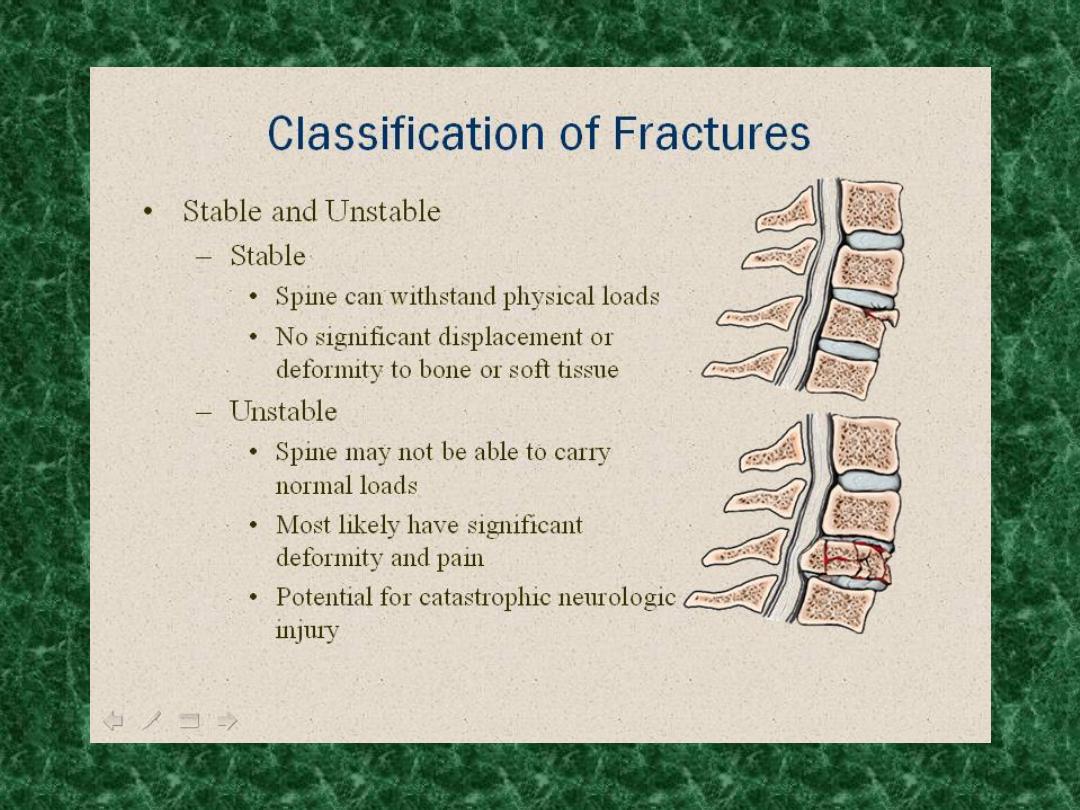
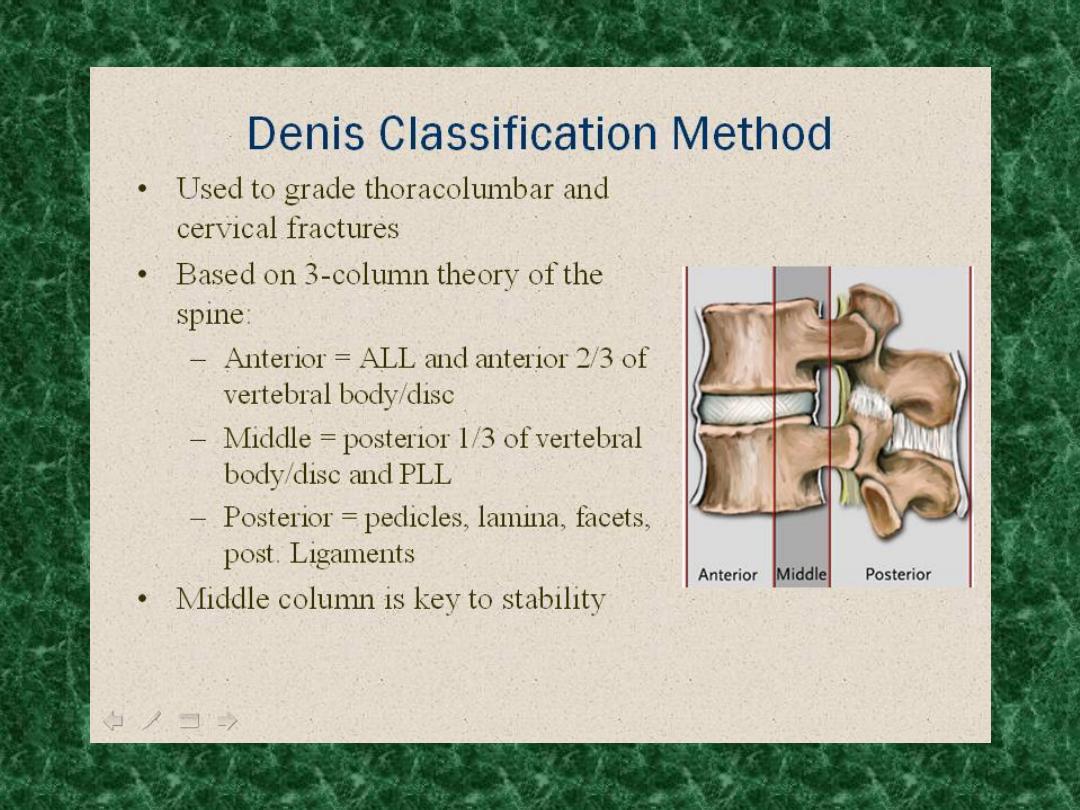
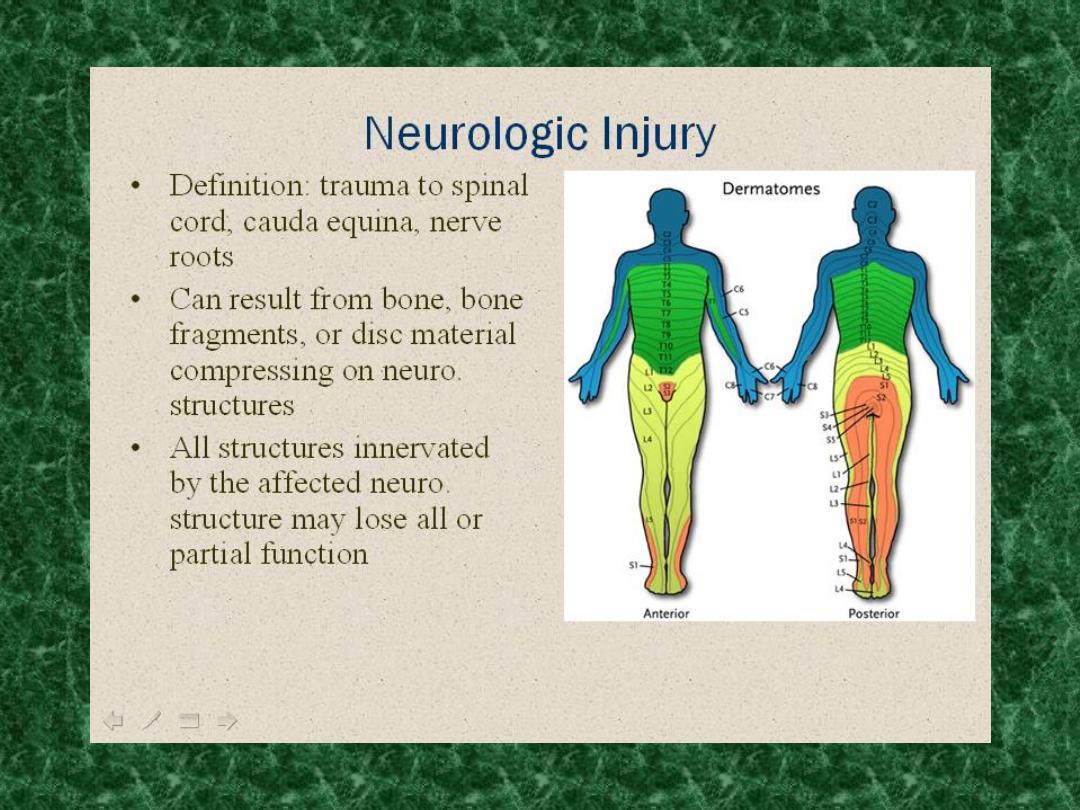
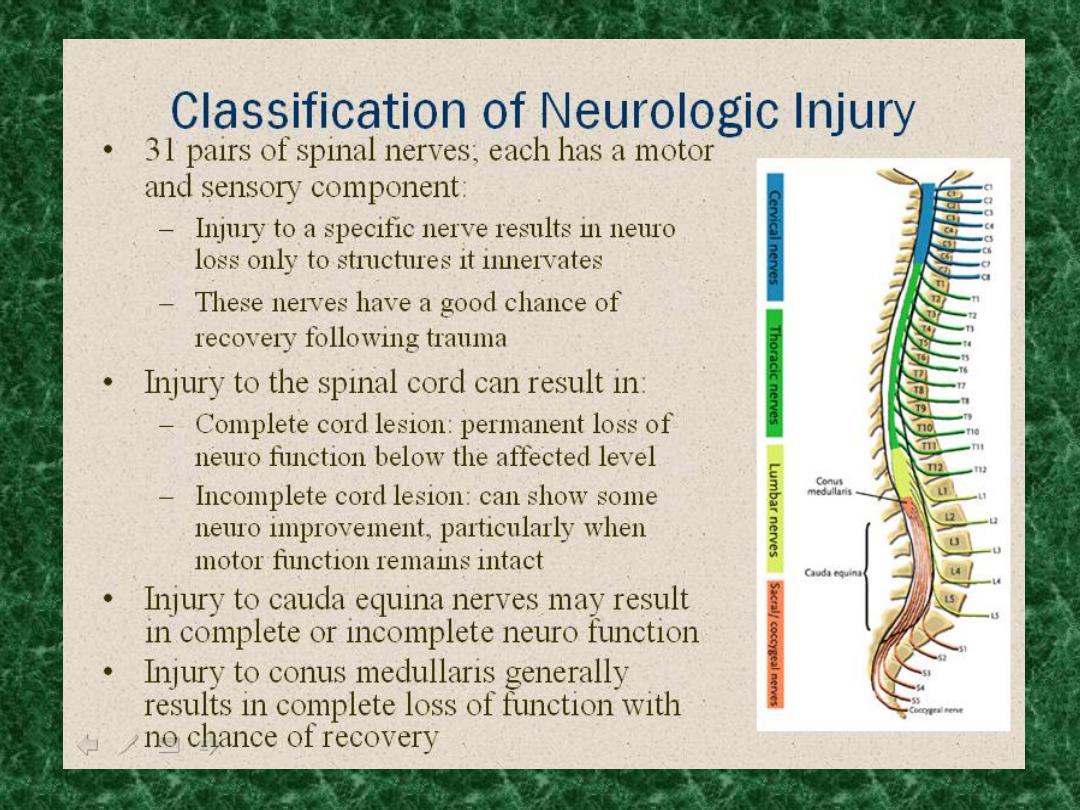

Diagnosis
• History:
ask about;
• 1-major accident.
2-head injury.
3-pain and neck stiffness
.

Dx
• Examination:
During examination move the patient
as a single piece.
•
1-bruising in the head.
2-spinous processes gap.
3-penetrating injury.
4-deformity.
5 - sever tenderness.

Dx
• Neurological examination:
1- cord longitudinal column function.
2- sacral sparing (anal tone; perianal sensation;
great toe flexion).

Imaging
1-X-ray:
Ap , Lateral and other views are needed.
2-C.T:
It demonstrates damage in bony parts of
column.
3-MRI.
demonstrates soft tissue damage (spinal
cord,lig., and neural tissues)
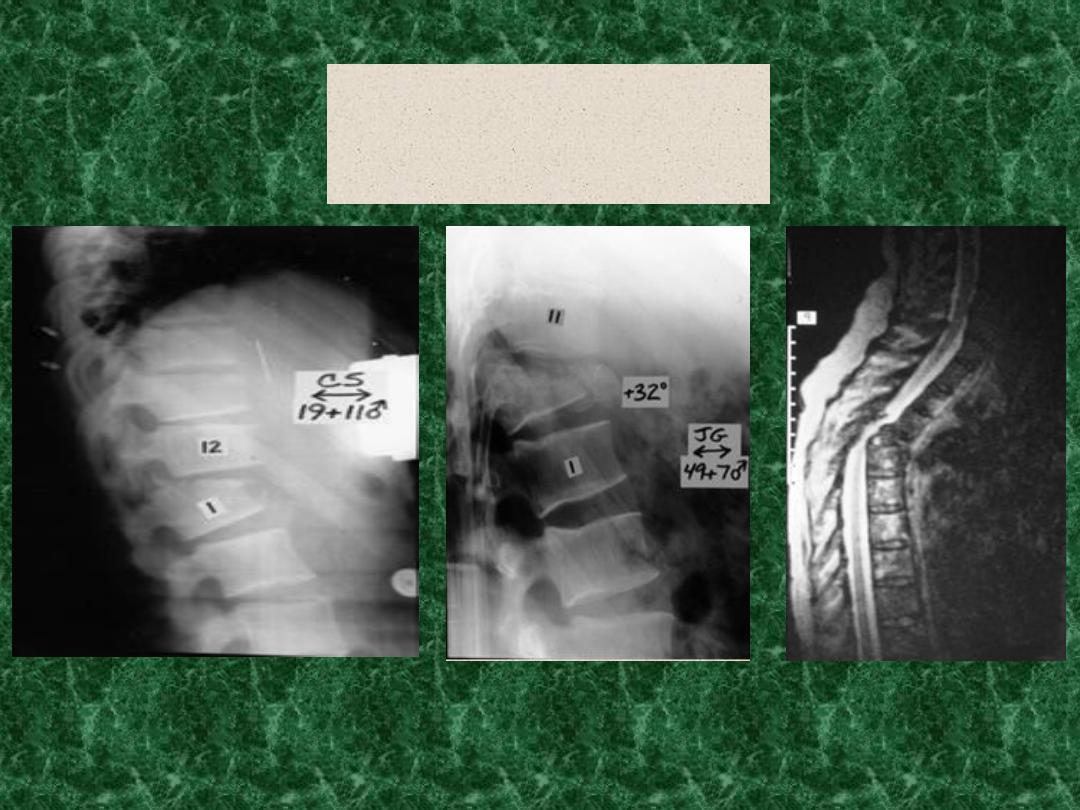
Radiology

Treatment
• Early treatment :
1-ensure adequate airway.
2-control bleeding.
3-care of uncoscious patient.
4-manag. Other injuries.
5-Immobilization (cervical : thoracolumbar).

Treat.
• Definitive treatment :
1-to preserve neurological function.
2-to relieve any reversible compression.
3-to restore alignment of spine.
4- to immobilize the spine.
5- to rehabilitate the spine.

Treat.
• Patient with no neurological injury:
-If the spinal injury is stable:
treated by rest,firm collars or lumbar brace.
-If the spinal injury is unstable:
it should be held sequre until the tissues heal ;usually
treated by traction;or alternativly by internal fixation.

Treat.
•
Patient with a neurological injury:
-
If the spinal injury is stable:
usually treated
conservatively.
•
-If the injury is unstable:
treated usually
conservatively ,but can be treated by surgery ,in order
to reduce pain and facilitates nursing.

Methods of treatment
• Cervical spine:
1-collars.
2-tongs.
3-halo ring.
4-fixation.
.

Methods of treatment
Thoraco-lumbar spine:
1-beds.
2-brace.
3-decompression and stabilization.

Thank you
