
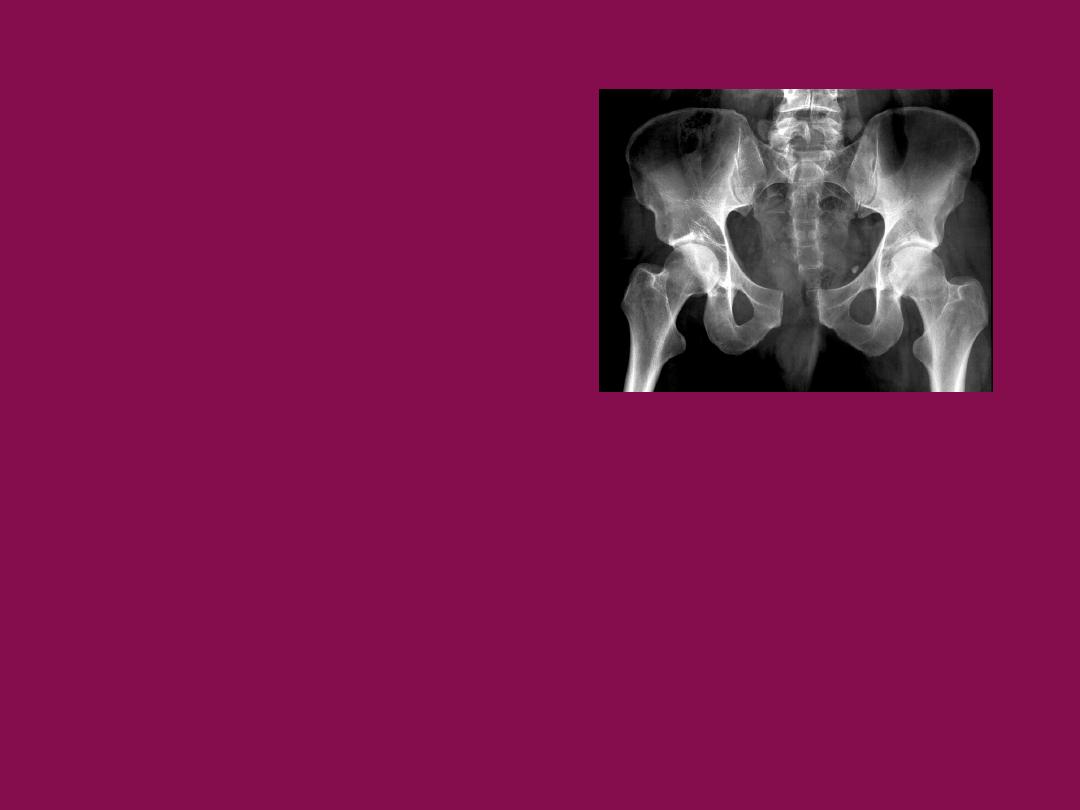
Pelvic injury
FIFTH YEAR – TIKRIT MEDICAL COLLEGE

pelvic bones function
•
transmit Weight to both limbs.
•
Protection of pelvic viscera.
Types of pelvic injury
pelvic ring fractures.
acetabular fractures.
isolated fractures (intact pelvic ring).
sacrococcygeal fractures.
1-pelvic ring fractures.
rigid bony ring … any break in a point within
that ring is associated with injury at
another point of the ring except:-
•
fractures in children.
•
Direct trauma.
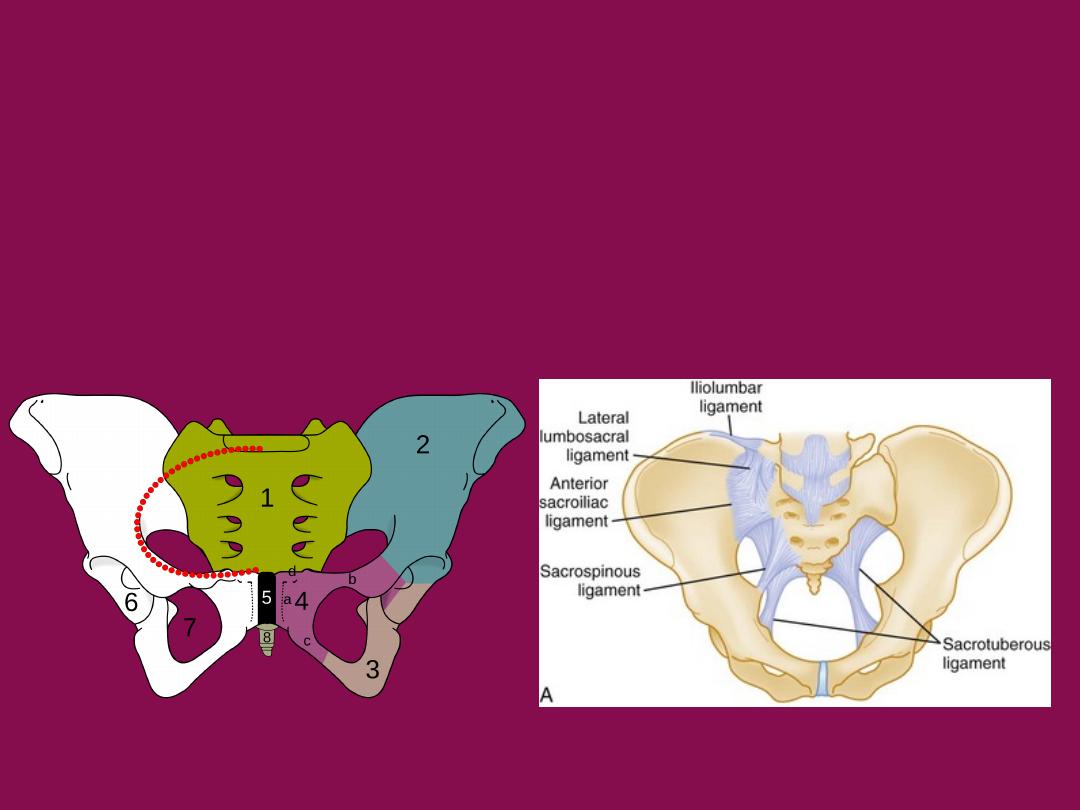
The stability of this ring is maintained by the integrity of
•2 innominate hip bones
•symphysis pubis
•sacroiliac ligaments (anterior and posterior sacroiliac ligaments)
•
the posterior sacroiliac ligament is the most important structure.
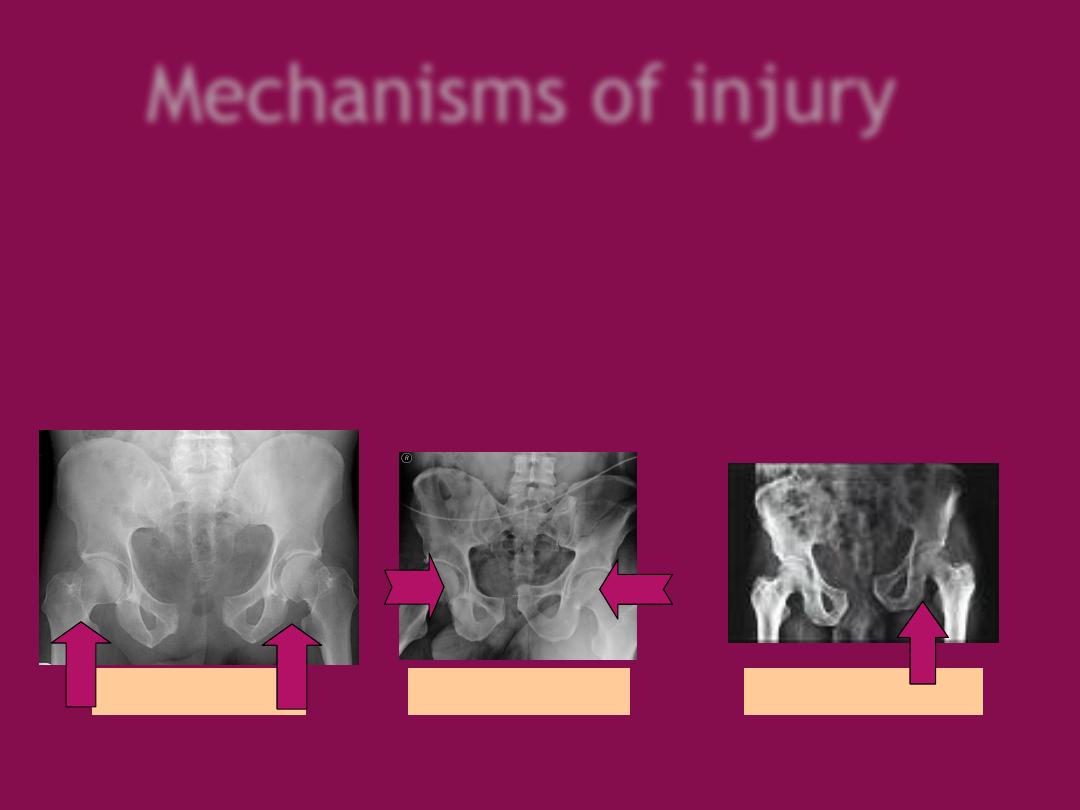
Mechanisms of injury
1- AP compression: frontal collision (RTA) leads to
open book
fracture.
2- Lateral compression: side on impact, roll over accidents leads to
closed book fractures.
3- Vertical shear: FFH (standing) severely unstable fracture.
4- Complex injuries: more than one mechanism.
Open book
Closed book
Vertical shear

Clinical approach
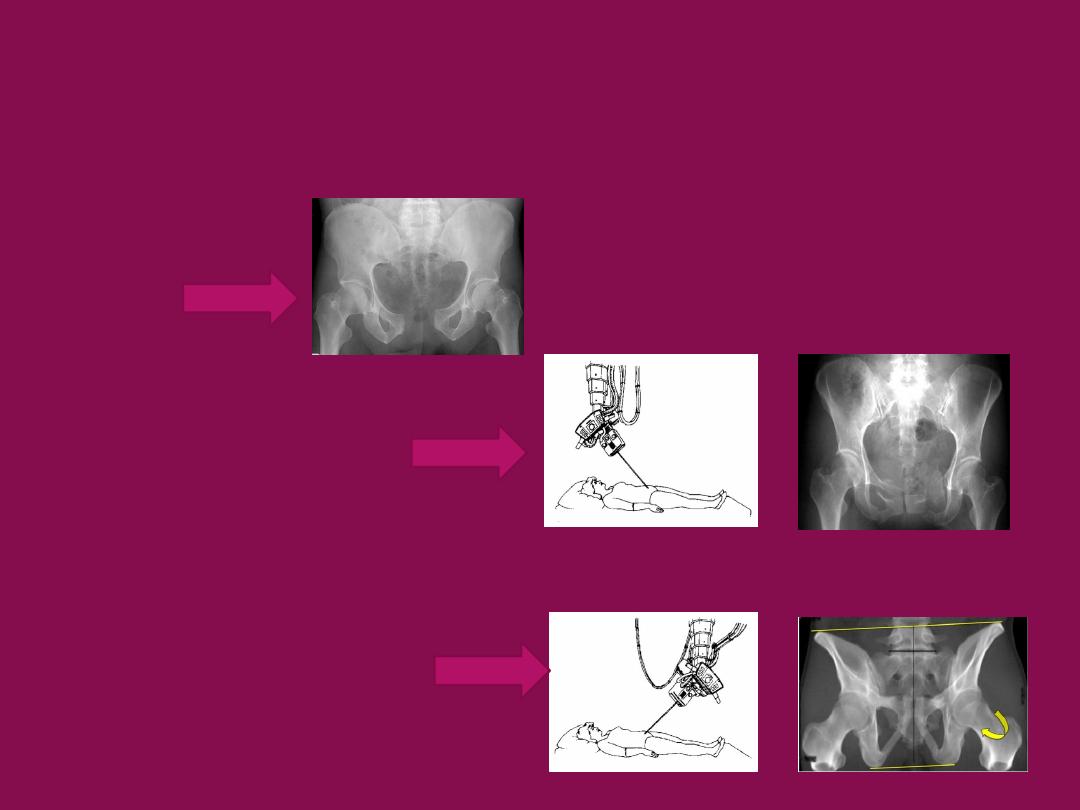
Imaging:
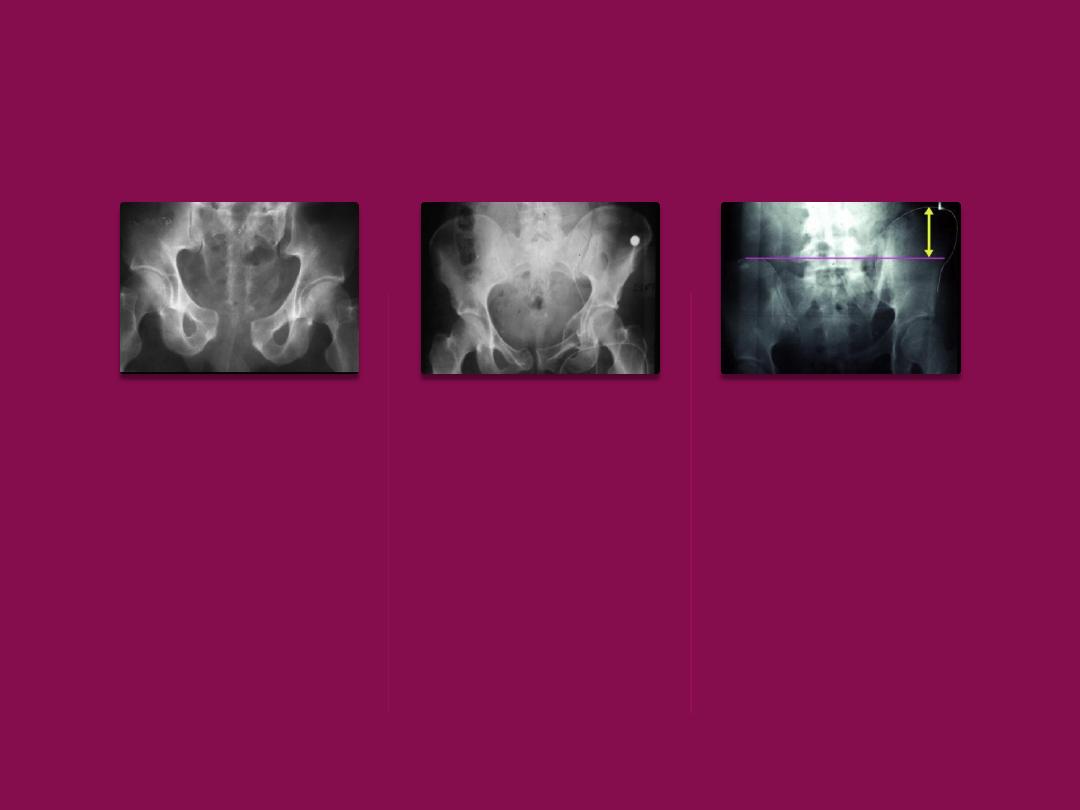
X- ray:-
for
pattern of injury and displacement
•AP view
•Pelvic inlet view
•Pelvic outlet view
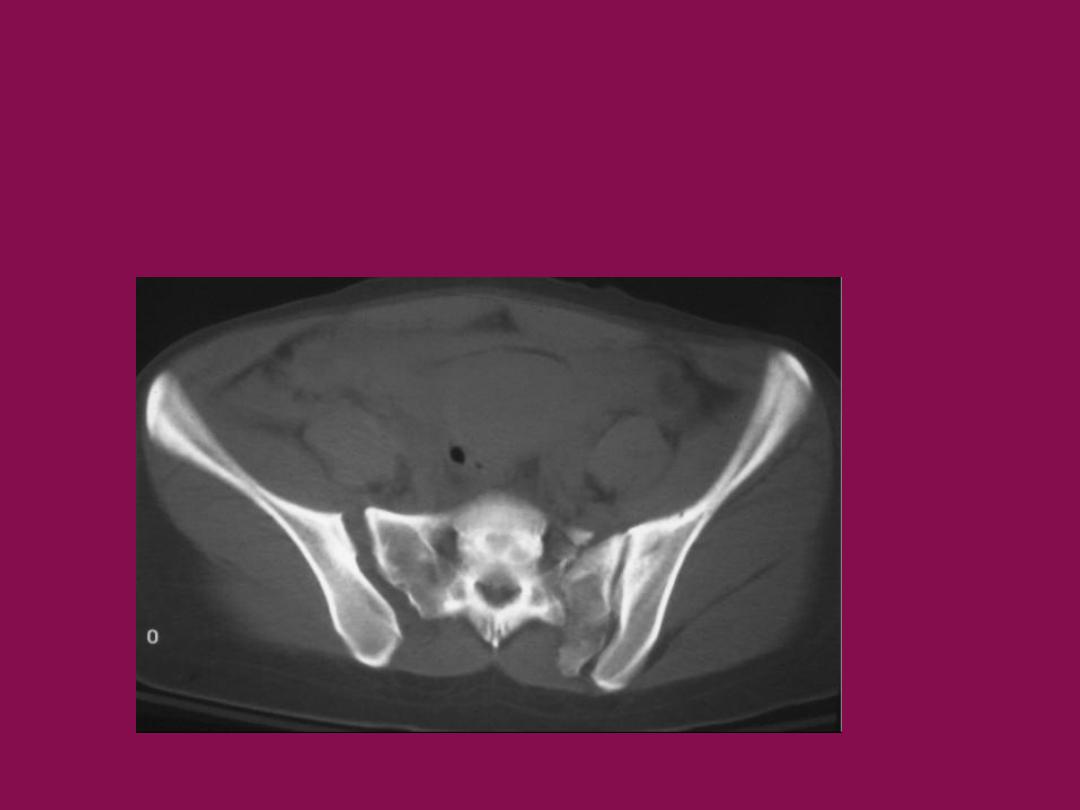
CT scan:-
show the exact picture of the fracture and displacement
pattern
Young-Burgess Classification of pelvic
ring fracture
APC
antero posterior
compression
LC
Lateral
compression
Vertical shear

Management of pelvic fracture
•
Resuscitation .. ABC
•
PRBC:FFP:Platelets ideally should be transfused 1:1:1
•
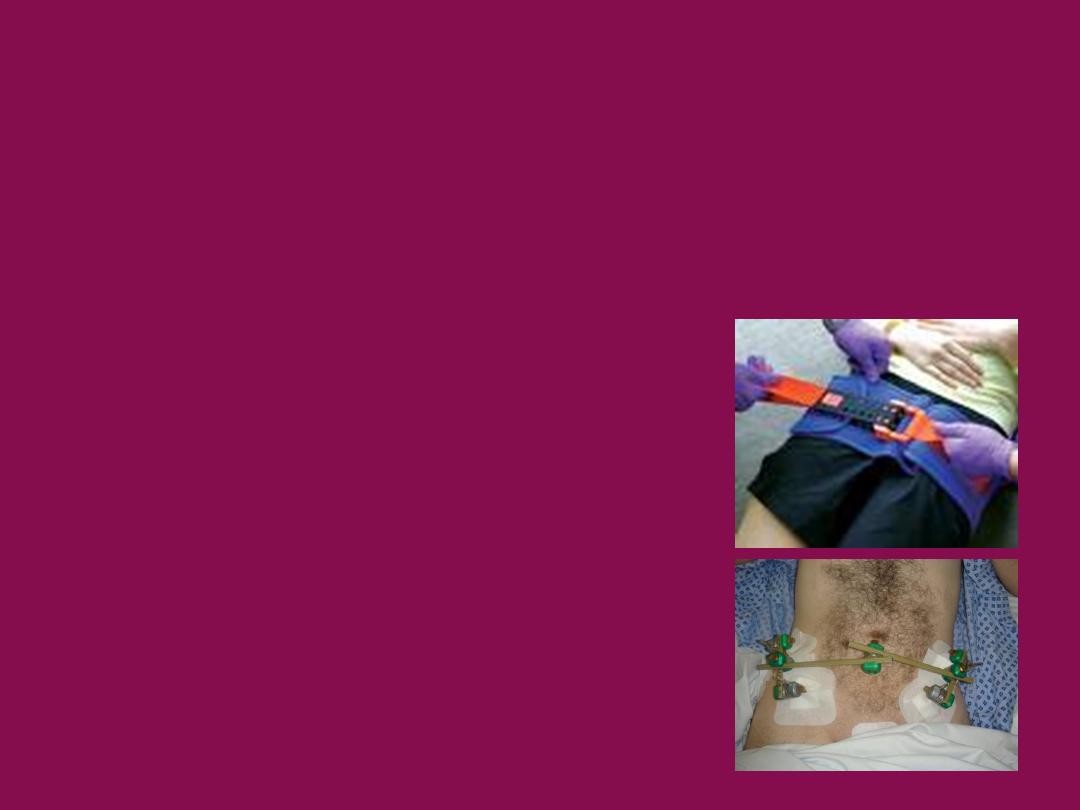
pelvic binder/sheet
•
initial management of an unstable ring injury
•
external fixation
•
unstable ring injury with ongoing blood loss
•
pelvic ring injuries with an external rotation
component

Definitive treatment of pelvic ring fracture
•
Nonoperative .. weight bearing as tolerated
•
APC1widening of symphysis < 2.5 cm with intact posterior pelvic ring
•
isolated pubic ramus fractures
•
Operative .. ORIF ..
•
symphysis diastasis > 2.5 cm
•
SI joint displacement > 1 cm
•
displacement or rotation of hemipelvis

Complications
•
Neurologic injury
•
Visceral injury
•
DVT and PE
•
Urogenital Injuries
•
posterior urethral tear
•
bladder
rupture
•
Chronic instability
•
Chronic pelvic pain
Acetabular Fractures
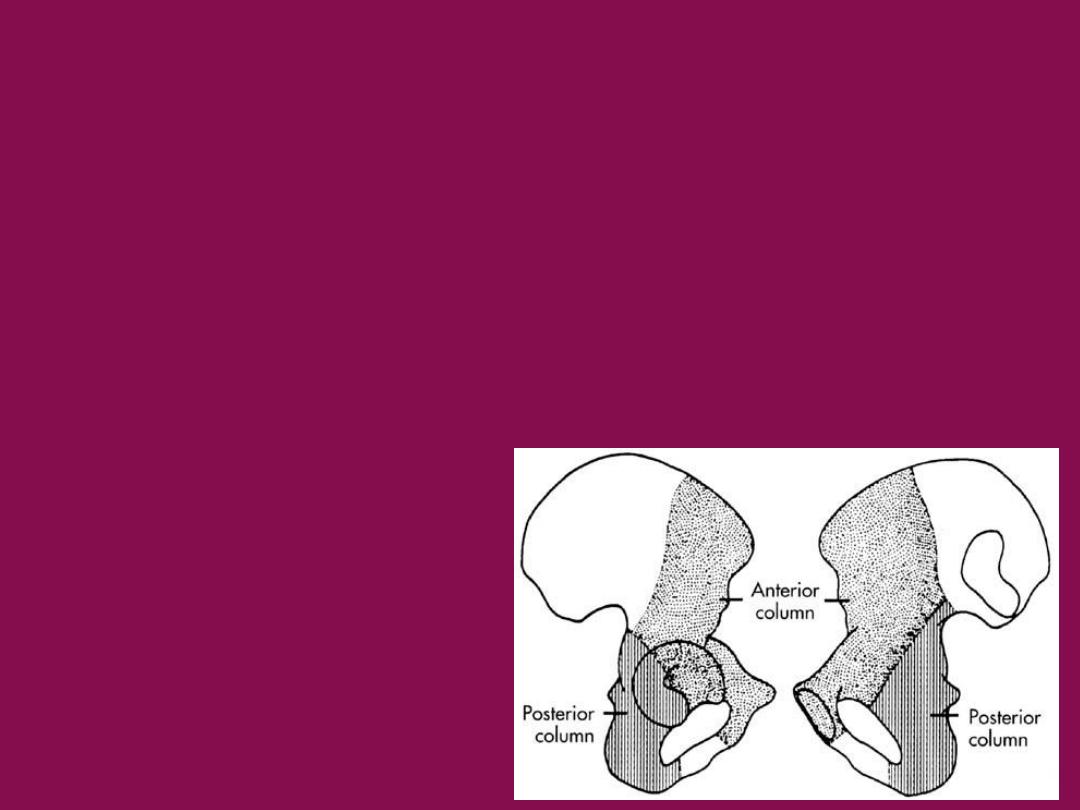
Anatomy
•
The acetabulum is formed by the three pelvic bones
( ilium. Ischium and pubis )
•
acetabulum is supported by two columns of pelvic
bone
•
posterior column
•
anterior column

Epidemiology
•
bimodal distribution
•
high energy blunt trauma for young patients
•
low energy (fall from standing height) for elderly patients
•
posterior wall fractures are most common
•
Associated conditions
•
extremity injury (36%)
•
Sciatic nerve palsy (13%)
•
spine injury (4%)
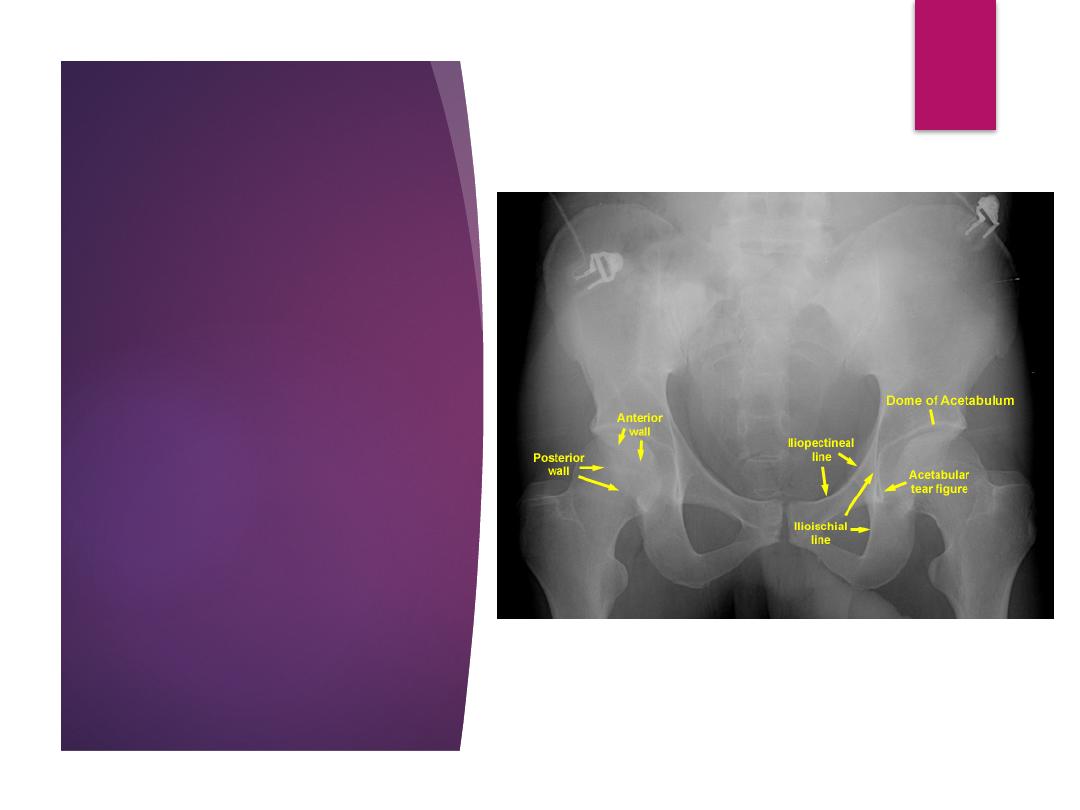
6 radiographic
landmarks of the
acetabulum
iliopectineal line
(anterior column)
ilioischial line (posterior
column)
anterior rim
posterior rim
teardrop
weight bearing roof
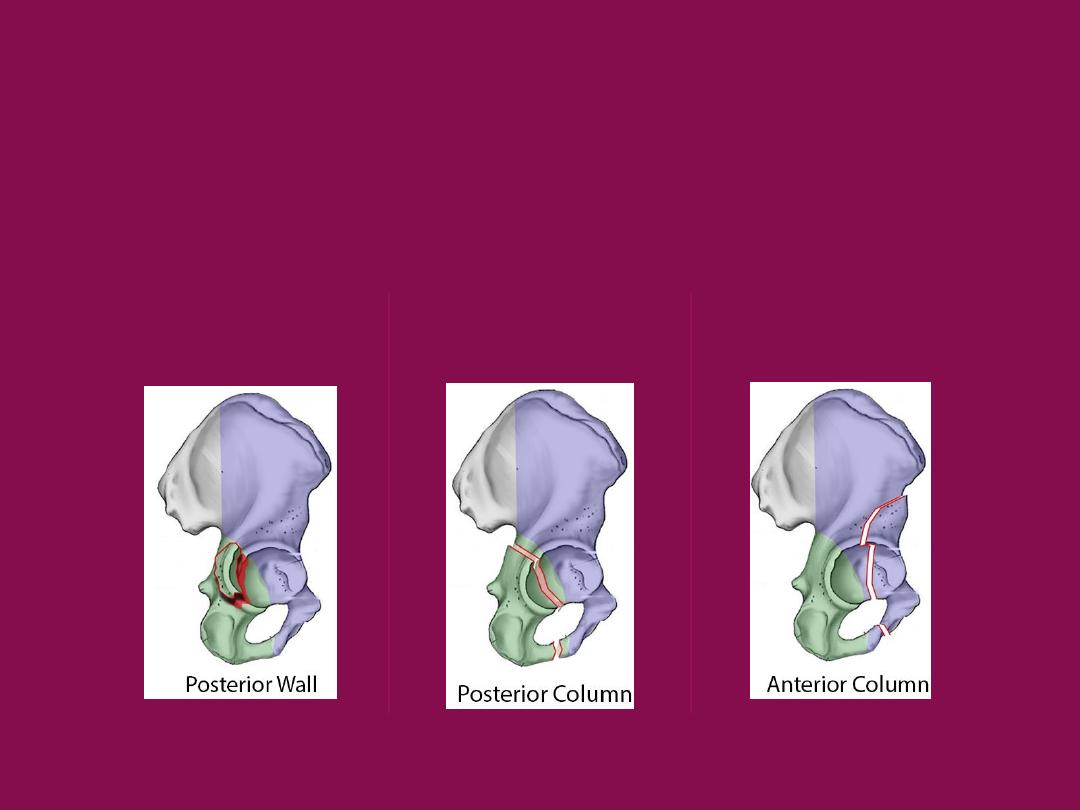
Jude and lotournel classification
of acetabular fracture
A- elementary
Posterior wall
Posterior column
Anterior column
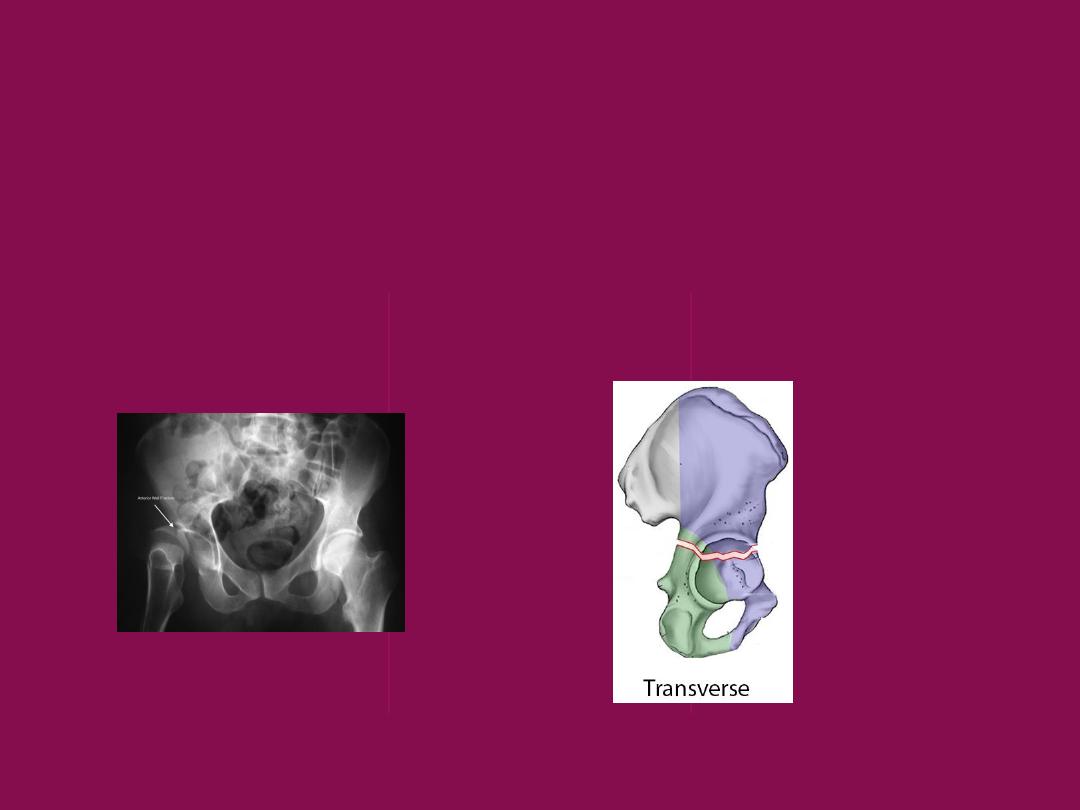
Jude and lotournel classification of
acetabular fracture
A- elementary
Anterior wall
Transverse
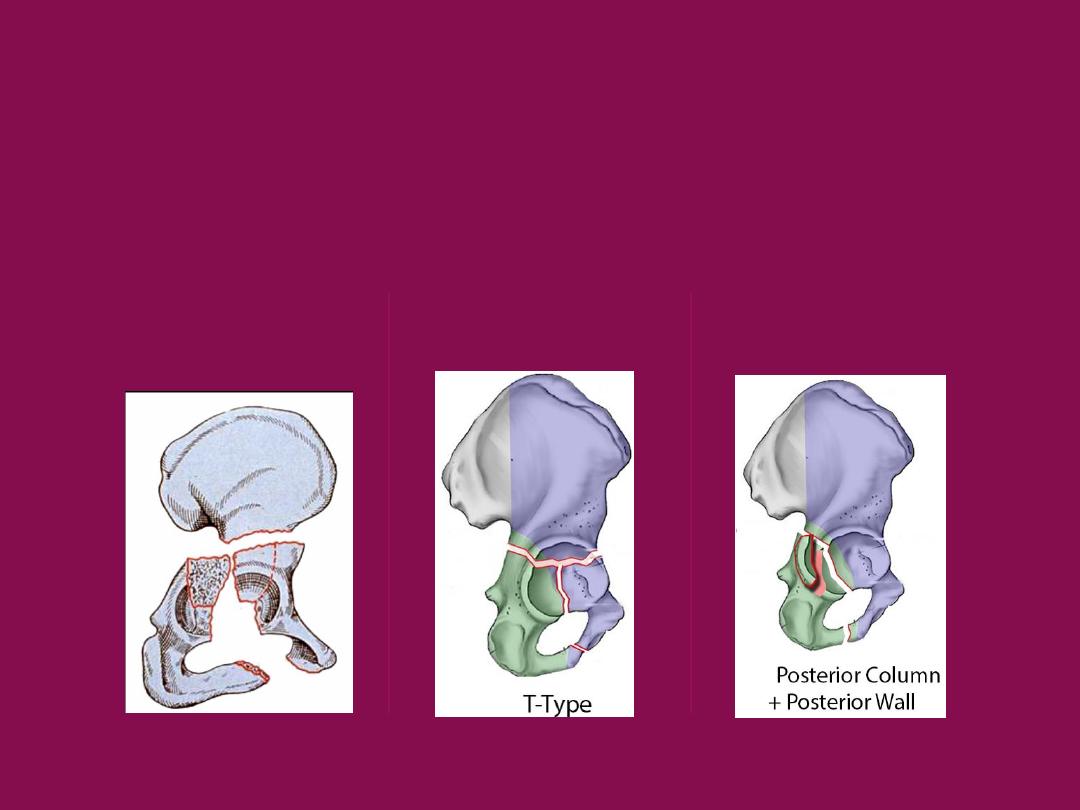
Jude and lotournel classification of
acetabular fracture
B- Associated
Associated Both Column
T Shaped
Post. column +
Post. Wall
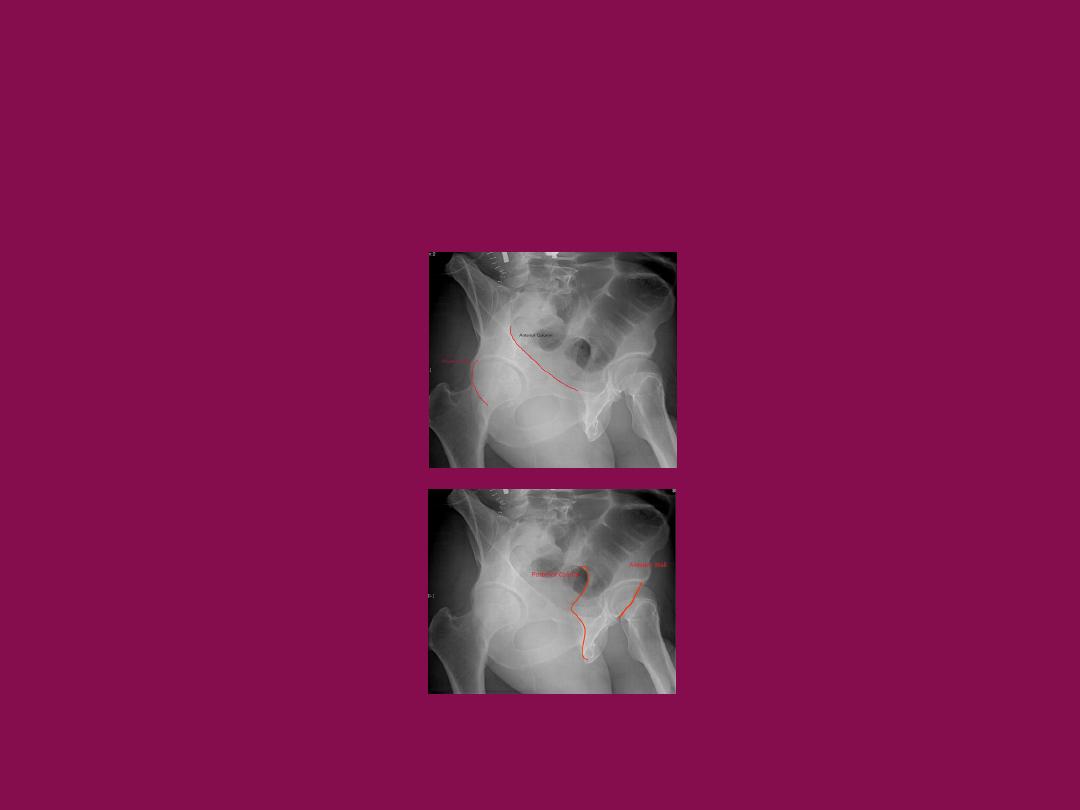
Radiographs
•
AP pelvis
•
Judet views (45 degree oblique views)
•
obturator oblique
•
iliac oblique
•
inlet and outlet
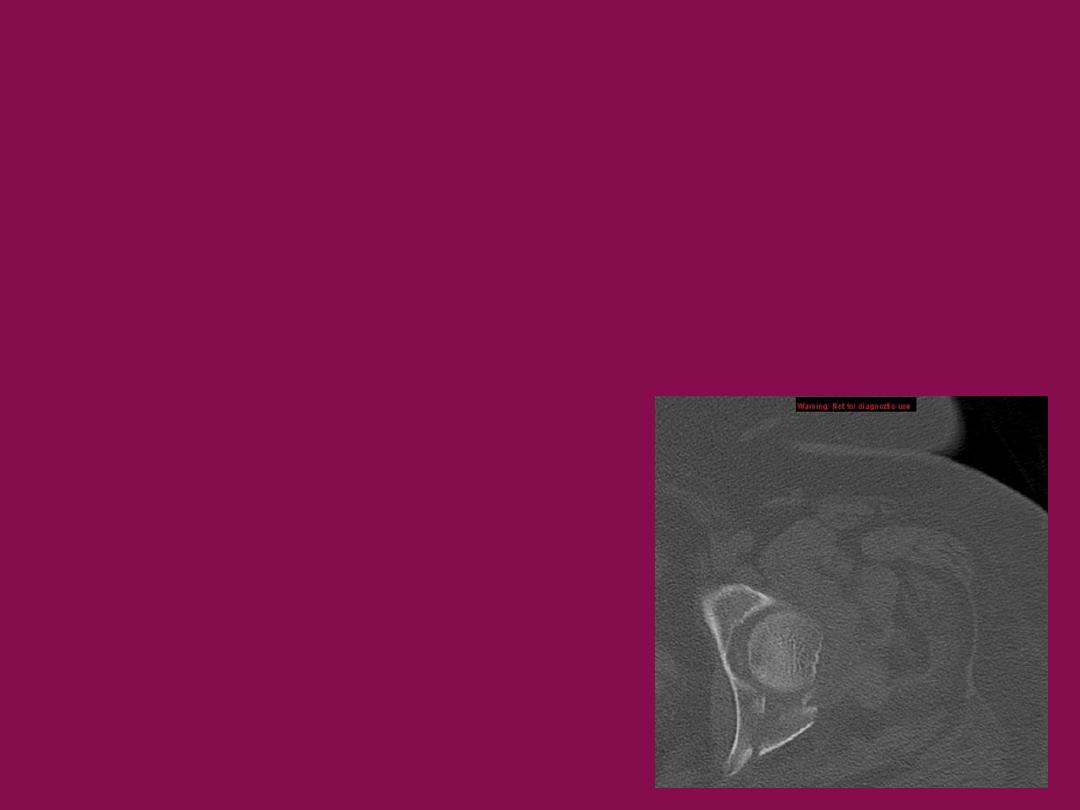
CT scan
•
define fragment size and orientation
•
identify loose bodies
•
look for articular gap or step-of

Treatment
1- Nonoperative .. Traction then protected weight bearing for 6-8
weeks in :
•
minimally displaced fracture (< 2mm)
•
< 20% posterior wall fractures
•
femoral head remains congruent with weight bearing roof
Operative treatment …ORIF in :
•
displacement of roof (>2mm)
•
posterior wall fracture involving > 40-50%
•
marginal impaction
•
intra-articular loose bodies
•
irreducible fracture-dislocation

Complications
•
Post-traumatic DJD
•
Heterotopic Ossification
•
Osteonecrosis
•
DVT and PE
•
Infection
•
Bleeding
•
Neurovascular injury
