
Osteonecrosis
Avascular necrosis is bone death due to severance of blood
supply.
Classification
A-Traumatic e.g after fracture and dislocation
B-Non-traumatic
1-infection a-osteomyelitis b-septic arthritis
2-Haemoglobinopathy e.g sickle cell anemia
3-Storage disorder e.g gaucher disease
4-Caisson disease
5-Coagulation disorders a-familial thrombophilia b-
hypofibrinolysis c-hypolipoproteinemia d-thrombocytopenic
purpura
6-Others a-Perths disease b-cortisone adminstation c-alcohol
abuse d-SLE e-pregnancy f-anaphylactic shock g-ionizonig
radiation
Most commonly affect a-femoral head b-femoral condyle c-
head of humerus d-capitulum e-proximal parts of scaphoid and
talus
Aetiology and pathogenesis
It tend to affect most distant parts of the bone vascular
territory with limited collateral connections.Vascular sinusoids
which nourish marrow and bone cells have no adventitial layer
and ther patency is determined by volume and ptessure of the
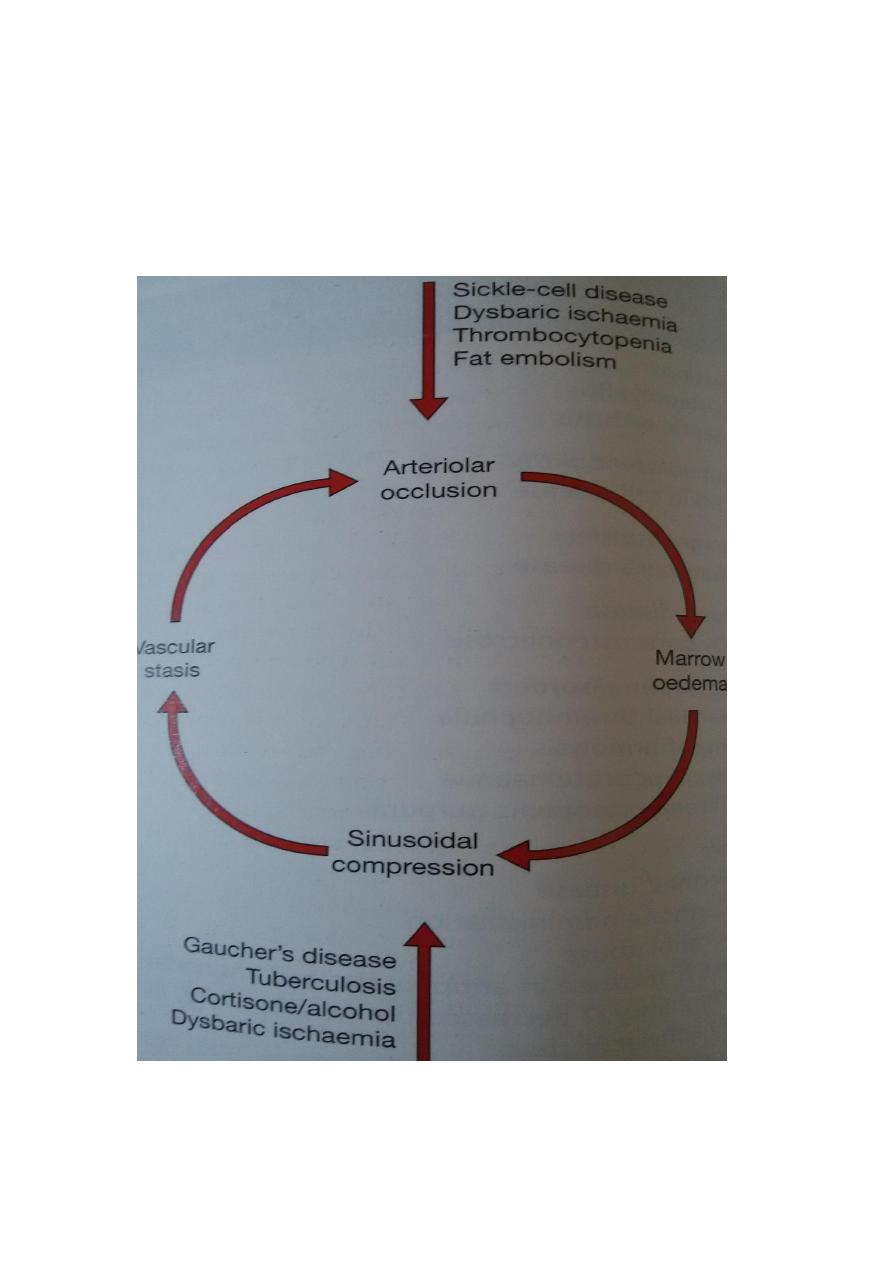
surrounding marrow tissue; so local changes such as
haemorrage and decrease blood supply rapidly spiral to a
vicious cycle.This process can be initiated in 4 different ways 1-
severance of blood supply 2- venous stasis 3- compression of
capillaries and sinusoids by marrow swelling.
Clinical features

The earlist stage of bone death is asymptomatic ,in advanced
stage there will be a- pain in or near a joint and perhaps with
certain movements. b- click in the joint, probably due to
snapping or catching of a loose articular fragment.c-
stiffnessand deformity in later stages.d-local tenderness. e-
swelling may be seen in superficial bone. f-restricted
movement. g-fixed deformities may be seen in advanced cases.
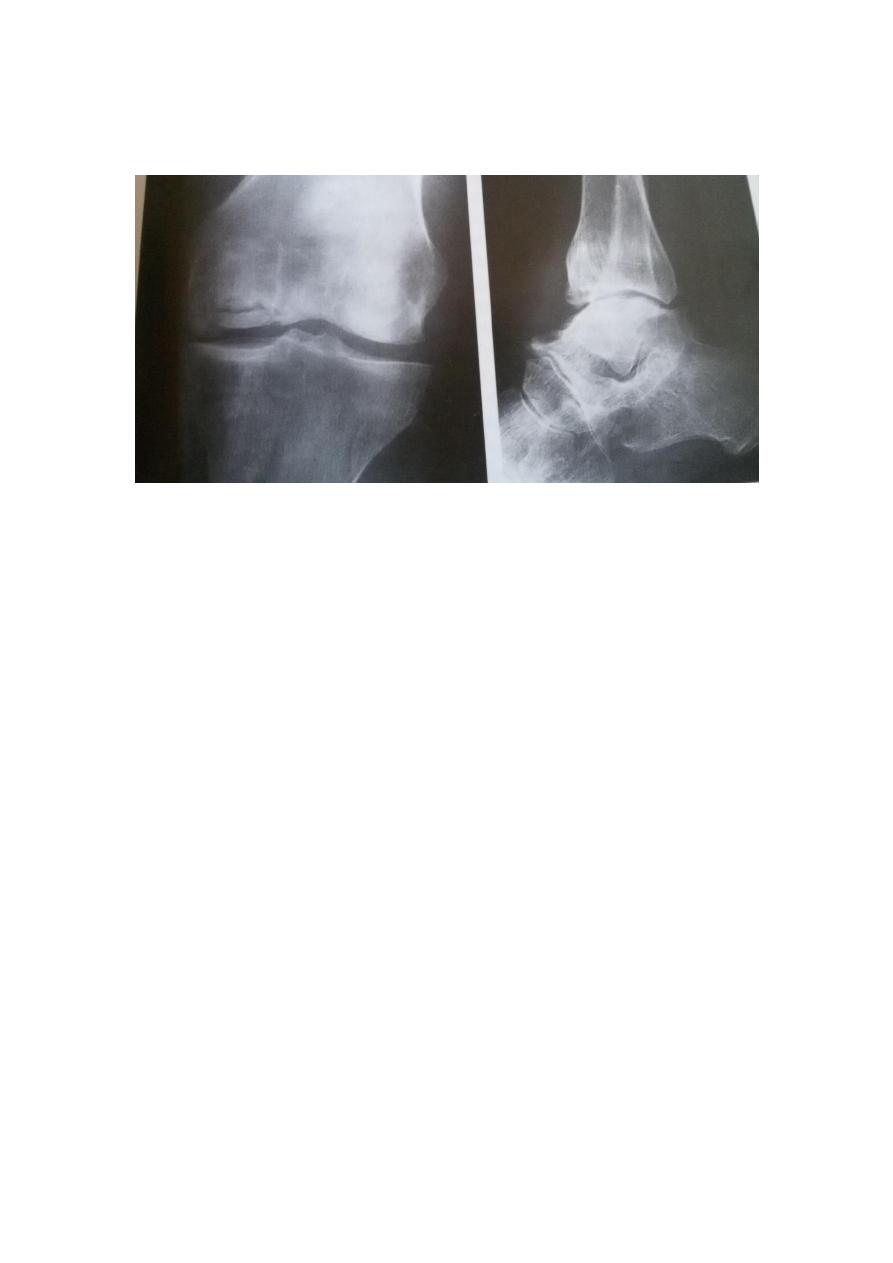
Imaging
1-x-ray:usually after 3 months of bone death a-area of
increased bone density in the subchondral boneand may show
thin tangential fracture line below the articular surface. b-
distortion of the articular surface in late stages. C- occasionally
the necrotic portion separates from parent bone as a discrete
fragment.
2-Radioscintigraphy-tc 99 sulphur colloid is using may reveal
avascular segment.
3-MRI is the most reliable wat of diagnosis marrow changes
and bone ischemia at early stage.
4-CT scan-It does show the area of bone destruction very
clearly and it may be useful in planning surgery.
Treatment
1-Early osteonecrosis
If bone contour is intact ; there is alaways the hope that
structural failure can be prevented esp. in areas which are not
severly stressed. a-oral alenodronate for 25 weeks b-unloading
osteotomy esp. in knee and hip c- medullary decompresion and
bone grafting of femoral head.
2-Intermediate osteonecrosis; there is structural damage a-
realignment osteotomy alone or combined with curettage and
bone grafting of the necrotic segment. b-arthrodesis.
3-Late stage osteonecrosis a- non-operative treatment include
control of pain, modivication of daily activities and splintage of
the joint. b-arthrodesis of the joint c-partial or total joint
replacement e.g knee and hip.
