Prostatic gland diseases
Asst. prof. dr. Wadhah A. MarzooqFIBMS (uro)
Dr_wadhah_uro@yahoo.com
2020
Objectives
1. Give the student a summary about most common disease of prostate gland.2. Enable the student evaluate pt. with LUTS.
3. Give the student an idea about the head line of treatment of prostatic gland disease
Benign prostatic hyperplasia(BPH)
It is an increment in the size of prostate gland due to increase in the number of the cellsAnatomy
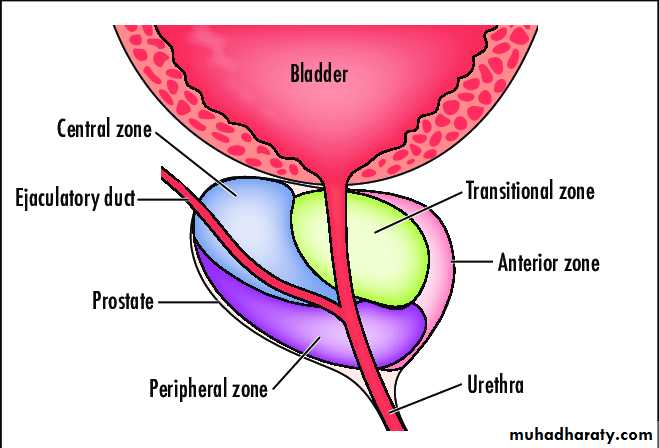
Prostate gland can be divided in to 3 distinct zonePeripheral account 70% of prost. Size
Central account 25% = =
Transitional 5% = =
Zones of prostate gland
Note• 60-70% of ca. prostate occur at peripheral zone.
• 20-30% occur at the central zone.
• 5-10% occur at the transition zone.
• BPH occur exclusively at transition zone.
Epidemiology
BPH is the most common benign Tr. Of adult menHistological BPH occur in about 90% of men after 80 years
Clinical BPH occur in about 50% of men after 75 years.
Etiology
Exact etiology is not well understood• Genetic factor ….1st degree relative is more vulnerable.
• Hormonal factor….. with age increase estrogen level lead to increase sensitivity of testosterone receptors to testosterone.
pathology
Prost. Gland composed of:
• Stromal part …collage fiber and smooth muscle cell
• Epithelial part…epithelial cells
Hyperplasia occur in both component in varying percentage.
Clinical presentation
Old age man (more than 50-60 years)Storage symptoms
Voiding symptomsurgency
Poor urine stream
frequency
intermittency
nocturia
hesitancy
Urge incontinence
Post micturition drippling
dysuria
Double voiding
Feeling of incomplete bladder empty
Examination
The most important part of examination is DREThe size and consistency of the prostate is noted, even though prostate size does not correlate with severity of symptoms or degree of obstruction.
DRE aim is to differentiate between benign and malignant enlargement,
Any localized or generalized nodule detected by DRE should be considered malignant until prove otherwise.
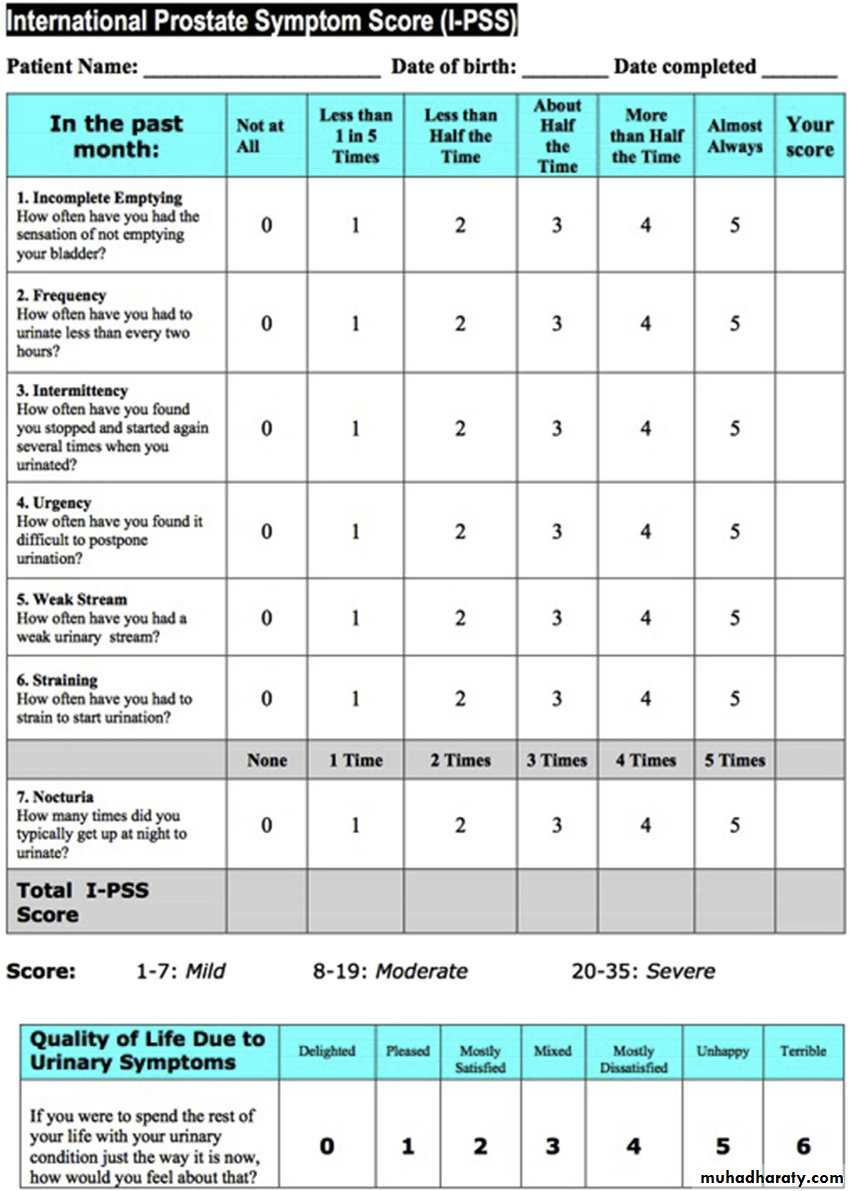
AUA (IPSS)
investigations
UrinalysisAbd. US or TRUS
RFT.
S. PSA.
Cystoscopy.
Treatment
Treatment depend on the degree of bothersome of the symptom.Medical treatment
Alpha blocker Side Effect (postural HT, retrograde ejaculation)
Non selective (doxazocine, terazocine)
Selective alfa-1 alfazocine. 10 mg single daily dose
Highly selective alfa-1-a tamsulucine 0.4 mg single daily dose.
Hormonal (5 alfa reductase inhibitors) side effect (decrease libido, gynecomastia)
finasteride 5 mg single daily dose or dutasteride 0.5mg single daily dose
Anticholinergic drug to decrease the storage symtoms, side effect dry mouth, constipation, urine retention
like oxybutinine, tolterodine, solifenacine etc.
Herbal extract
Surgical treatment
Indications.
• Recurrent urine retention due to BPH.
• Recurrent UTI due to BPH.
• Recurrent gross hematuria due to BPH.
• impaired renal function due to BPH.
• Failed medical treatment.
Types.
Invasive (open prostatectomy) trnsvesical or retropubic.Minimally invasive
(TURP) gold standard.
Laser prostatectomy.
Immediate complication of surgical treatment.
• bleeding.
• Infection.
• DVT.
• TURP syndrome only with TURP due to water intoxication and hyponatremia
Long term complication of surgical treatment
1- retrograde ejaculation 90%
2- urine incontinence.
3- impotence very low
4- urethral stricture or bladder neck contracture.
THANKS