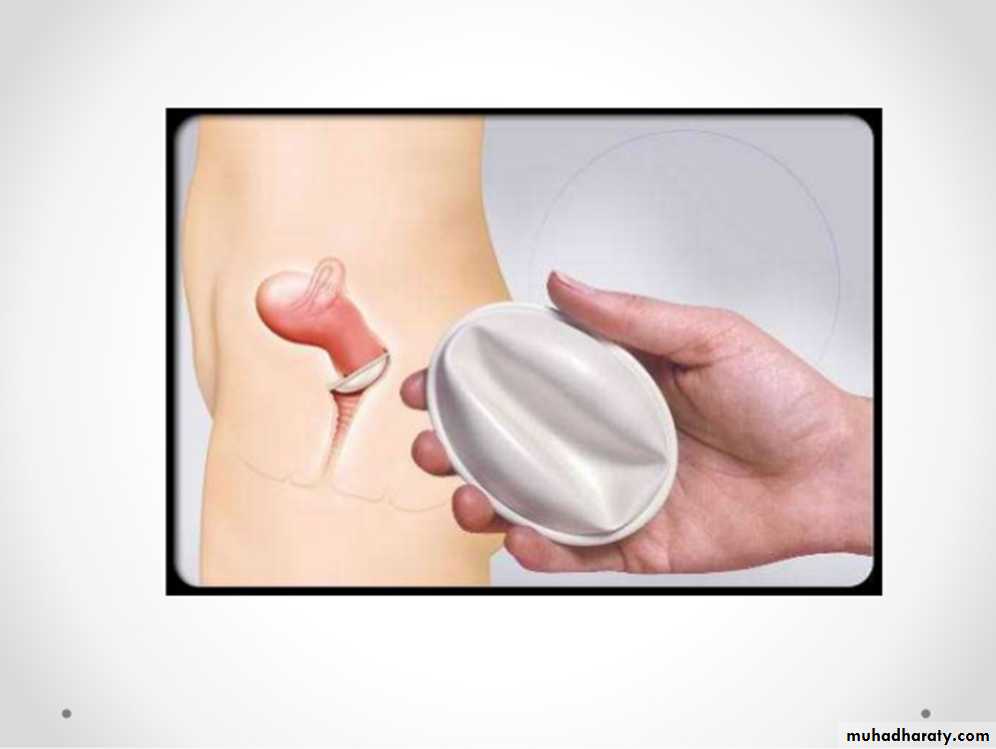
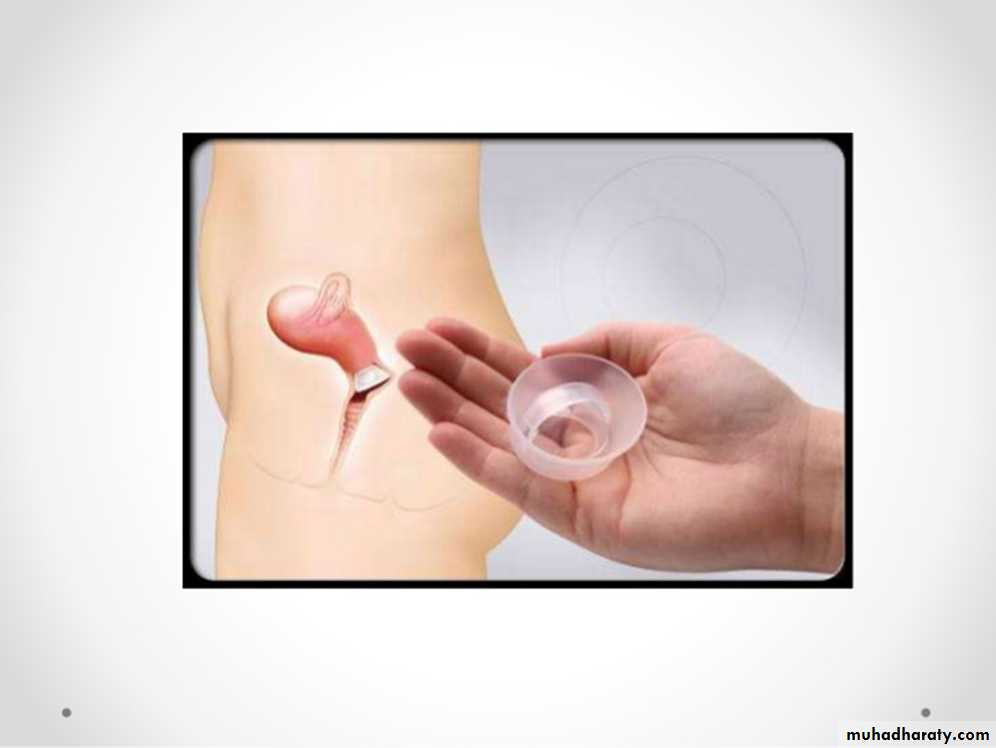
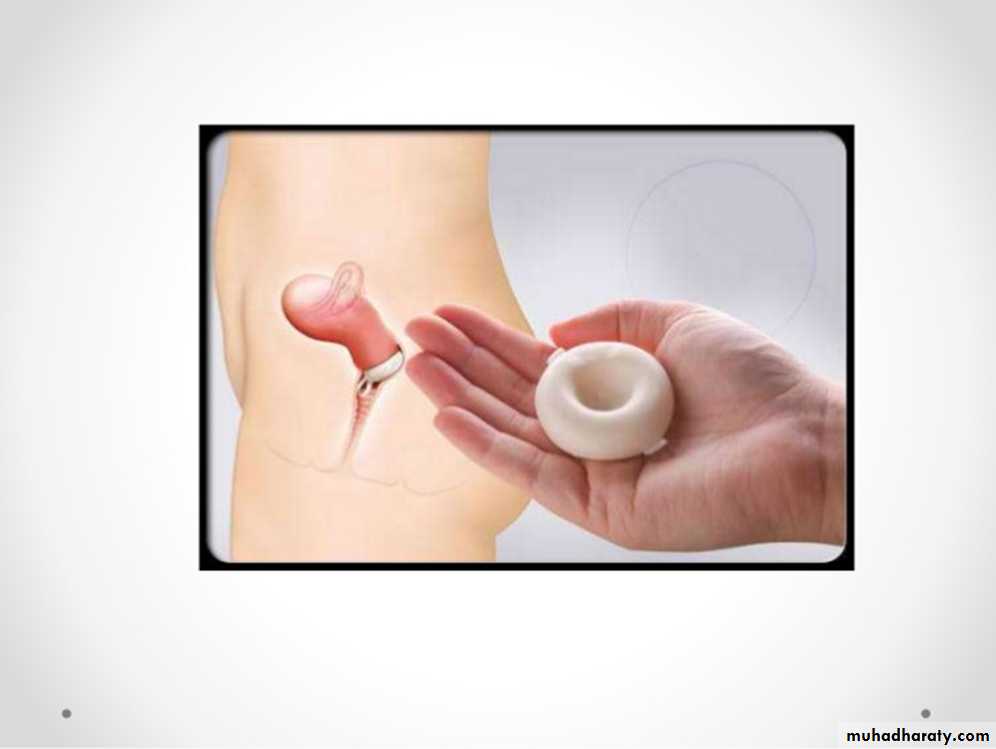
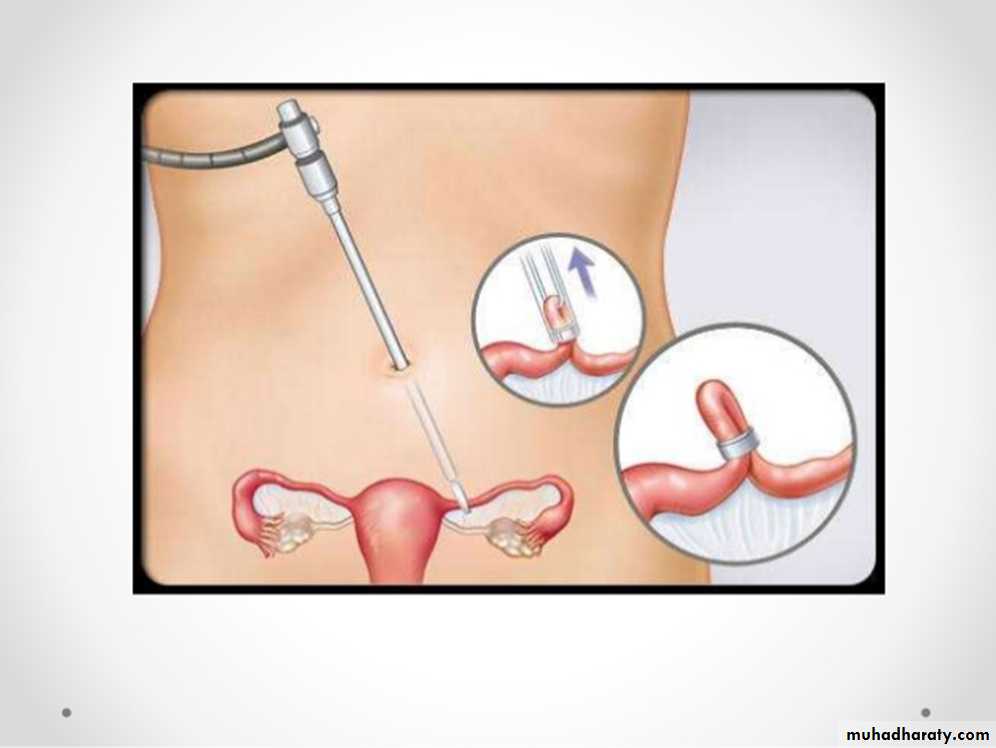
Family Planning
Lectures in Community Medicine
Dr.Sijal Fadhil Farhood AL-JOBORAEFICMS (Baghdad)
MSc Community (Nahrain)
MBChB (Babylon University)
Motto of family planning
Having children by choice not by chanceFacts
-The perfect method does not existAbstinence-practiced perfectly
Contraceptives methods change based on the clients circumstances
-30% of married and 61 % of unmarried females(in the west) change methods within 2years
-Careful consideration of all factors can help a woman choose the best method
Introduction:
Waiting until the mother is at least 18 years old before trying to have children improves maternal and child health.If additional children are desired after a child is born, it is healthier for the mother to wait at least 2 years after the previous birth before attempting to conceive (but not more than 5 years).
After a miscarriage or abortion, it is healthier to wait at least 6 months.
When planning a family women who are over the age of 35 should be aware of the risks of having a child at that age.
Introduction:
Older women are at a higher risk of having a child with autism and down syndrome, the chances of having multiple births increases, which cause further late-pregnancy risks, they have an increased chance of developing gestational diabetes, the need for a Caesarian-section is greater, older women's bodies are not as well-suited for delivering a baby. The risk of prolonged labor is higher. Older mothers have a higher risk of a long labor, putting the baby in distress.Introduction:
Family PlanningDEFINITION
W H O
A way of thinking and living that is adopted voluntarily, upon the basis of knowledge ,attitudes and responsible decisions by individuals and couples…..in order to…
Promote the health and welfare of the family group and thus contribute effectively to the social development of a country (WHO 1971)Globally….
Family planning is among the most cost-effective of all health interventionsOBJECTIVES
To avoid unwanted births and to bring about wanted births (for the sub fertile)OBJECTIVES
To regulate the intervals between pregnancies (spacing)OBJECTIVES
To control the time at which births occurs in relation to the ages of the parents (timing)OBJECTIVES
To determine the number of children in the family (family size)
SCOPE OF FAMILY PLANNING SERVICES
1-The proper spacing and limitation of births
SCOPE OF FAMILY PLANNING SERVICES
2-Advice on sterility
SCOPE OF FAMILY PLANNING SERVICES
3-Education for parenthood
SCOPE OF FAMILY PLANNING SERVICES
4-
Sex education
SCOPE OF FAMILY PLANNING SERVICES
5-Screening for pathological conditions related to the reproductive system (e.g. cervical cancer)
SCOPE OF FAMILY PLANNING SERVICES
6-Genetic counselling
SCOPE OF FAMILY PLANNING SERVICES
7-Premarital consultation and examination
SCOPE OF FAMILY PLANNING SERVICES
8-Carrying out pregnancy tests
SCOPE OF FAMILY PLANNING SERVICES
9-Marriage counselling
SCOPE OF FAMILY PLANNING SERVICES
10-The preparation of couples for the arrival of their first child
SCOPE OF FAMILY PLANNING SERVICES
11-Providing services for unmarried mothers
SCOPE OF FAMILY PLANNING SERVICES
12-Teaching home economics and nutrition
SCOPE OF FAMILY PLANNING SERVICES
13-Providing adoption services
F
Family Planning Services..
Definition
Family planning services are defined as "educational, comprehensive medical or social activities which enable individuals, including minors, to determine freely the number and spacing of their children and to select the means by which this may be achieved."
IMPACT OF FAMILY PLANNING
WOMEN’S HEALTH
i-Avoidance of Unwanted PregnanciesAn unwanted pregnancy may lead to an induced abortion. Abortion outside the medical setting (criminal abortion) is one of the most dangerous consequences. There is also evidence of higher incidence of mental disturbances among mothers who have had unwanted pregnancies
WOMEN’S HEALTH
ii- Limiting the number of births and proper spacingRepeated pregnancies increases the risk of maternal mortality and morbidity. These risks rise with each pregnancy beyond the third and increase significantly beyond the fifth.
With increased parity the following increase:
1- Rupture of the uterus2- Uterine atony
3- Toxaemia
4- Eclampsia
5- Placenta previa
6- Nutritional anaemia
7- Stillbirths
8- Cancer of the cervix.. family planning is the only way to limit the size and control the interval between births
WOMEN’S HEALTH
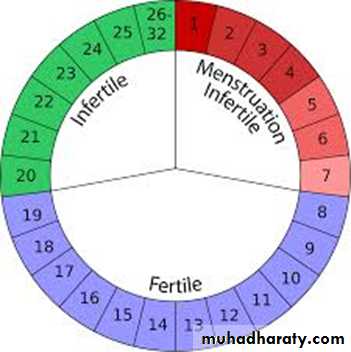
iii-Timing of birthsGenerally mothers face greater risk of death below 20 and above 30-35.
IMPACT OF FAMILY PLANNING ON…….
FOETAL HEALTH
A number of congenital anamolies are associated with advanced maternal age which can be avoided by timing pregnancy in relation to maternal age.CHILD HEALTH
A- Child mortality: It is well known that this increases if pregnancies occur in rapid succession. A birth interval of 2-3 years is considered desirable to reduce child mortality.B- Child growth, development and nutrition: The child is not likely to receive his full share of love and care, including nutrtional needs
CHILD HEALTH
C- Infectious diseases: Children living in large sized families have an increased risk of infection especially gastroenteritis respiratory and skin infections.Natural Family Planning
2-3 percent of the world’s reproductive age population depends on NFP which limits sexual intercourse to naturally infertile periods.
BIRTH CONTROL - CONTRACEPTION
Refers to methods or devices used to prevent pregnancy. Planning and provision of birth control is the essence of family planning.BENEFITS OF CONTRACEPTION
Contraception in developing countries has cut maternal deaths by 44% (270,000 deaths averted in 2008). Teenage pregnancies are at greatest risk of adverse outcomes e.g. preterm birth, LBW & infant mortality, thus adolescents need comprehensive sex education and access to reproductive health services, including contraception.Birth control increases economic growth because of fewer dependent children, more women participating in the workforce, and less consumption of scare resources. their children's schooling and body mass index all substantially improve with greater access to contraception.
Birth Control Methods:
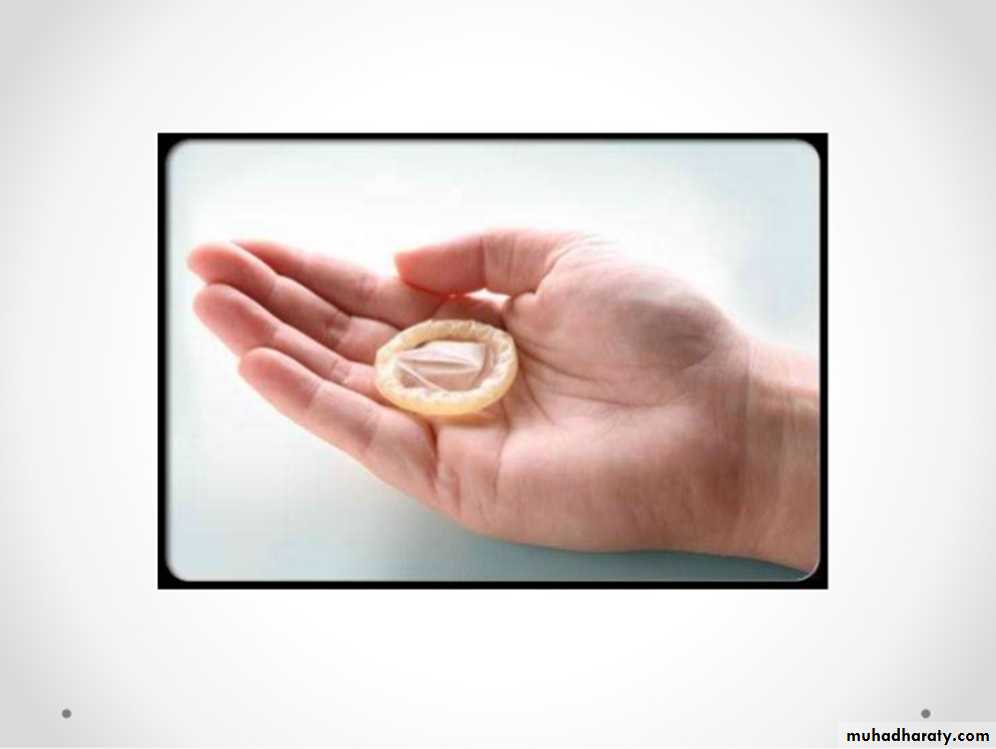
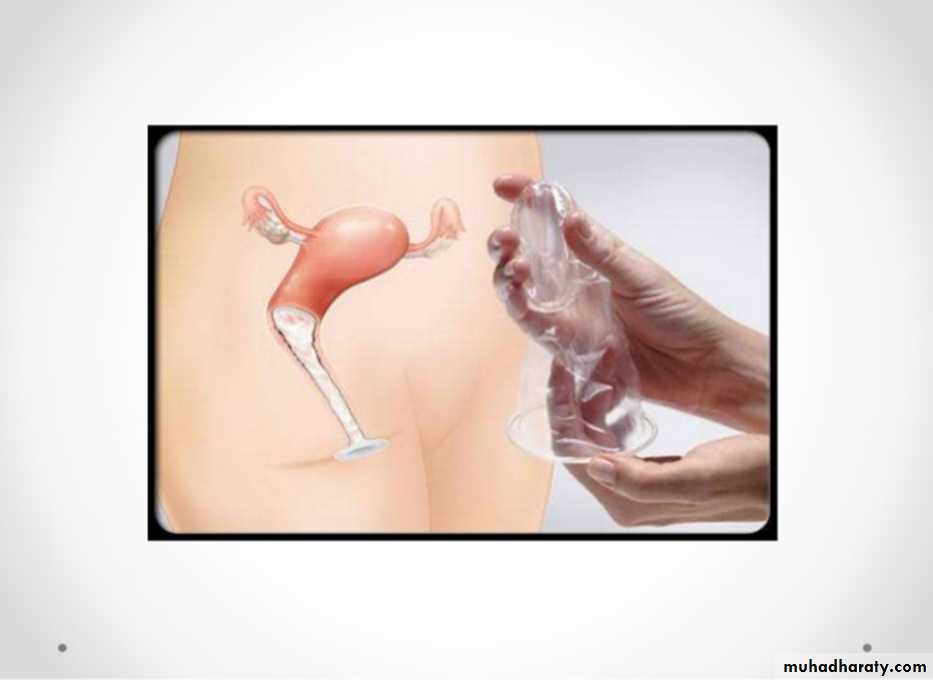
A- Barriers: such as condoms, diaphragms, and the contraceptive sponge;B- Hormonal contraception :includes oral pills, patches, vaginal rings, and injectable contraceptives;
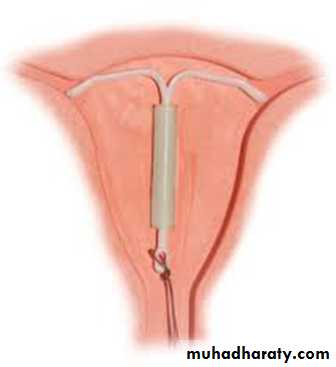
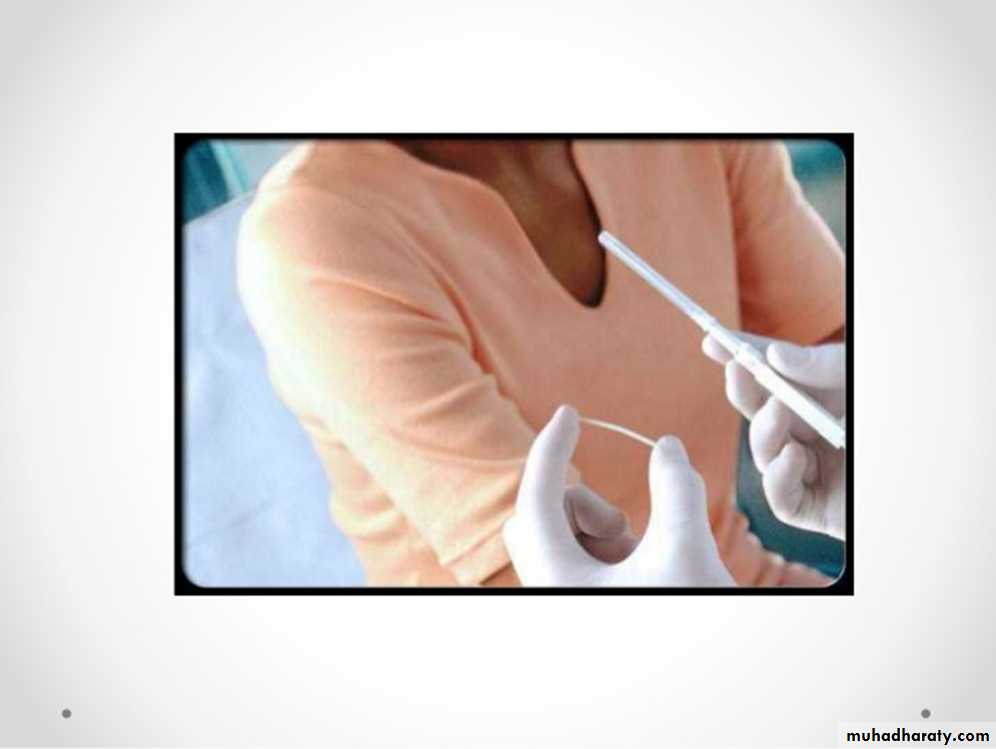
C- Intrauterine devices (IUDs).
e.g. transdermal patch
Emergency contraception can prevent pregnancy after unprotected sex.
Long-acting reversible contraception such as implants, IUDs, or vaginal rings are recommended to reduce teenage pregnancy.eg. Split dose emergency contrceptive pills
Chance of pregnancy during first year of use:
MethodTypical use
Perfect use
No birth control
85%
85%
Combination pill
8%
0.3%
Progestin-only pill
13%
1.1%
Sterilization (female)
0.5%
0.5%
Sterilization (male)
0.15%
0.10%
Condom (female)
21%
5%
Condom (male)
15%
2%
Copper IUD
0.8%
0.6%
Hormone IUD
0.2%
0.2%
Patch
8%
0.3%
Vaginal ring
8%
0.3%
Depo Provera
3%
0.3%
Implant
0.05%
0.05%
Diaphragm and spermicide
16%
6%
Withdrawal
27%
4%
Standard Days Method
~12-25%
~1-9%
STERILIZATION
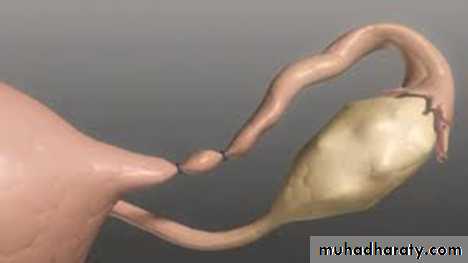
Sterilization by means such as vasectomy and tubal ligation is permanent contraception
Percentage of women using modern contraception:
Blue to pink :60-90%Dark brown to black:6-18%
•
FAMILY PLANNING IN IRAQ
Barriers to birth spacing:1-The influence of persons in the. community(traditional ,religious).
2-Availability of variety of methods.
3-Accessibility of FP services.
Cost.
Grounds on which abortion is permitted:
To save the life of the woman Yes
To preserve physical health NoTo preserve mental health No
Rape or incest No
Foetal impairment Yes
Economic or social reasons No
Available on request No
Additional requirements:
Approval from THREE physicians is needed in order to obtain a legal abortion AND THIS SHOULD BE DONE IN A STATE HOSPITAL.