By
Dr. Ashraf MA. Hussain
Msc./PhD. Community Medicine
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

Occupational Health
: is a multidisciplinary
activity, defined by
I.L.O.
(
International Labor
Organization
), as
the promotion and maintenance of highest degree of
physical, mental and social wellbeing of workers in all
occupations.
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

Occupational health should aim at the
}
promotion and maintenance of the physical,
mental and social well-being of workers in all
occupations;
}
the prevention among workers of departures
from health caused by their working conditions;
}
The protection of workers in their employment
from risks resulting from factors adverse to
health;
}
The placing and maintenance of the worker in an
occupational environment adapted to his
physiological and psychological equipment, or,
the adaptation of work to man and of each man
to his job
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

}
Occupational health is a Preventive medicine
and have the
same aim - the prevention of disease and
maintenance of the of health. And the levels
of application of preventive measures are the
same –
health promotion, specific protection, early
diagnosis and treatment, disability limitation
and rehabilitation;
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version
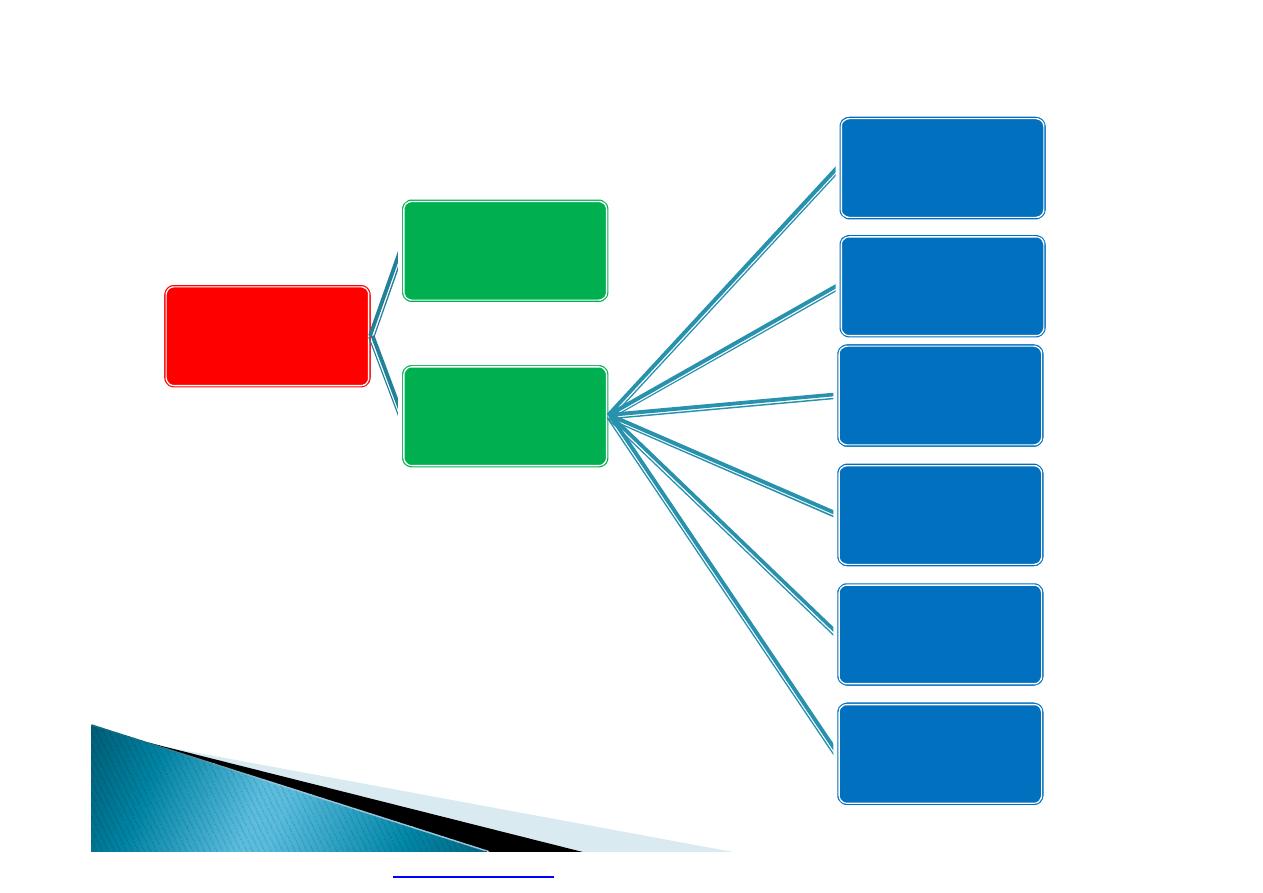
Occupational
Health
Occupational
Hygiene
Occupational
Medicine
Industrial
Medicine.
Agricultural
Medicine.
Navigation
Medicine.
Sport
Medicine.
Military
Medicine.
Aviation
Medicine.
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

}
The International Occupational Hygiene Association
(IOHA) refers to occupational hygiene
}
as the discipline of anticipating, recognizing,
evaluating and controlling health hazards in the
working environment with the objective of protecting
worker health and well-being and safeguarding the
community at large
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

The Practice of Occupational Hygiene
}
The recognition of the possible health
hazards in the work environment
}
The evaluation of hazards, which is the
process of assessing exposure and reaching
conclusions
}
Prevention and control of hazards, which is
the process of developing and implementing
strategies to eliminate, or reduce to
acceptable levels, the occurrence of harmful
agents and factors in the workplace, while
also accounting for environmental protection.
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

Activities of Occupational Medicine :
1. Medical exam. Of the workers;
a. pre employment exam.
b. periodic exam.
2. Health education.
3. First –aid facilities.
4. Rehabilitation.
5. Epidemiological studies and
medical records.
6. Environmental and biological
monitoring.
10 October 2019
٨
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

*
Types of occupational hazards :
1.
Physical hazards (noise, vibration,
temperature, electricity, radiation, light
and pressure ).
2.
Chemical hazards (dust, mists, fumes,
gases, fibers, vapors and liquids).
3.
Biological hazards (insects, mites, moulds,
yeasts, fungi, bacteria, viruses and
parasites) .
4.
Ergonomic : fitness of the work process
and work place to the workers (posture,
movement, repetitive motion and light) .
5.
Psychological hazards (tension, stress, and
phobia) .
6.
Accidents and mechanical hazards
.
10 October 2019
٩
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

1.
Occupational hazards can be controlled by a
variety of methods.
2.
The goal of controlling a hazard is to
prevent workers from being exposed to the
hazard.
3.
The most effective control measure is to
control hazards at the source by eliminating
the hazard or by substituting a hazardous
chemical, machine, work process, etc., with
a less dangerous one.
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

4.
It is important to recognize hazards and
health and safety problems in the
workplace.
5.
There are five general categories of control
measures: elimination, substitution,
engineering controls, administrative
controls and personal protective equipment.
6.
A combination of methods usually provides
a safer and healthier workplace than relying
on only one method.
7.
Personal protective equipment should be
the last choice in control measures.
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

}
Is the most effective method of control.
}
Elimination of a specific hazard or hazardous
work process, or preventing it from entering
the workplace (Eliminate hazards at the
“development stage”)
}
It is important to consider worker health and
safety when work processes are still in the
planning stages. For example, when
purchasing machines, safety should be the
first concern, not cost.
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

}
Machines that are not produced with the
proper guards on them may cost less to
purchase, but cost more in terms of
accidents, loss of production, compensation,
etc.
}
Unfortunately, many used machines that do
not meet safety standards are exported to
developing countries, causing workers to pay
the price with accidents, hearing loss from
noise, etc.
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

}
If a particularly dangerous chemical or work
process cannot be completely eliminated, then
try to replace it with a safer substitute
}
These materials can be more expensive to
purchase but they are safer for workers to
handle.
}
Ex:
}
less volatile (volatile liquids vaporize, or
evaporate easily) instead of a highly volatile one
}
many dry, dusty powders are also available in
brick, pellet, paste, flakes, oil damped powders,
and other forms that create less dust when
handled, and reduce the chance of inhaling the
dust.
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

}
detergent plus water-cleaning solutions
instead of organic solvents
}
leadless glazes in the ceramics industry
leadless pigments in paints
}
synthetic grinding wheels (such as aluminium
oxide, silicon carbide) instead of sandstone
wheels
}
vacuum cleaner when cleaning up toxic dust.
Never sweep toxic dust with brooms or
brushes
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

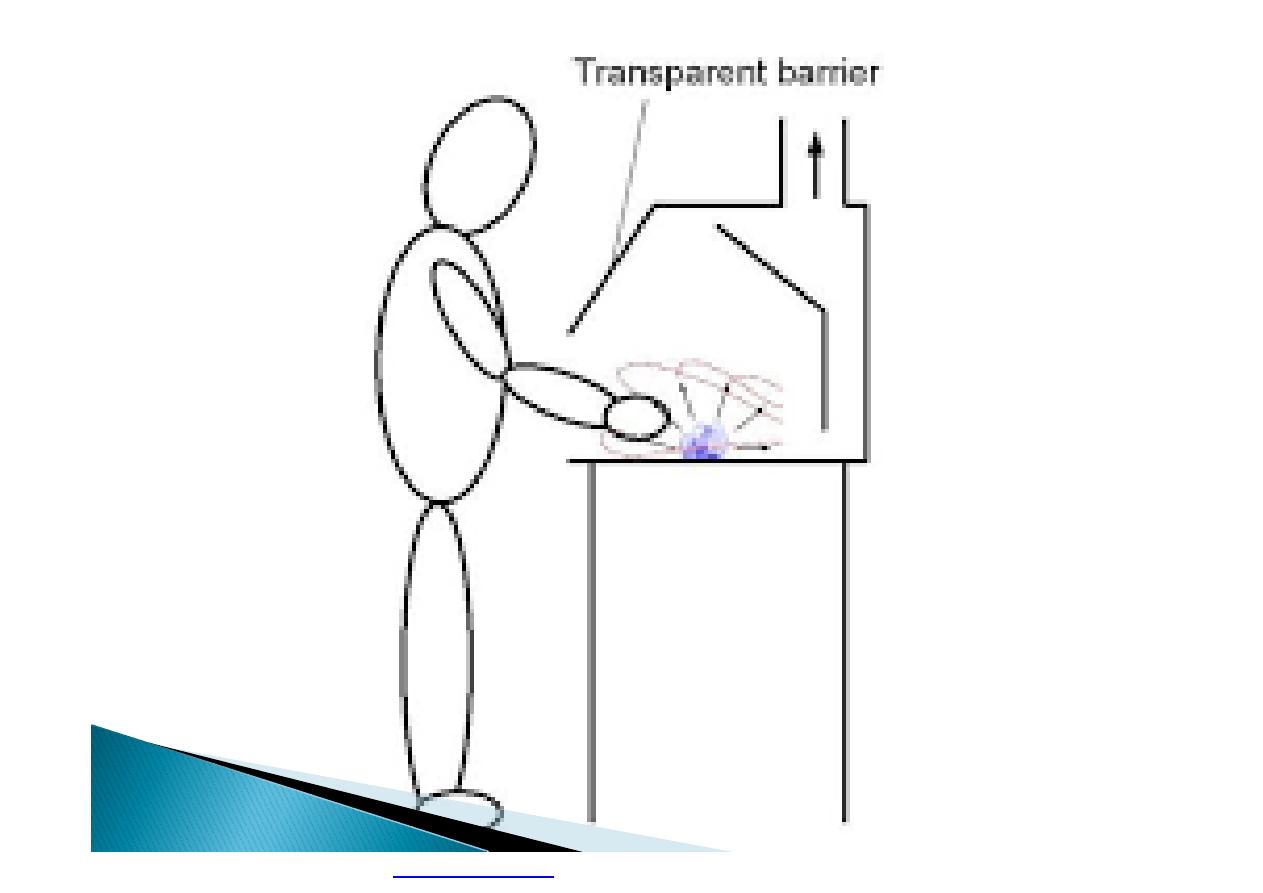
}
If a hazardous substance or work process
cannot be eliminated or substituted, then
enclosing it so workers are not exposed to
the hazard is the next best method of
control.
}
Many hazards can be controlled by partially
or totally enclosing the work process.
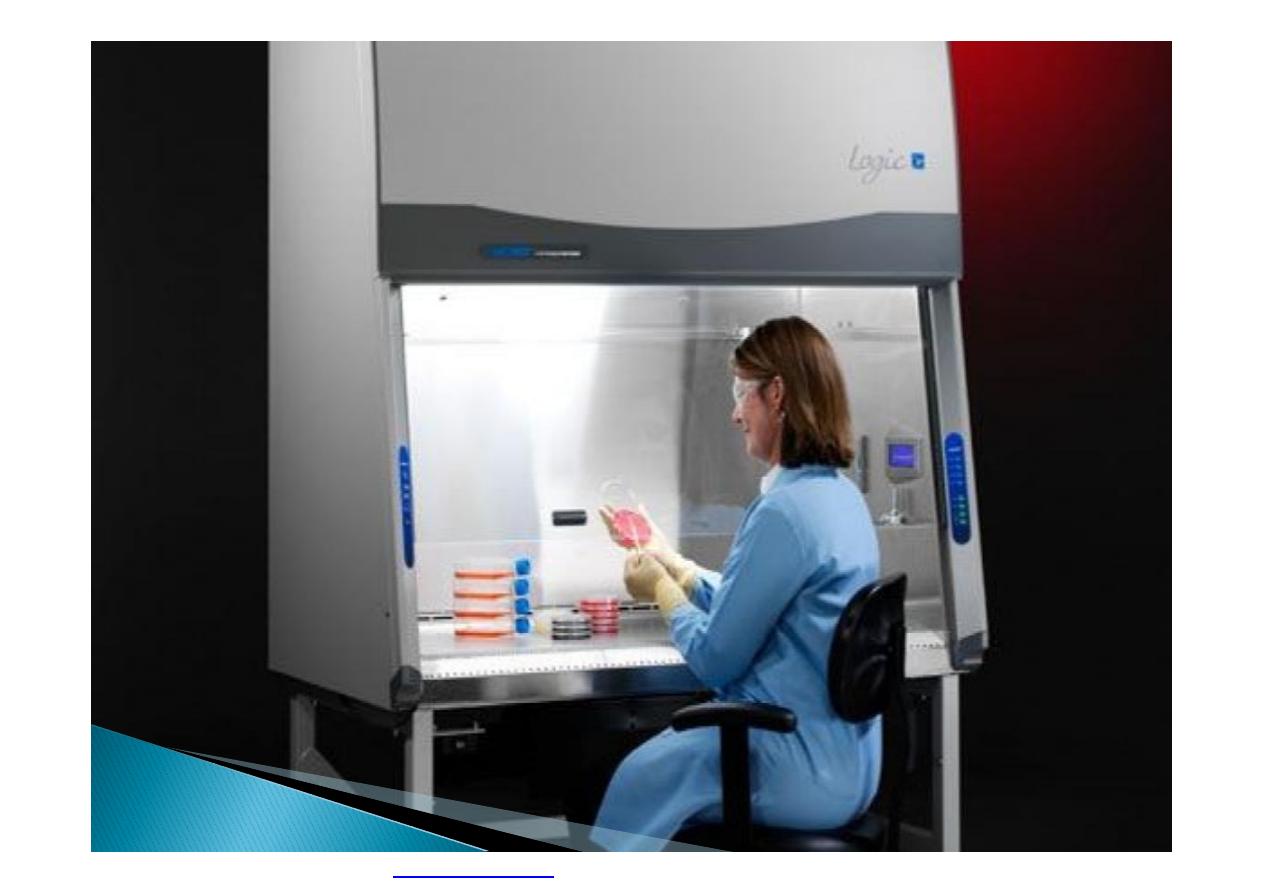
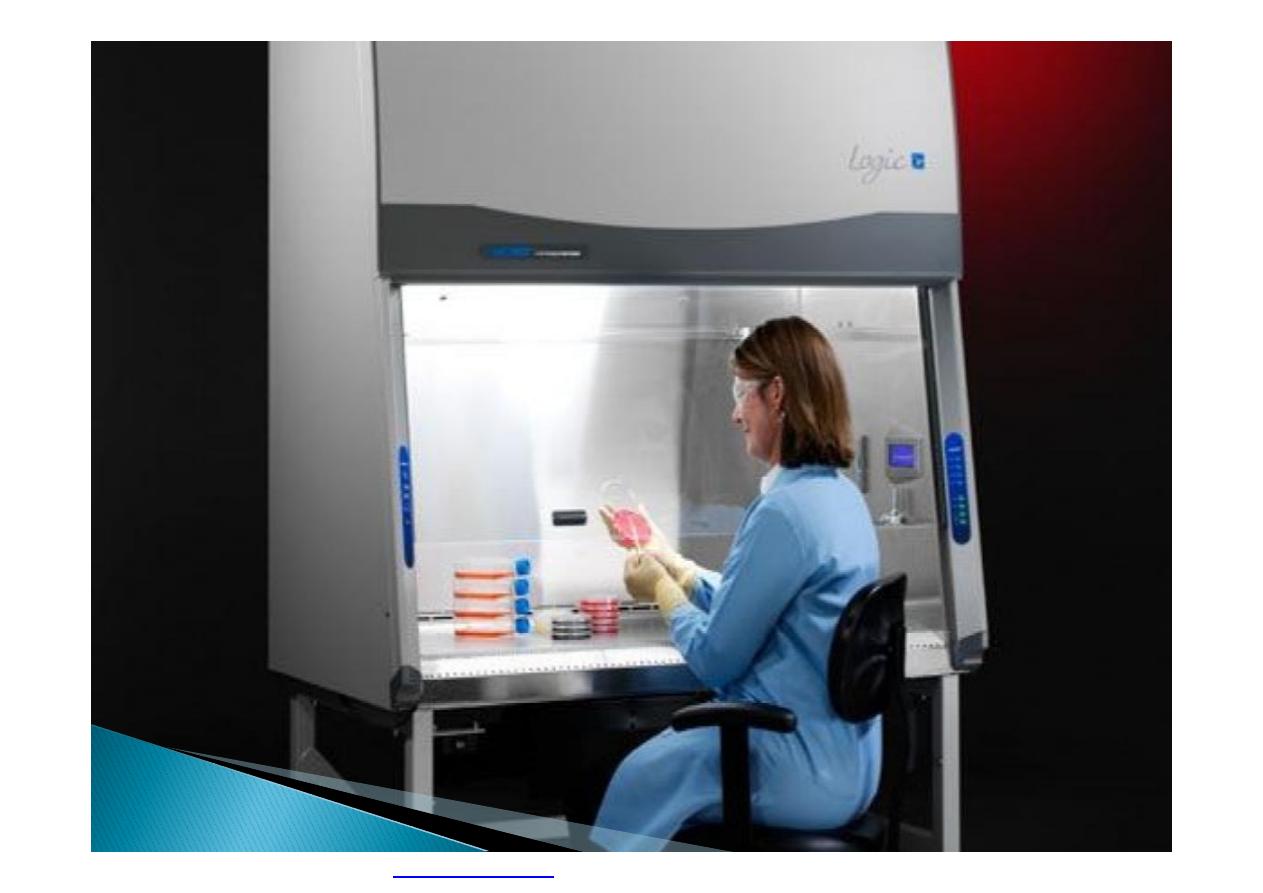
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

}
Highly toxic materials that can be released
into the air should be totally enclosed, usually
by using a mechanical handling device or a
closed glove system that can be operated
from the outside
}
Whole areas of a plant can be “enclosed” by
requiring workers to operate those areas
from a control room.
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

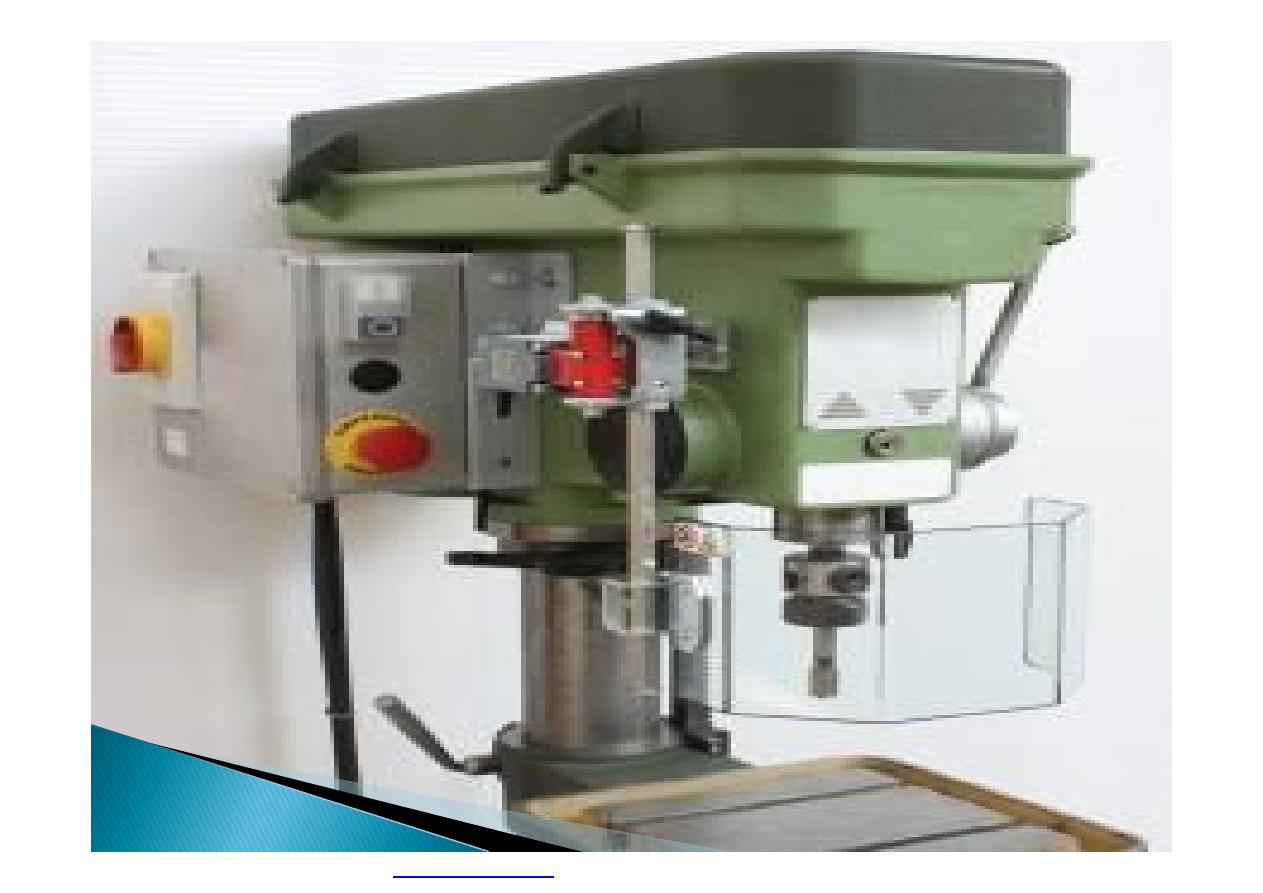
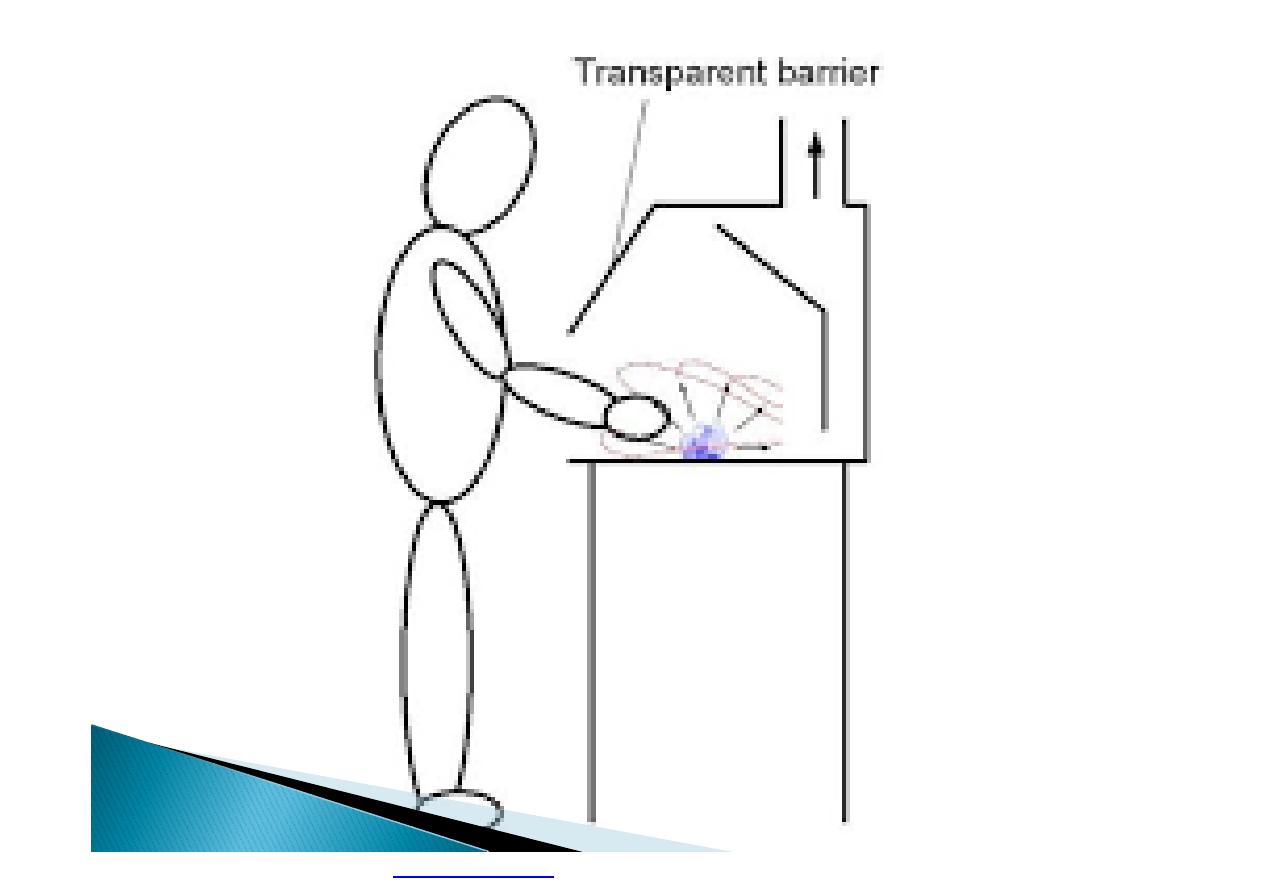
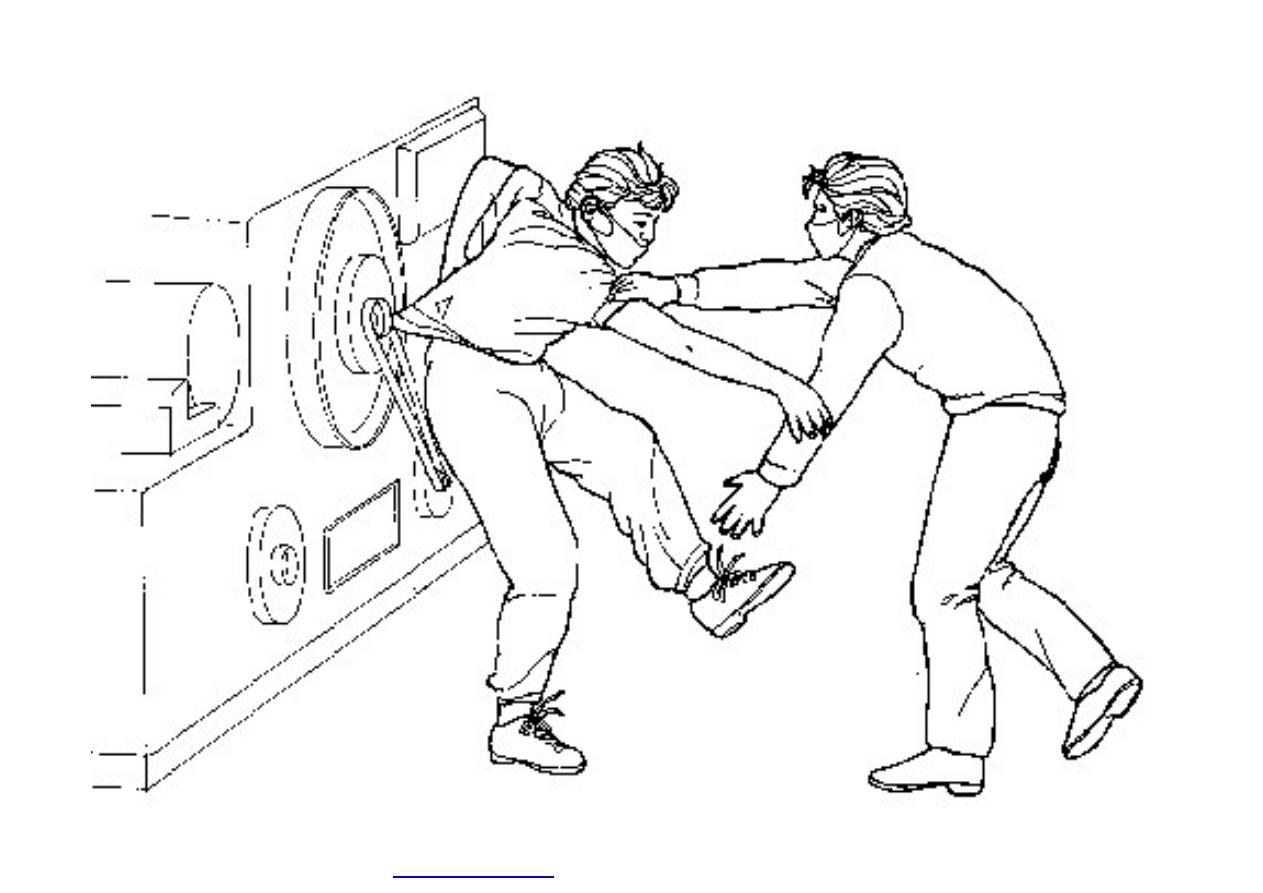
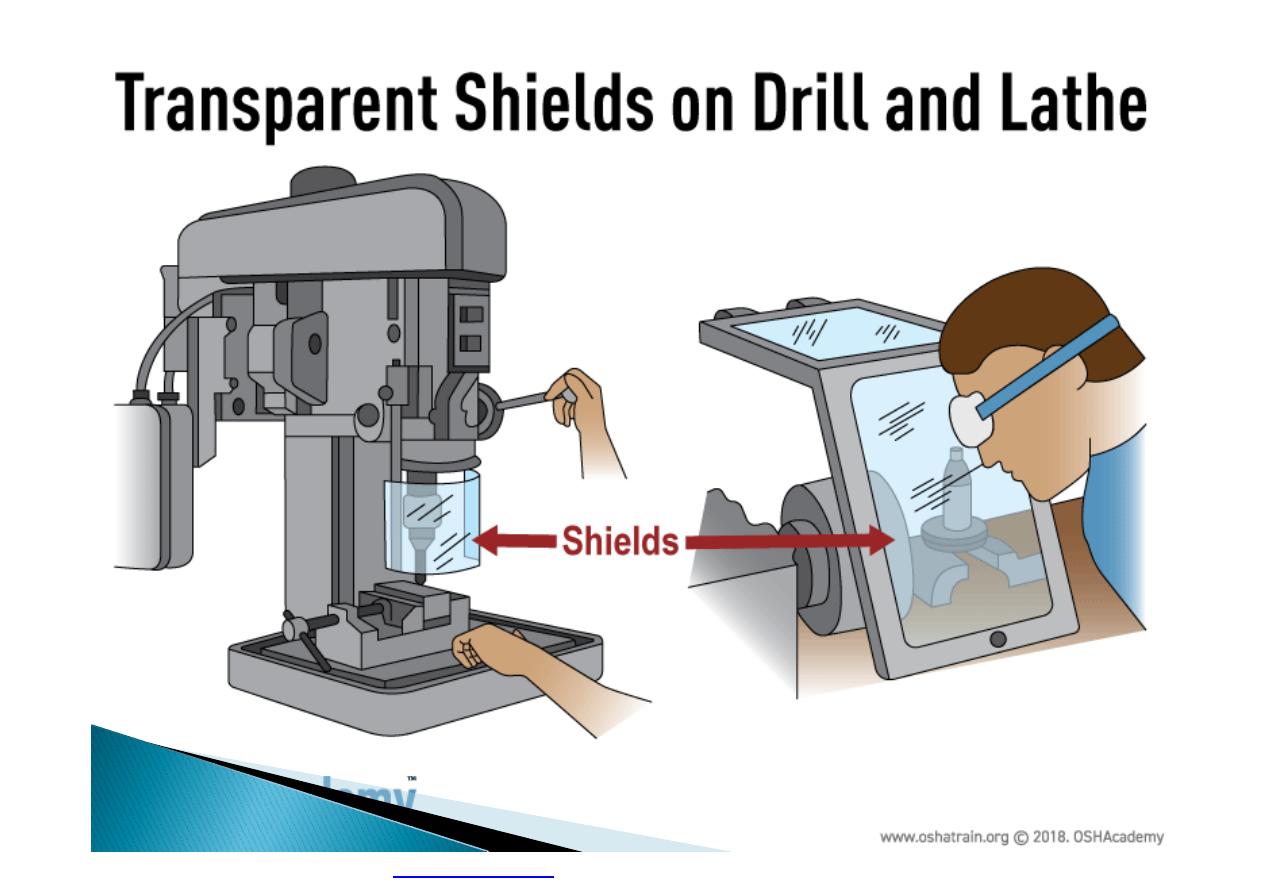
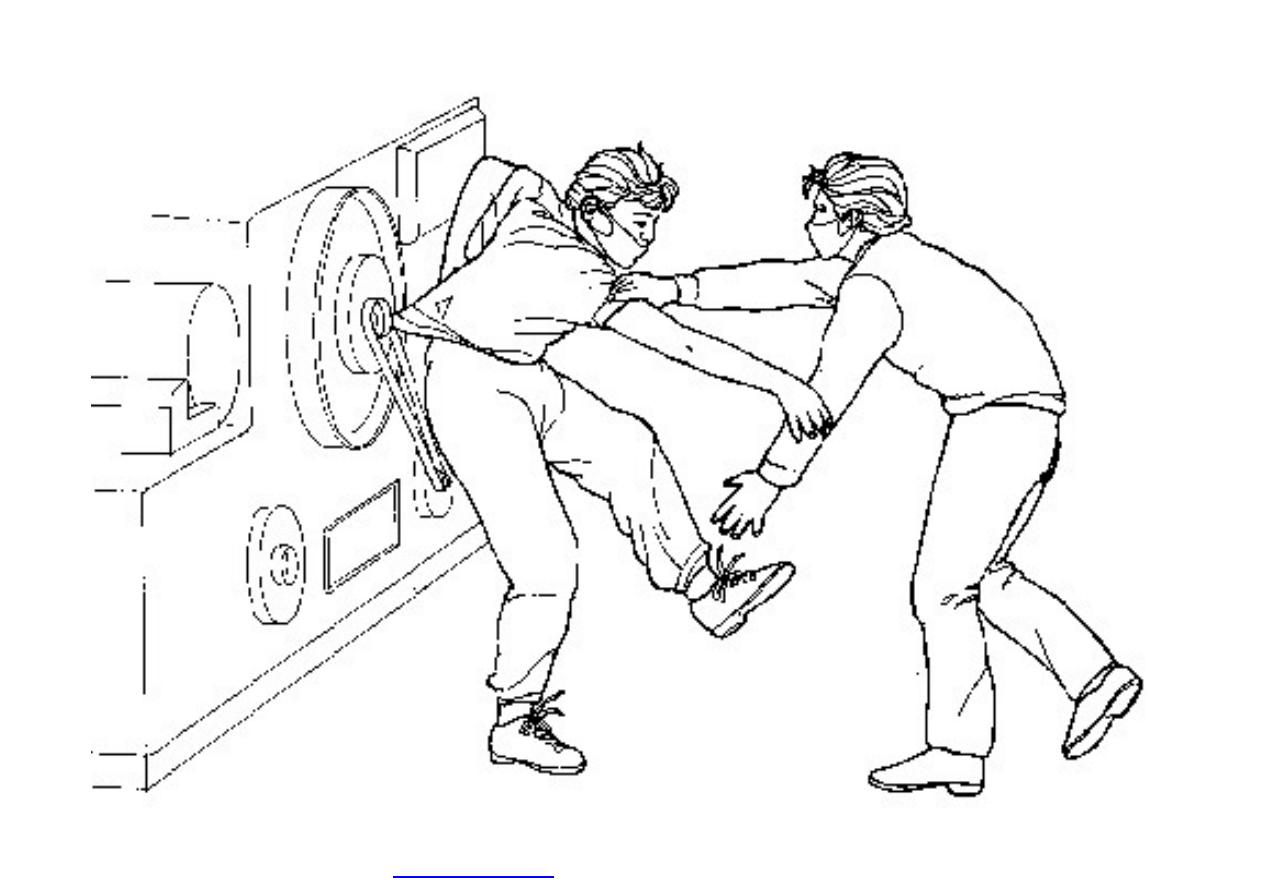
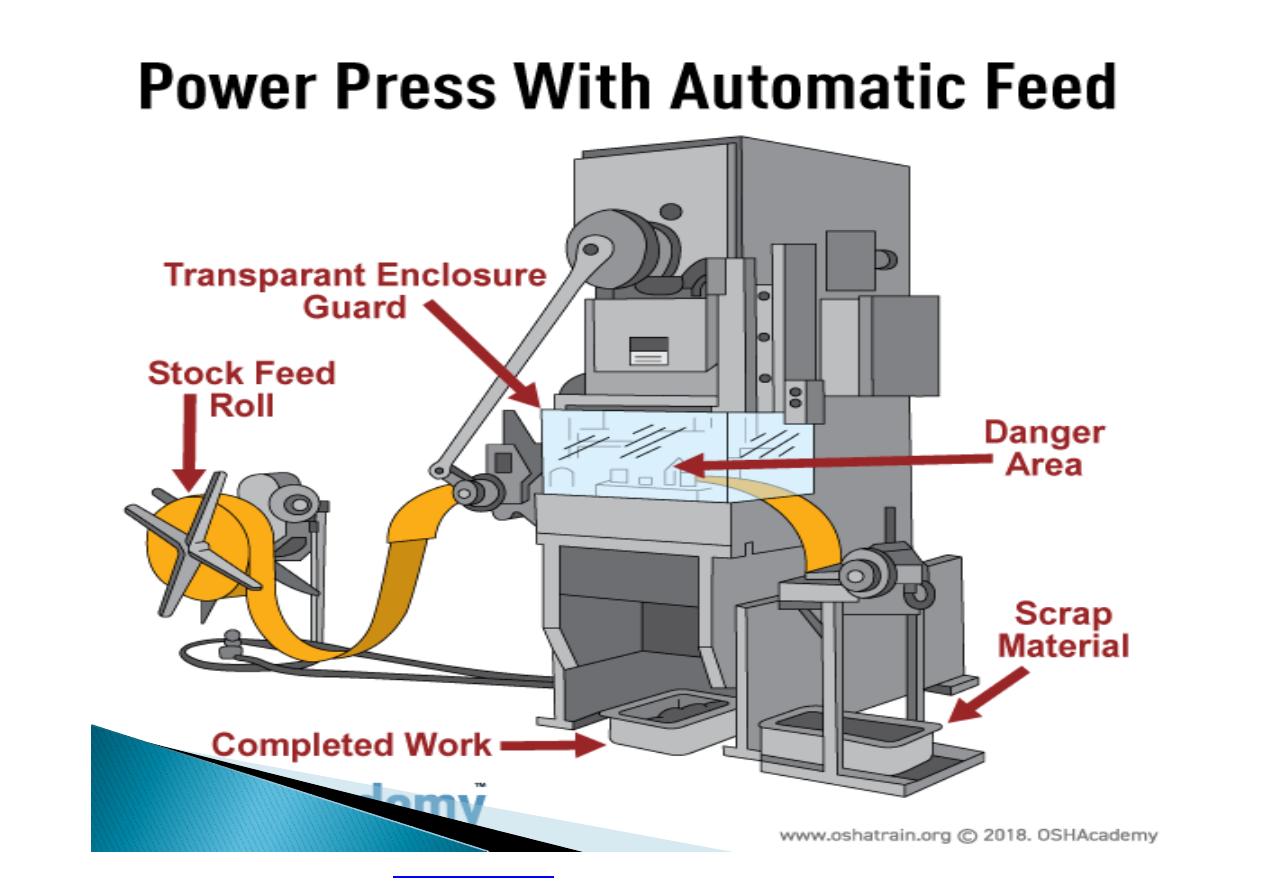
}
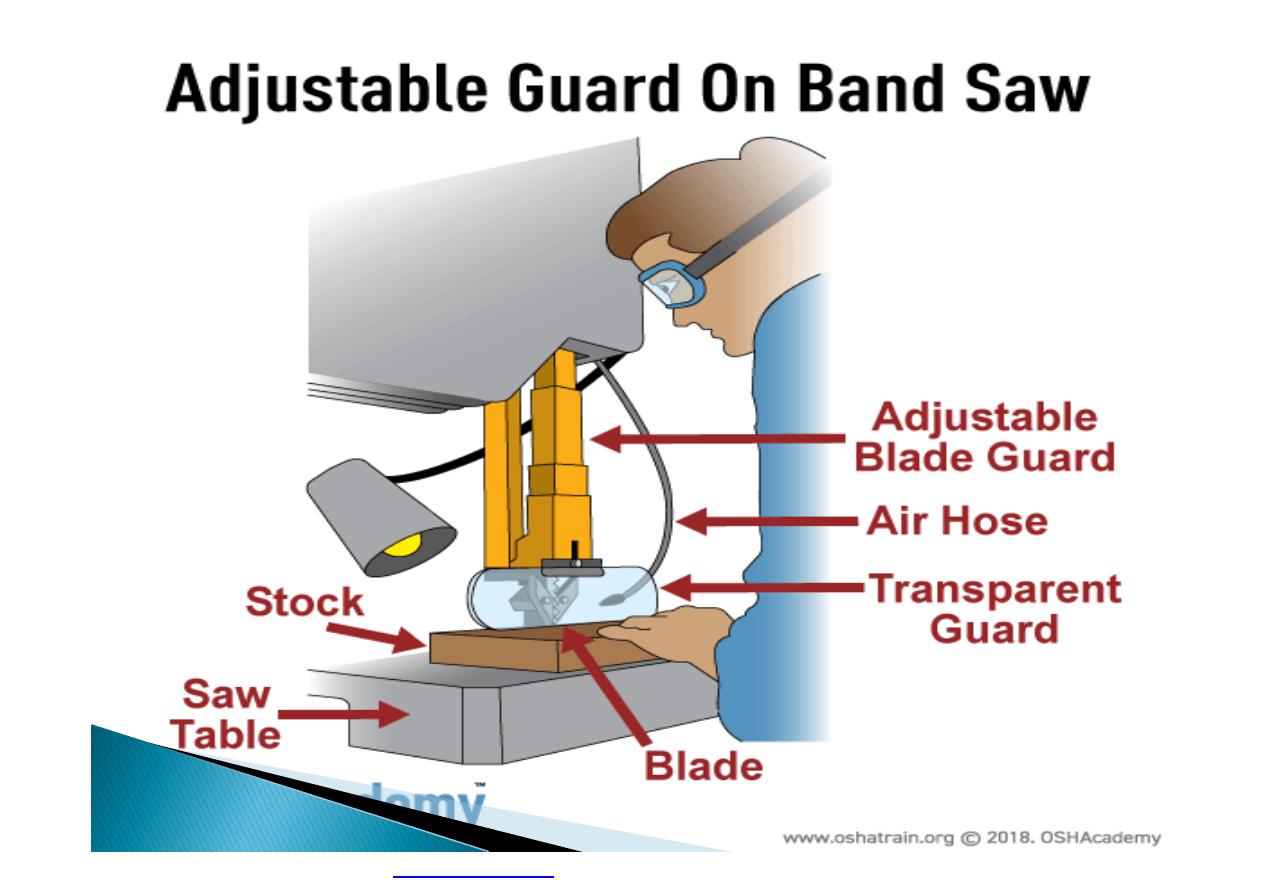
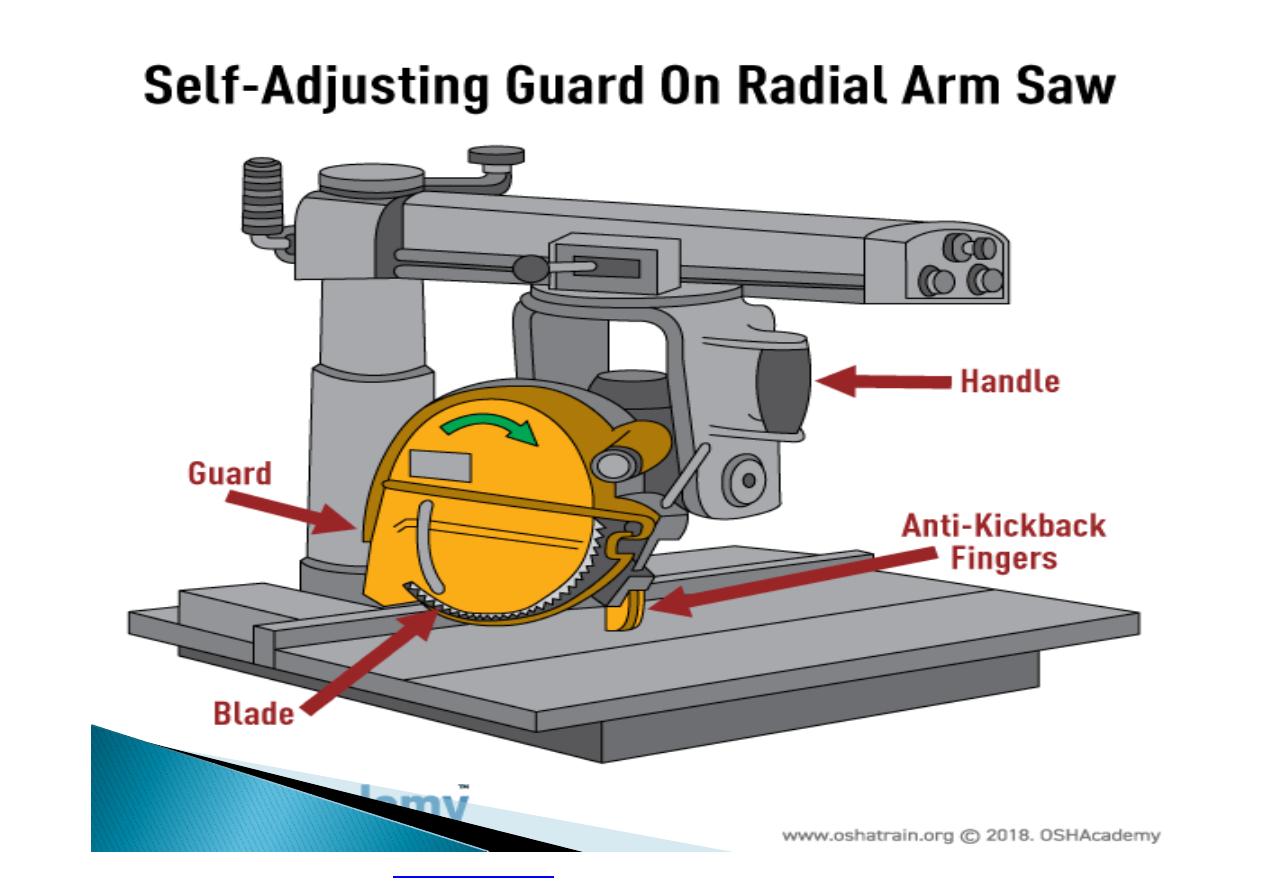
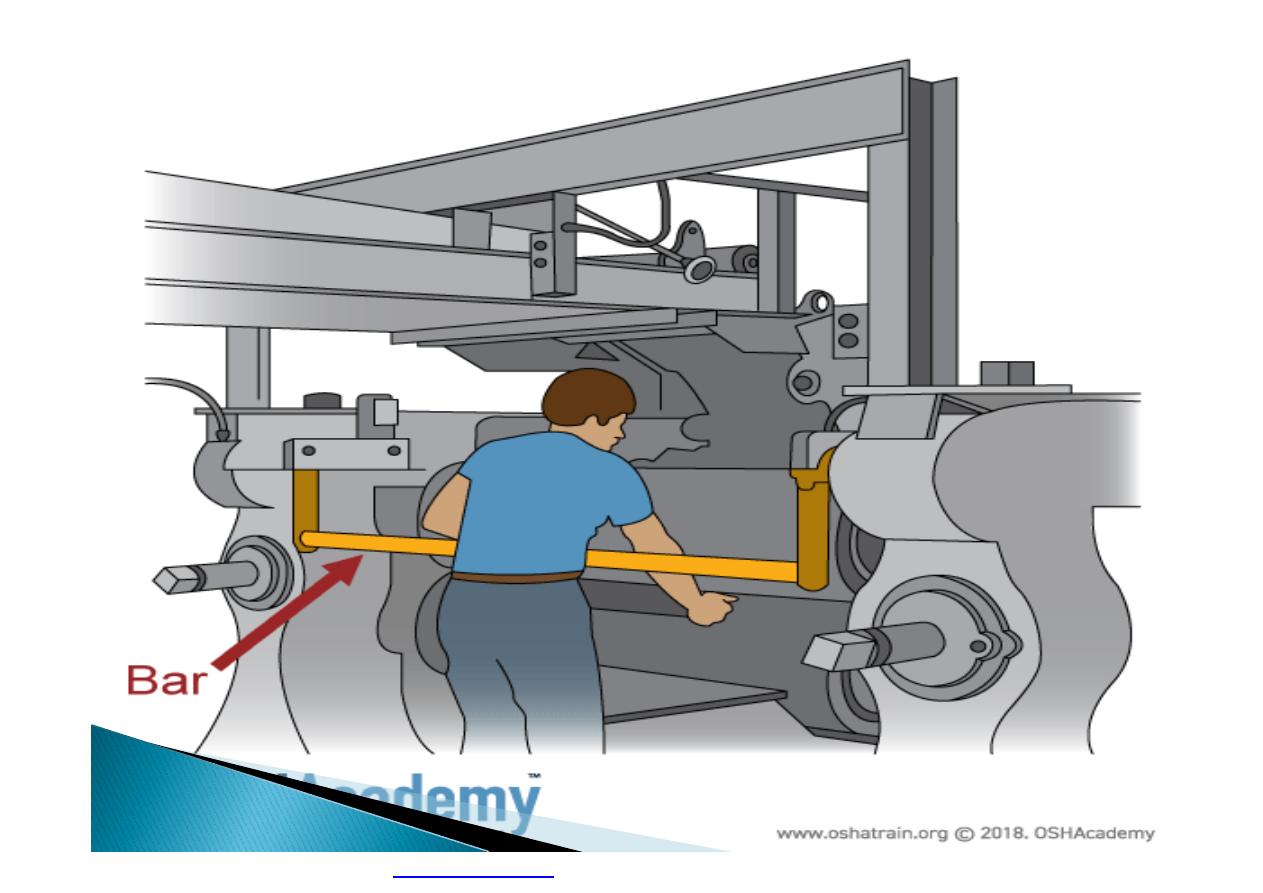
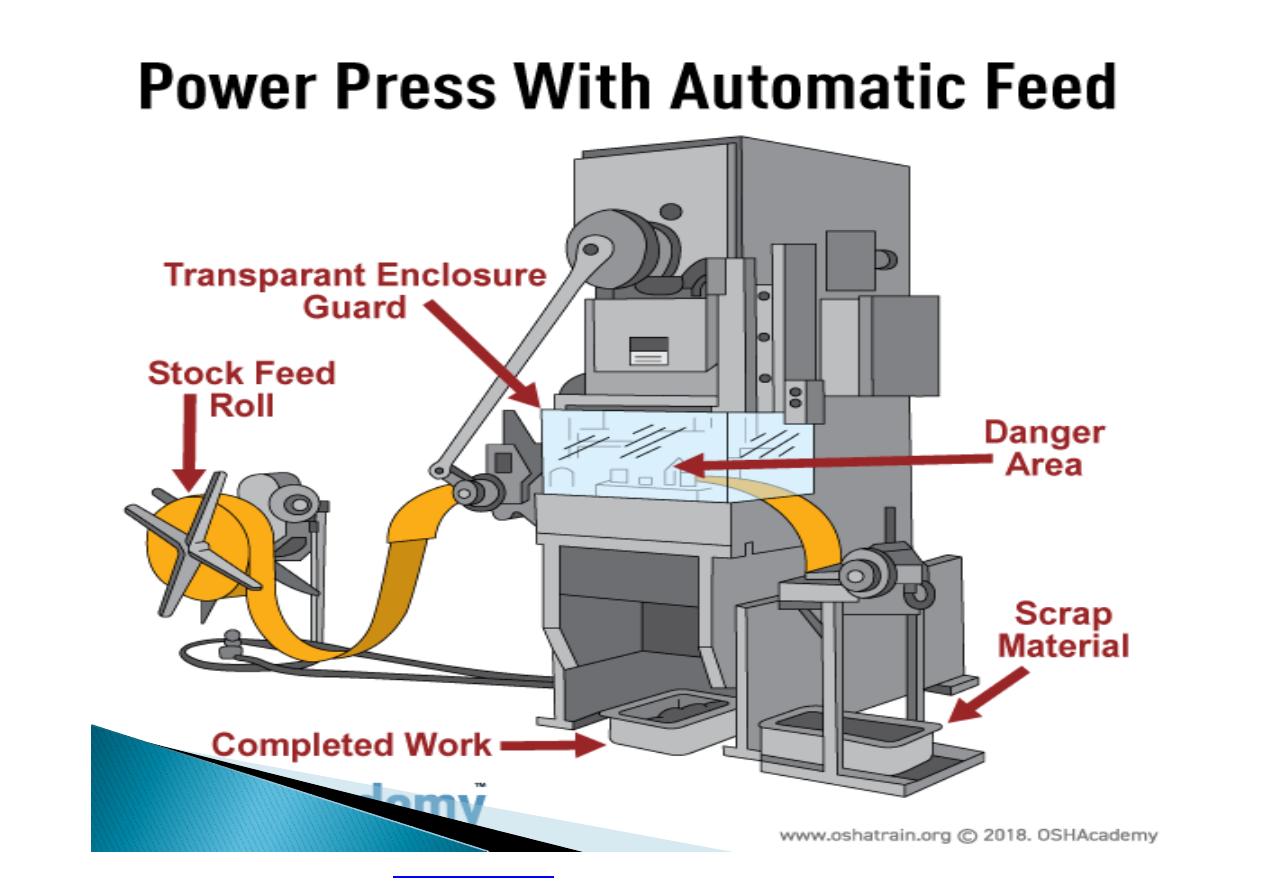
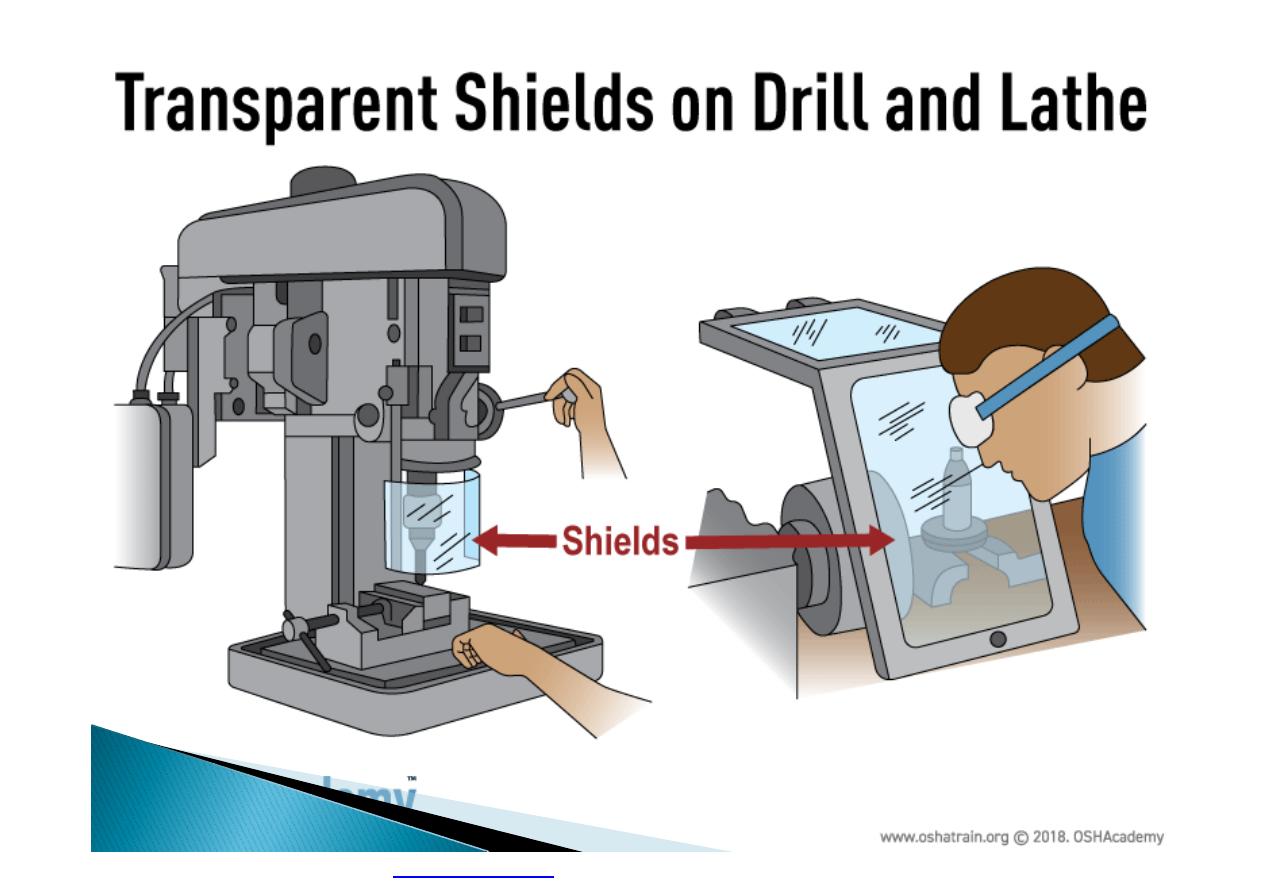
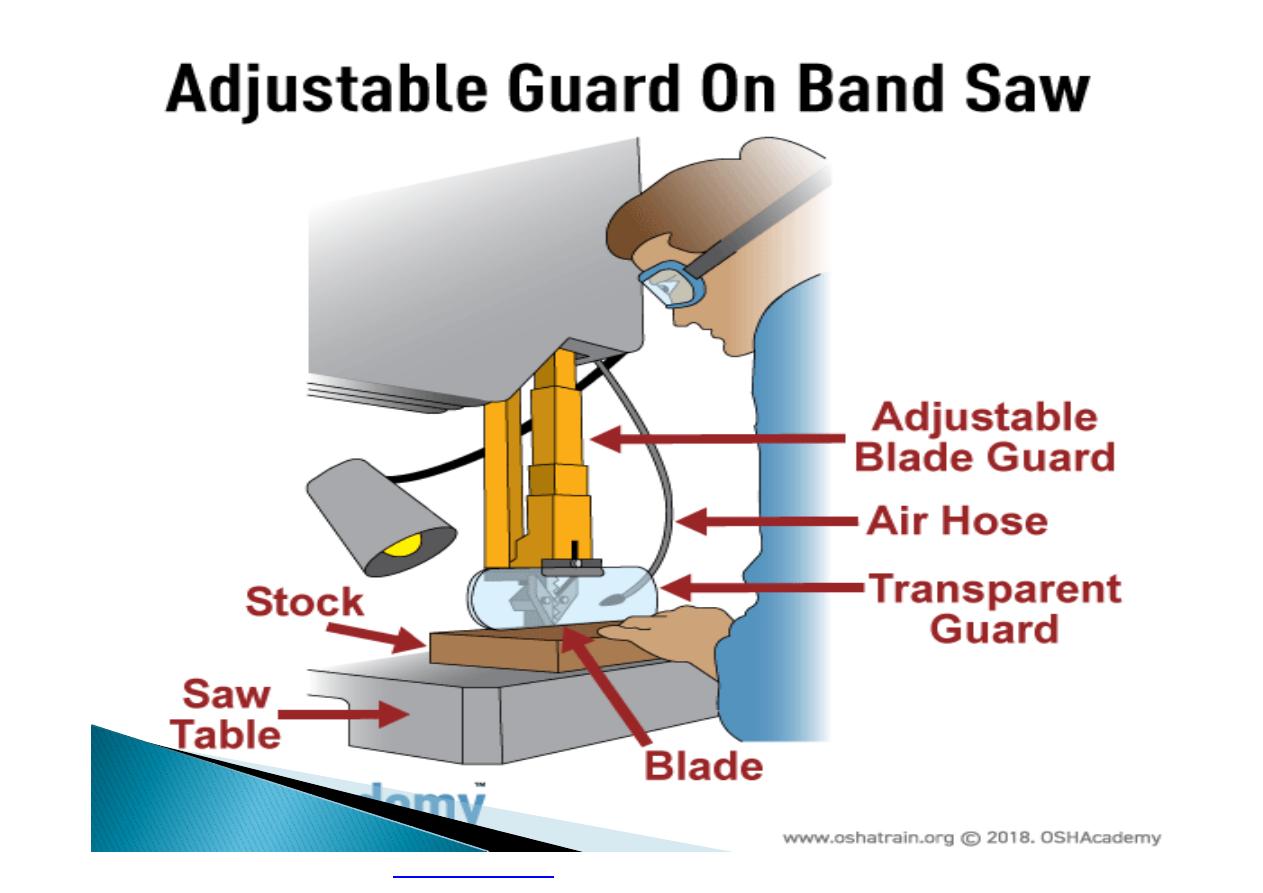
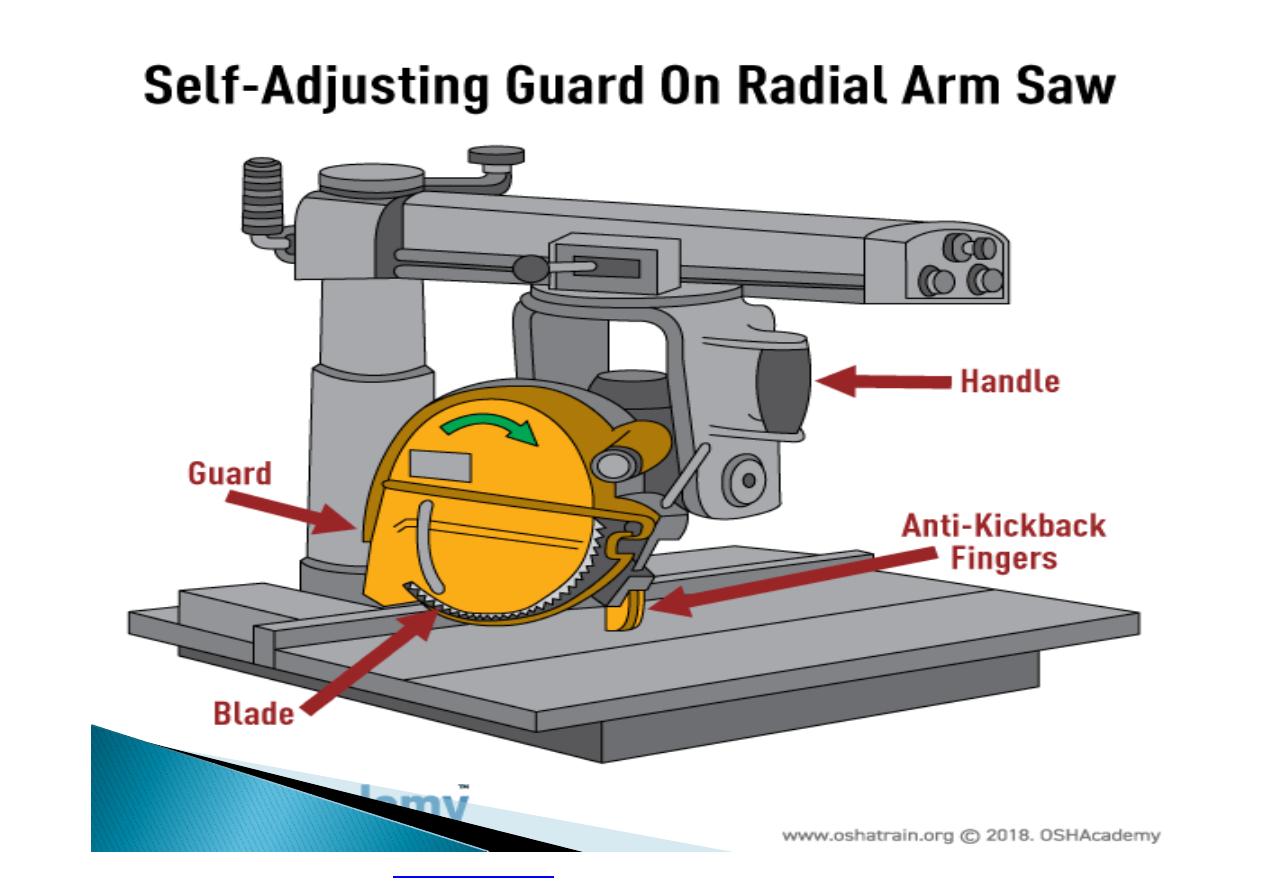
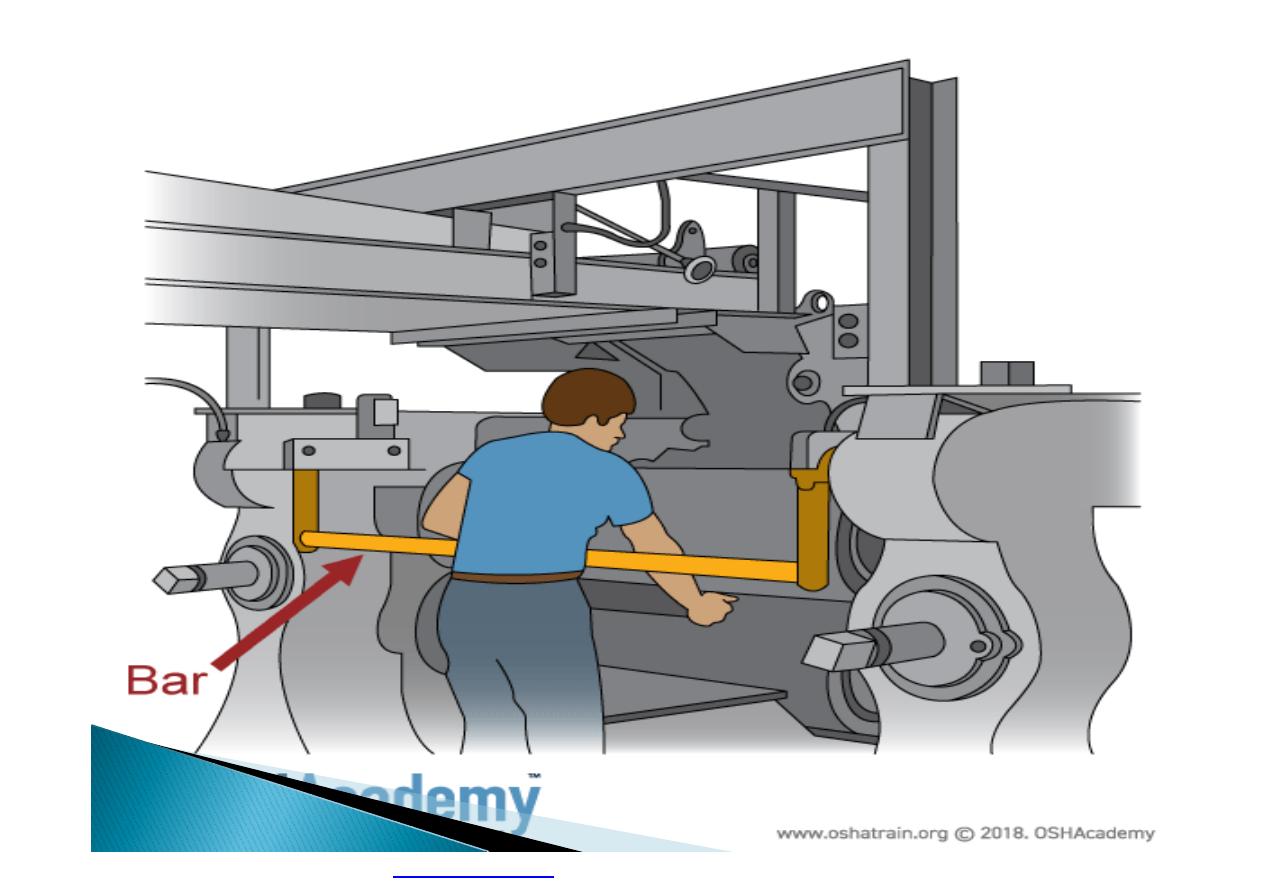
Machine guarding is another form of
enclosure that prevents workers from coming
into contact with dangerous parts of
machines.
}
Some of the areas of a machine that can
injure the worker are: the point of operation
pinch-points; sharp areas, such as blades;
exposed electrical components, which can
cause electrical shock or burns; presses,
which can crush; rotating parts; flying chips
and sparks.
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

}
Isolation can be an effective method of
control if a hazardous job can be moved to a
part of the workplace where fewer people will
be exposed,
}
or if a job can be changed to a shift when
fewer people are exposed (such as a weekend
or midnight shift).
}
The worker can also be isolated from a
hazardous job, for example by working in an
air-conditioned control booth.
}
isolating the work process or the worker does
not eliminate the hazard, which means
workers can still be exposed
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

}
Ventilation in the workplace can be used for
two reasons:
}
(1) to prevent the work environment from
being too hot, cold, dry or humid;
}
(2) to prevent contaminants in the air from
getting into the area where workers breathe.
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

}
Generally there are two categories of
ventilation:
1.
local exhaust ventilation
2.
general ventilation.
}
Ventilation should be used together with
other methods of control.
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

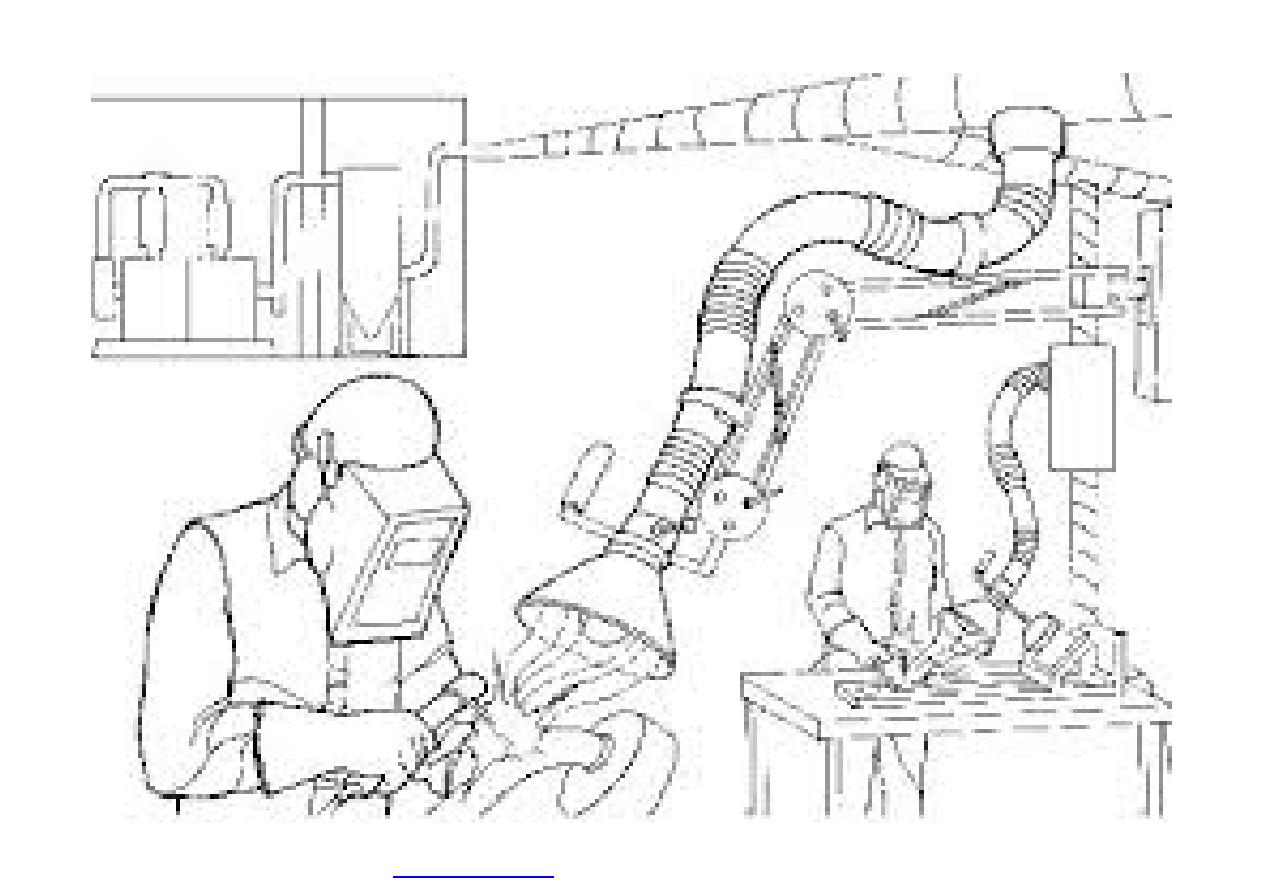
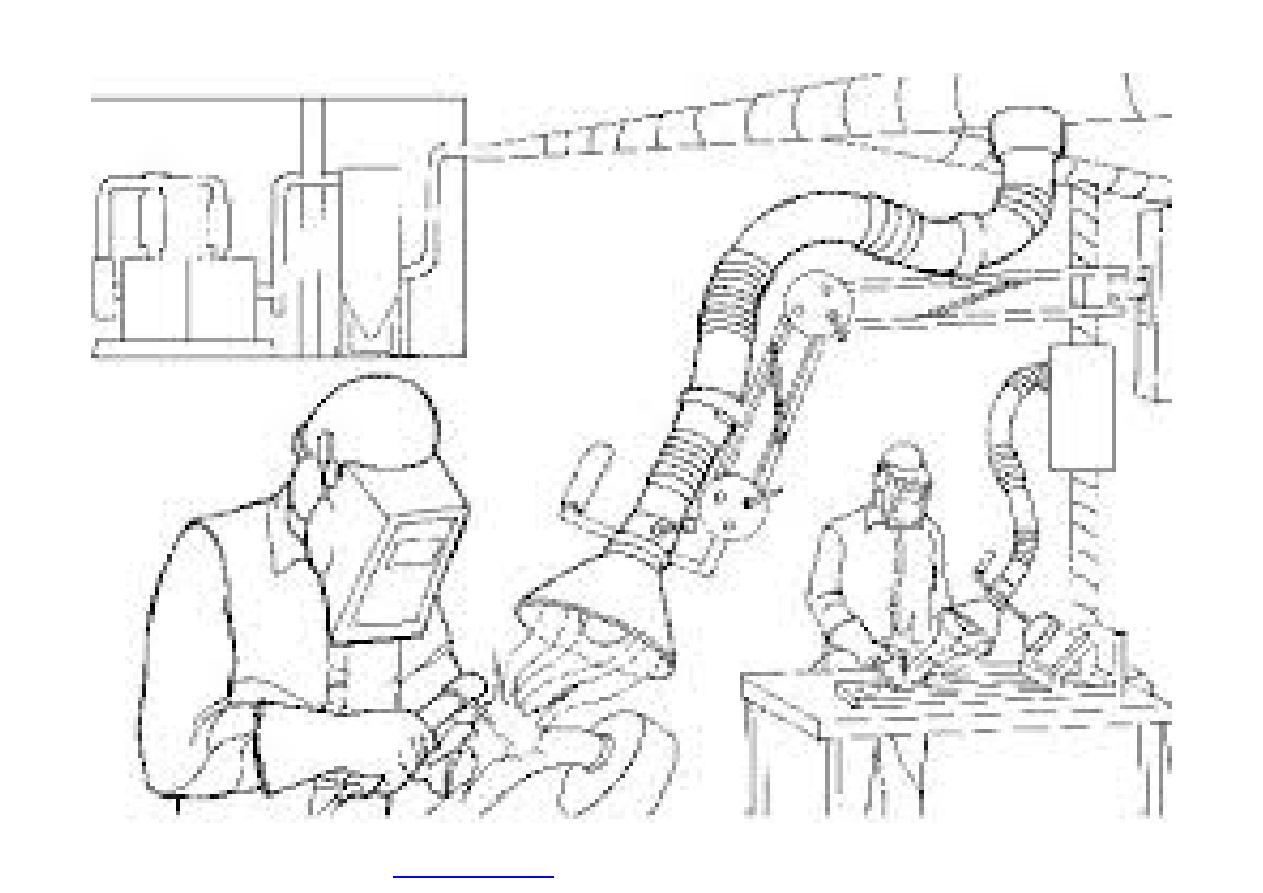
}
It usually uses suction, based on the principle of
a vacuum cleaner, to remove pollutants from the
air.
}
Exhaust ventilation can include the use of flexible
piping.
}
The end of the pipe that draws in the
contaminants (the inlet) must be placed as close
as possible to the source of the hazard in order
to be effective.
}
Flexible piping is often used to draw welding
fumes away from the worker and to draw away
contaminants in work areas that are hard to
reach.
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

}
Which is generally used for keeping the
workplace comfortable.
}
It is one of the least effective methods of
controlling hazards but one of the most
commonly used.
}
The purpose of any general ventilation
system is to remove contaminated air and
replace it with “fresh” air.
}
This system does not really remove
hazardous agents from the air; it simply
reduces the amounts in the air to levels that
are considered “safe” for breathing.
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

The effectiveness of a general ventilation
system depends on several things, including:
}
how quickly the hazardous agent is being
released into the air;
}
how much and how quickly fresh air is
coming in;
}
and how the contaminated air is being
removed.
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

By
Dr. Ashraf MA. Hussain
Msc./PhD. Community Medicine
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

Occupational Health
: is a multidisciplinary
activity, defined by
I.L.O.
(
International Labor
Organization
), as
the promotion and maintenance of highest degree of
physical, mental and social wellbeing of workers in all
occupations.
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

Occupational health should aim at the
}
promotion and maintenance of the physical,
mental and social well-being of workers in all
occupations;
}
the prevention among workers of departures
from health caused by their working conditions;
}
The protection of workers in their employment
from risks resulting from factors adverse to
health;
}
The placing and maintenance of the worker in an
occupational environment adapted to his
physiological and psychological equipment, or,
the adaptation of work to man and of each man
to his job
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

}
Occupational health is a Preventive medicine
and have the
same aim - the prevention of disease and
maintenance of the of health. And the levels
of application of preventive measures are the
same –
health promotion, specific protection, early
diagnosis and treatment, disability limitation
and rehabilitation;
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version
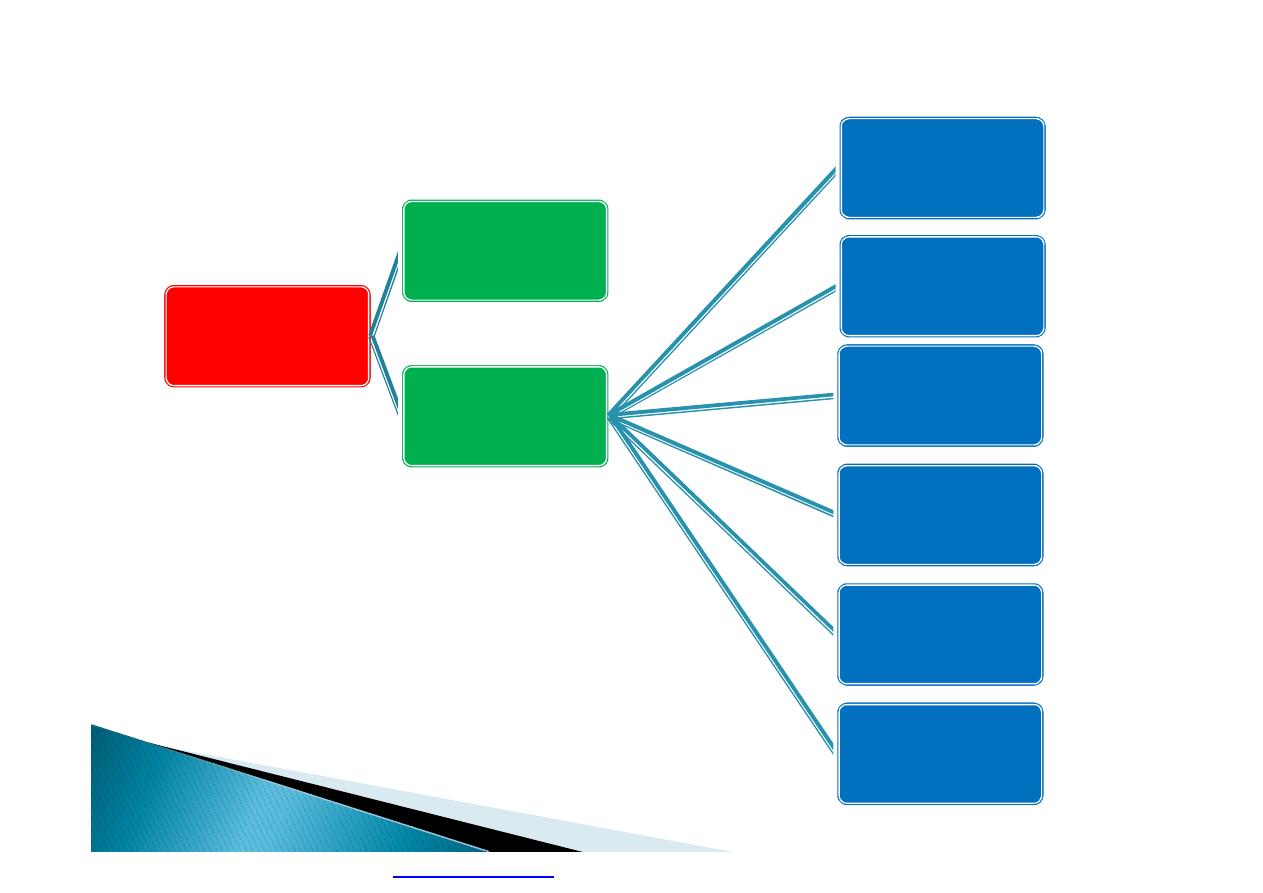
Occupational
Health
Occupational
Hygiene
Occupational
Medicine
Industrial
Medicine.
Agricultural
Medicine.
Navigation
Medicine.
Sport
Medicine.
Military
Medicine.
Aviation
Medicine.
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

}
The International Occupational Hygiene Association
(IOHA) refers to occupational hygiene
}
as the discipline of anticipating, recognizing,
evaluating and controlling health hazards in the
working environment with the objective of protecting
worker health and well-being and safeguarding the
community at large
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

The Practice of Occupational Hygiene
}
The recognition of the possible health
hazards in the work environment
}
The evaluation of hazards, which is the
process of assessing exposure and reaching
conclusions
}
Prevention and control of hazards, which is
the process of developing and implementing
strategies to eliminate, or reduce to
acceptable levels, the occurrence of harmful
agents and factors in the workplace, while
also accounting for environmental protection.
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

Activities of Occupational Medicine :
1. Medical exam. Of the workers;
a. pre employment exam.
b. periodic exam.
2. Health education.
3. First –aid facilities.
4. Rehabilitation.
5. Epidemiological studies and
medical records.
6. Environmental and biological
monitoring.
10 October 2019
٨
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

*
Types of occupational hazards :
1.
Physical hazards (noise, vibration,
temperature, electricity, radiation, light
and pressure ).
2.
Chemical hazards (dust, mists, fumes,
gases, fibers, vapors and liquids).
3.
Biological hazards (insects, mites, moulds,
yeasts, fungi, bacteria, viruses and
parasites) .
4.
Ergonomic : fitness of the work process
and work place to the workers (posture,
movement, repetitive motion and light) .
5.
Psychological hazards (tension, stress, and
phobia) .
6.
Accidents and mechanical hazards
.
10 October 2019
٩
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

1.
Occupational hazards can be controlled by a
variety of methods.
2.
The goal of controlling a hazard is to
prevent workers from being exposed to the
hazard.
3.
The most effective control measure is to
control hazards at the source by eliminating
the hazard or by substituting a hazardous
chemical, machine, work process, etc., with
a less dangerous one.
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

4.
It is important to recognize hazards and
health and safety problems in the
workplace.
5.
There are five general categories of control
measures: elimination, substitution,
engineering controls, administrative
controls and personal protective equipment.
6.
A combination of methods usually provides
a safer and healthier workplace than relying
on only one method.
7.
Personal protective equipment should be
the last choice in control measures.
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

}
Is the most effective method of control.
}
Elimination of a specific hazard or hazardous
work process, or preventing it from entering
the workplace (Eliminate hazards at the
“development stage”)
}
It is important to consider worker health and
safety when work processes are still in the
planning stages. For example, when
purchasing machines, safety should be the
first concern, not cost.
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

}
Machines that are not produced with the
proper guards on them may cost less to
purchase, but cost more in terms of
accidents, loss of production, compensation,
etc.
}
Unfortunately, many used machines that do
not meet safety standards are exported to
developing countries, causing workers to pay
the price with accidents, hearing loss from
noise, etc.
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

}
If a particularly dangerous chemical or work
process cannot be completely eliminated, then
try to replace it with a safer substitute
}
These materials can be more expensive to
purchase but they are safer for workers to
handle.
}
Ex:
}
less volatile (volatile liquids vaporize, or
evaporate easily) instead of a highly volatile one
}
many dry, dusty powders are also available in
brick, pellet, paste, flakes, oil damped powders,
and other forms that create less dust when
handled, and reduce the chance of inhaling the
dust.
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

}
detergent plus water-cleaning solutions
instead of organic solvents
}
leadless glazes in the ceramics industry
leadless pigments in paints
}
synthetic grinding wheels (such as aluminium
oxide, silicon carbide) instead of sandstone
wheels
}
vacuum cleaner when cleaning up toxic dust.
Never sweep toxic dust with brooms or
brushes
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

}
If a hazardous substance or work process
cannot be eliminated or substituted, then
enclosing it so workers are not exposed to
the hazard is the next best method of
control.
}
Many hazards can be controlled by partially
or totally enclosing the work process.
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

}
Highly toxic materials that can be released
into the air should be totally enclosed, usually
by using a mechanical handling device or a
closed glove system that can be operated
from the outside
}
Whole areas of a plant can be “enclosed” by
requiring workers to operate those areas
from a control room.
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

}
Machine guarding is another form of
enclosure that prevents workers from coming
into contact with dangerous parts of
machines.
}
Some of the areas of a machine that can
injure the worker are: the point of operation
pinch-points; sharp areas, such as blades;
exposed electrical components, which can
cause electrical shock or burns; presses,
which can crush; rotating parts; flying chips
and sparks.
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

}
Isolation can be an effective method of
control if a hazardous job can be moved to a
part of the workplace where fewer people will
be exposed,
}
or if a job can be changed to a shift when
fewer people are exposed (such as a weekend
or midnight shift).
}
The worker can also be isolated from a
hazardous job, for example by working in an
air-conditioned control booth.
}
isolating the work process or the worker does
not eliminate the hazard, which means
workers can still be exposed
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

}
Ventilation in the workplace can be used for
two reasons:
}
(1) to prevent the work environment from
being too hot, cold, dry or humid;
}
(2) to prevent contaminants in the air from
getting into the area where workers breathe.
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

}
Generally there are two categories of
ventilation:
1.
local exhaust ventilation
2.
general ventilation.
}
Ventilation should be used together with
other methods of control.
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

}
It usually uses suction, based on the principle of
a vacuum cleaner, to remove pollutants from the
air.
}
Exhaust ventilation can include the use of flexible
piping.
}
The end of the pipe that draws in the
contaminants (the inlet) must be placed as close
as possible to the source of the hazard in order
to be effective.
}
Flexible piping is often used to draw welding
fumes away from the worker and to draw away
contaminants in work areas that are hard to
reach.
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

}
Which is generally used for keeping the
workplace comfortable.
}
It is one of the least effective methods of
controlling hazards but one of the most
commonly used.
}
The purpose of any general ventilation
system is to remove contaminated air and
replace it with “fresh” air.
}
This system does not really remove
hazardous agents from the air; it simply
reduces the amounts in the air to levels that
are considered “safe” for breathing.
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

The effectiveness of a general ventilation
system depends on several things, including:
}
how quickly the hazardous agent is being
released into the air;
}
how much and how quickly fresh air is
coming in;
}
and how the contaminated air is being
removed.
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version