}
A hazard refers to any source of potential
damage, harm or adverse health effect on
something or someone under certain
condition at work.
}
cause harm or adverse effects
( to individual as health effects)
or
(to the organization as property or equipment
losses or damage)
}
Risk; the chance or probability that a worker
will be harmed if exposed to a hazard.
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

1.
Physical hazards (noise, vibration,
temperature, electricity, radiation, light
and pressure ).
2.
Chemical hazards (dust, mists, fumes,
gases, fibers, vapors and liquids).
3.
Biological hazards (insects, mites, moulds,
yeasts, fungi, bacteria, viruses and
parasites) .
4.
Ergonomic : fitness of the work process
and work place to the workers (posture,
movement, repetitive motion and light) .
5.
Psychological hazards (tension, stress, and
phobia) .
6.
Accidents and mechanical hazards
.
24 October 2019
٤
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

}
Physical hazards can be defined as hazards
that arise at work due to the influence of
various forms of
energy
.
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

•
Load on a worker that arise from the
combined metabolic heat, environmental
factors, and clothing worn which results in
an increase in heat storage in the body.
•
Workers who are exposed to extreme heat
or work in hot environments indoors or
outdoors,
or even those engaged in strenuous
physical activities may be at risk for
heat
stress
.
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

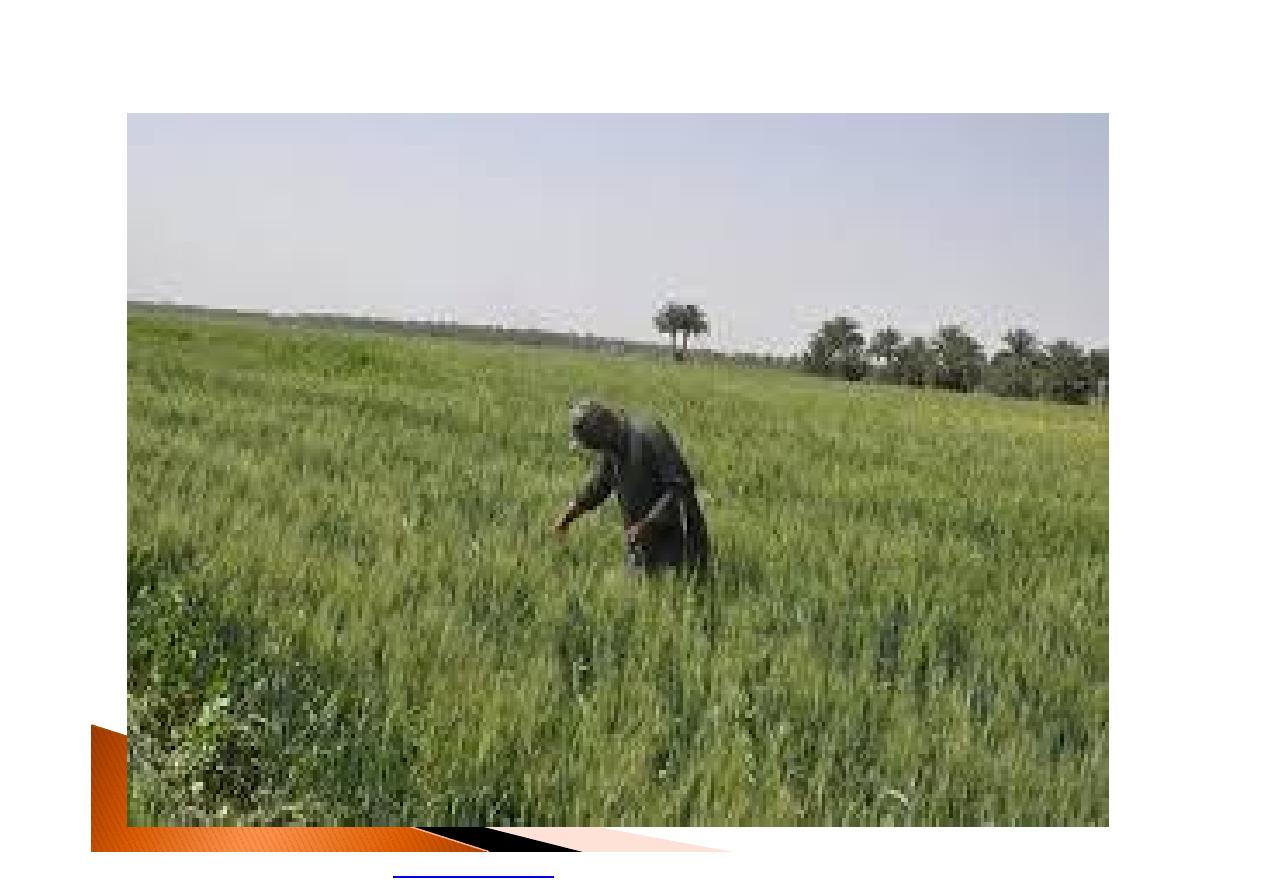
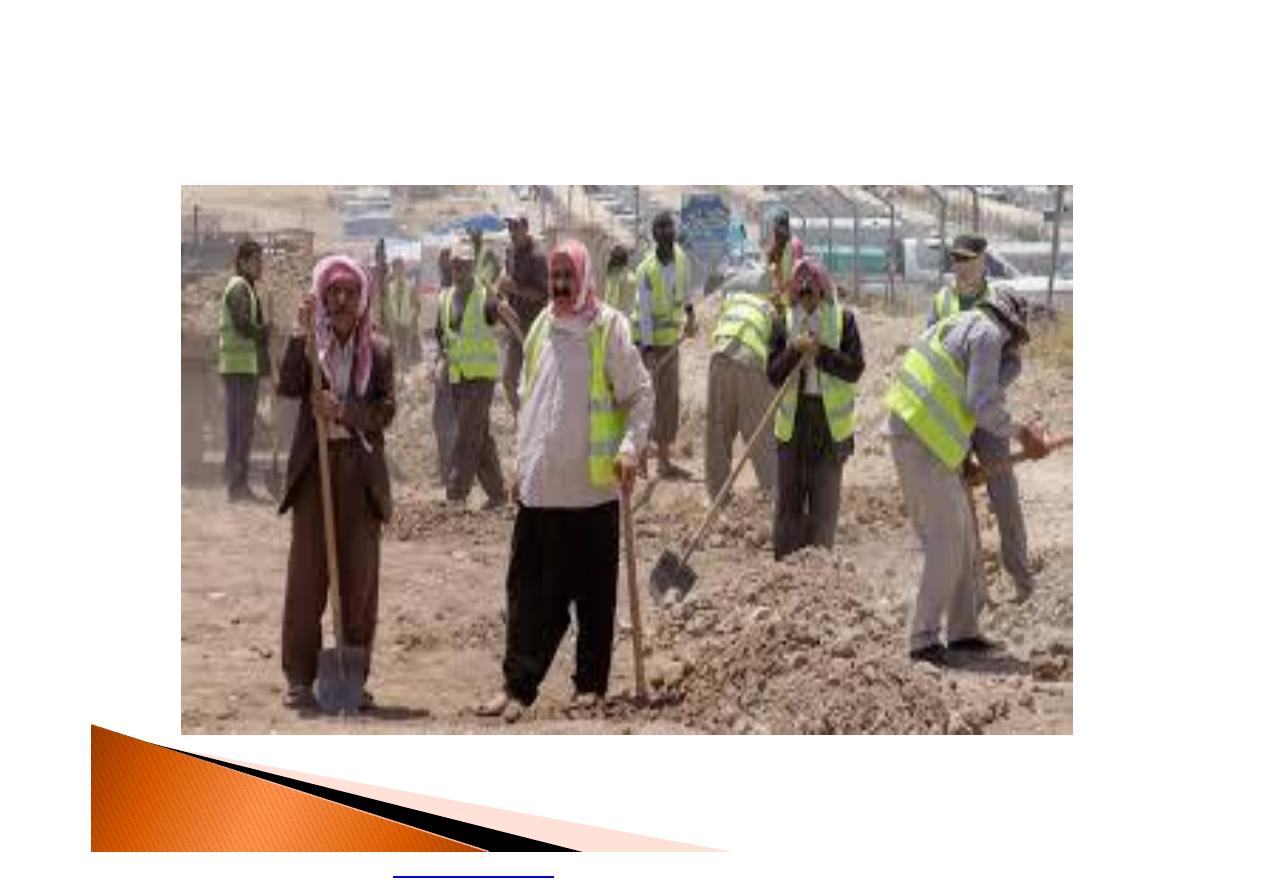
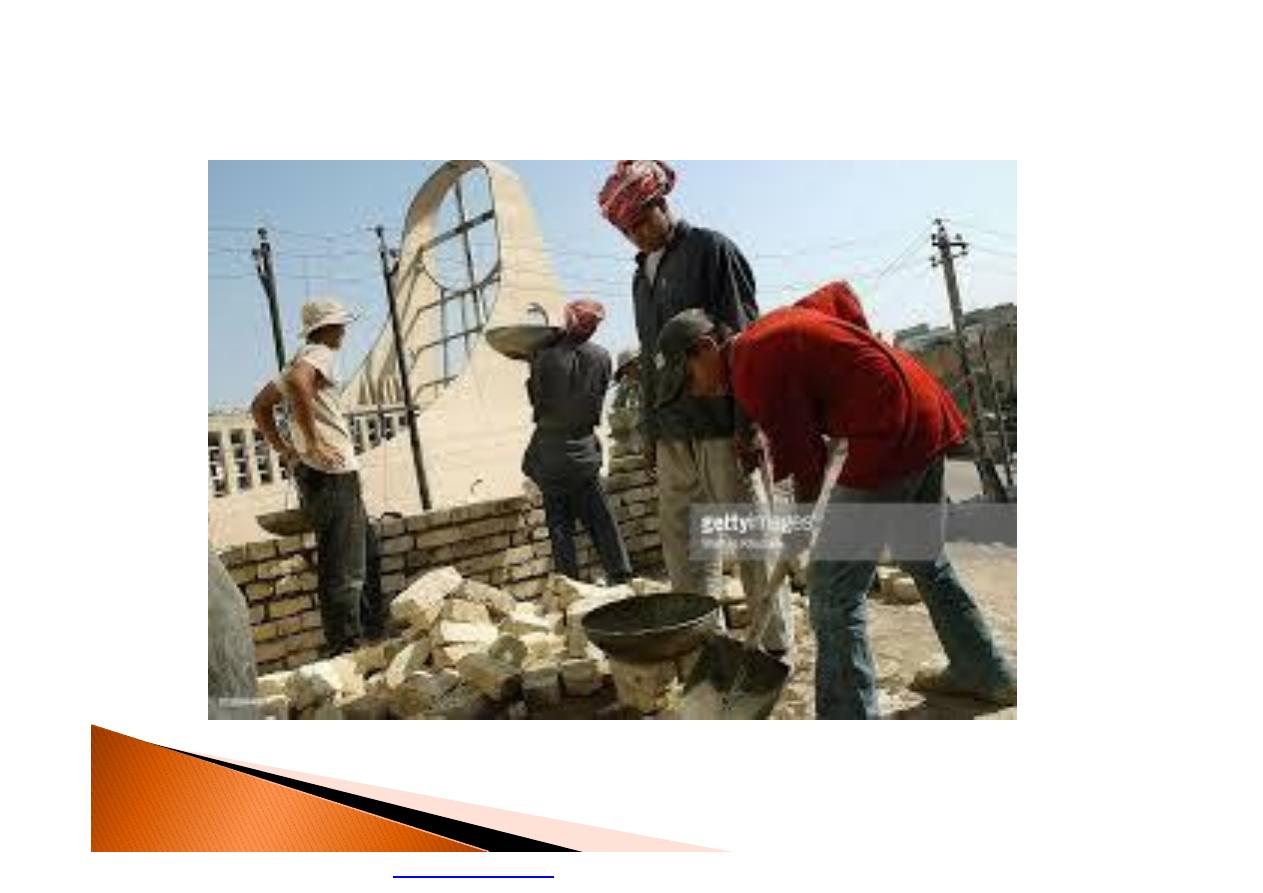
Those at risk include outdoor workers as
farmers, construction workers, traffic
policeman
and »»»
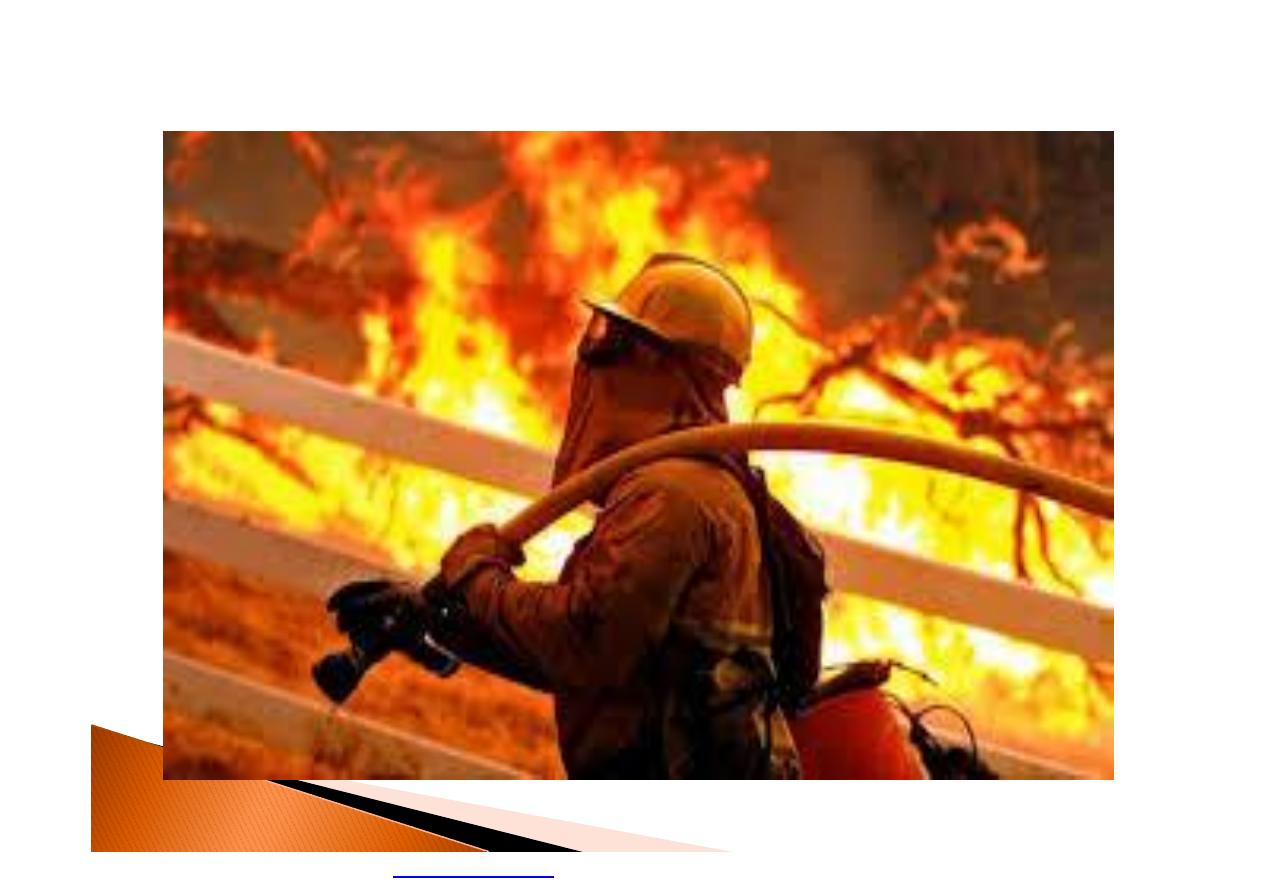
workers in hot environments, such as fire
fighters, bakery workers, boiler room
workers, and factory workers.
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

}
Exposure to extreme heat can result in
occupational illnesses caused by heat stress,
including heat rashes, heat cramps, heat
exhaustion, heat stroke and sometimes
death.
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

}
Heat can also increase workers’ risk of
injuries, as it may result in sweaty palms,
fogged-up safety glasses, dizziness, and may
reduce brain function responsible for
reasoning ability, creating additional hazards.
}
Others such as burns, may occur as a result
of contact with hot surfaces, steam, or fire.
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

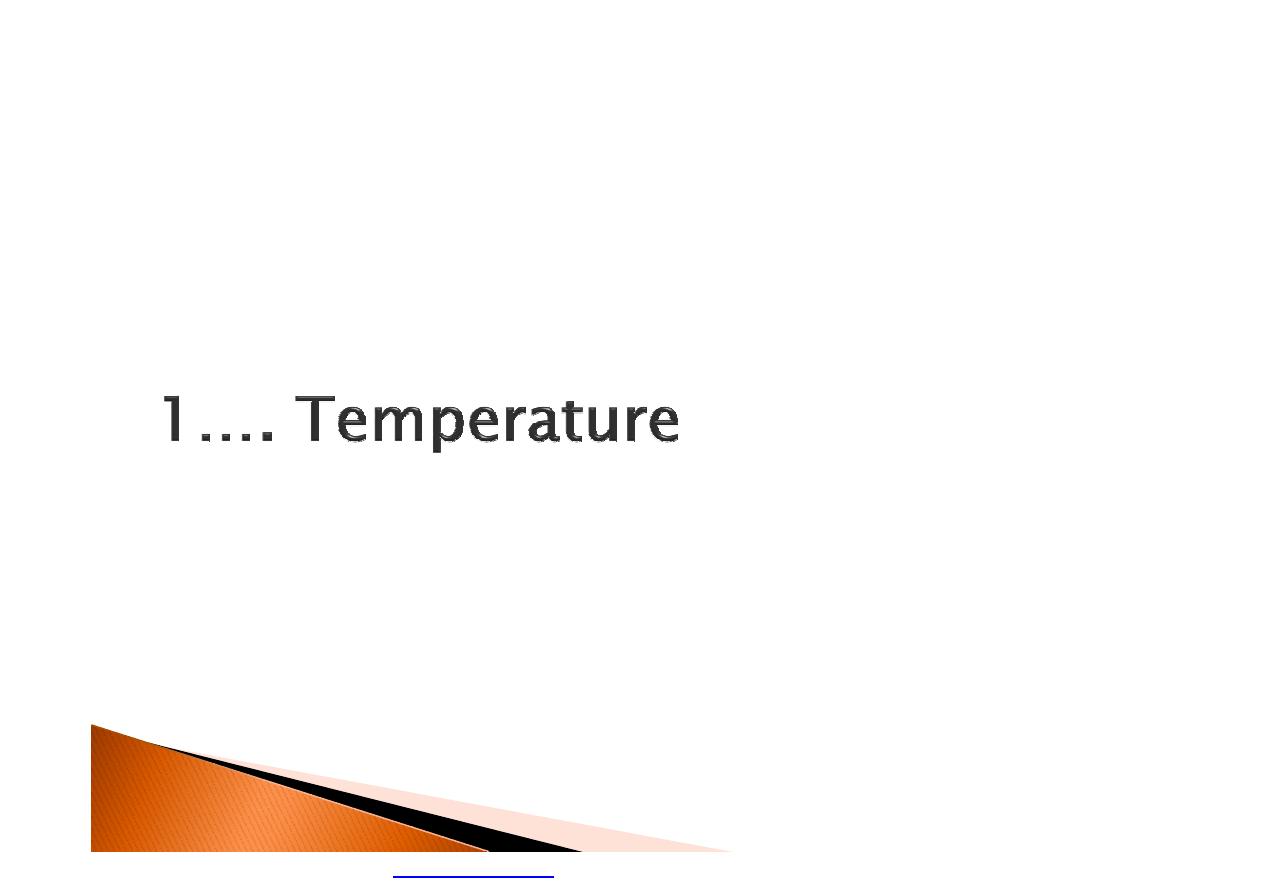
}
most common problem in hot working
environments.
}
caused by excessive sweating in hot humid
environment mostly with wearing heavy
protective clothing.
}
Looks like a red cluster of pimples or small
blisters.
}
may appear on the neck, upper chest, groin,
under the breasts and elbow creases.
}
The best treatment for heat rash is to provide
a cooler, less humid work environment.
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

}
Painful muscle spasms that occur when a
person drinks large amounts of water but
fails to replace the body salt loss
}
Usually controlled by drinking fluids that
contain electrolyte replacements (sport
drinks)
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

Heat Exhaustion
}
fatigue and collapse resulting from prolonged
exposure to excessive or unaccustomed heat.
}
Signs and symptoms are intense thirst, heavy
sweating and body temperature greater than
38C.
}
Also headache, nausea, dizziness, weakness,
irritability and confusion.
}
Typically treated by rest in a cool place and
replacing fluids and minerals.
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

}
Heat Stroke
}
It is the most serious heat-related health
problem.
}
occurs when the body’s temperature
regulating system fails and body temperature
rises to critical levels (greater than 40 C).
}
It is a medical emergency that may result in
brain damage or death.
}
Signs are confusion, loss of consciousness,
and seizures.
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

Heat stroke (continue):
Measures
}
move the worker to a shady, cool area and
}
remove as much clothing as possible.
}
Wet the worker with cool water and circulate
the air to speed cooling.
}
Place cold wet cloths, wet towels or ice all
over the body or soak the worker’s clothing
with cold water.
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

Occupational Factors that may
contribute to Heat Illness
}
High temperature and humidity
}
Direct sun exposure (with no shade) or extreme
heat
}
Limited air movement (no breeze or wind)
}
Strenuous physical exertion
}
Low fluid consumption
}
Use of bulky protective clothing and equipment.
}
Personal factors as extreme age, weak health
status, chronic medical disease.
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

Heat Illness Prevention Program
key elements include:
• Hazard Identification
• Water. Rest. Shade Message
• Acclimatization
• Modified Work Schedules.
• Training
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

}
Provide or ensure that fully shaded or air-
conditioned areas are available for resting
and cooling down
}
Ensure that cool drinking water is available
and easily accessible.
}
Encourage workers to drink a liter of water
over one hour, which is about one cup every
fifteen minutes.
}
(Note: Certain beverages, such as caffeine and alcohol can
lead to dehydration.)
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

}
It occurs by gradually increasing workloads
and exposure and taking frequent breaks for
water and rest in the shade.
}
New workers and those returning from a
prolonged absence and even experienced
workers should begin an acclimatization
program for several days during a rapid
change at the work leading to excessively hot
weather or conditions such as a heat wave.
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

}
Hypothermia
}
A body temperature that is too low affects the
brain, making the victim unable to think
clearly or move well.
}
hypothermia particularly dangerous because
a person may not know it is happening and
will not be able to do anything about it.
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version
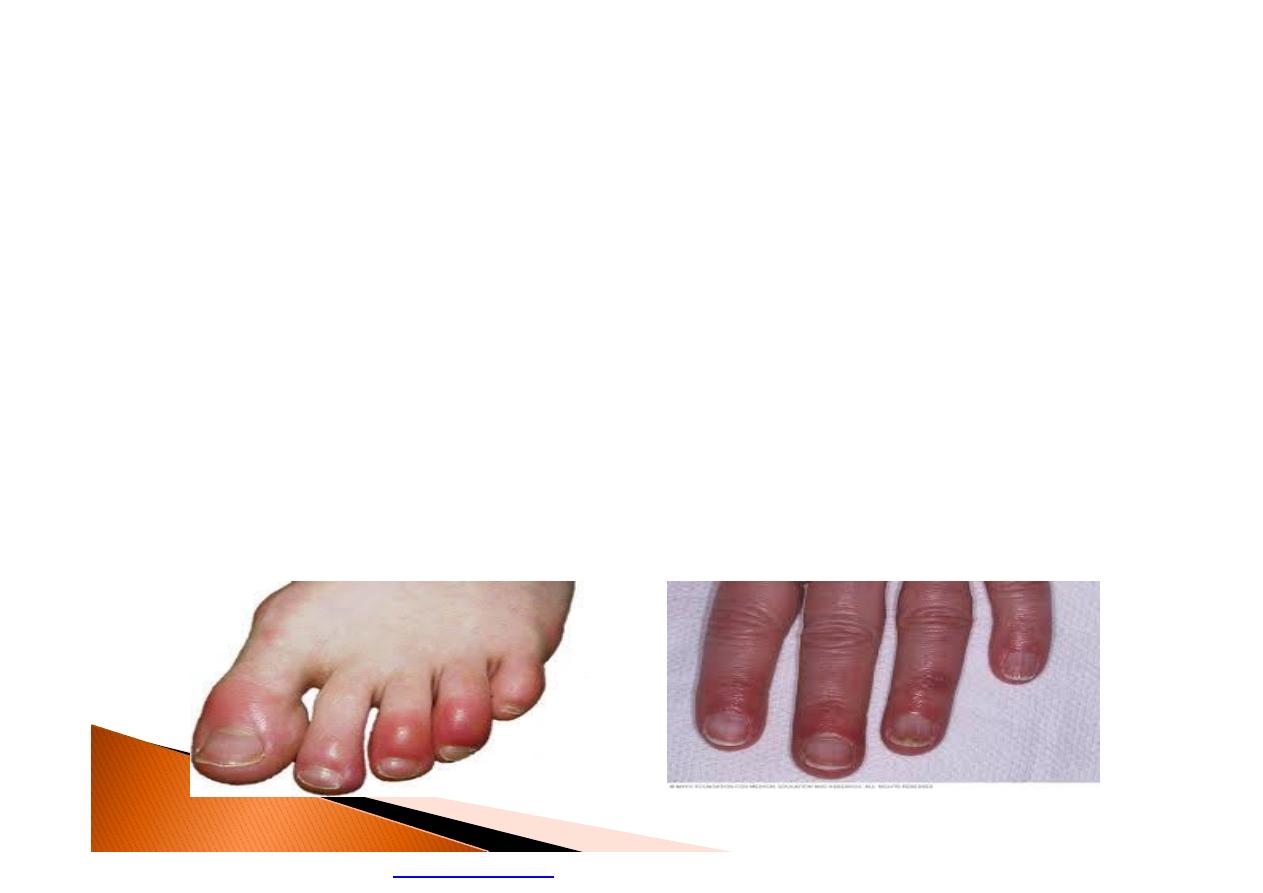
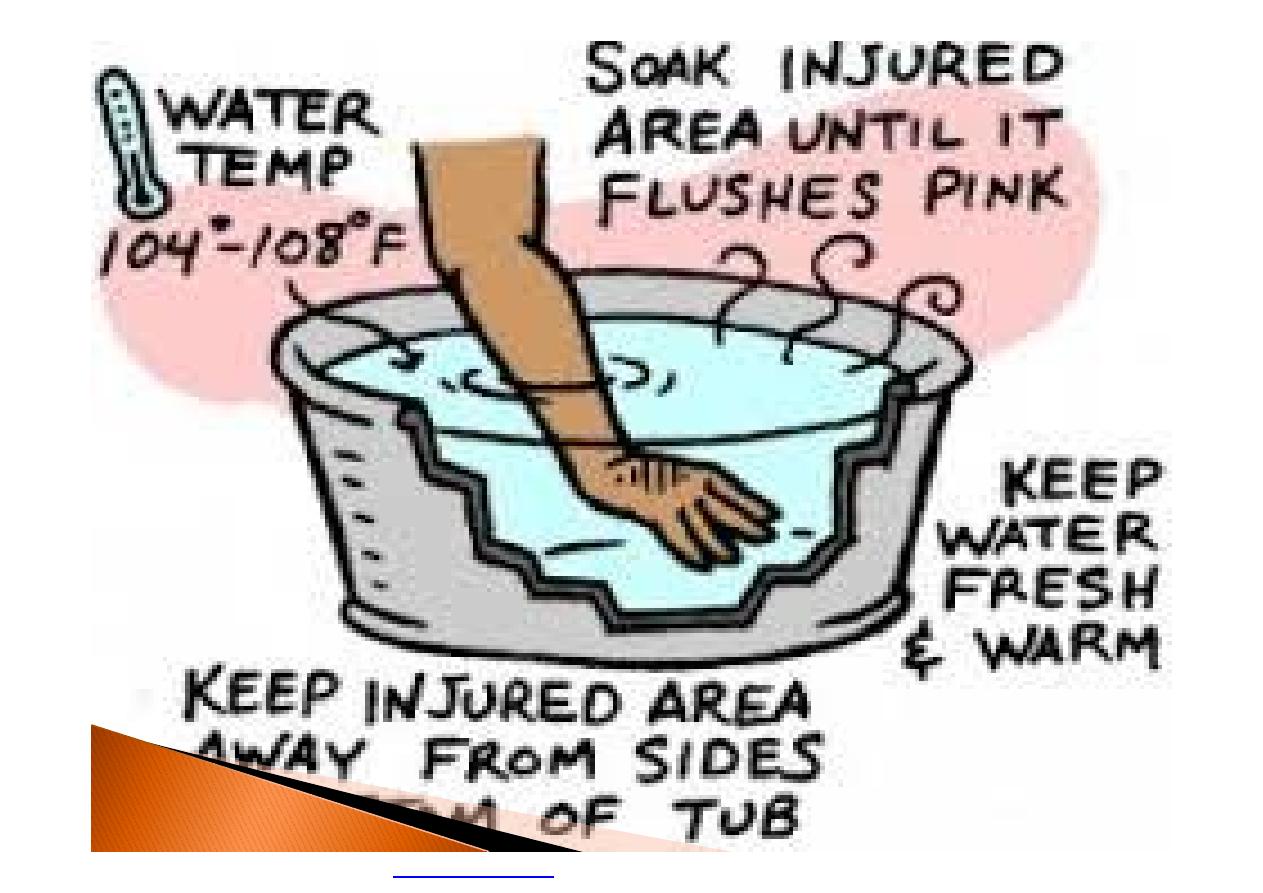
Chilblains
}
Chilblains are caused by the repeated
exposure of skin to temperatures just above
freezing to as high as 15 C
}
Symptoms: Redness, Itching, Possible
blistering, Inflammation, Possible ulceration
in severe cases
}
The redness and itching typically occurs on
cheeks, ears, fingers, and toes.
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version

}
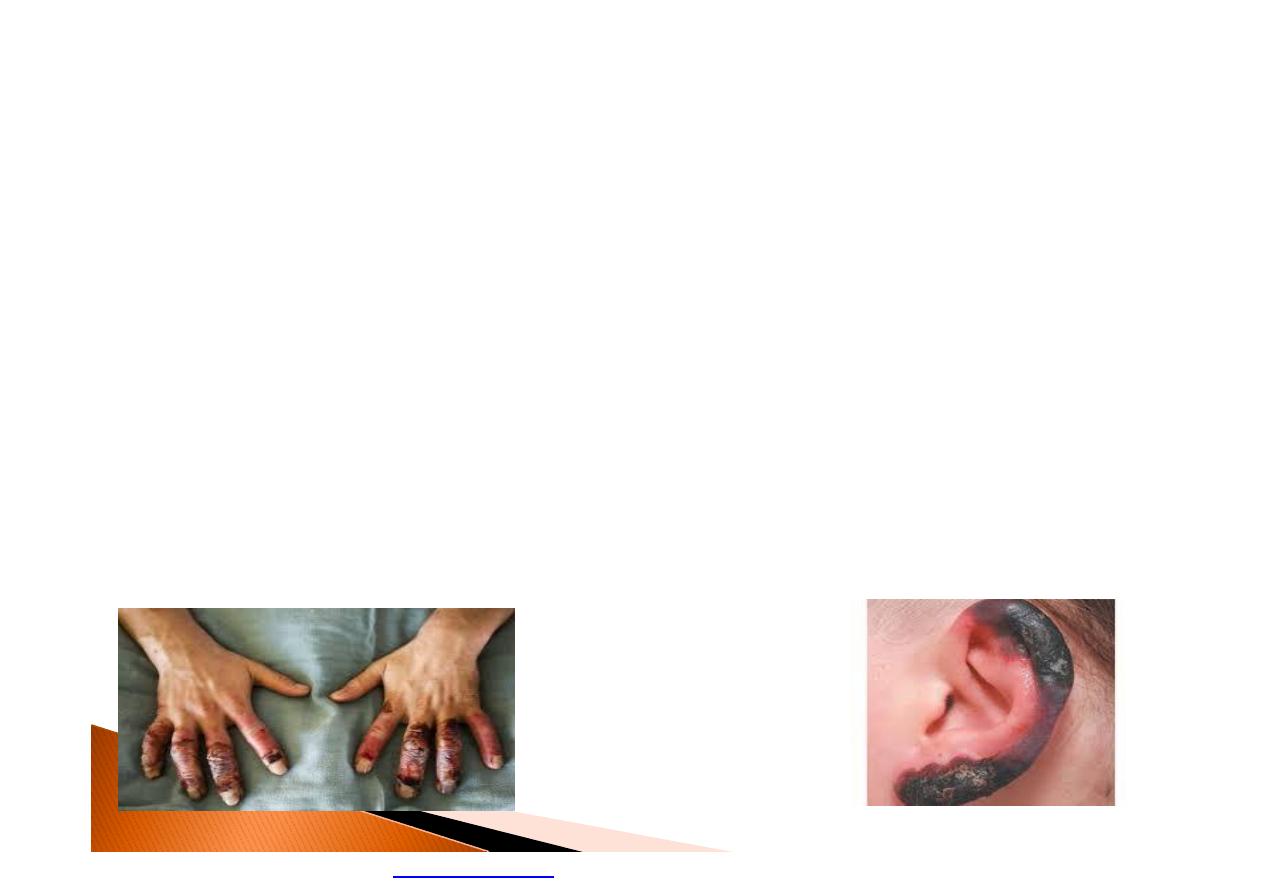
Frostbite
}
Ice crystal formation in skin and other
tissues of the body.
}
Result in permanent damage and
destruction to blood vessels and other
structures which can result in
amputation.
}
Most often affects the nose, ears,
cheeks, chin, fingers, or toes.
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version
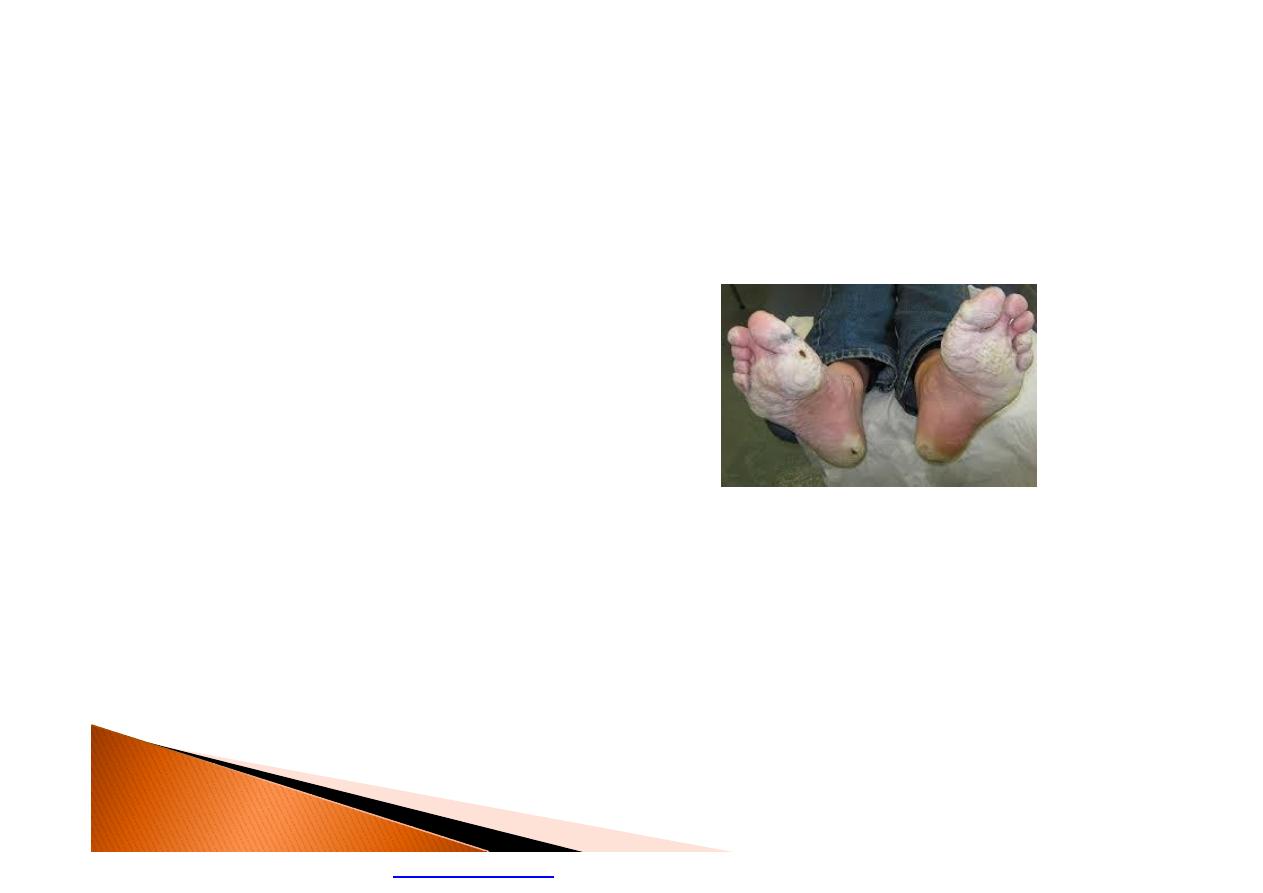
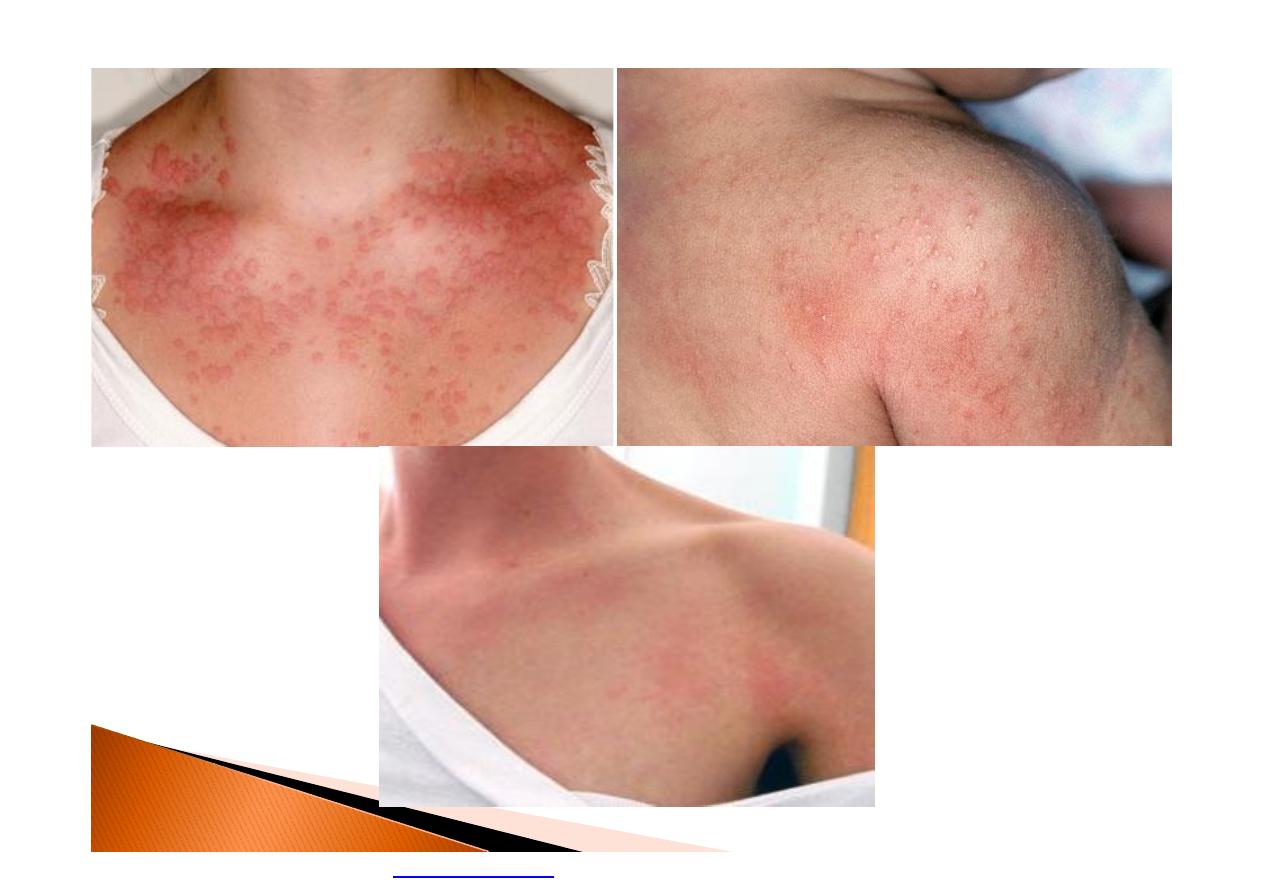
}
Trench Foot
Or (immersion foot), is an injury of the feet
resulting from prolonged exposure to wet
and cold conditions.
}
Treatment
}
RAPID re-worming in worm water until color
of skin return to normal
}
NO dry heat as oven or others
PDF created with pdfFactory Pro trial version