
1
Obstetrics
Lec. 3 د. بان عامر موسى
Antenatal Care
Definition:- Antenatal care is the care that pregnant lady
receive it from healthcare professionals during her pregnancy to
maintain the physical, mental and social health of mother and
baby by providing education on nutrition, personal hygiene and
birthing process then detect and manage complications during
pregnancy, whether medical, surgical or obstetrical.
Objectives of ANC
Promoting health and preventing disease
Preparation for birth and potential complications
Tetanus toxoid, nutritional supplementation, etc
Detection of existing diseases and treatment, HIV, syphilis,
tuberculosis, other co-existing medical diseases ((e.g.,
hypertension, diabetes)).
Early detection and management of complications, Help
prepare mother to breastfeed successfully, experience normal
puerperium, and take good care of the child physically,
psychologically and socially. Diagnose Pregnancy through an
understanding of the symptoms and positive signs of pregnancy
Given the date of the last menstrual period: calculate the EDD
and the gestational age at any time Describe the interventions
appropriate to the expected physiologic and psychological
changes of pregnancy

2
Describe the care of the pregnant patient at the initial
prenatal visit and follow up visits. Taken the patient’s
OB/GYN history, determine the gravidity and parity.
Teach patients how to manage common pregnancy
discomforts.
Analyze risk factors of the pregnant patient Consider
developmental level and cultural background when planning
pregnancy care and delivery.
The Initial “Booking” Antenatal Visit
A booking visit :: - is a risk assessment which will outline
factors such as mother health, diet, any illnesses and several
other factors surrounding her lifestyle.
Medical history; Menstrual history; Physical exam ;
Investigations; Diagnostic tests; Screening Tests Assess risk
factors and building up a strategy for the antenatal care
Health Education with exhaustive efforts and advices.
Age
Occupation
Education
Residence
Ethnicity
Race
Religion

3
Important Demographic Data
Medical and Family History
Prior or current health issues
Medications and allergies
Possible inherited diseases in the families
Significant health issues in family members
Use of tobacco, alcohol, street drugs
Menstrual History
Expected Date of Delivery
Duration of pregnancy
280 days or 40 weeks or 10 lunar months
Naegele's rule::-Add seven days to and subtract three months [or
add 9 months] The concept of reliable dates

4
Measurement Symphyseal Fundal height
Evidence supports either palpation or S- F measurement at every
AN visit to monitor fetal growth
measurement should start at the variable point (F) and continue to
the fixed point (S)
SF measurement should be recorded in a consistent manner
((therefore in cms ))
Causes of oversized uterus (larger than period of amenorrhea)
.Wrong dates
.Polyhydramnios
.Hydatidiform mole
.Macrocosmic fetus
.Concealed accidental hemorrhage
.Twins
.Tumors as fibroids and ovarian cysts Fetal malformations as
.hydrocephalus
Causes of undersized uterus (smaller than period of
amenorrhea)
.Wrong dates
.Oligohydramnios
.Fetal death
.IUGR or Small fetus
.Pregnancy during period of amenorrhea as lactation or
injectable contraception

5
Malpresentations as transverse lie
Gravidity and Parity G P A
Gravida G-number of pregnancies Para P-number of births after
24 weeks A-abortions and miscarriages (before 24weeks)
Laboratory Analysis and Testing
Blood tests
Blood type and Rh status
Antibody screen (Coombs’ test)
CBC
Rubella titer
HIV Hepatitis B
Syphilis
Sickle cell
Glucose screen
Triple screen
Cystic fibrosis
Varicella
Other Testing
Ultrasound( dating U/S)
Urinalysis Pap smear
GC culture Chlamydia culture Group B
streptococci
6
Body Mass Index (BMI)
A commonly used measure to differentiate underweight, normal
.weight, overweight and obesity
Obtained by dividing the weight of the subject (in kilos) by the
.square of her height in meters
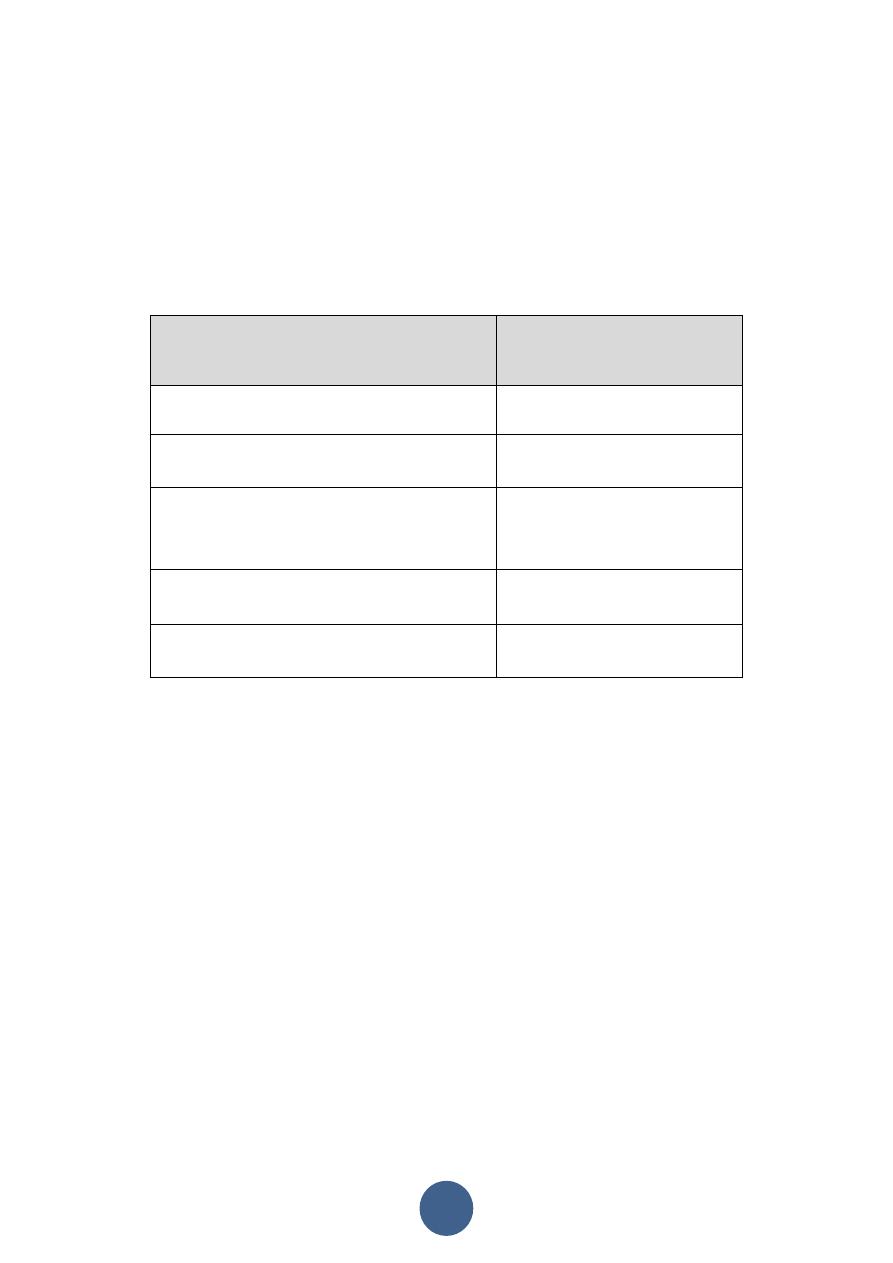
Pre-pregnant weight status
Recommended range of
weight gain
A. Twin Pregnancy
15- 20 Kg.
B. Underweight (BMI<18.5)
12-17 kg.
C. Normal Weight (BMI 18.5 to
24.9)
11-15 Kg.
D. Overweight (BMI 25.0 to 29.9)
6-11 Kg.
E. Obese (BMI > 30.0)
6 Kg.
Immunization
--Live attenuated virus vaccines as measles, rubella, mumps,
poliomyelitis are contraindicated
--Inactivated virus vaccines as influenza, and rabies are safe to
be given
--Inactivated bacterial vaccines as cholera, meningococcal, and
typhoid are safe to be given
--Toxoids as tetanus and diphtheria toxoid are safe to be given
--Immune globulins as for hepatitis, tetanus and rabies can be
given

7
Warning signs:
The pregnant woman must immediately report if any one of the
following signals occur:
.Vaginal bleeding
.Swelling of the face, fingers and limbs
.Swollen tender calf muscles
.Severe headache
.Blurring of vision
.Abdominal pain
.Persistent vomiting
.Chills and fever
Escape of fluid from the vagina
Visit Schedule
The return visits are
Every 4 weeks until 28 weeks then
Every 2 weeks until 36 weeks then
Weekly thereafter. A more flexible schedule is at times better
Perinatal outcome benefits were more pronounced with
antenatal care after 30 weeks
The mother is advised to call or come when she feels undue
worry. In each visit the well-being of mother and fetus are
assessed

8
First appointment
The first appointment needs to be earlier in pregnancy (prior to
12 weeks) than may have traditionally occurred and, because ‘of
the large volume of information needs in early pregnancy .two
appointments may be required :At the first (and second)
antenatal appointment give information, with an opportunity to
discuss issues and ask questions; offer verbal information
supported by written information (on topics such as diet and
lifestyle considerations, pregnancy care services available,
maternity benefits and sufficient information to enable informed
decision making about screening tests identify women who may
need additional care and plan pattern of care for. the pregnancy
check blood group and RhD status offer screening for anaemia,
red-cell alloantibodies, Hepatitis B virus, HIV, rubella
susceptibility and syphilis offer screening for asymptomatic
bacteriuria (ASB) offering screening for Down’s syndrome offer
early ultrasound scan for gestational age assessment (offer
ultrasound screening for structural anomalies (20 weeks)
measure BMI, blood pressure (BP) and test urine for proteinuria
Pre- and Periconceptional Folic acid supplementation to prevent
recurrent neural tube defects Iodine supplementation in
populations with a high incidence of endemic cretinism.
