Lec 5:dr.hassan aljumaily
Inflammatory bowel diseases
UC and Crohn’s
protracted relapsing and remitting
course, usually extending over years.
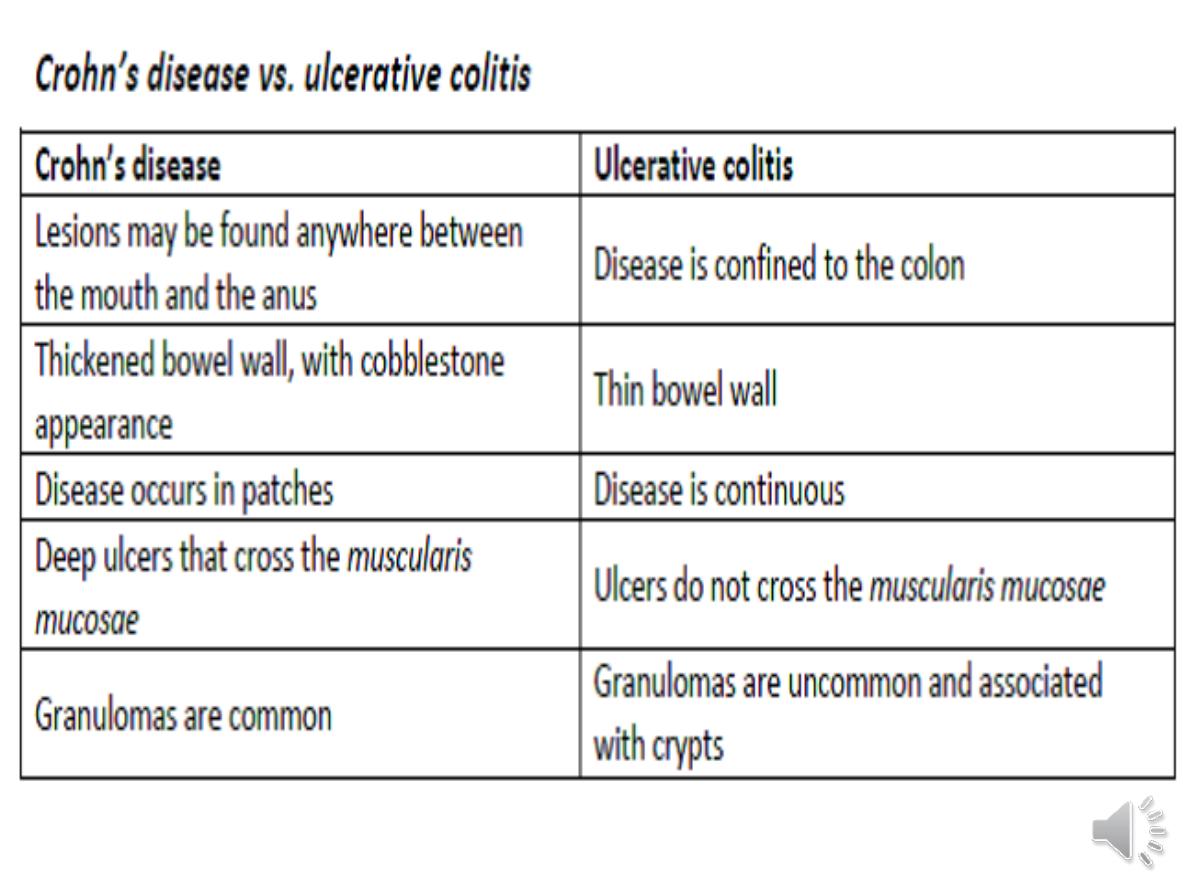
A crucial distinction is that ulcerative
colitis
only involves the colon
, while
Crohn’s disease can involve
any part
of the GIT from mouth to anus.

Pathophysiology
Genetic:
1-Both CD and UC common in Ashkenazi Jews
2- High concordance in identical twins (40–50% CD;
20–25% UC)
3- UC and CD both associated with genetic variants at
HLA locus.
4-
HLA-DR 103
associated with severe UC
Environmental
• UC more common in non-smokers
• CD more common in smokers
• CD associated with high-refined-sugar diet
• Appendicectomy protects against UC

Ulcerative colitis
-Proctitis
40–50%
,Left-sided colitis
30–40%
and
Extensive colitis
20%
.
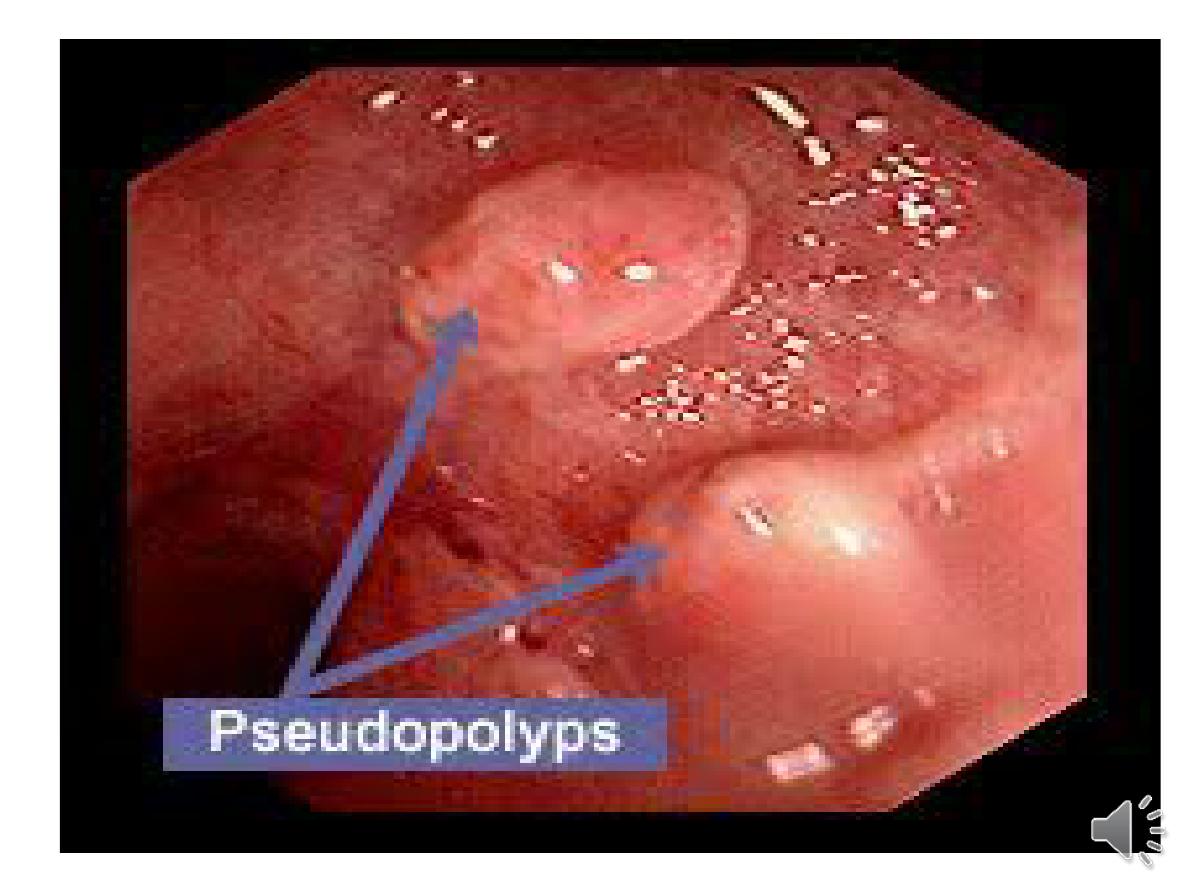
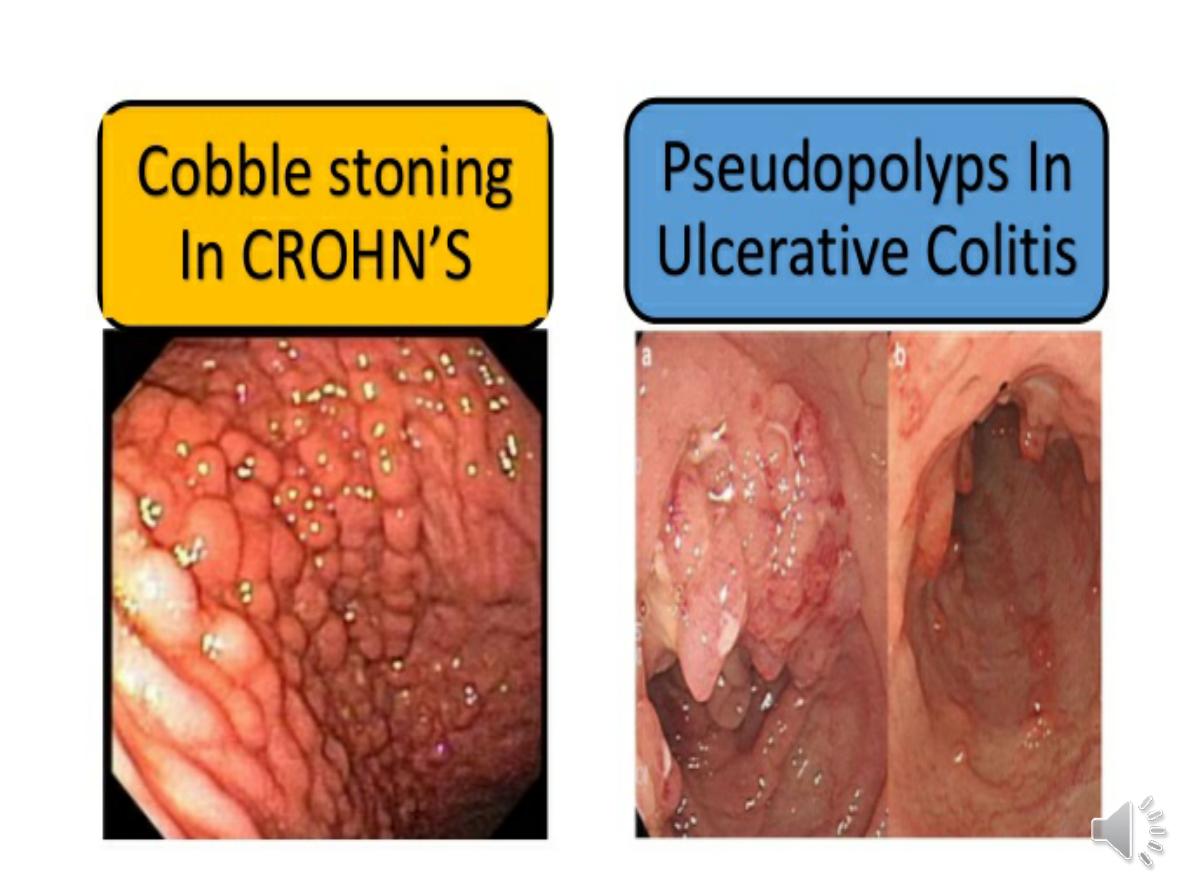
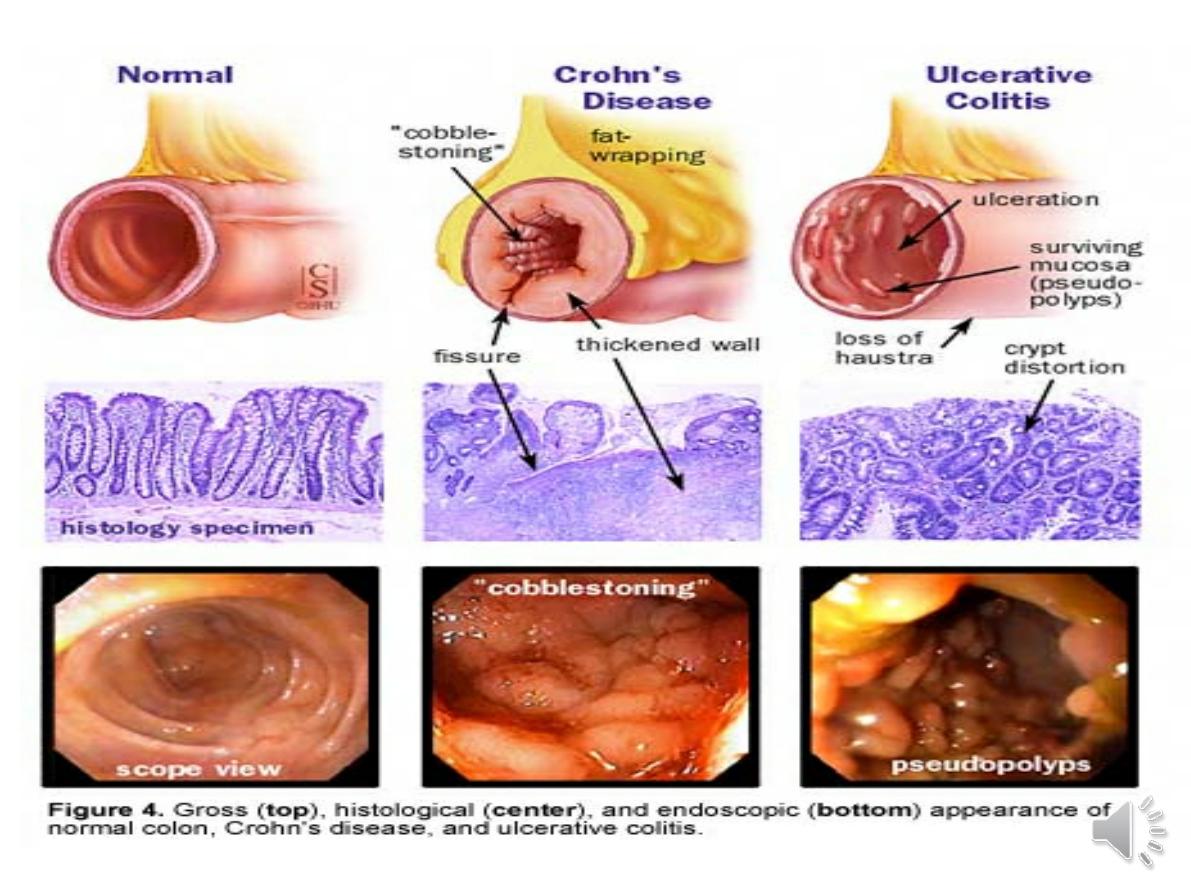
- In long-standing pancolitis, the bowel can become
shortened
and post-inflammatory ‘
pseudopolyps’
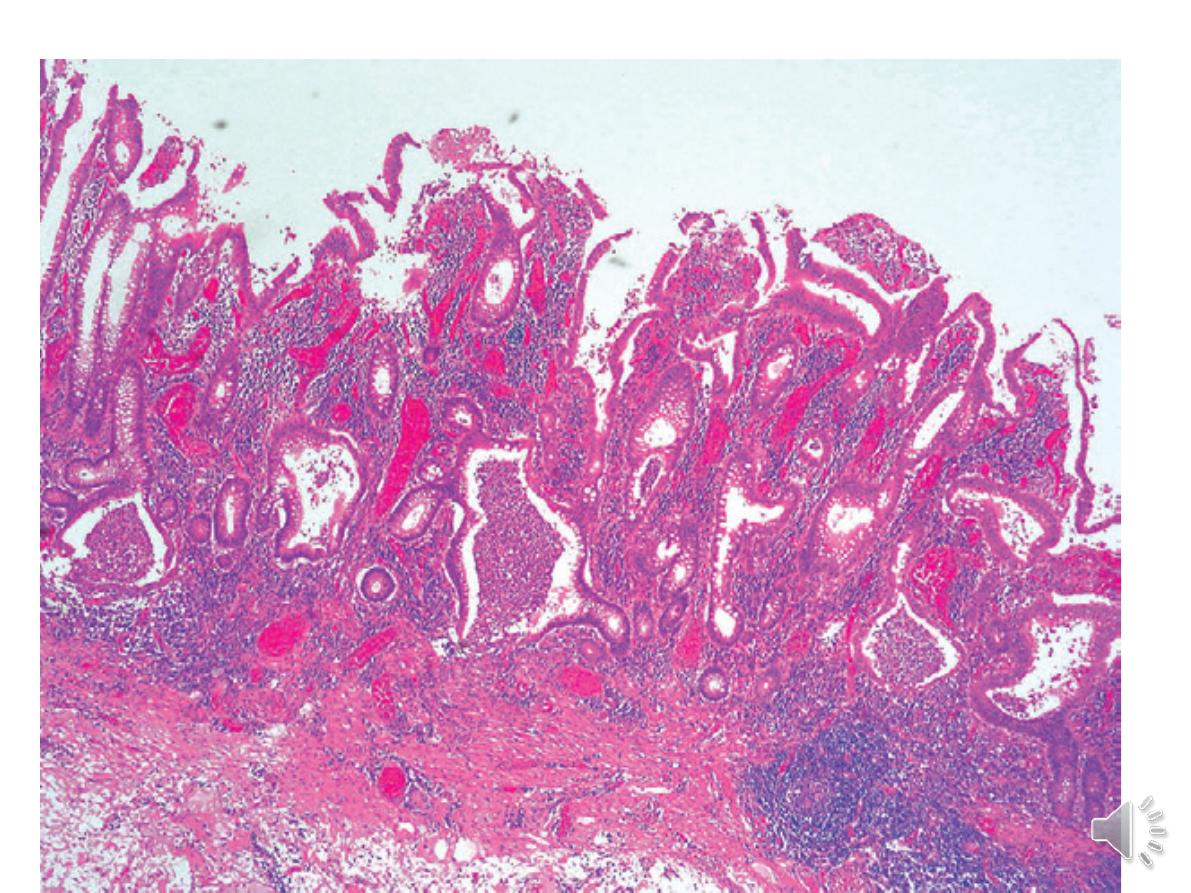
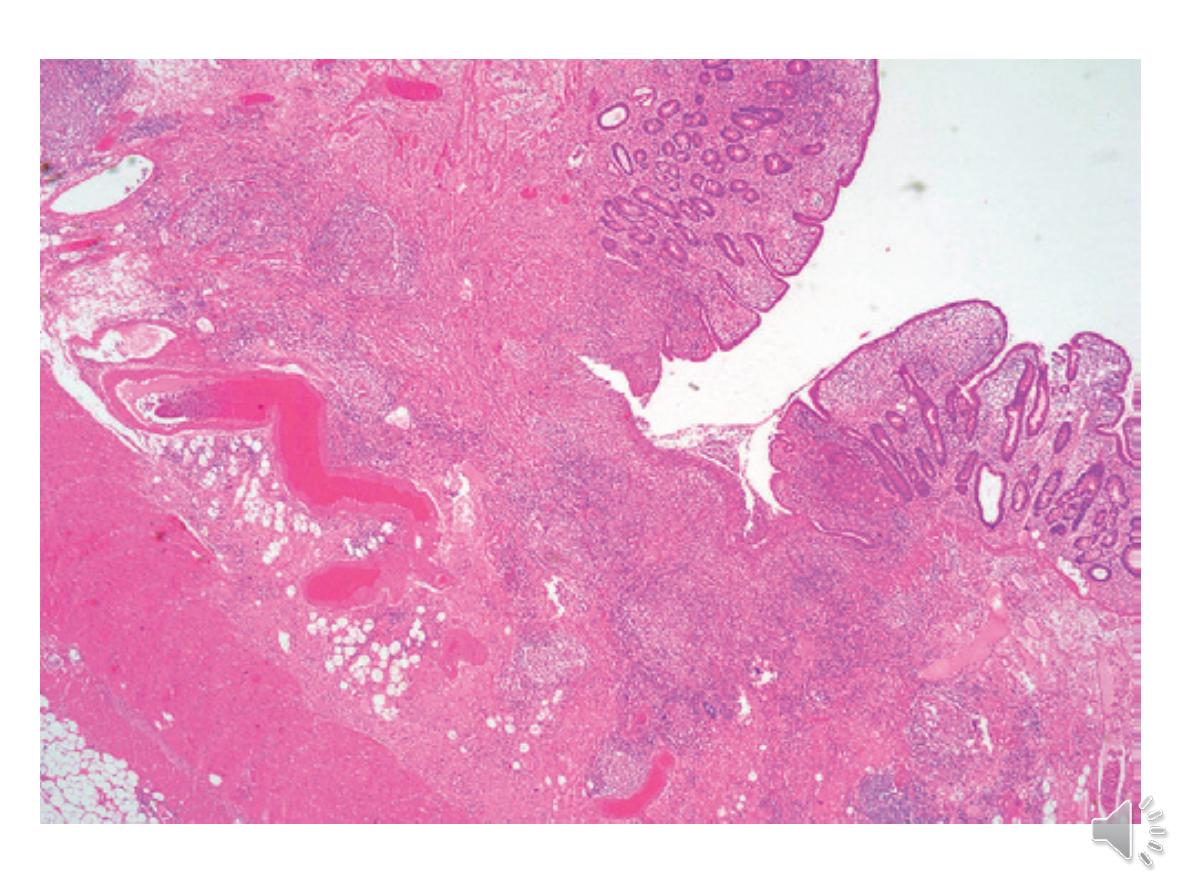
-The inflammatory process is limited to
the mucosa
and spares the deeper layers of the bowel wall
,both
acute and chronic inflammatory cells infiltrate the
lamina propria and the crypts
(‘cryptitis
’). Crypt
abscesses are typical.
-
Dysplasia, nuclear atypia and increased mitotic rate,
may herald development of colon cancer.

Crohn’s disease
:most common site in order of frequency
1-terminal ileum and right side of colon
2-colon alone
3- terminal ileum alone
4-ileum and jejunum.
--
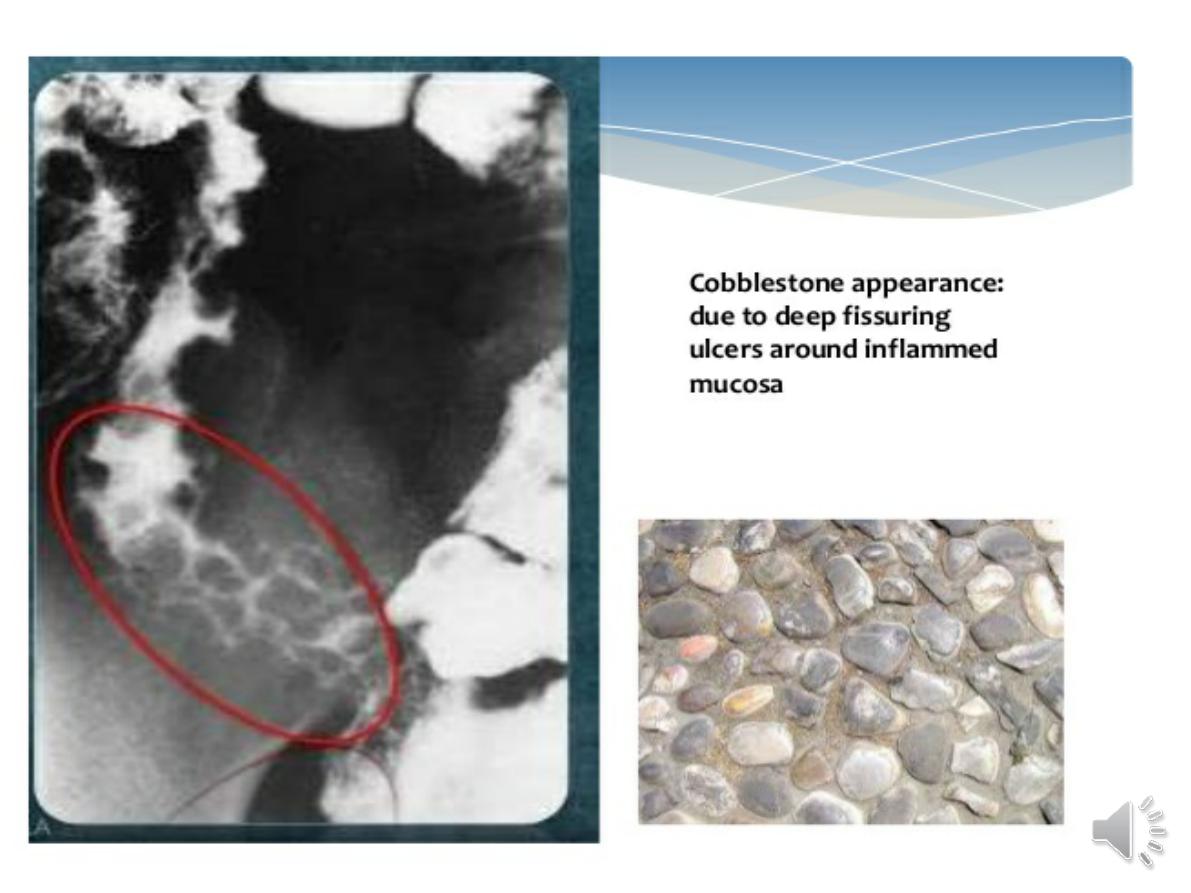
deep ulcers
which often appear as linear
fissures; thus the mucosa between them is
described as ‘
cobblestone
’. These
may
penetrate
through the bowel wall to initiate
abscesses or fistulae involving the bowel,
bladder, uterus, vagina and skin of the
perineum.

Clinical features
Ulcerative colitis:
-rectal bleeding with ,bloody diarrhoea.
-Emotional stress, intercurrent infection, gastroenteritis,
antibiotics or NSAID therapy may all provoke a relapse. - .
-Some patients pass frequent, small volume fluid stools,
while others pass pellety stools due to constipation.
-assessment of severity depend on:
-
Daily bowel frequency , Blood in stools , Stool volume ,
Pulse ,Temperature ,Haemoglobin , ESR &
C-reactive protein ,Serum albumin , Abdominal X-ray and
Sigmoidoscopic finding
.
The Truelove–Witts
criteria for acute severe ulcerative
colitis are ≥ 6 bloody stools/24 hrs plus one or more of
anaemia, fever, tachycardia and high inflammatory markers
.

Crohn’s disease:
-abdominal pain, diarrhoea watery and does not contain
blood or mucus. and weight loss.
-Ileal Crohn’s disease
→intestinal obstruction.
-Weight loss because
they avoid food
, since eating
provokes pain also due to
malabsorption
, and some
patients present with features of fat, protein or vitamin
deficiencies.
-Crohn’s presents in an identical manner to ulcerative
colitis, but rectal sparing and the presence of perianal
disease are features which favour a diagnosis of Crohn’s
disease.
-other:
-
perianal disease
, Perianal skin tags, fissures or fistulae
are found in at least 50% of patients.
-
vomiting
from jejuna strictures
- severe
oral ulceration.
-

Differential diagnosis
1-Infective
-Bacterial •
Salmonella
•
Shigella
•
Campylobacter
jejuni
•
E. coli
O157 • Pseudomembranous colitis
-Viral • Herpes simplex proctitis •
Cytomegalovirus
Protozoal • Amoebiasis
Non-infective
• Ischaemic colitis
• Radiation proctitis
• Collagenous colitis
• Behçet’s disease
• NSAIDs
• Colonic carcinoma
• Diverticulitis

Complications
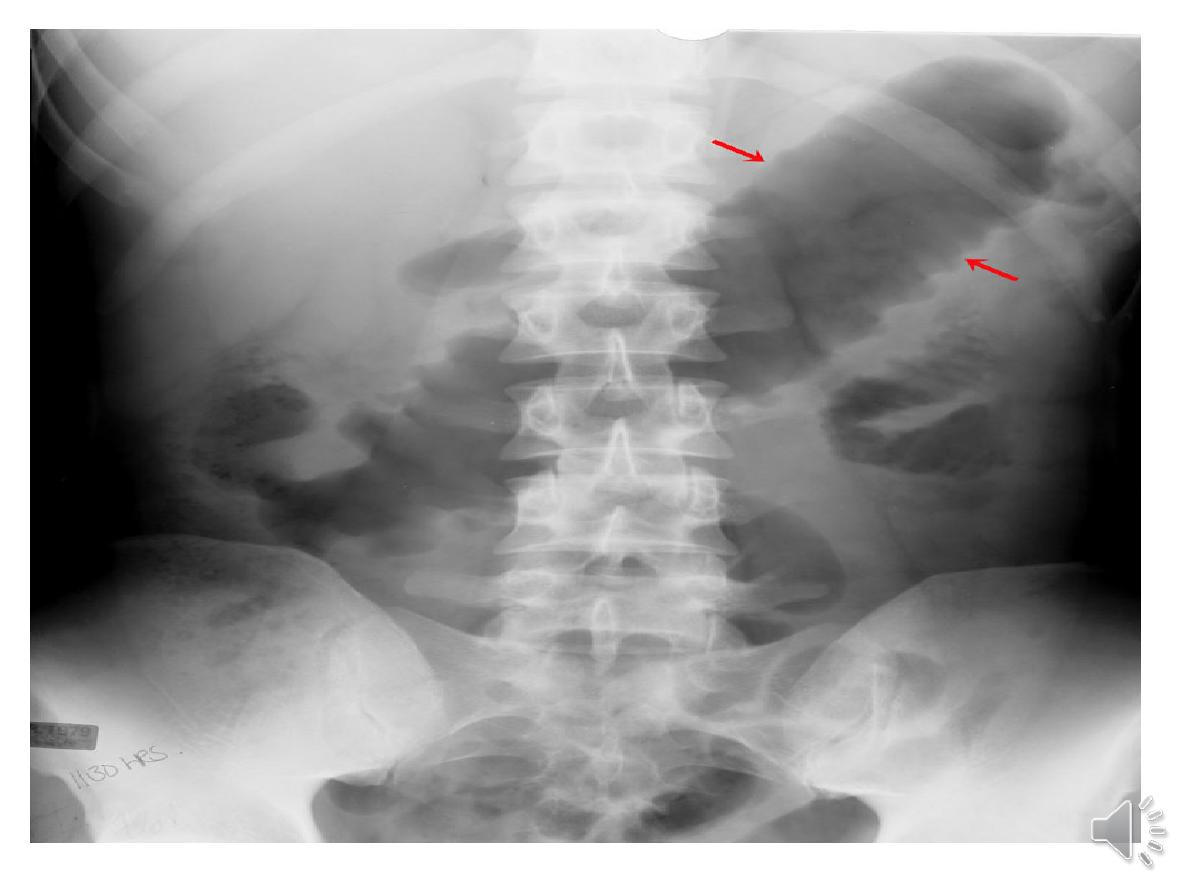
1-Life-threatening colonic inflammation:
Intoxic megacolontoxins pass freely across the
diseased mucosa into the portal and then systemic
circulation.
. An abdominal X-ray :transverse colon is dilated to
more than 6 cm
2-
Haemorrhage
:
due to erosion of a major artery.
3-Fistulae
These are specific to Crohn’s disease.
Enteroenteric
fistulae.
Enterovesical
fistulation causes
recurrent urinary infections and pneumaturia.
enterovaginal fistula
causes a faeculent vaginal
discharge.

4-Cancer
-
The risk of dysplasia and cancer increases with the duration
and extent of uncontrolled colonic inflammation..
-
Oral mesalazine
therapy reduces the risk of dysplasia and
neoplasia in ulcerative colitis.
Azathioprine
reduce the risk of colorectal cancer in ulcerative
colitis and Crohn’s colitis.
- surveillance programmes beginning
10 years
after diagnosis.
Targeted biopsies of areas that show abnormalities on
staining with indigo carmine or methylene blue increase the
chance of detecting dysplasia and this technique (termed
pancolonic chromo-endoscopy) has replaced colonoscopy
with random biopsies taken every 10 cm in screening for
malignancy
..
If high-grade dysplasia is found, panproctocolectomy is
usually recommended because of the high risk of colon
cancer.
.
.

Investigations
▲Blood:
1- anaemia resulting from bleeding or malabsorption of iron, folic
acid or vitamin B12.
2-Serum albumin concentration falls as a consequence of protein-
losing enteropathy, inflammatory disease or poor nutrition.
3- The ESR and CRP are elevated.
4-Faecal calproctectin
▲
Bacteriology
-stool microscopy, culture, blood cultures and serological tests
should be performed.
▲
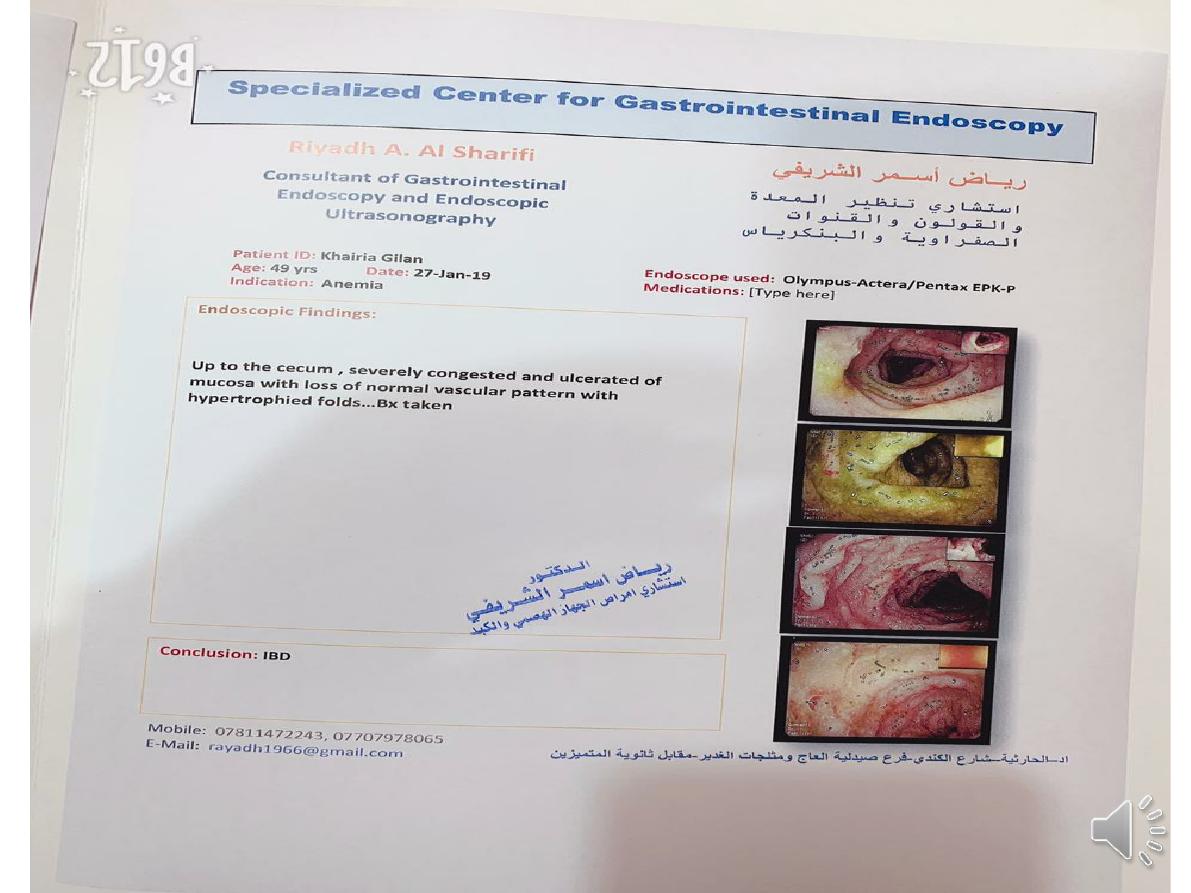
Endoscopy
-Patients who present with diarrhoea plus raised inflammatory
markers or alarm features, such as weight loss, bleeding and
anaemia
-
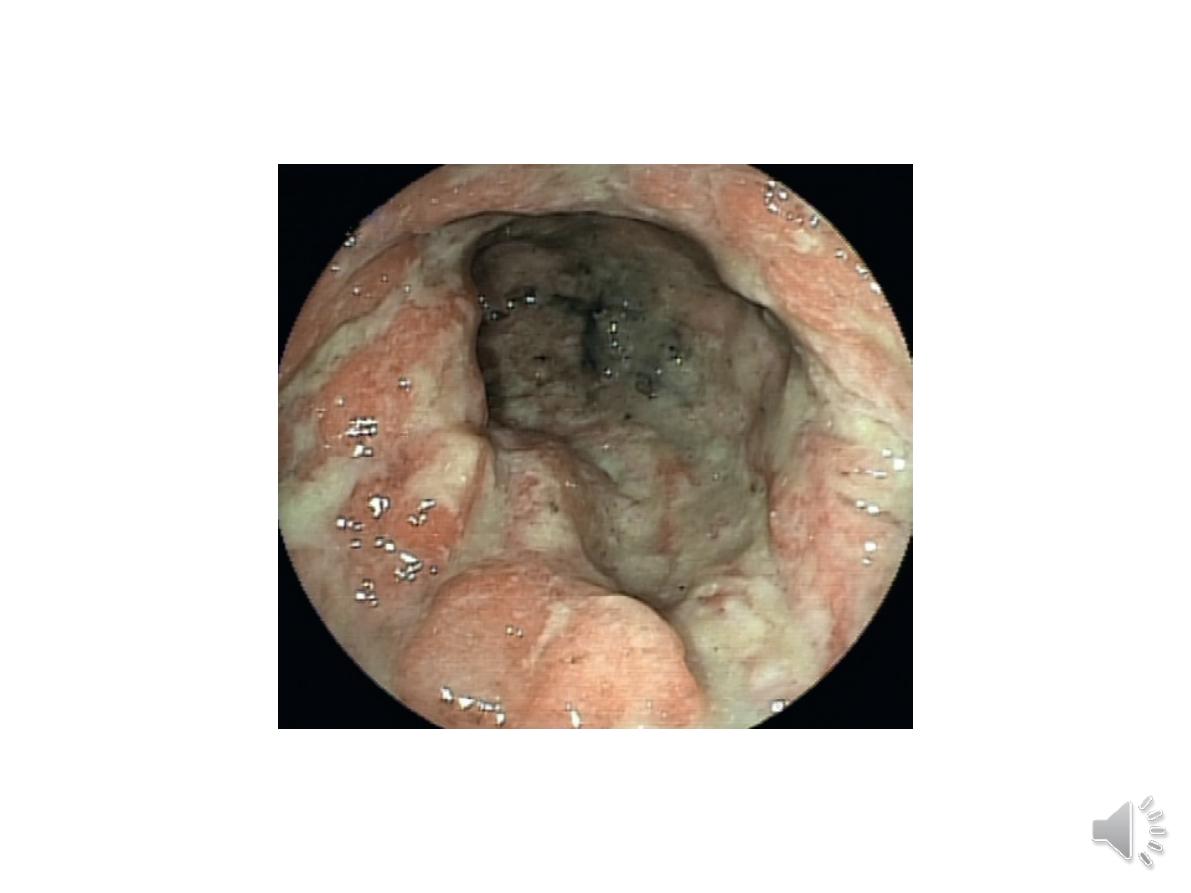
In ulcerative colitis, there is loss of vascular pattern, granularity,
friability and contact bleeding,with or without ulceration.
-
In Crohn’s disease, patchy inflammation, with discrete, deep ulcers,
strictures and perianal disease (fissures, fistulae and skin tags), is
typically observed, often with rectal sparing.
▲
Radiology
1-
Barium enema
is a less sensitive
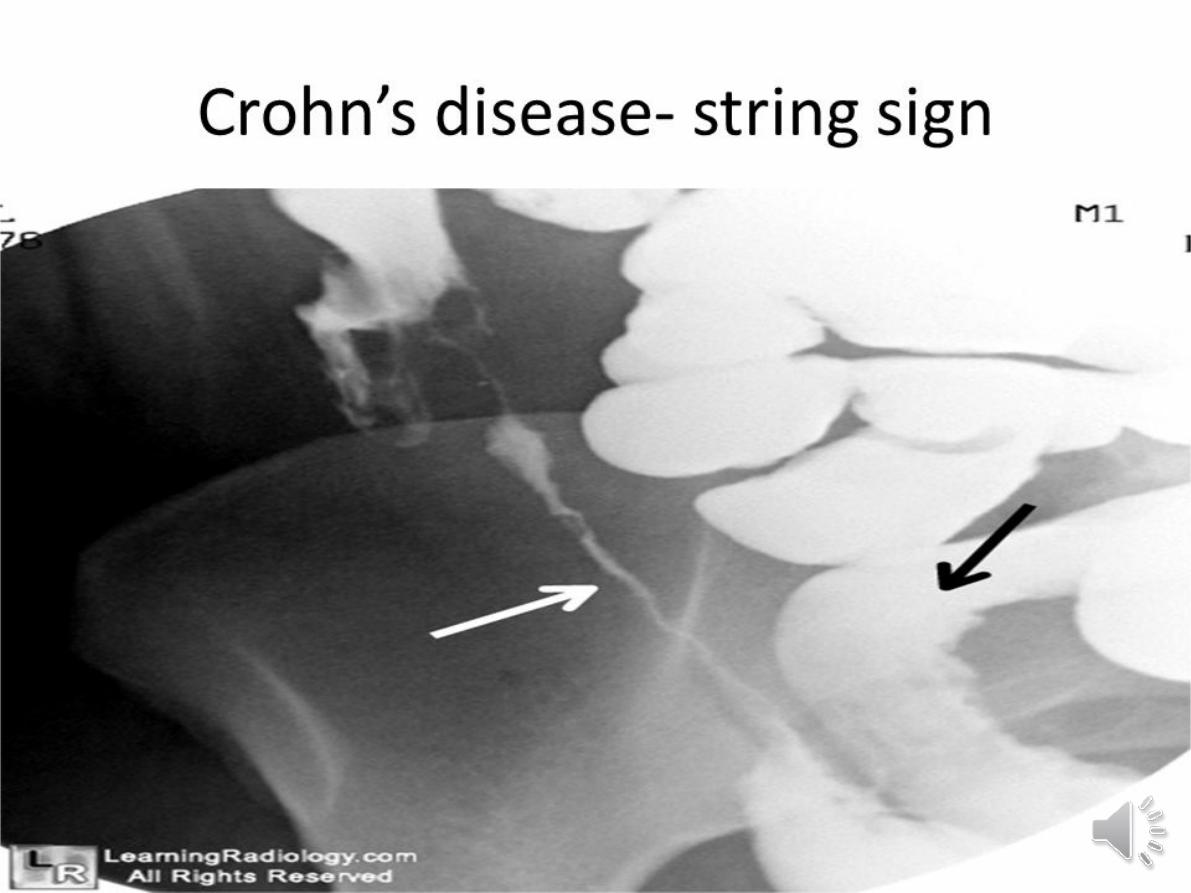
2- barium follow-through
demonstrates affected areas of the
bowel as narrowed and ulcerated, often with multiple
strictures This has now largely been replaced by MRI
enterography
3- A plain abdominal X-ray
is essential in the management of
patients who present with severe active disease.
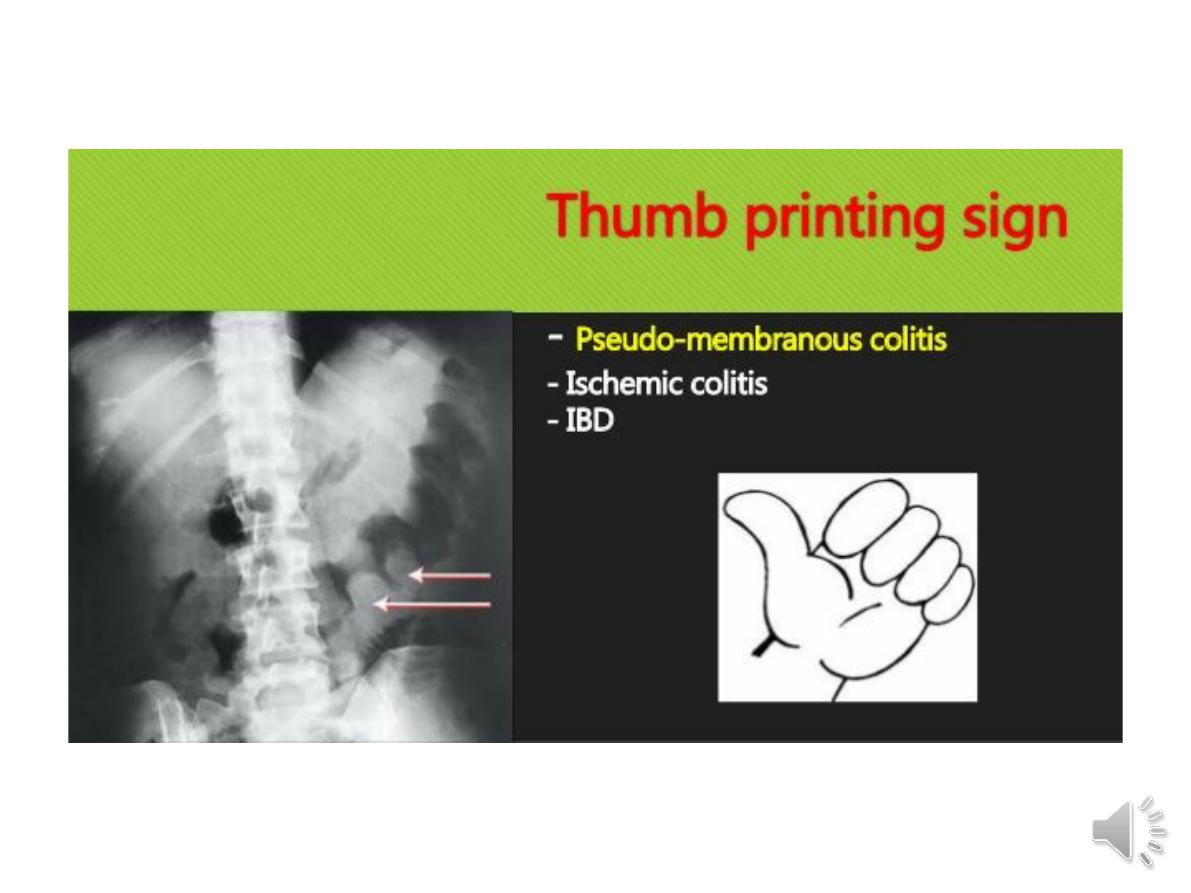
Dilatation of
the colon, mucosal oedema (thumb-printing) or evidence of
perforation
. In small bowel Crohn’s disease, there may be
evidence of intestinal obstruction or displacement of bowel
loops by a mass.
4-Ultrasound is a very powerful tool to detect small bowel
inflammation and stricture formation
5-The role of CT
in perforation or abscess formation
.

Management
. The key aims of medical therapy are
to:
• treat acute attacks (induce
remission)
• prevent relapses (maintain
remission)
• prevent bowel damage
• detect dysplasia and prevent
carcinoma
• select appropriate patients for
surgery

.
Aminosalicylates
(mesalazine)
Corticosteroids (prednisolone, hydrocortisone, budesonide)Anti-
inflammatory
Bisphosphonates are co-prescribed to prevent osteopenia
Thiopurines (azathioprine, mmunomodulation by inducing T-cell
MethotrexateAnti-inflammatory
Ciclosporin Suppresses T-cell expansion'Rescue' therapy to prevent
surgery in ulcerative colitis responding poorly to corticosteroids. No
value in CD
Anti-TNF antibodies (infliximab and adalimumab)Suppress inflammation
and induce apoptosis of inflammatory cells :Moderately to severely
active Crohn's disease, especially fistulating ;Severe active ulcerative
colitis.Anaphylactic reactions after multiple infusion
Contraindicated in the presence of infections; reactivation of
tuberculosis, increased risk of infections and malignancy
Antibiotics Antibacterial Useful in perianal Crohn's disease .
metronidazole
Antidiarrhoeal agents
(loperamide, lomotil)Reduce gut motility and small
bowel secretion improves anal function .Avoided in acute flare-ups of
disease May precipitate colonic dilatation
.
.
.

♠Ulcerative colitis
1-Active proctitis.
suppository ± oral 5-
aminosalicylate (5-ASA). resistant disease
→corticosteroids and immunosuppressants.
2-Active left-sided or extensive ulcerative colitis.
mild to moderate :
- combination of oral and a topical 5-ASA preparation
-In patients who do not respond to this approach
within 2–4 weeks, steroid indicated.
-If corticosteroid resistance (lack of efficacy) or in
patients who require high corticosteroid doses to
maintain control
→ immunosuppressive therapy with a
thiopurine should be introduced.

Severe ulcerative colitis
.
• Admission
• IVF and correction of electrolyte imbalance
• Transfusion if Hb < 10 g/dL
• IV methyl prednisolone or hydrocortisone
• AB until enteric infection excluded
• Nutritional support
• LMWH: prophylaxis of venous thromboembolism
• Avoidance of opiates and antidiarrhoeal agents
• Consider infliximab or ciclosporin in stable patients
not responding to 3–5 days of corticosteroids

♠
Crohn’s disease
A-Induction of remission
.
1-
Aminosalicylates and corticosteroids are both effective
and usually induce remission in active ileocolitis and colitis
2-
Calcium and vitamin D
supplements.
3-
enteral nutrition
with either an elemental
(constituent amino acids) or polymeric (liquid protein)
diet may induce remission.
4-In severe disease, induction therapy with an
anti-TNF
agent
(infliximab and adalimumab) is appropriate,
unless there is abscess.
-
combination therapy with an anti-TNF antibody and a
thiopurine
is the most effective strategy for inducing
and maintaining remission

B-Maintenance therapy
.
-
thiopurines
(azathioprine and
mercaptopurine) Or methotrexate…
note : methotrexate is teratogenic.
-
Combination
therapy with an
immunosuppressant and an anti-TNF
antibody is the most effective strategy
but
costs
are high and there is an
increased risk of
serious adverse effects
.
-
stop smoking
.

C-Fistulae and perianal disease
.
-
Fistulae
often associated with sepsis.treat:Sx
-Corticosteroids are ineffective.
- For simple perianal disease,
metronidazole and/or
ciprofloxacin are first-line therapies
.
-
Thiopurines
can be used in chronic disease but do not
usually result in fistula healing.
Patients who are
intolerant of or resistant to thiopurines should be
treated with once-weekly methotrexate combined
with folic acid
-
Infliximab and adalimumab
can heal fistulae and
perianal disease in many patients and are indicated
when the measures described above have been
ineffective.

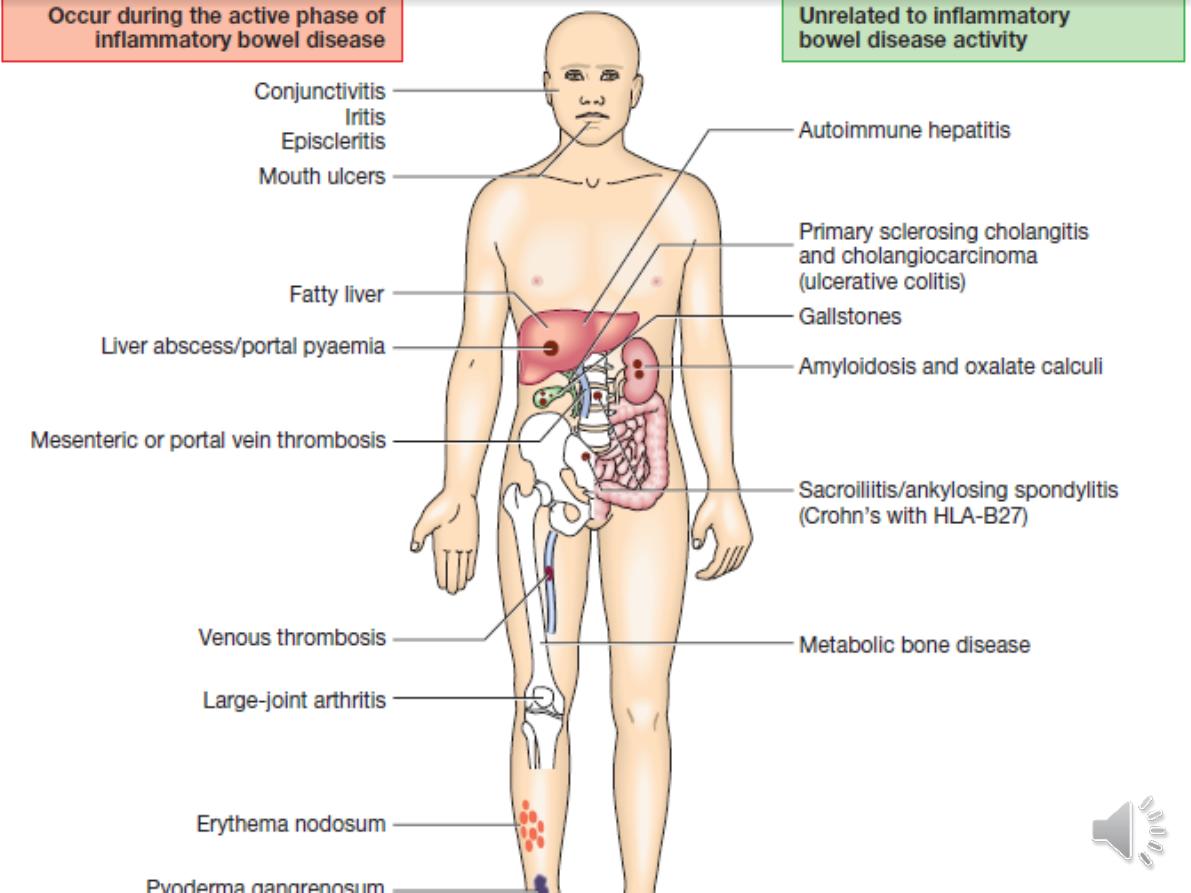
Indication of Sx:in UC
1-Impaired quality of life
• Loss of occupation or education
• Disruption of family life
2-Failure of medical therapy
• Dependence on oral corticosteroids
• Complications of drug therapy
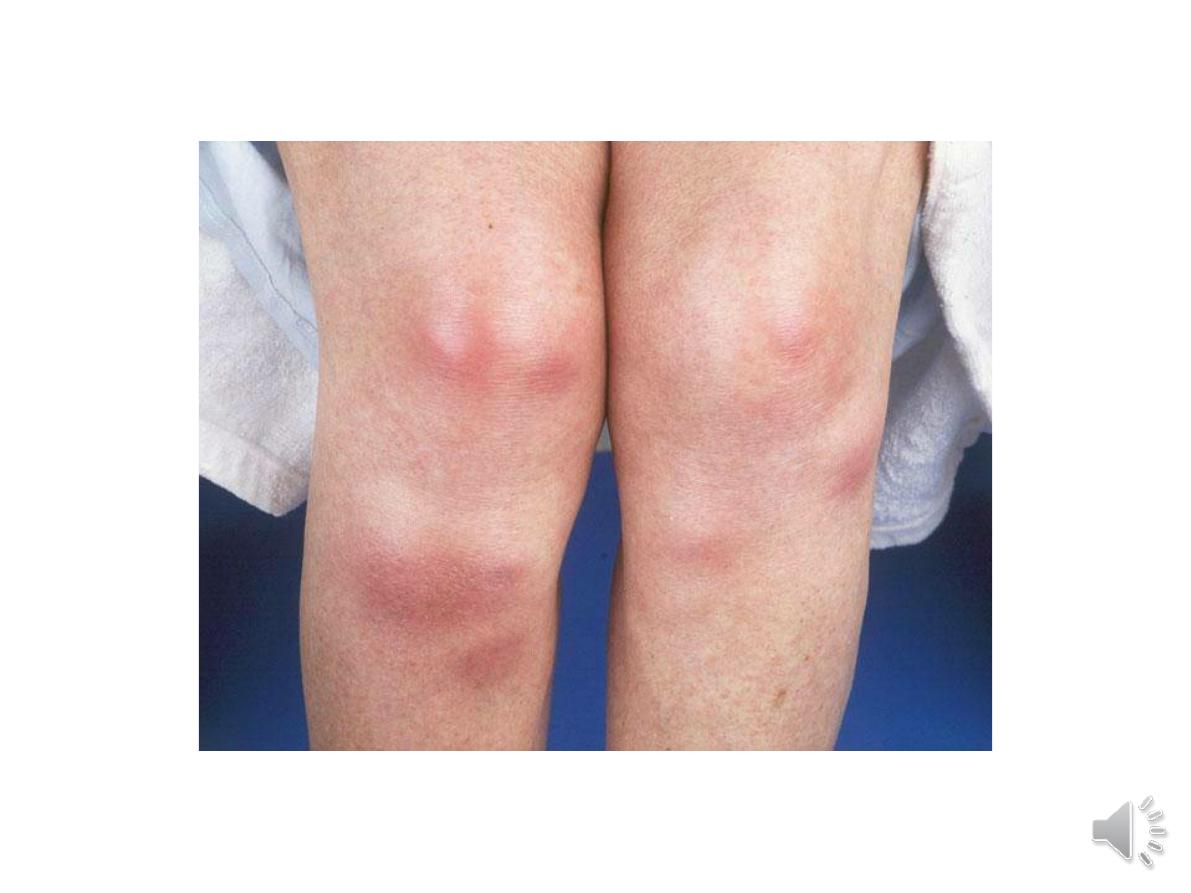
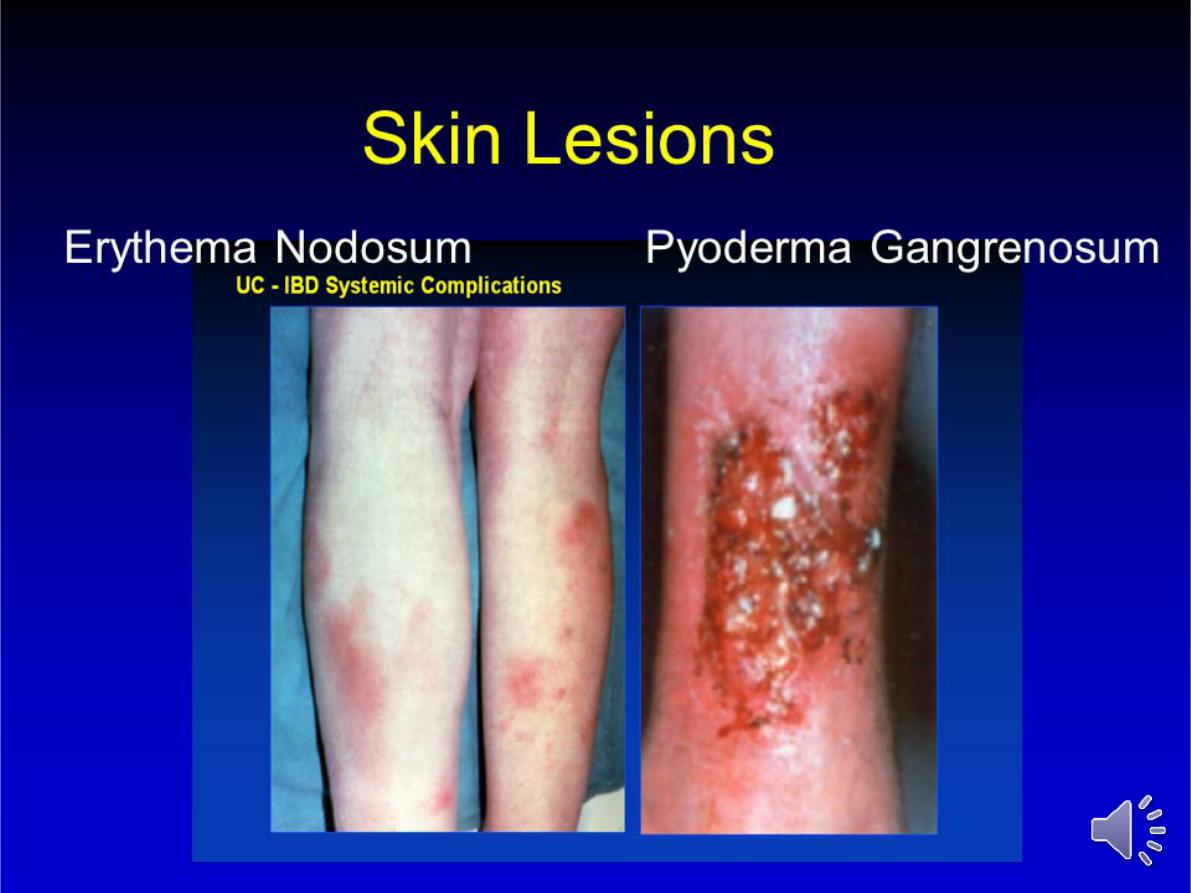
3-Fulminant colitis
4-Disease complications unresponsive to
medical therapy • Arthritis • Pyoderma
gangrenosum
5-Colon cancer or severe dysplasia

♠
Crohn’s disease:
-The indications for surgery are similar to
those for ulcerative colitis.
-
Operations
are often necessary to deal with
fistulae, abscesses and perianal disease, and
relieve small or large bowel obstruction.
- Incontrast to ulcerative colitis, surgery is not
curative and disease recurrence is the rule.
-The only method that has consistently been
shown to reduce post-operative recurrence is
smoking cessation
.