
Professor Dr. Mohanned Alshalah
Pancreas
Lecture 2
Course 2

Assessment and management of chronic pancreatitis
Learning objectives
Diagnosis and treatment of pancreatic cancer
Management sever acute pancreatitis and Pseudocysts
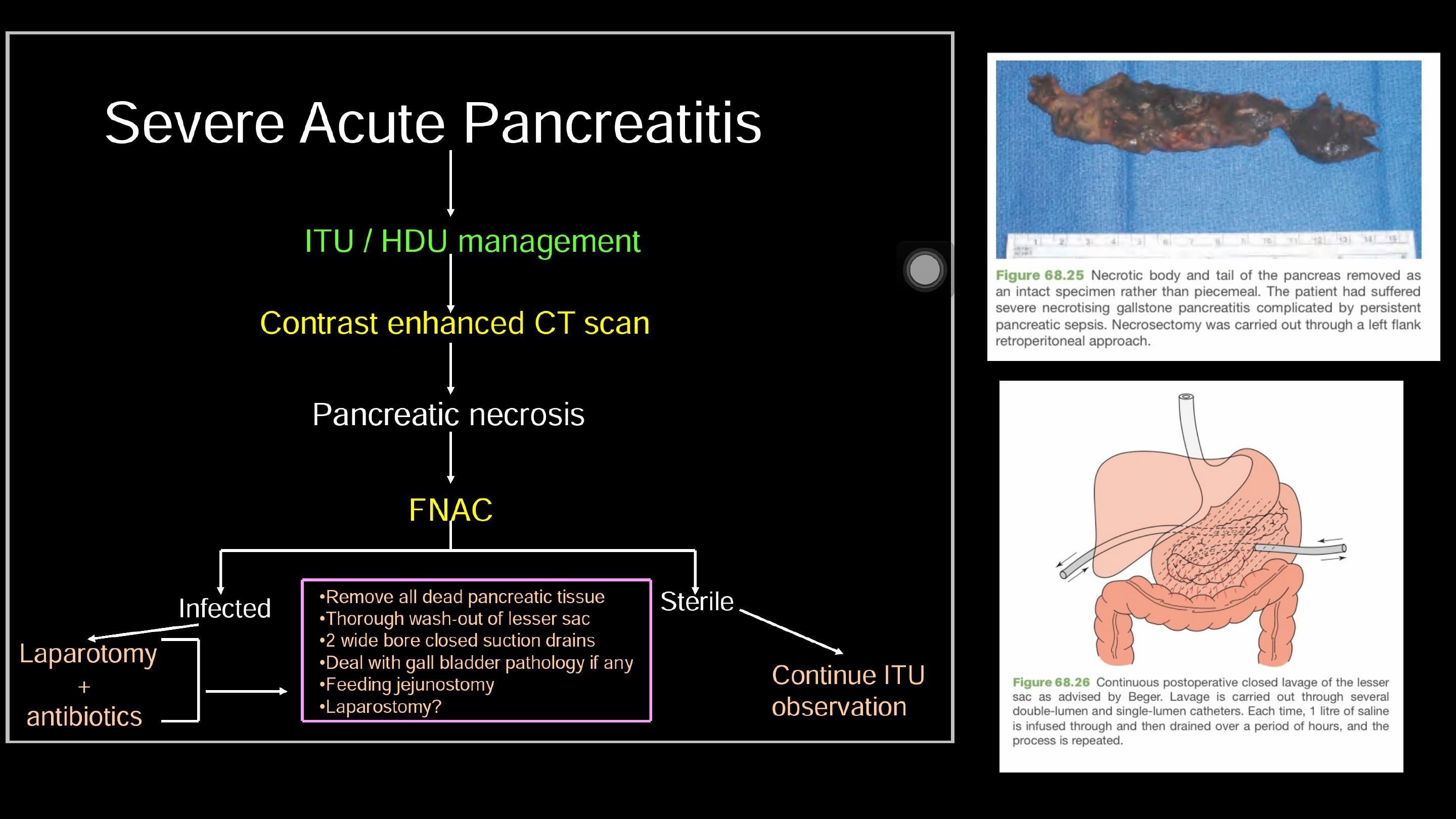

The overwhelming majority of patients with peripancreatic
sepsis can be successfully treated by conservative means,
and
necrosectomy
should be necessary in a very small
proportion of patients.

In a patient who has gallstone pancreatitis, the
gallbladder and gallstones should be removed as soon
as the patient is fit to undergo surgery and, preferably,
before discharge from hospital.

In a patient who has gallstone pancreatitis, the
gallbladder and gallstones should be removed as
soon as the patient is fit to undergo surgery and,
preferably, before discharge from hospital.
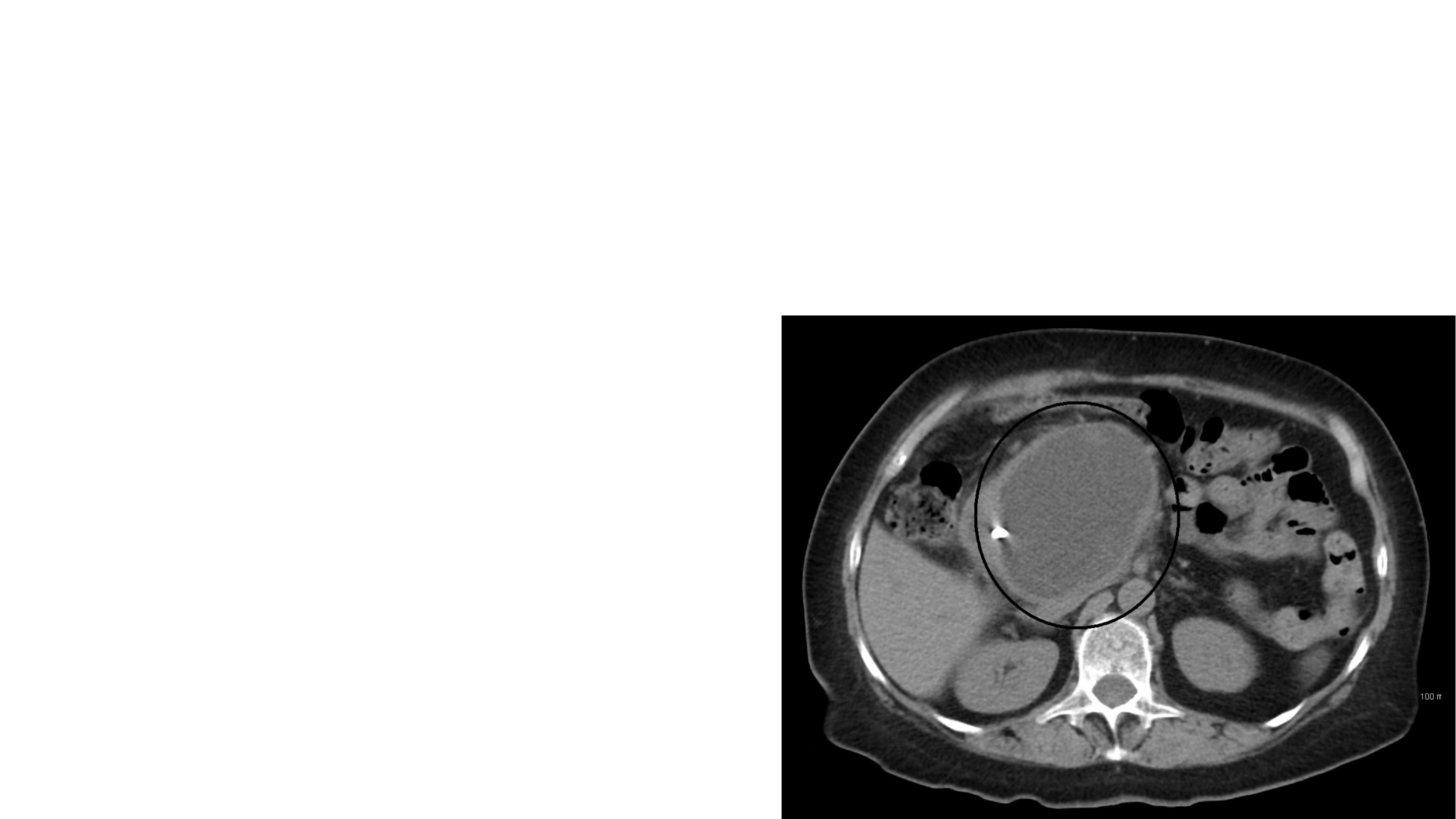
A pseudocyst is a collection of amylase-rich
fluid enclosed in a well-defined wall of
fibrous or granulation tissue.
Formation of a pseudocyst requires 4 weeks
or more from the onset of acute pancreatitis.
PSEUDOCYST
More than half of these will be found to have
a communication with the main pancreatic
duct.
A pseudocyst is usually identified on
ultrasound or a CT scan.

EUS and aspiration of the cyst fluid is very useful.
The fluid should be sent for measurement of carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA)
levels, amylase levels and cytology.
Fluid from a pseudocyst typically has a low CEA level.
Pseudocyst fluid usually has a high amylase level
Cytology typically reveals inflammatory cells in pseudocyst fluid.
Pseudocysts that are thick-walled or
large (over 6 cm in diameter), have lasted
for a long time (over 12 weeks), or have
arisen in the context of chronic
pancreatitis are less likely to resolve
spontaneously.
Therapeutic interventions are advised only if the pseudocyst causes symptoms, if
complications develop, or if a distinction has to be made between a pseudocyst and
a tumour.
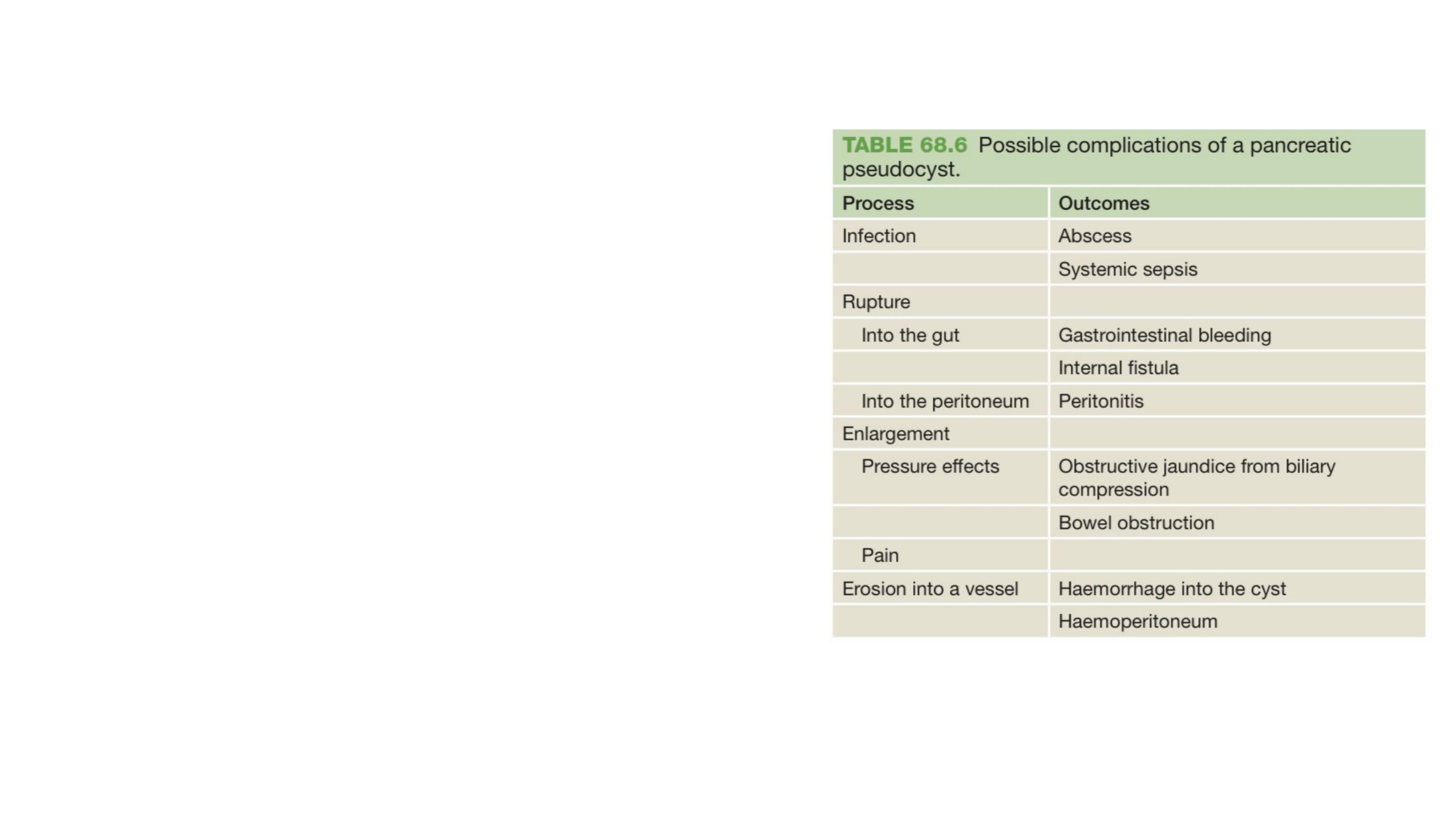
Pseudocysts will resolve spontaneously in most instances.
Complications can develop.
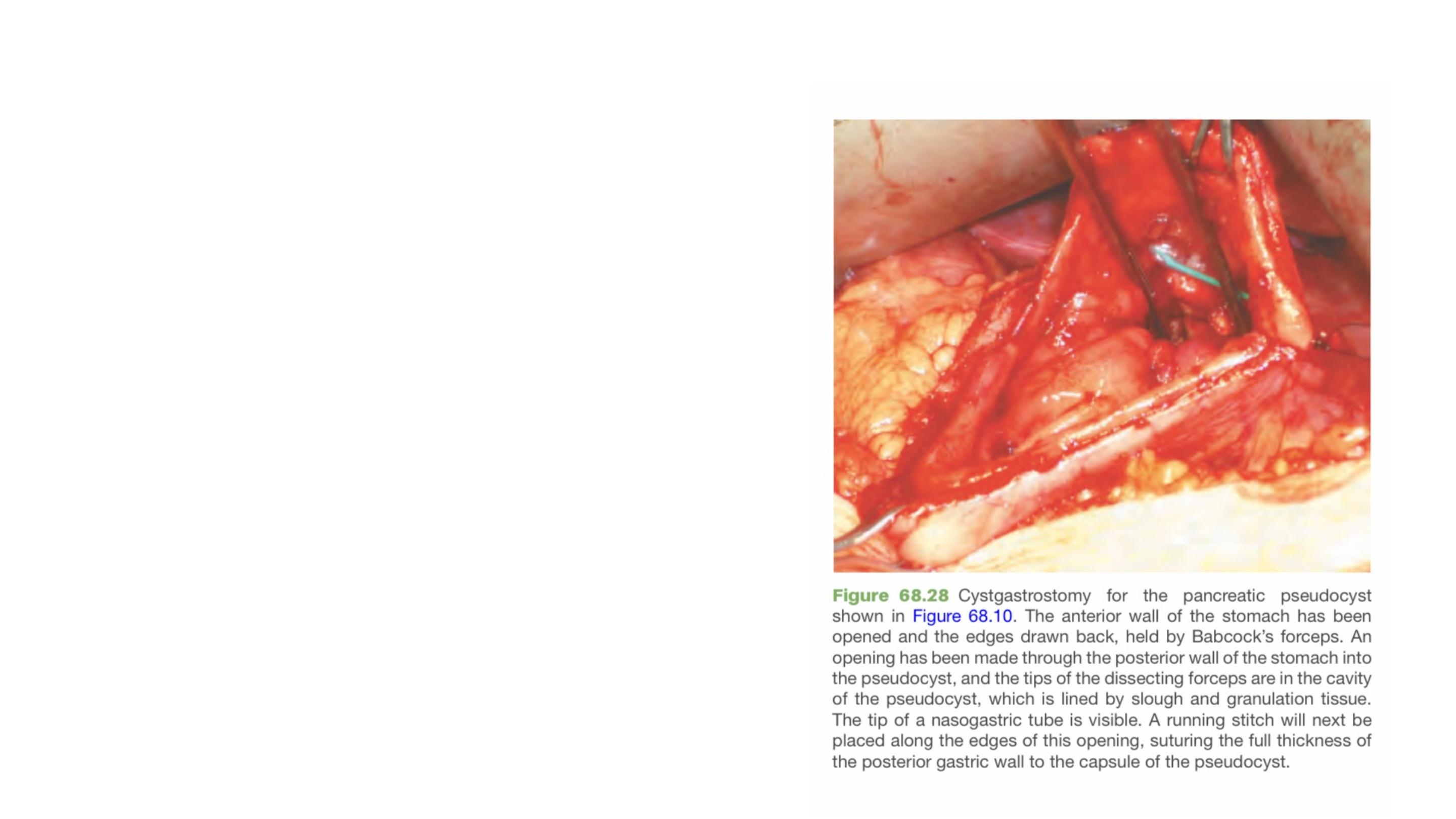
There are three possible approaches to draining a pseudocyst:
•
Percutaneous
•
Endoscopic
•
Surgical.

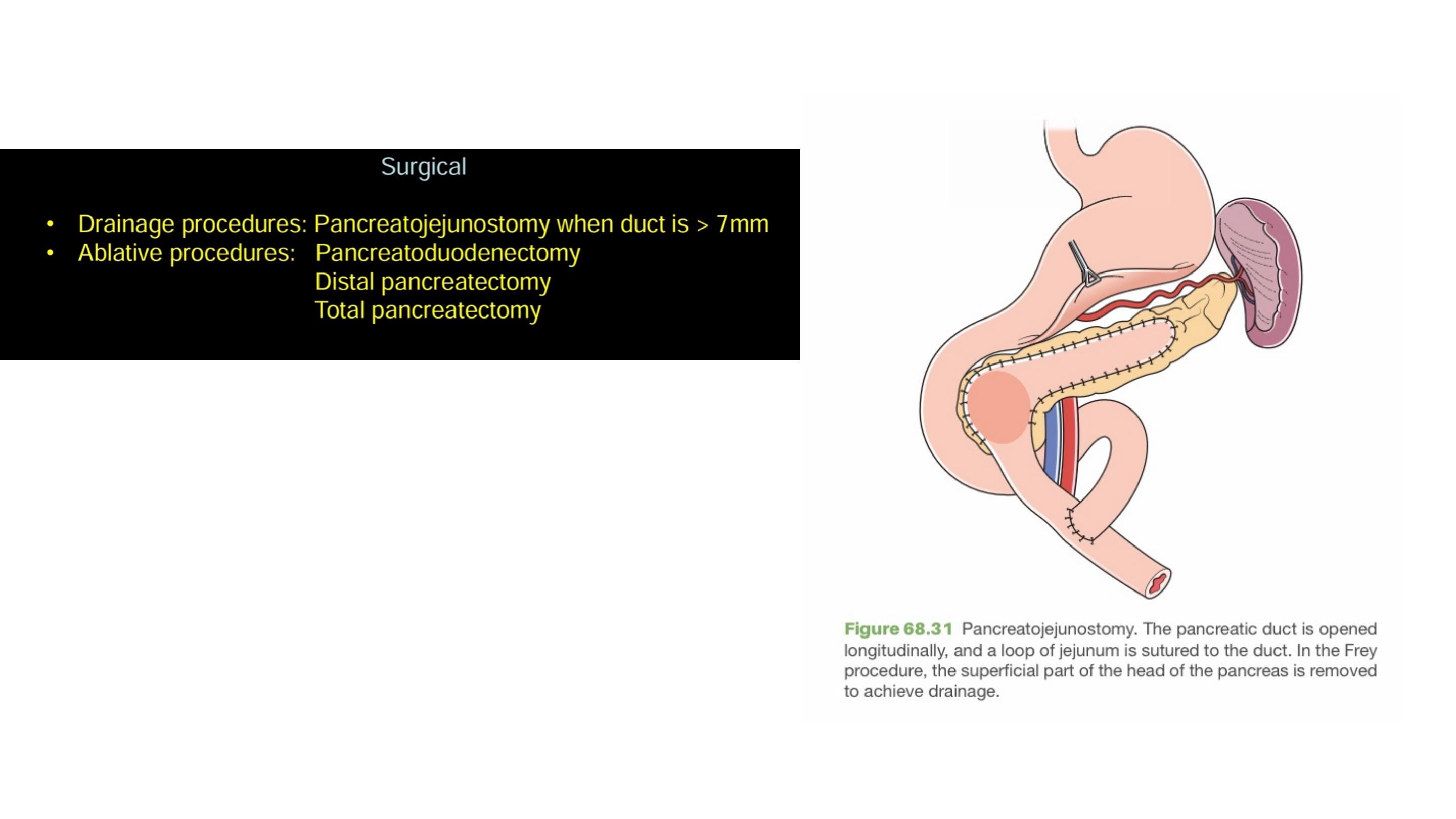
Chronic pancreatitis is a progressive inflammatory disease in which
there is irreversible destruction of pancreatic tissue.
Chronic pancreatitis
Its clinical course is characterised by severe pain and, in the
later stages, exocrine and endocrine pancreatic insufficiency.




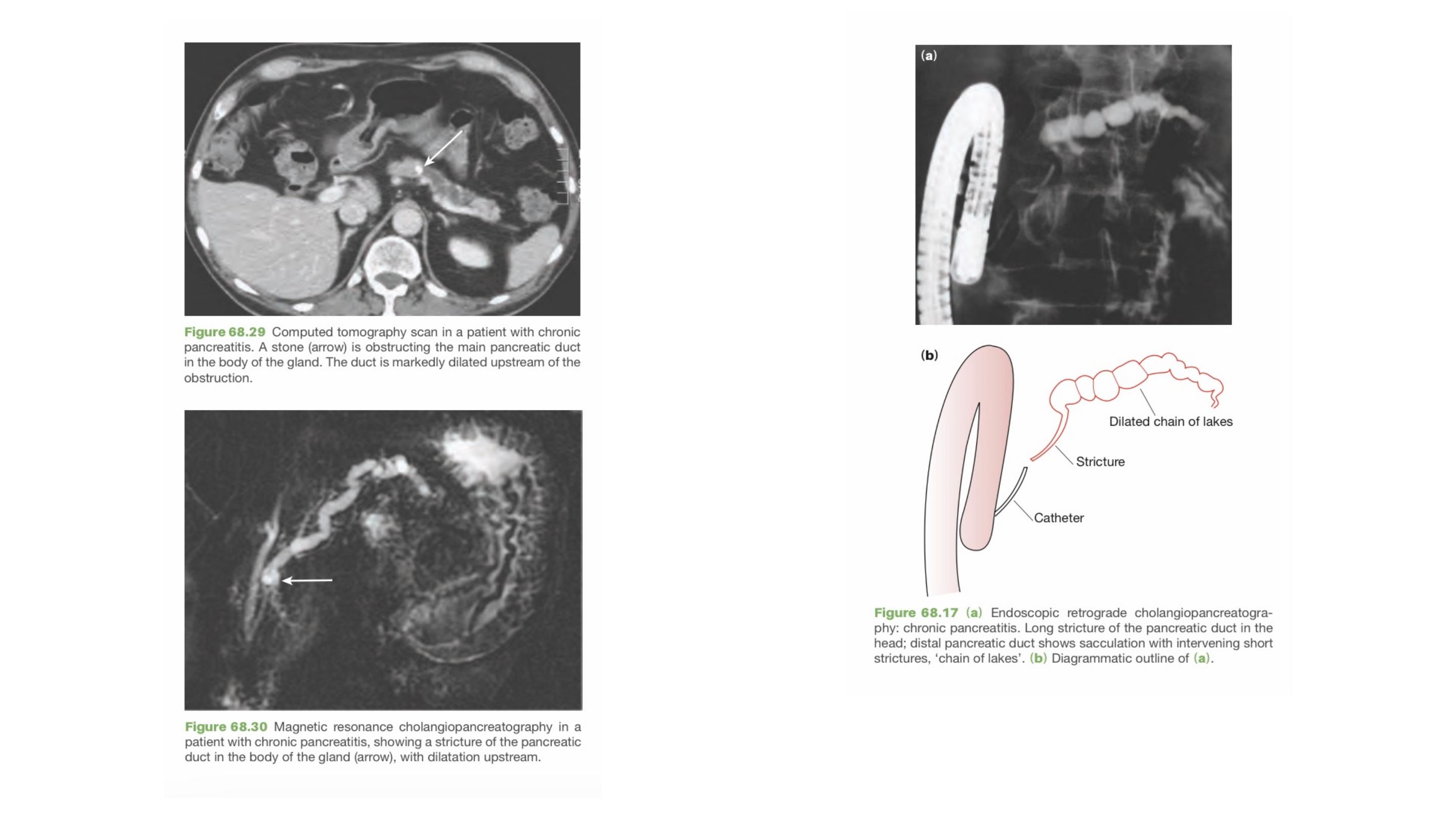


Endoscopic, radiological or surgical interventions are indicated
mainly to relieve obstruction of the pancreatic duct, bile duct or the
duodenum, or in dealing with complications (e.g. pseudocyst,
abscess, fistula, ascites or variceal haemorrhage).

Carcinoma of the pancreas
Eighty-five per cent of pancreatic cancers arise in the head of the pancreas.

Jaundice secondary to obstruction of the distal bile duct is the most
common symptom that draws attention to ampullary and pancreatic
head tumours.
Clinical features
Pruritus, dark urine and pale stools with steatorrhoea are common
accompaniments of jaundice.
It is characteristically painless jaundice but may be associated
with nausea and epigastric discomfort.
Tumours of the body and tail of the gland often grow silently, and present at
an advanced unresectable stage.
Back pain is a worrying symptom, raising the possibility of retroperitoneal
infiltration.

On examination, there many be evidence of jaundice, weight loss, a
palpable liver and a palpable gall bladder.
Courvoisier sign is positive
Other signs of intra-abdominal malignancy should be looked for with care, such
as a palpable mass, ascites, supraclavicular nodes and tumour deposits in the
pelvis; when present, they indicate a grim prognosis.
Examination

More than 85% of pancreatic cancers are ductal adenocarcinomas.
Endocrine tumours of the pancreas are rare.
Pathology
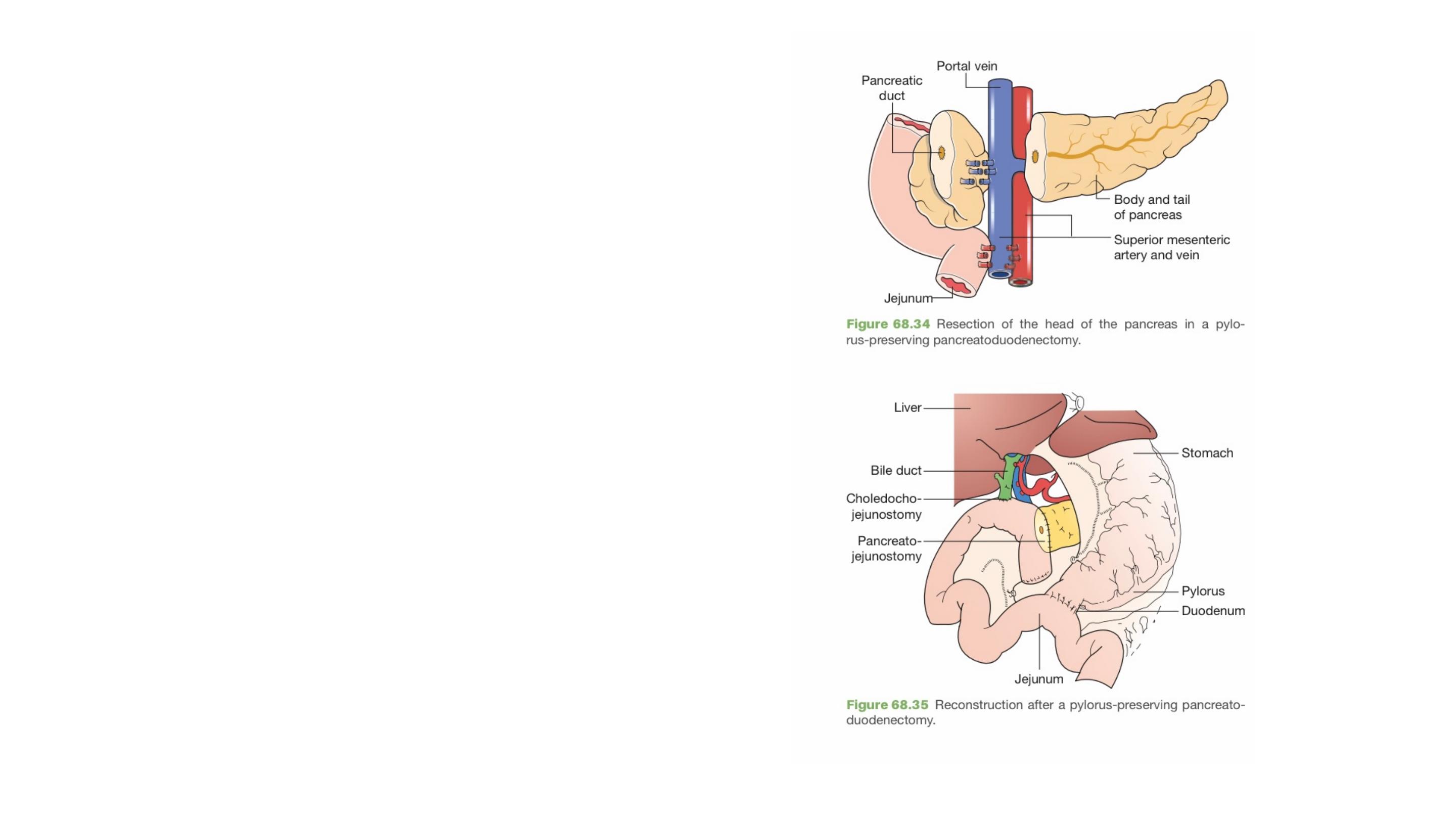
The standard resection for a tumour of the
pancreatic head or the ampulla is a pylorus-
preserving pancreatoduodenectomy (PPPD)
Surgical resection
At the time of presentation, more than 85%
of patients with ductal adenocarcinoma are
unsuitable for resection because the disease
is too advanced.

There is evidence that the laparoscopic and robotic approaches are also feasible
and may yield comparable results.
Majority of pancreatic resections continue to be performed via the open approach

For tumours of the body and tail, distal pancreatectomy with
splenectomy is the standard.
Tumours of the ampulla have a good prognosis and should, if at all
possible, be resected.
Some of the rare tumours and the neuroendocrine lesions should also
be resected if at all possible.

If unresectable disease is found in the course of a laparotomy that was
commenced with the intent to resect, a choledochoenterostomy and a
gastroenterostomy should be carried out to relieve (or pre-empt) jaundice
and duodenal obstruction.
Palliation
The median survival of patients with unresectable, locally advanced,
non-metastatic pancreatic cancer is 6–10 months and, in patients with
metastatic disease, it is 2–6 months.
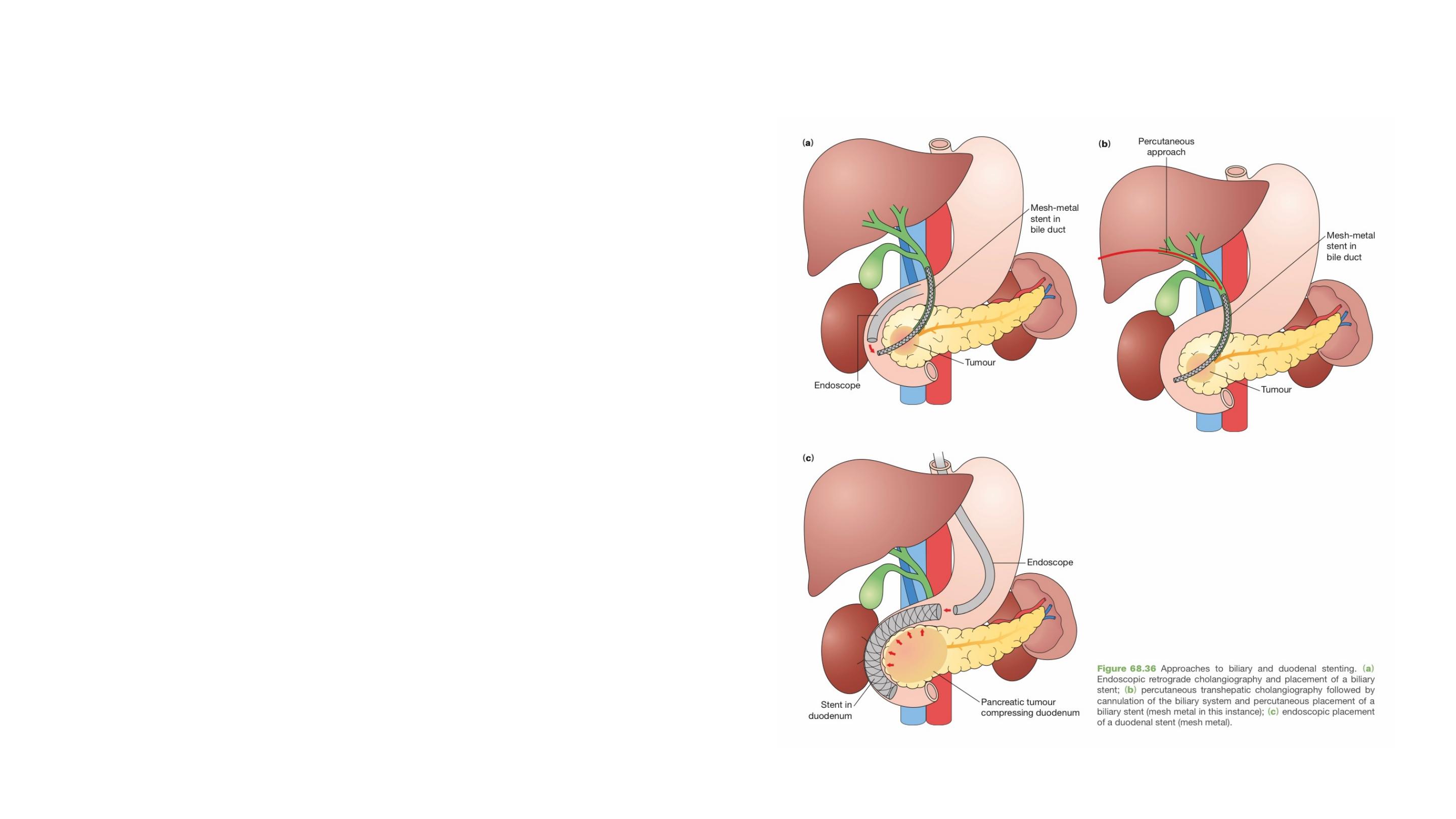
Palliation
In patients found to have unresectable
disease on imaging, jaundice is relieved
by stenting at ERCP
If the patient is not a suitable candidate for
endoscopic biliary stenting, a percutaneous
transhepatic stent can be placed

