
By
Dr. Ashraf Hussain
Msc., PhD. Community Medicine

Definition
:
The presence in the atmosphere of one or
more air contaminants in such quantities that
are harmful to human, plant, or animal life, or
that interfere with the comfortable enjoyment
of life or the conduct of business or other
human activities

Air is a mechanical mixture of gases
The normal composition of external air by
volume is approximately as follows:
Nitrogen 78%,
Oxygen 21%,
CO
2
0.03%,
Argon, Neon, Helium, Krypton &Xenon <1%
In addition to these gases, air also contains
water vapor, traces of ammonia and
suspended matter such as dust, bacteria,
spores and vegetable debris.

According to a WHO assessment,
The requirement for air is relatively constant
(about 10-20m3 per day)
more than 3 million premature deaths each year
can be attributed to the effects of ambient
(outdoor) air pollution.
4.3 million deaths every year as a result of
household exposure to smoke from dirty
cookstoves and fuels
92%of the world’s population lives in places where
air quality exceeds WHO guideline limits
More than half of this disease burden is borne by
the populations of developing countries.

Air is rendered impure by
Respiration of men and animals
Combustion of coal, gas, oil, etc.
Decomposition of organic matter and
Trade, traffic and manufacturing processes
which give off dust, fumes, vapors and gases.
Under ordinary conditions, the composition of
outdoor air is remarkably constant.

Wind: Wind dilutes and sweeps away the impurities
by its movement.
Sunlight : The atmospheric temperature and
sunlight play their own part by oxidizing impurities,
and killing bacteria.
Rain : It cleanses the atmosphere by removing the
suspended and gaseous impurities.
Plant life : The green plants utilize the carbon
dioxide and generate oxygen; this process is
reversed during the night time.
When the rate of pollution becomes too high or when
the cleansing process becomes ineffective, it
constitutes a health hazard.

More than 100 substances which pollute air
have been identified.
The important ones are
carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, hydrogen
sulphide, sulphur dioxide, and nitrous oxide.
Organic compounds (e.g., hydrocarbons,
aldehydes, ketones, organic acids),
Metallic contaminants (e.g., arsenic, zinc, iron
resulting from smelting operation),
radio-active compounds as radon
photochemical oxidants (e.g., ozone).

Air pollutants may be either emitted into the
atmosphere or formed within the atmosphere
itself.
SO, they are either:
1. Primary air pollutants : Primary air pollutants
are those
that are emitted into the
atmosphere from a source such as a factory
chimney or exhaust pipe, or through
suspension of contaminated dusts by the
wind.
In principle it is possible to measure the
amounts emitted at the source itself.
.

2. Secondary air pollutants are
those
formed within the atmosphere itself.
They arise from chemical reactions of
primary pollutants, possibly involving the
natural components of the atmosphere,
especially oxygen and water. The most
familiar example is ozone,
Because of this mode of formation,
secondary pollutants cannot readily be
included in emissions inventories.

Another important distinction must be is the
physical state of a pollutant.

1. Gaseous air pollutants are those
present as
gases or vapors.
As individual small molecules capable of
passing through filters, provided they do not
adsorb to or chemically react with the filter
medium.
Gaseous air pollutants are readily taken into
the human respiratory system, although if
water-soluble, they may very quickly be
deposited in the upper respiratory tract and
not penetrate to the deep lung.

2. Particulate air pollutants
comprise material in solid or liquid phase
suspended in the atmosphere.
Such particles can be either primary or
secondary and cover a wide range of sizes.
It consists of a complex mixture of solid and
liquid particles of organic and inorganic
substances.
The major components of PM are sulfate,
nitrates, ammonia, sodium chloride, black
carbon, mineral dust and water.

Particulate matter of diameter smaller than
2.5 μm are more dangerous since, when
inhaled, there is high probability of
deposition in the smaller conducting airways
and alveoli, so interfere with gas exchange
inside the lungs.
Chronic exposure to particles contributes to
the risk of developing cardiovascular and
respiratory diseases, as well as of lung
cancer.

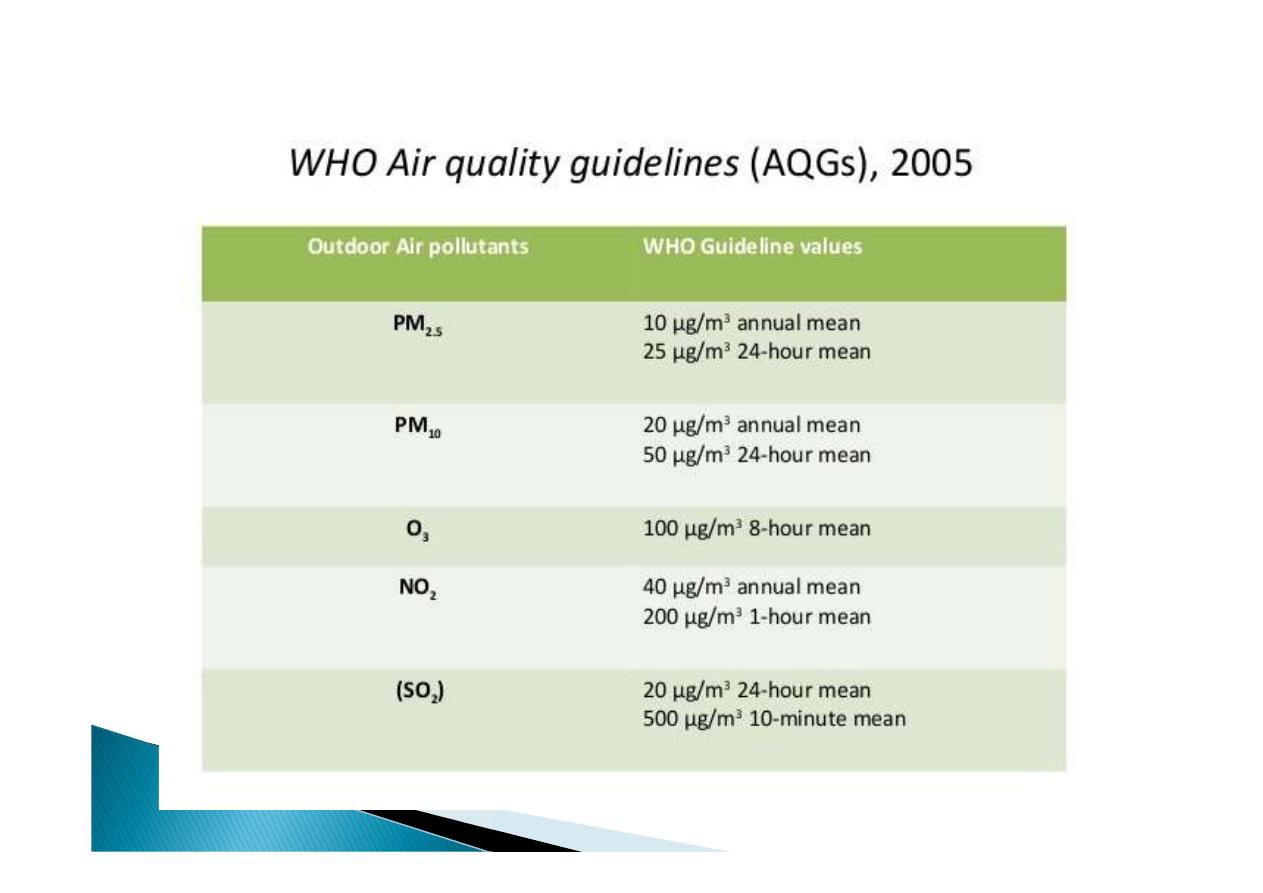
The 2005 AQG set for the first time a
guideline value for particular matter (PM) as:
10 μg/m3 annual mean and 25 μg/m3 24-
hour mean for PM2 .5
and 20 μg/m3 annual mean and 50 μg/m3
24-hour mean for PM10

most common and widely distributed air
pollutants.
It is a product of incomplete combustion of
carbon containing materials, such as in
automobiles, industrial process, heating
facilities and incinerators.
Concentrations in urban areas depend on
weather and traffic density.
Variations in these levels are also influenced
by topography.

Sulphur dioxide (S02) is a colourless gas with a
sharp odour, results from the combustion of
sulphur containing fossil fuel, the smelting of
sulphur-containing ores, and other industrial
processes.
Domestic fires, power generation and motor
vehicles can also produce emissions
containing sulphur dioxide.
S02 can affect the respiratory system and the
function of lungs, causes irritation of eyes
and exacerbation of asthma.

Sulphur dioxide: This gas is a major
contaminant in many urban and industrial
areas.
When S02 combines with water, it forms
sulphuric acid; this is the main component of
acid rain which is a cause of deforestation.
Its concentration is estimated in all air
pollution surveys.

The combustion of alkyl lead additives in
motor fuels accounts for the major part of all
lead emissions into the atmosphere.
An estimated 80-90 per cent of lead in
ambient air derives from the combustion of
leaded petrol.
The degree of pollution from this source differs
from country to country, depending on motor
vehicle density and the efficiency of effort to
reduce the lead content of petrol.

Children up to 6 years of age are a population at
increased risk for lead exposure, as well as for
adverse health effects due to:
A.
a. children have behaviour characteristics
(outdoor activity) which increase the risk of lead
exposure.
B.
b. The blood-brain barrier is not yet fully
developed in young children.
C.
c. haematological and neurological effects of
lead occur at lower threshold in children than in
adults.
Since the placenta is no effective biological barrier,
pregnant women represent a second group at the
increased risk because of exposure of the foetus
to lead.

Lead poisons many systems in the body and is
particularly dangerous to children developing
brain and nervous system.
Elevated lead levels in children have been
associated with impaired neuropsychologic
development as measured by loss of IQ, poor
school performance and behavioural
difficulties

This is not commonly regarded as an air
pollutant, although man generates enormous
amount of it in combustion process using
coal, oil and gas.
Carbon dioxide is a natural constituent of the
air.
It does not take part in any significant chemical
reactions with other substances in the air.
However, its global concentration is rising
above the natural level by an amount that
could increase global temperature enough to
affect climate markedly

Man-made sources of hydrocarbons include
incineration, combustion of coal, wood,
processing and use of petroleum.
Hydrocarbons exert their pollutant action by
taking part in the chemical reactions that
cause photochemical smog.
Their main health effect is lung cancer.

Ozone at ground level not to be confused
with the ozone layer in the upper atmosphere.
It is one of the major constituents of photochemical
smog.
It is formed by the photochemical reaction of
sunlight with pollutants such as nitrogen oxides
from vehicle, industry emissions and volatile
organic compounds (VOCs) emitted by vehicles,
solvents and industry.
Excessive ozone in the air can have a marked effect
on human health. It can cause breathing problems,
trigger asthma, reduce lung function and cause
lung diseases

The pollutant of far greater concern in relation
to human health is nitrogen dioxide.
Coal is the most important fuel in this context
Other sources are road traffic and electricity
generation.
Epidemiological studies have shown that
symptoms of bronchitis in asthmatic children
increase in association with long-term
exposure to nitrogen dioxide.
Reduced lung function is also linked to
nitrogen dioxide at concentrations currently
measured (or observed) in the large cities.

Criteria pollutants are the only air pollutants with
national air quality standards that define
allowable concentrations of these substances in
ambient air.
They are carbon monoxide, nitrogen dioxide,
sulfur dioxide, ozone, particulate matter, and
lead.
Exposure to these substances can cause health
effects, environmental effects, and property
damage.
Health effects include heart or lung disease,
respiratory damage, or premature death.
Environmental effects include smog, acid rain,
and ozone depletion.

Hazardous air pollutants, also known as toxic
air pollutants or air toxics, are those
pollutants that are known or suspected to
cause cancer or other serious health effects,
such as reproductive effects or birth defects,
or adverse environmental effects.
Examples of air toxics include dioxin,
asbestos, toluene, and metals such as
cadmium, mercury, chromium, and lead
compounds.


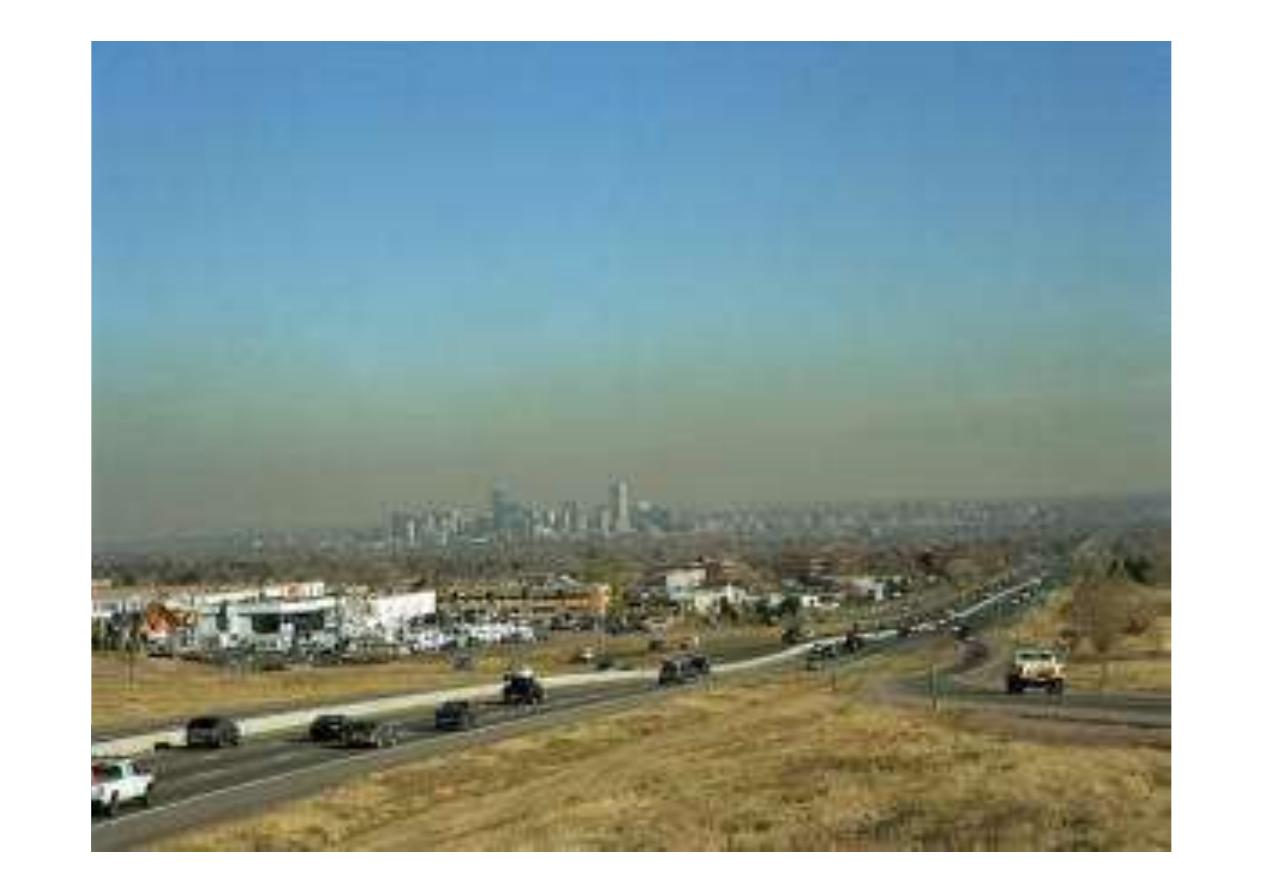
Smog (a combination of the words "smoke" and
"fog") forms when sunlight acts on a cocktail of
pollutant gases such as nitrogen and sulfur
oxides, unburned hydrocarbons, and carbon
monoxide; that's why it's sometimes called
photochemical smog
One of the most harmful constituents of smog is
the ozone, which can cause serious breathing
difficulties and even, sometimes, death.
When smog is rich in ozone, it tends to be a
blueish color, otherwise it's more likely to be
brown.


The best indicators of air pollution are sulphur
dioxide, smoke and suspended particles.
These are monitored on a daily basis over
several sites.
The results are then collected by a central
agency.
(a)
Sulphur dioxide: major
contaminant in
many urban and industrial areas and Its
concentration is estimated in all air pollution
surveys.

Smoke or soiling index:
A known volume of
air is filtered through a white filter paper
under specified conditions and the stain is
measured by photoelectric meter. Smoke
concentration is estimated and expressed as
micrograms/ cubic metre of air as an average
level over a period of time.
Grit and dust measurement : Deposit gauges
collect grit,
dust and other solids. These are
analyzed monthly.
Coefficient of haze : A factor used,
particularly in the
USA in assessing the
amount of smoke or other aerosol in air.

Health aspects :
The health effects of air pollution are both
immediate and delayed.
The immediate effects are borne by the
respiratory system and resulting in acute
bronchitis.
If the air pollution is intense, it may result
even in immediate death by suffocation.
This has taken place in the air pollution
epidemic which occurred in London in
1952.

The delayed effects most commonly linked
with air pollution are chronic bronchitis, lung
cancer, bronchial asthma, emphysema, and
respiratory allergies
Elderly, children, smokers and those with
chronic respiratory difficulties are most
vulnerable.

(b) Social and economic aspects :
These comprise
Destruction of plant and animal life;
Corrosion of metals
Damage to buildings
Cost of cleaning and maintenance and repairs
Aesthetic nuisance.
Also reduces visibility in towns.
Soil and damage clothings.

The WHO has recommended the following procedures
for the prevention and control of air pollution
Containment : That is, prevention of escape of toxic
substances into the ambient air. Containment can be
achieved by a variety of engineering methods such as
enclosure, ventilation and air cleaning. A major
contribution in this field is the development of
"arresters" for the removal of contaminants.
Replacement : That is, replacing a
technological
process causing air pollution, by a new process that
does not. Increased use of electricity, solar power
generation, natural gas, and central heating in place
of coal have greatly helped in smoke reduction.
There is a move now to reduce lead in petrol which is a
cumulative poison.

Dilution : Dilution is valid so long as it is within the
selfcleaning
capacity of the environment. For
example, some air pollutants are readily removed
by vegetation. The establishment of "green belts"
between industrial and residential areas is an
attempt at dilution. The capacity for dilution is,
however, limited and trouble occurs when the
atmosphere is overburdened with pollutants.
Legislation: Air pollution is controlled in many
countries
by suitable legislation, e.g., Clean Air
Acts. Legislation covers such matters as height of
chimneys, powers to local authorities to carry out
investigations, research and education
concerning air pollution, creation of smokeless
zones and enforcement of standard for ambient
air quality.

International action : To deal
with air pollution
on a world-wide scale, the WHO has
established an international network of
laboratories for the monitoring and study of
air pollution.
These centres
will issue warnings of air
pollution where and when necessary.

In recent years, the concept of disinfection of air has
received much attention. The methods employed are
Mechanical ventilation : This reduces vitiated air and
bacterial density.
Ultraviolet Radiation : This has been found to be
effective in special situations such as operation
theatres and infectious disease wards. Ultraviolet
rays have proved effective for general use in public
assembly and school rooms.
Chemical Mists Triethylene glucol vapours have been
found to be effective air bactericides, particularly
against droplet nuclei and dust.
Dust Control : Application of oil to floors of hospital
wards reduces the bacterial content of the air

indoor air pollution,
originating from both outdoor and indoor
sources, people spend a large part of
their time each day indoors.

Fuel-burning combustion appliances
Tobacco products
Products for household cleaning and maintenance,
personal care, or hobbies
Central heating and cooling systems and
humidification devices
Excess moisture
Outdoor air pollutants
Emissions from construction materials and
furnishings
Deteriorated asbestos-containing insulation
Newly installed flooring, upholstery or carpet
Cabinetry or furniture made of certain pressed
wood products
