
I. U .G.R.

Significance
I.U.G.R. is a major cause of neonatal
morbidity & mortality.
Certain adult diseases including
hypertension & diabetes are related to
I.U.G.R.

Definition
I.U.G.R. Is defined as failure of the fetus to acheive
its genetic growth potential .
S.G.A.: fetus or neonate is below a certain defined
centile of weight or size for a particular
gestational age ( below 3
rd
or 5
th
centile ) ,and
SGA are constitutionally small due to normal
genetic influences.
While IUGR indicates that a particular pathological
process is operating to modify the intrinsic growth
potential of the fetus by reducing its growth rate .

Recent definition of IUGR
■
Early‐onset growth restriction < 32 weeks.
■
AC or EFW <3rd centile or absent EDF in the
umbilical artery
■
or
■
1) AC/EFW <10th centile combined with
■
2) Uterine artery PI >95th centile and/or
■
3) Umbilical artery PI >95th centile
■
Late‐onset growth restriction > 32 weeks.

Incidence of IUGR
3-5%

Aetiology
1-Reduced fetal growth potential
(intrinsic)
A-chromosome defect e.g trisomy 18 ,
triploidy.
B-single gene defects e.g seckel’s synd.
C-structional abn. e.g renal agenesis
D-infection e.g TORCH

Aetiology
2-Reduced fetal growth support (extrinsic)
A- maternal factors
:
1.Undernutrition e.g poverty , eating
disorders .
2.Maternal hypoxia e.g altitude , cyanotic
heart disease .
3.drugs:cigarette smoking , alcohol, cocaine ,
warfarin, phenytoin, cytotoxic drugs.

1-Reduced utero –placental perfusion: e.g
inadequate trophoblast invasion ( e.g HT, PET
),
Antiphospholipid syn. ,D.M with vascular
lesions advanced ), sickle cell disease ,
multiple pregnancy .

2-Reduced feto – placental
pefrusion
A-single umbelical artery.
B- twin – twin trasfusion syn.

Complications
Antepartum complications
1- stillbirth (fetal death in IUGR more
frequent after 35 weeks of gestation ) .
2- oligohydramnios ( in severe IUGR due
to vasoconstriction in the fetal kidney
results in impaired urine production ).
3- Antepartum fetal distress.

Intrapartum complications
Intrapartum fetal hypoxia & acidosis
Increased incidence of c/s
Due to marked depletion of energy stores in
the liver & subcutaneous tissues .

Neonatal complications
1- Related to perinatal asphyxia &
acidosis :
Persistent fetal circulation , meconium
aspiration syn. ,hypoxic – ischemic
encephalopathy .
2- Metabolic alterations : hypoglycemia ,
hypocalcemia , hyperviscosity
syn. ,hyperbilirubinemia, hypothermia .

Neon
atal complications
3- Related to the specific cause of IUGR
Infection , cong. Malformations ,
chromosomal abn.

Classifications
1-
Intrinsic IUGR (symmetric
) : due to fetal
condition e.g infection , chromosomal abn.
2-Extrinsic (Asymmetric)
: due to element
outside fetus ( placental condition or maternal
disease ) .
3- Combined IUGR
(both intrinsic & extrinsic
factors ).
4- Idiopathic IUGR.
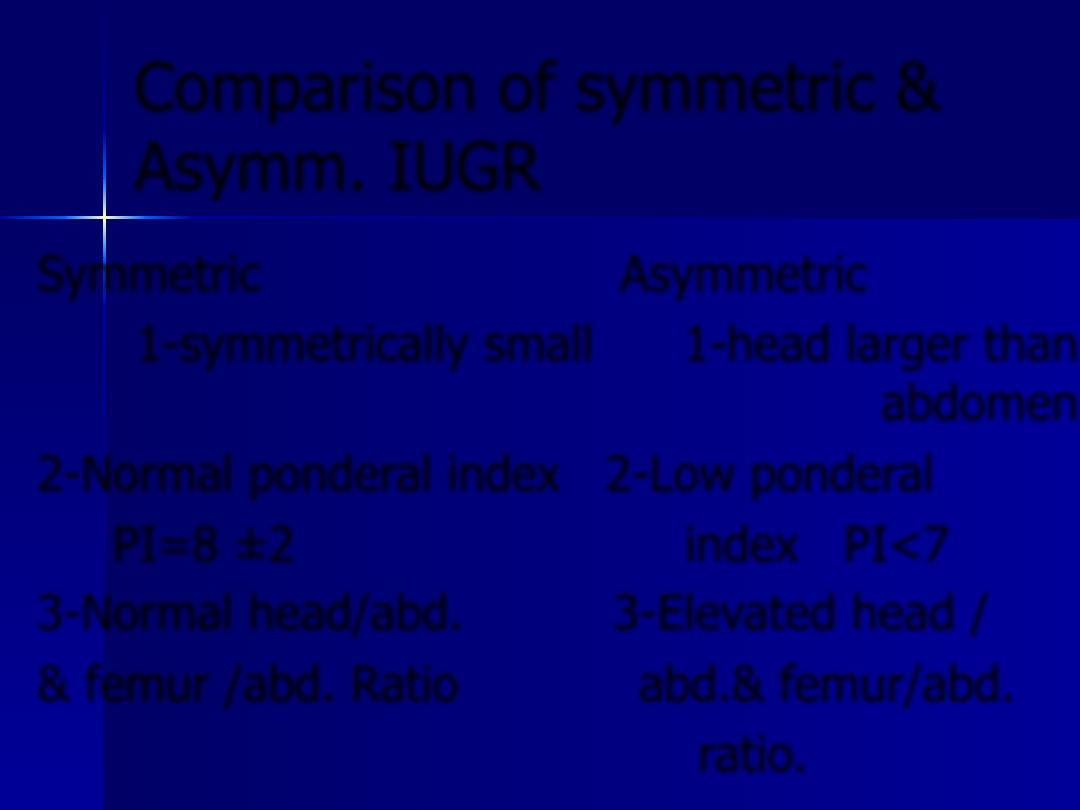
Comparison of symmetric &
Asymm. IUGR
Symmetric
Asymmetric
1-symmetrically small 1-head larger than
abdomen
2-Normal ponderal index 2-Low ponderal
PI=8 ±2 index PI<7
3-Normal head/abd. 3-Elevated head /
& femur /abd. Ratio abd.& femur/abd.
ratio.

4-Genetic disease , infection . 4-placental
vascular
insuffiency
5-complicated neonatal 5-benign
Course neonatal course
Poor prognosis

Diagnosis
1-clinical diagnosis:
A-medical & obs. History
Chronic HT , PET, Ch. Renal disease, twin
pregnancy, advanced DM, prior history of
delivery of IUGR .
B-Decrease maternal weight gain during
pregnancy ( insensitive sign ).
C- Uterine fundal height :is most common
method used .

Symphysis–fundal height
■
symphysis–fundal height (SFH), the distance
■
from the symphysis pubis to the uterine fundus, is
measured
■
at each midwife or antenatal attendance from 24
weeks’ gestation.
■
As a guide, the SFH in centimetres is equal to the
■
number of weeks of gestation plus or minus 2 cm.
■
After 36 weeks, the acceptable difference increases
to 3 cm.

Diagnosis
2- u/s biometry
BPD, head circumference, abd.
Circumference,femur length.
Amount of liquor :oligohydramnios.
Diagnosis
3- Doppler waveform analysis
During pregnancy:umbilical & uterine
artery have low resistance & low S/D
ratio .
In IUGR : decreased or absent diastolic
flow or reversed diastolic blood flow.

■
the concept of ‘brainsparing’
■
involves redistribution of blood by dilatation of the
cerebral vessels, thus increasing substrate and oxygen
supply to the brain, in response to fetal
chemoreceptor or baroreceptor stimulation.
■
results in
■
a reduction in fetal MCA PI.
■
this is associated with increasing impedance in the
■
umbilical artery.

Cerebroplacental ratio
■
By using the ratio of MCA to umbilical
artery Doppler PI –
■
the cerebroplacental ratio.
■
Reduced CPR in IUGR

Diagnosis
4- Amniocentesis
Every week after 36 weeks for fetal lung
maturation.
5- Cordocentesis
Umbilical cord blood sampling (rarely
indicated ).
For rapid determination of fetal karyotype
when chromosomal defect is suspected .
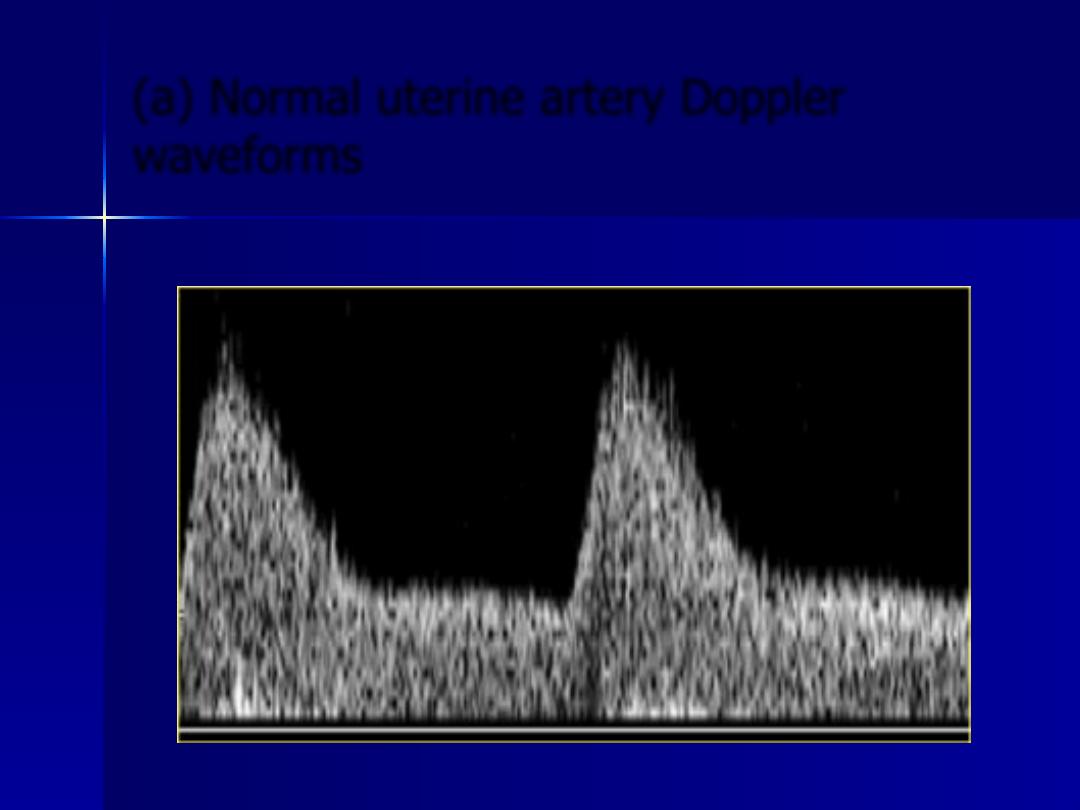
(a) Normal uterine artery Doppler
waveforms
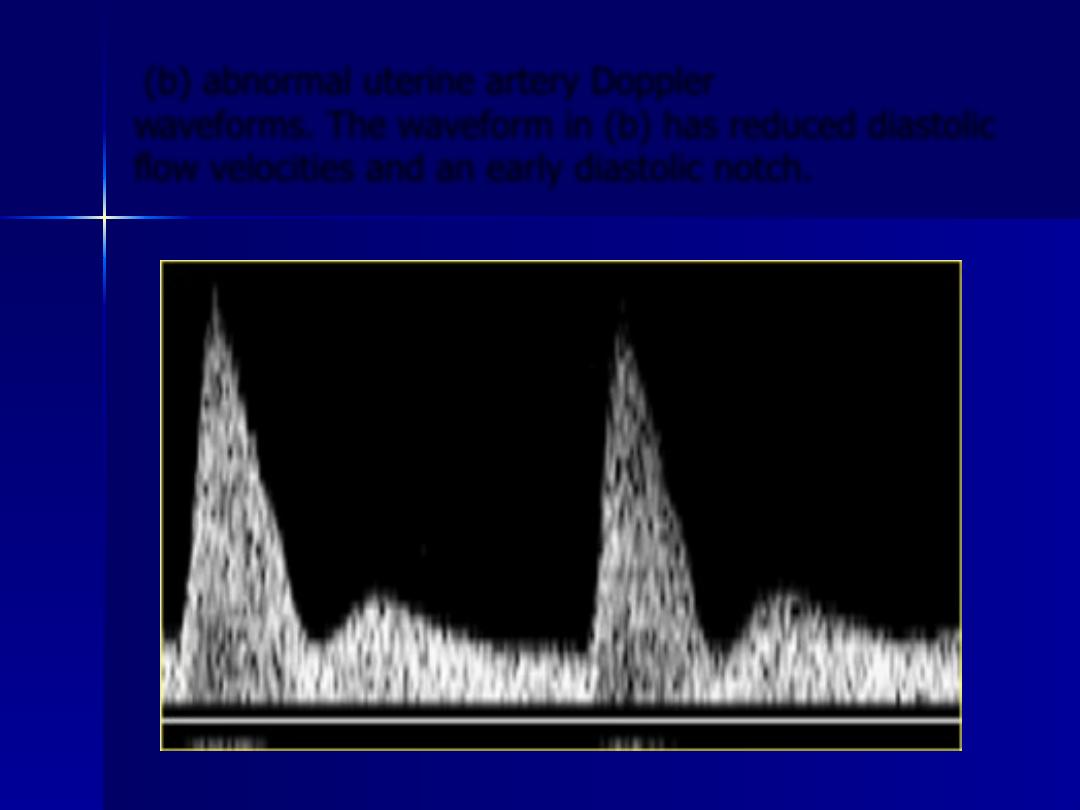
(b) abnormal uterine artery Doppler
waveforms. The waveform in (b) has reduced diastolic
flow velocities and an early diastolic notch.
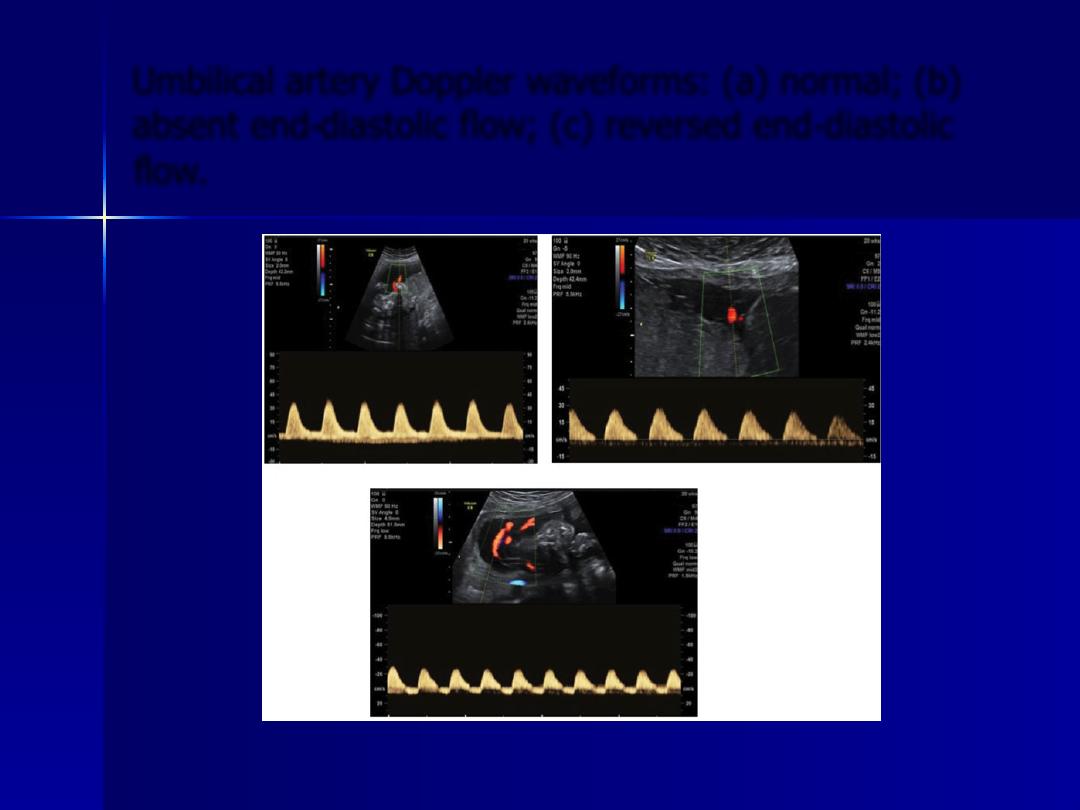
Umbilical artery Doppler waveforms: (a) normal; (b)
absent end‐diastolic flow; (c) reversed end‐diastolic
flow.

Management
1.At present no accepted treatment available
for growth restriction related to placental
dysfunction .
2.Obvious adverse factors :smoking, alcohol
&drug abuse should be stopped.
3.Health of the mother should be maximized
(optimal control of DM, thyroid dysfunction,
HT ).
4.When growth restriction is severe & the
fetus is considered too immature to be
delivered :bed rest in hospital is advised to

to maximize placental blood flow.
5. Antepartum assesment of fetal wellbeing
By fetal biometry every 2 weeks ,
Doppler u/s & fetal cardiotocography (NST).
Absence of blood flow in the umbilical artery
or reversed flow (i.e back towards the heart
requires delivery in the near future or when
NST is non- reactive .

NST daily in severe cases .
Less severe cases : NST weekly or twice
weekly .

No effective drug therapy for IUGR has yet been
found .Small studies suggested aspirin , nitric
oxide donors , or anti- oxidants may be helpful
in some cases .
These drugs may act by reducing platelet
activation in the utero- placental circulation , or
may be acting directly as vasodilators.

Labour
■
Because of the high incidence of hypoxia &
acidosis , labour & delivery should be
aggresively managed .
■
Continuous fetal heart monitoring ( scalp
monitoring electrode & uterine pressure
catheter .
■
Shorten the second stage of labour by
forceps .
■
Epidural anesthesia is the method of choice
for pain relieve .

Labour
■
Pediatrician should be present at delivery .
■
Placenta need careful examination by
pathologist :for cause of IUGR .

Prognosis
1.The length of the insult seems to be more
important than its severity in terms of both
somatic growth & neurologic development .so
the earlier in pregnancy that IUGR is detected
the greater the probability of developmental
problems later in life .
2. The probability of developmental problems is
lower when there is catch – up growth during
the first 6 months of life .

Prognosis
3. The worst prognosis is for babies with
IUGR caused by congenital infections or
chromosomal defects .
4. A link between IUGR & the adult
incidence of both hypertension & DM
has now been established .

■
Thank you
