MALPRESENTATION
Breech Presentation
Prof. D r. Bushra J. AL-Rubayae
University of Babylon
College of Medicine

Objectives:
●
What is breech presentation.
●
It’s importance to diagnose antenatal & intrapartum .
●
Types of breech .
●
Types of breech delivery.
●
Options of management antenatal & intrapartum.
●
Complications .

MALPRESENTATION
●
Malpresentation is the
situation where a fetus
within the uterus is in any
position that is not
cephalic

Etiologic factors in mal-presentation
●
Maternal
Grandmultiparity
Pelvic tumors
Pelvic contracture
Uterine malformation
●
Fetal
Prematurity
Multiple gestation
Hydramnios
Macrosomia
Hydrocephaly
Trisomies
Anencephaly
Placenta previa

Breech Presentation

Breech presentation occurs in 3-4% of all
deliveries.
The occurrence of breech presentation
decreases with advancing gestational age.
- It occurs in 20% of births that occur at 30
weeks’ gestation.
- 1-3% of births that occur at term.
.

●
Perinatal mortality is increased 2- to 4-
fold with breech presentation, regardless
of the mode of delivery.
●
Congenital malformation 6%.
●
Deaths most often are associated with
Malformations.
●
Prematurity.
●
Intrauterine fetal demise.

Predisposing factors
●
prematurity, uterine abnormalities (e.g, malformations,
fibroids),
●
fetal abnormalities (e.g, CNS malformations, neck
masses, aneuploidy), and multiple gestations.
●
AF abnormality. Abnormal placentat ion.
Contracted pelvis .MG . Pelvic tumor
.

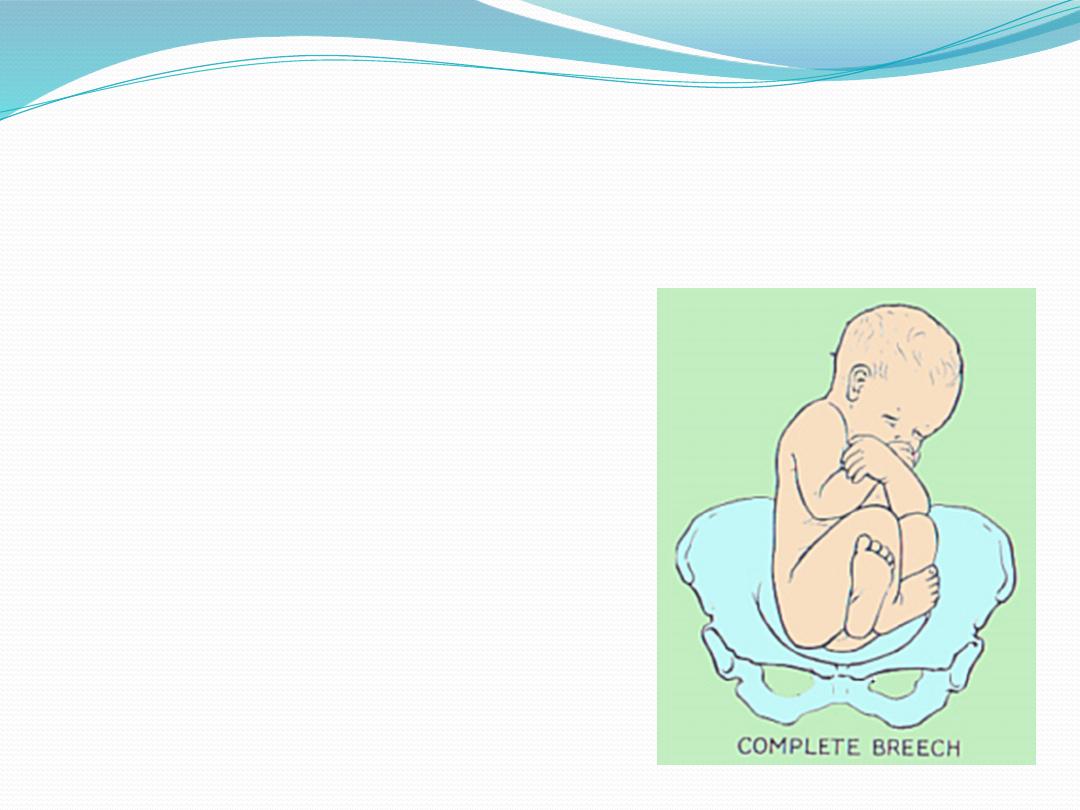
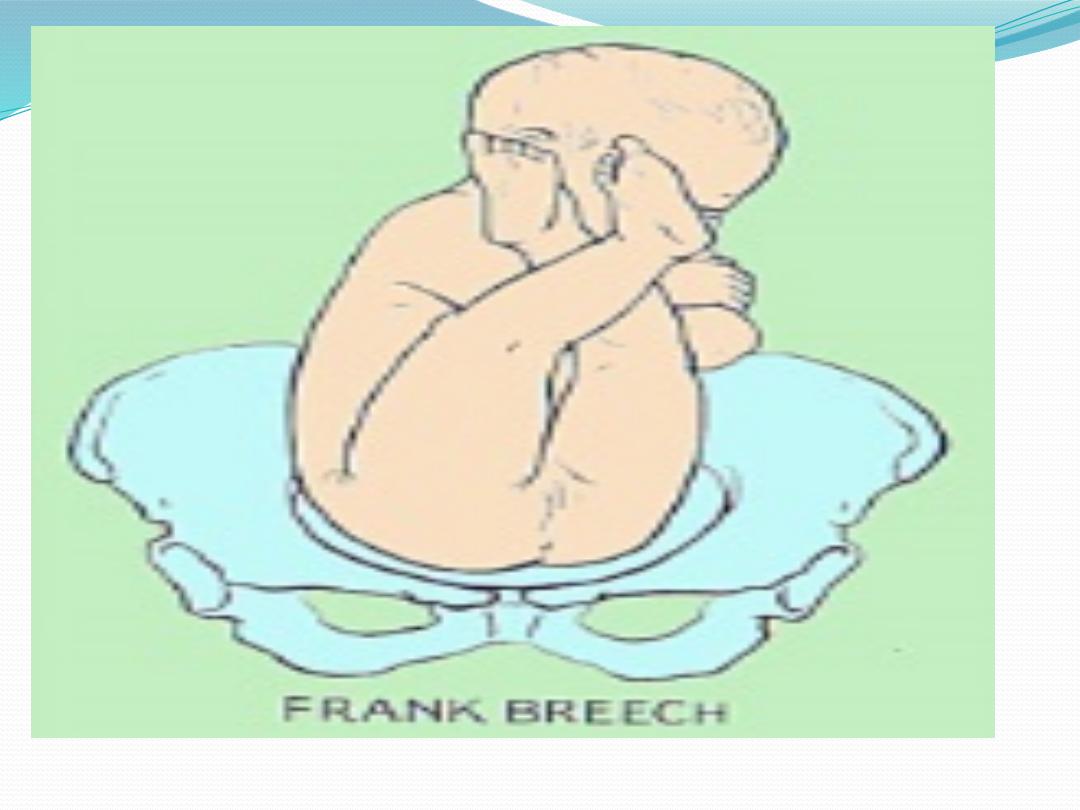
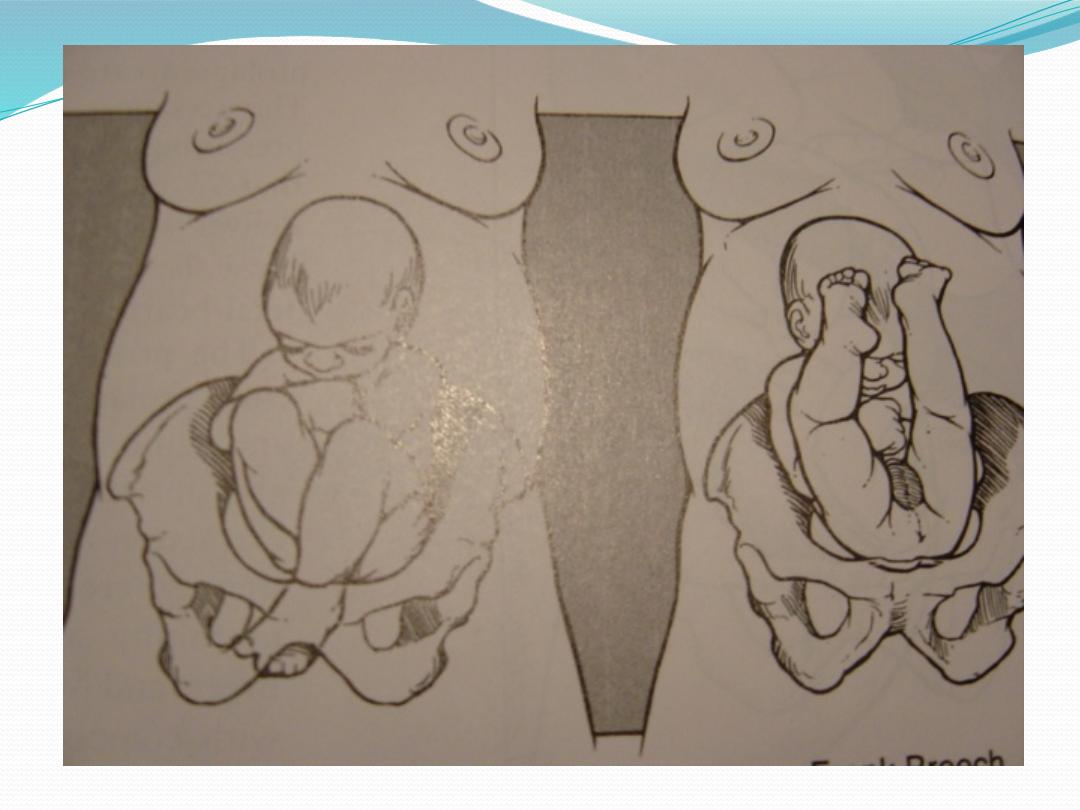
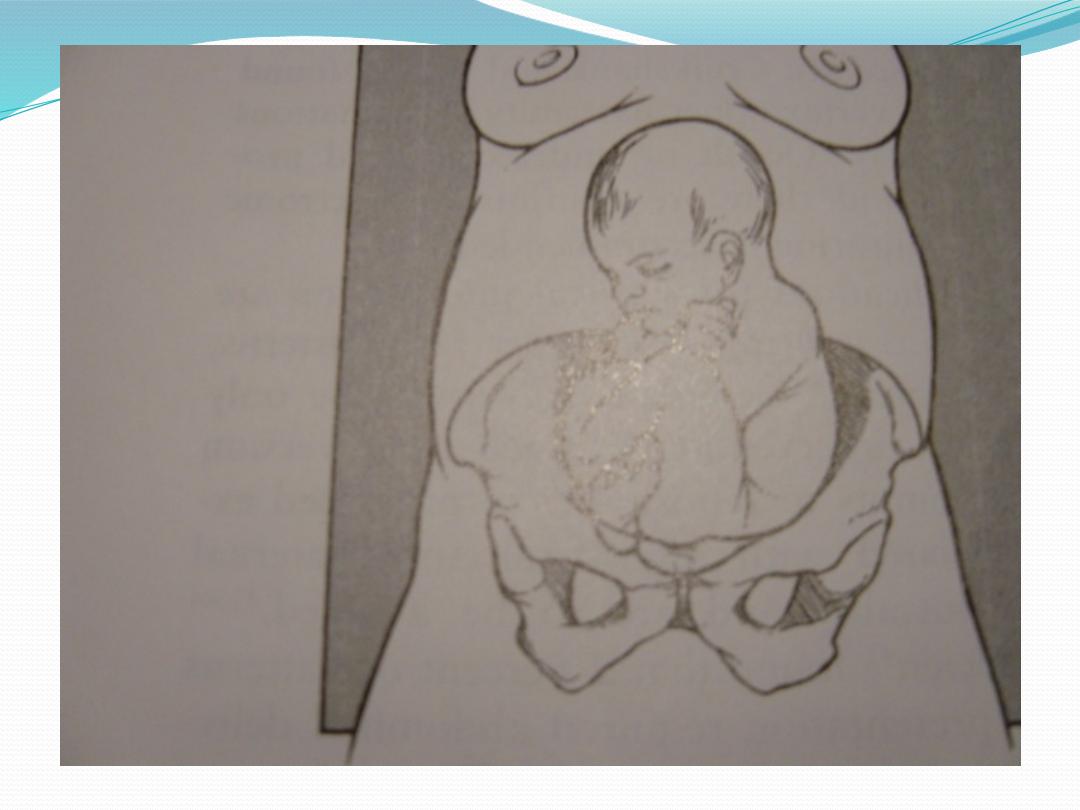
Types of breeches
●
Frank breech (50-70%)
- Hips flexed, knees extended.
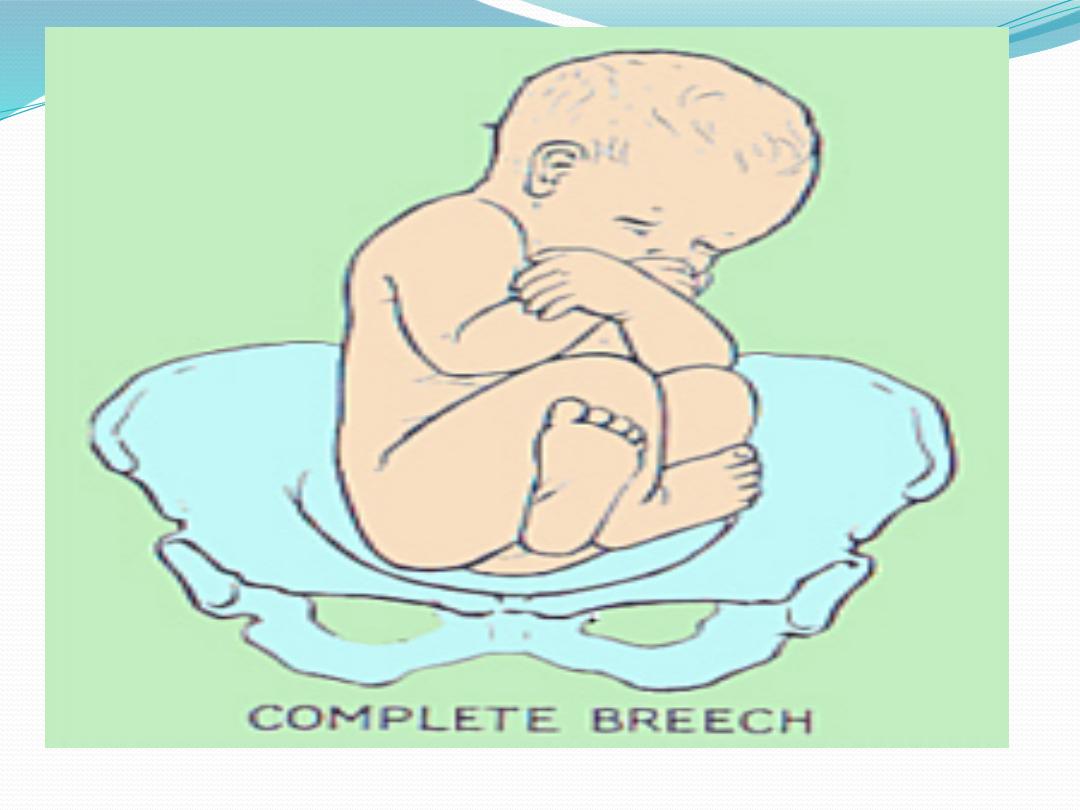
●
Complete breech (5-10%)
- Hips flexed, knees flexed.
●
Footling or incomplete (10-30%)
- One or both hips extended, foot
presenting
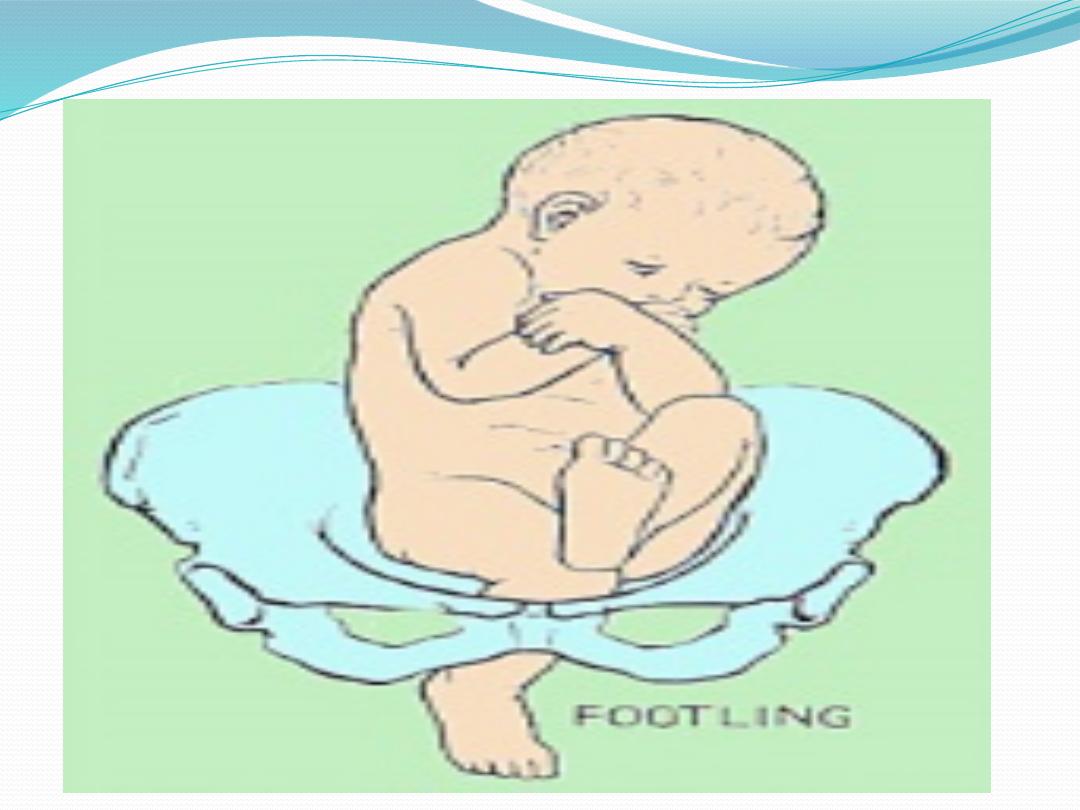


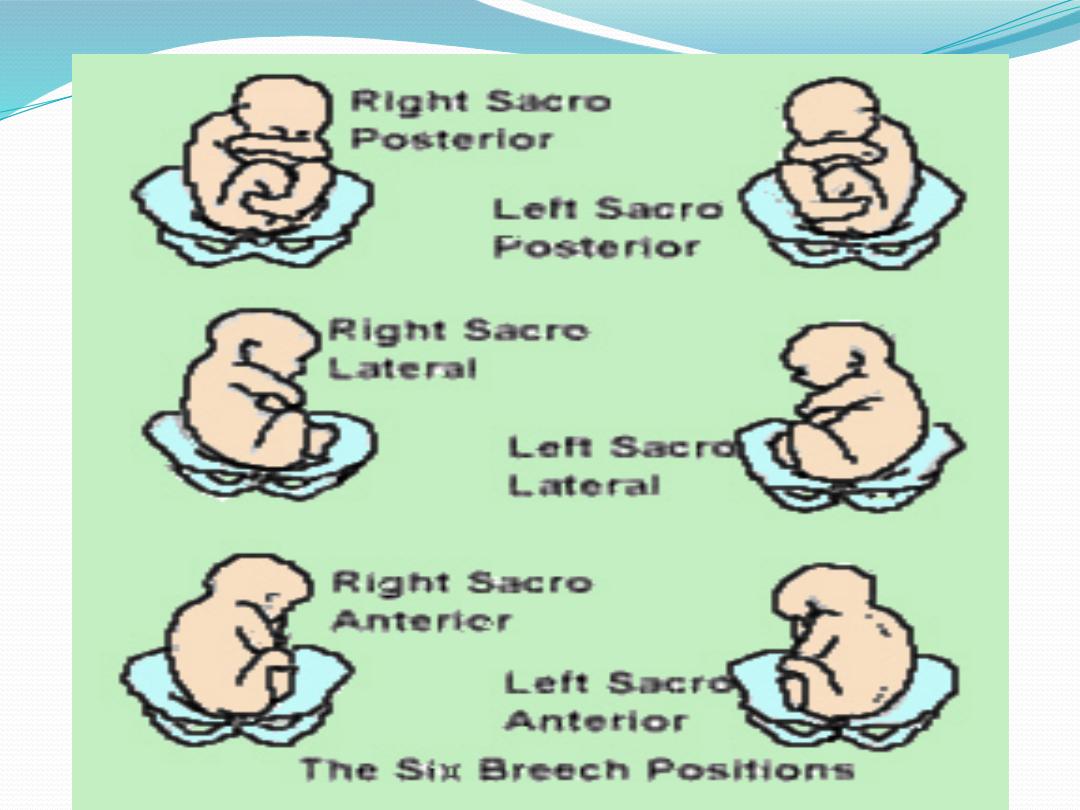
position
SA,SP,LST,RST
LSP,RSP.LSA,RSA

DIAGNOSIS
●
History.
●
Physical exam.
●
Palpations and ballottement
●
Pelvic exam
●
X-ray studies
●
Ultrasound

MANAGEMENT
●
Antenatal
●
Ante-partum
●
During labor
●
Delivery

Antenatal Management:
●
If found during obstetric exam in the third
trimester we re-assure her and explain that
spontaneous version could occur at any time.
●
We wait until 36 weeks of gestation .
●
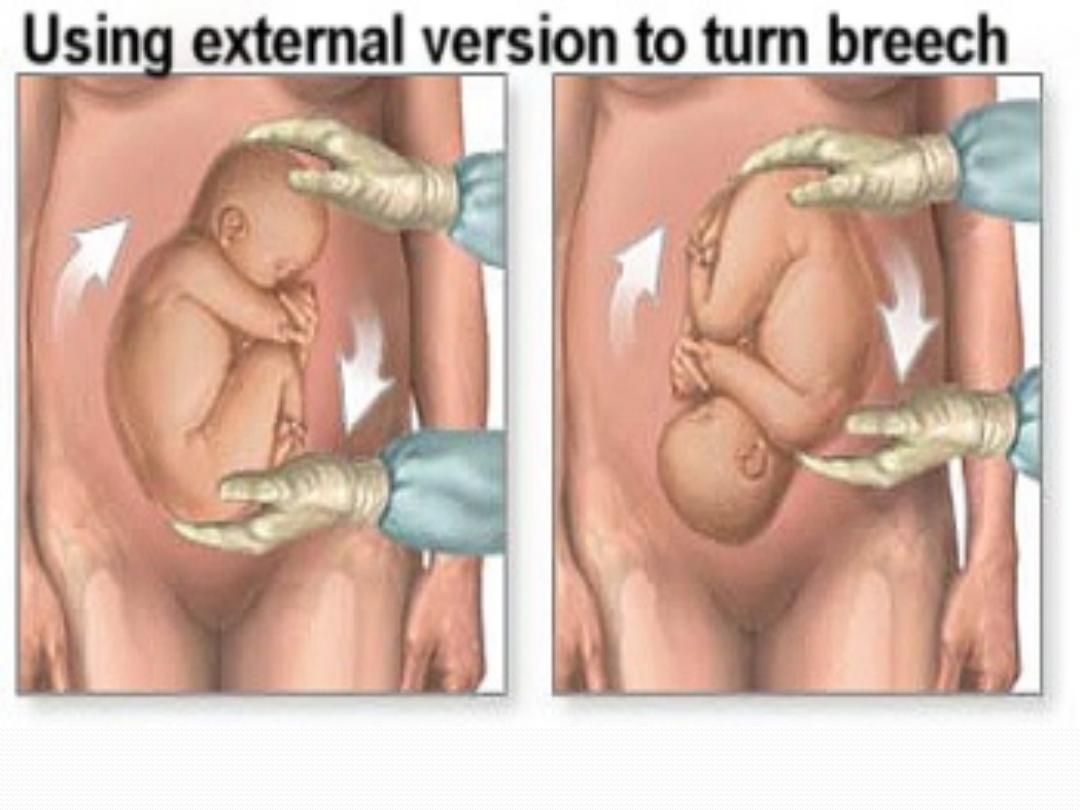
Then decision been one of three options:
1-to perform external cephalic version or,
2-operative delivery or,
3-trial of assisted vaginal delivery.

VERSION
●
External
●
Internal

external cephalic version
●
It has important personal benefits by helping avoid
major abdominal surgery, and lowering the overall
Cesarean rate.
●
If everyone with a breech at term attempted a version
then 50% been successful, Of them75% give birth
vaginally .
●
So more than a third with term breech pregnancies
could avoid a Cesarean if everyone attempted a
version.

complication
The rate of serious complications (placenta abruption
or stillbirth) was 0.24%.
●
stillbirths to the external version or unexplained.
The unexplained stillbirths within 10 to 31 days
after the version.
●
Placenta abruption abruptions resulted in an
emergency Cesarean.
●
Other complications included cord prolapse,
temporary abnormal fetal heart rate patterns, vaginal
bleeding , and PROM.

Contraindications:
●
Should NOT have a version
●
If they have a history of placenta abruption or if
placenta abruption is suspected,
●
If complicated pregnancy as severe pre-eclampsia,
DM.
●
If there are signs of fetal distress.
If vaginal birth is contraindicated then a version also
be contraindicated.
If multiple pregnancy.

Internal podalic version
●
It’s only indicated for delivery of second
twin if external cephalic version failed,
during second stage of labour.
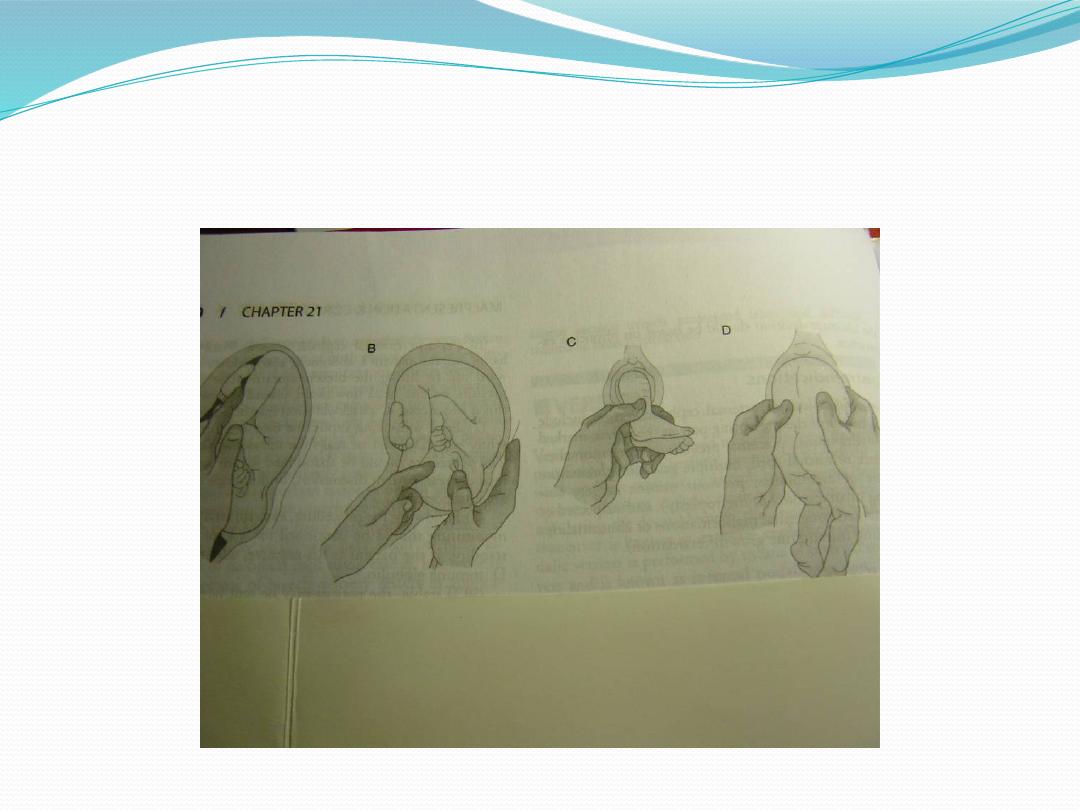
Internal podalic version

Criteria for VD orCS
●
VD
Frank
GA>34w
FW=2000-3500gr
Adequate pelvis
Flexed head
Nonviable fetus
No indication
Good progress labor
●
CS
FW<1500or> 3500gr
Footling
Small pelvis
Deflexed head
Arrest of labor
GA24-34w
Elderly PG
Inf or poor history
Fetal distress

VAGINAL BREECH DELIVERY
●
Three types of vaginal breech
deliveries:
1.
Spontaneous breech delivery
2.
Assisted breech delivery
3.
Total breech extraction
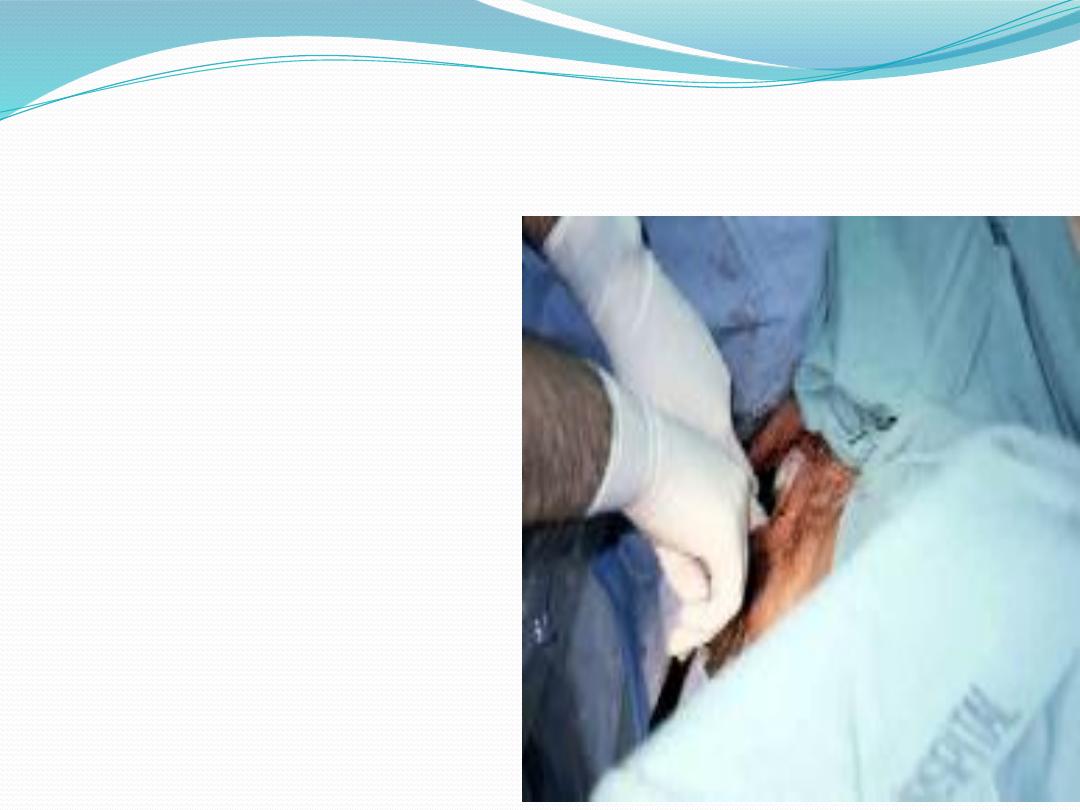
Assisted vaginal breech delivery
●
Thick meconium passage
is common as the breech is
squeezed through the birth
canal. This is not
associated with meconium
aspiration because the
meconium passes out of
the vagina and does not
mix with the amniotic
fluid.
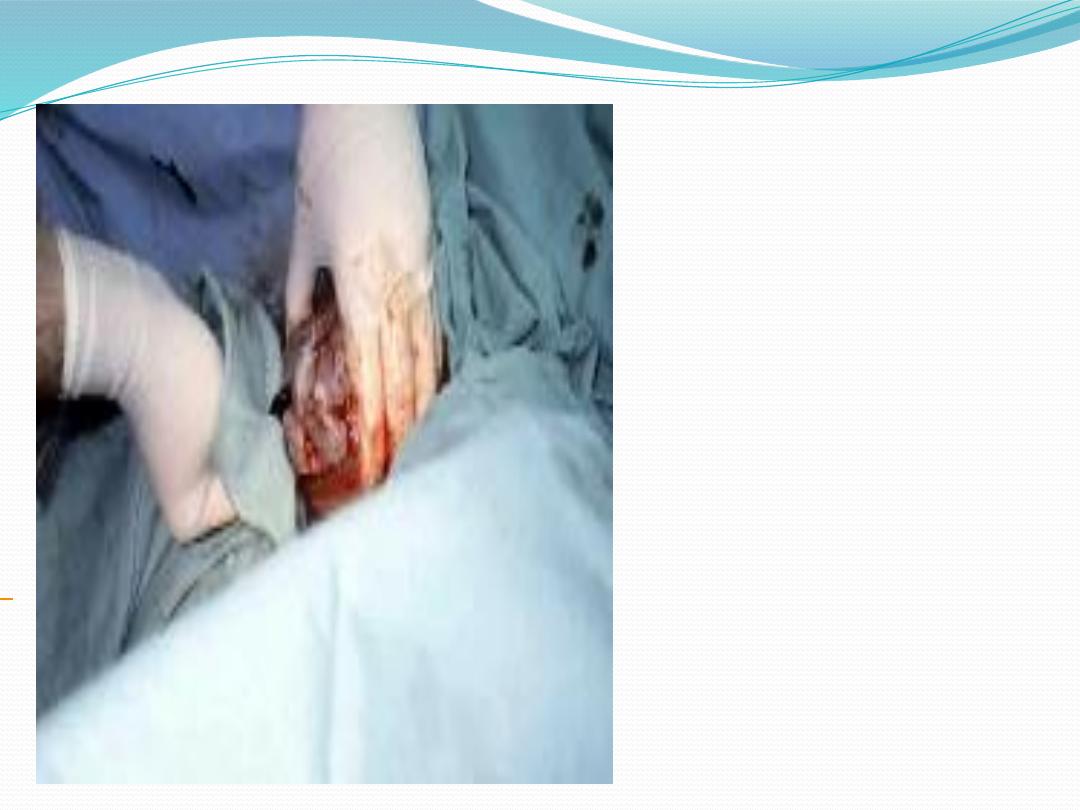
The Ritgen maneuver is
applied to take pressure off
the perineum during
vaginal delivery.
Episiotomies often are cut
for assisted vaginal breech
deliveries, even in
multiparous women, to
prevent soft-tissue dystocia.
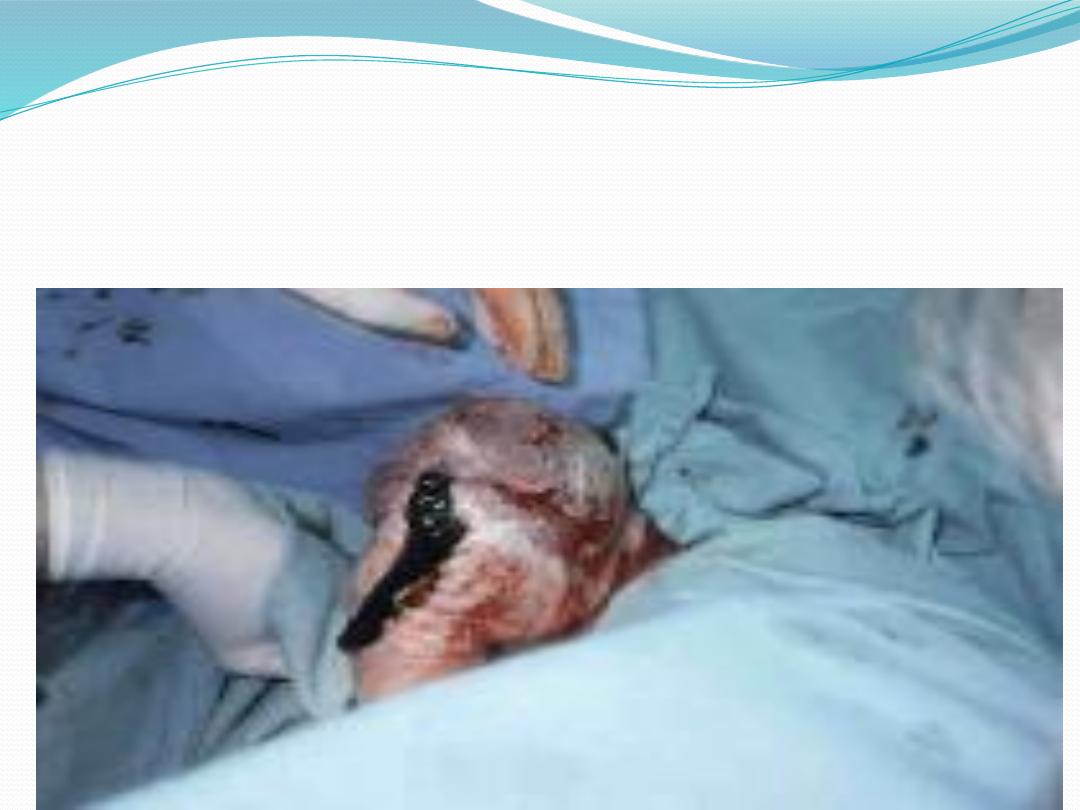
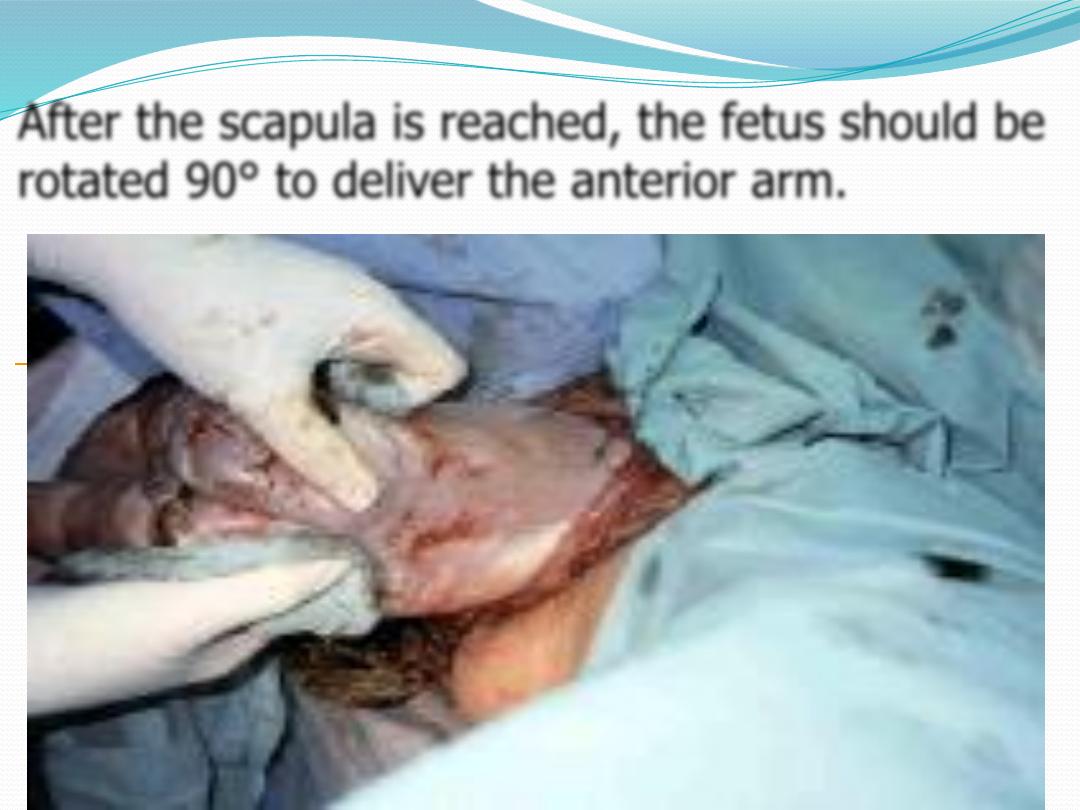
●
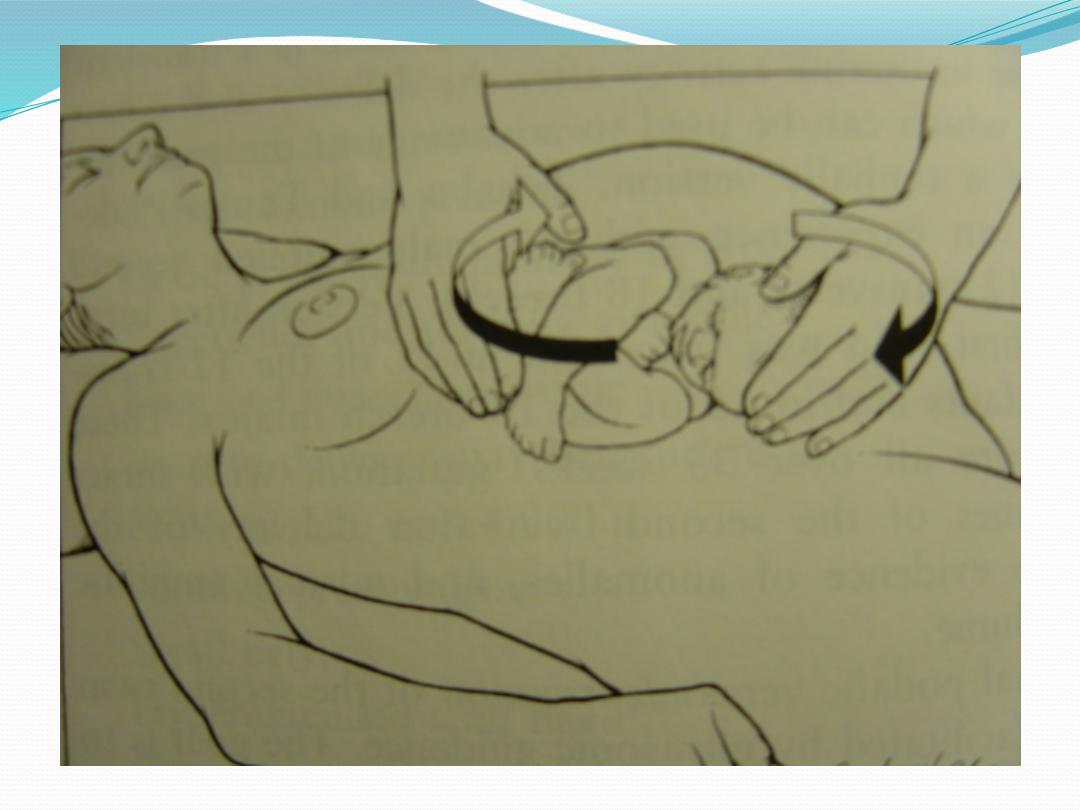
No downward or outward traction is applied to the
fetus until the umbilicus has been reached.
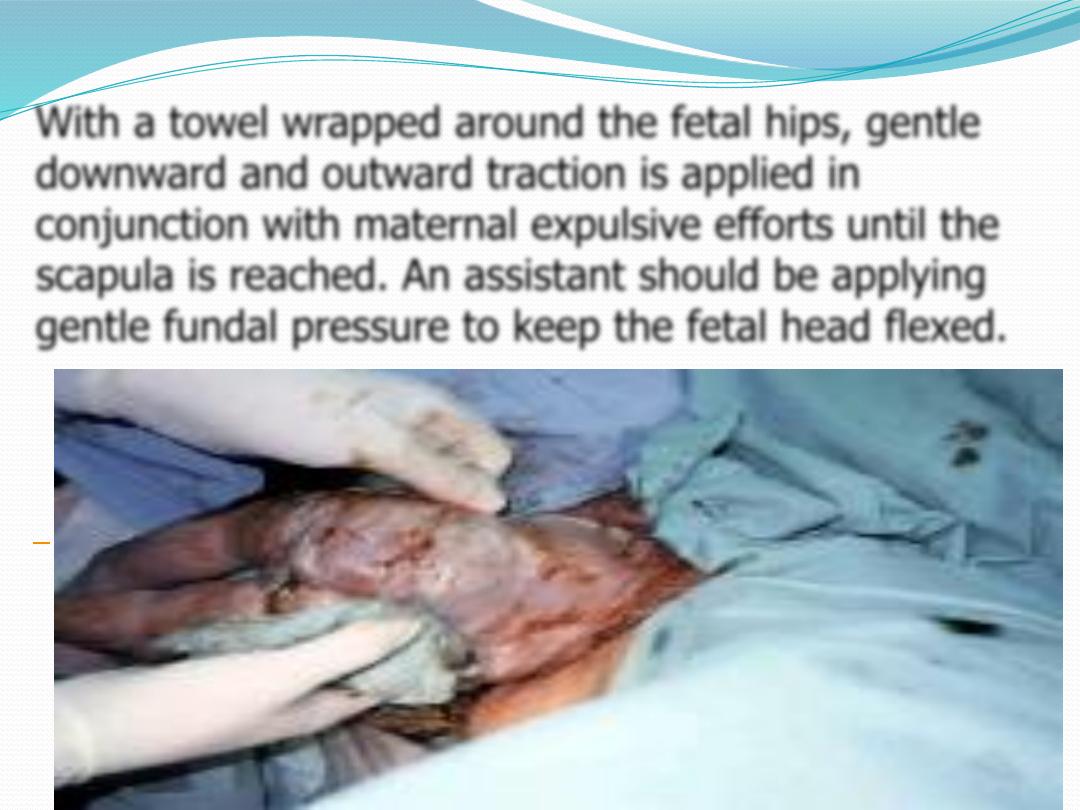
With a towel wrapped around the fetal hips, gentle
downward and outward traction is applied in
conjunction with maternal expulsive efforts until the
scapula is reached. An assistant should be applying
gentle fundal pressure to keep the fetal head flexed.
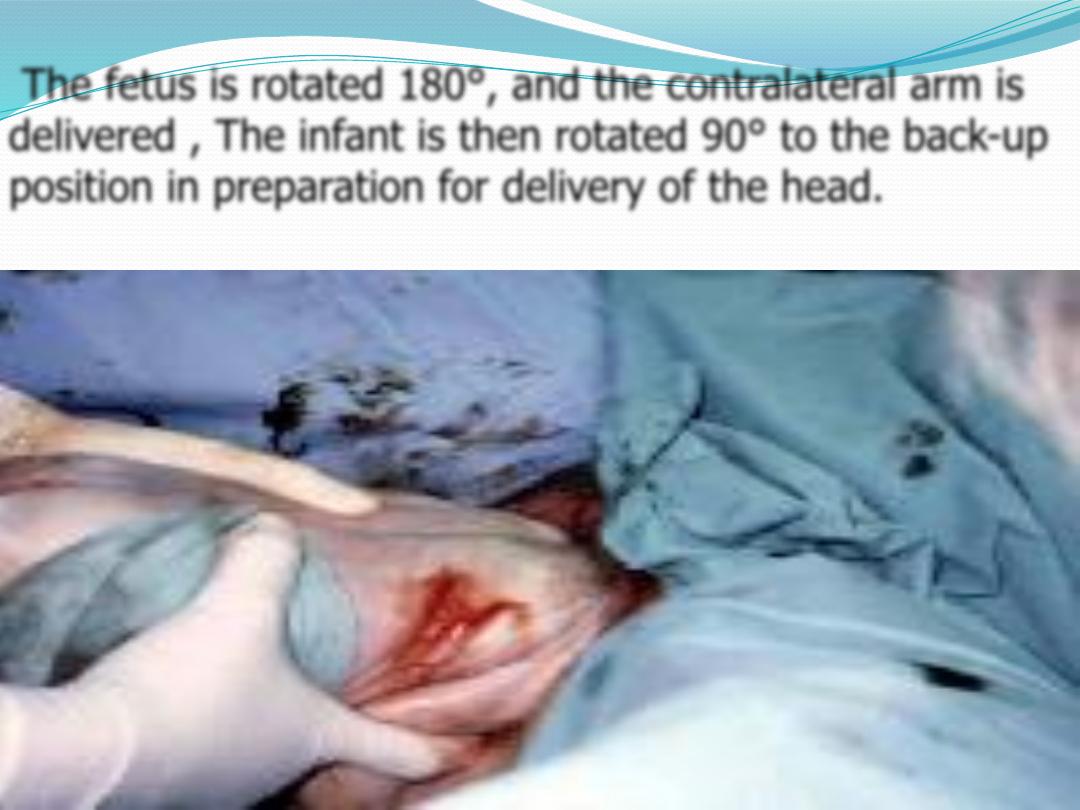
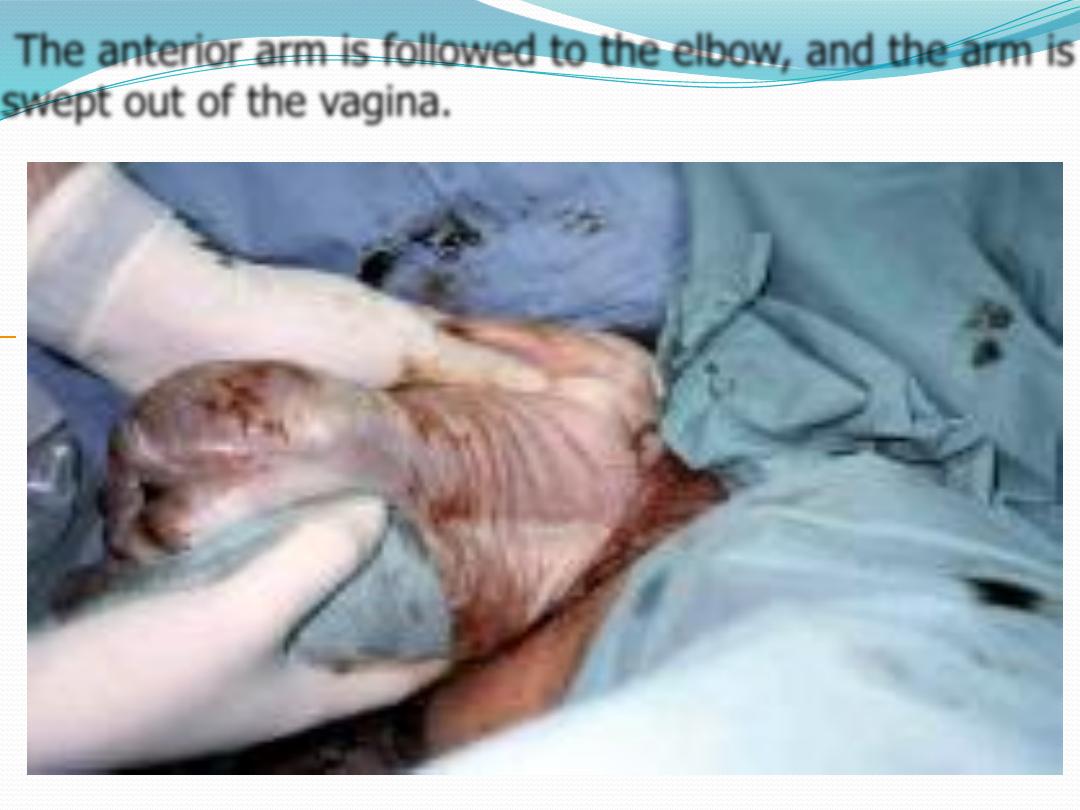
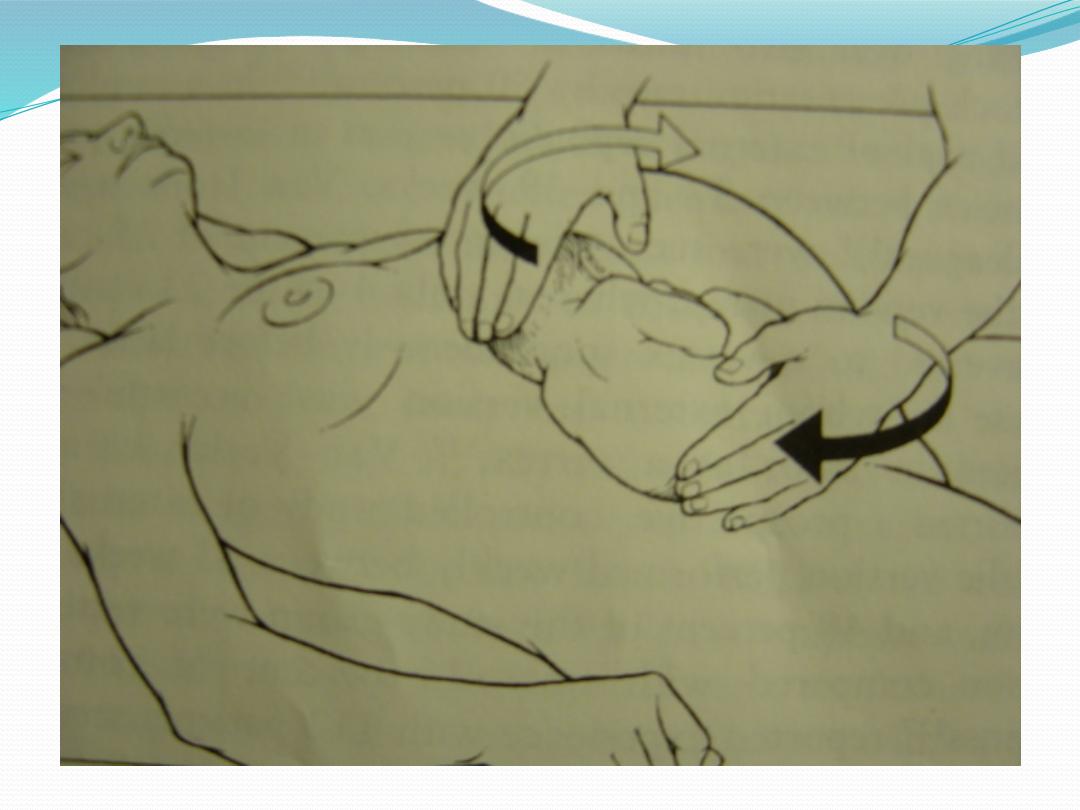
The fetus is rotated 180°, and the contralateral arm is
delivered , The infant is then rotated 90° to the back-up
position in preparation for delivery of the head.
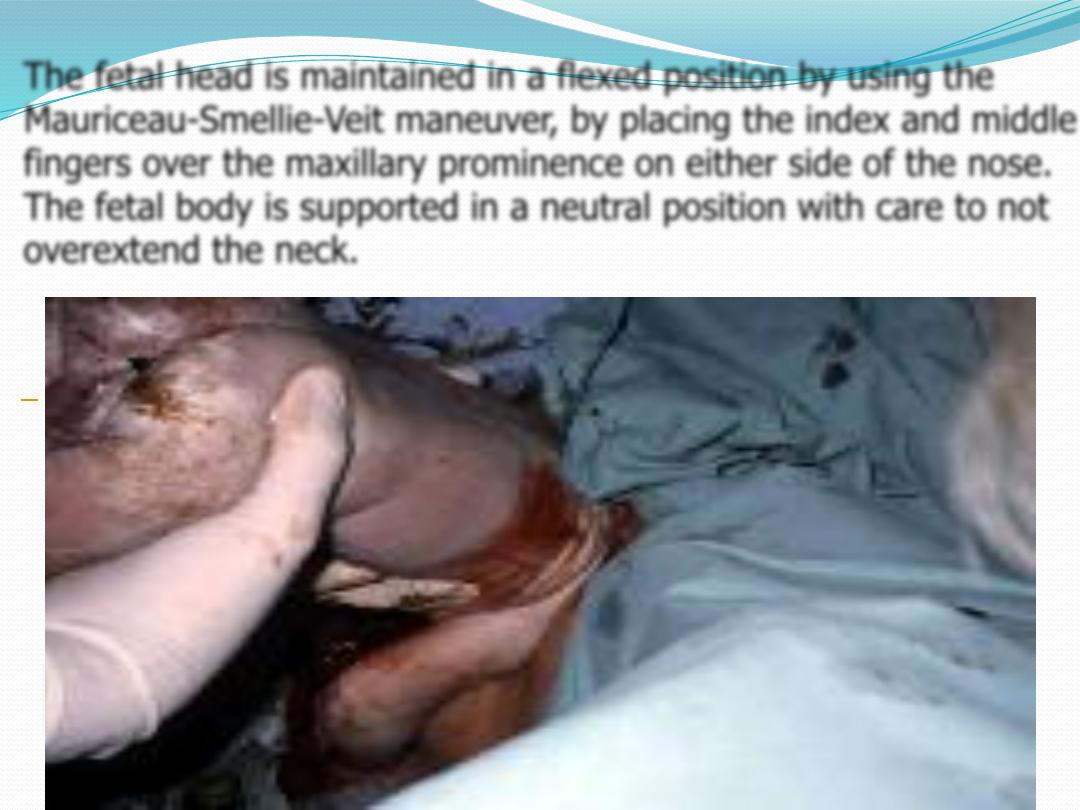
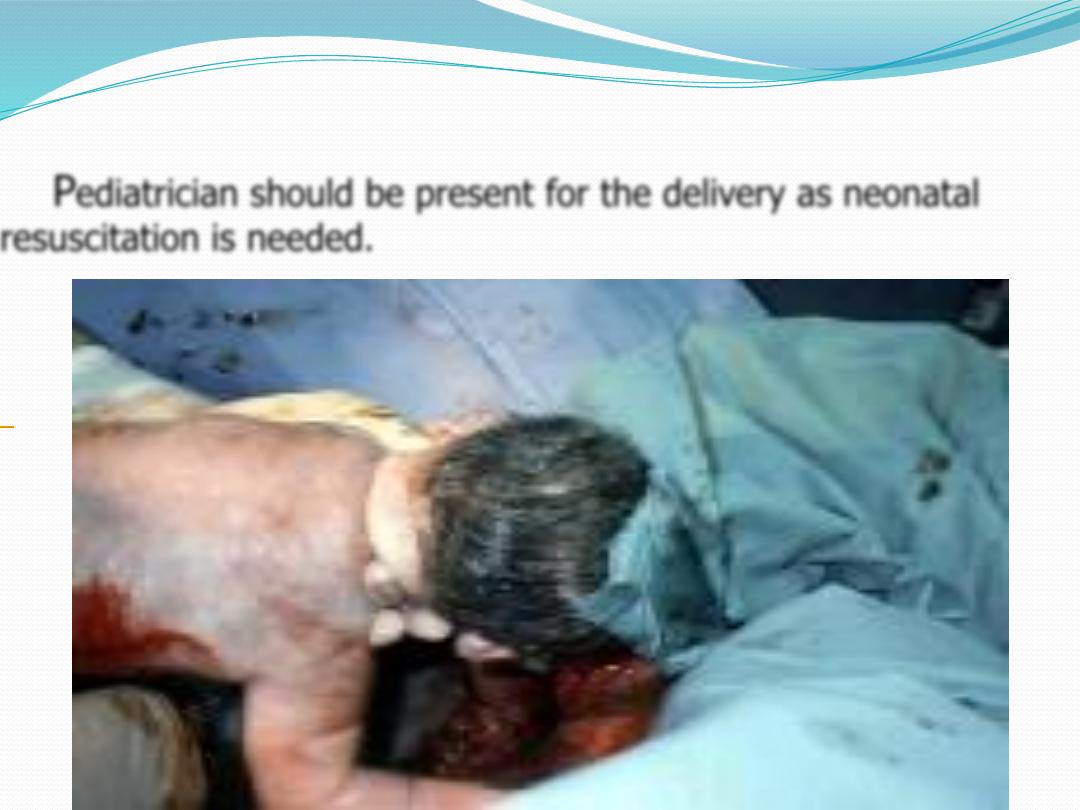
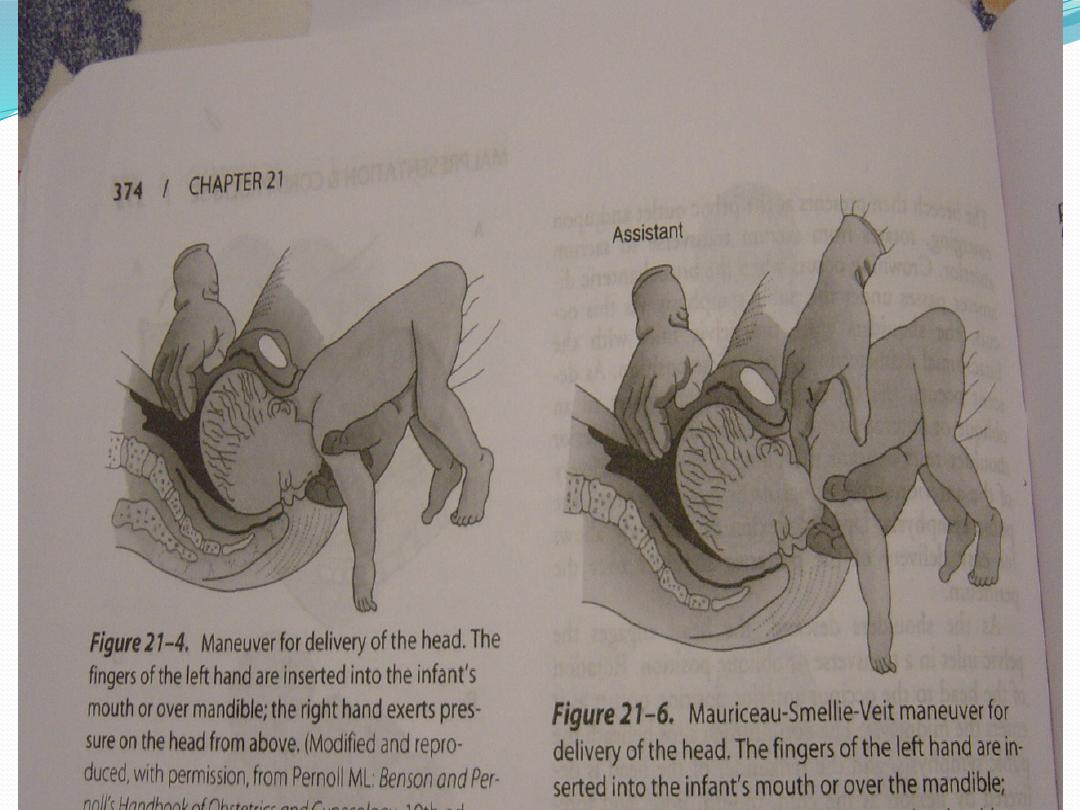
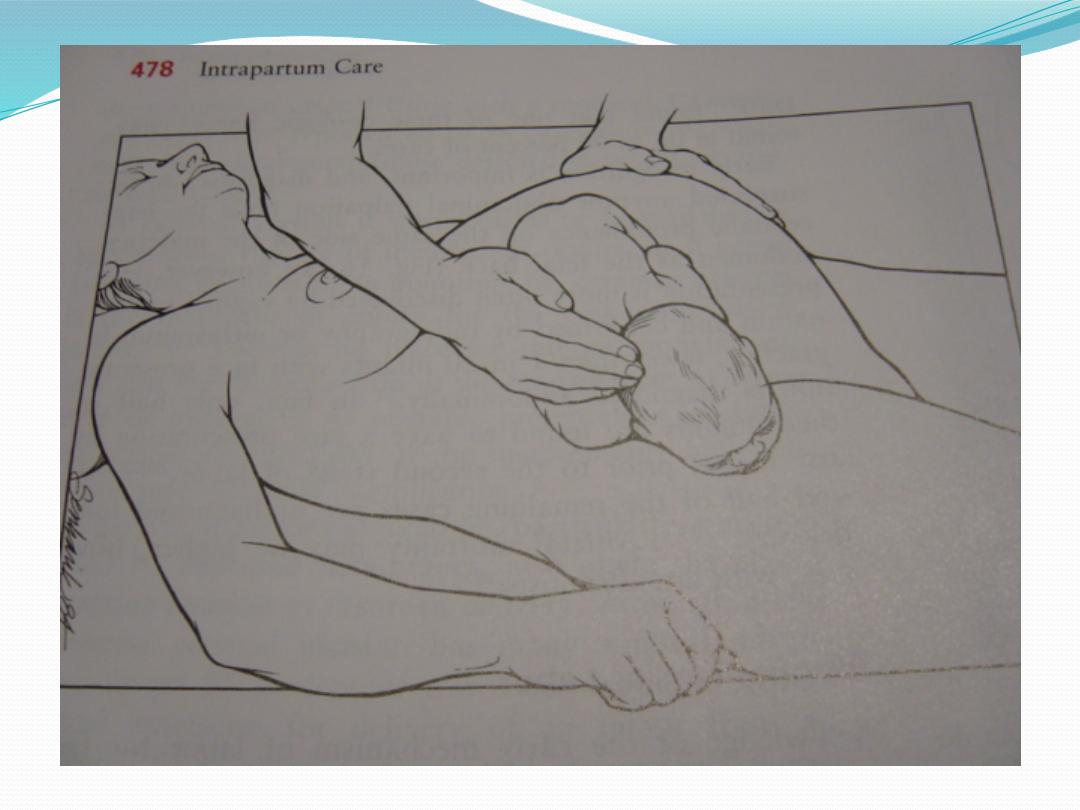
The fetal head is maintained in a flexed position by using the
Mauriceau-Smellie-Veit maneuver, by placing the index and middle
fingers over the maxillary prominence on either side of the nose.
The fetal body is supported in a neutral position with care to not
overextend the neck.
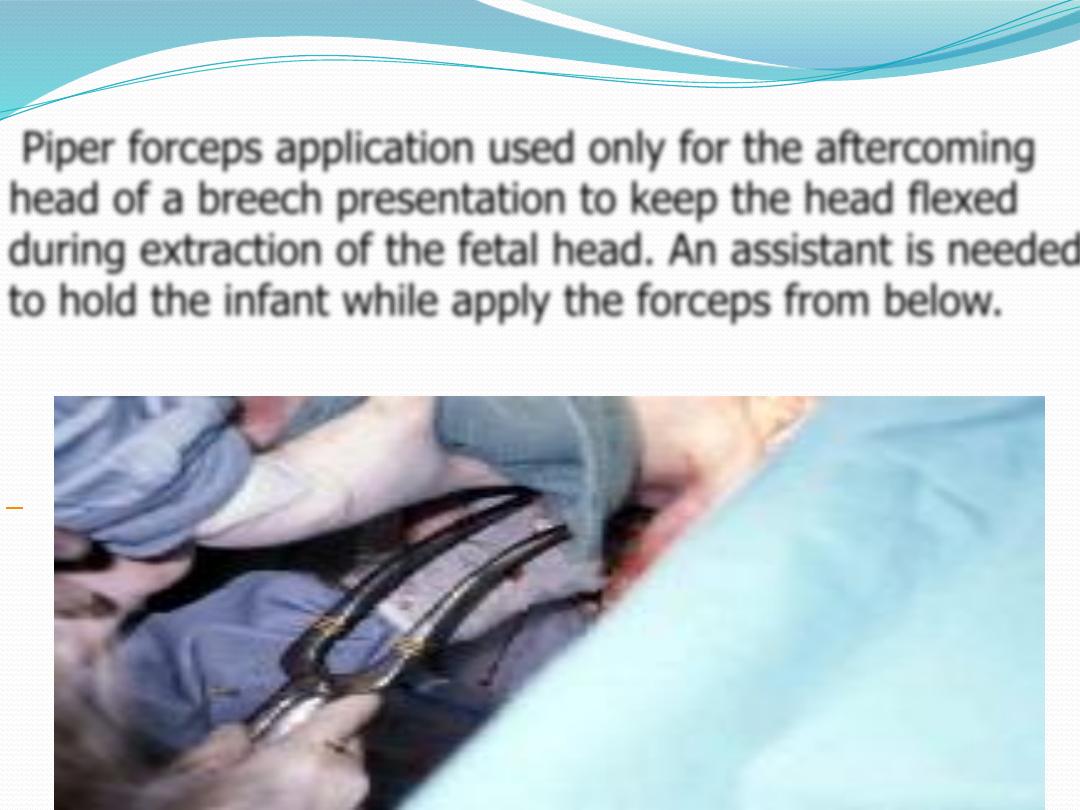
Piper forceps application used only for the aftercoming
head of a breech presentation to keep the head flexed
during extraction of the fetal head. An assistant is needed
to hold the infant while apply the forceps from below.

Risks:
●
Lower Apgar scors
●
An entrapped head
●
Nuchal arms
●
Cervical spine injury
●
Cord prolapse
,