
Labour, physiology of
onset, and stages
By reference textbook
Suhaila Al-Shaikh Obstetrics by ten teachers
20
th
ed(2017): ch 12; p 381-87

Learning objectives
Understand the physiology of labour
Understand factors that influencing uterine
activity
Physiological changes preparing to parturition
Define stages of labour and be able to
differentiate normal from abnormal labour
(prolonged or precipitous).
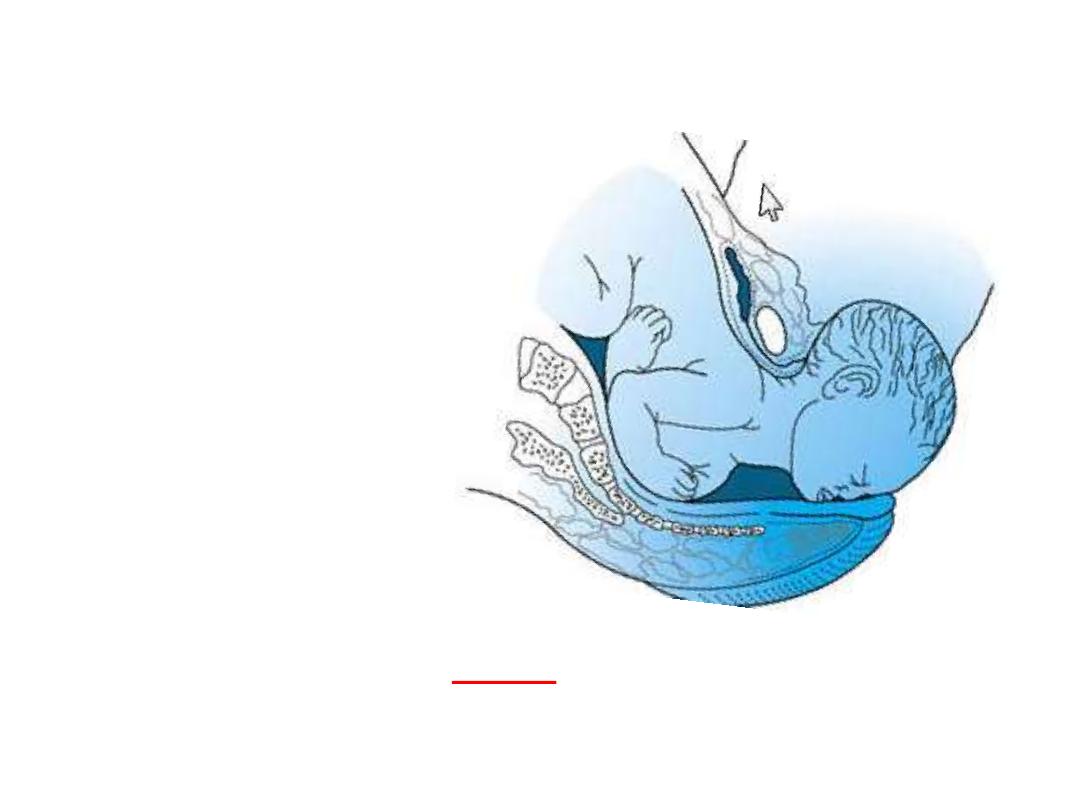
Definition of labour
Labor is defined as the
onset of a sequence of
painful regular uterine
contractions that
results in progressive
effacement and
dilatation of the cervix
with descent of the
presenting part and
voluntary maternal
bearing-down efforts
leading to the
expulsion of the
products of
conception through
the vagina.
Average duration of labour:
• 8 hours in primi
• 5 hours in multiparous

Onset of labour
The reason or the mechanism behind the
onset of labour is poorly understood
How the following events happen??
The cervix firm and closed soft and
stretchable, open and dilated?
The cervix long & thick short and thin
(effaced)?
The uterus quiescent & relaxed regularly,
strongly and frequently contracting?

Why labour starts at the end of gestation
why not before or after?
The mother and her baby play a role in this process.
the uterus:
Myometrial cells (myocytes) are interlacing,
synchronized in action
PG
Gap junctions
Myocytes contract and retract progressively shorten
Upper
(active and dominant) and
lower
(passive)
segments
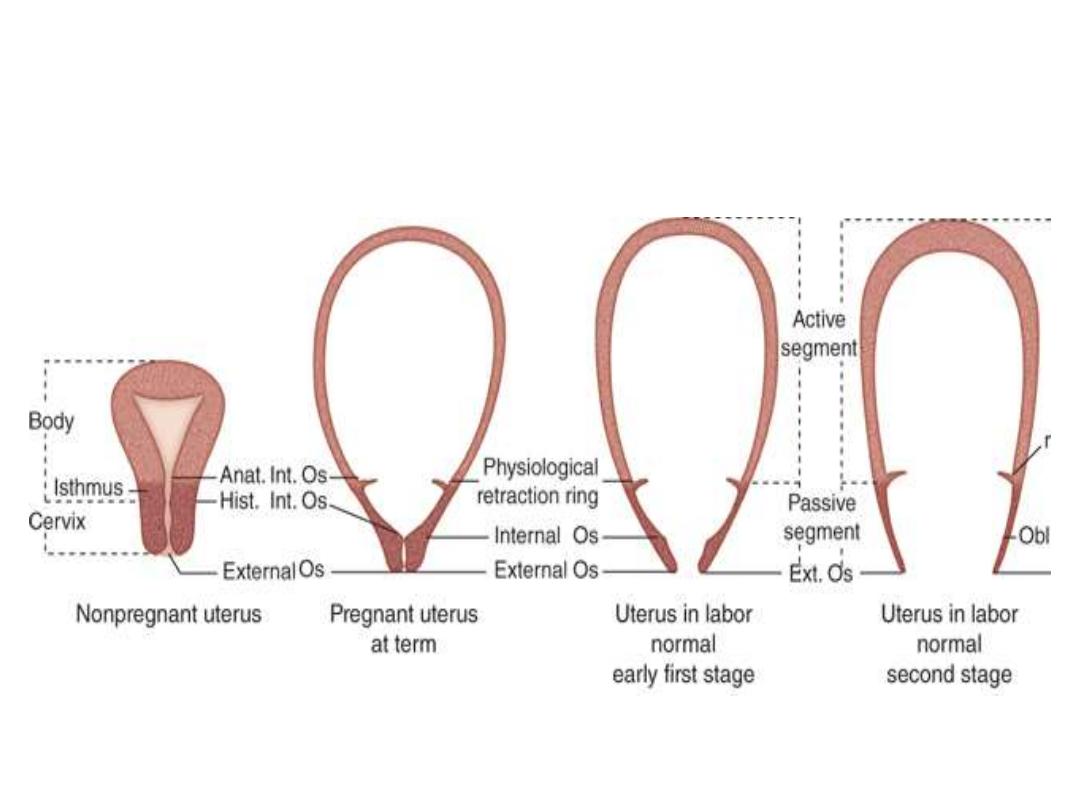
Upper (active) & lower (passive)
segments of the uterus

Uterine contractions of labour
are characterized:
Involuntary
Irregular in the beginning then become
regular
Frequency 2 /10 minutes in early labour
Frequency 4-5 /10 minutes in advanced
labour
Duration 30
– 60 seconds

Cervix: contains myocytes and
fibroblast.
Collagen
Fibronectin
dermatan sulphate (a proteoglycan)
Early in pregnancy: remain closed, firm and
not dilate in response to contractions.
Later (toward term):
Proteolytic activity soften and ripen and
easily dilate in response to uterine contractions.
(increased water content)
By effect of PG and
other humoral factors
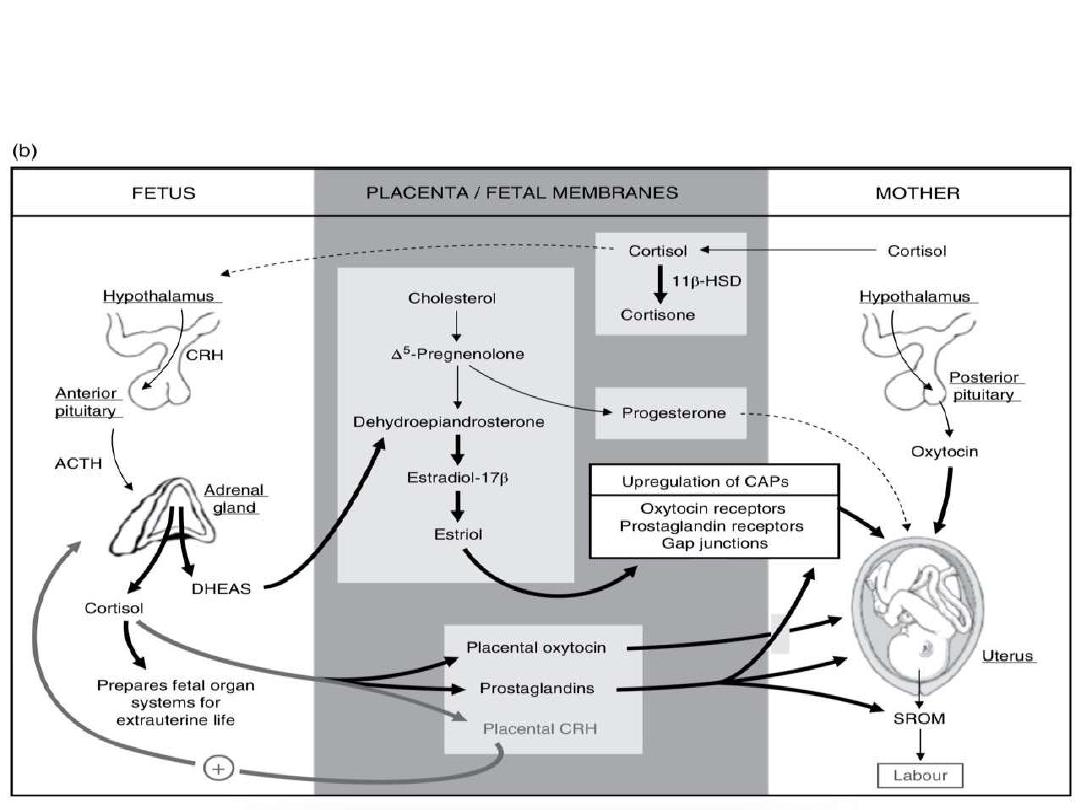
Factors initiating labour
Hormonal factors:
Progesterone and its receptor
Estrogen and its receptor
Progesterone/ Estrogen ratio
Cortisol (fetal adrenal)
CRH (placental)
Oxytocin (maternal and fetal)
Fergusson reflex

Mechanical factors:
Uterine stretching at full term
Over stretch in multiple pregnancy
and polyhydramniose premature
labour

physiologic Preparation for Labor
Lightening
: settling of the fetal head into the
brim of the pelvis.
Braxton Hicks contractions
: increase in
frequency.
Cervical ripening
: the cervix begins to
soften and become stretchable.

Lightening
: occurs 2 or more weeks before labor in first
pregnancies.
it does not occur until early labor in multiparous women.
Clinically, the mother may notice a flattening of the upper
abdomen and increased pressure in the pelvis.
Braxton Hicks contractions
: may occur more
frequently, sometimes every 10
–20 minutes, and with
greater intensity during the last weeks of pregnancy.
When these contractions occur early in the third
trimester, they must be distinguished from true preterm
labor.
These are a common cause of false labour.

DIAGNOSIS OF LABOUR

symptoms & signs of labour:
1- abdominal and back pain
2- increased vaginal discharge which may be bloody
stained discharge or watery (show).
(the
Show
: it means the passage of a small amount of
blood-tinged mucus from the vagina).
3- there may be nausea and vomiting due to pain
4- in advanced stage of labour (late 1
st
and 2
nd
stage) there
is increased pain and urge to (push) bearing down
5- increased frequency of micturition, and urge for bowel
evacuation when the baby’s head press on the bladder
and rectum
6- uterine tightening (contractions) by abdominal palpation
on regular intervals 2-4/10 minutes
7- cervical dilatation and effacement by serial vaginal exam

Duration of labour
There is no ideal length for normal labour
In nulliparous if > than 12 hrs prolonged
In multiparous if > than 8 hrs prolonged
Precipitous labour
: expulsion of the fetus
within < than 3 hours of the onset of regular
contractions.

STAGES OF LABOUR

Stages of labour:
First stage: from the time of the
beginning of labour until 10 cm cervical
dilatation.
Second stage: the period between full
cervical dilatation to delivery of the
baby.
third stage: the period from the
delivery of the baby to the complete
delivery of the placenta and
membranes.

1
st
stage
subdivided into two phases, the
latent
phase
and the
active
phase.
Latent
: from onset of labour 3-4 cm
duration 3-8 hours but shorter in
multiparous
Active
: from 3-4 cm up to 10 cm
duration 2-6 hours being shorter in
multiparous
Rate of cervical dilatation is
1 cm/hour
is
normal
Being faster in multiparous
If
< 1cm / 2hours
is considered
abnormal
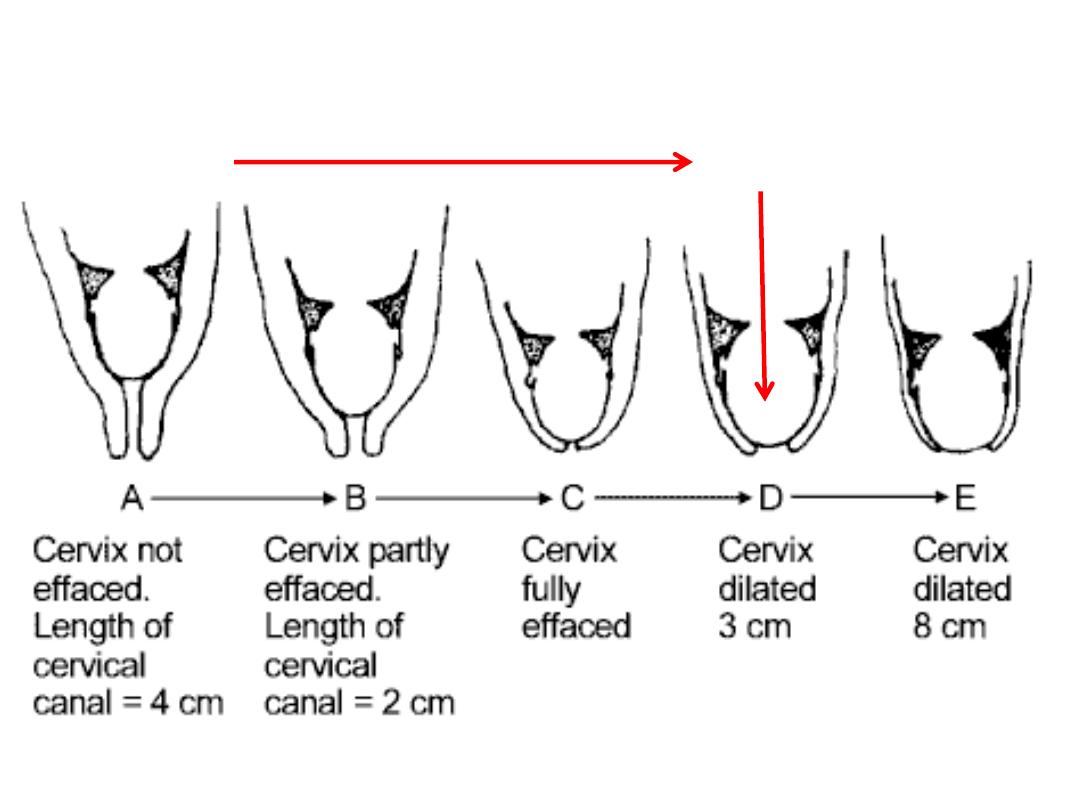
Effacement & dilatation in latent phase
Onset of
Labour(latent phase)
Beginning
of active phase

2
nd
stage
2
nd
stage is further subdivided into 2phases:
passive
and
active
2
nd
stage
Passive
: the time between full dilatation and
the onset of involuntary expulsive
contractions
duration 1-2 hrs (for desc. and rotation)
Active 2
nd
stage
: there is maternal urge to
push and the fetal head is visible at
the perineum
duration 2 hr in primi, 1 hr in multi
Epidural
usually cause prolongation of duration

3
rd
stage:
duration of the third stage is 0
–30
minutes for all pregnancies.
Separation of the placenta generally
occurs within 2
–10 minutes of the end
of the second stage
If 3
rd
stage managed physiologically
without oxytocic interference the
duration is up to 60 minutes

features of normal labour?
1. Spontaneous onset at 37
–42 weeks’ gestation.
2. Singleton pregnancy.
3. Cephalic vertex presentation.
4. No artificial interventions.
5. Cervical dilatation of at least 1 cm/ 2 hours in the
active phase of first stage.
6. Active second stage no more than 2 hours in
primiparous and 60 minutes in multiparous
woman.
7. Spontaneous vaginal delivery.
8. Third stage lasting no more than 30 minutes with
active management.
9. Healthy mother and baby
