
Management of labour (stage 2 and 3)
and
Fetal wellbeing assessment
during labour
reference textbook
Obstetrics by ten teachers
20
th
ed (2017),ch 12, pp:393-404

MANAGEMENT OF THE SECOND
STAGE
When the mother reach the active 2
nd
stage
and has urge to push she adopts a lithotomy
position, or left lateral position, or semi
sitting position.
the pushing should be organized with the
contractions to be effective.

When you notice the crowning (the
head passed the pelvic floor and under
the pubic arch, delivery is imminent).
Use the modified Ritgen's manoeuvre:
for the delivery of the head.
The goals of assisted spontaneous
vaginal delivery are reduction of
maternal trauma, prevention of fetal
injury, and initial support of the
newborn

Episiotomy
Episiotomy is an incision into the
perineal body to enlarge the vulval
outlet and facilitate delivery:
1- Midline episiotomy
2-Mediolateral episiotomy

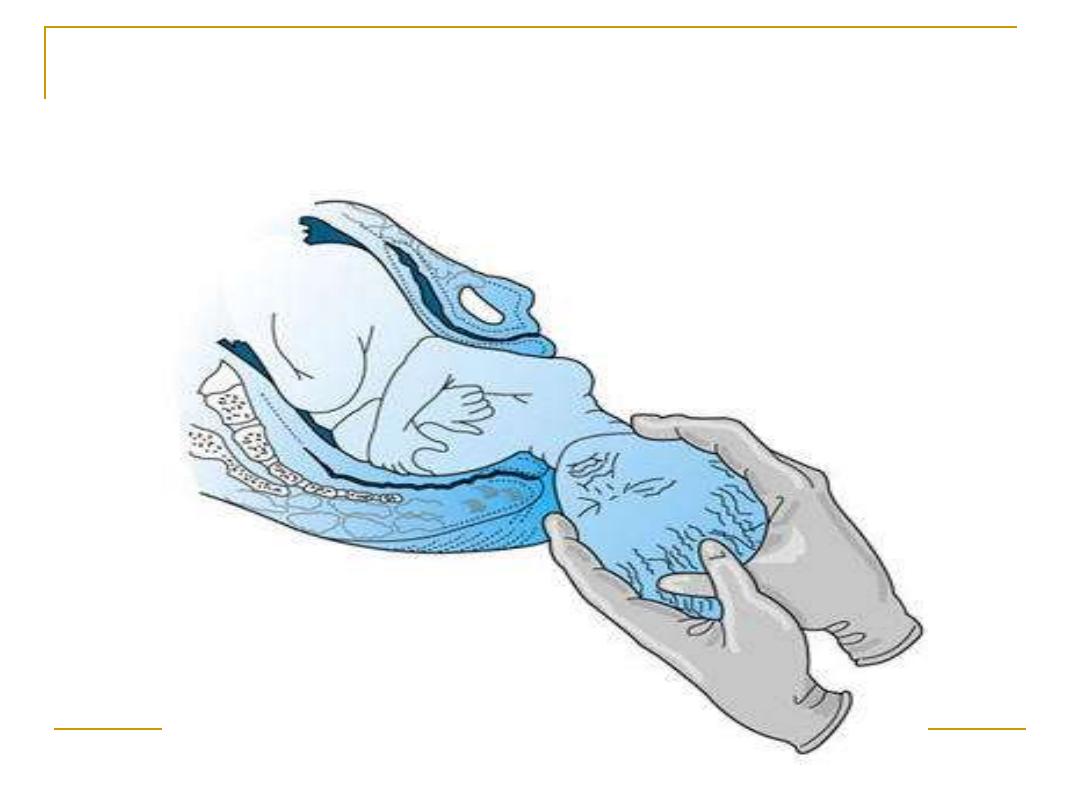
After head delivery
Then the delivery of the shoulders then the
delivery of the rest of the body
Delay cord clamping to get about 80 ml of
placental blood neonatal anemia
MANAGEMENT OF THE SECOND
STAGE
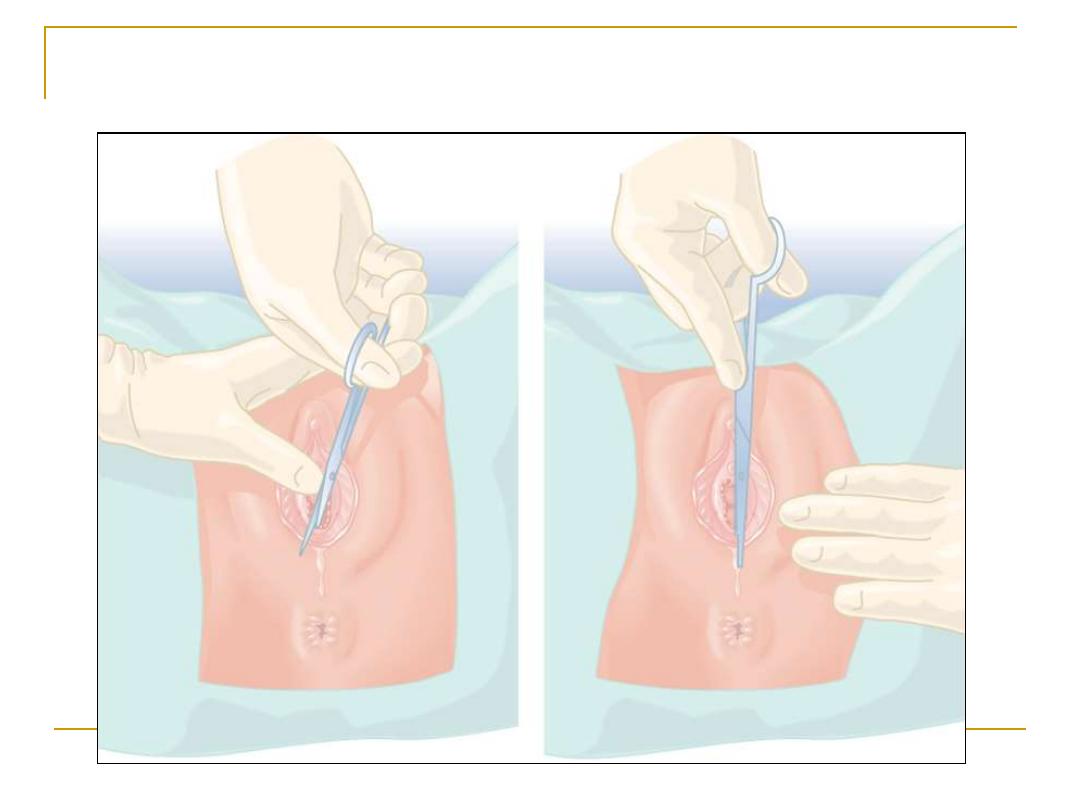
EPISIOTOMY
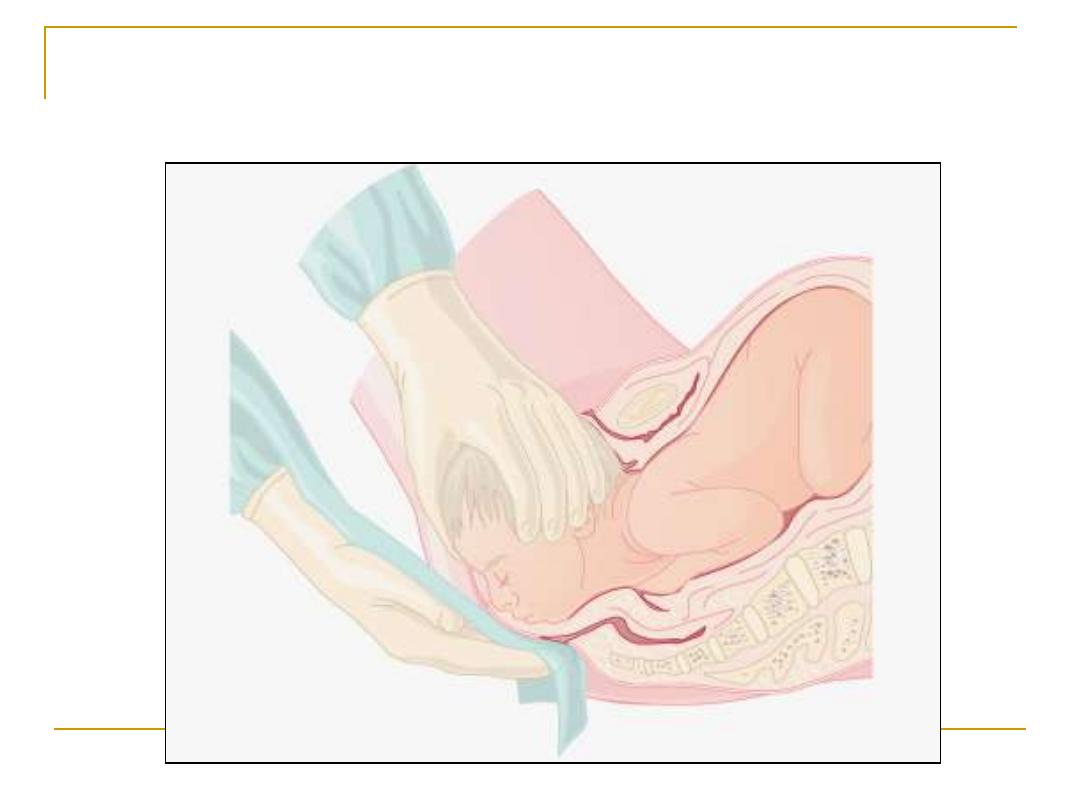
Perineal support for delivery of head
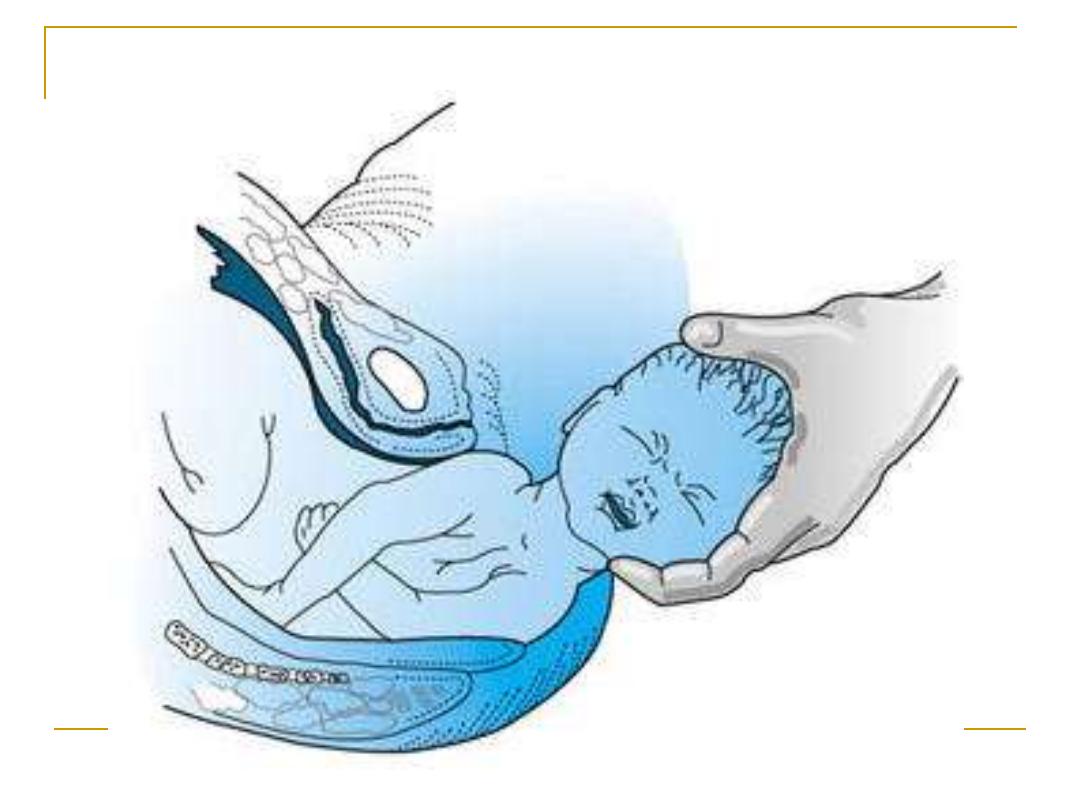
??? With this step give oxytocin 10 IU
injection i.m for active management of
3
rd
stage

MANAGEMENT OF THE THIRD
STAGE
Placental separation occurs as a result of
reduction of the volume of the uterine
cavity by the contractions and retraction
A cleavage plane developed within the
decidua basalis and the placenta lies free
in the lower uterine cavity.
Management either
A- active
B- physiological

rd stage
3
active management of the
1.
Give10 units oxytocin or syntometrin
with the delivery of the anterior shoulder
to induce uterine contractions
immediately after the delivery of the
baby.
2.
1-3 minutes after baby's delivery;
clamping of the cord

3.
Controlled cord traction to deliver
the placenta and membranes. never
pull the cord when the uterus is not
contracted risk of uterine
inversion

Active management of the 3
rd
stage
a- shortens the 3
rd
stage
b- and reduce the risk of
postpartum haemorrhage
from15% to 5%
Aim of active management
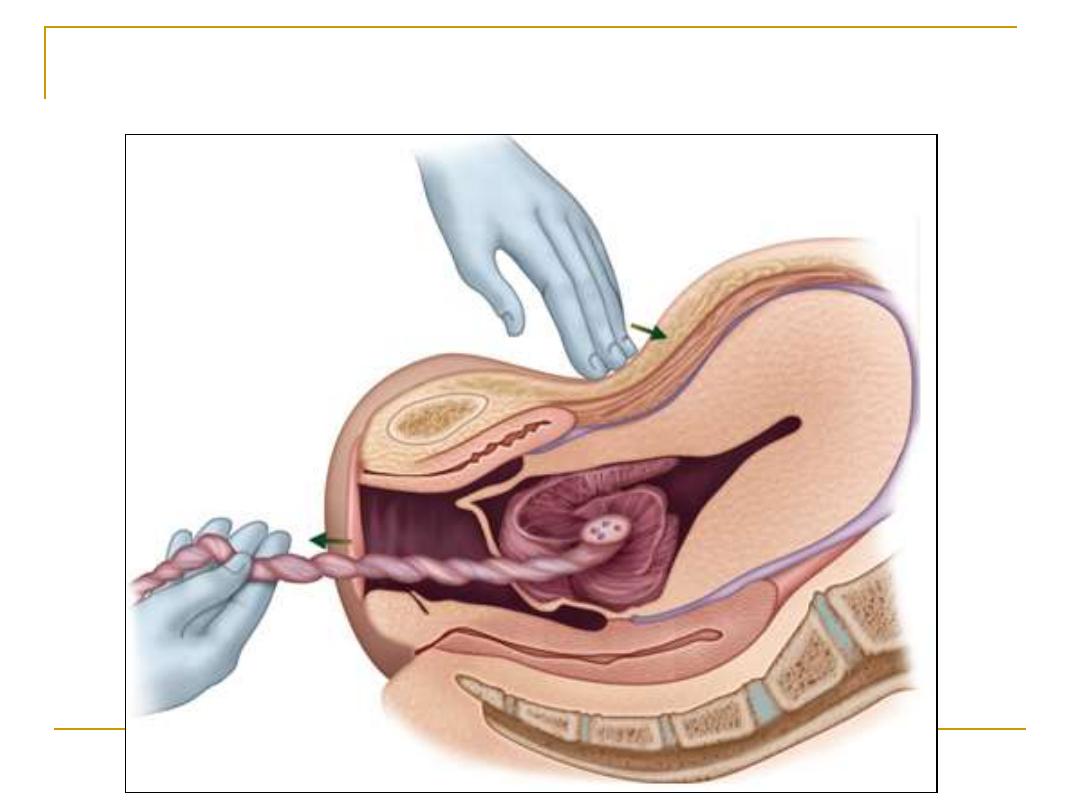
Controlled cord traction

After placental delivery it should be
inspected for any lost cotyledons or
succenturiate lobe.
Finally the vulva must be inspected
for any tears or lacerations in order
to repair them.

Fetal assessment
During labour uterine perfusion is
dramatically reduced during each
contraction, and fetal assessment is very
important because labor is very stressful
condition.
the use of operative delivery for ‘non
reassuring fetal status
’ remains to occur
every day in delivery wards.

Aim of fetal monitoring
The aim of monitoring of fetal well-being
during labour is to prevent birth asphyxia
and so reduce perinatal mortality, neonatal
intensive care unit (NICU) admissions at
term, umbilical cord acidosis (pH <7.2) and
base deficit >12 mmol/L, low Apgar scores,
neonatal hypoxic ischaemic
encephalopathy at term, and long-term
handicap.

One of the best methods available for
detection of fetal wellbeing is the FHR
because the
FHR
change with condition of
the fetus
screening test
Diagnostic
is fetal blood PH
which found
that only 35% of fetuses with abnormal
FHR are really acidotic

Methods of assessing FHR:
1- intermittent auscultation.
2- Continuous electronic fetal
monitoring
A- External by CTG
B- Internal by FSE

Monitoring the fetus during labor
There is probably little value in continuous
EFM (electronic fetal monitoring) in low-risk
pregnancies.
Such women may have a short (20 minutes)
CTG recording on admission to the labor
ward.
If the CTG is normal thereafter the fetal
heart is listened to every 15 minutes with a
Pinard stethoscope /or sonicaid.

The presence of any of the following risk factors at the
onset of labour would label a fetus as being at
‘high
risk’
of intrapartum hypoxia,
for which continuous fetal monitoring (EFM) should be
offered:
● hypertension /pre-eclampsia,
● diabetes,
● antepartum haemorrhage (APH),
● significant maternal medical disease,
● intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR),
● preterm gestation,
● isoimmunization,
● multiple pregnancy,

● If a fetal heart abnormality is recorded with the Pinard
stethoscope/sonicaid.
● breech presentation,
● previous caesarean section,
● Women who develop meconium staining of the amniotic
fluid during labor & those with significant meconium
staining of the amniotic fluid.
● pre-labour rupture of membranes for >24 hours,
● oligohydramnios abnormal umbilical artery Doppler
studies,
● post-term pregnancy,
● epidural analgesia,
● induced or augmented labour.

Fetal heart rate changes during labour
Accelerations normal
Decelerations
A- early physiological head compression
B-
late
may be pathological acidosis
C- variable cord compression
Tachycardia > 160
Bradycardia
< 100
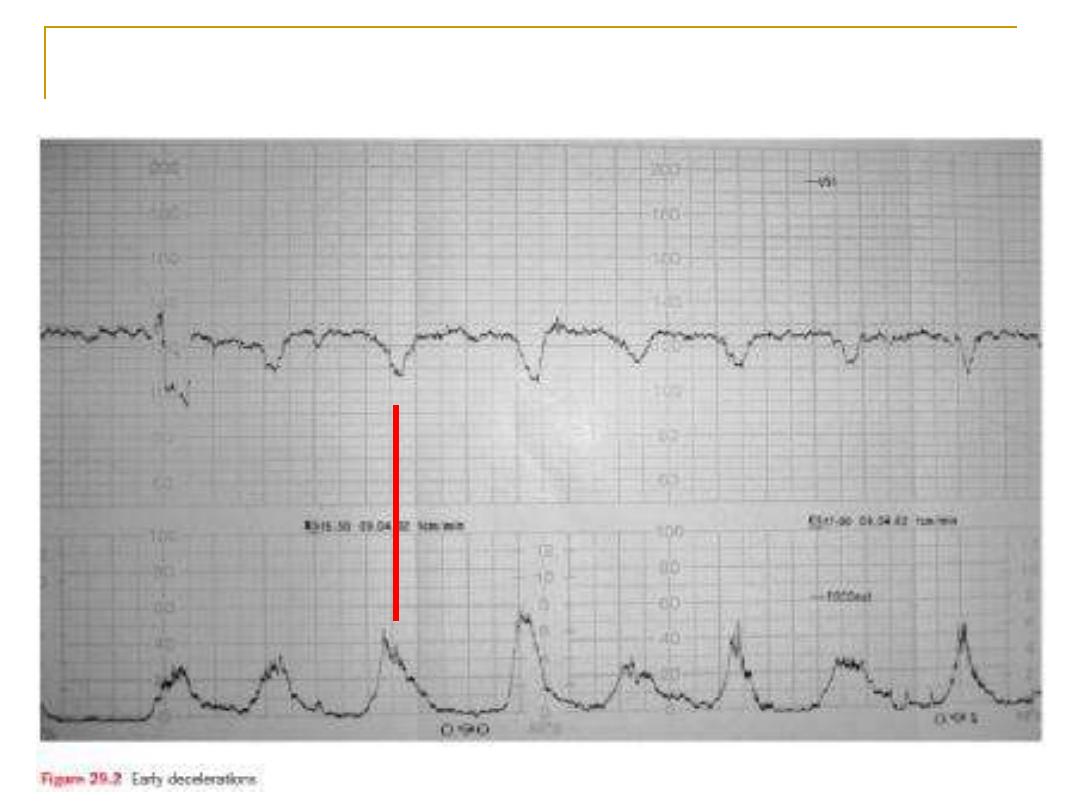
Early deceleration
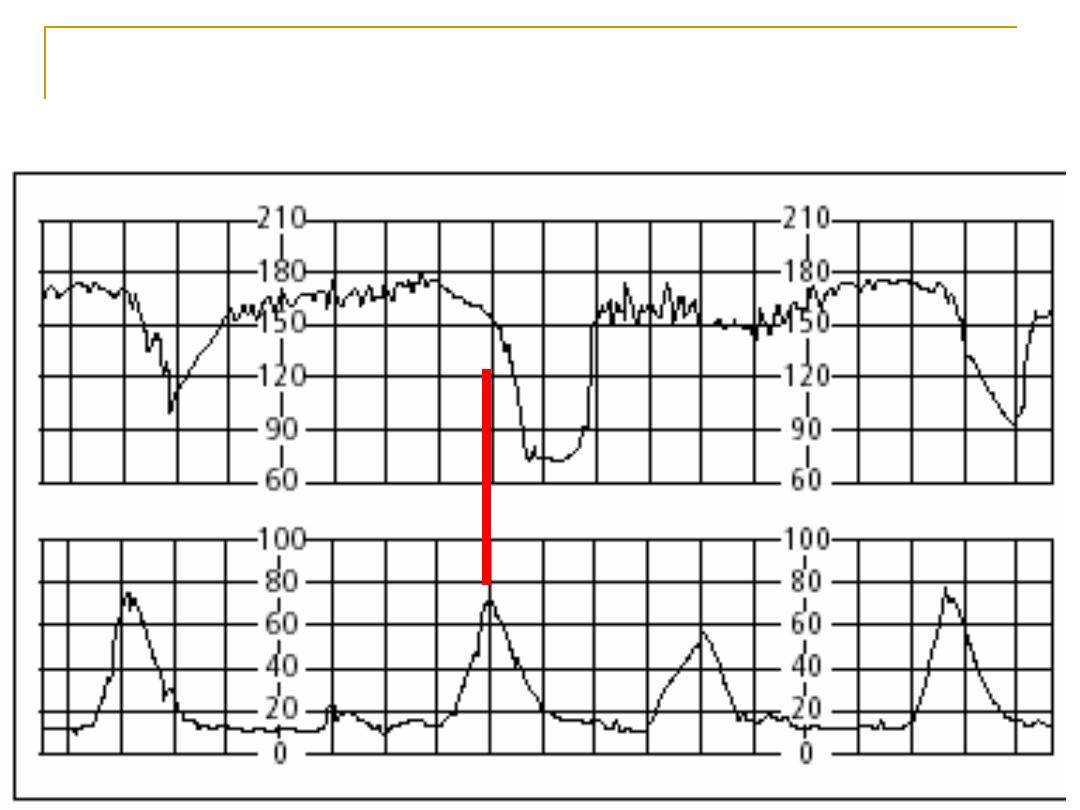
Late deceleration

meconium
Passage of meconium due to
Stimulation of the vagus in utero causes the
fetal gut to contract and the anal sphincter
to relax so that meconium (fetal stool) is
passed into the amniotic fluid.
If it associated with normal FHR NOT sig

Fetal blood sampling
Fetal blood sampling is a diagnostic test
for fetal acidosis.
The PH results are interpreted as follows:
• PH >7.25: normal.
• PH 7.21–7.24: pre-asphyxia.
• PH <7.20: asphyxia.

Other tests
Scalp stimulation
Fetal pulse oximetry
