Management of fractures
Dr. Wahby GhalibCABMS, FJMC, MRCS
Wahby Ghalib
2Reduction
ImmobilizationExercise
Wahby Ghalib3
The most important factor for healing is the:
state of the surrounding soft tissues &local blood supply.
Wahby Ghalib
4
Reduction
As soon as possible to avoid swelling
Wahby Ghalib
5Anatomic reduction
Intra-articular #
Physeal #
Forearm #Tenuous blood supply (scaphoid , FN)
Wahby Ghalib6
Wahby Ghalib
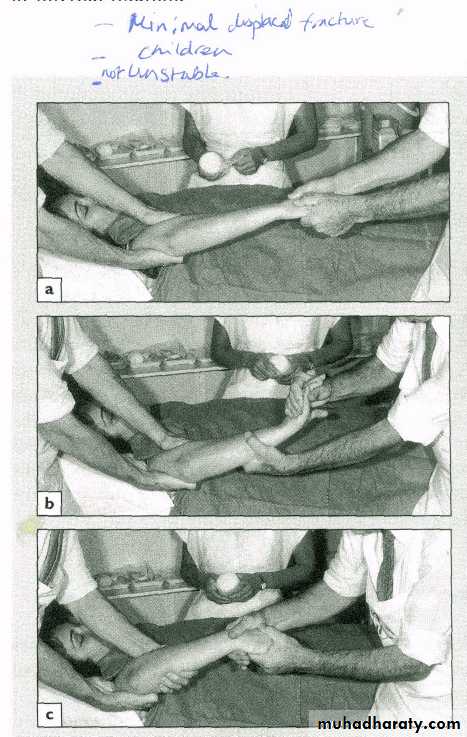
7Closed reduction
Anaesthesia & muscle relaxant :
Traction
Correction of deformity
Wahby Ghalib8
Wahby Ghalib
9Wahby Ghalib
10Wahby Ghalib
11Open reduction
CR fails
Perfect reduction needed
Internal fixation intendedWahby Ghalib
12Immobilization
Soft t. Healing
Faster bone healing
To avoid malunionWahby Ghalib
13Methods
(1) continuous traction
(2) cast splintage
(3) functional bracing
(4) internal fixation
(5) external fixation
Wahby Ghalib
14
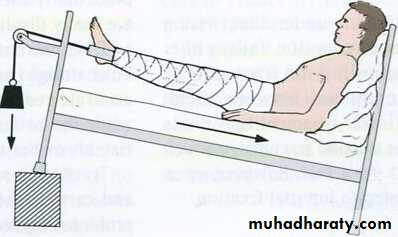
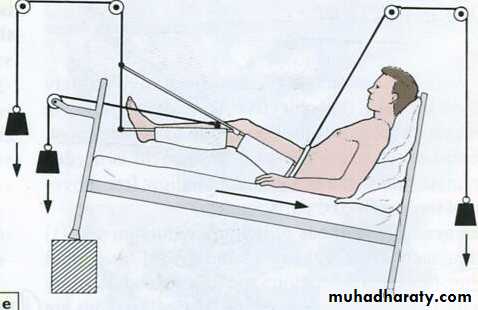
Continuous traction
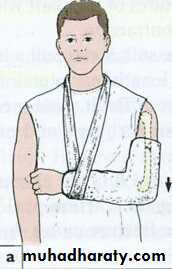
Traction by gravity:
in humerus fractures : hanging cast
Wahby Ghalib15
Wahby Ghalib
16Skin traction
Adhesive tape and bandage
Sustains pull of 4-5 kg
Wahby Ghalib
17
Skeletal traction
Steinmann pin
Sustains 1/10 of body weight
Wahby Ghalib18
Wahby Ghalib
19Advantage : joint exercise
Disadvantage : prolonged bed riding & hospitalizationWahby Ghalib
20Complications of traction
Circulatory embarrassment : specially in children
Nerve injury by pin or external rotation position
Pin-track infection
Wahby Ghalib21
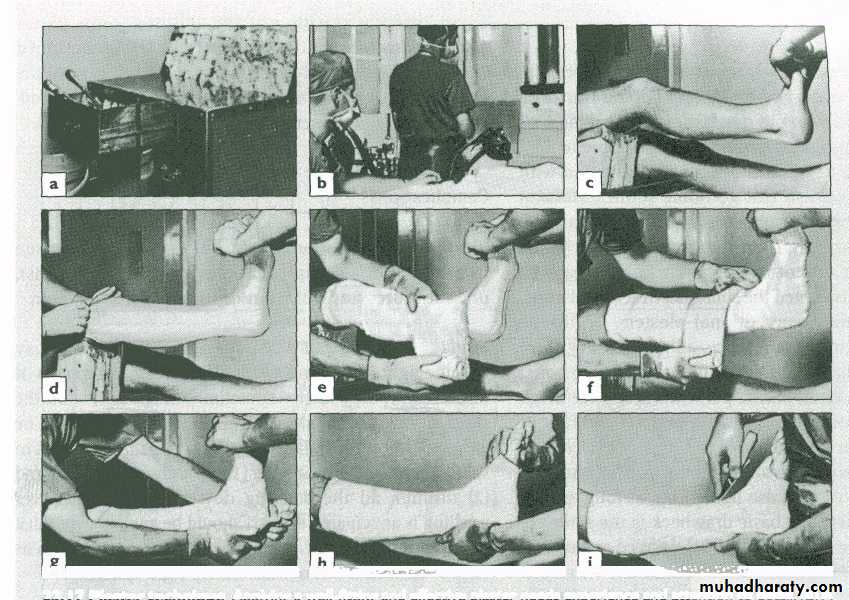
POP cast
Ca sulphate
On addition of water becomes hydrated & then hardens (exothermic reaction)
Wahby Ghalib22
Back slab
Cast cylinderWahby Ghalib
23Polyurethane cast
Lighter
Harder
Impervious to water
Less XR interference
Wahby Ghalib
24
Advantage : early discharge
Disadvantage : joint stiffnessWahby Ghalib
25Complications
Tight cast : compartment syndrome split or remove the cast
Loose cast : re-displacement
Plaster sores : pad bony prominancesWahby Ghalib
26Wahby Ghalib
27Wahby Ghalib
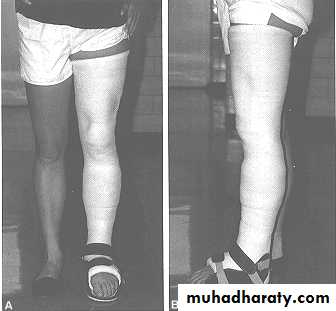
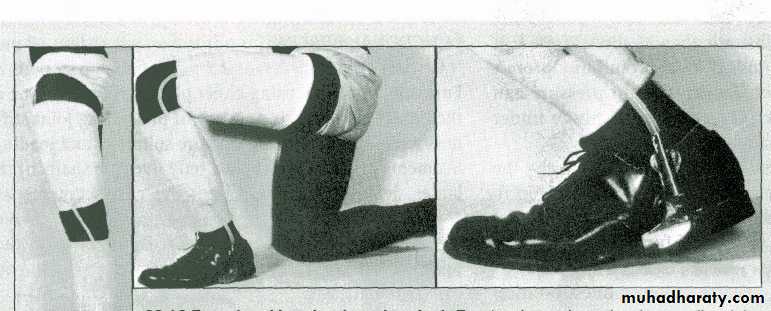
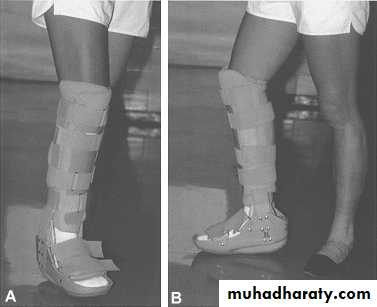
28Functional brace
Casts applied to shafts of bones connected by hinges to allow joint motion
Made of metal or plastic
Wahby Ghalib29
Wahby Ghalib
30Wahby Ghalib
31Adv. : no joint stiffness
Disadv. : not very rigid malunionSo: used after 3-6w
Wahby Ghalib32
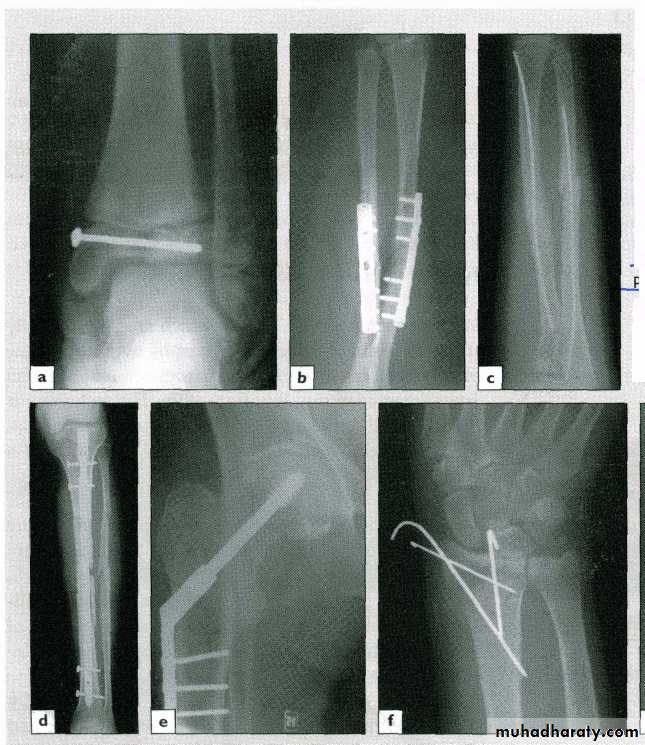
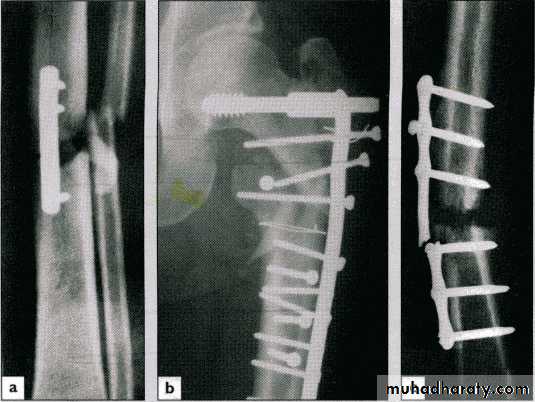
Internal fixation
Wires (e.g. Kirschner wire)
Screws
Plates
Intra-medullary nails
Wahby Ghalib
33Wahby Ghalib
34Indications
OR. Needed
Unstable #
# of poor & slow healing e.g. FN.Pathological #
Multiple #sPatient with nursing difficulty
Wahby Ghalib35
Adv. :
secure fixation
early joint motion
Disadv. :
soft t. damagerisk of infection
metal failure
Wahby Ghalib
36Wahby Ghalib
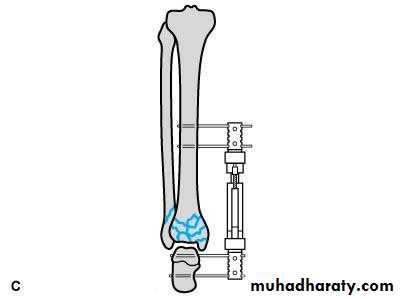
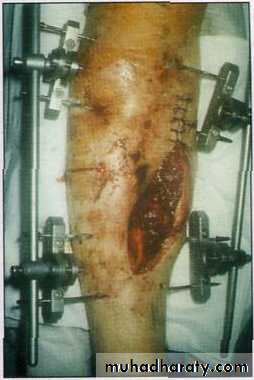
37External fixation
Screws (Schanz) pass above & below the # and are connected to an external frame
Wahby Ghalib
38
Wahby Ghalib
39Indications
Open #
Closed # with severe s.t. damage
Infected ## with bone loss (bone lengthening)
Pelvic fracturesAnaesthetic risk
Wahby Ghalib40
Complications
Nerve & vessel injury
Screw loosening
Pin-track infection
Wahby Ghalib
41
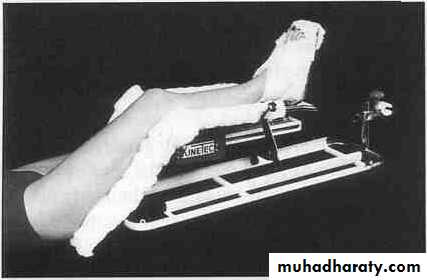
Exercise
To ↓ oedema ( fibrous t. stiffness)
To prevent joint stiffness
Elevation is also importantWahby Ghalib
42Active vs. passive ROM exercise
Weight bearingContinuous passive motion machine
Wahby Ghalib43
Wahby Ghalib
44Wahby Ghalib
45Treatment
ofOpen Fractures
Wahby Ghalib
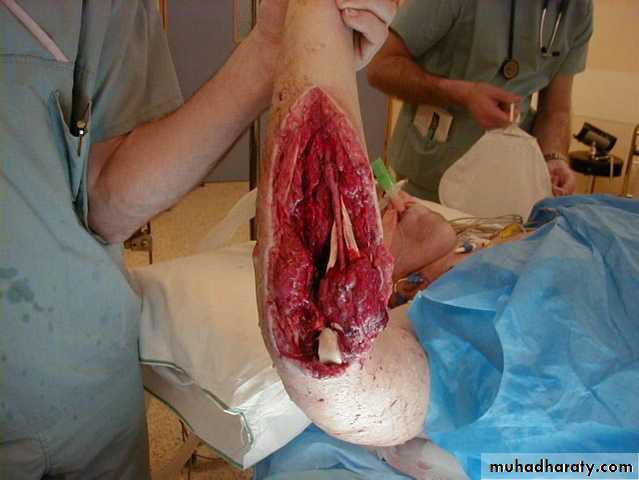
46Gustilo classification
Type I : wound < 1cm
little soft t. damage
no comminution
Type II : wound > 1 cm
moderate soft t. damage
moderate comminution
Both caused by low-energy trauma
Wahby Ghalib
47Type III : wound >10 cm
severe s.t. damagesevere comminution
hi-energy trauma
A: # can be covered with s.t.
B: cannotC: arterial injury needs repair
Wahby Ghalib
48Incidence of infection
< 2 % in type I
> 10 % in type III
Wahby Ghalib
49Management
antibiotic prophylaxis
wound debridement
stabilization of the fractureearly wound cover
Wahby Ghalib50
Antibiotic prophylaxis
I & II 2nd generation cephalosporin
6 hourly for 2 d
III add gentamicin & metronidazole
4-5 dWahby Ghalib
51
Debridement
Wound excision (margins)
Wound extension
Wound toilet (copious saline)Removal of F.Bs.
Removal of devitalized tissusWahby Ghalib
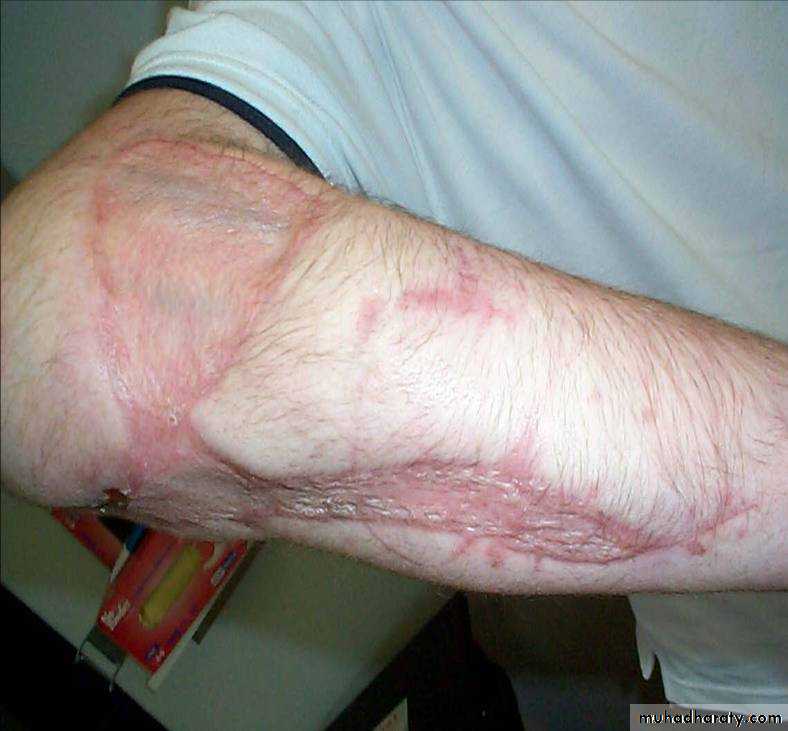
52Wound closure
Type I : close after debridement
Other types : inspect after 48 hours
Skin graft or flap may be neededWahby Ghalib
53
Wahby Ghalib
54Wahby Ghalib
55# stabilization
Up to IIIA like closed #
IIIB & C external fixation
Wahby Ghalib56
Objectives :
Training the students to deal with multitrauma cases in a systemic way.Training the students to approach injured limb according to priorities.
The useful and safe way to deal with skeletal XR.
Understanding the concept of balancing the three basic factors of fracture management.
Wahby Ghalib
57
Stressing the significance of compound fractures and the way they are classified and managed.
Understanding the various ways of fracture management and their indications and drawbacks.
Wahby Ghalib
58
Wahby Ghalib
59Thank you