
Gastro esophageal reflux disease (GERD):
1. What is the meaning of GERD?
2. causes of GERD?
3. Discuss the type and maneuver of feeding in patient with
GERD.
In which a significant amount of acid, bile, and food regurgitating into the lower
esophagus. This can lead to inflammatory changes called (reflux oesophagitis).
Reflux is normally followed by:-
1. Oesophageal peristalsis.
2. Alkaline saliva to neutralize gastric acid..
Therefore; the time for exposure of the oesophageal mucosa to acidity is short. If that
time is prolonged, it will lead to oesophagitis.
It is extremely common symptoms, with 20% of adults reporting at least weekly
episodes of heart burn and 7-10%complaining of daily symptoms. It contributes 30%
of the general population.
Causes and predisposing factors:-
1. external influences
Smoking&NSAID
Eating fat\chocolate
coffee\tea
Large meal
Alcohol
Drugs:-
Drugs that lead to relaxation of lower oesophageal sphincter and decrease
sphincter tone like
1. Hyosine group like antispasmodic drugs or drugs that have antispasmine like
activity .ex:-antidepressant tricycles.
2. bronchodilator ex:- aminophyline, theophylline
3. Antianginal drugs.
4. Antipsychotic drugs ex. Trifloperazine.
11. Defective oesophageal clearance:-
It leads to prolonged time of exposure to acidity, one third of patient with severe
GERD have diminished peristaltic clearance causes:-
a. sleep in which swallowing induced peristalsis is infrequent which in turn
prolong acid exposure time.
b. CREST syndrome (scleroderma)

c. Impaired salivation ex. Sjogren”s syndrome, anticholinergic drugs and oral
radiation therapy.
d. Hiatus hernia, because hernial sac may prevent esophageal clearance.
111. Abnormal lower oesophageal sphincter:-
The normal baseline lower oesophageal sphincter pressure is (more than 30 mmHg)
Mild symptoms may occur with 10-30 mmHg
Severe symptoms as Barrettes oesophagus less than 10 mmHg
It may be due to
1. drug effect like antispasmodic drugs
2. post surgical treatment for achalasia
3. Stent tube for CA oesophagus.
1V.delayed gastric emptying
:-
which is due to
1. Gastro paresis, as in DM, chronic alcoholism, old age and drug effect.
2. Partial gastric out let obstruction.
3. Hormonal effect, menstruation and pregnancy.
V.increase intra abdominal pressure.:-
Causes:-
1. obesity
2. pregnancy
3. Cosmetic instrument by female.
Clinical features:-
*the majority of pt. have heart burn, regurgitation which is provoked by bending,
straining, lying down,this mostly common after 30 -60 min. after meal.
*the symptoms relief with sitting in bed ,taking antacid or baking soda
* High degree of reliability with these symptoms
*Patient may have dyspepsia.
*clinical diagnosis has specificity 68%
And sensitivity of 78%.
The severity of heart burn is not correlated with the histological finding in
oesophageal biopsy, therefore; some pt with GERDhave severe symptoms with (-ve)
finding and some with severe histological finding have no symptoms.
Some pts have dysphagia which may be due to :-
1. Abnormal peristalsis.
2. Development of complications like:- stricture or barrette metaplasia.
GERD may present with increased manifestation of other dis like: - bronchial asthma,
chronic cough, laryngitis, sore throat and atypical chest pain.
GERD is either causative or provoked in 50%of those pts.
Investigations:-
1. most of the patient need no investigations in the absence of hard symptoms
like :-
a. weight loss
b. anemia (iron deficiency anemia)
c. Abnormal presentation (age more than 50 years).
d. Dysphagia
e. Cervical LAP
f. Poor response to therapy.
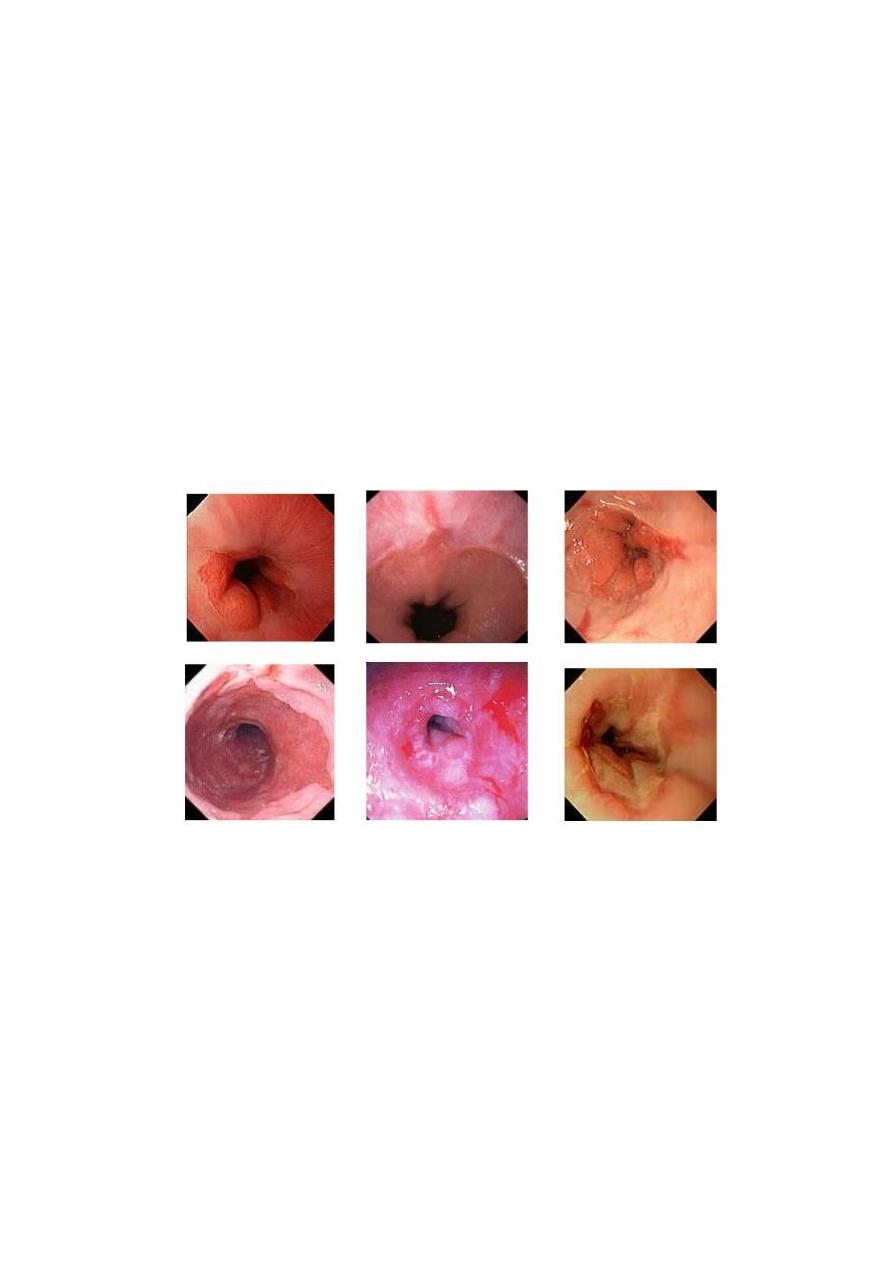
2. endoscope(OGD) IS THE INVESTIGATION OF CHOISE which help to :-
a. diagnosis performance
b. exclude other causes
c. Discover complications.
50 % of pt with GERDhave mucosal abnormality such as erythema and friability and
erosions.
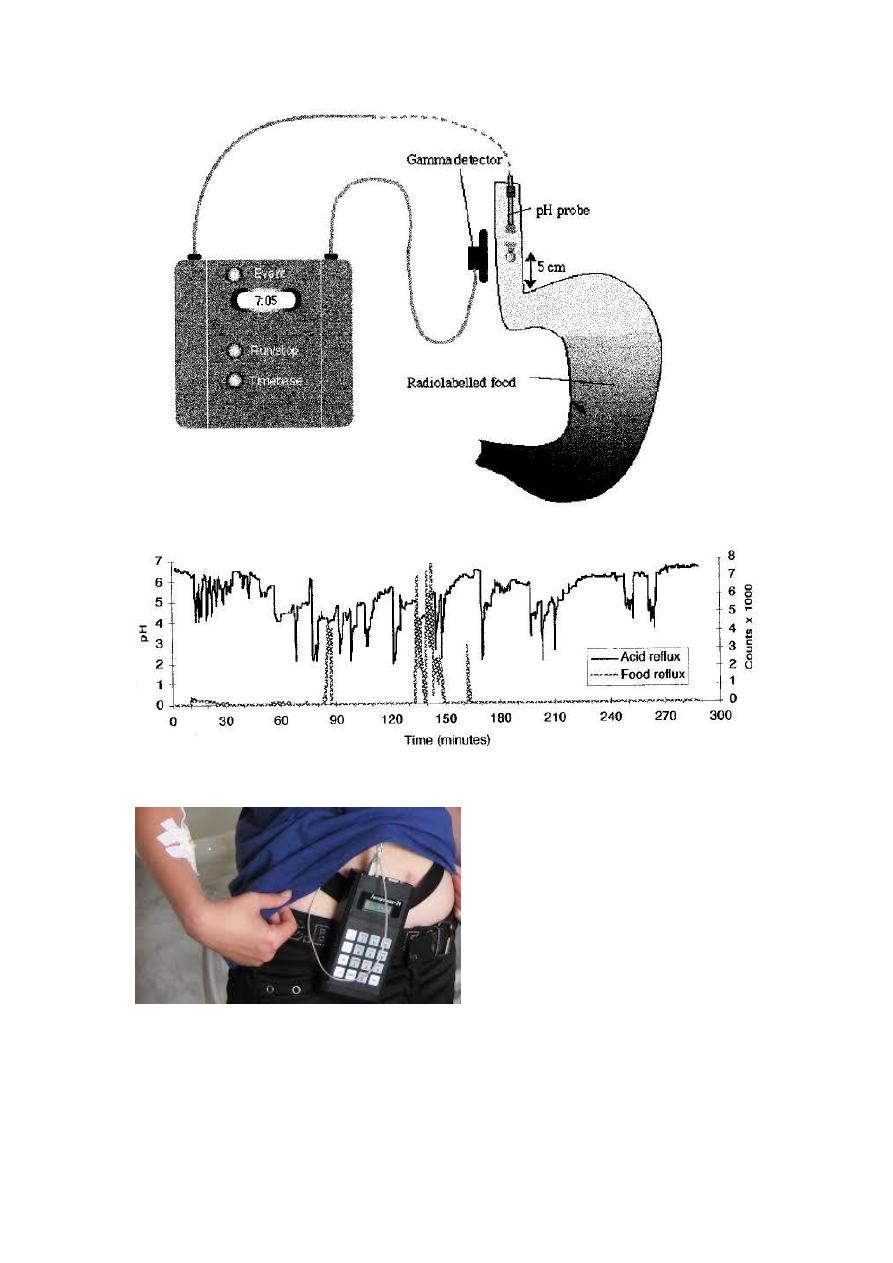
3. ambulatory oesophageal pH monitoring :- it is the best study for document
abnormal acid reflex, it is useful in
a. document abnormal acidity in oesophageal endoscope (-
ve)GERD.preoperative antireflex surgery.
b. GEDR (-ve)OGDpoor response to medical therapy
c. To document association with other dis. As BA
pH less than 4 for more than 7% of the study time is diagnostic.
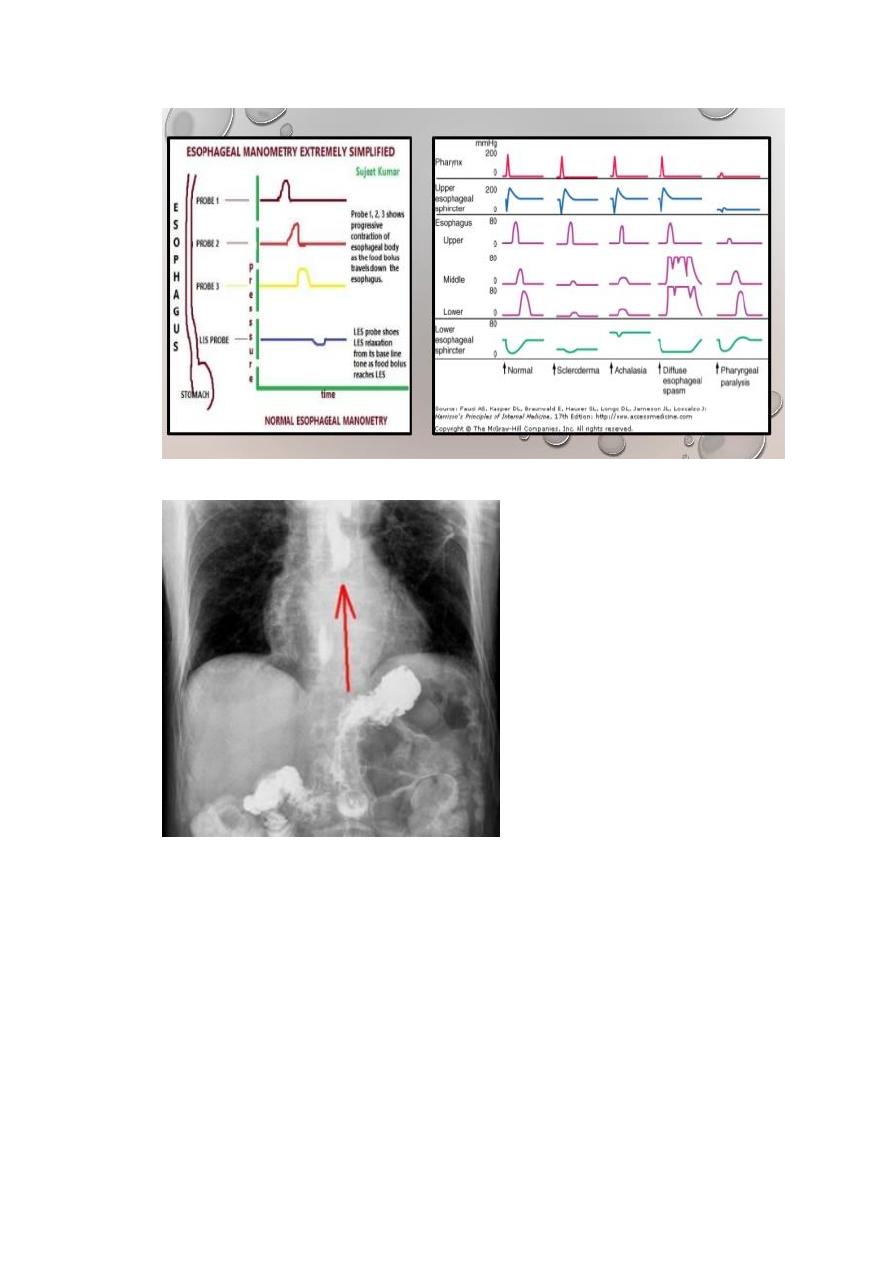
4. oesophageal manometry
it is indicated :-
a. localization of oesophageal sphincter before placement of oesophageal pH
monitoring probe.
b. Preoperative for antireflex surgery.
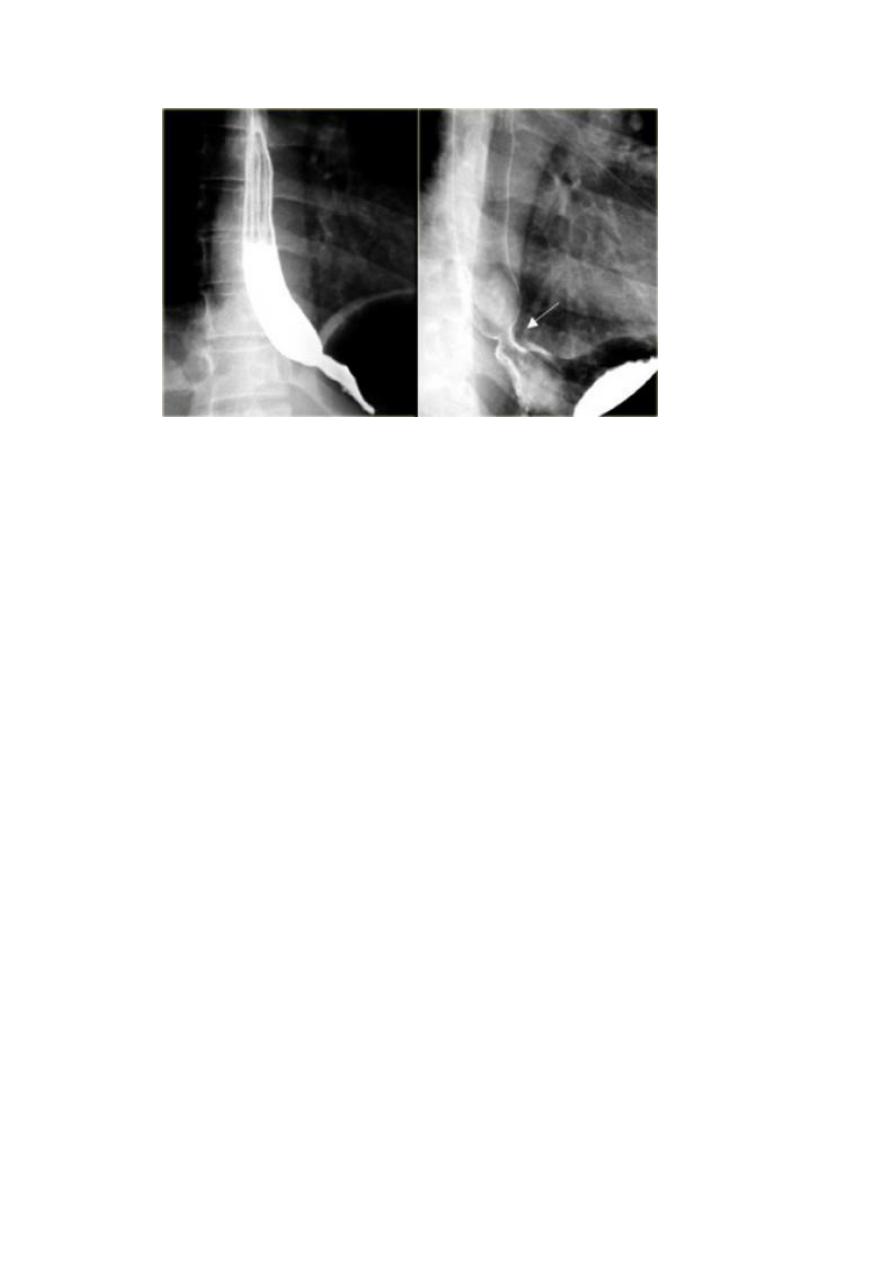
5. barium swallow which shows reflux of the gastric content to the esophagus.
Complication
1. oesophagitis
2. barrette “s oesophagus
3. anemia
4. benign oesophageal stricture.
5. malignant transformation.
Management:-
General measures
1. lose weight
2. Raise head of bed on blocks to 20 cm. or more may alleviate nocturnal
symptoms and regurgitation.
3. Avoidance of night or prebed meal.
4. Prevent sweaty or fatty meal post dinner.
5. Give about 4 hour’s interval before dinner and sleep time.
6. Avoid smoking and alcohol.
Medical measures:-
If the general measures are of no benefit, then you start medical therapy.
1. Simple heart burn:- give mixture of alginic acid and a simple antacid may be
effective.
2. mild symptoms and persistent symptoms :-
a. six weeks course of H2 receptor antagonist two times a day or full night days
may be of benefit.
b. If it is combined with prokinatic drugs (cisaprid, metoclopramide) not alone
will be of great value.
c. Several drugs to protect mucosal lining like alginic acid containing antacid. or
carbenoxolone
Prekinatic drugs are of great importance to increase the lower oesophageal
sphincter tone.
The treatment helps symptoms without healing oesophagitis
3. severe cases:-

Proton pump inhibitor is treatment of choice as omeprazole or lansoprazole
Symptom relief and oesophagitis heals in the majority
Recurrence is common when you stop treatment.
Many pts. Need small maintenance dose of omeprazole or H2 antagonist.
