Acyanotic heart diseases
By Dr. Ahmed Abdulameer Daffar( Cardiothoracic and vascular surgeon )
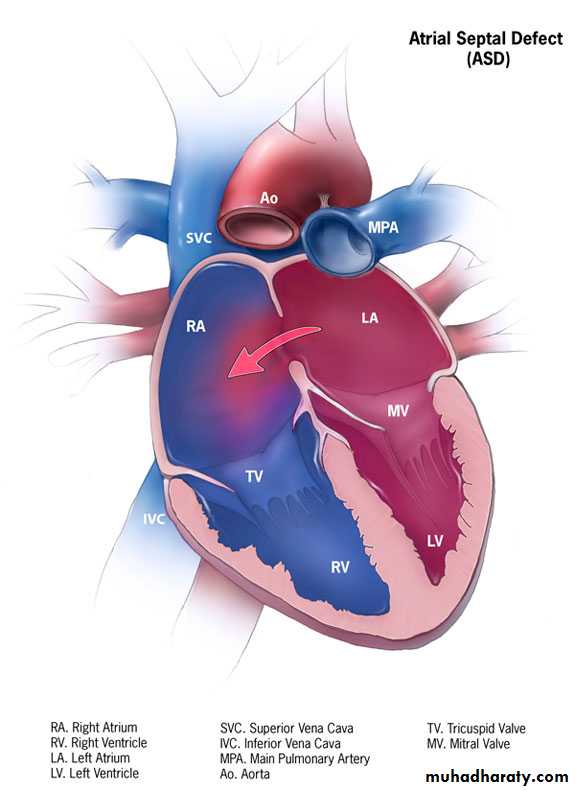
Atrial septal defect (ASD)
It is defined as an opening in the atrial septum that enables mixing of blood from the systemic and pulmonary venous circulations.Pathophysiology
left-to-right shunting of blood across the defect and a marked increase in pulmonary blood flow occurs.Eisenmenger’s complex develops when the pulmonary vascular resistance becomes highly elevated leading to reversal of shunting ( right to left )
Clinical Presentation
Asymptomatic.Failure to thrive may be observed.
Exertional dyspnea.
Recurrent respiratory infection occurs.
Auscultatory findings include a systolic flow (ejection systolic) murmur heard over the pulmonary area in the 2nd or 3rd left intercostal & a fixed split S2.
Investigations
-Chest X-ray
Plethoric lung fields or cardiomegaly may be seen.
-Electrocardiogram
-EchocardiographyIt is now the diagnostic modality of choice.
-Cardiac catheterization
It's seldomly employed in the diagnosis of ASDTreatment
Surgical intervention is indicated for large ASDs and for children with significant shunt after 2 years of life (unusual for ASD to close after 2 years of age).VENTRICULAR SEPTAL DEFECTS
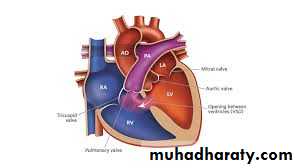
A ventricular septal defect (VSD) is a hole in the interventricular septum (IVS). VSD, in its isolated form, is the most commonly recognized congenital heart defect and represents 30% to 40% of all congenital heart malformations at birth.Pathophysiology
left-to-right shunting of blood across the defect and a marked increase in pulmonary blood flow occurs.Eisenmenger’s complex develops when the pulmonary vascular resistance becomes highly elevated leading to reversal of shunting ( right to left )
Clinical Presentation
Asymptomatic.Failure to thrive.
Exertional dyspnea.
Recurrent respiratory infection occurs.
Auscultatory findings include a pansystolic murmur is heard in the left lower sternal border.
Investigations
-Chest X-rayPlethoric lung fields or cardiomegaly may be seen.
-Electrocardiogram
-EchocardiographyIt is now the diagnostic modality of choice.
-Cardiac catheterization
It's seldomly employed in the diagnosis of ASD
Treatment
Surgery is indicated for large VSDs or for those VSDs which didn't close spontaneously.PDA ( Patent Ductus arteriosus )
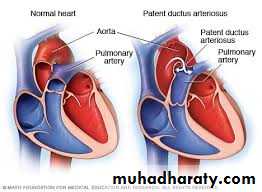
The ductus arteriosus normally extends from the main or left pulmonary artery to the descending aorta just distal to the origin of the left subclavian artery.Closure occurs usually after birth. Final closure may occur at any age but is uncommon after 6 months.
Incidence
The incidence increases greatly with prematurity and with decreasing birth weight.Clinical Presentation
Asymptomatic.Failure to thrive.
Exertional dyspnea.
Recurrent respiratory infection occurs.
Auscultatory findings include a machinery murmur which is heard best in the pulmonary area and radiates toward the middle third of the clavicle.
Investigations
-Chest X-ray
Plethoric lung fields or cardiomegaly may be seen.
-Electrocardiogram
-EchocardiographyIt is now the diagnostic modality of choice.
-Cardiac catheterization
It's seldomly employed in the diagnosis of PDATreatment
Pharmacologic closure with prostaglandin inhibitors such as indomethacin in premature Infants.Term infants are generally unresponsive to pharmacologic therapy.
Surgical closure
It is used if there is a contraindication to indomethacin or failure of the PDA to close in response to conservative measures.
Thank You
Thank you