UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
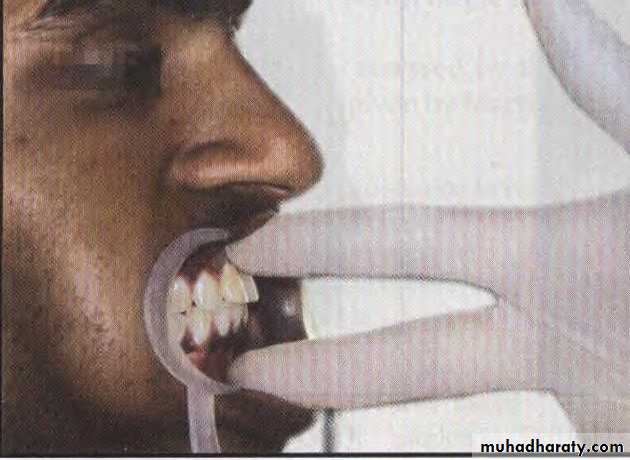
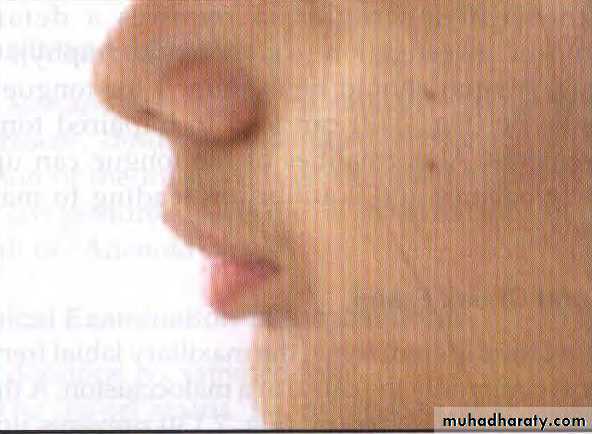
placing the index and middle fingers at the approximate A and B points after lip
retraction. Ideally, the maxilla is 2 to 3 mm anterior to the mandible in centric occlusion
Assessment of antero-posterior jaw relationship
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY
Department of:
HERE
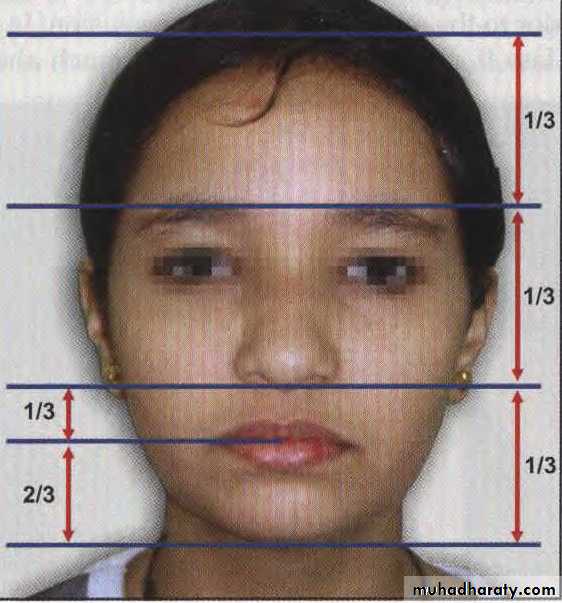
Assessment of vertical skeletal relationship
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
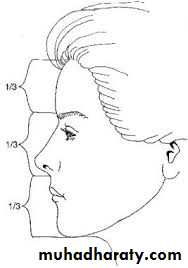
A normal vertical relationship is one where the distance between the glabella and subnasale is equal to the distance from the subnasale to the lower border of the chin.
We can observe symmetry by dividing the face into three thirds, where the nose represents the middle third of the face.
Lower facial third divided into 1/3 upper lip, and 2/3 lower lip
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
if we divide the face vertically into 5 equal parts (fifth), we can observe that the nasal width should be approximately equivalent to the width of each eye.
The role of fifth
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
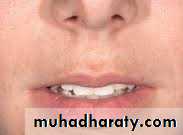
Lips : Lip length, width and curvature should be assessed. In a balanced face, the length of the upper lip measures one-third, the lower lip and chin two thirds of the lower face height. The upper incisal edge exposure with the upper lip at rest should be normally 2 mm.
Examination of the Soft Tissues
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
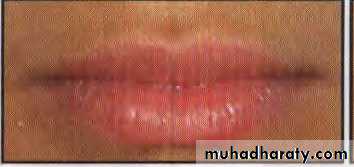
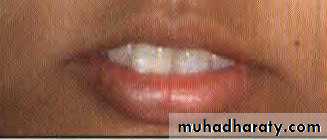
Lips can be classified into:
a. Competent lips: Slight contact of lips when musculature is relaxed.b. Incompetent lips: Anatomically short lips, which do not contact when musculature is relaxed. Lip seal is achieved only by active contraction of the orbicularis oris and mentalis muscles.
c. Potentially competent lips: Lip seal is prevented due to the protruding maxillary incisors despite normally developed lips
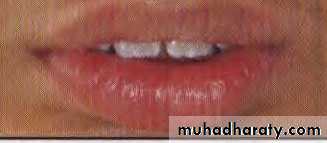
d. Everted lips: These are hypertrophied lips with redundant tissue but weak muscular tonicity
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
Everted lips
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
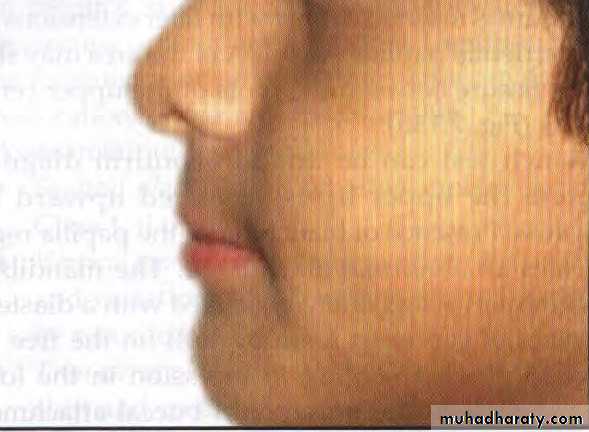
NASOLABIAL ANGLE
Normal value is 110 degrees.
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
Deep Mento-labial sulcus shallow Mento-labial sulcus
ChinThe configuration of the chin is determined not only by the bone structure, but also by the thickness and tone of the mentalis muscle.
Mentalis activity : mentalis muscle becomes hyperactive in certain malocclusions like Class II div 1
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
INTRAORAL EXAMINATION
Tongue
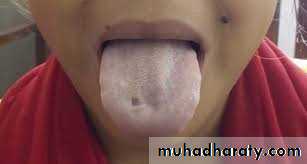
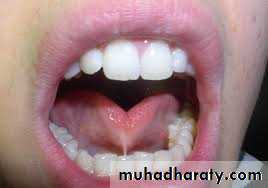
Tongue is examined for shape, color and configuration. It may be small, long on broad. An excessively large tongue (macroglossia) The lingual frenum should be examined for tongue tie. Tongue tie can lead to impaired tongue movements. Abnormalities of the tongue can upset muscle balance and equilibrium leading to maloclusion.
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
macroglosia
ankyloglosia
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
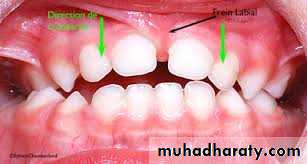
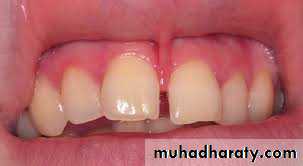
A thick, fibrous, low labial frenum , prevents upper central incisors from approximating each other leading to a midline diastema. A frenectomyis indicated when the frenum is inserted deeply with fiber extensions into the interdental papilla.
Lip and Cheek Frena
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY
Department of:
HERE
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
• Gingiva
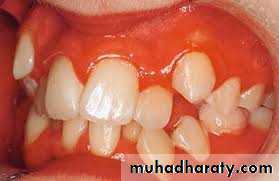
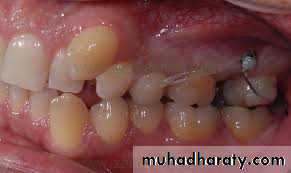
• The gingiva should be examined for the type (thick fibrous or thin fragile), inflammation and muco-gingival lesions. Gingivitis is a contraindication for orthodontic treatment. Treatment should be started only when the gingival condition improves.
Clinical Examination of the Dentition
The dentition is examined for:
1. The dental status, i.e. number of teeth present, un-erupted or missing.
2. Dental and occlusal anomalies should be recorded in detail. Carious teeth should be treated before beginning orthodontic treatment. Dentition should be examined for other malformation, hypoplasia, restorations, wear and discoloration.
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
3. Assessment of the apical bases.
4. Midline of the face and its coincidence with the dental midline should be examined.
5. Individual tooth irregularities, e.g. rotations, displacements, fractured tooth
6. Shape and symmetry of upper and lower arches.
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
New methods that have affected current orthodontic practice and have even greater potential for changing the way orthodontists will practice in the future include
digital photography, videography, 3D photography, computer imaging, virtual dental models, cone beam computed tomography, stereolithographic models
Technological Advances
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
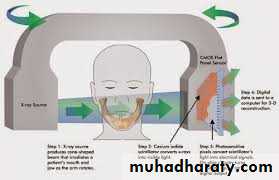
computed tomography
Three-dimensional images created by computed tomography (CT) have been used in medicine for many years now but were not used in evaluating orthodontic patients until recently for two reasons: the radiation dose and the cost.
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
3d
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
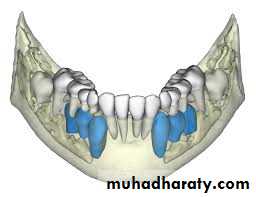
• Virtual Dental Models.
• Models of the teeth, the traditional diagnostic record from the beginning of orthodontics, have been used to view the relationships of the teeth from any orientation. The advent of digitized laser-scanned dental impressions that produce a three dimensional image of the teeth has overcome the problem of having to pour and trim plaster casts and has obviated the need to store and retrieve the models each time a patient is seen.
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY
virtual dental models
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
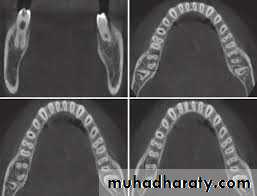
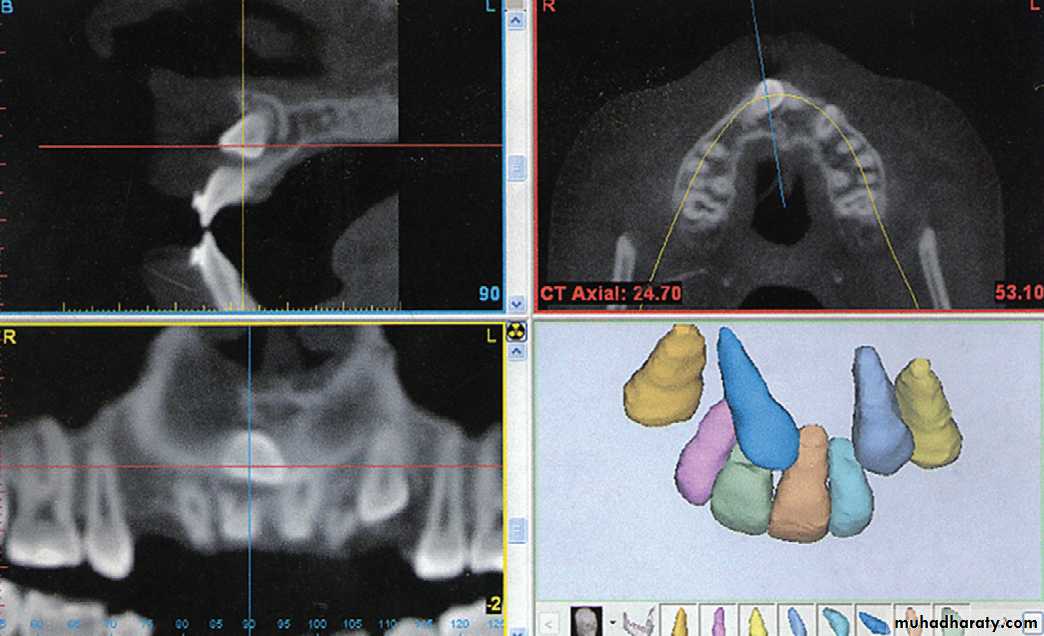
• Cone Beam Computed Tomography.
• Cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) produces three dimensional volumetric images that can be reliably measured. A major advantage of CBCT imaging is that all extraneous structures that would otherwise obscure the desired view can be excluded. This allows visualization of dimensions for the wanted structures.
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
cone beam computed tomography CBCT
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
CBCT
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
THE END
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY2020-2021