Examination and Diagnosis of Pulp, Root Canal, and Periapical/Periradicular Conditions Part 2
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY
By :Dr Ali Moayid
Lect. 2
2020-2021
Department of
Conservative Dentistry
5th YEARs
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY2020-2021
Mobility Test
Like percussion testing, an increase in tooth mobility is merely an indication of a compromised periodontal attachment apparatus
This compromise could be the result of acute or chronic physical trauma, occlusal trauma, parafunctional habits, periodontal disease, root fractures, rapid orthodontic movement, or the extension of pulpal disease, specifically an infection, into the periodontal ligament space
Because determining mobility by simple finger pressure can be visually subjective, the back ends of two mirror handles should be used, one on the buccal aspect and one on the lingual aspect of the tooth
Any mobility that exceeds + 1 should be considered abnormal. However, the teeth should be evaluated on the basis of how mobile they are relative to the adjacent and contralateral teeth.
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY2020-2021
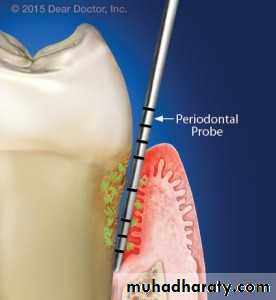
Periodontal Examination
The measurement of periodontal pocket depth is the distance between the height of the free gingival margin and the height of the attachment apparatus below, using a calibrated periodontal probe for all the aspects in millimitars.
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY2020-2021
Pulp Tests
Pulp testing involves attempting to make a determination of the responsiveness of pulpal sensory neurons
The tests involve thermal or electrical stimulation of a tooth in order to obtain a subjective response from the patient (i.e., to determine whether the pulpal nerves are functional), or the tests may involve a more objective approach using devices that detect the integrity of the pulpal vasculature.
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY
2020-2021
Unfortunately, the quantitative evaluation of the status of pulp tissue can only be determined histologically, as it has been shown that there is not necessarily a good correlation between the objective clinical signs and symptoms and the pulpal histology
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY2020-2021
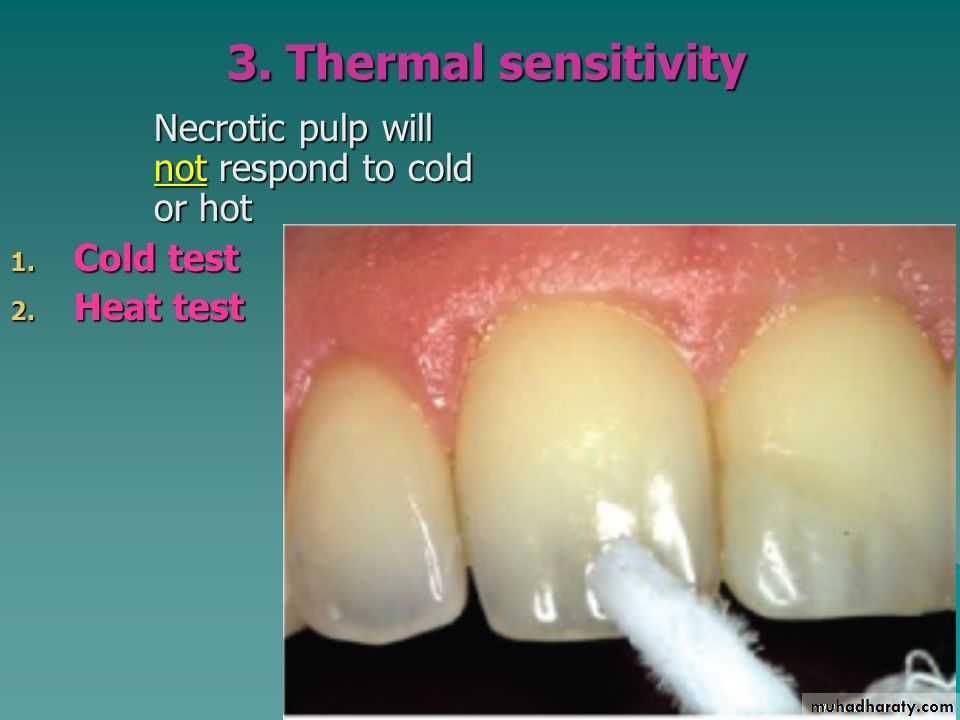
Thermal
Regaredless to the materials and methods, the response to the cold and hot is the basic
The baseline or normal response to either cold or hot is a patient’s report that a sensation is felt but disappears immediately upon removal of the thermal stimulus.
Abnormal responses include a lack of response to the stimulus, a lingering or intensification of a painful sensation after the stimulus is removed, or an immediate, excruciatingly painful sensation as soon as the stimulus is placed on the tooth
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY2020-2021
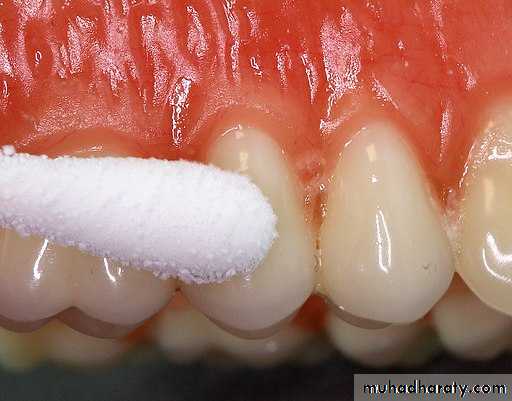
Cold testing is the primary pulp testing method used by many clinicians today. It is especially useful for patients presenting with porcelain jacket crowns or porcelain-fused-tometal crowns where no natural tooth surface (or much metal) is accessible. If a clinician chooses to perform this test with sticks of ice, then the use of a rubber dam is recommended, because melting ice will run onto adjacent teeth and gingiva yielding potentially false-positive responses.
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY2020-2021
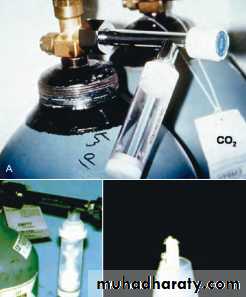
Frozen carbon dioxide (CO² ), also known as dry ice or carbon dioxide snow , or CO2 stick , has been found to be reliable in eliciting a positive response if vital pulp tissue is present in the tooth
For testing purposes, a solid stick of CO2 is prepared by delivering CO2 gas into a specially designed plastic cylinder.
resulting CO2 stick is applied to the facial surface of either the natural tooth structure or crown.
The teeth should be isolated and the oral soft tissues should be protected with a 2-by-2-inch gauze or cotton roll so the frozen CO2 will not come into contact with these structures. Because of the extremely cold temperature of the frozen CO2 ( −69°F to −119°F; −56°C to −98°C), burns of the soft tissues can occur
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY2020-2021
The most popular method of performing cold testing is with a refrigerant spray. It is readily available, easy to use, and provides test results that are reproducible, reliable, and equivalent to that of frozen CO2
Commonly the use of the dental triple syringe or cold water are questionable unless good isolation with rubber dam.
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY2020-2021
If a mature, non traumatized tooth does not respond to both cold testing and electric pulp testing, then the pulp should be considered necrotic.
However, a multirooted tooth, with at least one root containing vital pulp tissue, may respond to a cold test and electric pulp test even if one or more of the roots contain necrotic pulp tissue
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY2020-2021
Another thermal testing method involves the use of heat.
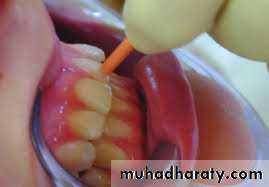
When a patient is unable to identify which tooth is sensitive, a heat test is appropriate. Starting with the most posterior tooth in that area of the mouth, each tooth is individually isolated with a rubber dam. An irrigating syringe is filled with a liquid (most commonly plain water) that has a temperature similar to that which would cause the painful sensation. The liquid is then expressed from the syringe onto the isolated tooth to determine whether the response is normal or abnormal.
With heat testing, a delayed response may occur, so waiting 10 seconds between each heat test will allow sufficient time for the onset of symptoms
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY
2020-2021
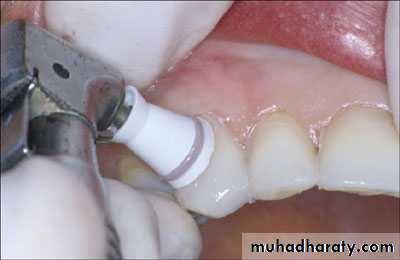
Another method for heat testing is to apply heated gutta -percha or compound stick to the surface of the tooth.
Heat can also be generated by the friction created when a dry rubber-polishing wheel is run at a high speed against the dry surface of a tooth
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY2020-2021
Often a tooth that is sensitive to heat may also be responsible for some spontaneous pain. The patient may present with cold liquids in hand just to minimize the pain
In such cases, the application of cold to a specific tooth may eliminate the pain and greatly assist in the diagnosis. Typically, a tooth that responds to heat and then is relieved by cold is found to be necrotic.
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY2020-2021
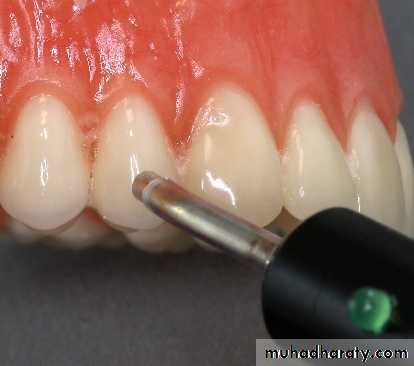
Electric Pulp Tester
Electric pulp testers of different designs and manufacturers have been used for this purpose.
Numeric readings on the pulp tester have significance only if the number differs significantly from the readings
obtained from a control tooth tested on the same patient with the electrode positioned at a similar area on both teeth
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY2020-2021
Laser Doppler Flowmetry
A diode is used to project an infrared light beam through the crown and pulp chamber of a tooth. The infrared light beam is scattered as it passes through the pulp tissue. The Doppler principle states that the light beam’s frequency will shift when hitting moving red blood cells but will remain unshifted as it passes through static tissue. The average Doppler frequency shift will measure the velocity at which the red blood cells are moving
This technology, however, is not being used routinely in the dental practice
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY2020-2021
Pulse Oximetry
The pulse oximeter is another noninvasive device Widely used in medicine, it is designed to measure the oxygen concentration in the blood and the pulse rate A pulse oximeter works by transmitting two wavelengths of light, red and infrared, through a translucent portion of a patient’s body (e.g., a finger, earlobe, or tooth). Some of the light is absorbed as it passes through the tissue; the amount absorbed depends on the ratio of oxygenated to deoxygenated hemoglobin in the blood. On the opposite side of the targeted tissue, a sensor detects the absorbed light. On the basis of the difference between the light emitted and the light received, a microprocessor calculates the pulse rate and oxygen concentration in the blood
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY2020-2021
Special TestsBite Test
Percussion and bite tests are indicated when a patient presents with pain while biting The tooth may be sensitive to biting when the pulpal pathosis has extended into the periodontal ligament space, creating a symptomatic apical periodontitis, or the sensitivity may be present secondary to a crack in the tooth..
A variety of devices have been used
for bite tests, including cotton tip applicators, toothpicks,
orangewood sticks, and rubber polishing wheels. There are
several devices specifically designed to perform this test.
The Tooth Slooth
As with all pulp tests, adjacent and contralateral teeth should
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY2020-2021
Test Cavity
The test cavity method for assessing pulp vitality is not rotinely used since, by definition, it is an invasive irreversible test. This method is used only when all other test methods are deemed impossible or the results of the other tests are inconclusive.
This is accomplished with a high-speed #1 or #2 round bur with proper air and water coolant. The patient is not anesthetized while this procedure is performed, and the patient is asked to respond if any painful sensation is felt during the drilling procedure. If the patient feels pain once the bur contacts sound dentin, the procedure is terminated and the class I cavity preparation is restored
If the patient fails to feel any sensation when the bur reaches the dentin, this is a good indication that the pulp is necrotic and root canal therapy is indicated.
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY2020-2021
Staining and Transillumination
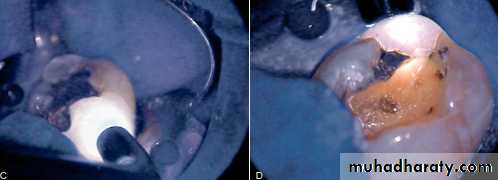
To determine the presence of a crack in the surface of a tooth, the application of a stain to the area is often of great assistance. It may be necessary to remove the restoration in the tooth to better visualize a crack or fracture. Methylene blue dye, when painted on the tooth surface with a cotton tip applicator, will penetrate into cracked areas. The excess dye may be removed with a moist application of 70% isopropyl alcohol. The dye will indicate the possible location of the crack.
Directing a high-intensity light directly on the exterior surface of the tooth at the cementum-enamel junction (CEJ) may reveal the extent of the fracture. Teeth with fractures block transilluminated light. The part of the tooth that is proximal to the light source will absorb this light and glow, whereas the area beyond this fracture will not have light transmitted to it and will show as gray by comparison
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY
2020-2021
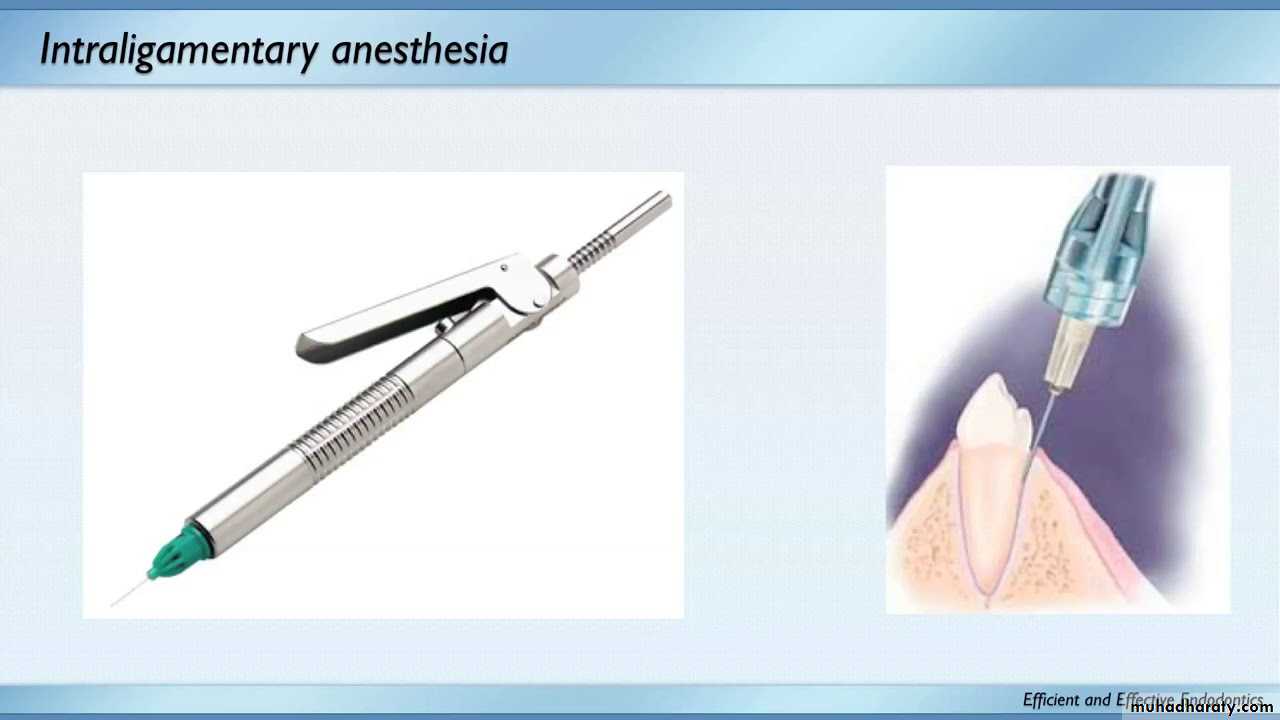
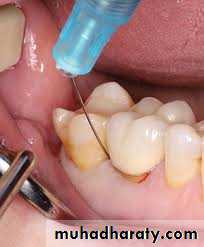
Selective Anesthesia
When symptoms are not localized or referred, the diagnosis may be challenging. Sometimes the patient may not even be able to specify whether the symptoms are emanating from the maxillary or mandibular arch. In these instances, when pulp testing is inconclusive, selective anesthesia may be helpful.
This should be accomplished by using a periodontal ligament (intraligamentary) injection. The injection is administered to the most posterior maxillary tooth in the quadrant of the arch that may be suspected, starting from the distal sulcus.
If the pain is not eliminated after an appropriate period of time, then the clinician should similarly repeat this
technique on the mandibular teeth below. It should be understood that periodontal ligament injections may anesthetize an adjacent tooth and thus are more useful for identifying the arch rather than the specific tooth
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY2020-2021
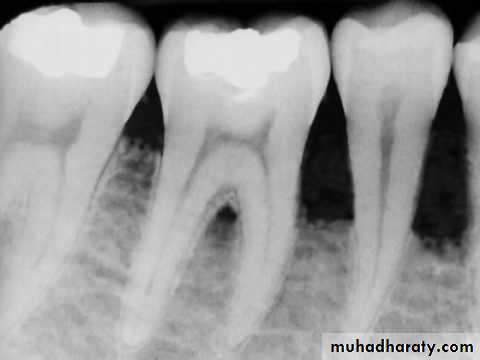
Radiographic Examination
The radiographic interpretation of a potential endodontic pathosis is an integral part of endodontic diagnosis and prognosis assessment.
For this reason, the clinician is sometimes tempted to prematurely make a definitive diagnosis based solely on radiographic interpretation
When not coupled with a proper history and clinical examination and testing, the radiograph alone can lead to a misinterpretation of normality and pathosis
The clinician should not subject the patient to unnecessary multiple radiation exposures; two pretreatment images from different angulations are often sufficient
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY2020-2021
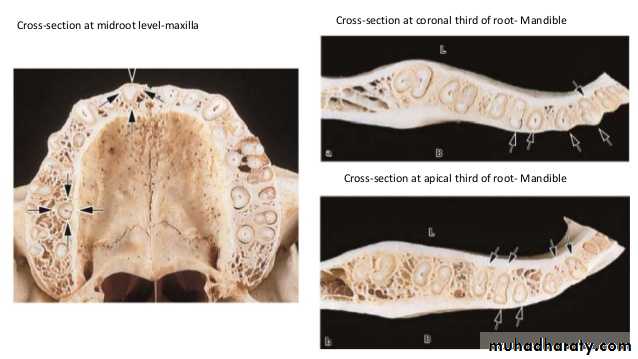
Variability in the radiographic expression of an osseous pathosis has much to do with the relative location of the root of the tooth and how it is oriented with respect to the cortical and cancellous bone
Radiographic changes from bone loss will not be detected if the loss is only in cancellous bone. However, the radiographic evidence of pathosis will be observed once this bone loss extends to the junction of the cortical and cancellous bone.
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY2020-2021
The apices of most anterior and premolar teeth are located close to the cortical-cancellous bone junction.
Therefore, periapical pathosis from these teeth is exhibited sooner on the radiograph
In addition, certain teeth are more prone to exhibit radiographic changes than others, depending on their
anatomic location
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY2020-2021
By comparison, the distal roots of mandibular first molars and both roots of mandibular second molars are generally positioned more centrally within the cancellous bone, as are maxillary molars, especially the palatal roots Periapical lesions from these roots must expand more before they reach the cortical-cancellous bone junction and are recognized as radiographic pathosis
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY2020-2021
For these reasons, it is important not to exclude the possibility of pulpal pathosis in situations in which there are no radiographic changes