Neonatology
ByDr. adnan Al-Rikabi
Definition of terms :
The normal human gestational period is 280 days or 40 weeks , calculated from the first day of the mother last menstrual cycle .a - Preterm gestation refers to delivery at less than 37 wks gestation .
b- Term gestation refers to delivery at 38 to less than 42 wks gestation .
c -Post term gestation refers to delivery at or after 42 wks gestation .
The neonatal period is defined as the first 28 days ( 4 wks) of life for term infant , although , from a practical standpoint it is extended in the case of prematurely delivered infant.
Fetal and neonatal growth :
A -Fetal growth,The fetal growth rate is 5 g /day at 14-15 wks gestation, 10 g/day at 20 wks and 30 g/day at 32-34 wks. The growth rate slows after 36 wks gestation.
B- Neonatal growth :
(1)- after birth , there is a loss of weight due to a loss of extracellular water and suboptimal caloric intake . term infant lose 5% of their birth weight , preterm infants lose up to 15% of their birth weight .
(2)- term infant regain their birth weight by the end of the first week of life and thereafter gain 20-30 g/ day .
Dilevary room management of the newborn
A - Goals .the goals of delivery room management are to assess and promptly attend the immediate needs (e.g oxygenations, ventilations ) and potential problems (e.g serious anomalies ) of the newborn .
B -Physical layout and equipment . the newborn resuscitation are should be in immediate proximity to the delivery room . it should have adequate lighting and space for personal and equipment for resuscitation, including a bed with a radiant warmer .
C -Preparation for delivery .
Obtaining perinatal information .the pediatrician must have specific information concerning the mother and the fetus to prepare for routine care of the mother and newborn as well as treatment of specific problems related to a particular delivery ,
Obstetric history
Should include all information that may be pertinent to the immediate fetal conditions .the information is best obtained from the obstetrician and the medical chart and by direct communication with parents .important issues are : ( maternal age , medical and previous obstetric history , length of gestations , blood group incompatibilities , maternal infections , maternal drug use , ultrasound evaluations of fetal growth and amniotic fluid volume or congenital anomalies , signs of chorioamnionitis including prolonged rupture of fetal membrane ,maternal fever , and leukocytosis ).Labor history
Should include ( fetal heart tracing , duration of fetal membrane rupture , evaluation of amniotic fluid (color and quantity ), progress of labor and fetal blood PH.
Composition of the resuscitation team
Personnel and their tasks vary with type of delivery that is anticipated .high risk deliveries include (maternal diabetic , RH and ABO incompatibility , preterm delivery at less than 37 wks ,post term delivery at more than 42 wks , multiple gestations ,maternal bleeding , severe pre eclampsia ,IUGR, fetal anomalies , breech presentations , cesarean delivery , fetal distress ) .So high –risk team include
Team leader to direct resuscitation and direct and institute airway management .One to assess heart rate and to initiate cardiac compression if needed .
One to assess with drying , suctioning , ventilation ,and prepare drugs for injection .
One to gain intravenous access and to administer drugs .
Equipment for resuscitation include
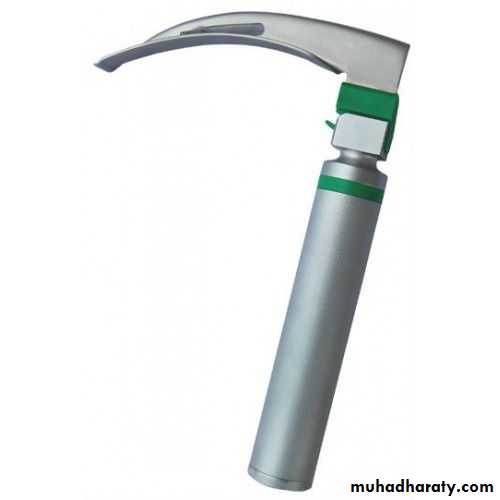
Airway management (suction pump with regulator ,DeLee suction catheter , oral airway with deferent sizes ,endotracheal tubes , laryngoscope , suction catheter .Ventilations and oxygenations ( oxygen source , mask of deferent sizes , bag with oxygen reservoir ) .
Intravenous access ( umbilical catheter 3.5 F and 5 F ,instruments for umbilical cut down , saline solution 0.9% .
Drugs like (epinephrine , plasma volume expander , sodium bicarbonate or naloxone ) .
Assessment of the newborn and the APGAR score .
The goal of the initial assessment is to determined the newborn state of oxygenation and ventilation. this is usually done by performing an abbreviated APGAR evaluation.APGAR SCORE
SIGNS
SCORES
0
1
2
HEART RATE
ABSENT
<100 BEATS/M
>100BEATS/M
RESPIRATORY EFFORT
ABSENT
WEAK,IRREGULAR
STRONG,REGULLAR
MUSCLE TONE
FLACCID
SOME FLEXION
WELL FLEXED
RESPONSE TO CATHETER IN NOSTRIL
NO RFESPONCE
GRIMACE
COUGH OR SNEEZE
SKIN COLOR
BLUE ,PALE
BODY PINK EXTREMETIES BLUE
ENTIRE BODY PINK
AThePGAR evaluation
Is performed at one and five minutes after birth .
Five signs – heart rate ,respiratory effort ,muscle tone ,reflex irritability and skin color __are examined and assigned a score of 0, 1, 2. The APGAR score is obtained by adding all individual scores .
A score of 8-10 reflect good oxygenation and ventilation and indicates no need for vigorous resuscitation .
A score 5-7 indicate a need for stimulation and supplemental oxygen .
A score lees than 5 indicates a need for assisted ventilation and possible cardiac support .
The apgar score
Is a useful method of communicating the well-being of the newborn .however urgently needed resuscitation should not be delayed while a full examination Is performed . bradycardia or poor respiratory effort alone indicate a need for immediate resuscitation .The apgar score at five minute reflects the adequacy of resuscitation and the degree of perinatal asphyxia and predict next futures sequel .
Resuscitation .
The purpose of resuscitation is to re-oxygenate the CNS of the newborn by providing oxygen , establishing ventilation , and ensuring an adequate cardiac output . although it may be difficult to differentiate primary apnea from secondary apnea , a quick assessment of the newborn skin color , respiratory activity , and heart rate should allow prompt institution of appropriate resuscitation .Routine procedures
• The evaluation and procedures that constitute the resuscitation of the newborn are listed in the order in which they should be initiated .A -Maintenance of body heat . the infant should be dried and provided with radiant heat to maintain body temperature . it is important to avoid hypothermia , which will increase the newborn oxygen consumption .
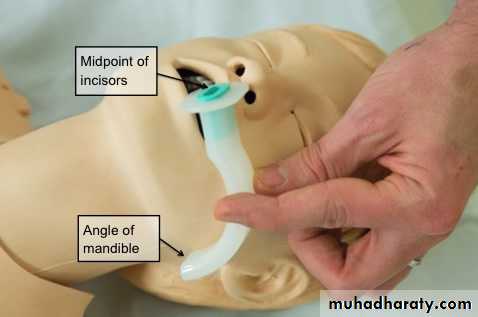
B -Establishment of an airway . immediately after delivery , the infant head should be placed in a neutral or slightly extended position and an airway established by clearing the mouth , nose and pharynx of thick secretion or meconium . deep and frequent oropharyngeal suctioning should be avoided because it will increase the vagal output causing apnea and bradycardia .
C -VENTILATION
If ventilation is adequate , supplemental oxygen may be given to improve heart rate or skin color .If supplemental oxygen does not improve heart rate or skin color , or if ventilation is inadequate , mechanical ventilation should be initiated , using mask and bag ventilation .
If spontaneous ventilation improves ,mechanical ventilation should be stopped and supplemental oxygen resumed .
If the response is poor or if airway obstruction occurs ,an endotracheal tube should be inserted and mechanical ventilation continued .
D- Circulation .
If mechanical ventilation does not improve the heart rate or skin color one of the following steps taken .
(1)- If heart rate is less than 60beats b/min or between 60 and 80 beats / min and not improving ,cardiac compression is initiated over the lower third of the sternum at a rate of 90 compression /min , the ratio of compression to ventilation is 3:1(90 compression , 30 breath ) if heart rate not improve , epinephrine is administered via an umbilical venous catheter or endotracheal tube .
(2)- If heart rate is 80 beats /min or greater but there is poor perfusion or weak pulse , a plasma volume –expanding agent is administered at a dose of 15 ml / kg .
E -Drug support .
The following drugs may be useful during resuscitation .Sodium bicarbonate (2 mEq/kg ) should be reserved until it is clear that a metabolic acidosis exists .
Naloxone (0.1mg/kg) may be helpful for poor spontaneous respiratory effort secondary to maternal narcotic use during labor . Naloxone is contraindicated in an infant born to mother who is addicted to narcotics .
Dopamine (5-20 ug/kg/min) improve myocardial function .