UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
Orthodontic study models are essential diagnostic records, which help to study the occlusion and dentition from all three dimensions
Study Models
The importance of study models
1. They are the only three dimensional records of the patient's dentition.
2. Occlusion can be visualized from the lingual aspect.
3. They provide a permanent record of the intermaxillary relationships
5. They serve as a reminder for the parent and the patient of the condition present at the start of treatment.
6. In case the patient has to be transferred to another clinician, study models are an important record.
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
The study models can be divided into two parts :
• The anatomic portion
• The artistic portion
- The anatomic portion is that part which is the actual impression of the dental arch and its surrounding soft tissue structures. This is the part, which must be preserved when trimming the model.
- The artistic portion is the stone base supporting the anatomic portion.
Parts of the study models
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
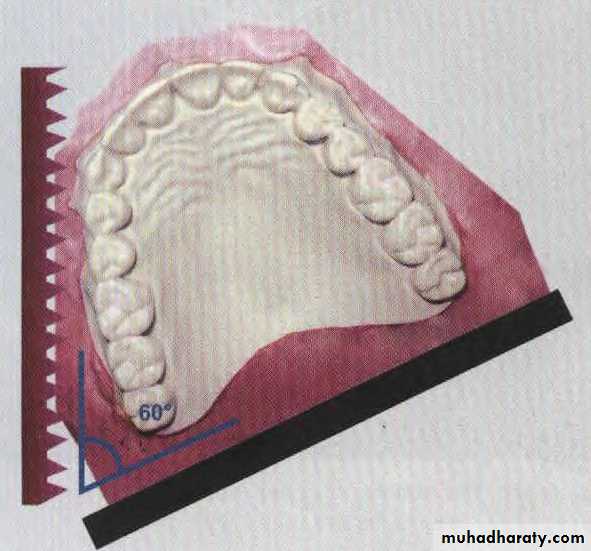
Trim lower base parallel to occlusal plane
Trim lower back perpendicular to base
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
With models in occlusion, trim upper back so it is flush with the lower back
Place upper model (on its back) on the model trimmer. Trim until the top base is flat
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
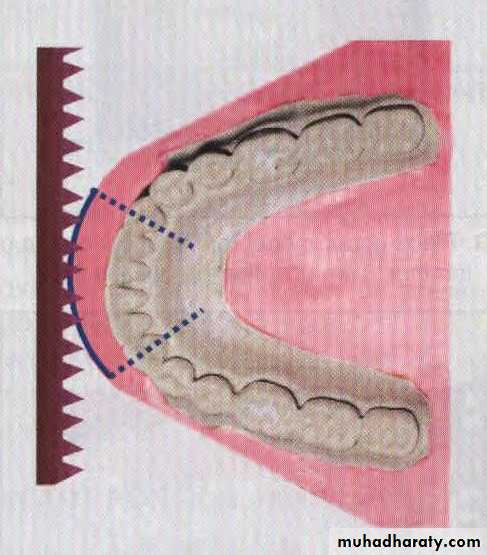
Make buccal cuts, at the edge of the vestibule
Make a smooth curve from canine to canineUNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
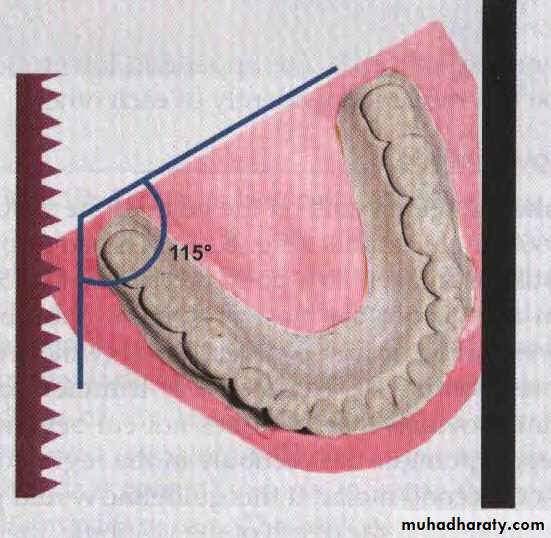
Extreme position to make the heel
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
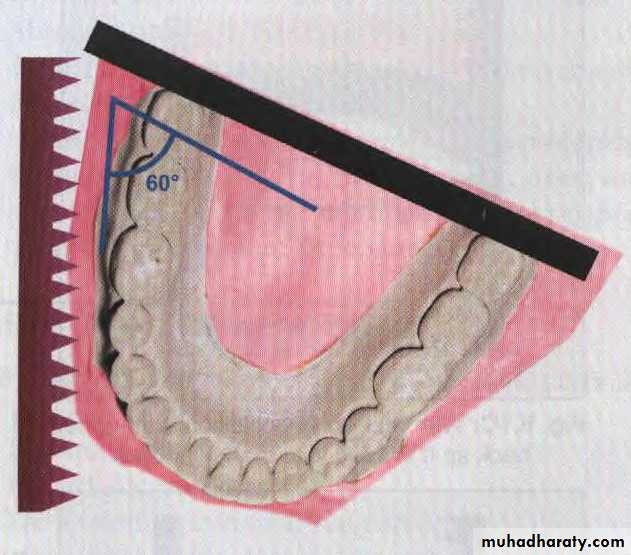
Make buccal cuts. at the edge of the vestibule 60° to back of the model
Occlude models. Trim upper heels so they are flush with lower heelsUNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
Make anterior cuts. the ends of which should be at the midline and the middle of each canine
Occluded models should have a sharp 90° angle between their base and back
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
Model analysis :
Pont's analysis
Linder harth index
Korkhaus analysis
Ashley Howe analysis
Bolton analysis
Moyer's mixed dentition analysis
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
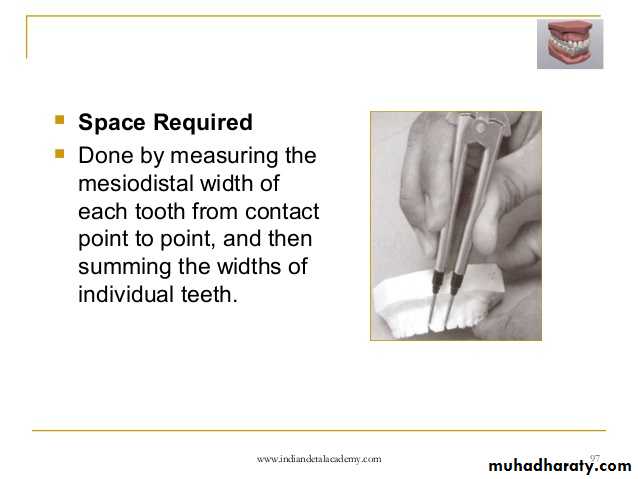
Tooth Size-Arch Length Relation
The crowding that exists in the adult dentition or the crowding that is predicted in a mixed dentition is recorded on the clinical form.
It requires a comparison between the amount of space available present in the dental arch, and space required to align the teeth properly.
The analysis done directly on the dental cast or computer after appropriate digitization of the arch and teeth dimensions.
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
The crowding that exists in the adult dentition or the crowding that is predicted in a mixed dentition is recorded on the clinical form.
Tooth Size-Arch Length Relation
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
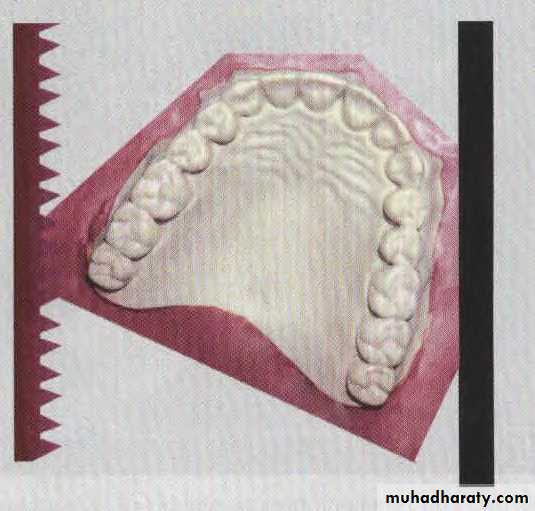
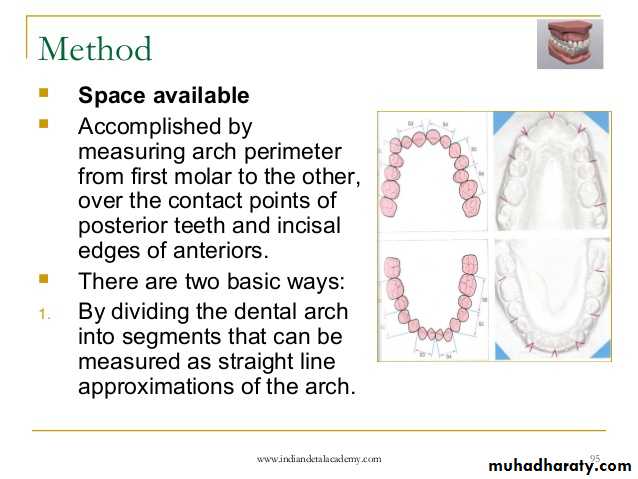
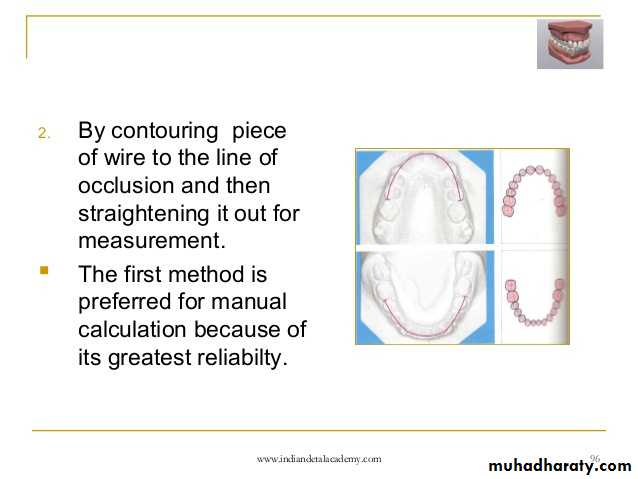
A- Arch length (perimeter) measurements, as segments
By dividing the arch into straight segments, measuring these segments are obtained with sharpened tips digital calipers . For the purpose of the analysis, only the arch length mesial to the permanent first molar is measured. The tips of the measuring instrument are placed in the buccal embrasures near the contact points between the teeth or on the alveolar ridge where the teeth are expected to contact one another in ideal alignment
space available
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
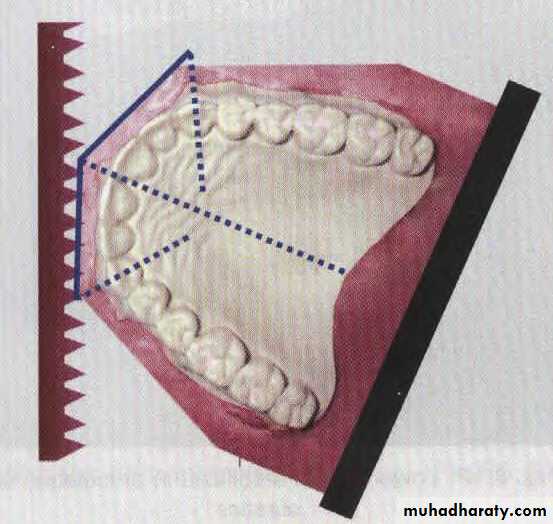
Measurements are done according to the following steps:
1. the posterior parts of the arch from the mesial contacts of the 1stmolar to the distal contact of the canines are measured.
2. the arch lengths around the canines are measured. These lengths are added to the lengths of the posterior segment.
3. The anterior segments extend from a point on the cast between the central incisors to the mesial contact points of the canines.
4. The sum of all these segments on both sides represents the arch length
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
Compare space required and space available to know arch length discrepancy.
Differences:
space required ( MD teeth width)
space available = (arch length)
0 – 2.5 mm - in this proximal stripping can be carried . out.
2.5 – 5 mm - extraction of 2nd premolar is indicated.Over 5 mm - extraction of 1st premolar is indicated.
Discrepancy
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
Many methods of mixed dentitions analysis have been suggested; mainly, directed to the sizes of the unerupted cuspids and premolars are estimated from measurements of the radiographic image
Measurement of tooth size arch length relationship in the mixed dentition
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
The purpose of a mixed dentition analysis is to evaluate the amount of space available in the arch for succeeding permanent teeth and necessary occlusal adjustments. Many methods of mixed dentitions analysis have been suggested
Moyer's mixed dentition analysis
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
1. Those in which the sizes of the unerupted cuspids and premolars are estimated from measurements of the radiographic image.
2. Those in which the sizes of the cuspids and premolars are derived from knowledge of the sizes of permanent teeth already erupted in the mouth.
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
The approach in measuring arch length in the mixed dentition is essentially the same as that described for the permanent dentition.
Measurement of the available arch length in the mixed dentition
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
In mixed dentition tooth size-arch length analysis depends on an accurate prediction of the mesiodistal widths of the unerupted permanent canines and premolars.
This analysis makes use of radiograph and cast to determine the width of unerupted teeth.
It based on principle if we measure an object on cast and radiograph, we can compensate the enlargement in the radiograph by equation:
Measurement of the space required in the mixed dentition
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
Real width of primary molar Real width of unerupted . premolar
ـــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــ = ــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــ
Apparent width of primary molar apparent width of unerupted . premolar
THE END
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY2020-2021