• The Liver & biliary system
• The Liver
• What is it ? It’s the largest gland of the body
• Completely surrounded by a capsule• Partially surrounded by peritoneum
• Functions:
• Bile secretion
• CHO, fat, and protein metabolism
• Heparin formation
• Remove waste
• Detoxifying toxins
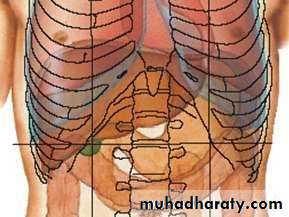
• Location :
• Rt upper abdomen
• Beneath diaphragm
• Under cover of Rt. Costal margin
• Under cover of Rt. Hemi diaphragm, which separates it from :
• Pleura
• Lungs
• Pericardium
• Heart
• Extends to under cover of Lt. hemi diaphragm
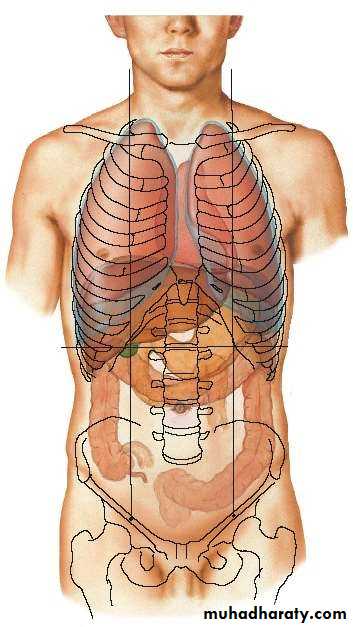
• SURFACES :
• 1. Antero-superior Surface• 2. Postero-inferior Surface
• S
• E• C
• Q
• K
• DU
• RCF
• Rt.
• Lt.
• G
• RSR
• B
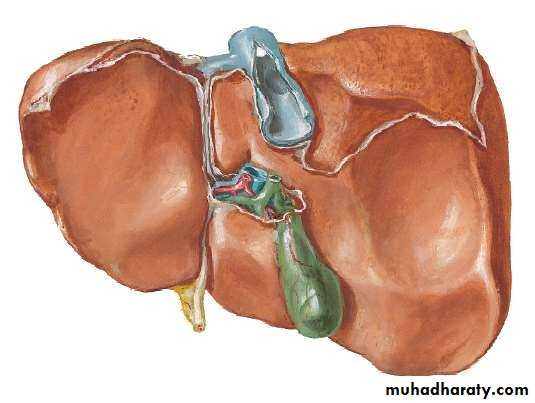
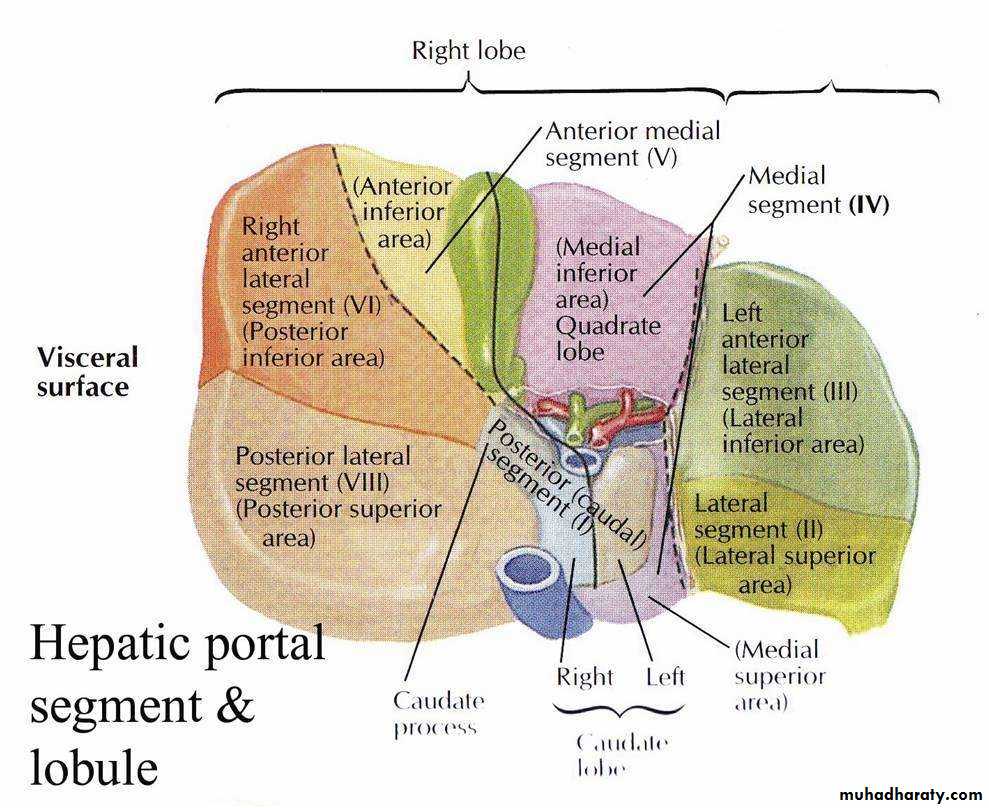
• LOBES OF LIVER
• By falciform ligament * its divided to :• 1. Right Lobe further subdivided to :
• Caudate Lobe (C)
• Quadrate Lobe (Q)
• 2. Left Lobe
• *
• Lt• Rt.
• C
• Q
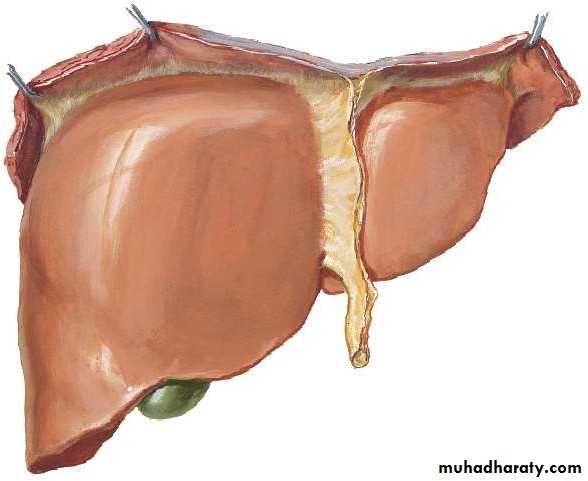
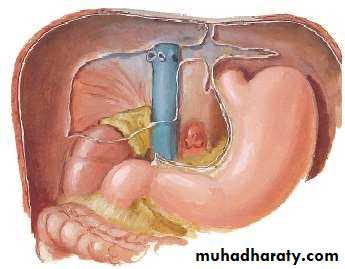
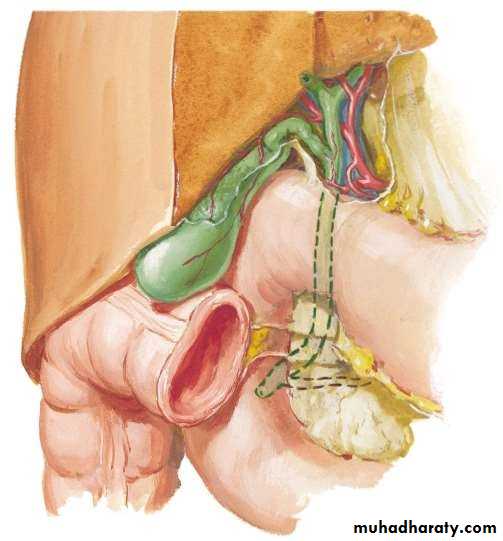
• PORTA HEPATIS( HILUM OF LIVER )
• At the visceral surface• Between C and Q
• Upper L. Omentum at margins
• Contents :
• Rt. & Lt. Hepatic ducts
• Rt. & Lt. branches of Hepatic artery
• Rt. & Lt. branches of Portal vein
• Sympathetic & Parasympathetics
• Hepatic LNs.
• RELATIONS:
• ANTERIORLY:• Diaphragm
• Rt. & Lt costal margins
• Rt. & Lt. pleura
• Lower margins of both lungs
• Xiphoid process
• Ant. Abdominal wall in subcostal angle
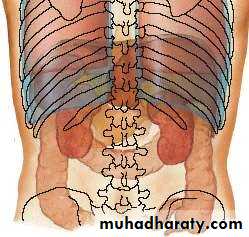
• POSTERIORLY:
• Diaphragm & pleura• Rt. & Lt. lungs
• Rt. Kidney
• Hepatic flexure of colon
• Duodenum
• Gallbladder
• IVC
• Esophagus
• Fundus of stomach
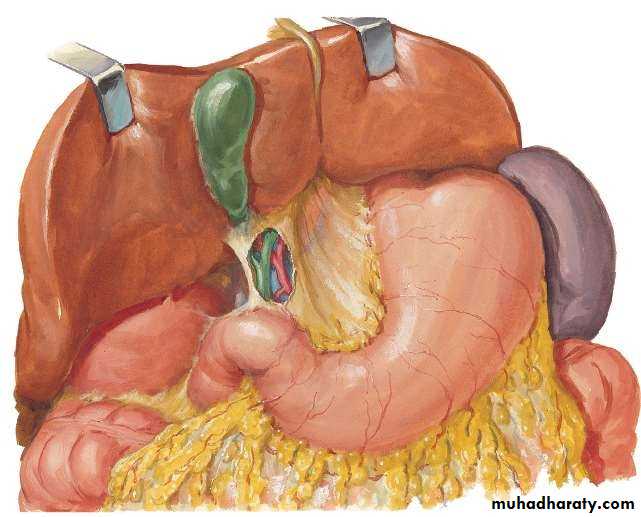
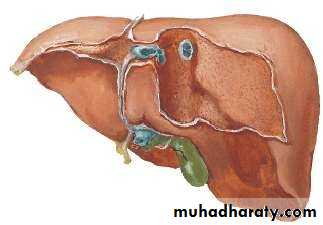
• PERITONEAL LIGAMENTS OF LIVER:
• Falciform ligament• Coronary ligament (upper & lower layers)
• Triangular ligament (Right & Left)
• Lesser omentum
• 1
• 2• 3
• 4
• 5. Ligamentum teres (Oblit. Lt. paraumb. v.)
• 6. Ligamentum venosum (Ductus venosus )• 5
• 5• 6
• what's Bare area?
• BARE
is a large triangular area on the diaphragmatic surface of the liver, devoid of peritoneal covering. It is attached directly to the diaphragm by loose connective tissue.• 1. ARTERIAL :
• Hepatic arteries, 30%
• 2. VENOUS :
• Portal vein, 70%
• Hepatic veins
• 3. LYMPHAICS :
• ½ of body lymph is formed by liver
• to LN in porta hepatis
• celiac nodes
• from bare area through
• diaphragm post. Mediastinal LNs.
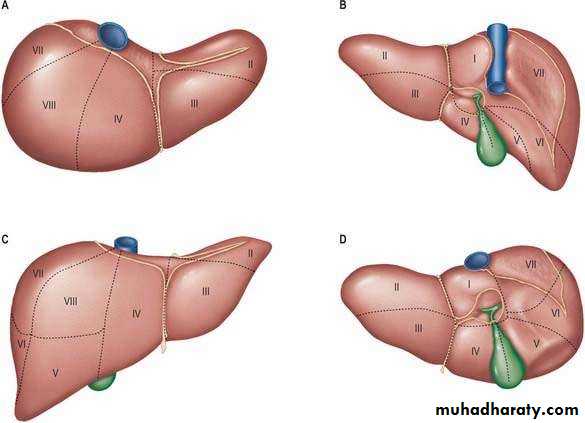
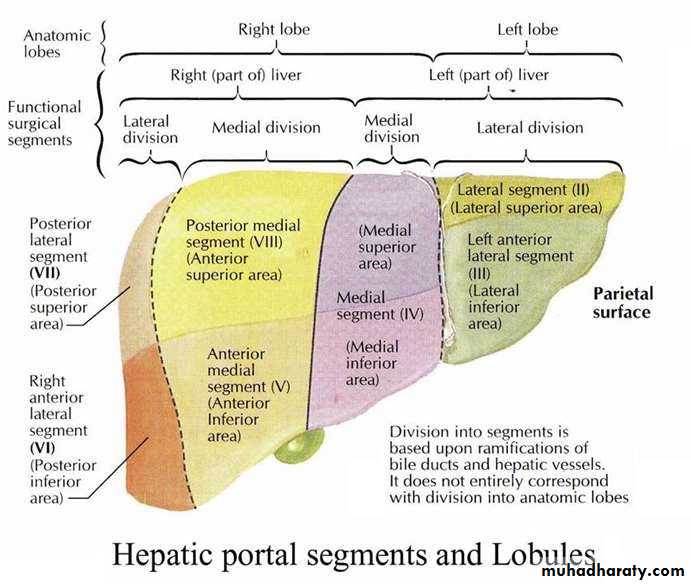
• Hepatic segments
• Left lobe
• 4. NERVE SUPPLY :• Symp. & Parasymp. from coeliac plexus
• Anterior vagal trunk gives a hepatic branch to liver.
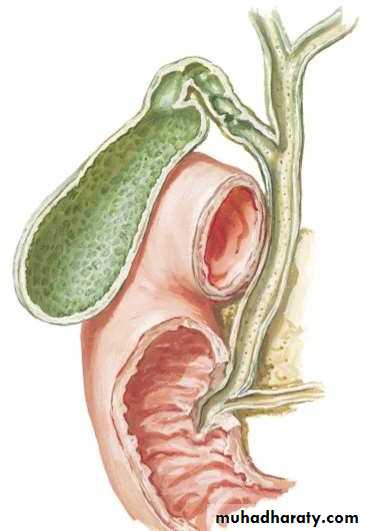
• BILIARY SYSTEM:
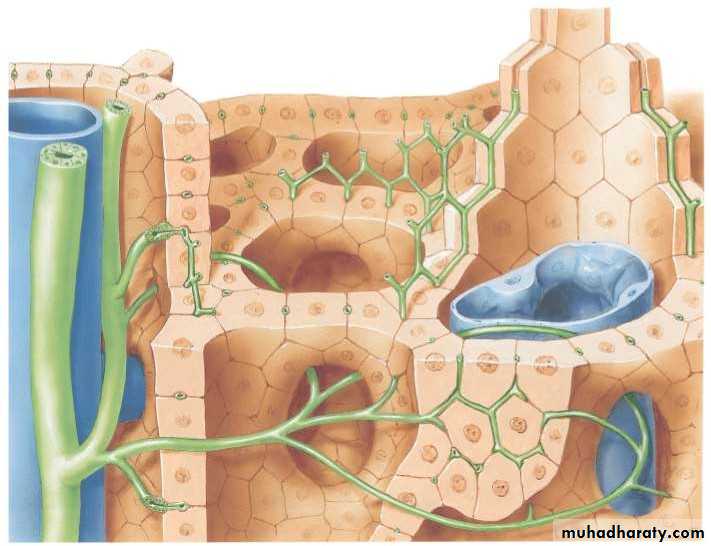
• Bile canaliculi
• H
• Interlobular ductules• Branch of portal vein
• Bile ducts• Periportal bile ductule
• INTRAHEPATIC BILIARY SYSTEM• EXTRAHEPATIC BILIARY SYSTEM Consists of :
• Rt. hepatic duct• Lt. hepatic duct
• Com. hepatic duct
• Cystic duct
• Com. Bile duct
• Gallbladder
• 3
• 4
• 5
• 6
• 3
• 4• 5
• 6
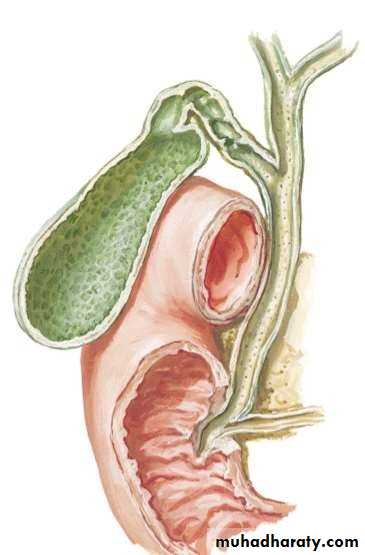
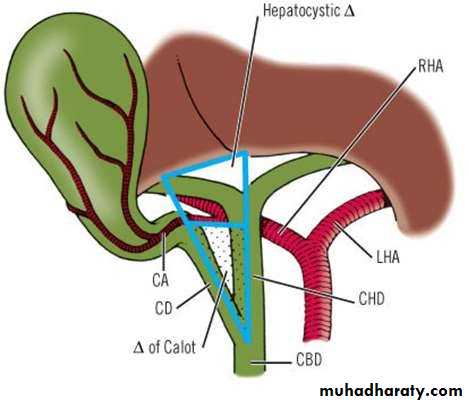
• HEPATIC DUCTS :
• Emerge from porta hepatis
• Rt. & Lt. HDs unite to form CHD
• CHD =4 cm
• CHD descend in lesser omentum
• Joined by cystic duct to form CBD
• 3
• 4• 5
• 6
• COMMON BILIARY DUCT:
• 8cm long
• 1st course (Lesser Omentum)
• 2nd course (behind 2nd Duo.)
• 3rd course ( post. To head of
• pancreas )
• 3
• 4• 5
• 6
• Hepatopancreatic ampulla of vater
• Major duodenal papilla
• Sphincter of Oddi
• GALLBLADDER:
• Under the liver• Stores 30-50 ml of bile
• Function
• Divided into :
• Fundus
• Body
• Neck
• 1
• 2• 3
• RELATIONS OF GALLBLADDER:
• ANTERIORLY:• Ant. Abdominal wall
• Inferior surface of liver
• POSTERIORLY:
• Transverse colon• 1st & 2nd duodenum
• BLOOD SUPPLY: ARTERIAL :
• Cystic artery• VENOUS :
• Cystic vein• LYMPHATICS :
• A cystic LN at the neck of GB• NERVES :
• Autonomic from coeliac plexus
• Cholecystokinin
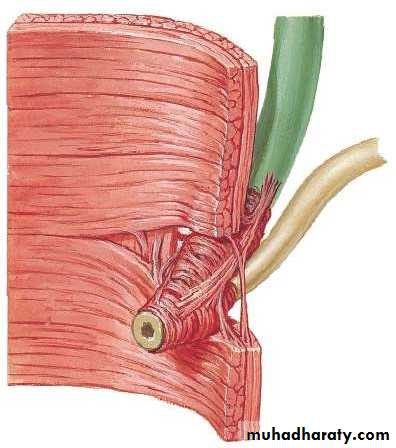
• CYSTIC DUCT
• 3.8 cm• Somewhat S shaped
• Its mucous membrane is forming a spiral fold
• ( the spiral valve )