Injuries of the spine
Spinal injuries carry a double threat : damage to the vertebral column and damage to the neural tissues. therefore it is important to establish whether the injury is stable or unstable and treating it as unstable until proved otherwise.
*Stable injury ; is one in which the vertebral components will not be displaced by normal movements ; if the neural elements are undamaged ,there is little or no risk of them becoming damaged.
*An unstable injury ; is one in which there is a significant risk of displacement and consequent damage to the neural tissues.
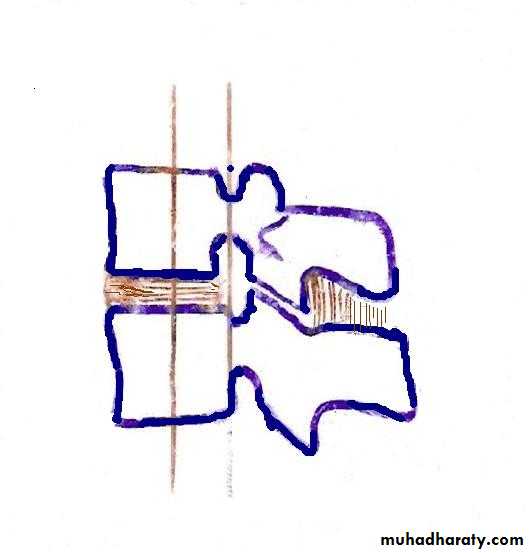
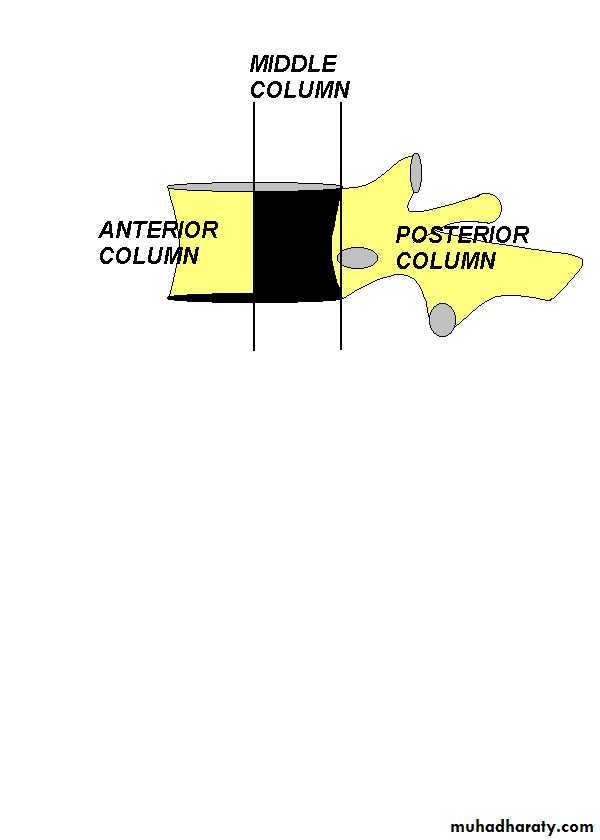
In assessing the stability of the spine, the spine is divided into three structural elements:
The posterior osseoligamentous complex (posterior column) consisting of the pedicles, facet joints, posterior bony arch,interspinous and supraspinous ligaments.
The middle column consisting of the posterior half of the vertebral body, the posterior part of the intervertebral disc and posterior longitudinal ligament.
The anterior column composed of the anterior half of the vertebral body ,the anterior part of intervertebral disc and the anterior longitudinal ligament.
.
All fractures involving the middle column and at least one other column should be regarded as unstable.
.
Mechanism of injury
Traction injury caused by resisted muscle contraction leading to avulsion of transverse process in the lumbar spine and the spinous process in the cervical spine.Direct injury caused by penetrating injury to the spine from knives other sharp objects .
Indirect injury this is the most common cause of spinal damage which typically occurs in a fall from height and in road traffic accident ,it caused by a variety of forces :
-axial compression ,flexion ,extension ,flexion-rotation ,flexion-distraction ,shear.
Early management
By resuscitation protocol (A,B,C)A: air way with cervical spine control.
B: Breathing with adequate ventilation and oxygenation.
C: circulation and hemorrhage control.
This also help to prevent secondary spinal cord injury.
And because spinal injury should be suspected in every patient with severe trauma ,the spine should be immobilized during the resuscitation ;
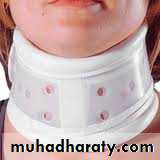
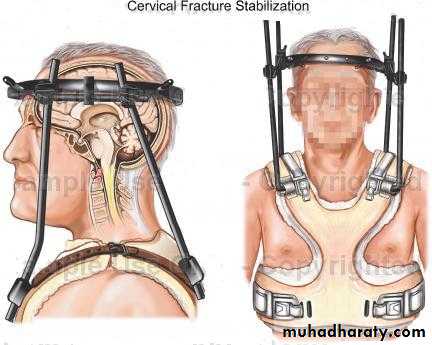
*for cervical spine by either in-line immobilization (the head and neck are supported in the neutral position) or by quadruple immobilization (by using a backboard, sandbags, a forehead tape and a semi-rigid collar).
*for Thoracolumber spine by scoop stretcher and spinal board .
Diagnosis
History : every patient with a blunt injury above the clavicle ,a head injury ,a loss of consciousness and neck pain and stiffness following trauma should be considered to have cervical spine injury until proven otherwise.
Every patient who involve in a fall from height ,high-speed deceleration accident or with back pain following trauma should be considered to have a Thoracolumbar spine injury. Any neurological symptoms in the limbs should rise the possibility of spinal injury.
Examination:
Neck ;look for any bruises in the head and face, any deformity or bruises or penetrating injury in the neck. Palpate the neck for any tenderness or increased space between spinous processes.Back ; look for any deformity,haematoma,bruises and penetrating injury. Palpate for any tenderness or increased space between spinous processes.
Shock ; three types of shock may occur in patient with spinal injury:
*Hypovolaemic shock, characterized by tachycardia and hypotension
*Neurogenic shock, result from loss of sympathetic innervations to the heart and blood vessels leading to hypotension,bradycardia and paralysis.
*Spinal shock, result from temporarily loss of spinal cord function following injury characterized by flaccid paralysis and loss of reflexes and sensation.
Neurological examination;
Imaging
X-ray :AP view including open mouth view ,lateral and oblique views.CT scan see the full extent of the fracture .
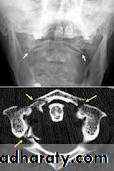
MRI show any disc ,cord and soft tissue damage.C1 Fracture (Jefferson’s fracture)
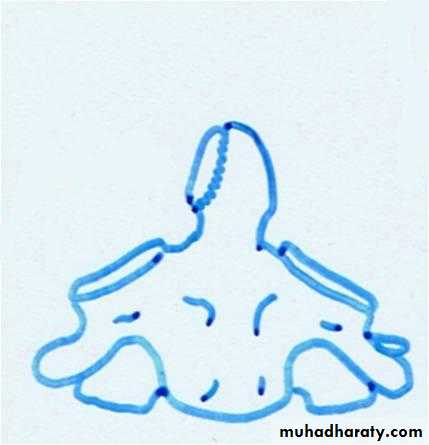
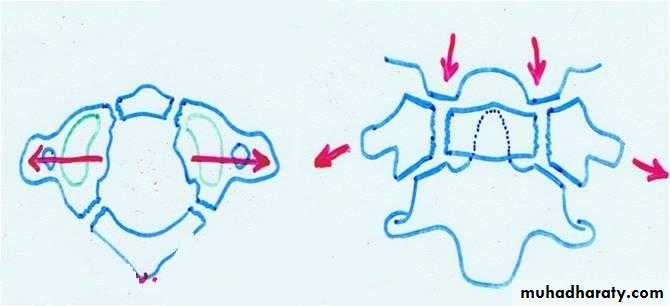
It is burst fracture of C1 ring*Mechanism of injury :sudden severe load on the top of the head leading to compression injury as in diving in a shallow water.
*Clinical features :severe neck pain ,stiffness, patient support his neck with his hands ,neck tenderness and usually no neurological damage.
*Imaging :x-ray mainly open mouth and CT scan reveal the fracture which could be undisplaced(stable) or displaced (unstable).
Jefferson’s #
*Treatment :
If the fracture undisplaced (stable) patient wear semi rigid collar or halo-vest until the fracture unites.If the fracture displaced then halo-vest for 6 weeks ,if there is persistent instability then a posterior C1/C2 arthrodesis.
Odontoid fracture (C2)
*Mechanism of injury :In young adult occur as flexion injury after high-velocity accident, in elderly osteoporotic people as hyperextension injury after low-energy accident.A displaced fracture is a fracture-dislocation of atlanto-axial joint in which the atlas is shifted forward or backward, taking the odontoid process with it.
*Clinical features : neck pain and stiffness from muscle spasm, neurological symptoms occur in 20% of cases.
classification :
Type I-An avulsion # of the tip of the odontoid process due to traction by the alar ligaments, the # is stable and unites without difficulty.Type II-A # at the junction of the odontoid process and the body of the axis, this is the most common &the most dangerous type, the # is unstable and prone to non-union.
.
Type III – A # through the body of the axis the # is stable & unites with immobilization.
*Treatment :
Type I # need immobilization in a rigid collar until discomfort subside.Type II # If undisplaced need halo-vest .Displaced # need reduction by traction &then held by either operative fixation or by halo-vest immobilization.
Type III # If undisplaced need halo-vest .Displaced # need reduction by traction then held by halo-vest immobilization.
Fractured pedicle(s) of C2 (Hangman’s fracture)
It is # of pedicle of C2 (axis) and damage of C1\C2 disc*Mechanism of injury:
Hyperextension with distraction ,in civilian injuries the mechanism involve varying degrees of extension, compression and flexion.
The # is potentially unstable but neurological damage is unusual because the # of the posterior arch tend to decompress the spinal cord.
*Treatment :
Undisplaced # which is stable ,treated in a semi-rigid collar or halo-vest for12 weeks.Displaced # need either closed reduction with halo-vest or ,if this fail, open reduction &internal fixation.