Back Pain
Examination, assessment, red flags,2020,Babylon collage of medicine
What factors are associated with development of low back pain?
Work that requires heavy lifting; bending and twisting; or whole-body vibration, such as truck drivingPhysical inactivity
Obesity
Arthritis or osteoporosis
Pregnancy
Age >30 years
Bad posture
Stress or depression
Smoking
Compression fracture
Associated with older age, white race, trauma, prolonged corticosteroid use
What serious underlying systemic conditions should clinicians consider?
• Nonskin cancer
Hx cancer: strongest risk factor for cancer-related back pain
Also: unexplained weight loss, no relief with bed rest, pain lasting >1 month, increased age
• Ankylosing spondylitis
≥4 of following: morning stiffness, decreased discomfort with exercise, onset of back pain before age 40, slow symptom onset, pain persisting >3 months
• Osteomyelitis
History of IV drug use, recent infection, fever
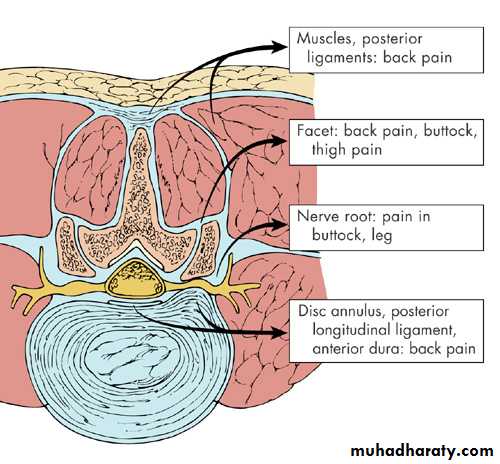
Causes of back pain 1
• Mechanical - Muscles and ligamentsLocal tenderness, muscle spasm, loss of lumbar lordosis, percussion tenderness over spinous process
NO MOTOR/SENSORY/REFLEXIC LOSS
Causes of back pain 1What factors should lead clinicians to suspect nerve root involvement?
• Consider if patient presents with back & leg painThe more distal the pain radiation, the more specific the symptom for nerve root involvement
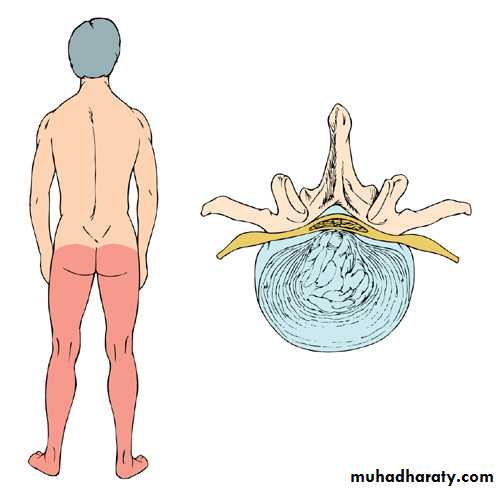
Pain that radiates from the back through the buttocks to the legs (sciatica) is common
Severe or progressive motor deficits warrant urgent evaluation (regardless of origin)
Symptoms of vascular claudication (not stenosis): leg pain with exertion, rather than with changes in position
Causes of low back pain 2
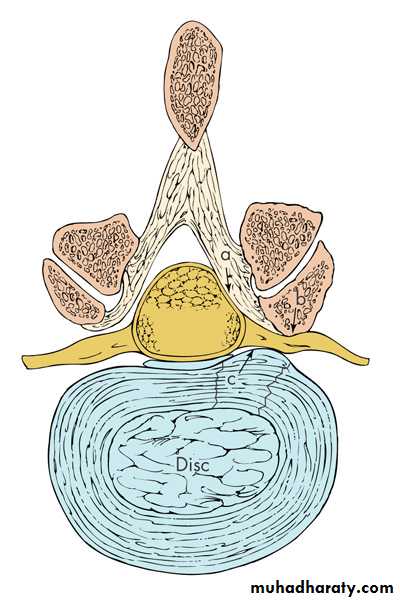
Radicular low back painHerniated intervertebral disc commonest cause but can be foraminal stenosis sec. OA / tumours / infection (rare)
TOP TIP not all pain referred down leg is sciatica (facet joint disease / hip / SIJ / piriformis syndrome etc.)
Structures that cause nerve root compression
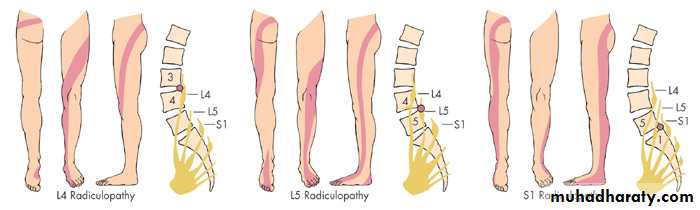
L4/L5/S1 Radiculopathy
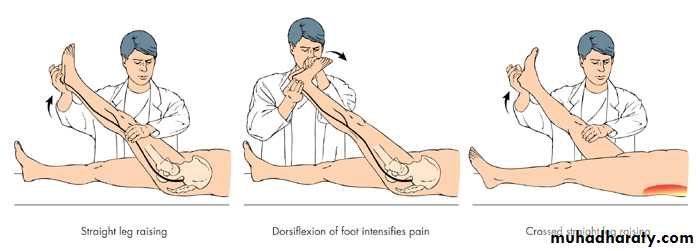
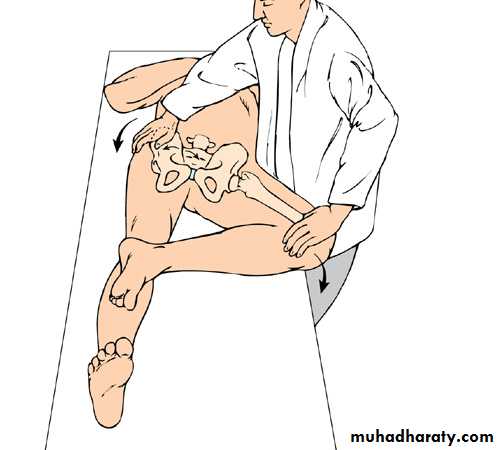
Straight Leg Raising
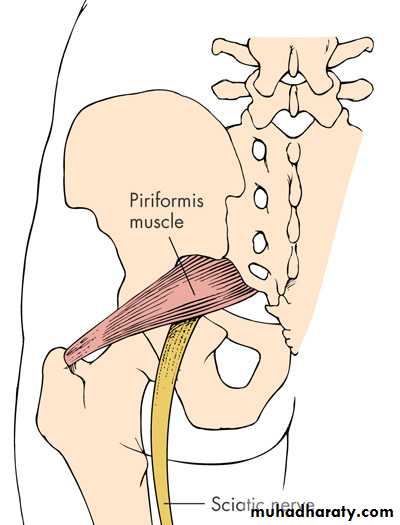
Piriformis syndrome
Pain from piriformis muscle – irritation of sciatic nerve passing deep or through it
Pain on resisted abduction / external rotation of legCauses of low back pain 3
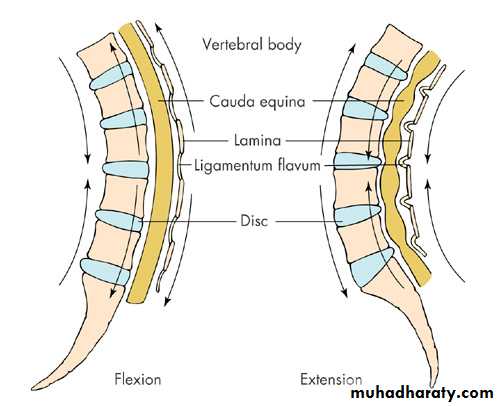
Lumbar Spinal StenosisSubtle presentation.
Bilateral radicular signs should alert to possibility.
Pain on walking- worse on flat –(eases if hunched over – shopping trolley sign!)
Can be mistaken for Claudication.
Admit if progressive / or else CT scan.
Cauda Equina syndrome (spinal canal compression)
Spinal Stenosis
When should clinicians consider imaging?
If history or physical suggests specific underlying causeNeurologic deficits are severe or progressive
Serious underlying conditions are suspected
If patients are candidates for surgery Persistent low back pain
Signs or symptoms of radiculopathy or spinal stenosis
Use MRI (preferred) or CT
Under what circumstances should clinicians consider electromyography and other laboratory tests?
Possible cancer but negative lumbar radiography
Check erythrocyte sedimentation rate: high elevation associated with presence of cancer
• Uncertainty about relationship of leg symptoms to anatomical findings on advanced imaging
Assess with electromyography and nerve conduction tests
• Possible myelopathy, radiculopathy, neuropathy, myopathy
Assess with electrophysiologic tests
Don’t test patients with duration of symptoms < 4 weeks
Radiculopathy or neuropathy: results might be unreliable in limb muscles until > 3 to 4 wks limb symptoms
Causes of low back pain 4
Inflammatory – Ankylosing Spondylitis
Difficult to diagnose if early stages but:
Morning stiffness for > 30 minutesPain that alternates from side to side of lumbar spine
Sternocostal pain
Reduced chest expansion
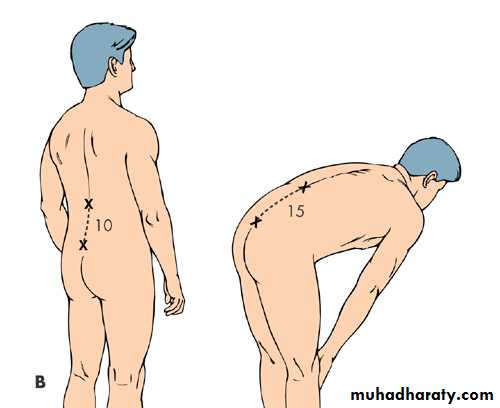
Schobers test
Schobers Test
Fabere test
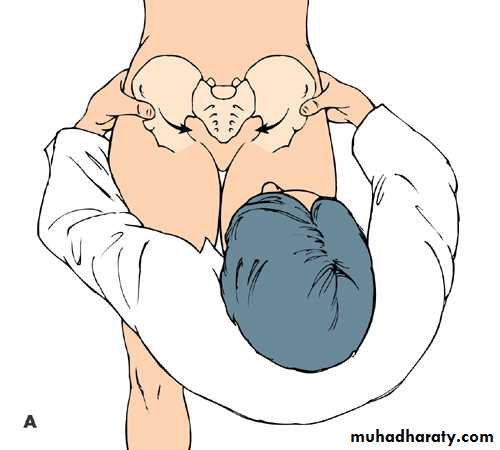
Pelvic Compression Test
Red Flags
Weight loss, fever, night sweatsHistory of malignancy
Acute onset in the elderly
Neurological disturbance Bilateral or alternating symptoms
Sphincter disturbance
Immunosuppression
Infection (current/recent)
Claudication or signs of peripheral ischaemia
Nocturnal pain
Yellow flags 1
Yellow Flags 2
Factors prolonging back painInternal factors-Opioid dependency
“External controller” patient-type; learned helplessness; factitious disorder
Mental health- depression or anxiety
Interpersonal factors "Sick role“
Stressors in relationships
Environmental / societal factors- Disability payments / Litigation / Malingering
Causes of back pain
Structural
MechanicalFacet joint arthritisProplapsed intervertebral discSpondylolysis / Spinal stenosis
Inflammatory
SacroiliitisSpondyloarthropathies
• Infection
• Metabolic
• Osteoporotic vertebral collapsePaget's diseaseOsteomalacia
• Neoplasm
• Ca Prostate
• Ca Breast
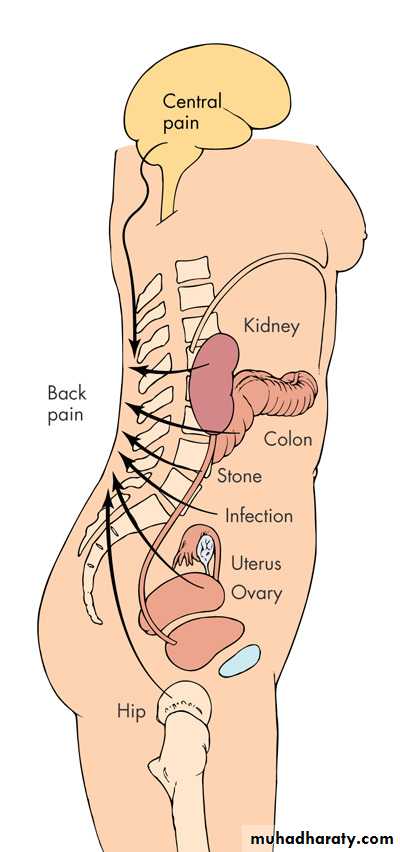
Referred pain
Pleuritic pain
Upper UTI / renal calculusAbdominal aortic aneurysm
Uterine pathology (fibroids)
Irritable bowel (SI pain)
Hip pathology
Imaging modalities
Xrays good first line Ix if red flags, osteoporotic fracture
Bone scan (also good initial Ix if Xray nad and red flags) - mets, infection, pagets, PMR
CT Scan bone tumours fractures and spinal stenosis
MRI spinal cord, nerve roots, discs, haemorrhage
Dexa Scan Bone density
TREATMENTS Simple Back Pain
(over 95% of cases)Aim: to relieve symptoms and mobilise early.
Avoid Bed rest
Paracetamol (+nsaid if insufficient)Avoid opiates if at all possible
No evidence that co-analgesics better than paracetamol alone.
Muscle relaxants (diazepam / methocarbamol) small additional benefit.
No evidence for:
Short wave diathermyTENS
Spinal manipulation
Traction
Acupuncture
Exercises
Spinal cortisone injections
Occupational issues
Occupational issues
More sick leave : Less chance of recovery4-12 w - 40% chance of still being off at 1 year.
Don’t need to be pain free to return to work
MDT Rehabilitation programs: psychological therapies; CBT; graduated return to work (light duties)
Blocks to returning to work (blue flags!)
perceived work loadlow pay
management attitudes
poor support
loss of confidence
depression
JD’s top tips for back pain.
Patient who attends a second time with “simple” back pain- get them to strip to their underwear!Top tips
True sciatica means that the leg pain is worse than the back pain- start examination with them sitting on the couch.