
Puberty and its disorders
By
Asmaa kadhim

Puberty
• is the process of reproductive and sexual development and maturation that
changes a child into an adult.
• During childhood, the HPO axis is suppressed and levels of GnRH, FSH and LH
are very low. From the age of 8–9 years GnRH is secreted in pulsations of
increasing amplitude and frequency.
• These are initially sleep-related, but as puberty progresses, these extend
throughout the day.
• This stimulates secretion of FSH and LH by the pituitary glands, which in turn
triggers follicular growth and steroidogenesis in the ovary.

• The oestrogen produced by the ovary then initiates the physical
changes of puberty.
• The exact mechanism determining the onset of puberty is still
unknown, but it is influenced by many factors including
race,
heredity,
body weight and exercise.
Leptin plays a permissive role in the onset of puberty.

The physical changes occurring in puberty
• breast development (thelarche),
• pubic and axillary hair growth (adrenarche),
• growth spurt and
• onset of menstruation (menarche).
• The first physical signs of puberty are breast budding and this occurs 2–3
years before menarche.
• The appearance of pubic hair is dependent on the secretion of adrenal
androgens and is usually after thelarche
• . In addition to increasing levels of adrenal and gonadal hormones, growth
hormone secretion also increases, leading to a pubertal growth spurt.

• The mean age of menarche is 12.8 years and it may take over 3 years
before the menstrual cycle establishes a regular pattern.
• Initial cycles are usually anovulatory and can be unpredictable and
irregular. The absence of menstruation is called amenorrhoea and
may be primary or secondary
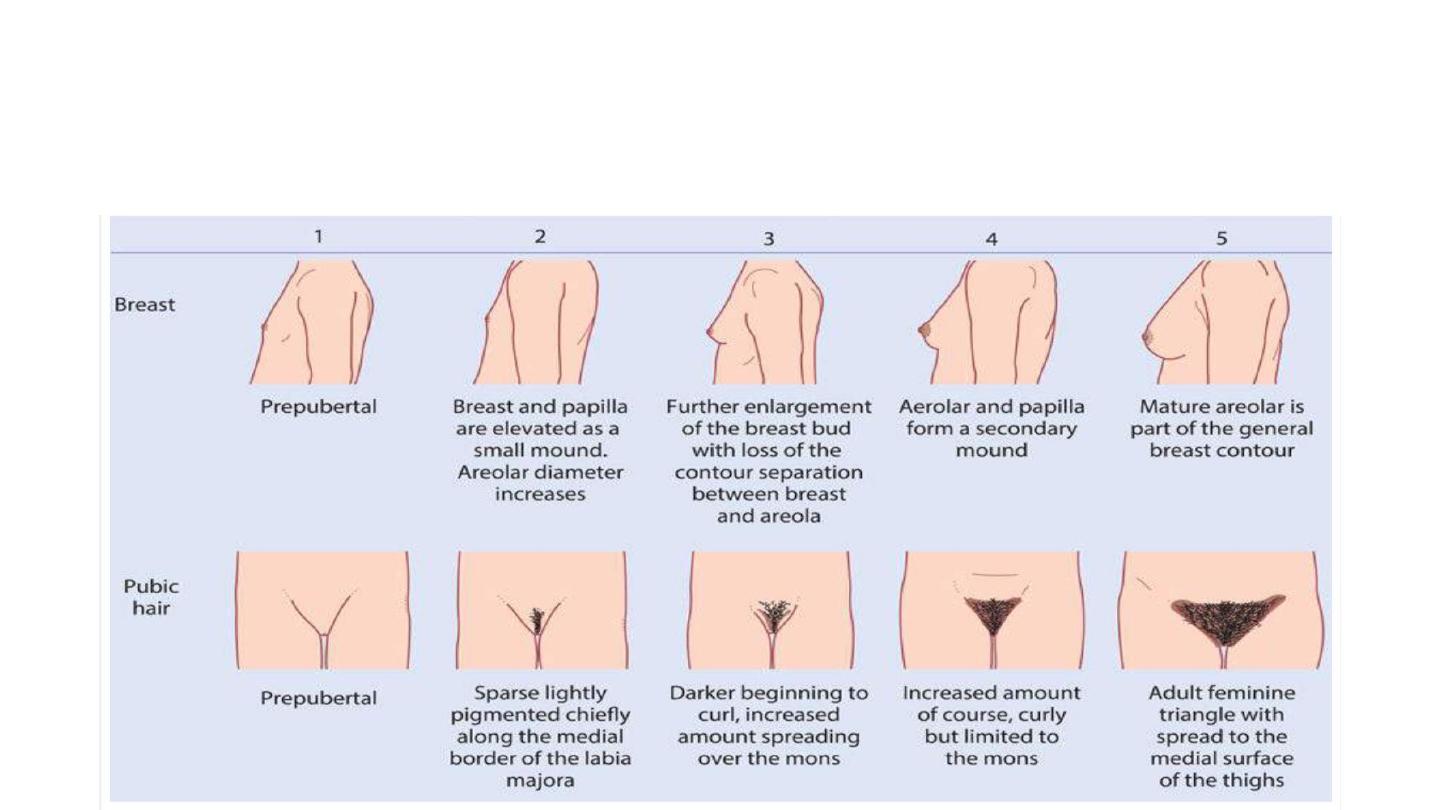
• Pubertal development was described by Tanner and the stages of
breast and pubic hair development are often referred to as Tanner
stages
Tanner staging

Precocious puberty
• Definition :
• the onset of puberty before the age of 8 in a girl or 9 in a boy.
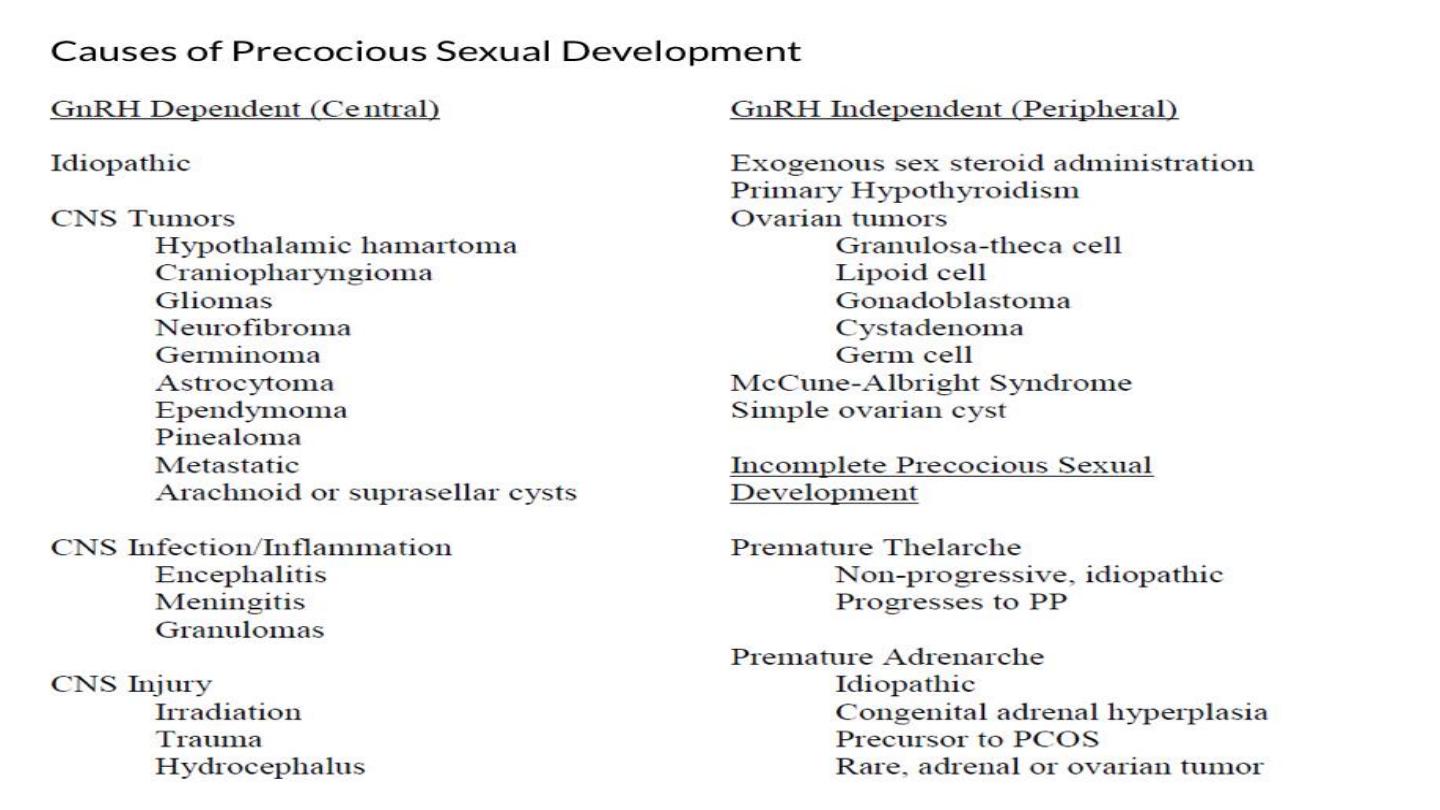
• Classification
• Central precocious puberty
• is gonadotrophin dependent.
• The aetiology is often unknown, although up to 25% are due to central
nervous system (CNS) malformations or brain tumours.

• Peripheral precocious puberty,
• which is gonadotrophin independent, is always pathological and can
be caused by oestrogen secretion, such as exogenous ingestion or a
hormone-producing tumour.

Evaluation of precocious puberty
• History
• Examination
• Investigation
•
Hormonal essay , FSH ,LH ,Estradiol
•
imaging (
•
x ray for bone age ,
•
CT , MRI for brain and pelvis
•
Ultrasound for abdomen and pelvis



Delayed puberty
• Delayed pubertyWhen there are no signs of secondary sexual
characteristics by the age of 14 years .
• It is due to either
• a central defect (hypogonadotrophic hypogonadism) or
• a failure of gonadal function (hypergonadotrophic hypogonadism),

Hypo- and Hypergonadotrophic
hypogonadism

Treatment

Thank you
