Blood Coagulation
ByDr-suroor mohamed
• Objectives1- what's mean by Coagulation or clotting process ?2- Describe the intrinsic pathway and extrinsic pathway .3-Role of Calcium Ions in the Intrinsic and Extrinsic Pathways , and the demanded vitamine( vitamin k)4- What are the bleeding disorder as HEMOPHILIA and von Willebrand disease:
Terms should be recognized..
Procoagulants or hemostatic agents are the substances which accelerate the process of blood coagulation. (chemical that promotes clotting)anticoagulant - chemical that inhibits clotting
A- intrinsic pathway - within the damaged vessel
B-.extrinsic pathway - in outer tissues around vessel
Coagulation or clotting is defined as the process in which blood loses its fluidity and becomes a jelly-like mass few minutes after it is shed out or collected in a container.
Cascade refers to a process that occurs through a series of steps, each step initiating the next, until the final step is reached
**The liver is the site of synthesis of all coagulation factors except VWF
Most of the clotting factors are proteins in the form of enzymes. Normally, all the factors are present in the form of inactive proenzyme. These proenzymes must be activated into enzymes to enforce clot formation. It is carried out by a series of proenzyme-enzyme conversion reactions. First one of the series is converted into an active enzyme that activates the second one, which activates the third one; this continues till the final active enzyme thrombin is formed.
In general, blood clotting occurs in three stages:
1.Formation of prothrombin activator
2.Conversion of prothrombin into thrombin
3. Conversion of fibrinogen into fibrin.
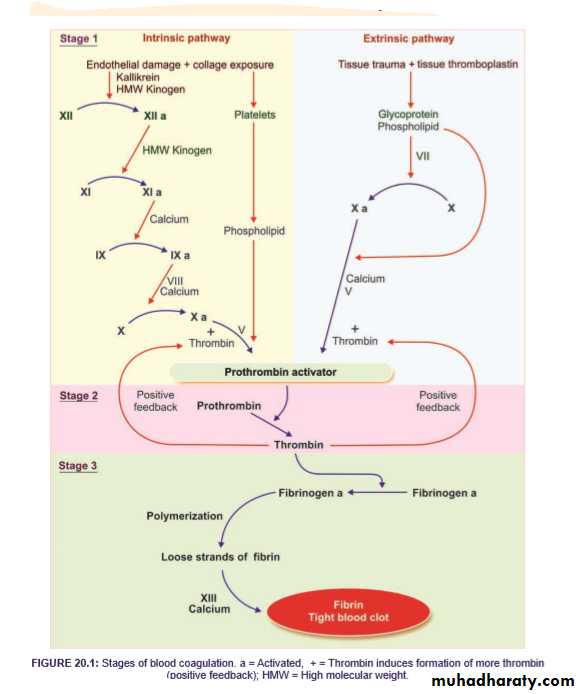
STAGE 1: FORMATION OF PROTHROMBIN ACTIVATOR
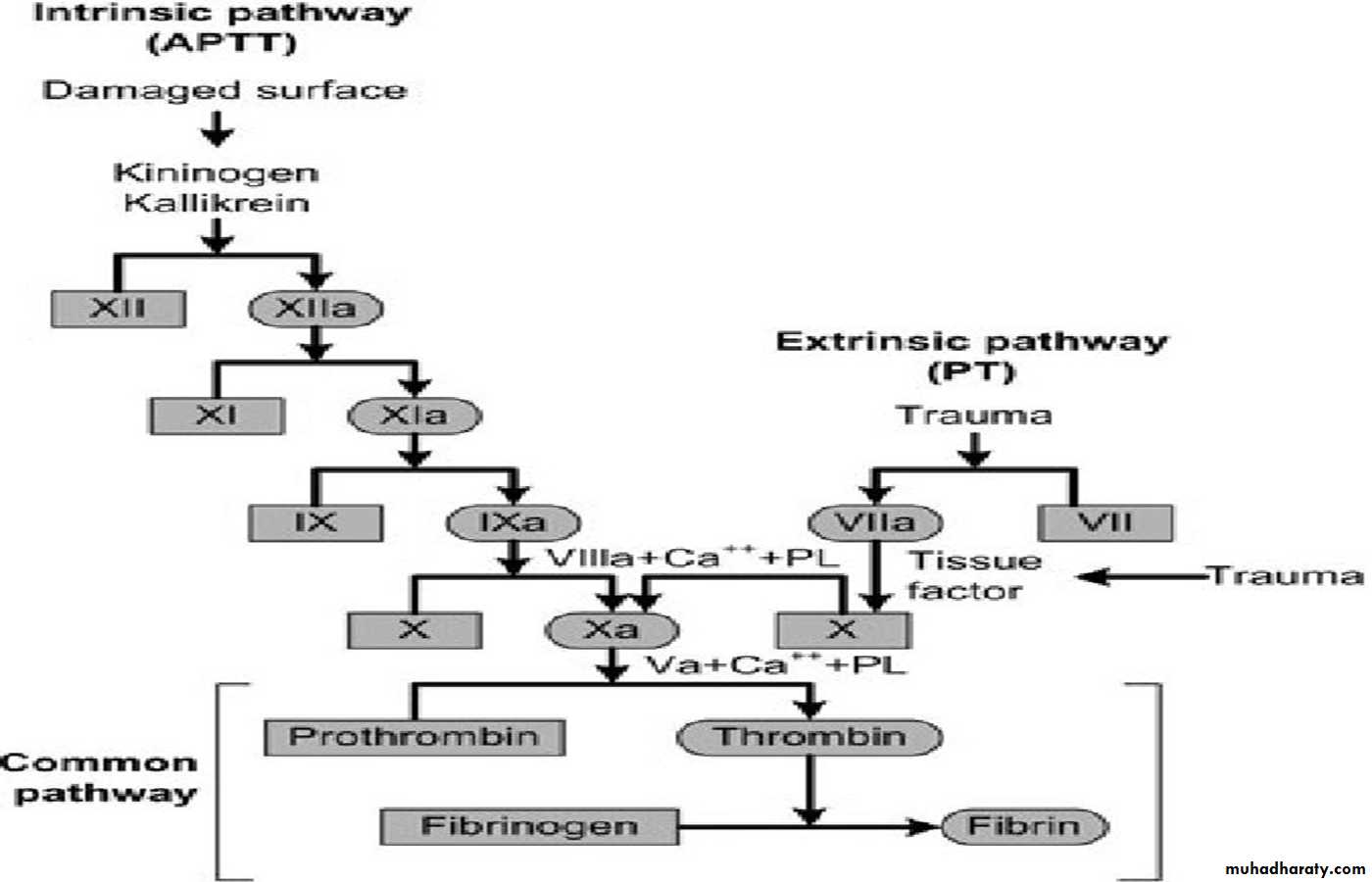
Blood clotting commences with the formation of a substance called prothrombin activator, which converts prothrombin into thrombin. Its formation is initiated by substances produced either within the blood or outside the blood. Thus, formation of prothrombin activator occursthrough two pathways: i. Intrinsic pathway ii. Extrinsic pathway.
• Intrinsic Pathway for the Formation of Prothrombin Activator is initiated by platelets, which are within the blood itself .
Sequence of Events in Intrinsic pathway
• During the injury, the blood vessel is ruptured. Endothelium is damaged and collagen beneath the endothelium is exposed.
• ii. When factor XII (Hageman factor) comes in contact with collagen, it is converted into activated factor XII in the presence of kallikrein and high molecular weight (HMW) kinogen.
• iii. The activated factor XII converts factor XI into activated factor XI in the presence of HMW kinogen.
• iv. The activated factor XI activates factor IX in the presence of factor IV (calcium).
• v. Activated factor IX activates factor X in the presence of factor VIII and calcium.
• vi. When platelet comes in contact with collagen of damaged blood vessel, it gets activated and releases phospholipids.
• vii. Now the activated factor X reacts with platelet phos pholipid and factor V to form prothrombin activa tor. This needs the presence of calcium ions.
• viii. Factor V is also activated by positive feedback effect of thrombin
ii. Extrinsic Pathway for the Formation of Prothrombin Activator is initiated by the tissue thromboplastin, which is formed from the injured tissues.
Sequence of Events in Extrinsic Pathway
• Tissues that are damaged during injury release tissue thromboplastin (factor III). Thromboplastin contains proteins, phospholipid and glycoprotein, which act as proteolytic enzymes.
• ii. Glycoprotein and phospholipid components of thromboplastin convert factor X into activated factor X, in the presence of factor VII.
• iii. Activated factor X reacts with factor V and phospholipid component of tissue thromboplastin to form prothrombin activator. This reaction requires the presence of calcium ions.
STAGE 2: CONVERSION OF PROTHROMBIN INTO THROMBIN
Blood clotting is all about thrombin formation. Once thrombin is formed, it definitely leads to clot formation.
Sequence of Events in Stage 2
• Prothrombin activator that is formed in intrinsic and extrinsic pathways converts prothrombin into thrombin in the presence of calcium (factor IV).
• ii. Once formed thrombin initiates the formation of more thrombin molecules. The initially formed thrombin activates Factor V. Factor V in turn accelerates formation of both extrinsic and intrinsic prothrombin activator, which converts prothrombin into thrombin. This effect of thrombin is called positive feedback effect
STAGE 3: CONVERSION OF FIBRINOGEN INTO FIBRIN
The final stage of blood clotting involves the conversion of fibrinogen into fibrin by thrombin.Sequence of Events in Stage 3
• Thrombin converts inactive fibrinogen into activated fibrinogen due to loss of 2 pairs of polypeptides from each fibrinogen molecule. The activated fibrinogen is called fibrin monomer.
• ii. Fibrin monomer polymerizes with other monomer molecules and form loosely arranged strands of fibrin.
iii. Later these loose strands are modified into dense and tight fibrin threads by fibrin-stabilizing factor (factor XIII) in the presence of calcium ions . All the tight fibrin threads are aggregated to form a meshwork of stable clot.
Role of Calcium Ions in the Intrinsic and Extrinsic Pathways
calcium ions are required for promotion or acceleration of all the bloodclotting reactions. in the absence of calcium ions, blood clotting by either pathway does not occur. . However, when blood is removed from a person, it can be prevented from clotting by reducing the calcium ion concentration below the threshold level for clotting, either by deionizing the calcium by causing it to react with substances such as citrate ion or by precipitating the calcium with substances such as oxalate ion.Red blood cells trapped in a fibrin mesh
TESTS FOR BLOOD CLOTTING
Blood clotting tests are used to diagnose blood disorders. Some tests are also used to monitor the patients treated with anticoagulant drugs such as heparin and warfarin.Bleeding time 2. Clotting time 3. Prothrombin time 4. Partial prothrombin time
5. International normalized ratio 6. Thrombin time.
BLEEDING TIME Bleeding time (BT) is the time interval from oozing of blood after a cut or injury till arrest of bleeding. Usually, it is determined by Duke method using blotting paper or filter paper method. Its normal duration is 3 to 5 minutes. It is prolonged in purpura.
CLOTTING TIME Clotting time (CT) is the time interval from oozing of blood after a cut or injury till the formation of clot. It is usually determined by capillary tube method. Its normal duration is 3 to 8 minutes. It is prolonged in hemophilia.
PROTHROMBIN TIME (PT)
is the time taken by blood to clot after adding tissue thromboplastin to it .Normal duration of prothrombin time is 10 to 12 seconds. It is prolonged in deficiency of prothrombin and other factors like factors I, V, VII and X. However, it is normal in hemophilia.( Extrinsic pathway) PARTIAL PROTHROMBIN TIME Or ACTIVATED PROTHROMBIN TIME a PTT
is the time taken for the blood to clot after adding an activator such as phospholipid, along with calcium to it. It is also called activated partial prothrombin time (aPTT). This test is useful in monitoring the patients taking anticoagulant drugs. Phospholipid serves as platelet substitute. Commonly used surface activator is kaolin. Its prolonged in Hemophilia ,( intrinsic pathway assess )
PTT: Factors XII, XI, IX, VIII PT: Factors VII, X, II, V
Bleeding time: a controlled incision is produced in the skin and bleeding commences. The time taken until bleeding ceases is measured. It assessed the platelets function .by ear prick 2mm depth which should be not more than 5 min. (2-5 is normal).More than 5 indicate plt dysfunction in the presence of normal plt count.
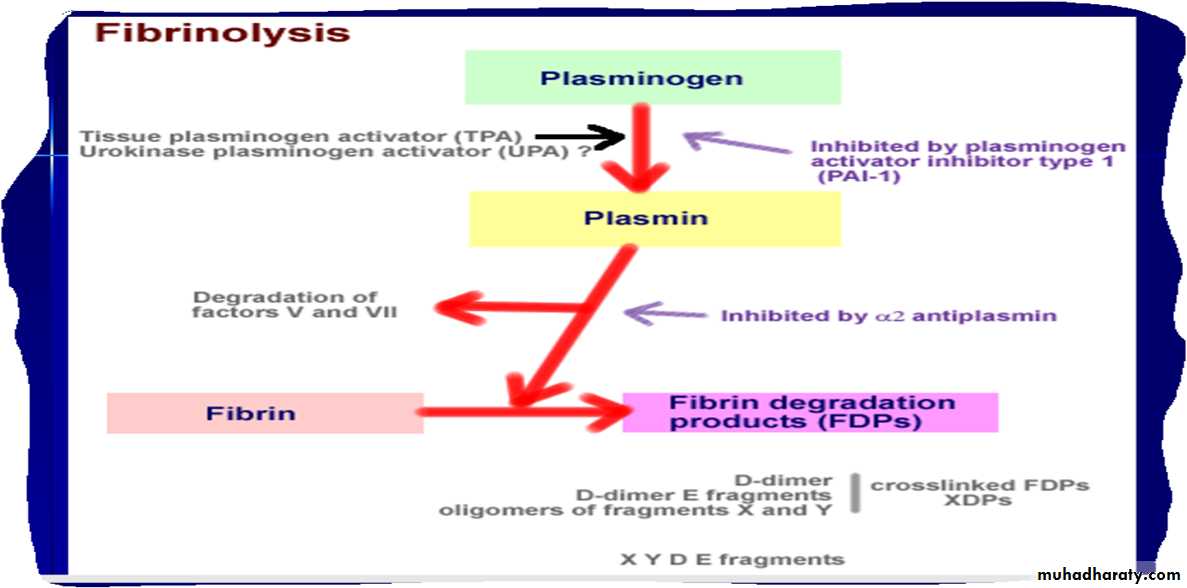
FIBRINOLYSIS
Degradation of fibrin clot by enzyme called plasminNecessary to remove clot so wound healing can proceed
Plasminogen activators from blood vessels and other cells convert plasminogen to plasmin to begin the process
Clot Eradication (Fibrinolysis)
1.healing occurs over 2 - 10 days
2.tissue plasminogen activator (TPA) - causes the activation of plasminogen
3.plasminogen--> plasmin
4.plasmin degrades proteins within the clot
VITAMIN K IS NEEDED FOR PRODUCTION OF SEVERAL CLOTTING PROTEINS
Fat-soluble vitamin present in many foods , Some made by bacteria in gutNecessary for synthesis of several components of coagulation cascade
Deficiency may lead to low levels of clotting factors, factors X, IX, VII, II, protein C and protein S. causing a bleeding tendency 1972
Warfarin (Coumadin™): a drug that interferes with vitamin K action , used as an anticoagulant (prevent thrombosis)
VITAMIN K DEFICIENCY
Newborn/premature infants
Poor intake
Defective absorption
generalized malabsorption
biliary disease
Diminished production by bacteria in gut (antibiotic treatment)
Vitamin K antagonists as warfarin (Coumadin)
certain antibiotics
INHERITED BLEEDING DISORDERS
Decreased production of single clotting factorHEMOPHILIA: complete absence of factor VIII (hemophilia A) or factor IX (hemophilia B)
sex-linked inheritance (99.99% of patients male) moderate or severe bleeding
Hemarthrosis (joint bleeding)
Haematoma A large bruise throughout the subcutaneous tissue or muscle (caused by extravasation into the perivascular tissue) resulting in changes in the colour and shape of the affected area. A haematoma may also be caused by a defect in the coagulation mechanism such as occurs in haemophilia, leukaemia or pathological fibrinolysis.
. Hemophilia Hemophilia is a group of sex-linked inherited blood disorders, characterized by prolonged clotting time. However, the bleeding time is normal. Usually, it affects the males, with the females being the carriers.
Because of prolonged clotting time, even a mild trauma causes excess bleeding which can lead to death. Damage of skin while falling or extraction of a tooth may cause excess bleeding for few weeks. Easy bruising and hemorrhage in muscles and joints are also common in this disease.
Causes of hemophilia
Hemophilia occurs due to lack of formation of prothrombin activator. That is why the coagulation time is prolonged. The formation of prothrombin activator is affected due to the deficiency of factor VIII, IX or XI.
Types of hemophilia Depending upon the deficiency of the factor involved, hemophilia is classified into three types:
. Hemophilia A or classic hemophilia: Due to the deficiency of factor VIII. 85% of people with hemophilia are affected by hemophilia A.
Hemophilia B or Christmas disease: Due to the deficiency of factor IX. 15% of people with hemophilia are affected by hemophilia B.
Hemophilia C or factor XI deficiency: Due to the deficiency of factor XI. It is a very rare bleeding disorder
Symptoms of hemophilia
i. Spontaneous bleeding. ii. Prolonged bleeding due to cuts, tooth extraction and surgery.iii. Hemorrhage in gastrointestinal and urinary tracts. iv. Bleeding in joints followed by swelling and pain v. Appearance of blood in urine.
Treatment for hemophilia Effective therapy for classical hemophilia involves replacement of missing clotting factor.
*von Willebrand disease: partial absence of von Willebrand factor
dominant inheritance mild or moderate bleeding
In this disorder there is either a reduced level or abnormal function of VWF resulting from a point mutation or major deletion. VWF is produced in endothelial cells and megakaryocytes. It has two roles.
1- It promotes platelet adhesion to damaged endothelium and
2- It is the carrier molecule for factor VIII, protecting it from premature destruction.
Three types of VWD have been described. Type 1 accounts for 75% of cases. VWD is the most common inherited bleeding disorder. Usually, the inheritance is autosomal dominant with varying expression.
The severity of the bleeding is variable , there is mucous membrane bleeding (e.g. epistaxes, menorrhagia), excessive blood loss from superficial cuts and abrasions.
Haemarthroses and muscle haematomas are rare, except in type 3 disease.
Laboratory findings …..The bleeding time can be prolonged.
Factor VIII levels are often low. If low, a factor VIII VWF binding assay is performed.
The APTT may be prolonged.
VWF levels are usually low.
Acquired Bleeding Disorder
Partial Absence of several clotting factorsLiver disease
Vitamin K deficiencyDisseminated Intravascular Coagulation & fibrinolysis (DIC)
Anticoagulant drugs: warfarin or heparin
Thrombolytic drugs (plasminogen activators)
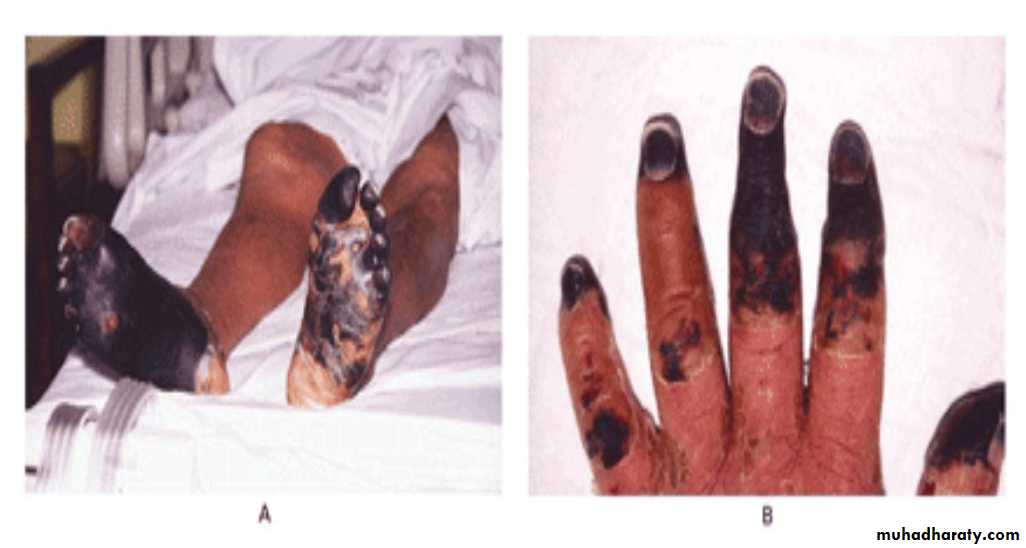
DISSEMINATED INTRAVASCULAR COAGULATION
Associated with many serious/lifethreatening diseasesCirculating blood exposed to excessive amount of tissue factor or other procoagulant
Breakdown of normal regulatory processes
Formation of circulating (soluble) fibrin
Consumption of clotting proteins and platelets
Accelerated fibrinolysis – clots break down too quickly
Bleeding and/or intravascular clotting in severe cases