
Pediatrics Breast Feeding Dr.Moayad
Objectives :
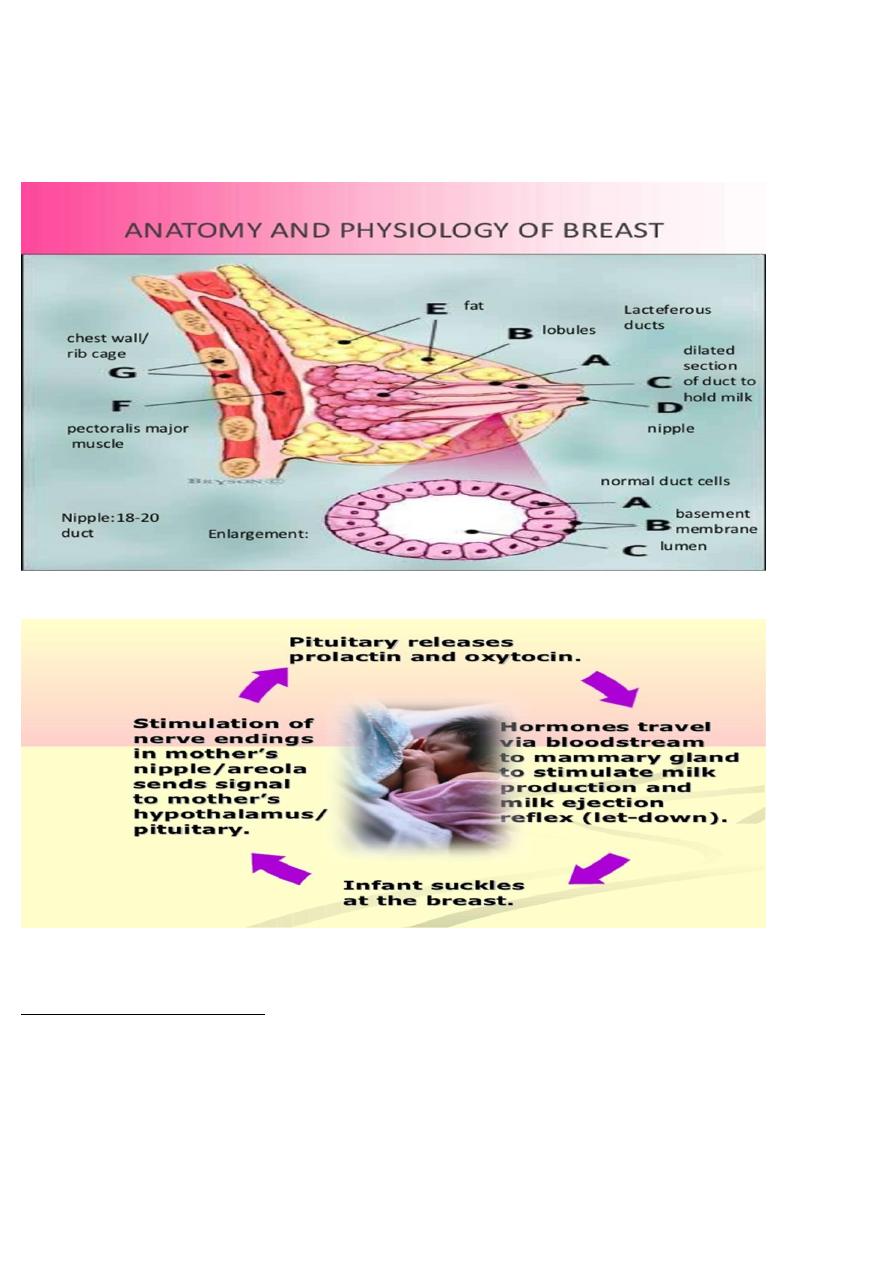
✓ To know the anatomy and physiology of breast feeding .
✓ To study the advantages of breast feeding to the infant,to the mother,and to the society.
✓ To understand the disadvantages of breast feeding.
✓ To learn the contraindications to breast feeding.
✓ To verify the let-down reflex .
✓ To explain the factors of successful br.feeding.
✓ To discuss the preparation of prospective mothering.
DEFINITIONS
—
Breast-feeding
Infant has received any breast milk, expressed or from breast
—
Exclusive breast feeging
Infant has received only breast milk and no other liquids or solids except vitamine supplements and
medicine
—
Predominant breast feeding
Breast milk the predominant source o f nourishmemt but other drinks (water, herbal drinks,
teas,…) may have been given
—
Full breast feeding
Exclusive or predominant breast feeding
Complementary feeding
• additional foods; solids; semi-solids; liquids including formula given to the breast-fed
infants.
• Bottle feeding
Infant has received liquid or semi-solid food from a bottle with a teat.
• Replacement food
Foods other than formula given to formula-fed infants
• Supplementary feeding
Infant has received formula or stored pumped breast milk after completion breast feeding when
mother go to work.
Physiology of Breast Feeding
At feeding time,baby touch mother breast → rooting reflex(opening the mouth in anticipation of
grasping the nipple) → contact of nipple with infant palate & post.tongue → suckling
reflex which squeeze the sinuses of the areola → milk in the mouth triggers swallowing reflex
Crying of baby, sight & sound of baby, rest, warmth quite conductive atmosphere and suckling
reflex all stimulate mother posterior pituitary gland to secret oxytocin which result in contraction

of myoepithelial cells surrounding the deep alveoli → squeezing of milk into larger ducts →
nipple→ suckling baby
Frequent feeding, chlorpromazine and feeding tube devices (lact aid) stimulate prolactin
secretion and stimulate milk production by the cuboidal cells in the acini and alveoli of the breasts
Certain medications, maternal fatigue and stress inhibit prolactin secretion
Let down reflex (milk ejection reflex)
1. tingling sensation in nipple,
2. dripping of milk before nursing ,
3. dripping of milk from opposite side while nursing,
4. relief of nipple discomfort &
5. uterine cramping.
Let down reflex absent during periods of pain,fatigue or emotional stress
Human milk is the ideal and uniquely superior food for infants for the first year of life and as the
sole source of nutrition for the first 6 months .
{WHO recommendation}.
Breast feeding offers advantages for the infants,for the mother and for the society.
Advantages of breast feeding to the society
1- Reduced health care costs owing to lower incidence of illnesses in breast fed infants and reduced
employee absteeism for care attributable to infant illnesses.
2- It is cheap,ready available and suitable for poor families.
Advantages of breast feeding to the mother
1. Decreased risk of post partum haemorrhage .
2. longer period of amenorrhea .
3. Reduced risk of ovarian and premenopausal
Breast cancers.
4. Reduced risk of osteoporosis .
5. Enhances mother_child bound relationship
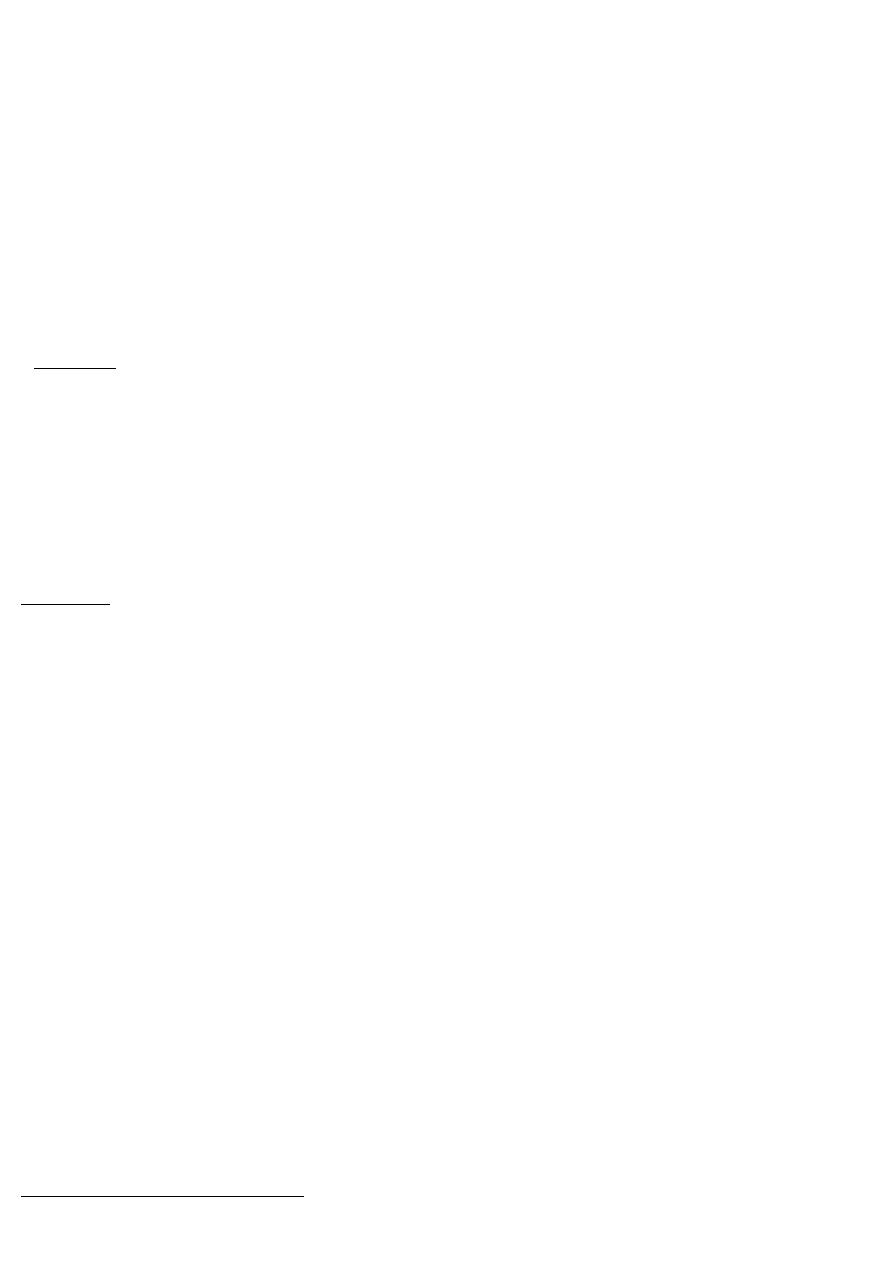
Advantages of Breast Feeding to Infants
1.Provide the ideal nutrition for infants during the first 6 months.
2.It is always available at proper temperature and require no time for preparation..
3.It is fresh and free of contaminating bacteria and thereby decreasing incidence or severity of
diarrhea, respiratory illnesses,otitis media, bactereamia,bacterial meningitis & necrotizing
enterocolitis[NEC].
4-has anti-infective properties:
A-Humoral
1. secretory IgA
2. bifidus factor: promotes growth of lactobacillus bifidus
3. bacteriolytic lyzozyme enzymes
4. iron binding protein; lactoferrin
5. anti viral agent; interferon
6. bile salt simulated lipase
B-Cellular
1.macrophages:phagocytic;synthesise lysosomes; lactoferrin & C3, C4 complements
2.lymphocytes:T-cells transfer delayed hypersensitivity responses to infants. B-cells synthesizes IgA
5-has good nutritional properties:
a) protein quality. More easily digested curd [whey: casein] ratio [ 60:40].
b) hypoallergic. less incidence of atopic diseases, intestinal bleeding ,occult malena ,spitting up
& infantil colic.
c) lipid quality. Rich in oleic acid ,essentional fatty acids & long chain unsaturated fatty acids
essentional for growth of brain tissue.
d) calcium: phosphorus ratio 2:1 prevents hypocalcaemic tetany and improved calcium
absorption.
e) low solute load on circulation and kidneys.
f) iron content relatively lower than formula,but higher bioavailability.
6.Breast feeding improves cognetive development.
7.Enhances mother-infant relationship.
8.Reduced incidences of IDDM, IBD, obesity, cows milk allergy, eczema, SIDS!! & hypertension.
Disadvantages of Breast Feeding

1.Unkown intake of milk volume may cause worrieness to mother.
2.Transmission of infection to the infant : e.g. hepatitis, CMV, HIV,…
3.Transmission of drugs: that may adversely affect the baby
depending on:(route of administration, dosage, molecular weight ,PH, and protein binding )
a) antimetabolites[cytotoxics].
b) anti-thyroid drugs.
c) radioactive compounds.
d) antibiotics:chloramphenicols,sulphanamides,tetracycline,metronidazoles,INH,…..
e) laxatives.
f) Narcotics: opiates, barbiturates, benzodiazepens.
g) lithium,lead,mercury.
h) antihypertensive drugs.
i) iodide,bromide,atropine.
j) oral contraceptives.
k) anticoagulants.
l) anthraquinones derivatives.
.Nutrient inadequancies:
4
Exclusively breast fed babies should be supplemented with vitamin D[200iu\day]at 2mon of age
and fluoride[10µg\day]for first 6mon and iron by4-6mon of age
5.Breast Milk Jaundice
Mild,self-limiting unconjugated hyberbilirubinemia due to exaggerated enterohepatic circulation
and interferance with conjugation by maternal hormones
6.Vitamine K Deficiency
Manifested as haemorrhagic disease of newborn
7.Potential transmission of environmental contaminants:nicotine,alcohol,caffein,
8.Less flexible:other family members cannot help or take part.More difficult in public places.
9.Emotional upsets if difficulties or lack of success can be upsetting
Contraindications to Breast Feeding
1. Risk to infant:transfer of infection
*HIV-positive mother in developed countries
*Active tuberculosis in mother

*Typhoid fever,septicemia,malaria
*Active herpes simplex lesions
*Breast abscess
2. Risk to infant:transfer of medication: cytotoxics,radioisotopes,chloramphenicol. other
medications are relatively contraindicated
3. Metabolic disorders in infant: galactoseamia & phenylketoneuria
4. Sever illnesses in infant: extreme prematurity,sepsis,cerebral trauma, congenital cardiac lesion,
cleft palate or micrognathia
5. Maternal chronic ill health
❑ sever cardiac,respiratory or renal diseases
❑ sever psychosis or neurosis
❑ substance abuse
Preperation of Prospective Mothering
Should be started before delivery in the midtrimester. Most women,if encouraged,educated
and protected from discouraging experiences and comments while milk secretion is becoming
established,can successfully breast their infants.
Training of maternity staff and adaption of the Baby-Friendly Hospital Initiative as
recommended by WHO are successful interventions to encourage breast feeding
Factors that are conductive to successful breast feeding are:
a. good nutritional health.
b. proper balance of rest and exercise.
c. freedom from worry.
d. treatment of any intercurrent diseases.
e. hygiene,dialy washing of breasts.
f. discouraging of alcohol & smoking.
g. care of the nipple:retracted nipple benefit from dialy manual breast pump suction during last
weeks of pregnancy
