Oral Ulceration
By:Dr. Ahmed Salih KhudhurBDS, MSc, PhD Newcastle University/ UK
دكتور احمد صالح خضر
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY2020-2021
Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
Department of:
HERE
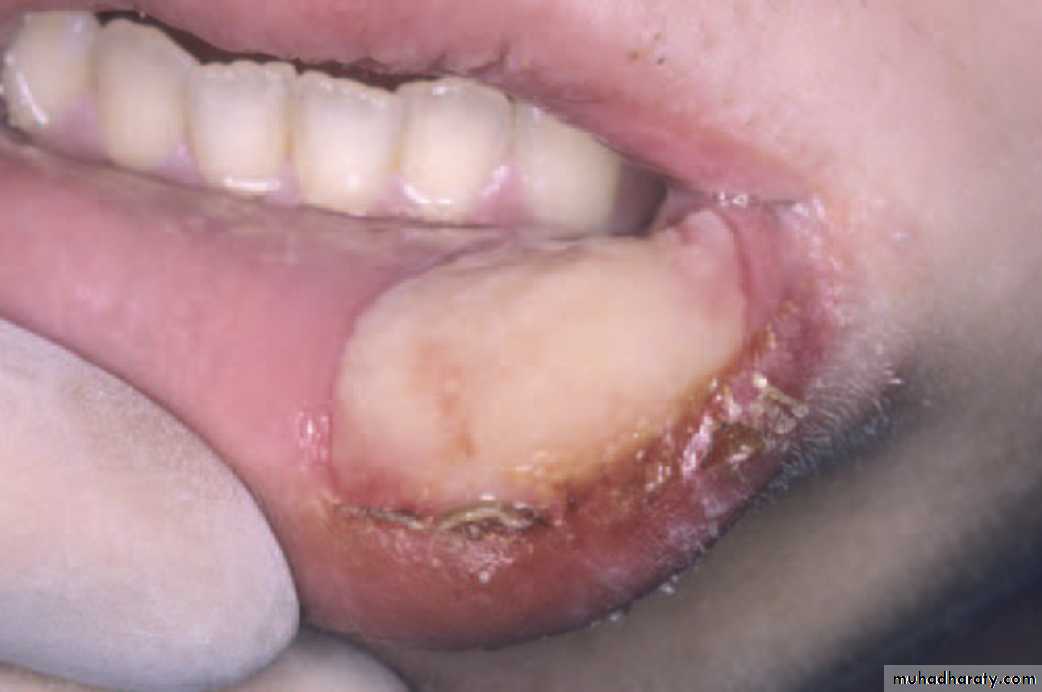
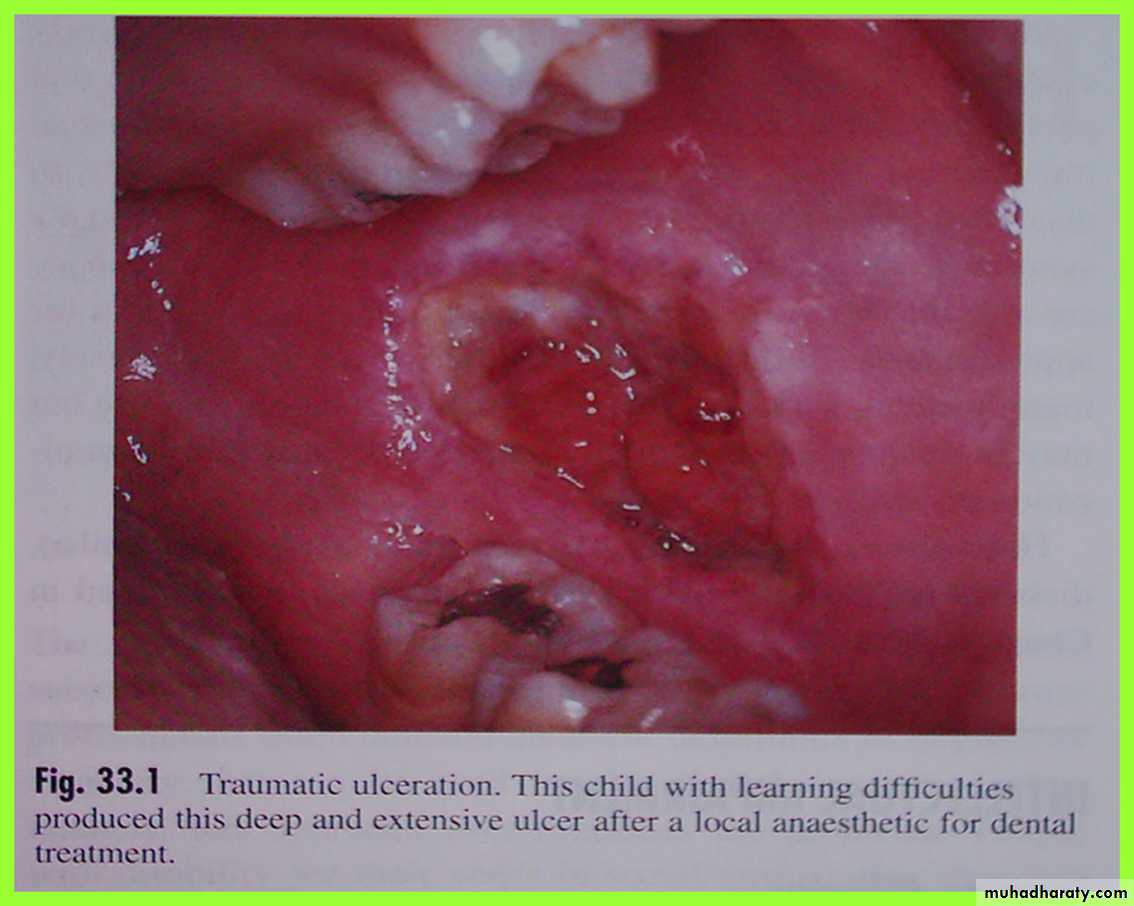
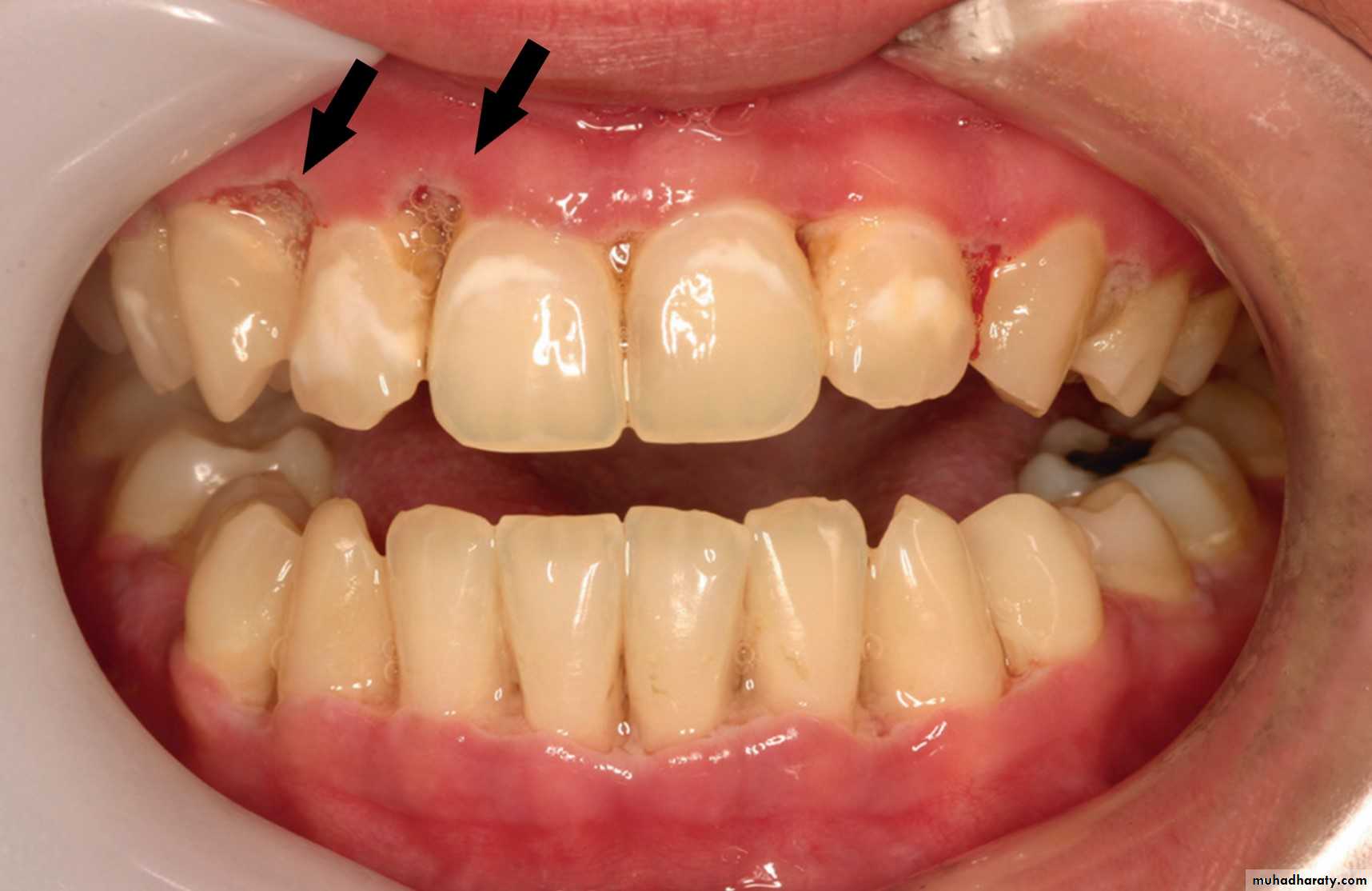
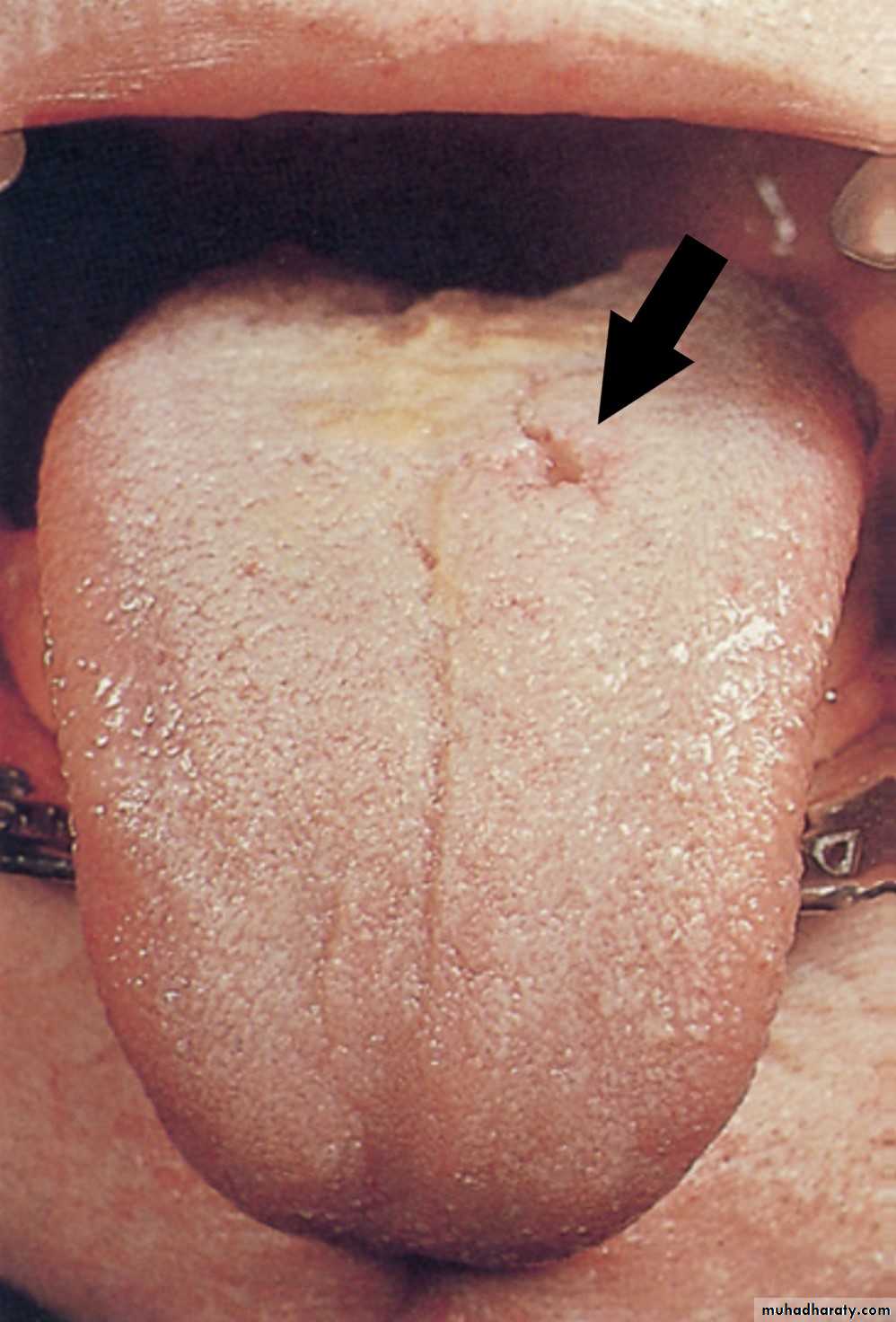
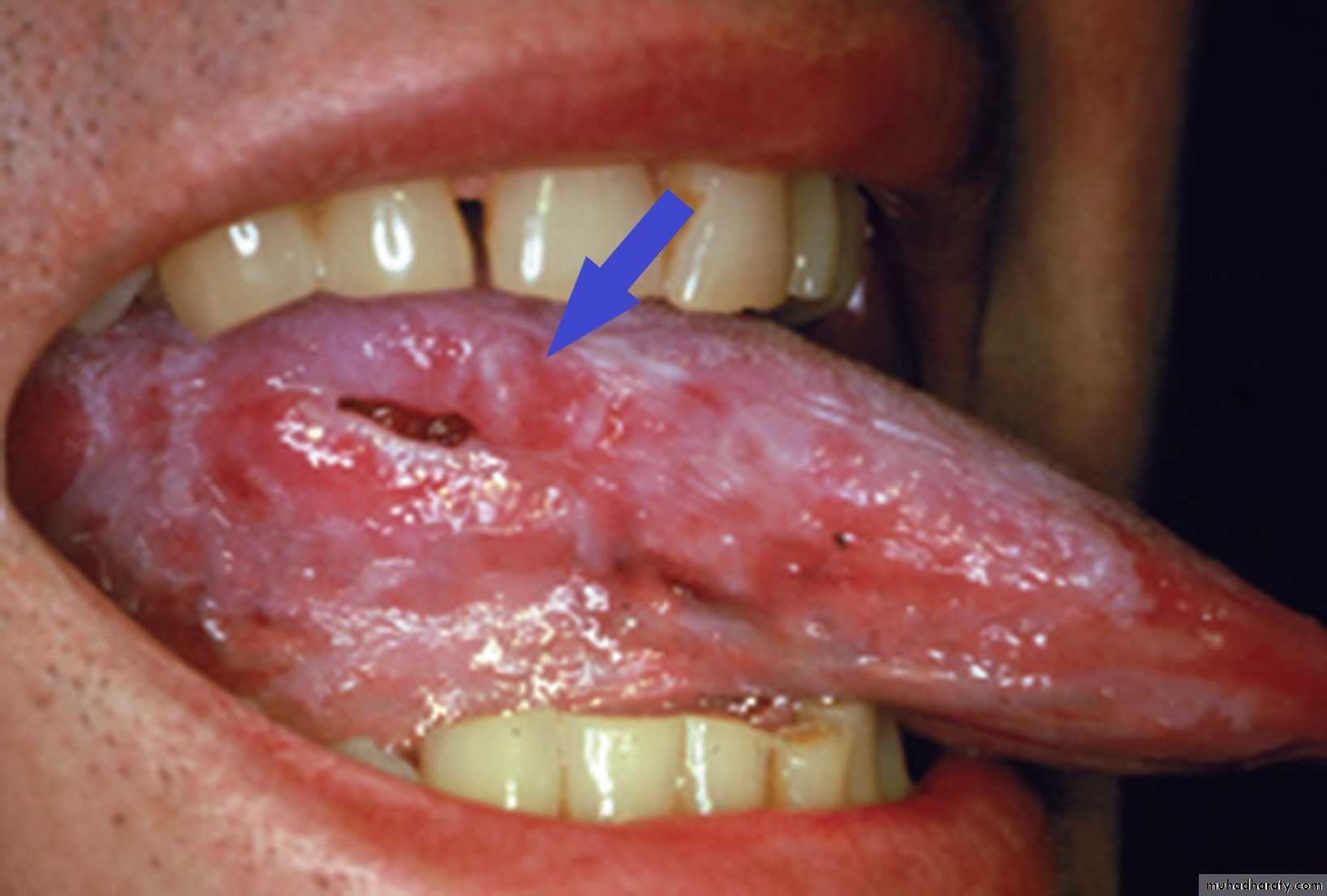
Traumatic Ulcer
•
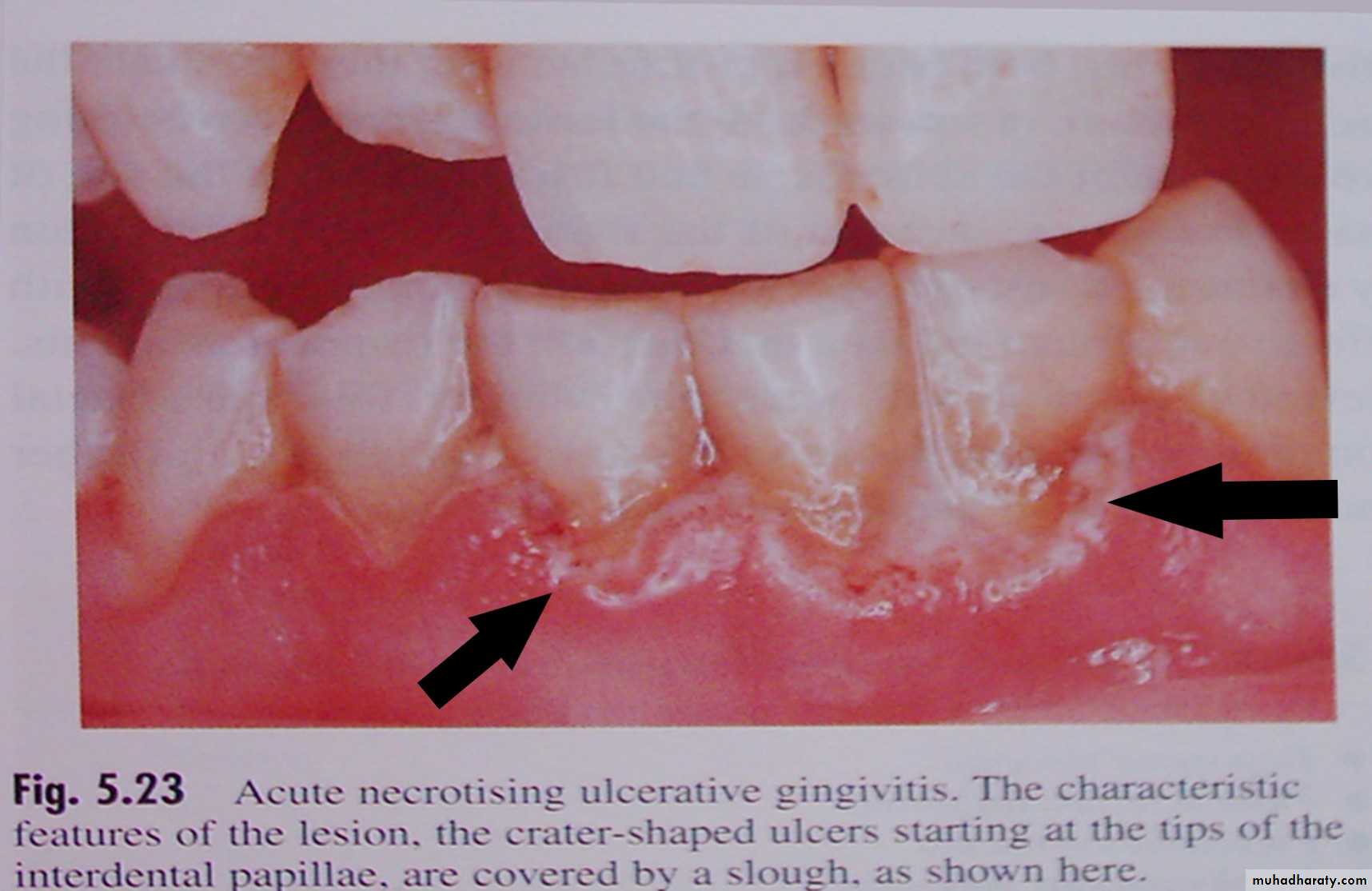
Acute Necrotizing Ulcerative Gingivitis (ANUG)
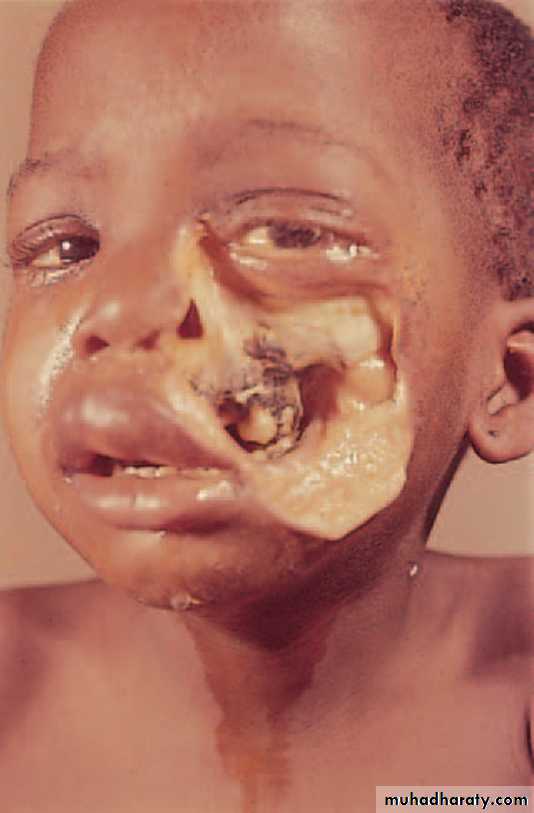
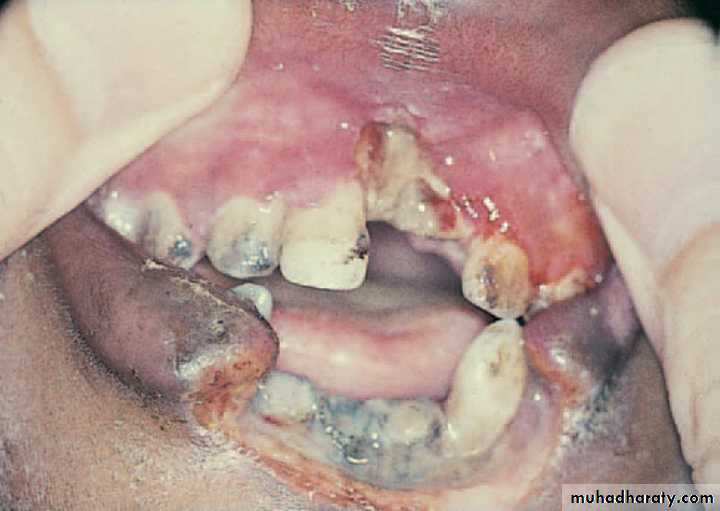
•NOMA (CANCRUM ORIS, NECROTISING STOMATITIS)
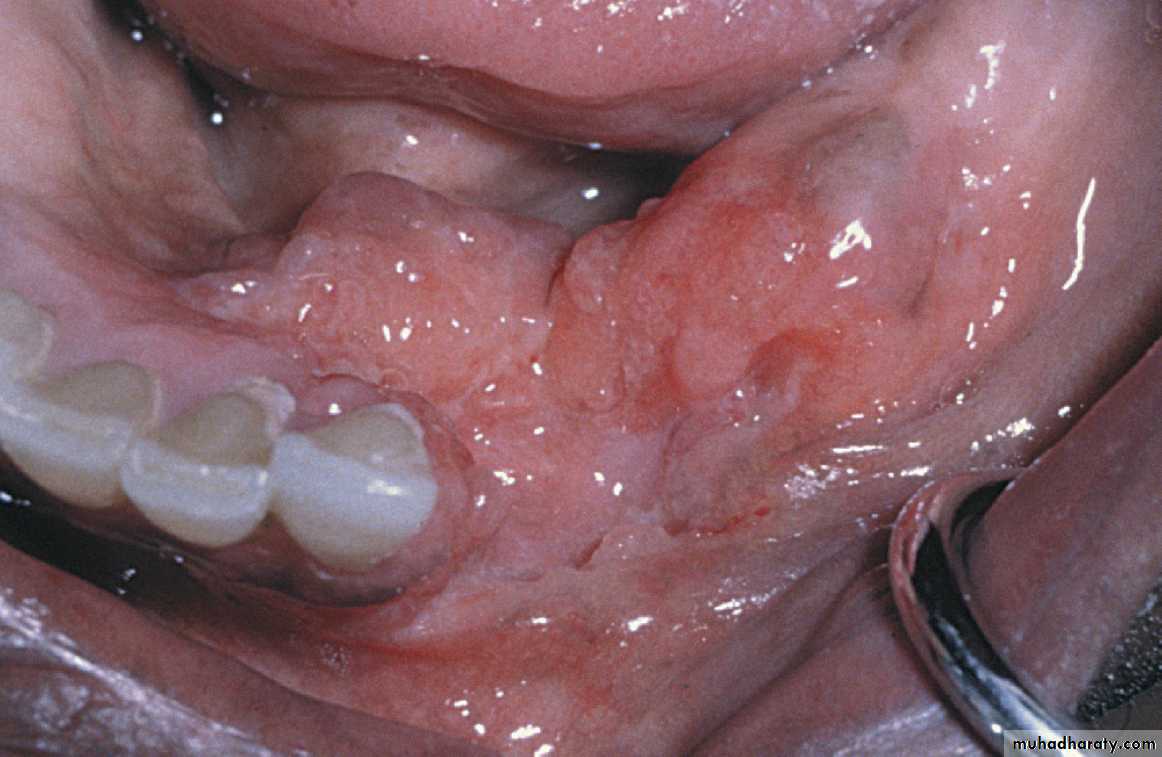
•Tuberculosis (TB) Ulcer
•
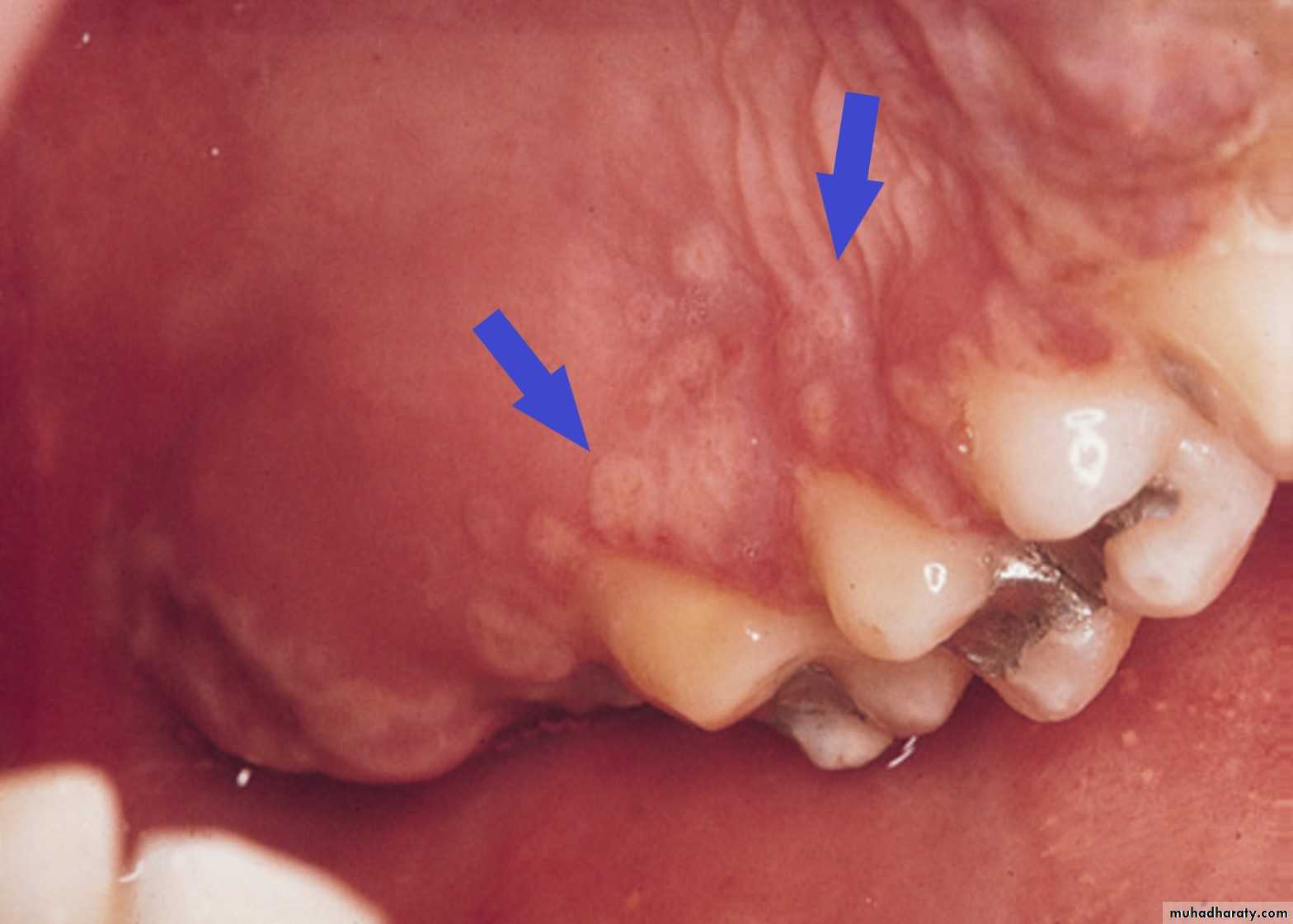
Area of granulation and ulceration of the lower alveolar ridge and floor of mouth.
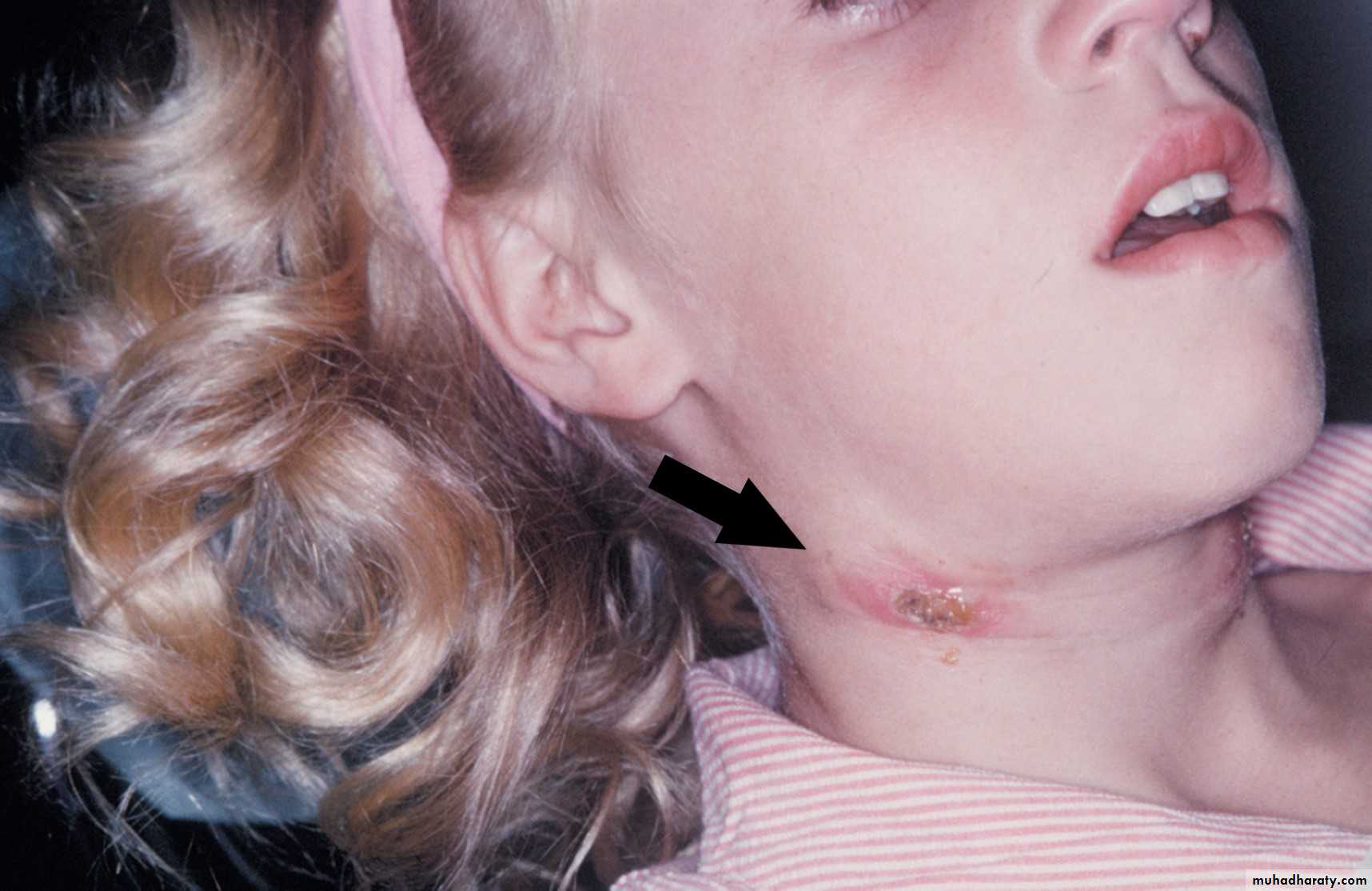
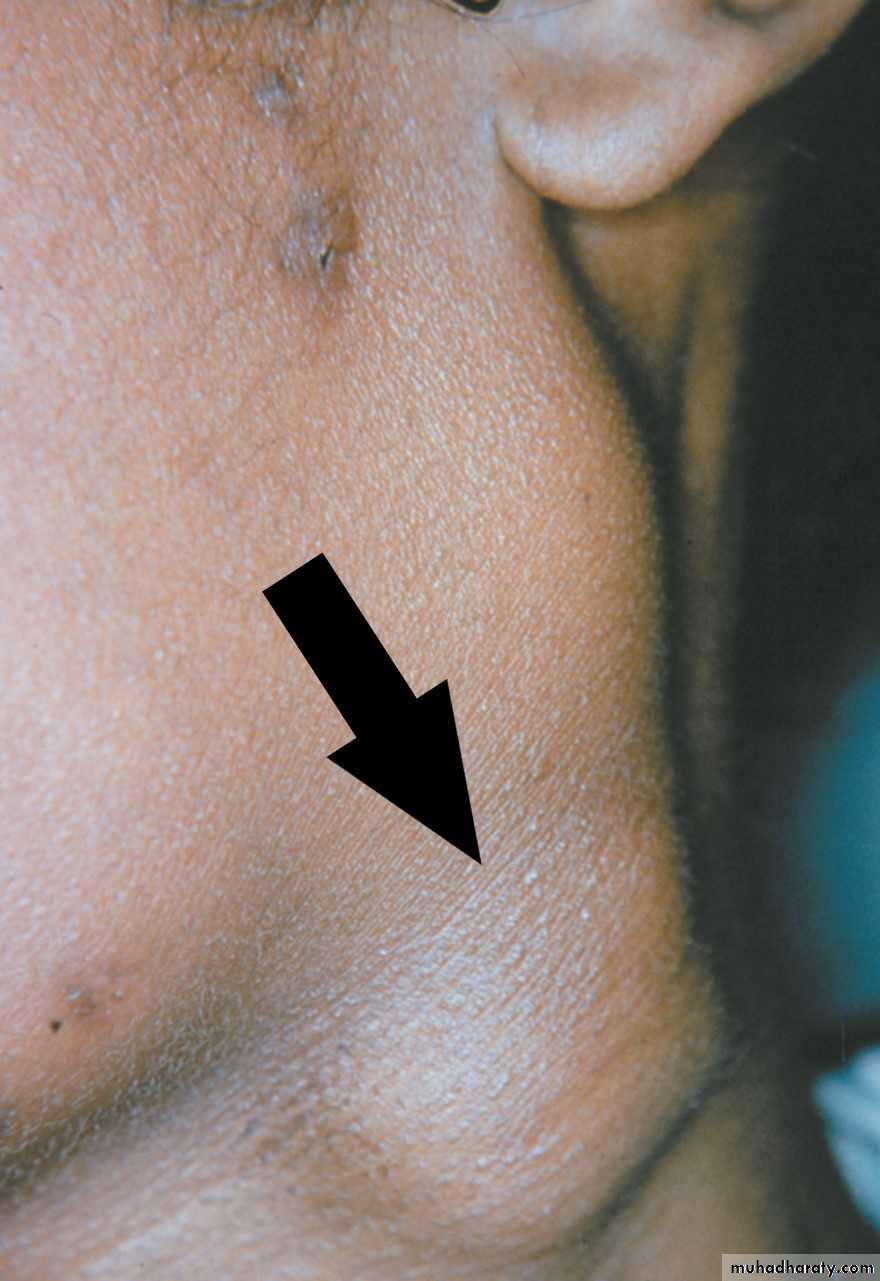
Tuberculosis (TB)
Enlargement of numerouscervical lymph nodes (scrofula).
Submandibular fistula secondary to involvement of underlying cervical lymph nodes.
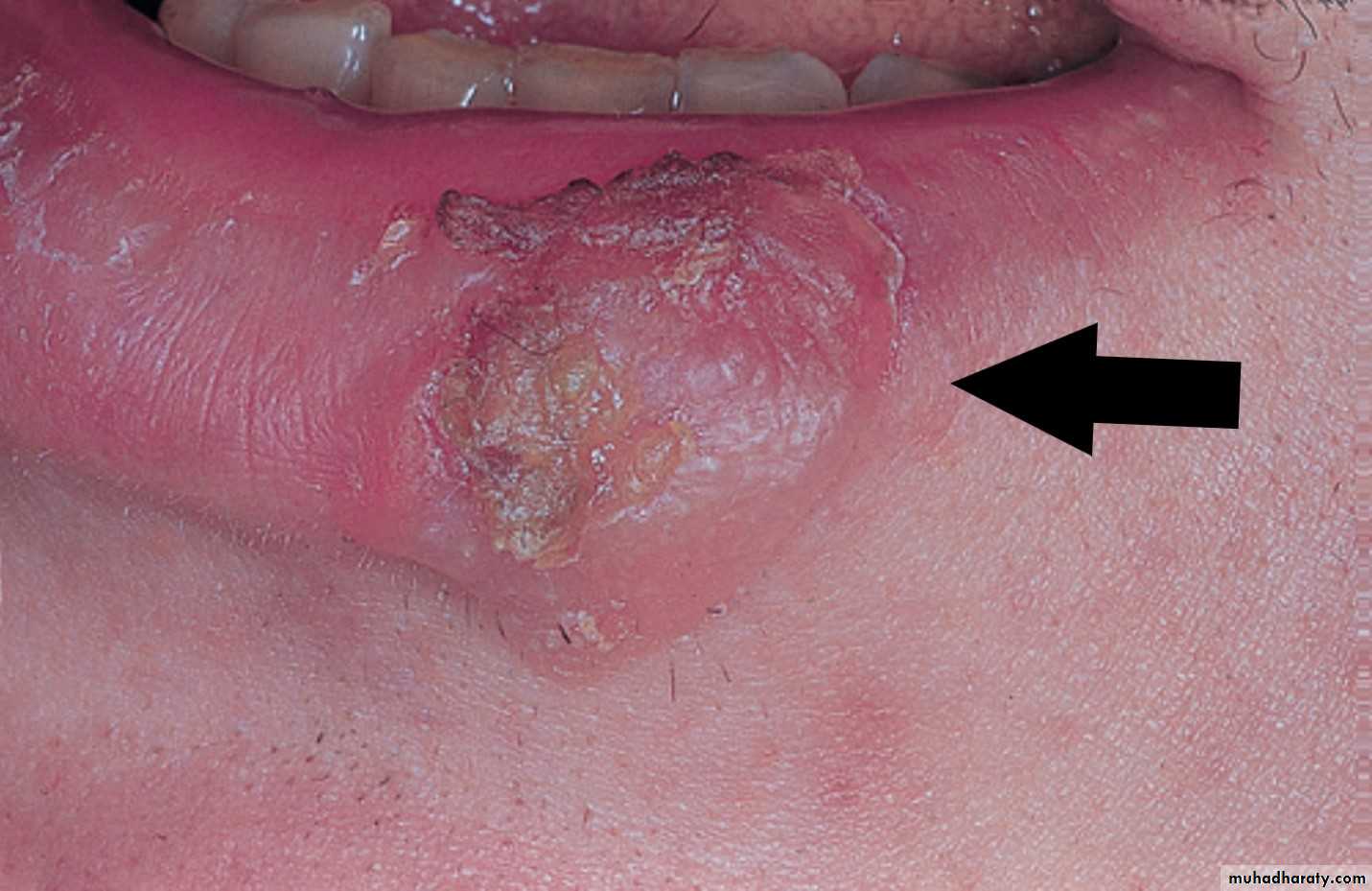
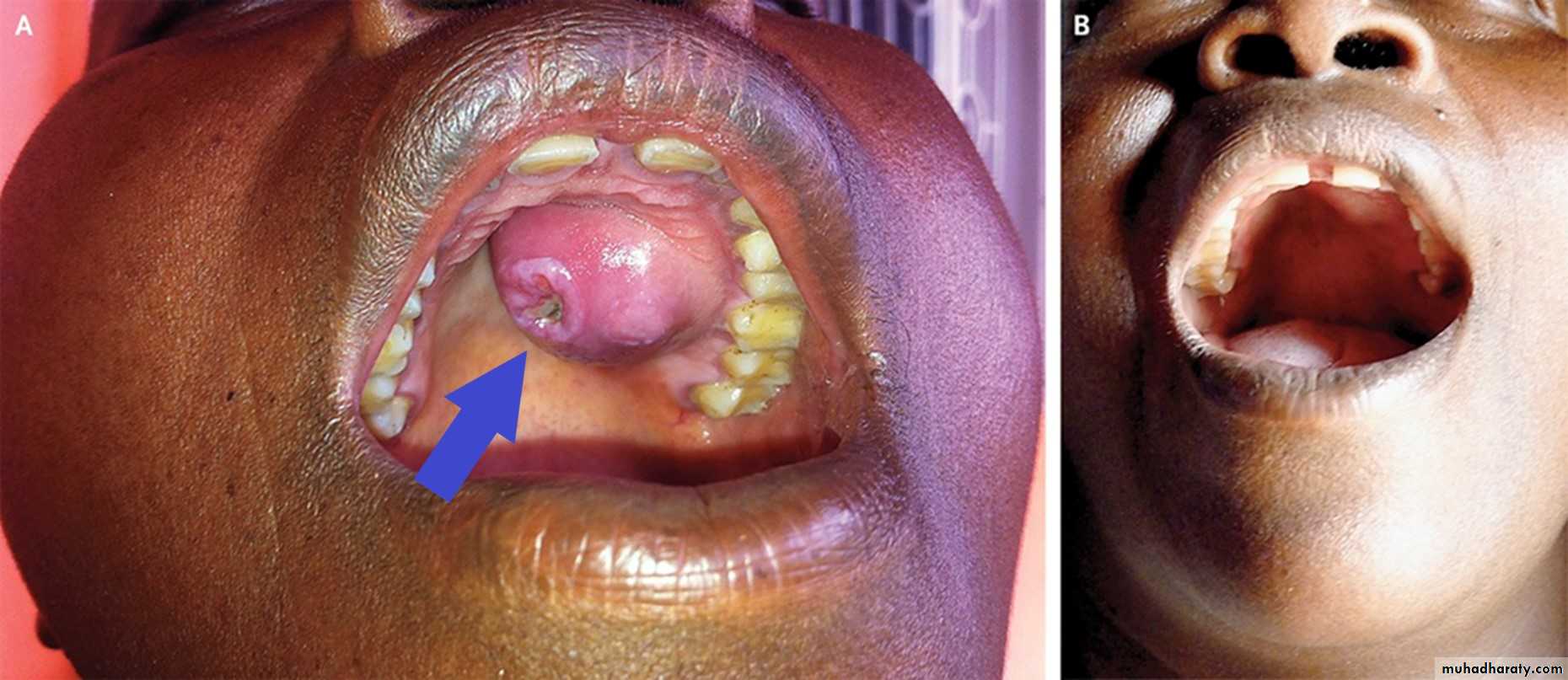
Primary Syphilis
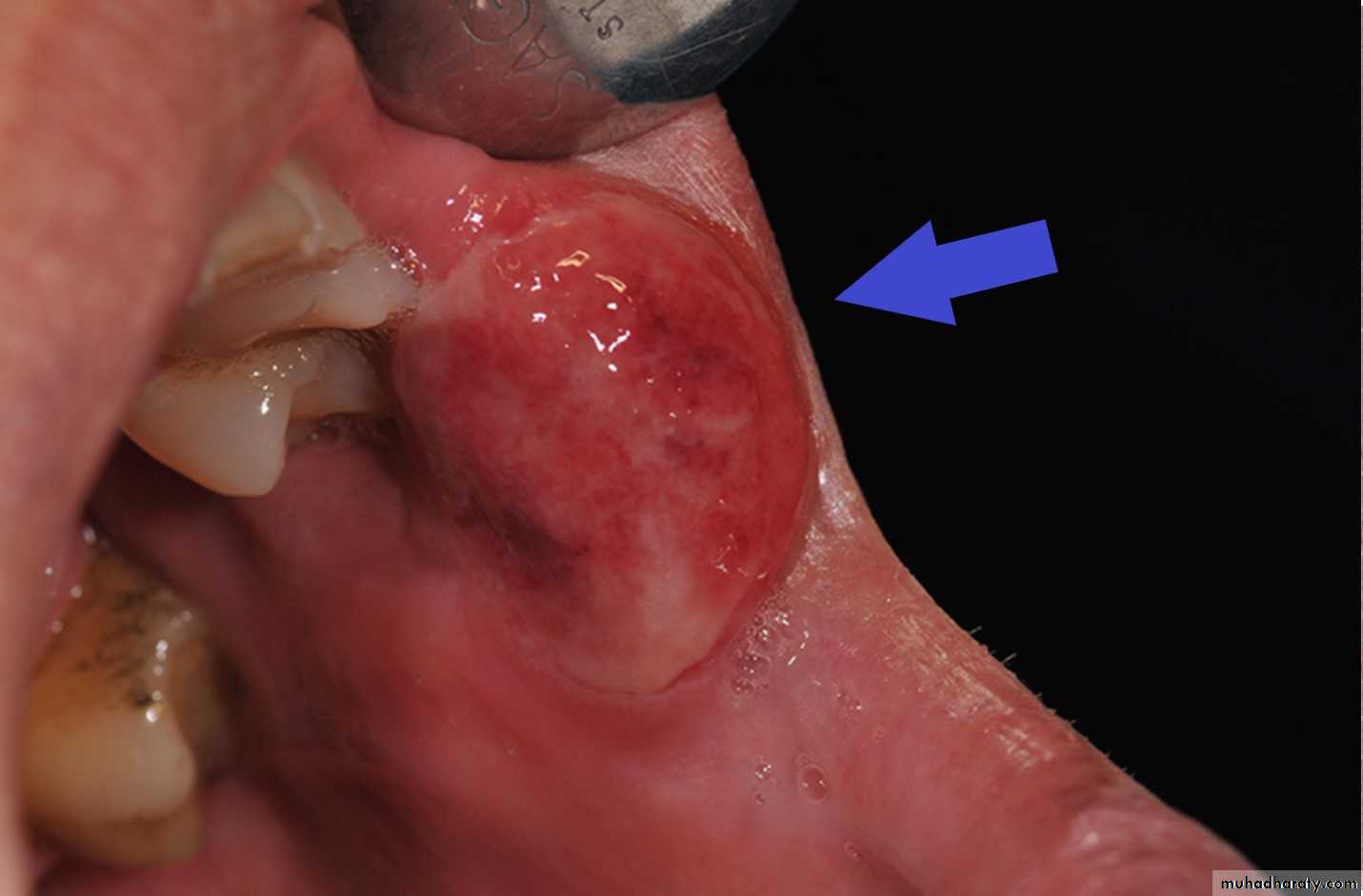
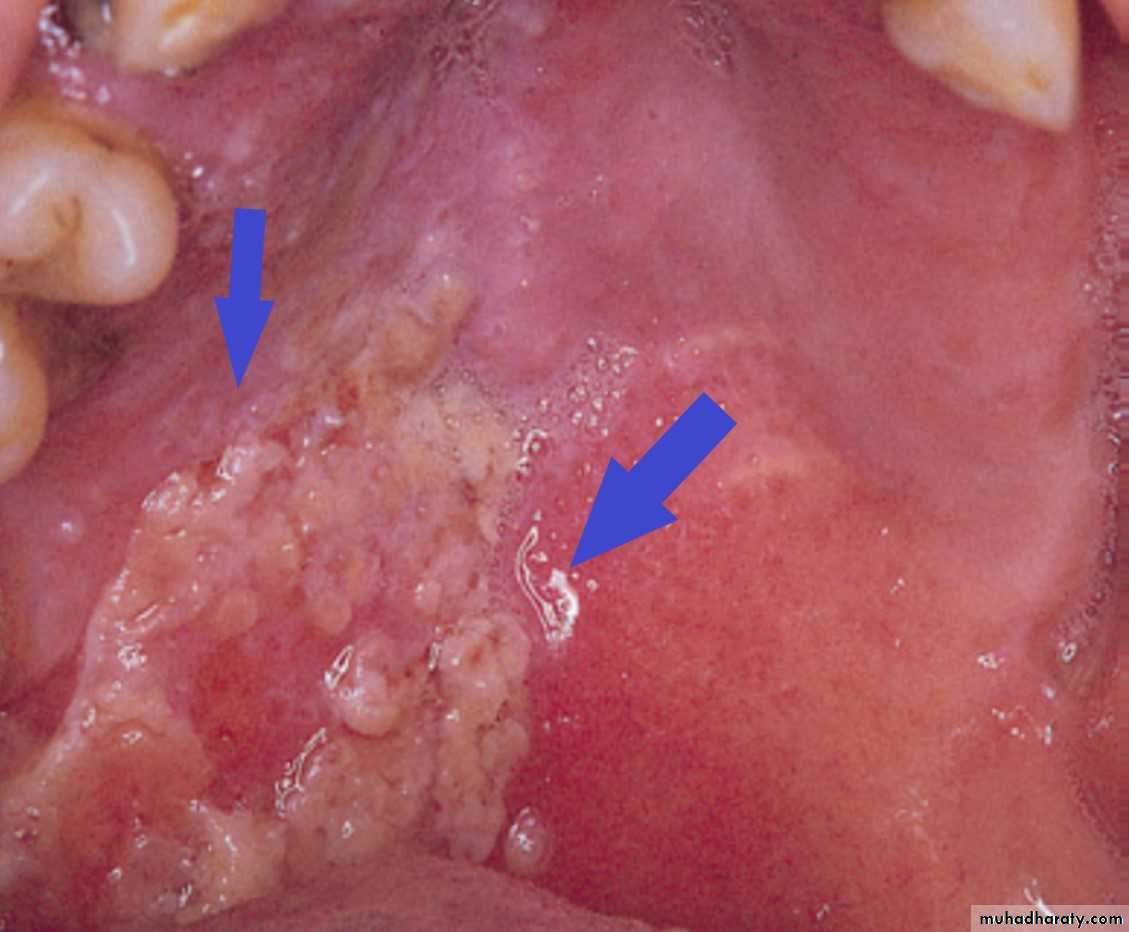
Primary chancre on the lower lipChancre of Primary Syphilis. Erythematous and ulcerated mass of the right anterior buccal mucosa.
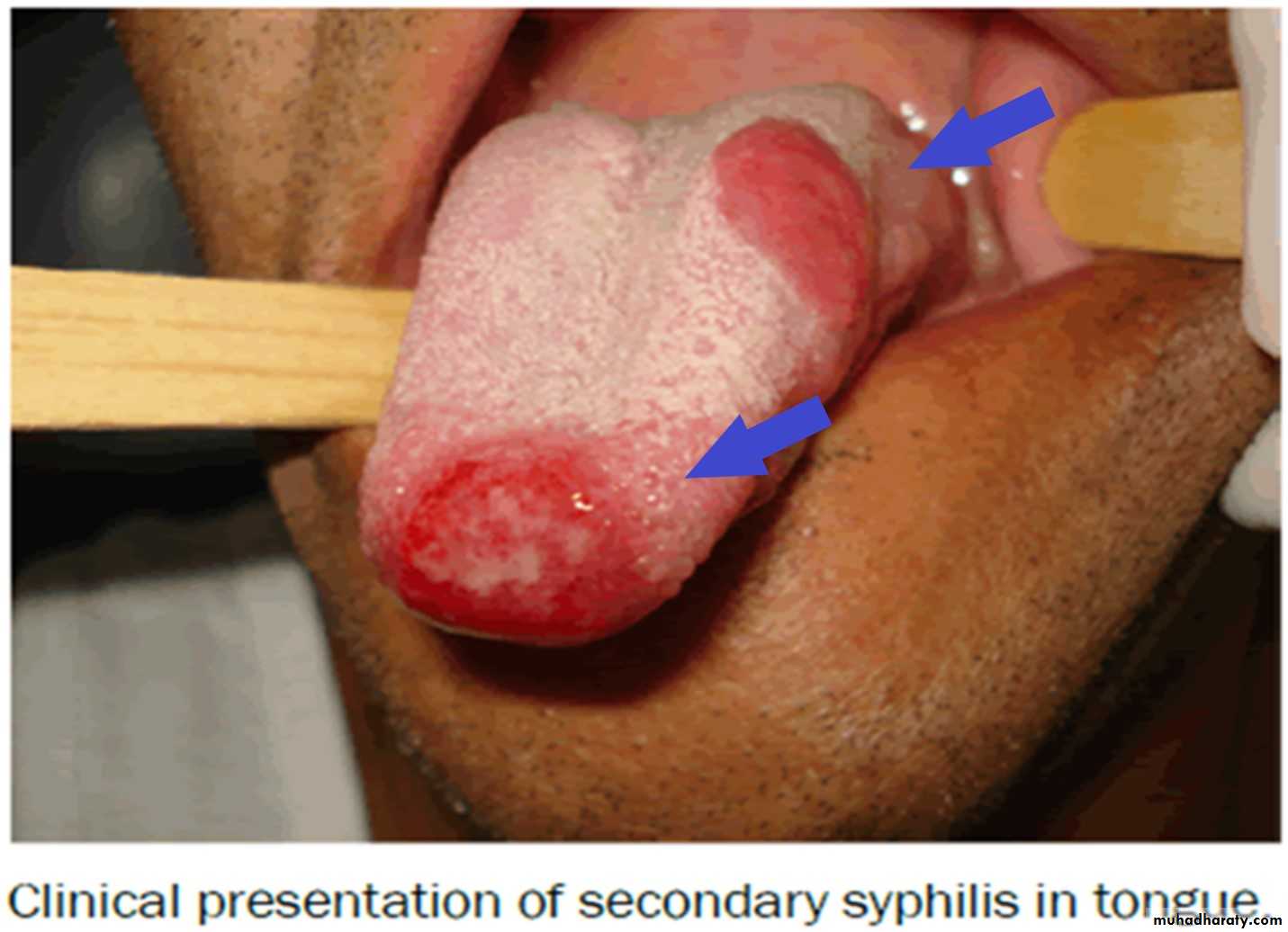
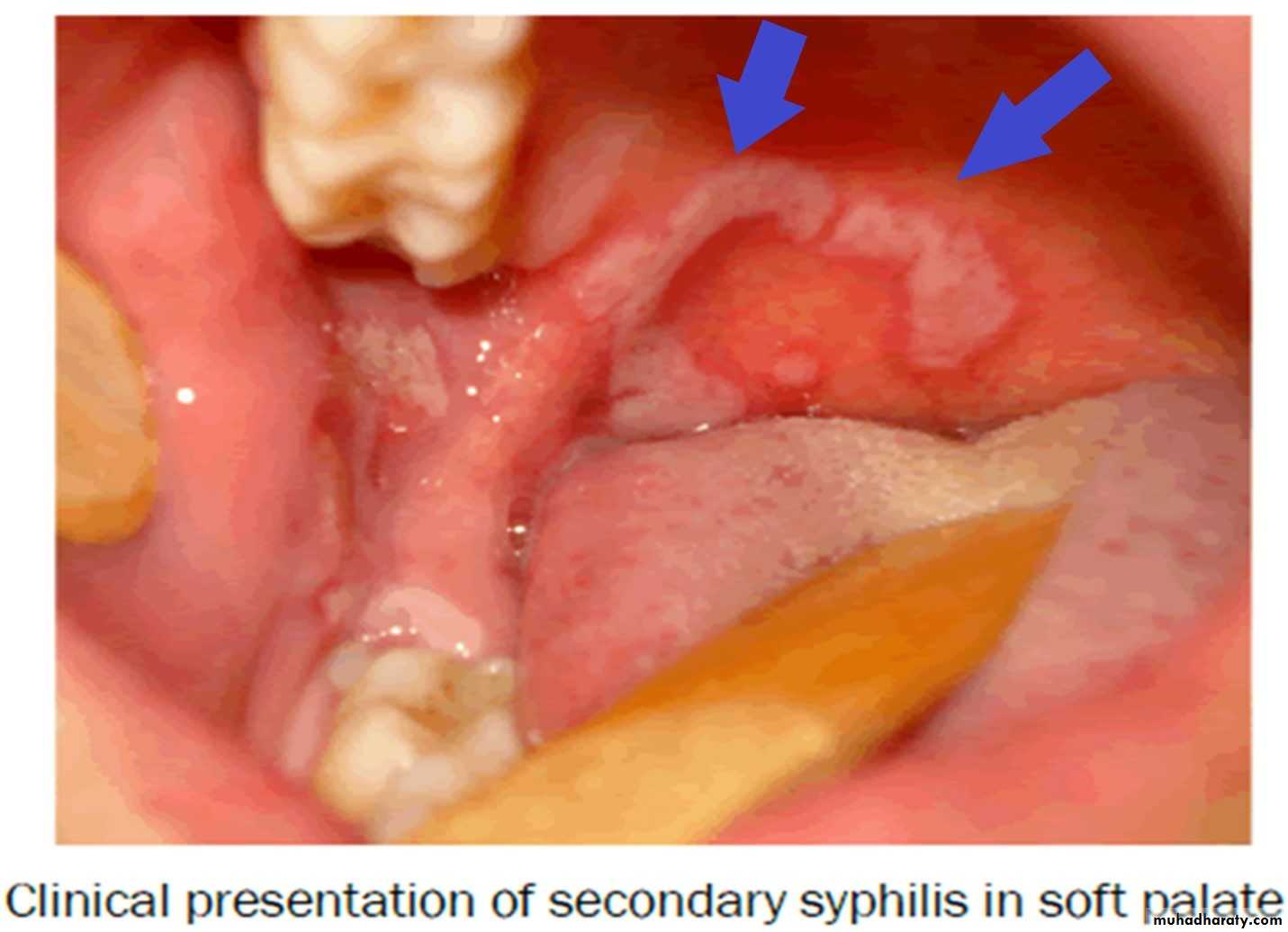
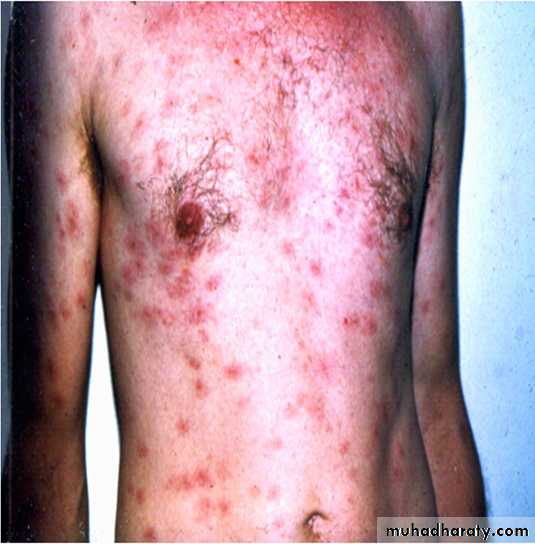
Secondary Syphilis
•Secondary Syphilis
•Tertiary Syphilis
•Tertiary Syphilis
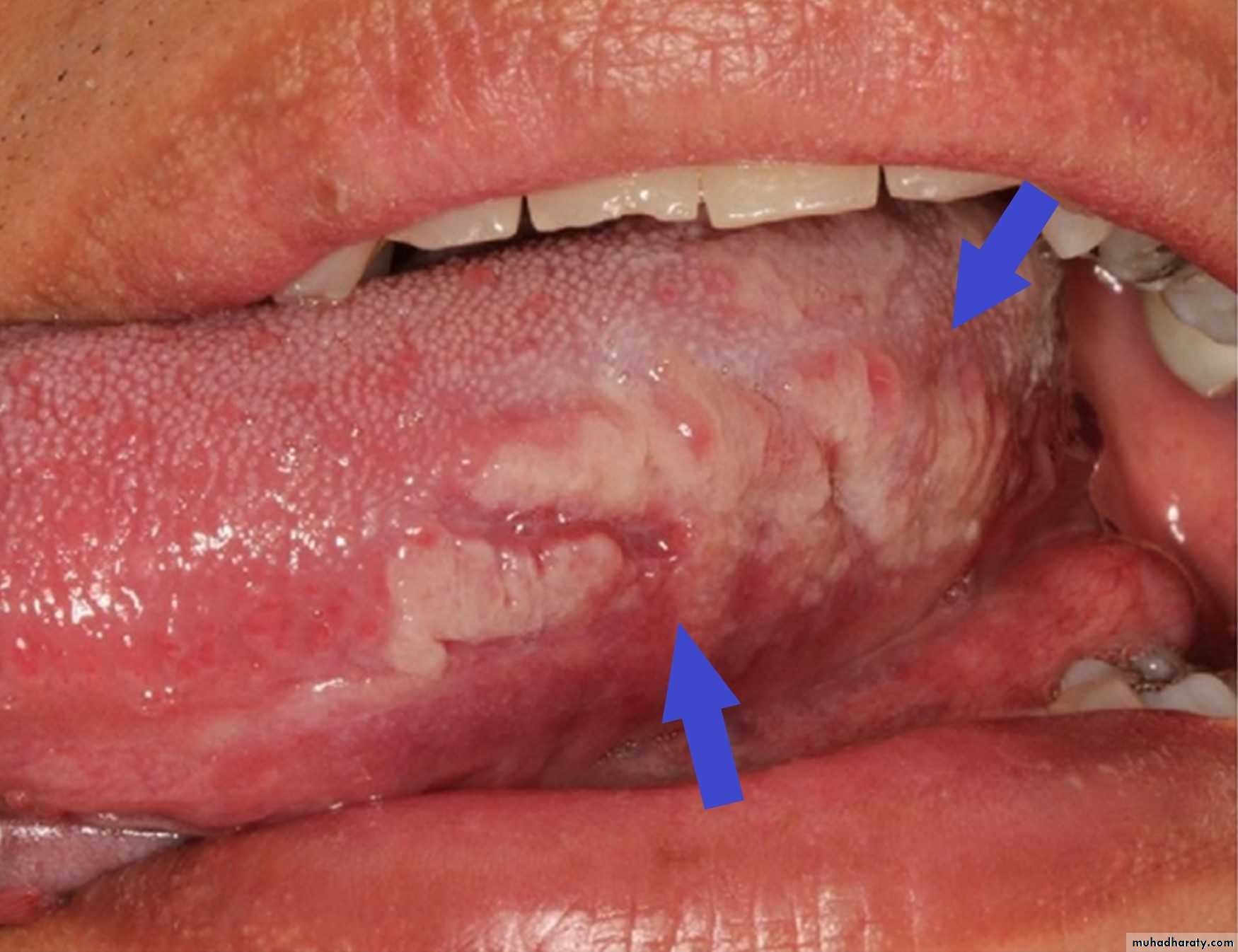
Syphilitic leukoplakiaD.D: Leukoplakia
Congenital Syphilis
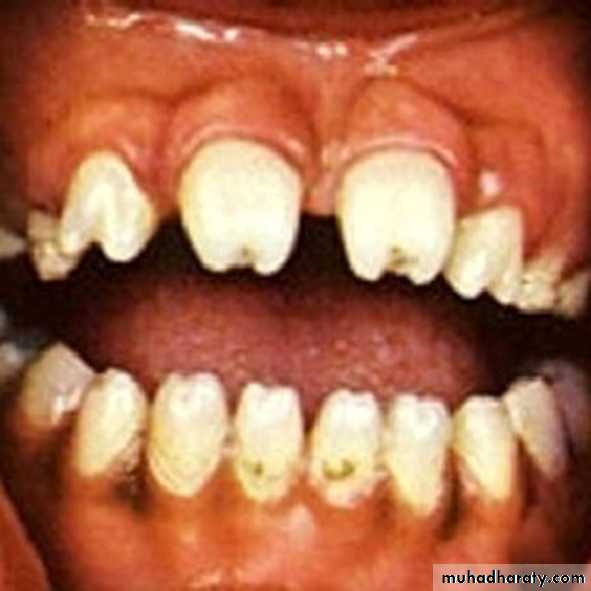
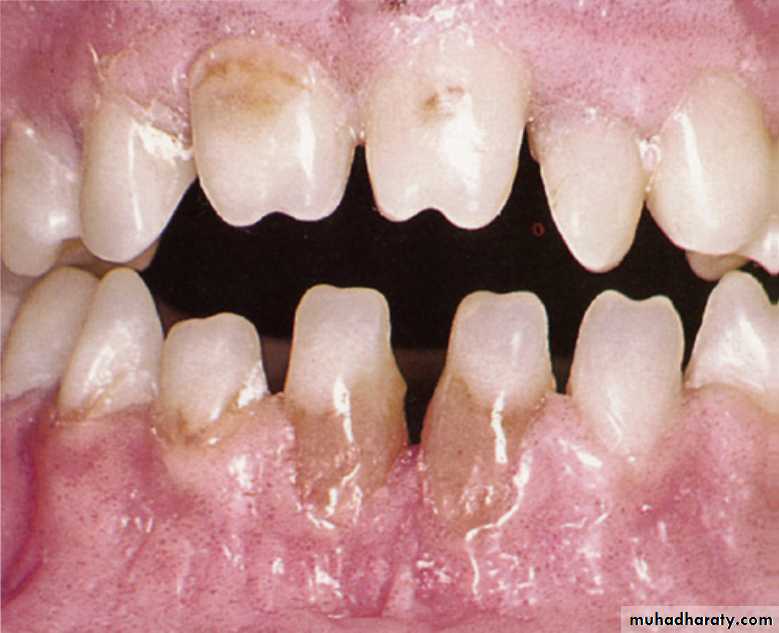
•Hutchinson’s incisors (screw-driver)
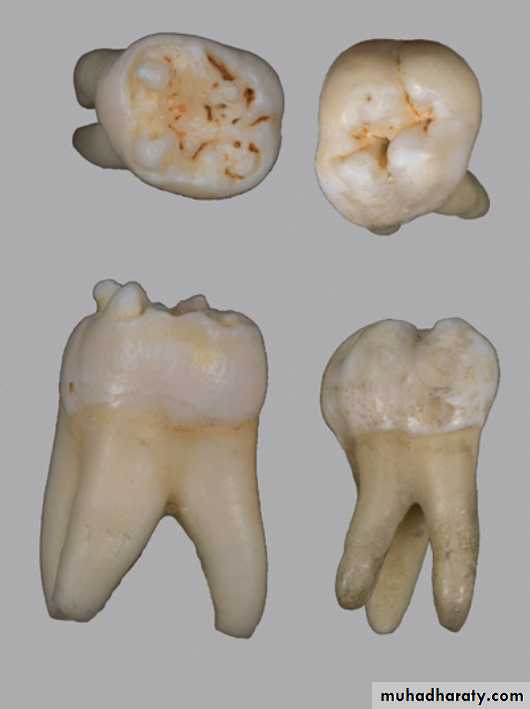
Mulberry molarMoon molar
Congenital Syphilis
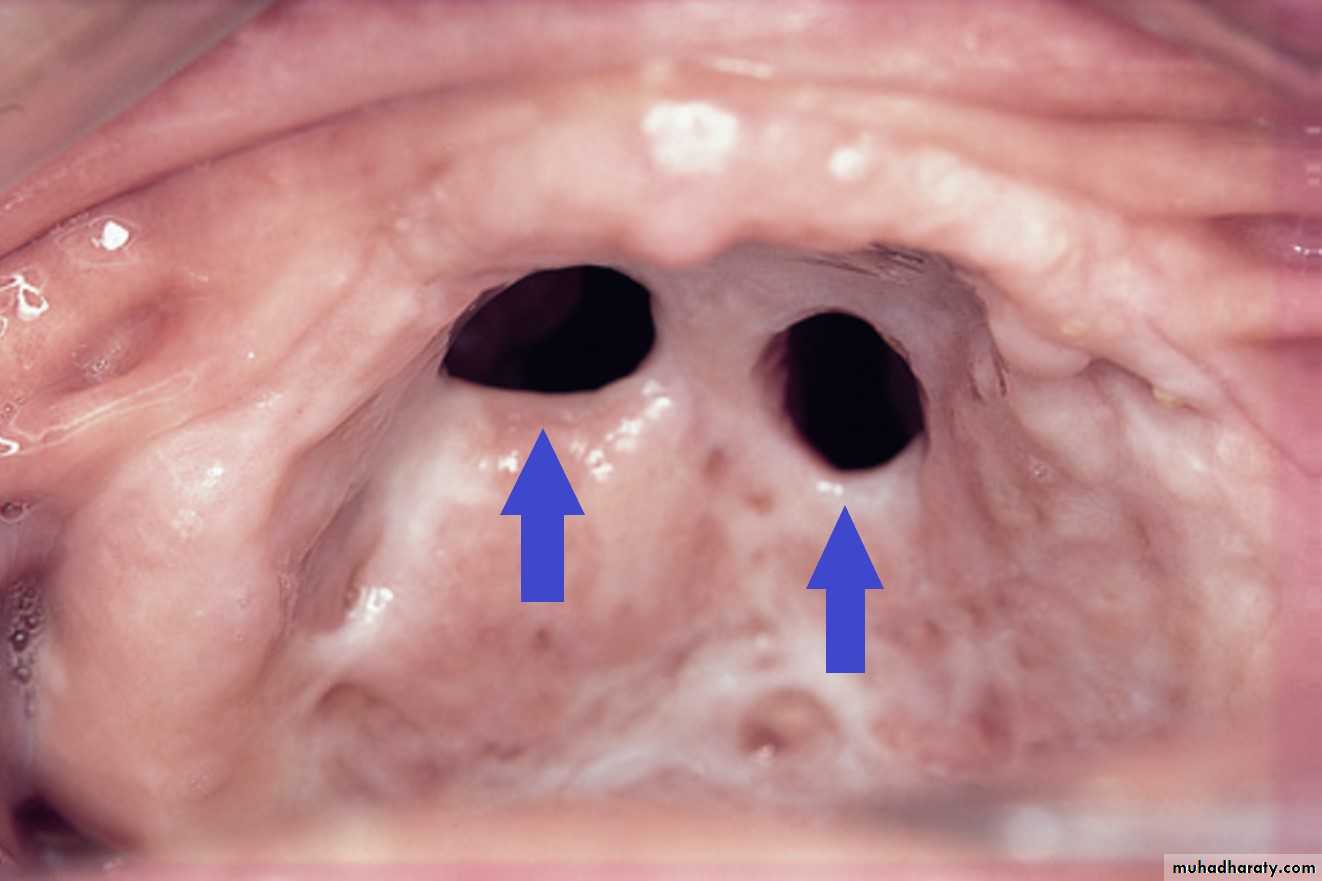
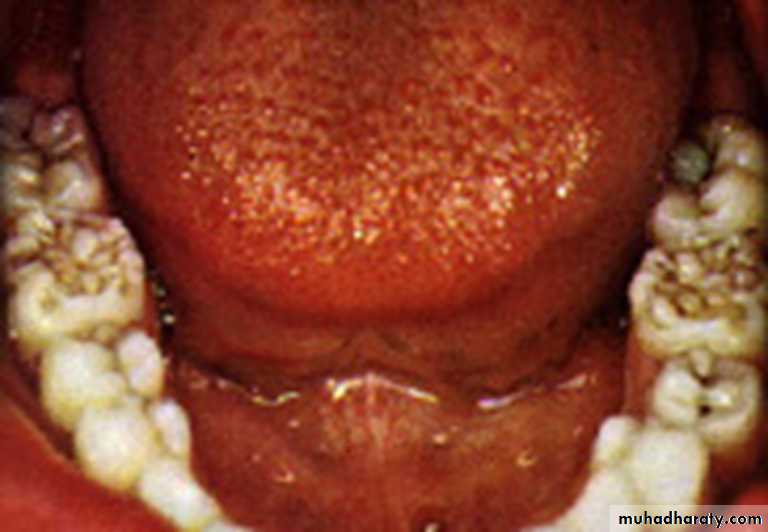
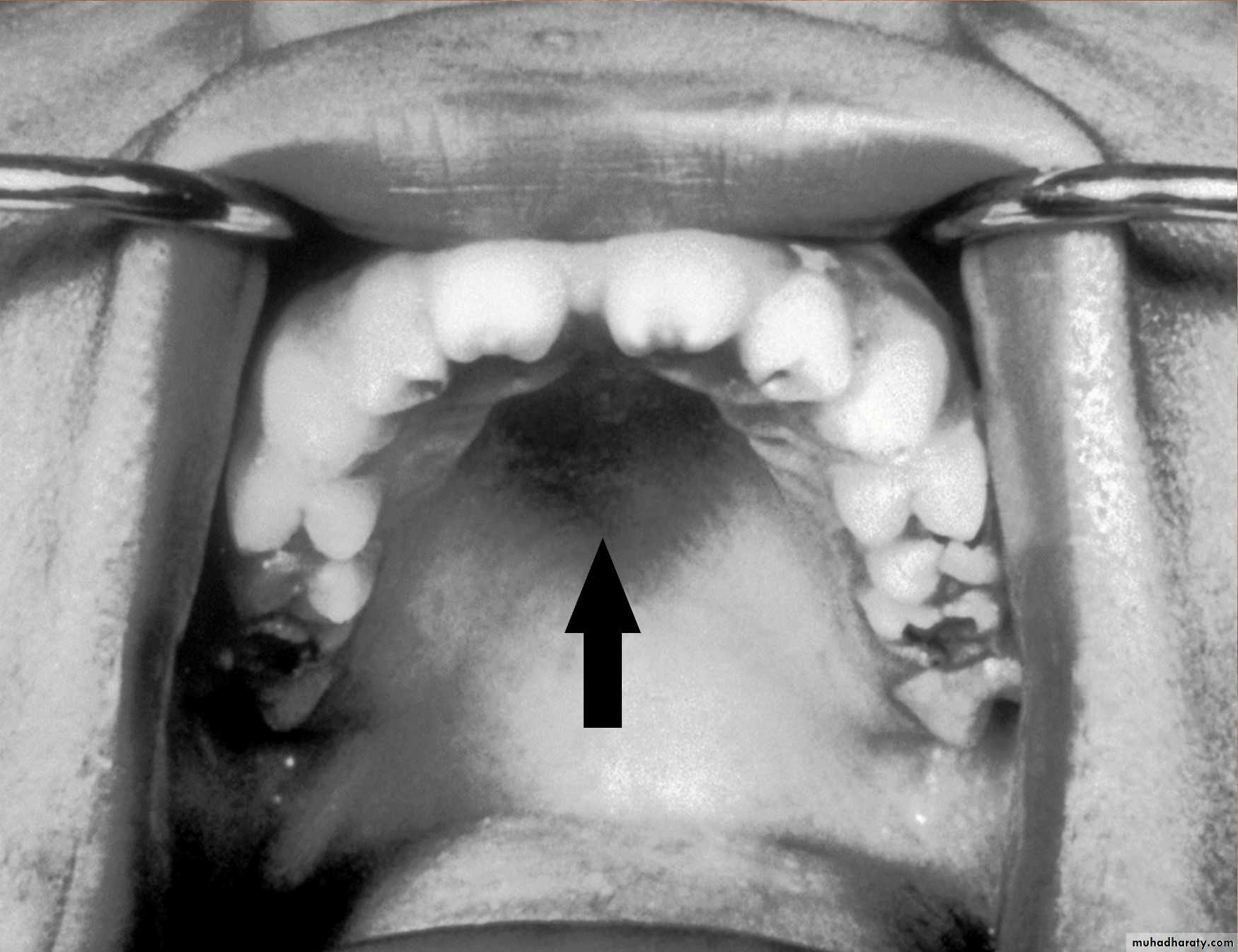
High palatal vault in congenital syphilis
Oral ulcers due to viral infections
Primary herpetic stomatitis- Herpetic gingivostomatitisSecondary/ Recurrent herpes- Herpes labialis
Herpes zoster and chickenpox
Hand-foot-and-mouth disease
Herpangina
Cytomegalovirus ulcers
Herpes
Primary Herpes- Herpetic stomatitisHerpetic gingivostomatitis
Secondary/ Recurrent Herpes
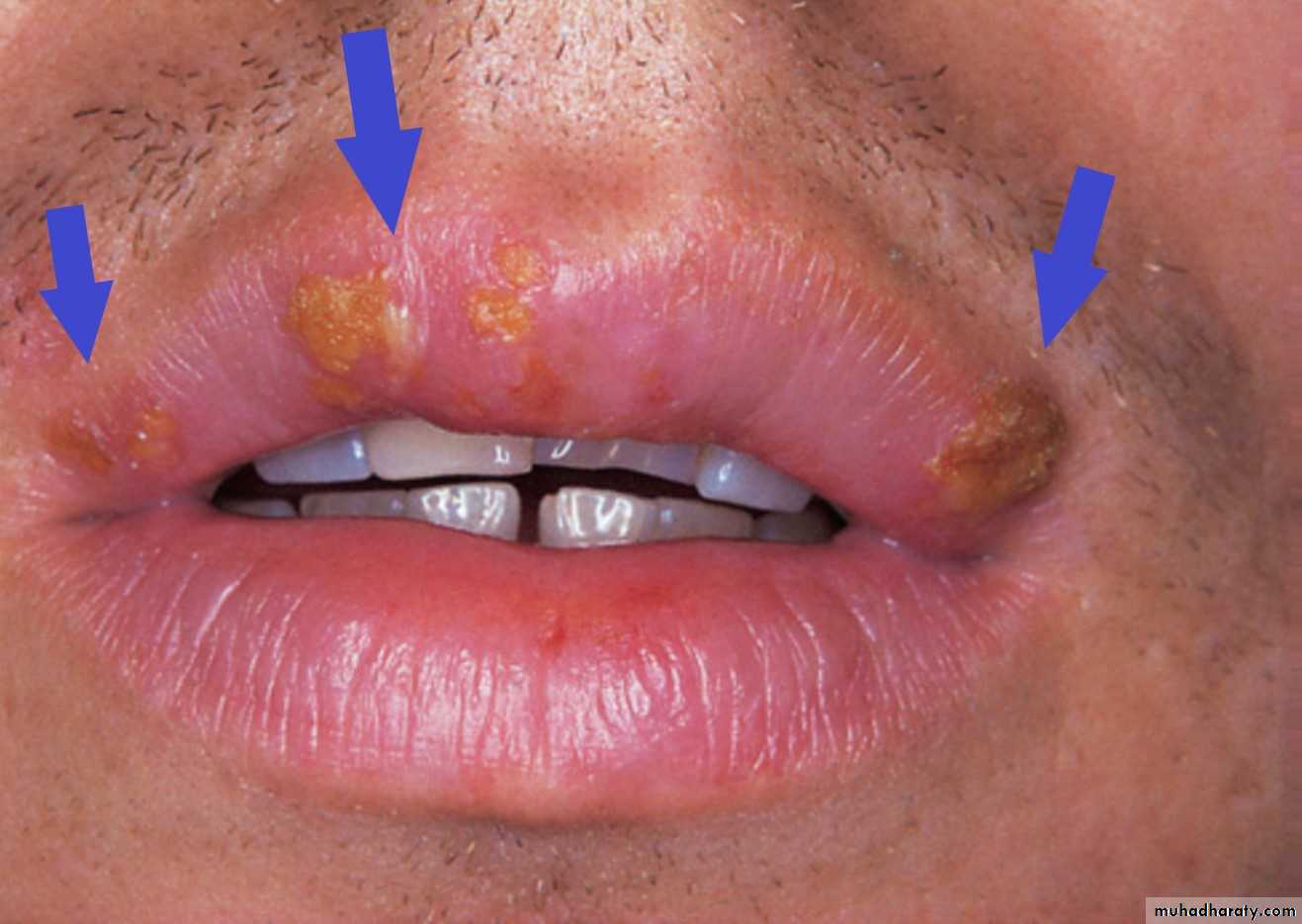
Herpes labialis
Herpes zoster
Herpes zoster. A severe attack in an older person shows confluent ulceration on the hard and soft palate on one side.Herpangina
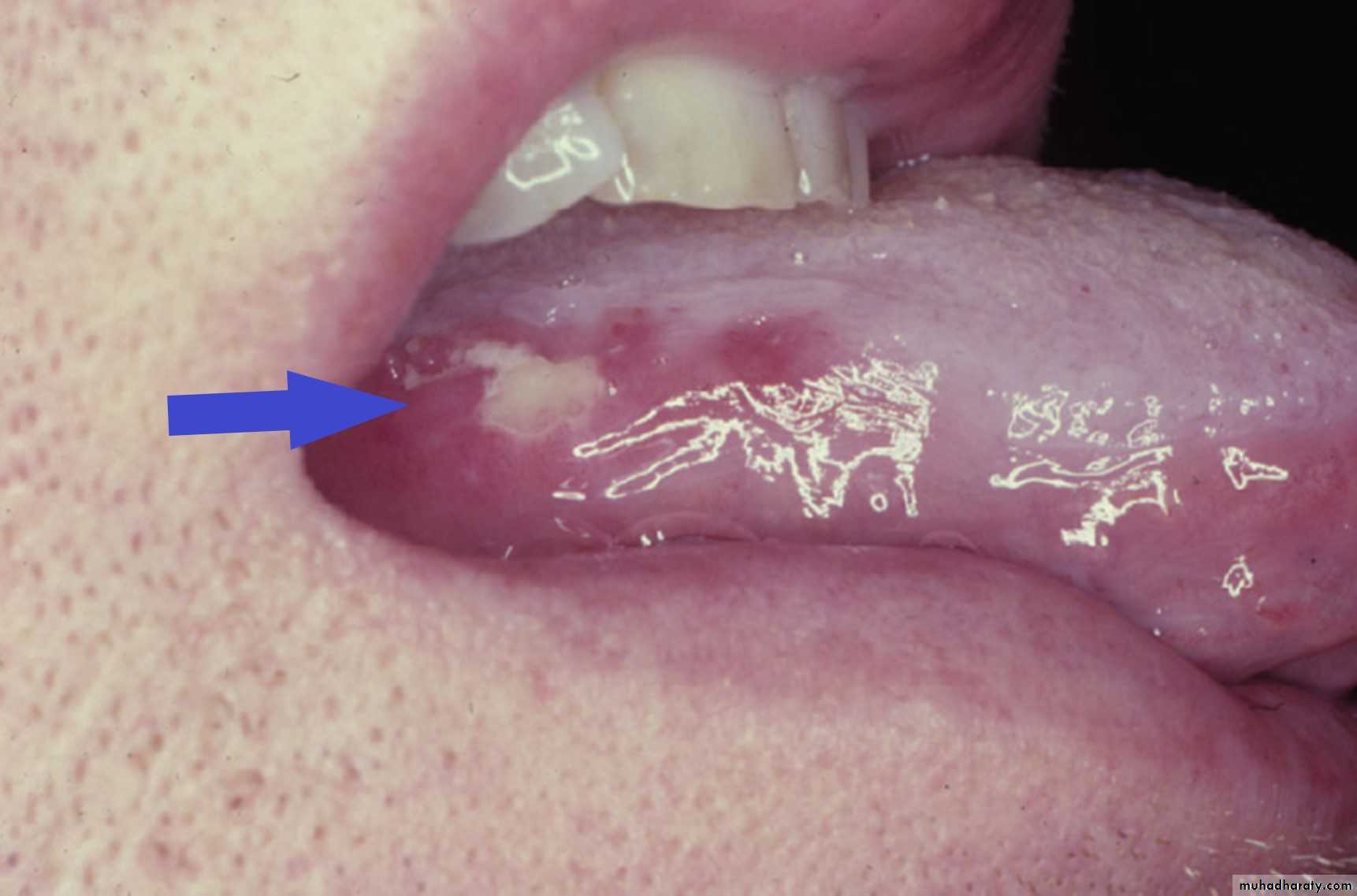
A cluster of ulcers on the tongue of a patient with herpangina. The patient also had lesions of the palate and posterior pharyngeal wall.Cytomegalovirus ulcer
Cytomegalovirus ulcer on a background of hairy leukoplakia in a patient with AIDS.THE END
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY
2020-2021