UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYBy :Dr Ali Moayid
2020-2021
Department of
Conservative Dentistry
5th YEARs
Periapical pathosisPart ii
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY2020-2021
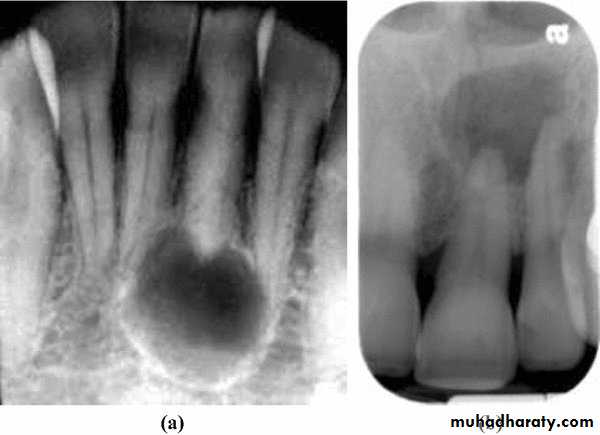
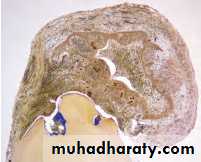
Periapical Cyst
A cyst is a sac-like structure lined by epithelium and containing
fluid or semisolid material.
There are two types of periapical cysts:
pocket cyst and true cyst.UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY2020-2021
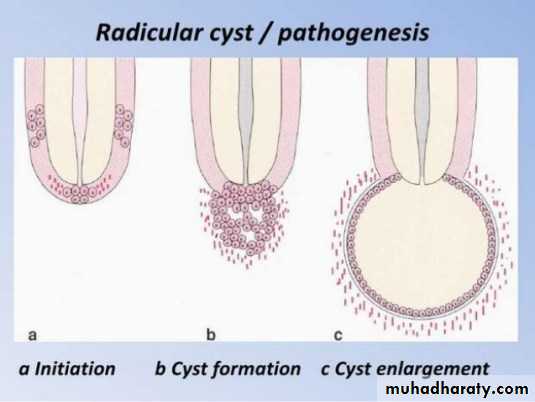
Both are essentially forms of chronic apical periodontitis that develop as a sequel to an infected root canal system but they have different histological appearances.
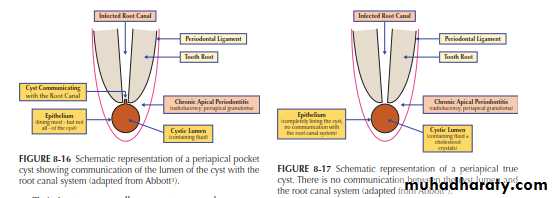
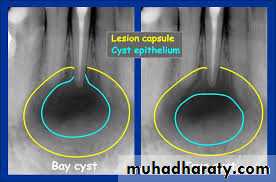
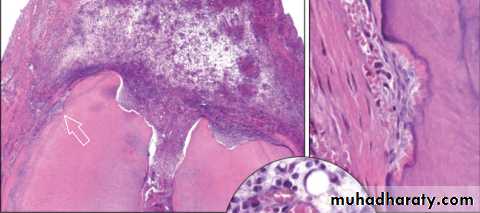
A pocket cyst has an opening that communicates with the root canal system (hence it is not a true cyst according to the definition. It is believed that pocket cysts are likely to heal after the root canal system has been treated, but if no treatment is provided a pocket cyst may “break away” from the root canal and the tooth apex, and the opening closes to become a “true cyst
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY2020-2021
.” Periapical pocket cysts and periapical true cysts cannot be differentiated clinically or radiographically from other periapical conditions that manifest as radiolucencies. In the past, many practitioners have erroneously thought that well-defined borders of the radiolucency indicated a cyst but this is only indicative of a slowly developing lesion. A diffuse border is more likely to indicate a rapidly developing lesion. Likewise, the size of the radiolucency is not indicative of a cyst if it is large—since apical periodontitis, abscesses and cysts can be small or large. A large radiolucency is more likely to indicate a long-standing problem. Periapical pocket cysts cannot be diagnosed clinically and can only be diagnosed histologically. However, clinicians should recognize that this condition does occur and it should be part of the differential diagnosis of a persistent radiolucency following endodontic treatment
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY2020-2021
Typical symptoms—usually no symptoms; may have symptoms if the cyst has become infected (e.g., becomes an acute apical abscess, chronic apical abscess or extra-radicular infection); the patient may report a history of occasional “awareness” of the tooth feeling different; usually a history of recent or current endodontic treatment without resolution of the periapical radiolucency and/or symptoms.
Clinical findings—may be caries, a restoration breaking down or a crack; the tooth has signs of recent root canal treatment (e.g., access cavity restoration); the tooth is not tender to percussion or palpation (unless it has become infected) or it may feel slightly “different” to percussion; no response to pulp sensibility tests.
Radiographic findings—caries may be seen if extensive enough; a periapical radiolucency is present; the radiolucency is persisting or may be increasing in size despite recent endodontic treatment; root canal filling or intracanal dressing evident.
Distinguish from an extra-radicular infection, a foreign body reaction, a periapical true cyst and a periapical scar by histological examination of a biopsy specimen.
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY2020-2021
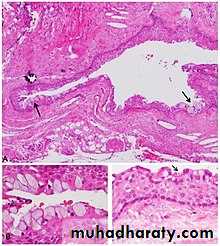
Periapical True Cyst : A true cyst has a complete epithelial lining and contains fluid
and often cholesterol crystals. It is a self-propagating lesion that is no longer dependent on the root canal system being infected.
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY2020-2021
Hence, root canal treatment alone will not resolve a periapical true cysts and surgical removal will be necessary.
The size of the radiolucency and the appearance of the borders are not specific diagnostic signs that can be used to diagnose a true cys and can only be diagnosed histologically. However, clinicians should recognize that this condition does occur and it should be part of the differential diagnosis of a persistent radiolucency following endodontic treatment.
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY2020-2021
Typical symptoms— and Radiographic findings : usually same as pocket cyst.
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY2020-2021
Distinguish from an extra-radicular infection, a foreign body reaction, a periapical pocket cyst and a periapical scar by histological examination of a biopsy specimen.
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY2020-2021
Periapical Scar
A periapical scar is not a disease or a pathological condition. It is a healing response where fibrous, connective tissue forms instead of bone and/or PDL. Typically the radiolucency reduces in size over time but it does not completely disappear (Scar tissue may form following either treatment of an inflammatory condition with bone resorption (i.e., any form of apical periodontitis) or following surgical endodontic treatment.
Periapical scars cannot be definitively diagnosed clinically; they can only be diagnosed histologically but surgery in order to biopsy a suspected periapical scar is not justified or indicated. Clinicians should recognize that this condition does occur and it should be part of the differential diagnosis of a persistent radiolucency following endodontic treatment.
Typical symptoms—no symptoms; history of root canal treatment or a surgical endodontic procedure.
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY
2020-2021
Clinical findings—the tooth will have a restoration; the tooth has signs of root canal treatment (e.g., access cavity restoration); there are normal responses to percussion and palpation; no response to pulp sensibility tests.
Radiographic findings—the tooth has a restoration; the periapical radiolucency is smaller than it was preoperatively and immediately postoperatively but it is persisting following root canal treatment or endodontic surgery; a root canal filling is evident; a root-end root canal filling may be evident if there is a history of previous endodontic surgery.
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY2020-2021
Distinguish from an extra-radicular infection, a foreign body reaction, and a periapical pocket cyst by histological examination of a biopsy specimen , simply observe and reassess over time).
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY2020-2021
WOUND HEALING OF APICALPERIODONTITIS
When irritants (microbial and nonmicrobial) in the canal systems or in the periapical tissues are eliminated by nonsurgical or surgical endodontic therapy, inflammatory mediators are no longer produced in the periapical tissues because of the reduction of inflammatory cells.
Wound healing appears to be a programmed event.
Pathologic processes such as extensive fibrosis do not occur often, and the damaged periapical tissues can be restored mostly to their original structure by the process of regeneration.UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY
2020-2021
During periapical wound healing, the cells of viable periodontal ligament from adjacent root surfaces proliferate to cover the root surfaces in which the periodontal ligament was damaged by apical periodontitis and removed by macrophages.
the extracellular matrix and growth factors of cementum (i.e., IGF-, FGFs, EGF, BMP, TGF- β , PDGF) sequestered after cemental resorption in mature teeth are capable of inducing proliferation, migration, attachment, and differentiation of multipotent stem cells in the periodontal ligament into cementoblast-like cells and produce cementoid tissue on the root surface denuded of periodontal ligament
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY2020-2021
Root resorption that involves cementum or both cementum and dentin can only be repaired by cementoid tissue, because multipotent stem cells of the periodontal ligament are incapable of differentiating into odontoblasts that produce dentin
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY2020-2021
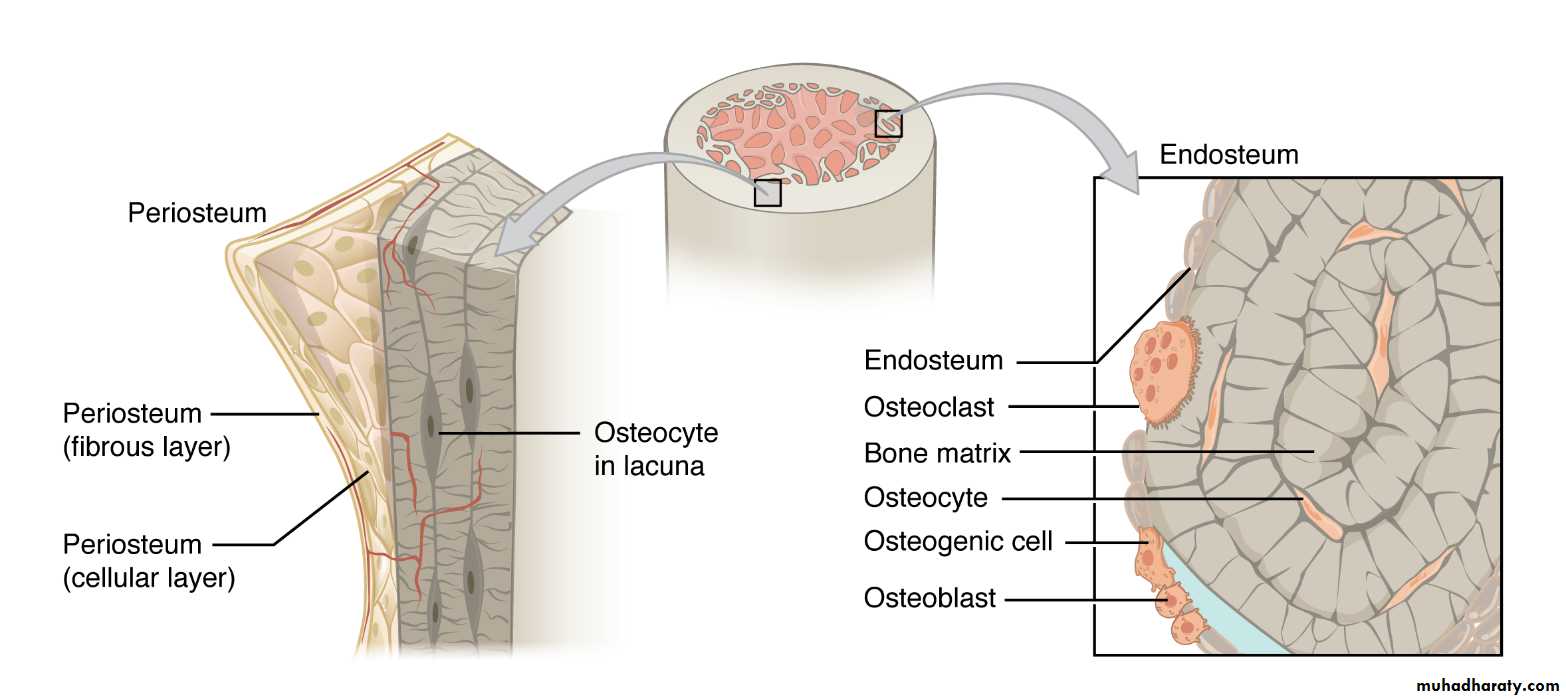
Bone has a remarkable capacity for regeneration in response to injury. During periapical wound healing, the osteoprogenitor cells or mesenchymal cells lining the surfaces of endosteum—stimulated by TGF- β , BMPs, IGFs, PDGF, VEGF, and cytokines released by stromal cells, osteoblasts, platelets, and bone matrix after bone resorption and can undergo proliferation and differentiation into osteoblasts and produce bone matrix
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY2020-2021
When one of the cortical bone plates (buccal or lingual/palatal) is destroyed, osteoprogenitor cells in the inner layer of periosteum beneath the oral mucosa—stimulated by TGF- β , BMPs, IGFs, PDGF, and VEGF—are also capable of proliferation and differentiation into osteoblasts and can produce bone matrix
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY2020-2021
If both buccal and lingual/palatal cortical bone plates are destroyed by large apical periodontitis lesions, it is possible that the lesion may be repaired with fibrous scar tissue because of extensive destruction of the periosteum beneath the oral mucosa
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY
2020-2021
The newly regenerated periodontal ligament will finally undergo remodeling into a mature periodontal ligament, with one group of collagen fibers (Sharpey fibers) inserted into the newly formed cementum and another group of collagen fibers inserted into the newly formed alveolar bone. Thereby, regeneration of damaged periapical tissues, cementum, periodontal ligament, and alveolar bone is completed.
Can Radicular Cysts in Apical PeriodontitisLesions Regress After NonsurgicalEndodontic Therapy?
It was suggested that pocket cysts in apical periodontitis lesions might regress after nonsurgical root canal therapy by the mechanism of apoptosis or programmed cell death, based on molecular cell biology.
In contrast, apical true cysts may be less likely to heal after nonsurgical root canal therapy because of their self-sustaining nature
Biologically, it is unlikely that the hyperplastic epithelial cells of inflammatory apical true cysts would suddenly transform into cells that behave like self-sustaining neoplasms
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY2020-2021
Regression of radicular cysts and regeneration of bone may occur concurrently; or during regression of radicular cysts, part of the cystic lining epithelium could disintegrate due to apoptosis of local epithelial cells.
this could allow a fibrous connective tissue capsule to grow into the lumen of radicular cysts. Eventually, the cystic lining epithelium will completely regress or become remnants of epithelial cell rests remaining in the periodontal ligament.
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY2020-2021
MORPHOLOGIC CHANGES OF
THE APICAL ROOT STRUCTURE
IN APICAL PERIODONTITIS LESIONS
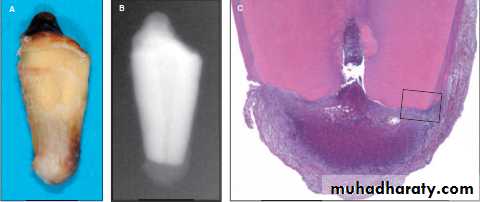
A. Root Resorption in Apical Periodontitis
Root resorption can be defined as the process of removal of cementum and dentin by multinucleated clastic cells often referred to as odontoclasts. Pathologic root resorption is also caused by traumatic injuries to the teeth, neoplastic processes in the jaws and dental treatment procedures, among which orthodontic forces and intentional replantation are most common.
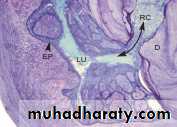
Depending on the amount of calcified tissue lost, root resorption can be detected by periapical radiographs. However, in many cases, the condition can be disclosed only by histologic sections Osteoclasts and odontoclasts possess similar enzymatic properties and resorb their target tissues in a similar manner.
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY2020-2021
Both create resorption depressions termed Howship’s lacunae on the surface of the mineralized tissues. After adhesion of the cells, the bone surface beneath the clastic cell becomes segregated from the environment. Consequently, acids and enzymes released by
the clastic cell concentrate on the surface of the subjacent mineralized tissue, leading to resorption.
Odontoclasts do not normally adhere to nonmineralized layers of the precementum covering the apical root surface. Similar to what happens in internal root resorption, where a breach in integrity of the predentin and odontoblast layer is necessary for resorption to occur, the precementum and cementoblast layers need to be lost in order to stimulate cementum resorption.
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY2020-2021
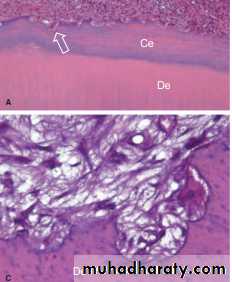
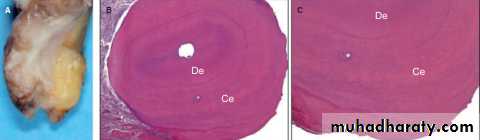
B. Hypercementosis
Less frequent than resorption, the pathologic deposition of several layers of cementum around the apical structure can be observed in association with some periradicular lesions.
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYTHE END
2020-2021
Hope to you life without apical pathosis