Cardiovascular disease (CVD) Control and Preventive Strategies
Presentation Objectives
Public health importance of CVDTypes of cardiovascular diseases
Importance and Potential for CVD Prevention
Barriers to CVD Prevention in Developing Countries
Prevention Strategies
CVD Control Programs
Population based and high risk approaches.
Public Health Significance of CVD
CVD has the same impact on health care today as the epidemics of communicable diseases in earlier timesCVD is the leading cause of mortality in developed countries (50%) with a rising tendency in developing countries (30%)
CVD has major impact on life expectancy, by contributing to death rates in the middle age, thus potential life years lost and affecting labor force and family life
Morbidity: nearly 30% of all disability cases, leading to deterioration of the quality of life.
Types of Cardiovascular Diseases
• Coronary heart disease (CHD, ischemic heart disease)• Cerebrovascular disease (transient ischemic attack, stroke or CVA)
• Hypertension and hypertensive heart disease
• Heart failure
• Peripheral vascular disease
• Rheumatic heart disease (from streptococcal infection)
• Congenital heart disease
• Cardiomyopathies.
Importance of Prevention
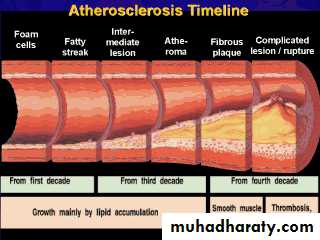
Natural History of CHDAsymptomatic Reversible Irreversible
ischemia ischemia (Angina) ischemiaPrehospital phase Very early
20% mortality profound ischemiaEvolving infarction
Hospital phase10% mortality
Completed infarction
Posthospital phase
10% mortalityPotential for Prevention
CVD risk factors: large potential for preventionNonmodifiable RF:
Age, Sex, FM history of CVD
Behavioral RF: *
Smoking, Unhealthy diet
Sedentary Lifestyles
Socioeconomic and cultural
determinants *
Early life Characteristics *
* Modifiable
Medical RF:
Hypertension
Cholesterol
Diabetes
Obesity
Endpoints:
Heart Disease
Stroke
Vascular Disease
Cancer
Some Constraints for CVD Prevention in Developing Countries
Limited recognition of CVD, with limited data availability on the subjectPrevention is not considered important, due to market pressure which favors therapy
CHD and stroke are seen as diseases that only specialists can treat
Health care needs are not addressed “prospectively” by existing health system (poor planning)
Costs are rising and resources are decreasing
The medical education system is focused towards secondary and tertiary care, rather than public health and prevention.
Why preventing NCD/CVD in developing countries is an opportunity?
• Relatively low levels of some risk factors in several developing countries• Opportunity for ‘primordial prevention’, unlike for western countries (where CVD epidemic was understood at its peak and dealt with mainly by case-management)
• Prevention is the best option. An approach mainly based on case-management is not affordable and costly for most developing countries.
•
Essential components of CVD Control Programs
• Efficient systems for estimation of CVD-related burden (morbidity and mortality) and its trends.• Estimation of the levels of CVD risk factors in representative population samples to identify risk factors requiring immediate intervention.
• Evaluation of emerging risk factors
• Develop disease surveillance system, CVD registries and data centers.
• Development of a health policy integrating population-based measures for CVD risk modification and case management strategies for high risk group.
•
Types of Prevention Strategies I
Three types of prevention are advocated by WHO:Primordial: prevention of appearance of risk factors, e.g. smoking, sedentary life and unhealthy food habits
Primary: Limit the number of cases by control of risk factors of CVD
e.g. Hypertension, smoking...etc
Secondary: control of CVD to control complications and further deterioration
e.g. RHD, MI or Angina
Strategies to prevent CVDs II
Two complementary strategies advocated for primary prevention are the Population based and the High risk strategies.Population based approach
Community wide interventions
Modify behavior
Influence the distribution of risk factors in a population
Modest changes in risk factors substantial reduction in the cumulative population risk of CVD in a community
Small benefits to each individual.
Strategies to prevent CVDs III
High risk approachIdentify the few who are at high risk
Targeted behavioral or pharmacological interventions
Greatest risk reduction in individuals.