Precision Attachments
By:Dr, Ahmed Asim
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY2020-2021
Department of Prosthodontics
Department of:
HEREUNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYDepartment of:
HERE
Definition
A precision attachment is a precision connector made up of two or more parts. One part is attached to the root or crown of a tooth or to a dental implant, and the other to the prosthesis.
020-2021
How do they work?The attachments work by using wires, springs, or hinges which in turn allow the denture to move slightly whilst chewing, reducing strain on the surrounding teeth. In some cases the attachment can be used in conjunction with an implant.
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY
020-2021
IndicationsPartial dentures
Over denturesUnilateral or bilateral free - end dentures
Fixed – movable bridge work
Implantology (removable or fixed super structure)
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY020-2021
Precision attachment successPrecision attachment success depends on:
A well motivated patient with good oral and general health.
A good level of knowledge about attachments (team work between the clinician and technician).
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY020-2021
Patient selectionRegular adjustment of the attachments and relining of the prostheses will be required during the life span of the prosthesis.
This requires the patient to be fully aware of this type of restorative treatment.
The costs involved in both time and resources for this type of restorative treatment are great and the patient must be aware of this before starting treatment.
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY020-2021
Intra oral assessmentThe intra oral examination include
The teeth assessed for caries, vitality, bone support, mobility and angulation.Clincal crown length and crown root ratio.
Full periodontal assessment include full arch pocket charting, oral hygiene status, and a full radiographic assessment of bone support.
Occlusal examination.
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY020-2021
Pre prosthetic treatment
Hard and soft tissue problems should be assessed and treated before starting treatment, such as:
Poor gingival contour
Soft tissue hyper plasia
Inadequate crown length
Bony tori and undercuts
High frenal attachments
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY020-2021
Prosthetic considerationThe selection of abutment teeth influenced by:
The number and distribution of the remaining teeth.Adequacy of periodontal support.
Analysis of occlusion.
Frame work design, location of major connectors, and type of retainers should be studied carefully.
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY020-2021
Attachment selectionLocation
FunctionRetention
Space
cost
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY020-2021
Location
Intra coronal attachments.
Extra coronal attachments.Radicular/intraradicular attachments.
Bar type attachments.
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY020-2021
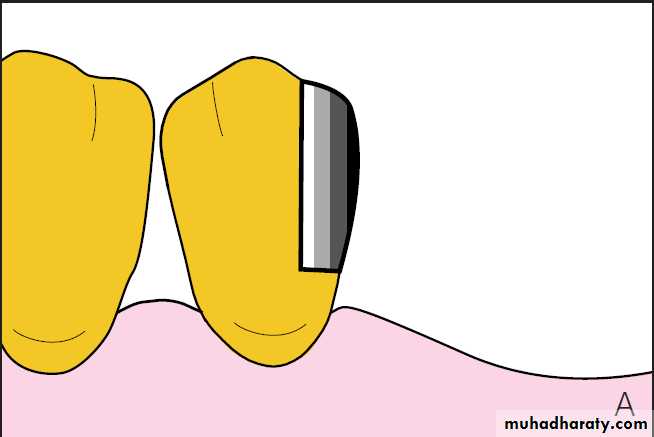
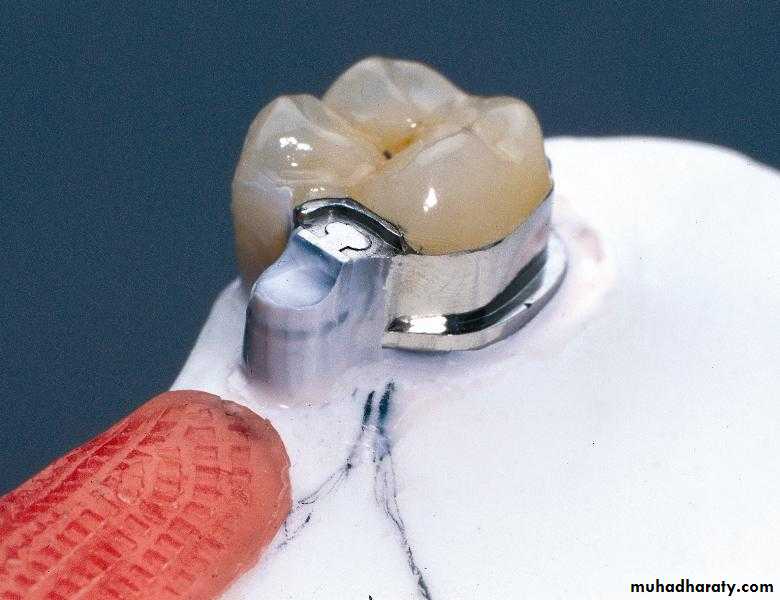
Intra coronal attachmentsA matrix component part housed within the coronal tissue of the abutment tooth.
There are two types of intra coronal attachments:Those where retention is entirely frictional.
Those where retention is supplemented by some mechanical means.
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY020-2021
Intra coronal attachments Indications:Removable bounded saddle prosthesis (resilient type).
Fixed movable design of fixed prosthesis (non resilient type).UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY
020-2021
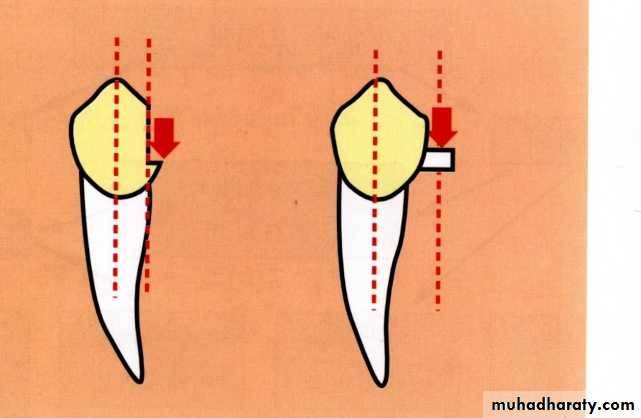
Intra coronal attachments Advantages:The contour of the abutment is not altered as in the extra coronal types.
In fixed prosthodontics this attachment can over come the problem of non parallel abutments.UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY020-2021
Intra coronal attachments Disadvantages:The size of attachment may encroaches upon the pulp chamber, if the tooth is small or high in position.
Wearing of the component parts of the removable prosthesis, so reactivation is required.
Adequate preparation of the tooth is required where the component part is to be housed.
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY020-2021
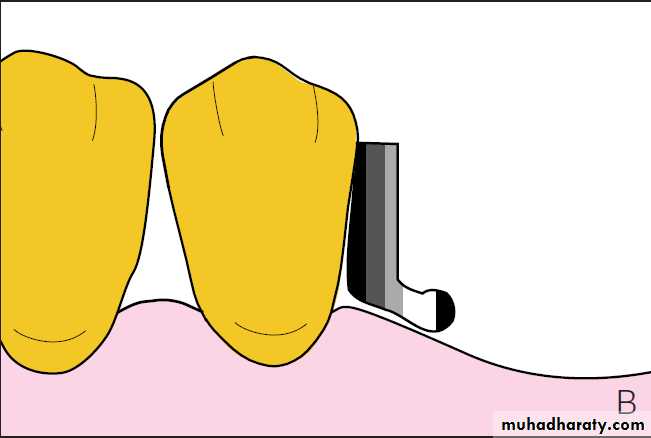
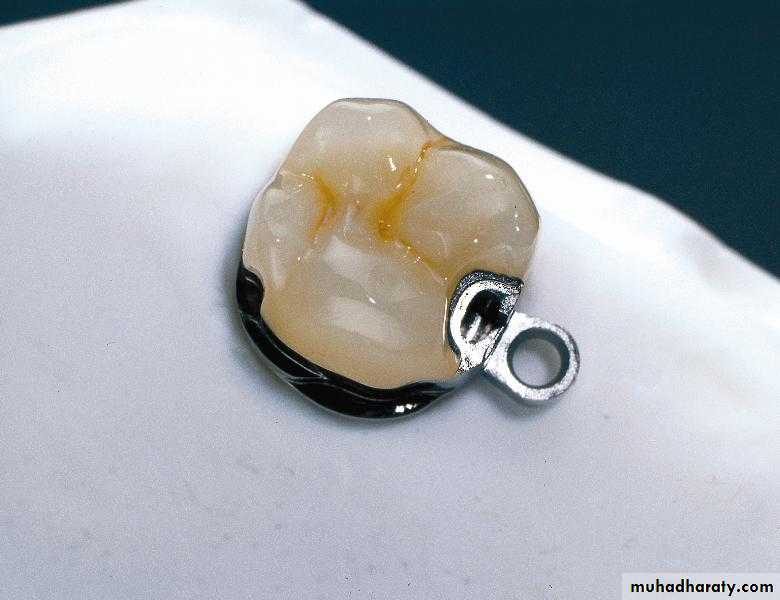
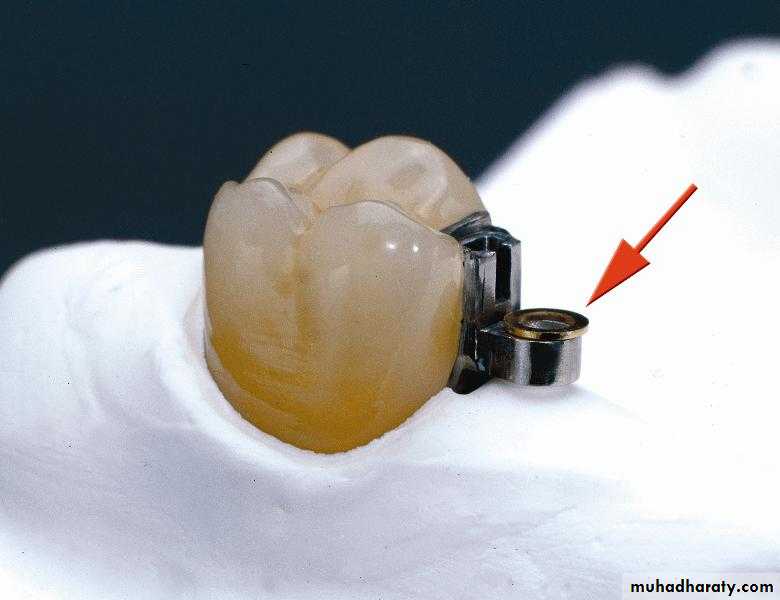
Extra coronal attachmentAn attachment having part or all of their mechanism outside the contour of the tooth.
These attachments have a particular application in the free end saddle situation.UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY020-2021
There are three types of extra coronal attachments:
Projection units: this major group of attachments project from abutment crown.
Connection units: this group are joints allowing movement between two sections of denture.Combined units: this group consists of two types of attachment an extra coronal hinge type element connected to an intra coronal attachment.
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY020-2021
Extracoronal precision attachments for removable partial dentures are recommended when:Less tooth reduction is required. Retaining abutments are small to avoid over-contoured intracoronal attachment abutments and/or pulpal exposure.
Extracoronal precision attachment are traditionally easier to insert and remove. These are used for patients with limited manual dexterity, or the prosthesis has a difficult path of insertion and removal.
The patient does not always wear the removable prosthesis. Intracoronal females in retaining abutments will collect food and present problems when the patient attempts to seat the intracoronal retained prosthesis.
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY020-2021
Extracoronal Precision attachments are normally resilient to allow free movement of the prosthesis to distribute potentially destructive forces or loads away from the abutments to supportive bone and tissue. Three distinctive movements are defined in function: (1) Hinge, (2) Vertical, and (3) rotational.UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY020-2021
ParagraphUNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY
020-2021
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY020-2021
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY020-2021
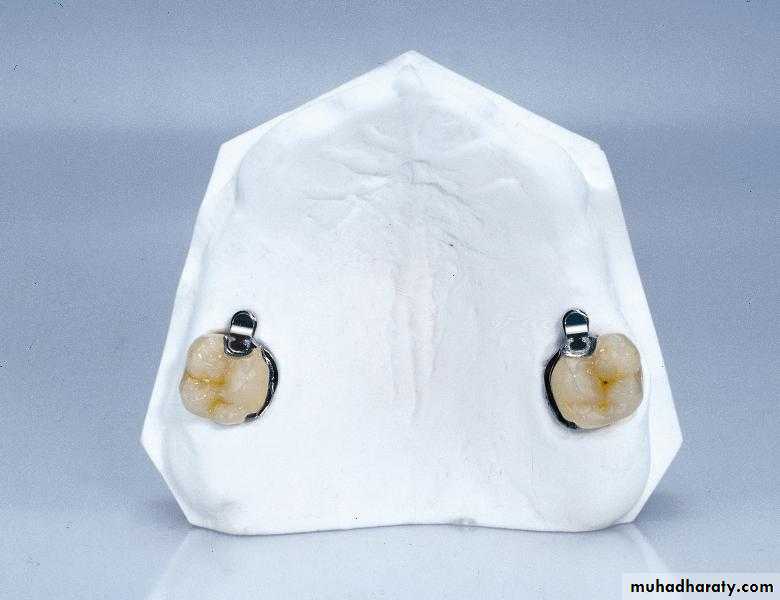
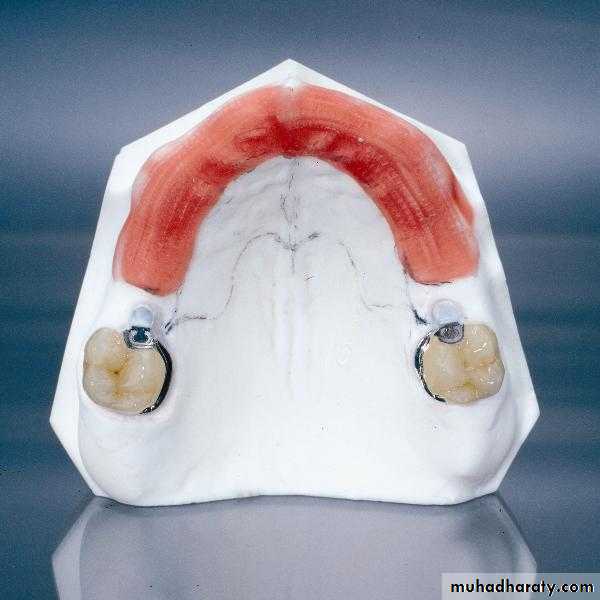
Extracoronal Precision AttachmentsExtracoronal attachments can be rigid but are generally resilient, distributing the potentially harmful forces away from the abutments to the edentulous ridges. This is especially useful with free-end saddles.
The patrix of extracoronal attachments is either soldered or cast to the retainer adjoining a saddle area and is completely outside the normal contour of that retainer. The matrix is housed within the prosthesis.
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY020-2021
Intracoronal Slide AttachmentsHere the matrix is contained within the contour of the crown. For this the clinician will need to prepare boxes in order to accommodate the attachment.
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY020-2021
Anchors
These attachments are used on either roots or implants to retain overdentures or removable partial dentures.
The patrix is soldered to the diaphragm of a cast post and the matrix contained in the denture.
There are two basic types: rigid and resilient.
The rigid attachments are used in bounded unilateral or bilateral saddle cases.
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY020-2021
The resilient attachments, which allow a degree of movement between the patrix and matrix, reducing the stress on the abutment roots, are used in bilateral free-end saddle cases. If used unilaterally to retain a removable partial denture, a transversal connector must be used to give cross-arch stabilization which will lessen the stress on the abutment tooth or teeth.UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY
020-2021
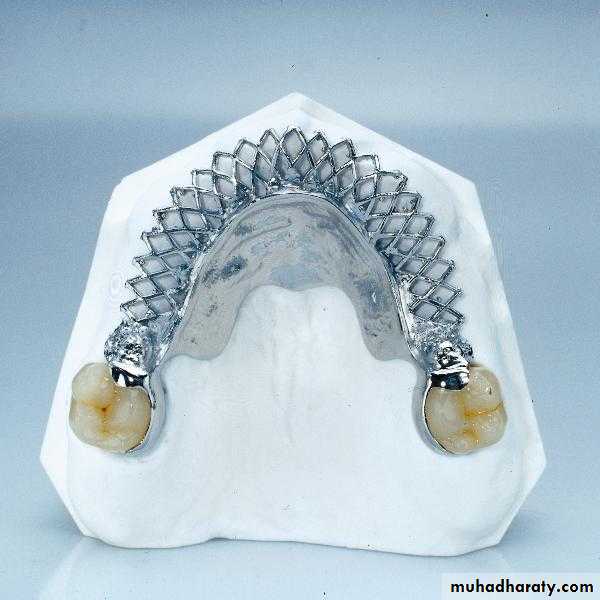
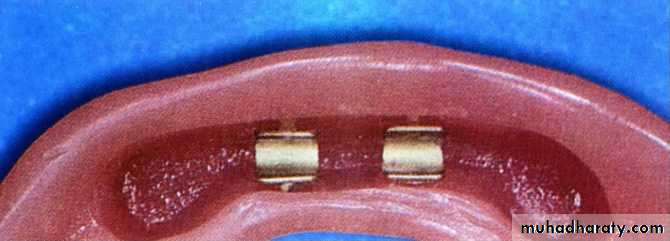
BarsThe bar, being the patrix, is attached to retainers while the matrix sleeve or clips/riders are processed into the denture.
They are used to retain over-dentures or removable partial dentures.
The bar is usually soldered to two or more posts and diaphragms with enough space between them to allow the matrix sleeve or riders to be processed in the denture to give the necessary retention.
They can also be used in conjunction with crowns and implants.
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYThey are either commercially or laboratory manufactured.
Bars can be either rigid or resilient.UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY020-2021
Auxiliary AttachmentsThis group of attachments covers a wide range of applications.
They can be used to:(a) allow contingency planning which will enable the clinician to remove the prosthesis for repair or conversion.
(b) overcome alignment problems which arise when abutments converge, making it impossible to prepare them so that they can be mutually withdrawable when constructing fixed partial denture.
(c) replace the loss of soft tissue in anterior fixed partial dentures. Supplements retention on bars and telescopic crowns.
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRYTHE END
UNIVERSITY OF MOSUL
COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY2020-2021