Third To Eighth Weeks :The Embryonic Period-1-
• The embryonic period, or period of organogenesis, occurs from the third to the eighth weeks of development and is the time when each of the three germ layers, ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm, gives rise to a number of specific tissues and organs. By the end of the embryonic period, the main organ systems have been established , rendering the major features of the external body form recongnizable by the end of the second month.• Derivatives Of The Ectodermal Germ Layer
• At the beginning of the third week of development, the ectodermal germ layer has the shape of a disc that is broader in the cephalic than in the caudal region. Appearance of the notochord and prechordal mesoderm induces the overlying ectoderm to thicken and form the neural plate. Cells of the plate make up the neuroectoderm, and their induction represents the initial event in the process of neurulation.
• Neurulation
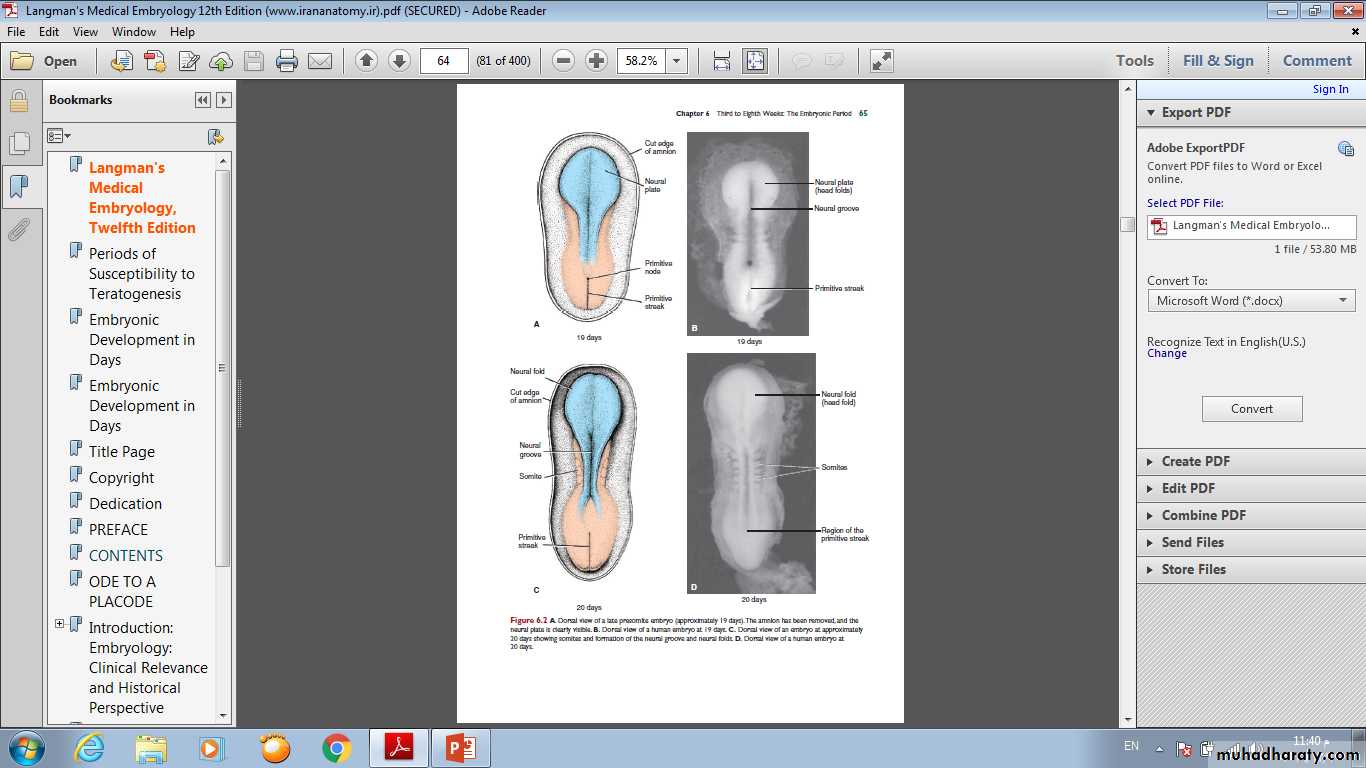
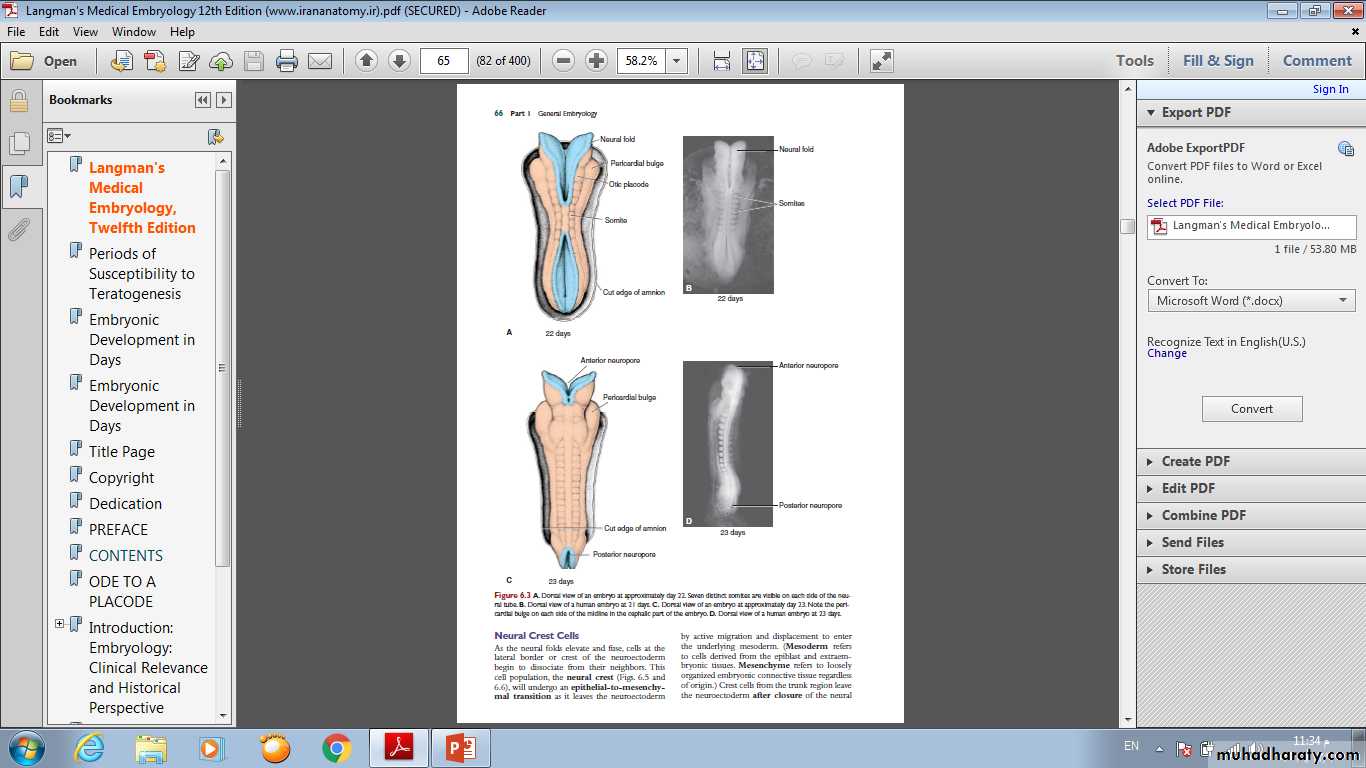
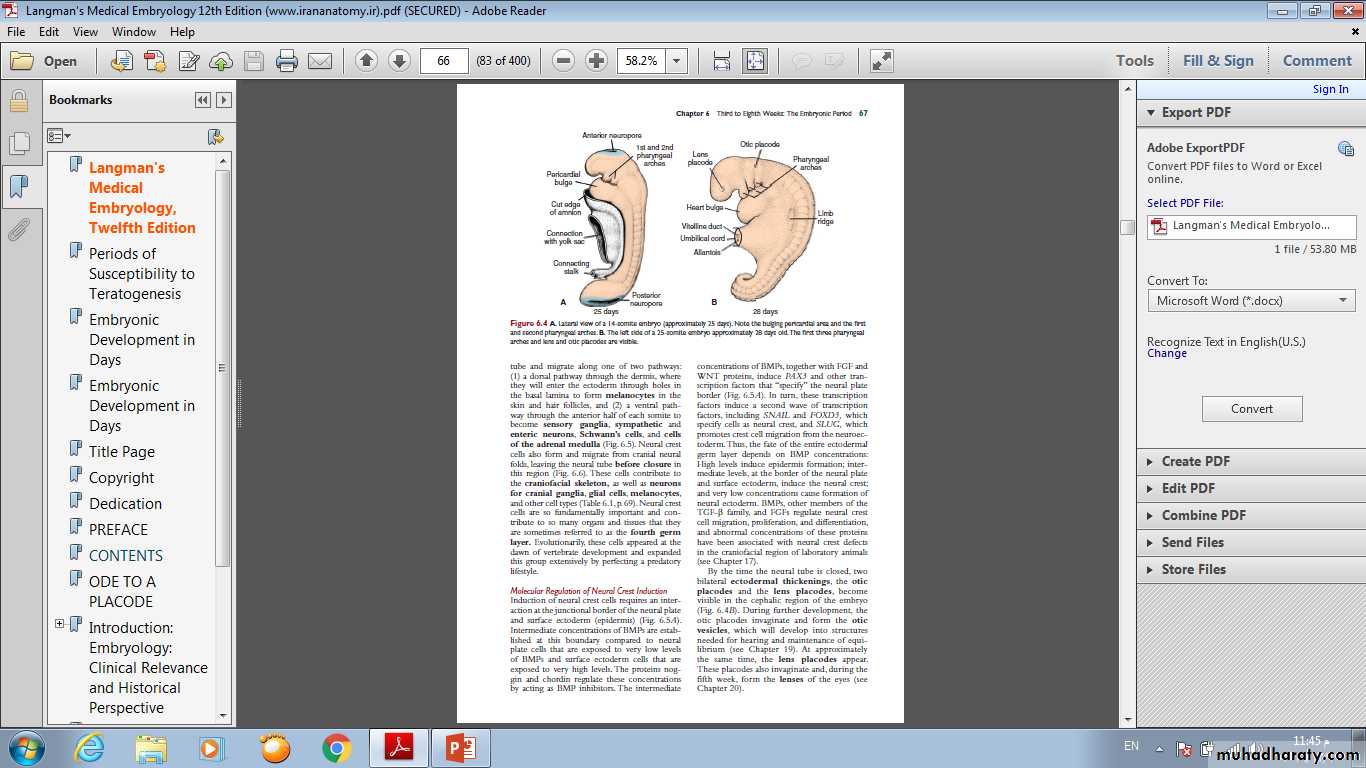
• Neurulation is the process whereby the neural plate forms the neural tube. By the end of the third week, the lateral edges of the neural plate become elevated to form neural folds, and the depressed mid region forms the neural groove. Gradually, the neural folds approach each other in the midline, where they fuse . Fusion begins in the cervical region (fifth somite) and proceeds cranially and caudally . As a result, the neural tube is formed. Until fusion is complete the cephalic and caudal ends of the neural tube communicate with the amniotic cavity by way of the anterior (cranial) and posterior (caudal) neuropores, respectively.• Closure of the cranial neuropore occurs at approximately day 25 (18- to 20-somite stage). whereas the posterior neuropore closes at day 28 (25-somite stage).
• Neurulation is then complete, and the central nervous system is represented by a closed tubular structure with a narrow caudal portion, the spinal cord, and a much broader cephalic portion characterized by a number of dilations, the brain vesicles.
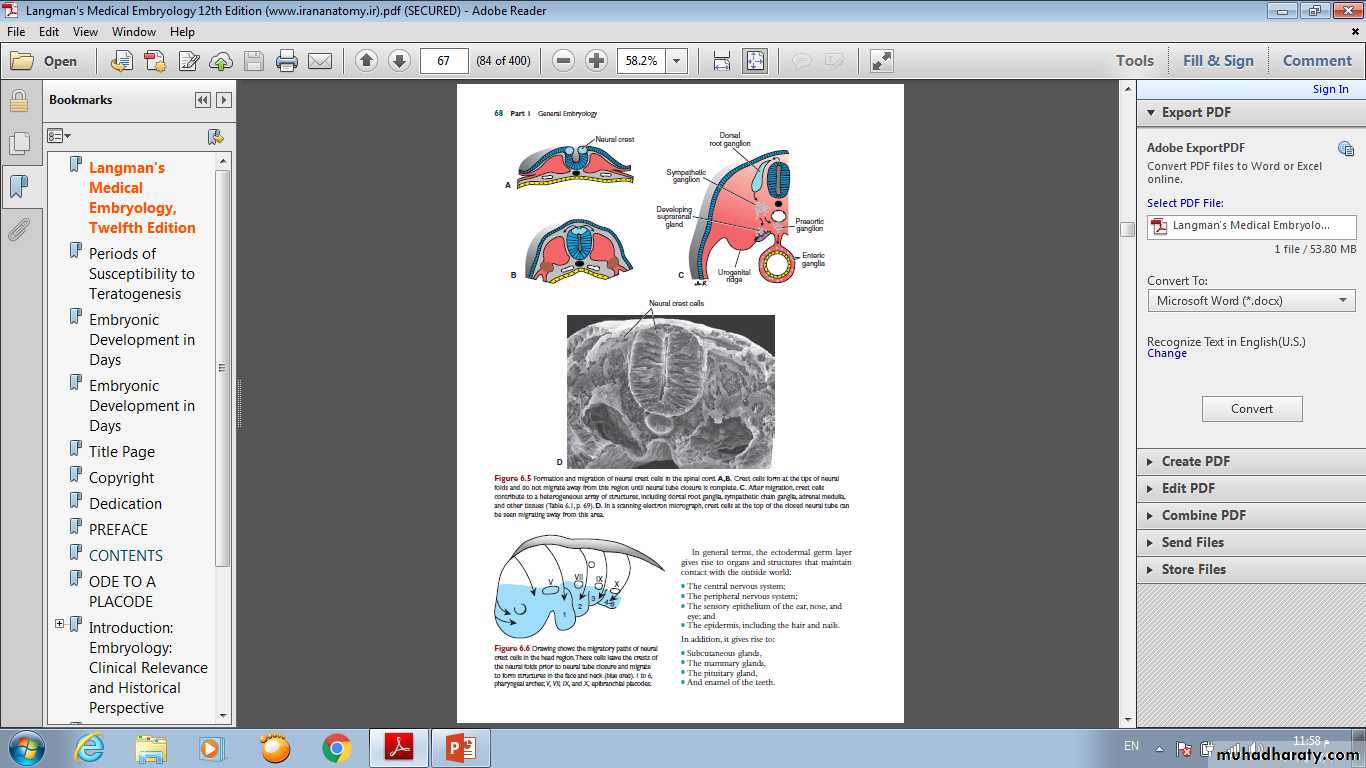
Neural Crest Cells
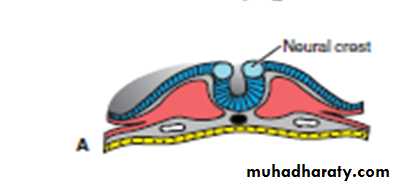
As the neural folds elevate and fuse, cells at the lateral border or crest of the neuroectoderm• begin to dissociate from their neighbors. This
cell population, the neural crest will undergo an epithelial-to- mesenchymal transition as
it leaves the neuroectoderm by active migration and displacement to enter the under-
lying mesoderm.
Neural Crest Derivatives
• 1-Dermis of the face and skin.• 2-Schwann cells, Glial cells .
• 3-Spinal ganglia.
• 4- Melanocytes.
• 5-Adrenal medulla.
• 6-parasympathetic ganglia.
• 7-Meninges.
The ectodermal germ layer gives rise to organs and structures that maintain contact with the outside world:
● The central nervous system
● The peripheral nervous system
● The sensory epithelium of the ear, nose, and eye
The epidermis, including the hair and nails.
In addition, it gives rise to:
● Subcutaneous glands.
● The mammary glands.
● The pituitary gland.
● Enamel of the teeth.