Third To Eighth Weeks :The Embryonic Period-2-
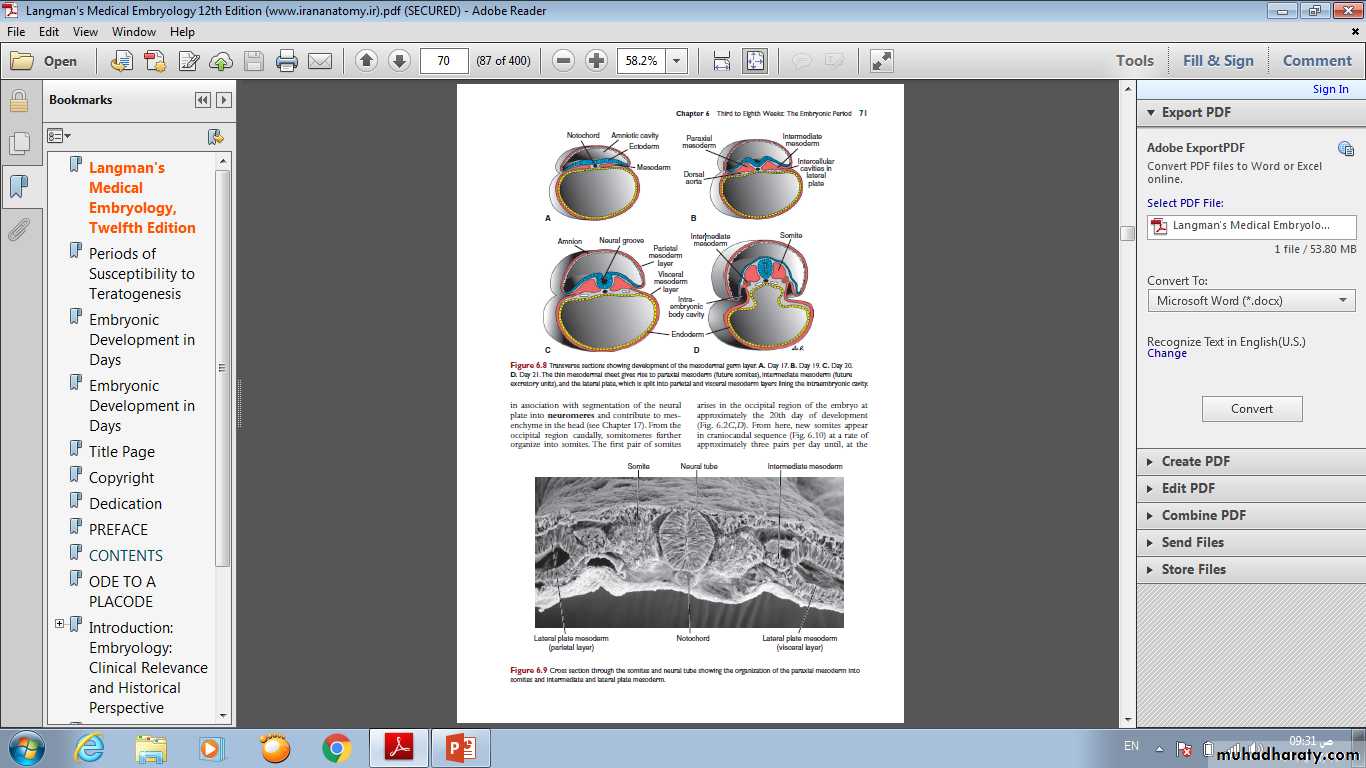
Derivatives of The Mesodermal LayerInitially , cells of the mesodermal germ layer form a thin sheet of loosely woven tissue on each side of the midline . By approximately the 17 th day, however , cells close to the midline proliferate and form a thickened plate of tissue known as paraxial mesoderm . More laterally, the mesodermal remain thin and is known as the lateral plate, this tissue divided into two layers:
1-Somatic or parietal mesoderm layer.
2-Visceral or splanchnic mesoderm layer.
Intermediate mesoderm connects paraxial and lateral plate mesoderm.
Paraxial Mesoderm
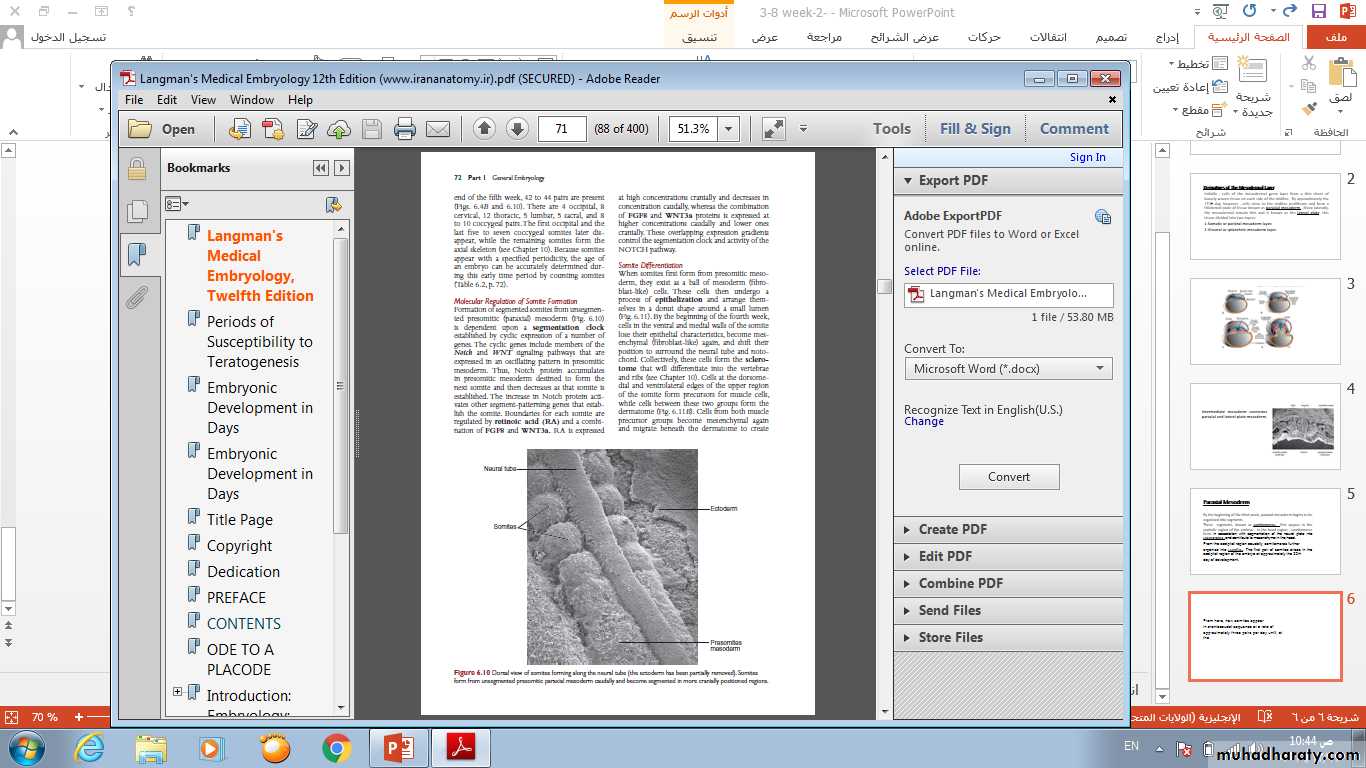
• By the beginning of the third week, paraxial mesoderm begins to be organized into segments.• These segments, known as somitomeres, first appear in the cephalic region of the embryo . In the head region , somitomeres form in association with segmentation of the neural plate into neuromeres and contribute to mesenchyme in the head.
• From the occipital region caudally, somitomeres further organize into somites. The first pair of somites arises in the occipital region of the embryo at approximately the 20th day of development.
From here, new somites appear in cranio caudal
sequence at a rate of approximately three pairs per day until, at the end of the fifth week, 42 to 44 pairs are present.• There are 4 occipital, 8 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral, and 8 to 10 coccygeal pairs.
• The age of an embryo can be accurately determined during this early time period by counting somites . Like approximate age of embryo (20 days), so that, the number of somites = 1-4.
• Somites give rise to the myotome (muscle tissue), sclerotome (cartilage and bone), and dermatome(dermis of the skin ), which are all supporting tissues of the body.
• Intermediate Mesoderm differentiates into urogenital structures.
• Lateral Plate Mesoderm splits into parietal (somatic) and visceral (splanchnic) layers, which line the intraembryonic cavity and surround the organs. Mesoderm from the parietal layer , together with overlying ectoderm ,forms the lateral body wall folds . The visceral layer , together with embryonic endoderm , forms the wall of the gut tube.
Blood cells and blood vessels also arise from mesoderm. Blood vessels form in two ways: vasculogenesis , and angiogenesis.The first blood islands appear in mesoderm surrounding the wall of the yolk sac at 3 weeks of development and slightly later in lateral plate mesoderm and other regions.
Derivatives of The Endodermal Germ Layer
The gastrointestinal tract is the main organ system derived from the endodermal germ layer.This germ layer covers the ventral surface of the embryo and forms the roof of the yolk sac.
The endodermal germ layer initially forms the epithelial lining of the primitive gut and the intra
embryonic portions of the allantois and vitelline duct. During further development, endoderm gives rise to:
1-The epithelial lining of the respiratory tract.
2-The parenchyma of the thyroid, parathyroids, liver, and pancreas .
3-The reticular stroma of the tonsils and the thymus.
4-The epithelial lining of the urinary bladder and the urethra.
5-The epithelial lining of the tympanic cavity and auditory tube.