• DIABETES MELLITUS IN PREGNANCY
Dr .Adel Gassab MohammedMD. CABMS. MSc of Specialized Endocrine and Diabetes, Specialist Endocrinologist,
College of medicine
ORCID iD: https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9084-1038.
Email: adelgassab@utq.edu.iq
• DEFINITIONS
• Diabetes Mellitus in Pregnancy falls into 2 categories:• Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM) – Any degree of glucose intolerance with onset or first recognition during pregnancy. Does not exclude possibility that unrecognised glucose intolerance may have been present before onset of pregnancy.
• Pre-gestational Diabetes Mellitus – diagnosed when the woman has diabetes before pregnancy.
• GESTATIONAL DIABETES MELLITUS (GDM)
• Physiology• Pregnancy ↑ Human placental lactogen (HPL) + cortisol (insulin antagonists)
• Mother relative insulin resistance esp 3rd trimester
• Maternal pancreas ↑ insulin to maintain carbohydrate metabolism ↓ FPG
• Carbohydrate intake ↑ glucose than non-pregnant lady
• Glucose crosses placenta by facilitated diffusion and the fetal blood glucose level closely follows the maternal level
• Therefore, fetal glucose levels therefore is normally maintained within normal limits, as in mother.
• Modified Penderson Theory: Impact of Maternal Hyperglycaemia During Pregnancy
• MATERNAL↓ Insulin release
↓ glucose utilisation• PLACENTA
• ? Altered structure and/or functionfetal
• Birth weight ↑• ↑ Lipid &
• ↑ Glycogen• ↑ Insulin (hyperinsulinaemia)
Hyperglycaemia
• Hyperglycaemia• GDM IN FIRST TRIMESTER
• Women found to have fasting hyperglycaemia or abnormal glucose intolerance in the first trimester might have pre-existing diabetes• Should be treated as women with glucose intolerance before pregnancy
• First trimester hyperglycemia high risk of congenital abnormalities in fetus
Detection and diagnosis
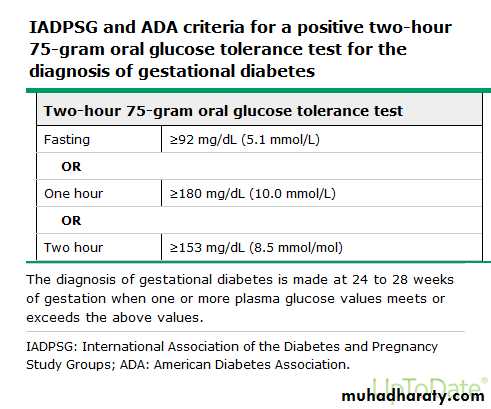
Risk assessment for GDM should be undertaken at the first prenatal visit.Women with clinical characteristics consistent with a high risk of GDM (marked obesity, personal history of GDM, glycosuria, or a strong family history of diabetes) should undergo glucose testing as soon as feasible. If they are found not to have GDM at that initial screening, they should be retested between 24 and 28 weeks of gestation.
• SCREENING FOR GDM
Women with high risk of GDM:• Previous poor obstetrics outcomes usually associated with diabetes
• Family origin with high diabetes prevalance (South Asian, African-Caribbean,Middle-Eastern)
• BMI >30kg/m2
• First degree relative with Diabetes• Personal history of GDM
• Previous macrosomic baby ≥4.5kg
• PRE-GESTATIONAL DIABETES
• TYPE 1 AND TYPE 2 DIABETES• Pre-conception care is essential
• If untreated in first few weeks gestation, associated with:
• Spontaneous abortions
• Birth defects
• If untreated during 2nd or 3rd trimester, associated with:
• Fetal macrosomia and metabolic abnormalities
• Birth injury
• Maternal hypertension and pre-eclampsia
• Future diabetes and/or obesity in child
• PRE-PREGNANCY COUNSELLING
• To assess suitability for pregnancy• To look for complications of diabetes, evaluate and treat complications prior to onset of pregnancy
• To achieve optimal control prior to and during very early pregnancy
• To provide an opportunity for pre-pregnancy advice and folate supplements
• MEDICAL ASSESSMENT IN PRE- CONCEPTION CARE
• Duration and type of diabetes
• Medical history and current medical management plan
• Chronic diabetes complications:
• Retinopathy
• Nephropathy
• Neuropathy
• Co-morbid conditions (in addition to diabetic complications)
• Hypertension (ideal blood pressure <120/80)
• Coronary Artery Disease
• Hyper- or Hypothyroidism
• Other auto-immune disease
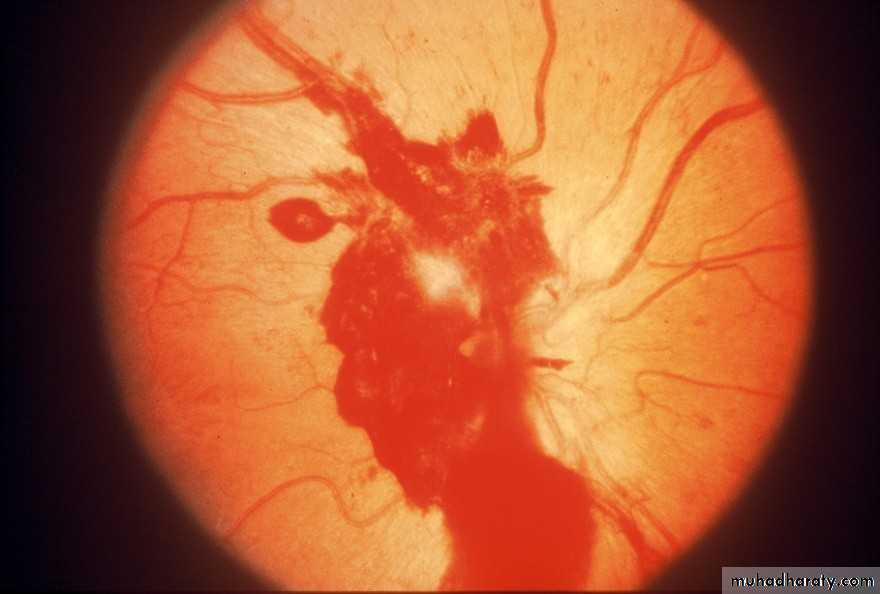
• PREVENTING RETINOPATHY PROGRESSION
• Rapid normalization of blood glucose during pregnancy can trigger retinopathy progression
• Retinal status should stabilized prior to conception
• Reassess retinal status each trimester (more frequently if retinopathy is present)
• RECOMMENDATIONS
• Plan pregnancies
• Attain a pre-conception HbA1c of < 7%
• If planning pregnancy:
• Needs retinal screening prior to conception
• Screen for diabetic retinopathy and coronary heart disease
• Discontinue oral hypoglycaemic agents and attain glycaemic targets using insulin, if possible
• Replace ACEI and ARBs to other hypertensives that are safe to take in pregnancy
• Stop statins
• POSSIBLE CONTRA-INDICATIONS TO PREGNANCY
• Ischaemic Heart Disease• Active, unrelated proliferative retinopathy
• Renal insufficiency
• Severe Gastroparesis
• Inability or unwillingness to use Insulin
• RISKS TO MOTHER WITH GESTATIONAL DIABETES
• Increased risk of Caesarian Section• Pre-eclampsia (2-4 x esp with co-existing microalbuminuria/frank nephropathy)
• Polyhydramnios
• Pre-term labour
• Post-Partum Haemorrhage
• Temporary worsening of renal function
• Progression of retinopathy
• ↑ incidence of infection, severe hyperglycaemia/hypoglycaemia, DKA
• In future:
• Recurrent GDM Pregnancies
• Risk of developing T2DM (50% in 5 - 10 years)
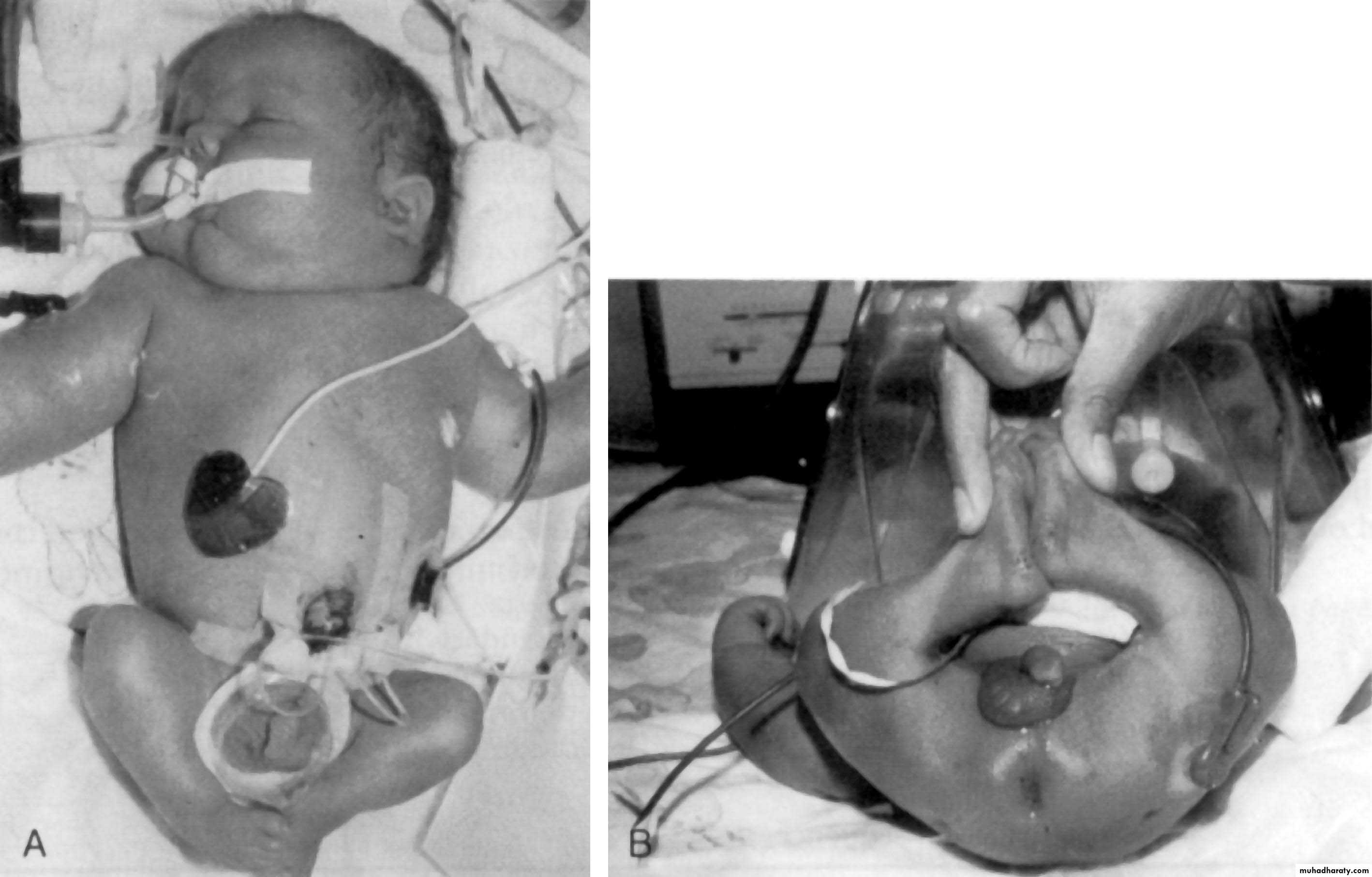
• POTENTIAL COMPLICATIONS IN INFANTS OF MOTHERS WITH DIABETES
• Intra-uterine demise
• Spontaneous abortions
• Stillbirth (10-30%)
• Congenital malformations
• Neural tube defects
• Cardiac defects
• Caudal Regression syndrome (rare)
• POTENTIAL COMPLICATIONS IN INFANTS OF MOTHERS WITH DIABETES
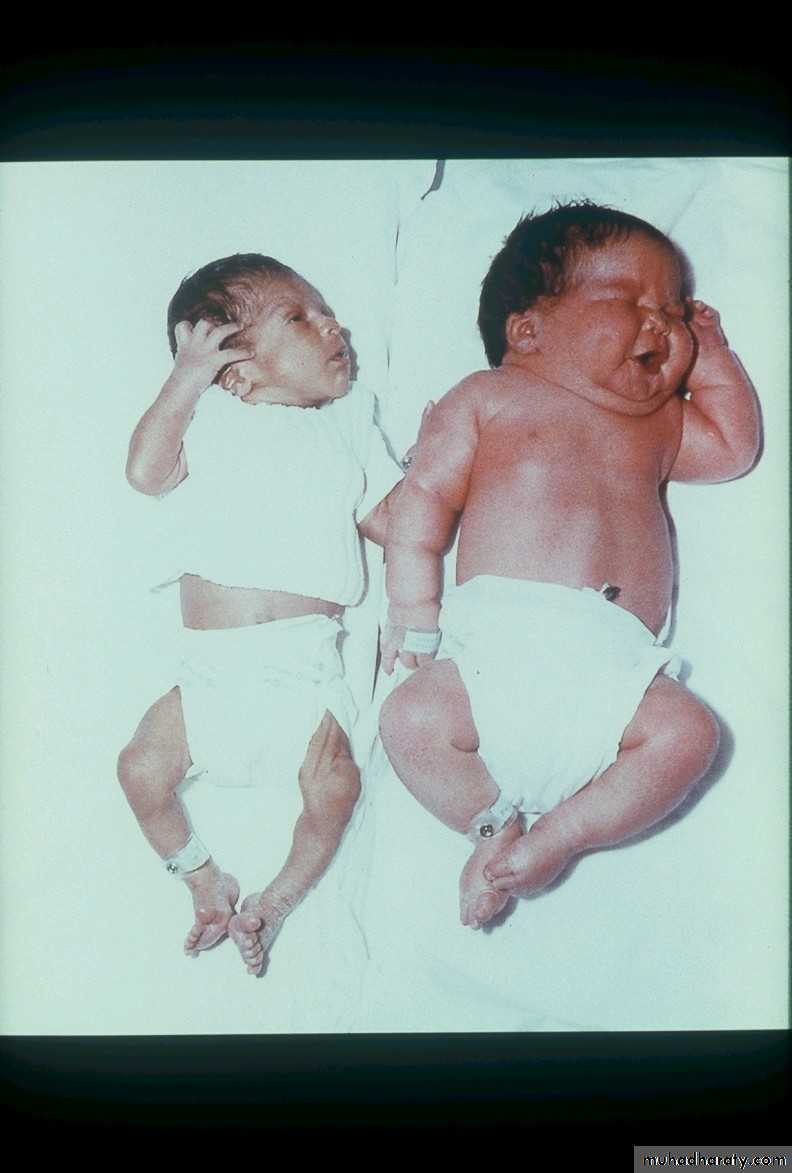
• Macrosomia• Visceromegaly
• Cardiac enlargement
• Hepatic enlargement
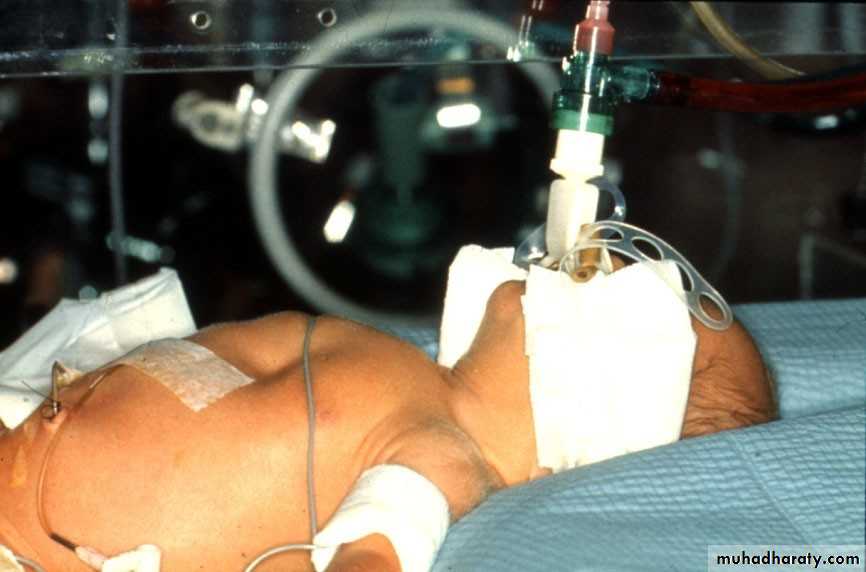
• Respiratory Distress Syndrome
• Asphyxia
• Birth injury
• Shoulder Dystocia
• Erb’s Palsy
• Diaphragmatic paralysis
• Facial paralysis
• MACROSOMIA
• POTENTIAL COMPLICATIONS IN INFANTS OF MOTHERS WITH DIABETES
• Metabolic complications• Hypoglycaemia (high insulin production in immediate neonatal period due to recent fetal hyperglycaemia)
• Mothers encouraged to breastfeed ASAP; monitor baby’s blood glucose; formula-fed or glucose infusion prn
• Hypocalcaemia, magnesium deficiency apnoeic episodes and fits
• Polycythaemia hyperbilirubinaemia jaundice
• Partial exchange transfusion
• Management: Obstetrics
• Nuchal Traslucency Scan• Detailed US for fetal anomalies
• fetal echocardiography
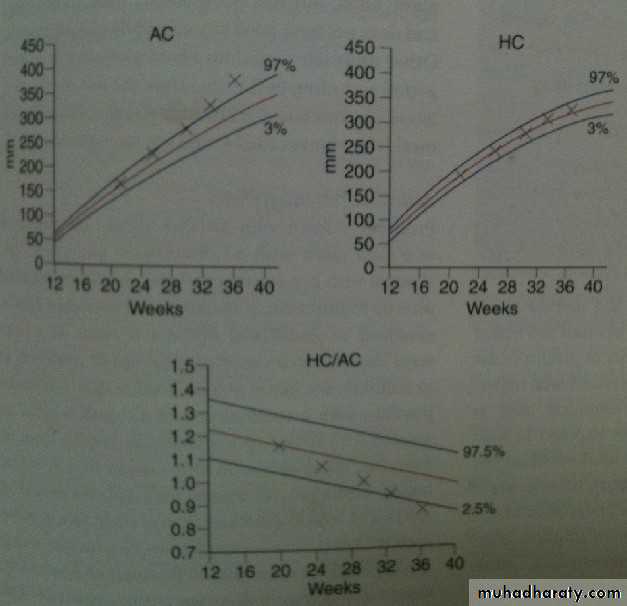
• Serial growth scan
• Monitor fetal well-being (doppler US & Cardiotocography( CTG))
• Aim: vaginal delivery between 38 – 40 weeks
• 50% Ceasarian section because of macrosomia, pre-eclampsia and failed induction of labour
Treatment for gestational diabetes aims to keep blood glucose levels equal to those of pregnant women who don't have gestational diabetes. The treatment always includes special meal plans and scheduled physical activity, and it may also include daily blood glucose testing and insulin injections.
the American Diabetes Association suggests the following targets for women who develop gestational diabetes during pregnancy. More or less stringent glycemic goals may be appropriate for each individual.
Target blod glucose before a meal (preprandial): 95 mg/dl or less
One hour after a meal (postprandial): 140 mg/dl or less
Two hours after a meal (postprandial): 120 mg/dl or less
Human insulin should be used when insulin is prescribed, and SMBG should guide the doses and timing of the insulin regimen. The use of insulin analogs has not been adequately tested in GDM.
• Management: preterm labour & polyhydramnios
• Difficult• Tocolytics (e.g. ritodrine, salbutamol) are diabetogenic
• I/M steroid for fetal lung maturation
• destabilize diabetic control
• I/V insulin / glucose infusion if required to ensure normoglycaemia
• Management: Intrapartum
• Induced/Spontaneous labour• sliding scale of insulin to maintain normoglycaemia
• Test maternal blood glucose hourly
• Continuous fetal monitoring advised
• fetal scalp blood sampling if Cardiotocography (CTG) abnormal
• Management: Post-delivery
• Insulin requirements return to pre-pregnant levels
• If GDM, stop insulin
• OGTT 6/52 post-delivery to ensure diabetes has resolved