ThiQar college of MedicineFamily & Community medicine dept.
Nutrition Lecture 2Third stage by: Dr. Muslim N. SaeedFebruary 11th ,20211.Primary tissue building
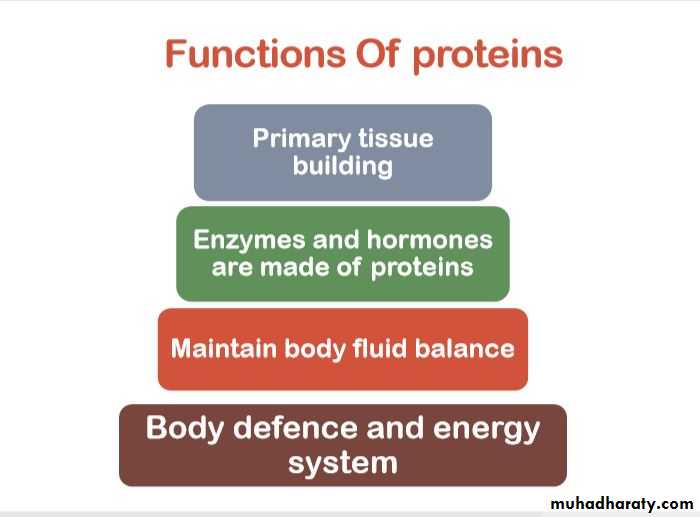
Protein is the fundamental structural material of every body cell.Protein makes up the bulk of muscles, internal organs, brain, hair, skin and nails.
The main function of protein is to build new tissues (growth) and to repair damaged tissues (healing).
Therefore protein needs are higher in stages of growth and recovery.
2.Metabolism and regulatory function
Protein aids metabolic functions through enzymes, transport agents and hormones.Enzymes needed for digestion like amylase, lipase and protease are made of protein.
Hormones like insulin are made of protein.
Transport agents like haemoglobin that transfer oxygen to body cells is made of protein.
3.Water and pH balance
• Fluids within the body are divided into 3 compartments intracellular, intravascular and interstitial.• These compartments are separated by cell membranes,
to hold water within each compartment plasma proteins like albumin attracts water through what so called osmotic pressure.4.Body defense system
Protein is used to build special white cells and antibodies, as part of the immune system.
Energy supply
Although carbs are the primary body fuel, followed by fats, in times of need protein can be used as a fuel. • One gram of protein provides 4 Kcal.
Dietary proteins
• Protein is a fundamental element of cell structure, therefore protein is found in most food.• A diet with inadequate protein intake usually leads to different forms of malnutrition e.g protein energy malnutrition, failure to thrive,…etc.
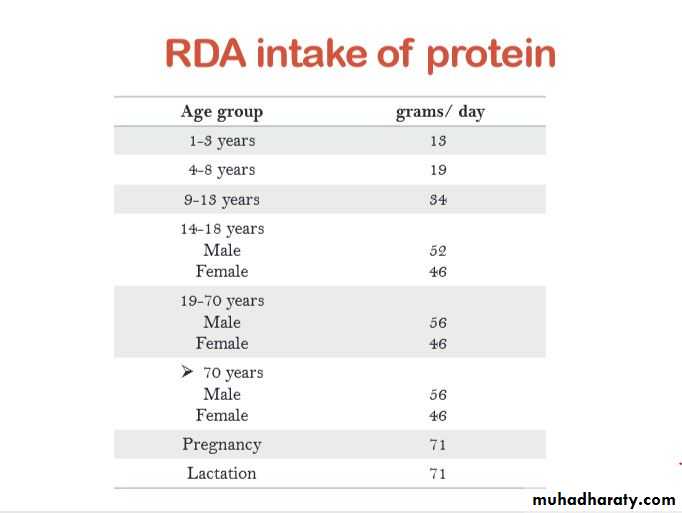
• The are many factors that affect the requirements of protein like age, sex, physical activity, pregnancy and lactation, post- operative recovery, diseases… etc.
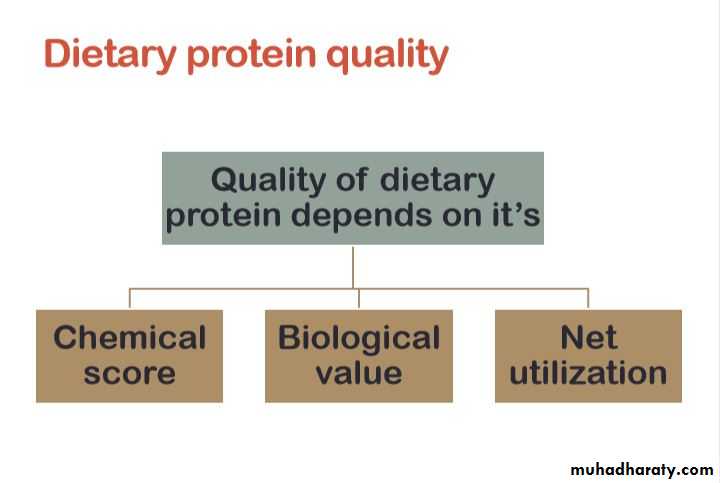
Dietary protein quality
• Chemical score: it refers to the amino acids composition of a protein compared to high quality reference protein (e.g egg).• Biological value: it’s a quantitative measure of protein quality, defined by the amount of nitrogen absorbed and retained in the body, biological value score is out of 100.
The perfect protein has a biological value of 100 like egg. Milk and fish have BV 85 while meat has score of 75, Cereals and pulses have low biological value when consumed alone but mixing them increases their BV.
• Net utilization: it is the degree of digestibility of protein.
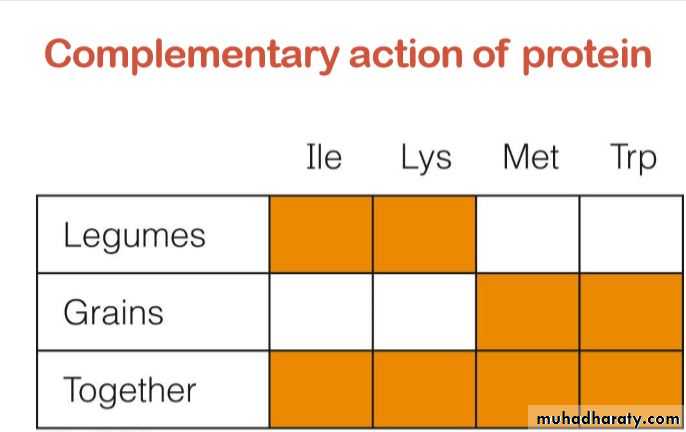
Complementary action of proteins
• Although eating animal protein is the best way to get all the essential amino acids, mixing two or more types of plant protein may achieve the same target, this is called the complementary action of protein.
• Eating a combination of plant protein in one meal compensate for the deficiency of amino acids, like eating cereals and pulses e.g rice and lentils (Koshari), Beans and bread, this is helpful for vegetarians and in populations who don’t consume enough animal protein.
Dietary sources of proteins
• Animal protein:meat, poultry, fish ,eggs, milk and cheese.
• Plant protein:
cereals, legumes, nuts and seeds.
Which contains fat?
Structure and classes of fats
Fats and oils belong to the chemical group called lipids.They are mainly made of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen.
They are more concentrated source of energy than carbs and proteins.
They are characterized by greasy feel, insolubility in water and soluble in organic solvents.
Fatty acids are the building blocks of lipids.
Classification of fatty acids
Fatty acids are classified according to the absence or presence of double bonds into:Saturated fatty acids : no double bonds between carbon atoms, and all the carbon atoms are saturated or filled with hydrogen.
Unsaturated fatty acids: one or more double bonds are present between carbon atoms, mono unsaturated (MUFA) where there is only one double bond, poly unsaturated (PUFA) where there is many double bonds.
Functions of fat
Energy: Fat serves as a condensed source of energy, 1gm = 9 kcal.Fatty food is a source of fat soluble vitamins and aid in their absorption.
Flavour and satiety: fat is responsible for the good flavour of food and satisfaction in addition it slow down digestion leading to longer time of fullness
Fats in food
Functions of fat
Fat in the body:Thermal insulation: subcutaneous fat protects against cold.
Protection of vital organs e.g kidneys and the heart.
Synthesis of hormones e.g steroid hormones.Precursors of prostaglandins.
Dietary fatsSaturated
Saturated fats are heavy and dense, therefore they are solid at room temp.
Usually of animal origin e.g meat, dairy and eggs.
Some plant oils are saturated e.g Palm oil and Coconut oil.
UnsaturatedUnsaturated fats are less heavy and less dense, therefore they are liquid at room temp.
Usually of plant origin, they are either MUFA or PUFA
MUFA e.g olive oil.
PUFA e.g corn oil, sunflower oil, cottonseed oil.
Dietary fats
VisibleEasy to see and separate from food.
Easier to control in diet.
They are butter, ghee, added cream, oils, dressings, fatty meats like sausages and bacon, visible fat of any meat, skin of poultry.
Invisible
Less visible and difficult to separate from food.
Difficult to control in diet, so people should be aware of them.
They are in cheese, full cream milk, nuts, seeds, and the fat serrounding the muscles fibers in lean meat.
Dietary sources of fat
Mono unsaturated fats
Sources :Olive oil, Canola oil, Safflower oil, Peanut oil, Sesame oil
Avocado
Health benefits:
Reduce levels of LDL (bad cholesterol) therefore decrease risk of heart disease and stroke.Provide the body with vitamin E (antioxidant).
Poly unsaturated fats
Sources :Oils ( corn oil, flaxseed oil, sunflower oil, cotton seed oil)
Nuts (walnut, almonds, peanuts, macadamia)
Seeds (Pumpkin seeds, sunflower seeds)
Fatty fish (Salmon, mackerel, herring, Trout)
Health benefits:
Reduce levels of LDL (bad cholesterol) therefore decrease risk of heart disease and stroke.Provide the body with vitamin E (antioxidant)
Provide the body with essential fatty acids (omega 6, omega 3)
Omega 3 and omega 6
The body can produce all the fatty acids it needs except for alpha linolenic acid (omega 3) and linoleic acid (omega 6) fatty acids.Food rich in poly unsaturated fatty acids are sources of omega 3 and omega 6.
Omega 3 and omega 6 are the precursore of other fatty acids.
Saturated fats
Sources:Meat fats, Poultry skin, milk fats, butter, ghee, cheese,
Egg yolks, Palm oil, Coconut oil
Health issues:
Consuming food high in saturated fat may increase the levels of LDL (bad cholesterol) and increase the risk of heart diseases and stroke.Trans fats
Sources:Hydrogenated vegetable oils, pizza, doughnut, fried food, baked foods, cookies and cakes.
Health issues:
Trans fats increases levels of LDL and reducethe level of HDL.
Trans fats increases the risk of heart diseases and stroke.
Trans fats is associated with higher risk of
developing type 2 diabetes.
Recommended intake of fat
Dietary guidelines: 20-35% of total calories should be from fat.Saturated fat intake should not exceed 10% of total daily calories.
To reduce the risk of heart diseases, The American Heart Association recommend that only 7% of total calories come from saturated fat.
(Remember 1 gram of fat = 9 kcal)
Thank you